Selective α3β4 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Ligand as a Potential Tracer for Drug Addiction
Abstract
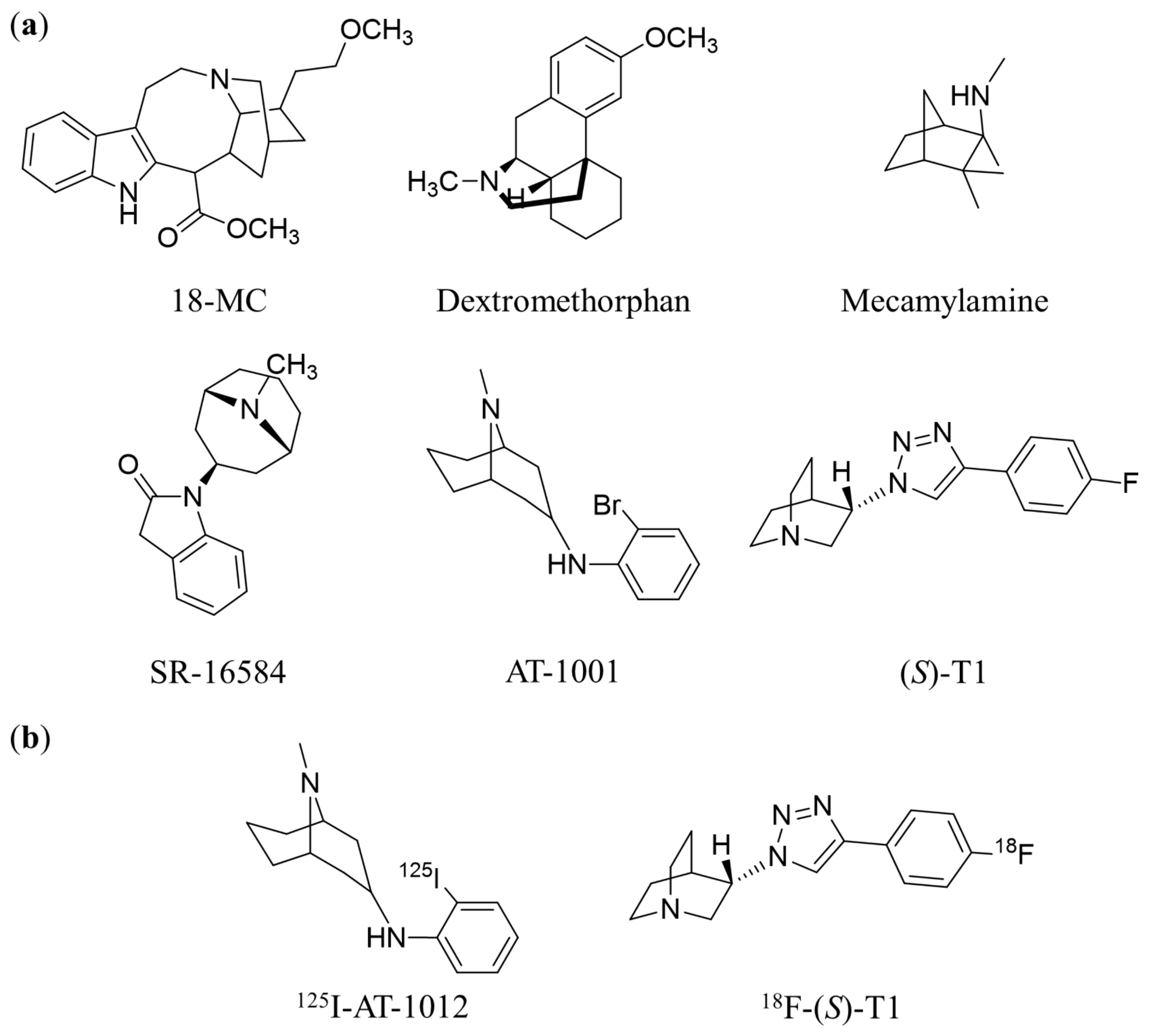
1. Introduction
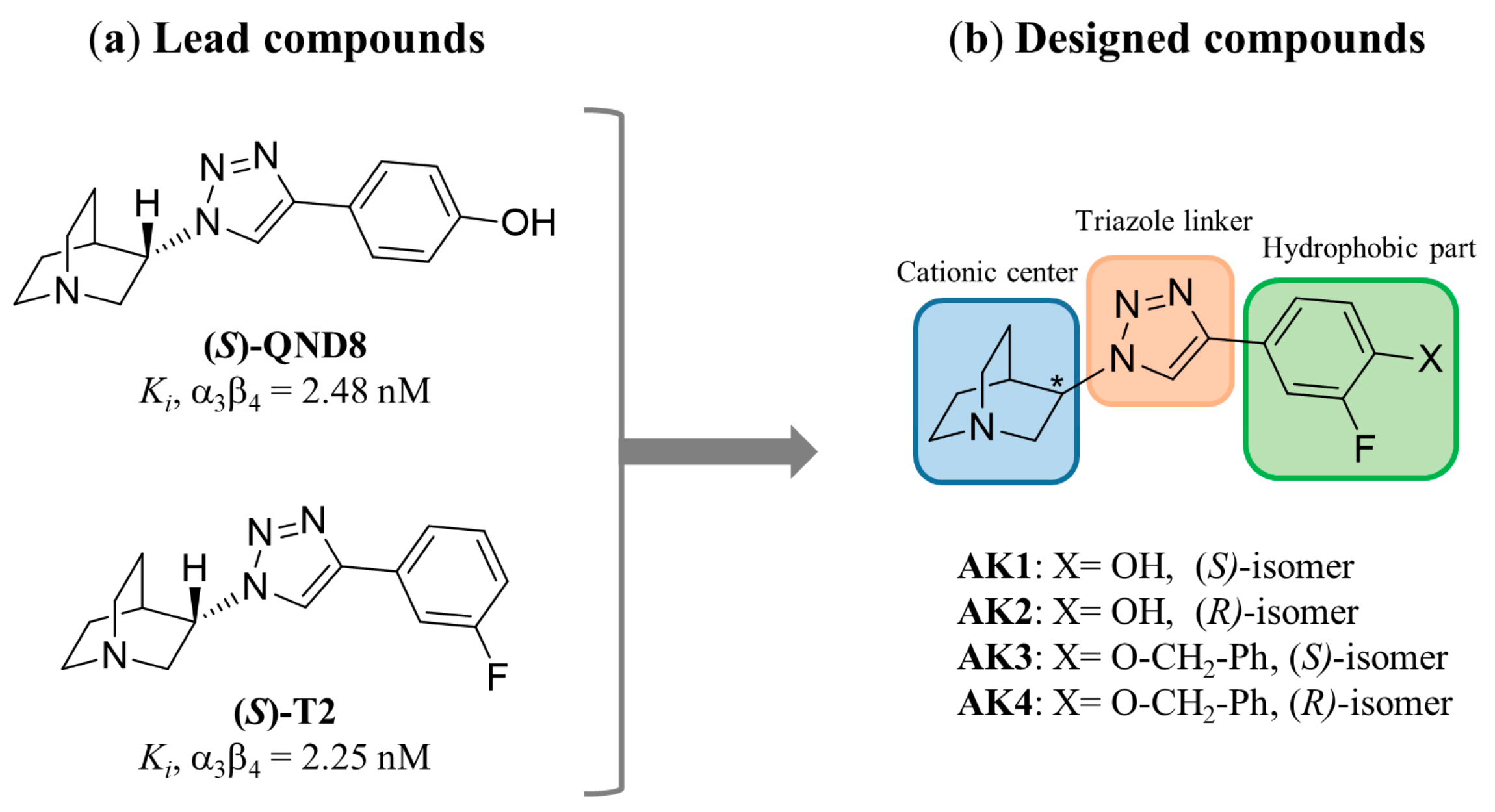
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
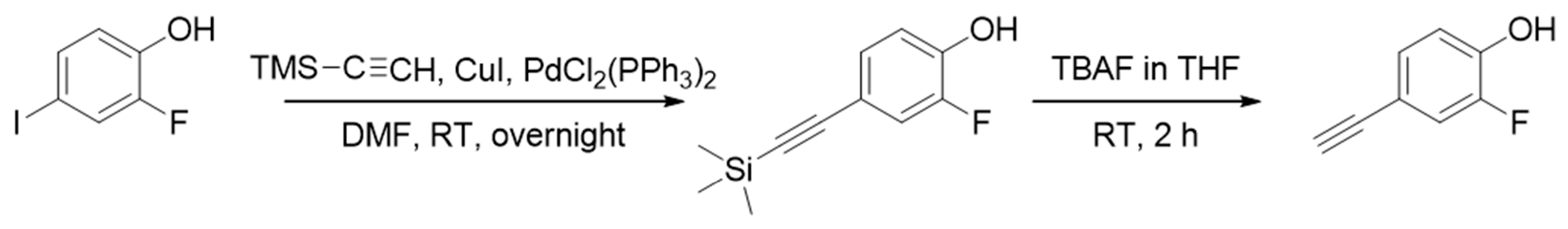
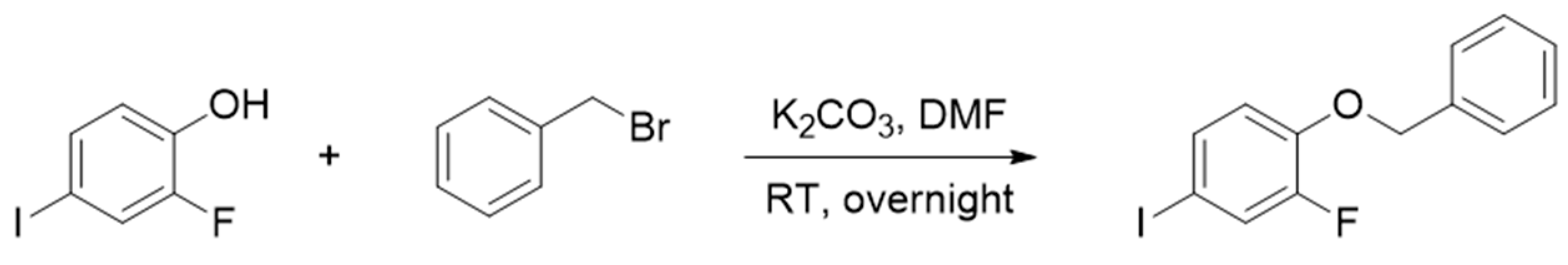
3.1. Synthesis
3.2. Binding Affinity
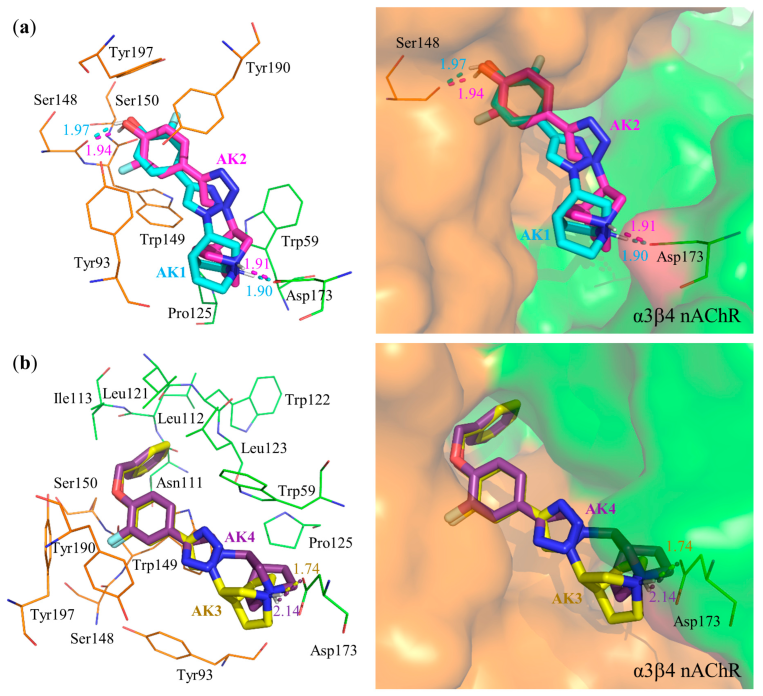
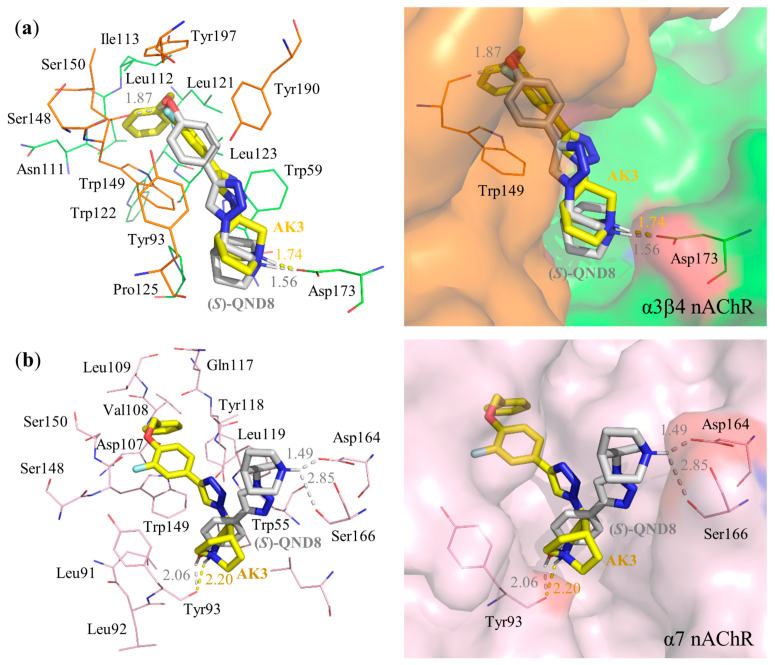
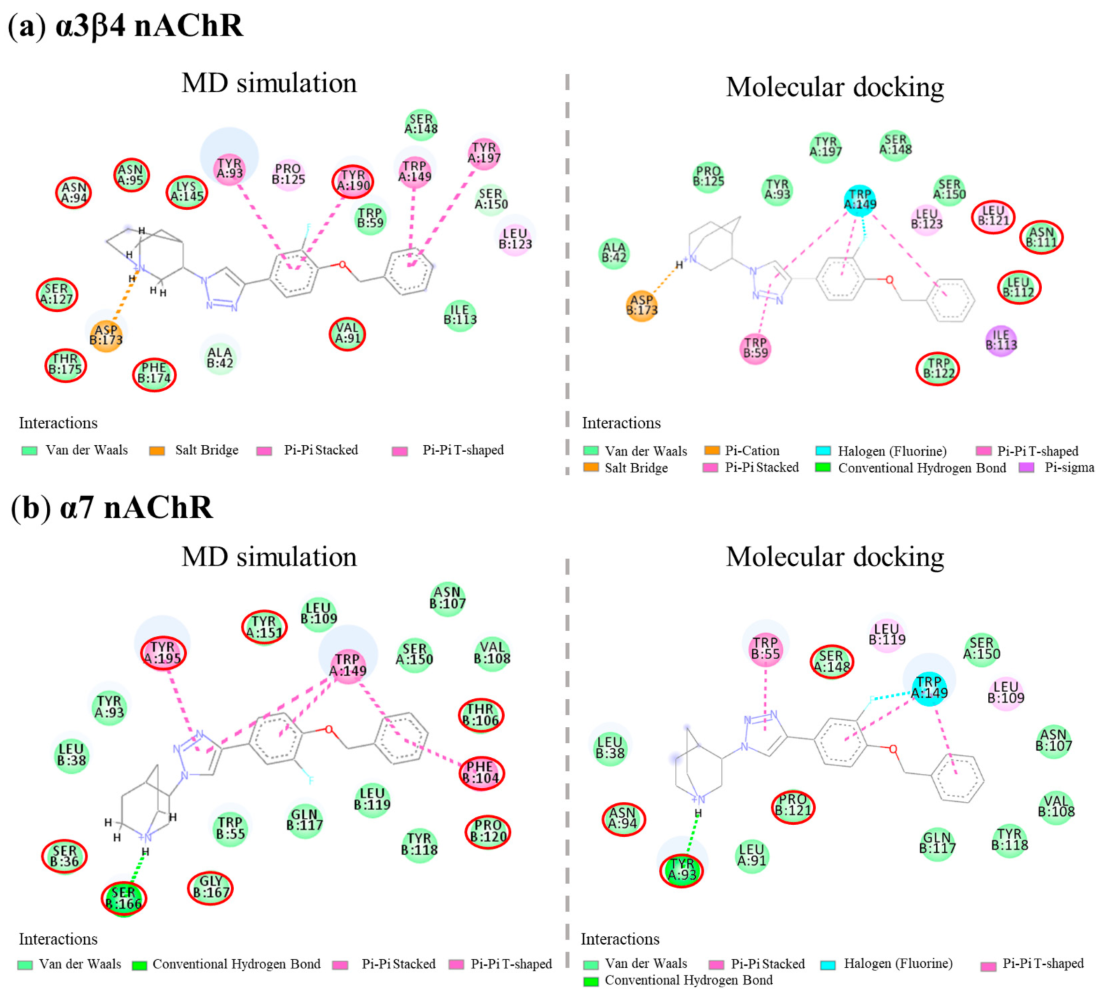
3.3. Molecular Docking
3.4. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulation
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dani, J.A. Neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor structure and function and response to nicotine. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2015, 124, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dineley, K.T.; Pandya, A.A.; Yakel, J.L. Nicotinic ACh receptors as therapeutic targets in CNS disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotti, C.; Clementi, F.; Fornari, A.; Gaimarri, A.; Guiducci, S.; Manfredi, I.; Moretti, M.; Pedrazzi, P.; Pucci, L.; Zoli, M. Structural and functional diversity of native brain neuronal nicotinic receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, J.P.; Stokoe, S.A.; Sathler, M.F.; Nichols, R.A.; Kim, S. Selective coactivation of α7- and α4β2-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors reverses beta-amyloid-induced synaptic dysfunction. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letsinger, A.C.; Gu, Z.; Yakel, J.L. α7 Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the hippocampal circuit: Taming complexity. Trends Neurosci. 2022, 45, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posadas, I.; López-Hernández, B.; Fau-Ceña, V.; Ceña, V. Nicotinic receptors in neurodegeneration. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2013, 11, 298–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyohara, J.; Hashimoto, K. α7 Nicotinic receptor agonists: Potential therapeutic drugs for treatment of cognitive impairments in Schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s Disease. Open Med. Chem. J. 2010, 4, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dani, J.A.; Bertrand, D. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and nicotinic cholinergic mechanisms of the central nervous system. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007, 47, 699–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilens, T.E.; Decker, M.W. Neuronal nicotinic receptor agonists for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Focus on cognition. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 1212–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haydar, N.S.; Dunlop, J. Neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors—Targets for the development of drugs to treat cognitive impairment associated with schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glick, S.D.; Maisonneuve, I.M.; Dickinson, H.A. 18-MC reduces methamphetamine and nicotine self-administration in rats. NeuroReport 2000, 11, 2013–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taraschenko, O.D.; Panchal, V.; Maisonneuve, I.M.; Glick, S.D. Is antagonism of α3β4 nicotinic receptors a strategy to reduce morphine dependence? Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 513, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, L.; Kenny, P.J. Addiction-related neuroadaptations following chronic nicotine exposure. J. Neurochem. 2021, 157, 1652–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittenberg, R.E.; Wolfman, S.L.; De Biasi, M.; Dani, J.A. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and nicotine addiction: A brief introduction. Neuropharmacology 2020, 177, 108256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, P.J.; Markou, A. Neurobiology of the nicotine withdrawal syndrome. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2001, 70, 531–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picciotto, M.R.; Kenny, P.J. Molecular mechanisms underlying behaviors related to nicotine addiction. Cold. Spring. Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a012112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro-Neto, A.G.; Rameh-de-Albuquerque, R.C.; de Medeiros, P.F.P.; Uchôa, R.; Santos, B.S. Chapter 49—Neuroscience of tobacco and crack cocaine use: Metabolism, effects, and symptomatology. In Neuroscience of Alcohol: Mechanisms and Treatment; Preedy, V.R., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019; pp. 403–410. [Google Scholar]
- Fowler, C.D.; Lu, Q.; Johnson, P.M.; Marks, M.J.; Kenny, P.J. Habenular α5 nicotinic receptor subunit signalling controls nicotine intake. Nature 2011, 471, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elayouby, K.S.; Ishikawa, M.; Dukes, A.J.; Smith, A.C.W.; Lu, Q.; Fowler, C.D.; Kenny, P.J. α3* Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the habenula-interpeduncular nucleus circuit regulate nicotine intake. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 1779–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccone, N.L.; Wang, J.C.; Breslau, N.; Johnson, E.O.; Hatsukami, D.; Saccone, S.F.; Grucza, R.A.; Sun, L.; Duan, W.; Budde, J.; et al. The CHRNA5-CHRNA3-CHRNB4 nicotinic receptor subunit gene cluster affects risk for nicotine dependence in African-Americans and in European-Americans. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6848–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, J.J.; van den Bree, M.B.; Munafo, M.R. Association of the CHRNA5-A3-B4 gene cluster with heaviness of smoking: A meta-analysis. Nicotine. Tob. Res. 2011, 13, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitz, M.R.; Amos, C.I.; Dong, Q.; Lin, J.; Wu, X. The CHRNA5-A3 region on chromosome 15q24-25.1 is a risk factor both for nicotine dependence and for lung cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Instig. 2008, 100, 1552–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholze, P.; Huck, S. The α5 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit differentially modulates α4β2* and α3β4* receptors. Front. Synaptic. Neurosci. 2020, 12, 607959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grady, S.R.; Moretti, M.; Zoli, M.; Marks, M.J.; Zanardi, A.; Pucci, L.; Clementi, F.; Gotti, C. Rodent habenulo-interpeduncular pathway expresses a large variety of uncommon nAChR subtypes, but only the alpha3beta4* and alpha3beta3beta4* subtypes mediate acetylcholine release. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 2272–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, R.J.; Taraschenko, O.D.; Glick, S.D. Effects of nicotine, methamphetamine and cocaine on extracellular levels of acetylcholine in the interpeduncular nucleus of rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 440, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khroyan, T.V.; Yasuda, D.; Toll, L.; Polgar, W.E.; Zaveri, N.T. High affinity α3β4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligands AT-1001 and AT-1012 attenuate cocaine-induced conditioned place preference and behavioral sensitization in mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 97, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Liu, L.; Ngolab, J.; Zhao-Shea, R.; McIntosh, J.M.; Gardner, P.D.; Tapper, A.R. Habenula cholinergic neurons regulate anxiety during nicotine withdrawal via nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuropharmacology 2016, 107, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, I.; Dani, J.A.; De Biasi, M. Nicotine withdrawal. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 24, 99–123. [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin, I.; Dani, J.A.; De Biasi, M. The medial habenula and interpeduncular nucleus circuitry is critical in addiction, anxiety, and mood regulation. J. Neurochem. 2017, 142 (Suppl. S2), 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaveri, N.; Jiang, F.; Olsen, C.; Polgar, W.; Toll, L. Novel α3β4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-selective ligands. Discovery, structure-activity studies, and pharmacological evaluation. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 8187–8191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, N.S.; Gotti, C. Diversity of vertebrate nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glick, S.; Sell, E.; Maisonneuve, I. Brain regions mediating α3β4 nicotinic antagonist effects of 18-MC on methamphetamine and sucrose self-administration. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 599, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, S.; Bertolino, M.; Xiao, Y.; Pringle, K.E.; Caruso, F.; Kellar, K. Dextromethorphan and its metabolite dextrorphan block α3β4 neuronal nicotinic receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther 2000, 293, 962–967. [Google Scholar]
- Nickell, J.R.; Grinevich, V.P.; Siripurapu, K.B.; Smith, A.M.; Dwoskin, L.P. Potential therapeutic uses of mecamylamine and its stereoisomers. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2013, 108, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Cohen, S.M.; Arnold, L.L.; Pennington, K.L.; Kato, H.; Naiki, T.; Naiki-Ito, A.; Yamashita, Y.; Takahashi, S. Cotinine, a major nicotine metabolite, induces cell proliferation on urothelium in vitro and in vivo. Toxicol. 2020, 429, 152325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasamkan, J.; Fischer, S.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Ludwig, F.A.; Scheunemann, M.; Arunrungvichian, K.; Vajragupta, O.; Brust, P. Radiosynthesis of (S)-[18F]T1: The first PET radioligand for molecular imaging of α3β4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2017, 124, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cippitelli, A.; Wu, J.; Gaiolini, K.A.; Mercatelli, D.; Schoch, J.; Gorman, M.; Ramirez, A.; Ciccocioppo, R.; Khroyan, T.V.; Yasuda, D.; et al. AT-1001: A high-affinity α3β4 nAChR ligand with novel nicotine-suppressive pharmacology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 1834–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio, T.; Childers, S.R.; Rothman, R.B.; Dersch, C.M.; King, C.; Kuehne, M.; Bornmann, W.G.; Eshleman, A.J.; Janowsky, A.; Simon, E.R.; et al. Effect of Iboga alkaloids on micro-opioid receptor-coupled G protein activation. PLoS. ONE. 2013, 8, e77262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, H.R.; Rosenberg, A.; Feuerbach, D.; Targowska-Duda, K.M.; Maciejewski, R.; Jozwiak, K.; Moaddel, R.; Glick, S.D.; Wainer, I.W. Interaction of 18-methoxycoronaridine with nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in different conformational states. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1798, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, C.S.; Moerke, M.J.; McMahon, L.R. Discriminative stimulus effects of mecamylamine and nicotine in rhesus monkeys: Central and peripheral mechanisms. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2019, 179, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, S.M. Dextromethorphan/Bupropion: A novel oral NMDA (N-methyl-d-aspartate) receptor antagonist with multimodal activity. CNS Spectr. 2019, 24, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Perry, D.C.; Bupp, J.E.; Jiang, F.; Polgar, W.E.; Toll, L.; Zaveri, N.T. [125I]AT-1012, a new high affinity radioligand for the α3β4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuropharmacology 2014, 77, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, D.W. Positron emission tomography/computed tomography. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2008, 38, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherry, S.R. Fundamentals of positron emission tomography and applications in preclinical drug development. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2001, 41, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korat, S.; Bidesi, N.S.R.; Bonanno, F.; Di Nanni, A.; Hoang, A.N.N.; Herfert, K.; Maurer, A.; Battisti, U.M.; Bowden, G.D.; Thonon, D.; et al. Alpha-synuclein PET tracer development-an overview about current efforts. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasamkan, J.; Scheunemann, M.; Apaijai, N.; Palee, S.; Parichatikanond, W.; Arunrungvichian, K.; Fischer, S.; Chattipakorn, S.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Schuurmann, G.; et al. Varying chirality across nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes: Selective binding of quinuclidine triazole compounds. ACS. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunrungvichian, K.; Fokin, V.V.; Vajragupta, O.; Taylor, P. Selectivity optimization of substituted 1,2,3-triazoles as α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists. ACS. Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 1317–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunrungvichian, K.; Chongruchiroj, S.; Sarasamkan, J.; Schuurmann, G.; Brust, P.; Vajragupta, O. In silico finding of key interaction mediated α3β4 and α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligand selectivity of quinuclidine-triazole chemotype. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, P.; Harrison, P.; Clulow, S. A novel method for determination of the affinity of protein: Protein interactions in homogeneous assays. J. Biomol. Screen. 2008, 13, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.C.; Braun, R.; Wang, W.; Gumbart, J.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Villa, E.; Chipot, C.; Skeel, R.D.; Kalé, L.; Schulten, K. Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1781–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanommeslaeghe, K.; Hatcher, E.; Acharya, C.; Kundu, S.; Zhong, S.; Shim, J.; Darian, E.; Guvench, O.; Lopes, P.; Vorobyov, I.; et al. CHARMM general force field: A force field for drug-like molecules compatible with the CHARMM all-atom additive biological force fields. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 671–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N⋅log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BIOVIA; Dassault Systèmes. BIOVIA Discovery Studio; Dassault Systèmes: San Diego, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]


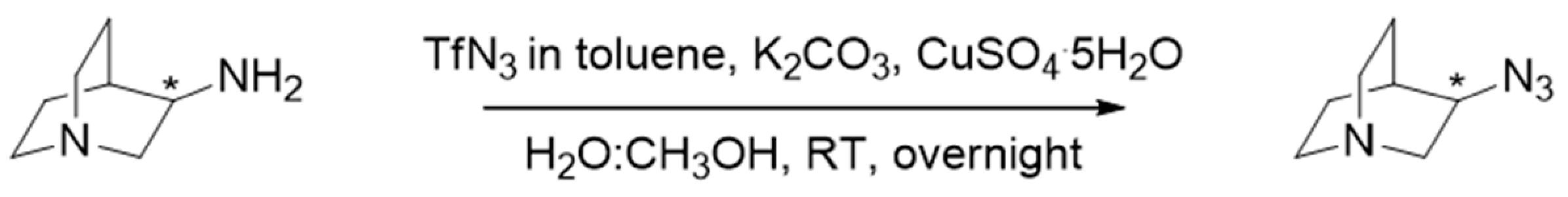
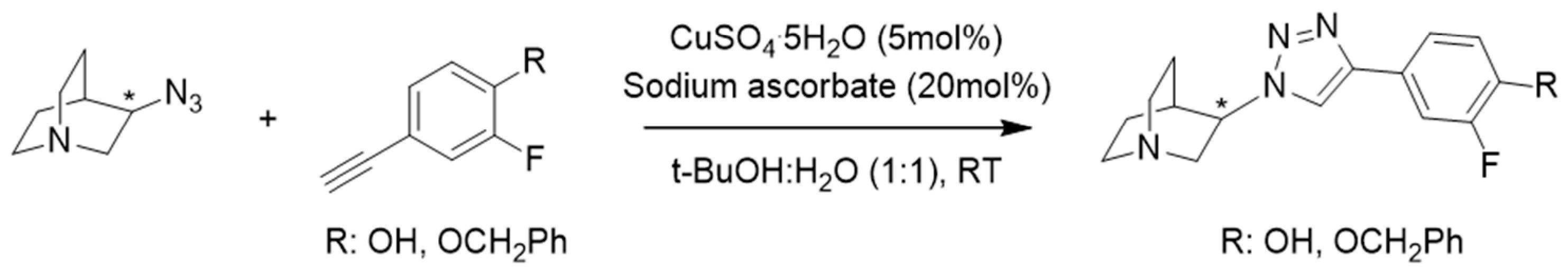
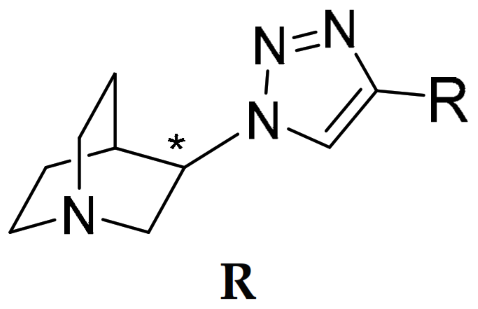 R | Binding Affinity Ki (nM) a | Selectivity Ratios | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α3β4 b | α7 c | α4β2 c | α7/α3β4 | α4β2/α3β4 | α4β2/α7 | |
| Synthesized compounds | ||||||
 AK1 (S-isomer) | 2.28 (1.72; 2.85) | 26.7 $ (20.0; 33.4) | 504 (196; 813) | 11.7 | 221 | 18.9 |
 AK2 (R-isomer) | 601 #,$ (432; 770) | 4.49 $ (3.56; 5.43) | 5977 #,$ (4939; 7015) | 0.01 | 9.95 | 1331 |
 AK3 (S-isomer) | 3.18 (2.17; 4.18) | 9760 #,$ (9565; 9955) | 180 (160; 201) | 3069 | 56.6 | 0.02 |
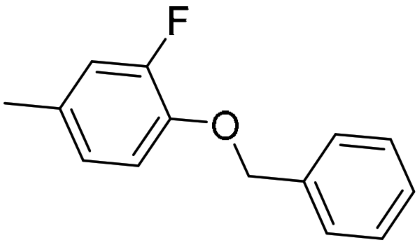 AK4 (R-isomer) | 112 (81.3; 142) | 53.6 $ (50.2; 57.1) | 4176 #,$ (4059; 4293) | 0.48 | 37.3 | 77.9 |
| Lead compounds | ||||||
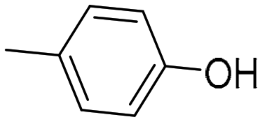 (S)-QND8 [46] | 2.48 ± 0.04 | 29.3 ± 0.18 $ | 461 ± 89 | 11.8 | 186 | 15.7 |
 (S)-T2 [46] | 2.25 ± 0.42 | 660 ± 1.39 # | 519 ± 20 | 294 | 231 | 0.79 |
| Cpds | α3β4 nAChRs | Binding Free Energy (ΔG, kcal/mol) | Ligand Efficiency * (LE) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-Bond (Distance in Å) | Cation-π | π-π | Halogen | |||
| AK1 | Ser148 (1.97), Asp173 (1.90) | Asp173, Trp59 | Trp59, Trp149, Tyr190, Tyr197 | Trp149 | −10.94 | −0.52 |
| AK2 | Ser148 (1.94), Asp173 (1.91) | Asp173 | Trp59, Tyr190, Tyr197 | Ser148, Trp149 | −11.36 | −0.54 |
| AK3 | Asp173 (1.74) | Asp173 | Trp59, Trp149 | Trp149 | −14.21 | −0.51 |
| AK4 | Asp173 (2.14) | Asp173 | Trp59, Trp149 | Trp149 | −14.14 | −0.51 |
| (S)-QND8 | Trp149 (1.87), Asp173 (1.56) | Asp173 | Tyr190 | - | −13.28 | −0.66 |
| (S)-T2 | Asp173 (1.85) | Asp173 | Trp59, Trp149, Tyr190, Tyr197 | Ser148 | −10.42 | −0.52 |
| Cpds | α7 nAChRs | Binding Free Energy (ΔG, kcal/mol) | Ligand Efficiency * (LE) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-Bond (Distance in Å) | Cation-π | π-π | Halogen | |||
| AK1 | Tyr93 (2.06, 2.03), Ser148 (2.66) | Tyr195 | Trp55, Trp149, Tyr188 | - | −11.08 | −0.53 |
| AK2 | Tyr93 (2.13), Trp149 (1.86) | Trp149 | Trp55, Trp149 | - | −10.98 | −0.52 |
| AK3 | Tyr93 (2.20) | - | Trp55, Trp149 | Trp149 | −13.10 | −0.47 |
| AK4 | Tyr93 (2.15) | - | Trp149 | Ser148, Trp149 | −13.20 | −0.47 |
| (S)-QND8 | Tyr93 (2.06), Asp164 (1.49), Ser166 (2.85) | - | Trp55 | - | −11.18 | −0.56 |
| (S)-T2 | - | Tyr55 | Trp149, Tyr195 | Ser148, Trp149 | −9.99 | −0.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kanasuwan, A.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Chongruchiroj, S.; Sarasamkan, J.; Chotipanich, C.; Vajragupta, O.; Arunrungvichian, K. Selective α3β4 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Ligand as a Potential Tracer for Drug Addiction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3614. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043614
Kanasuwan A, Deuther-Conrad W, Chongruchiroj S, Sarasamkan J, Chotipanich C, Vajragupta O, Arunrungvichian K. Selective α3β4 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Ligand as a Potential Tracer for Drug Addiction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(4):3614. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043614
Chicago/Turabian StyleKanasuwan, Apinan, Winnie Deuther-Conrad, Sumet Chongruchiroj, Jiradanai Sarasamkan, Chanisa Chotipanich, Opa Vajragupta, and Kuntarat Arunrungvichian. 2023. "Selective α3β4 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Ligand as a Potential Tracer for Drug Addiction" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 4: 3614. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043614
APA StyleKanasuwan, A., Deuther-Conrad, W., Chongruchiroj, S., Sarasamkan, J., Chotipanich, C., Vajragupta, O., & Arunrungvichian, K. (2023). Selective α3β4 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Ligand as a Potential Tracer for Drug Addiction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(4), 3614. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043614


_Putnam.png)





