Severe Asthma Remissions Induced by Biologics Targeting IL5/IL5r: Results from a Multicenter Real-Life Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Blood Eosinophil Counts
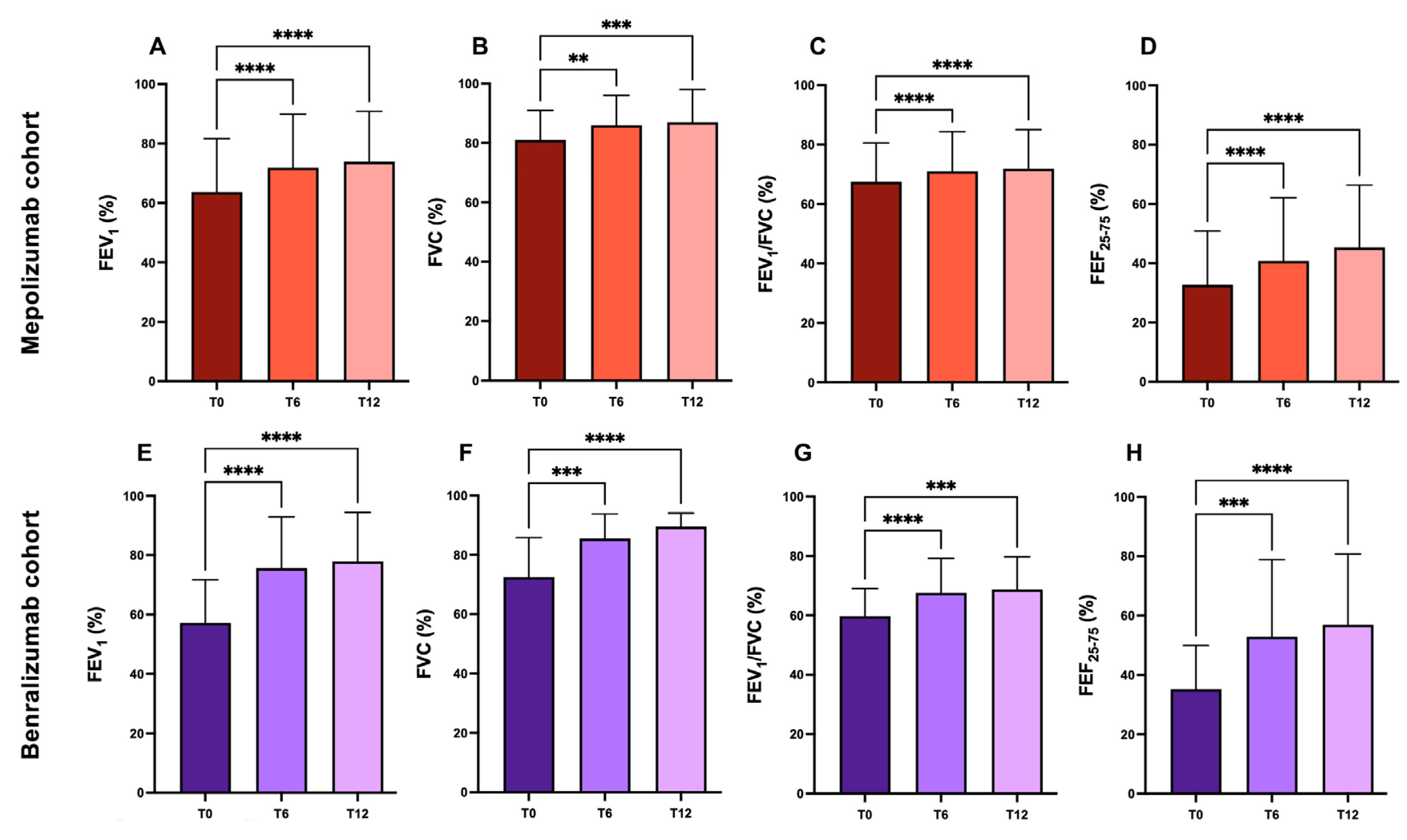
2.2. Pulmonary Function
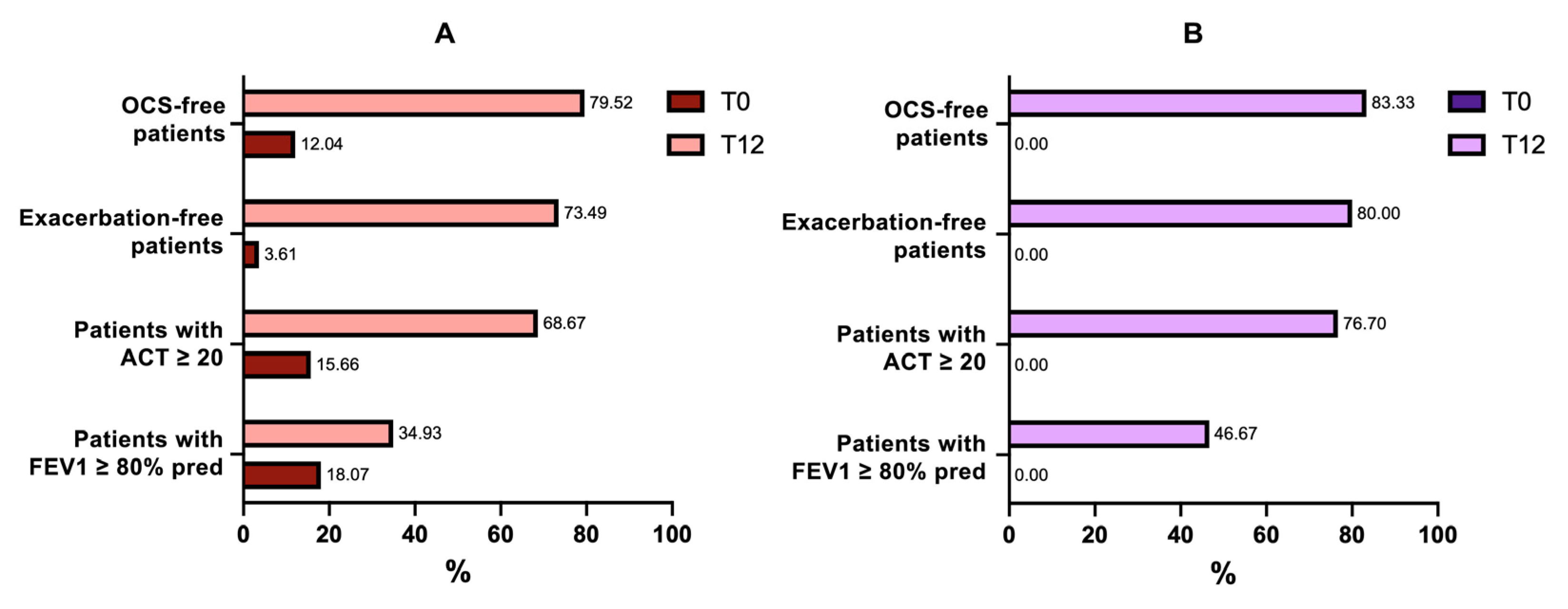
2.3. Exacerbations and Use of Systemic Corticosteroids
2.4. Asthma Control Test
2.5. Asthma Clinical Remissions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GINA Main Report. Available online: https://ginasthma.org/gina-reports/ (accessed on 14 December 2022).
- Soriano, J.B.; Abajobir, A.A.; Abate, K.H.; Abera, S.F.; Agrawal, A.; Ahmed, M.B.; Aichour, A.N.; Aichour, I.; Aichour, M.T.E.; Alam, K.; et al. Global, regional, and national deaths, prevalence, disability-adjusted life years, and years lived with disability for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaia, C.; Pelaia, G.; Crimi, C.; Maglio, A.; Gallelli, L.; Terracciano, R.; Vatrella, A. Tezepelumab: A Potential New Biological Therapy for Severe Refractory Asthma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikov, A.; Oğuzülgen, I.K.; Baiardini, I.; Contoli, M.; Emelyanov, A.; Fassio, O.; Ivancevich, J.C.; Kaidashev, I.; Kowal, K.; Labor, M.; et al. Beliefs and preferences regarding biological treatments for severe asthma. World Allergy Organ. J. 2020, 13, 100441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upham, J.W.; James, A.L. Remission of asthma: The next therapeutic frontier? Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 130, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Bafadhel, M.; Busse, W.W.; Casale, T.B.; Kocks, J.W.; Pavord, I.D.; Szefler, S.J.; Woodruff, P.G.; de Giorgio-Miller, A.; Trudo, F.; et al. An expert consensus framework for asthma remission as a treatment goal. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; McDonald, V.M.; Pavord, I.D.; Gibson, P.G. Asthma remission: What is it and how can it be achieved? Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2102583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribas, C.D.; Díaz, T.C.; Aparicio, M.B.; Moragón, E.M.; Conejero, D.B.; Herrero, M.G.S.; Muñoz, M.; Cabrerizo, H.; Valero, A.; Arismendi, E.; et al. REal worlD Effectiveness and Safety of Mepolizumab in a Multicentric Spanish Cohort of Asthma Patients Stratified by Eosinophils: The REDES Study. Drugs 2021, 81, 1763–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numata, T.; Araya, J.; Okuda, K.; Miyagawa, H.; Minagawa, S.; Ishikawa, T.; Hara, H.; Kuwano, K. Long-Term Efficacy and Clinical Remission After Benralizumab Treatment in Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: A Retrospective Study. J. Asthma Allergy 2022, ume 15, 1731–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eger, K.; Kroes, J.A.; Brinke, A.T.; Bel, E.H. Long-Term Therapy Response to Anti–IL-5 Biologics in Severe Asthma—A Real-Life Evaluation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pr. 2021, 9, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Hoyte, F.L.; Price, D.B.; Cohen, D.; Barker, P.; Kreindler, J.; Jison, M.; Brooks, C.L.; Papeleu, P.; Katial, R. Clinical Remission in Severe Asthma: A Pooled Post Hoc Analysis of the Patient Journey with Benralizumab. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 2065–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglio, A.; Vitale, C.; Pellegrino, S.; Calabrese, C.; D’Amato, M.; Molino, A.; Pelaia, C.; Triggiani, M.; Pelaia, G.; Stellato, C.; et al. Real-Life Effectiveness of Mepolizumab on Forced Expiratory Flow between 25% and 75% of Forced Vital Capacity in Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, A.G.-B.; Gallardo, J.F.M.; Romero, J.D.; Falcón, A.R.; Bernáldez, C.B.; Borrego, J.G.; Álvarez-Gutiérrez, F.J. Effectiveness of Switching to Benralizumab in Severe Refractory Eosinophilic Asthma. J. Asthma Allergy 2022, ume 15, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, J.E.; D’Ancona, G.; Elstad, M.; Green, L.; Fernandes, M.; Thomson, L.; Roxas, C.; Dhariwal, J.; Nanzer, A.M.; Kent, B.D.; et al. Real-World Effectiveness and the Characteristics of a “Super-Responder” to Mepolizumab in Severe Eosinophilic Asthma. Chest 2020, 158, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavanagh, J.E.; Hearn, A.P.; Dhariwal, J.; D’Ancona, G.; Douiri, A.; Roxas, C.; Fernandes, M.; Green, L.; Thomson, L.; Nanzer, A.M.; et al. Real-World Effectiveness of Benralizumab in Severe Eosinophilic Asthma. Chest 2020, 159, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo Ribas, C.; Pavord, I.; Price, R.G.; Howarth, P.; Oppenheimer, J.; Heaney, L.; Nagase, H.; Pizzichini, E.; Banas Conejero, D.; Gardiner, F. Mepolizumab Treatment Leads to Clinical Remission in Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: Results from the Real-World REDES Study. In C101. Expanding the Use of Asthma Biologics and Other Novel Therapeutics to Additional Patient Populations; American Thoracic Society International Conference Abstracts; American Thoracic Society: New York, NY, USA, 2022; p. A4834. [Google Scholar]
- Kayser, M.Z.; Drick, N.; Milger, K.; Fuge, J.; Kneidinger, N.; Korn, S.; Buhl, R.; Behr, J.; Welte, T.; Suhling, H. Real-World Multicenter Experience with Mepolizumab and Benralizumab in the Treatment of Uncontrolled Severe Eosinophilic Asthma Over 12 Months. J. Asthma Allergy 2021, ume 14, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Farne, H.; Wilson, A.; Milan, S.; Banchoff, E.; Yang, F.; Powell, C.V. Anti-IL-5 therapies for asthma. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Busceti, M.T.; Solinas, S.; Terracciano, R.; Pelaia, G. Real-life evaluation of the clinical, functional, and hematological effects of mepolizumab in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma: Results of a single-centre observational study. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 53, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sposato, B.; Camiciottoli, G.; Bacci, E.; Scalese, M.; Carpagnano, G.E.; Pelaia, C.; Santus, P.; Maniscalco, M.; Masieri, S.; Corsico, A.G.; et al. Mepolizumab effectiveness on small airway obstruction, corticosteroid sparing and maintenance therapy step-down in real life. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 61, 101899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sposato, B.; Scalese, M.; Camiciottoli, G.; Carpagnano, G.E.; Pelaia, C.; Santus, P.; Pelaia, G.; Palmiero, G.; Di Tomassi, M.; Ronchi, M.C.; et al. Severe Asthma and Long-Term Benralizumab Effectiveness in Real-Life. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 7461–7473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzella, F.; Ruggiero, P.; Galeone, C.; Scelfo, C.; Bagnasco, D.; Facciolongo, N. Significant improvement in lung function and asthma control after benralizumab treatment for severe refractory eosinophilic asthma. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 64, 101966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Szefler, S.J.; Busse, W.W. The Relationship of Asthma Biologics to Remission for Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pr. 2020, 9, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rial, M.J.; Domínguez-Ortega, J. Inflammatory Remission in T2 Severe Asthma. Front. Allergy 2022, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, W.; Chupp, G.; Nagase, H.; Albers, F.C.; Doyle, S.; Shen, Q.; Bratton, D.J.; Gunsoy, N.B. Anti–IL-5 treatments in patients with severe asthma by blood eosinophil thresholds: Indirect treatment comparison. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 190–200.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagase, H.; Suzukawa, M.; Oishi, K.; Matsunaga, K. Biologics for severe asthma: The real-world evidence, effectiveness of switching, and prediction factors for the efficacy. Allergol. Int. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourdin, A.; Husereau, D.; Molinari, N.; Golam, S.; Siddiqui, M.K.; Lindner, L.; Xu, X. Matching-adjusted indirect comparison of benralizumab versus interleukin-5 inhibitors for the treatment of severe asthma: A systematic review. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1801393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, K.; Oishi, K.; Murata, Y.; Hirano, T.; Matsunaga, K. Feasibility of Discontinuing Biologics in Severe Asthma: An Algorithmic Approach. J. Asthma Allergy 2021, ume 14, 1463–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soendergaard, M.B.; Hansen, S.; Bjerrum, A.-S.; Hilberg, O.; Lock-Johansson, S.; Haakansson, K.E.J.; Ingebrigtsen, T.S.; Johnsen, C.R.; Rasmussen, L.M.; von Bülow, A.; et al. Complete response to anti-interleukin-5 biologics in a real-life setting: Results from the nationwide Danish Severe Asthma Register. ERJ Open Res. 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardas, G.; Panek, M.; Kuna, P.; Damiański, P.; Kupczyk, M. Monoclonal antibodies in the management of asthma: Dead ends, current status and future perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upham, J.W.; Le Lievre, C.; Jackson, D.J.; Masoli, M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Price, D.B.; Mansur, A.; Detoraki, A.; Altraja, A.; James, A.; et al. Defining a Severe Asthma Super-Responder: Findings from a Delphi Process. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pr. 2021, 9, 3997–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Patients, n | 113 (83 m; 30 b) |
| Age (mean ± SD) | 57.5 ± 8.9 |
| Gender (male) | 41 M (36.28%) |
| Smokers/former smokers/ non-smokers | 16/32/65 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 mean ± SD | 27.2 ± 3.4 |
| Asthma duration median (IQR) | 21.5 (18.75) |
| Age at asthma onset Mean ± SD | 35.9 ± 10.9 |
| OCS-dependent patients | 83 (75.45%) |
| Comorbidities | |
| Obesity (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2) | 26 (23%) |
| Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis | 48 (42.47%) |
| Gastroesophageal reflux disease | 40 (35.39%) |
| Treated with Mepolizumab (n = 83) | Treated with Benralizumab (n = 30) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T6 | T12 | T0 | T6 | T12 | |
| ACT score | 14.3 ± 4.8 | 19.4 ± 4.2 | 20.6 ± 4.5 | 13.9 ± 2.8 | 21.9 ± 2.9 | 22.4 ± 2.6 |
| ACT ≥ 20 | 13 (15.66%) | 39 (46.98%) | 49 (59.03%) | 0 (0%) | 23 (76.6%) | 25 (83.3%) |
| Blood eosinophils (cells/μL) mean ± SD | 584.3 ± 333.6 | 101.5 ± 82.72 | 91.85 ± 112.9 | 867.7 ± 537.9 | 0 | 0 |
| Exacerbation history, previous year (n/y) | 4.27 ± 2.57 | 0.71 ± 1.05 | 0.39 ± 0.80 | 6.67 ± 2.2 | 0.13 ± 0.35 | 0.2 ± 0.48 |
| OCS users, n | 53 (63.8%) | 21 (25.3%) | 15 (18.07%) | 30 (100%) | 3 (10%) | 5 (16.6%) |
| OCS (prednisone-equivalent mg/die) mean ± SD | 12.4 ± 11.9 | 3.47 ± 6.83 | 1.36 ± 3.55 | 14.6 ± 8.75 | 1.17 ± 2.9 | 1.1 ± 2.8 |
| FEV1 %th mean ± SD | 63.62 ± 17.13 | 71.99 ± 16.57 | 73.91 ± 16.95 | 54.57 ± 14.7 | 76.7 ± 16.9 | 77.8 ± 16.5 |
| FVC %th mean ± SD | 80.26 ± 15.43 | 85.84 ± 15.33 | 86.63 ± 15.5 | 72.78 ± 14.5 | 86.3 ± 12.3 | 86.7 ± 13.1 |
| FEV1/FVC %th mean ± SD | 66.53 ± 12.89 | 70.2 ± 13.2 | 71.87 ± 13.2 | 59.21 ± 9.72 | 68.16 ± 11.88 | 68.6 ± 11 |
| FEF25-75 %th mean ± SD | 32.65 ± 16.64 | 38.87 ± 17.16 | 45.3 ± 21 | 33.47 ± 15.1 | 53.5 ± 27.9 | 56.9 ± 23.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maglio, A.; Vitale, C.; Pelaia, C.; D’Amato, M.; Ciampo, L.; Sferra, E.; Molino, A.; Pelaia, G.; Vatrella, A. Severe Asthma Remissions Induced by Biologics Targeting IL5/IL5r: Results from a Multicenter Real-Life Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032455
Maglio A, Vitale C, Pelaia C, D’Amato M, Ciampo L, Sferra E, Molino A, Pelaia G, Vatrella A. Severe Asthma Remissions Induced by Biologics Targeting IL5/IL5r: Results from a Multicenter Real-Life Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(3):2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032455
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaglio, Angelantonio, Carolina Vitale, Corrado Pelaia, Maria D’Amato, Luigi Ciampo, Eliana Sferra, Antonio Molino, Giulia Pelaia, and Alessandro Vatrella. 2023. "Severe Asthma Remissions Induced by Biologics Targeting IL5/IL5r: Results from a Multicenter Real-Life Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 3: 2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032455
APA StyleMaglio, A., Vitale, C., Pelaia, C., D’Amato, M., Ciampo, L., Sferra, E., Molino, A., Pelaia, G., & Vatrella, A. (2023). Severe Asthma Remissions Induced by Biologics Targeting IL5/IL5r: Results from a Multicenter Real-Life Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(3), 2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032455









