Isosinensetin Stimulates Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Secretion via Activation of hTAS2R50 and the Gβγ-Mediated Signaling Pathway
Abstract
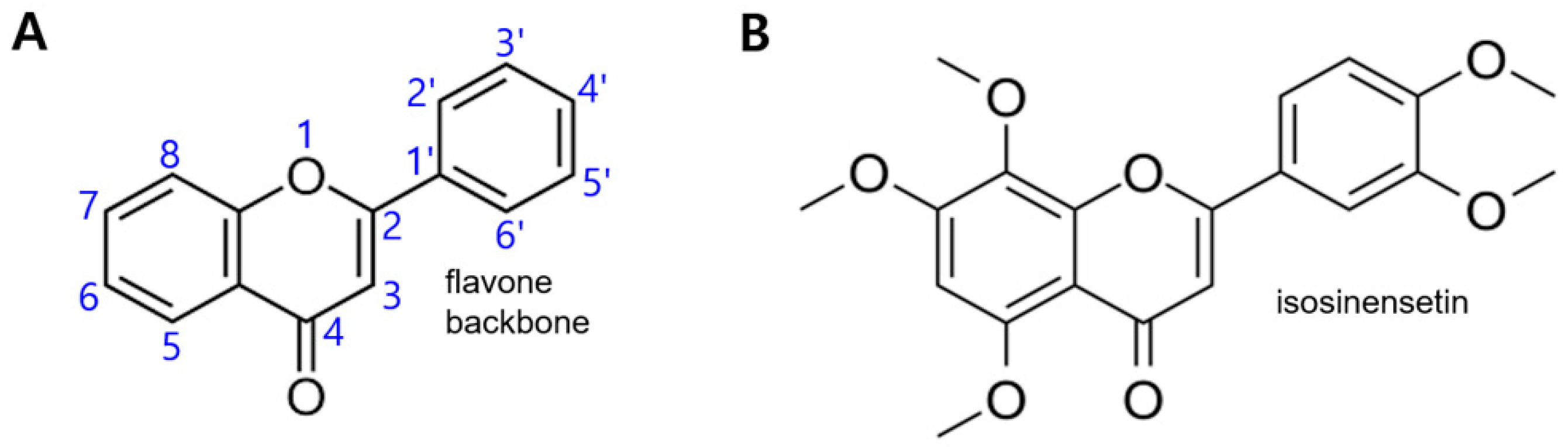
1. Introduction
2. Results
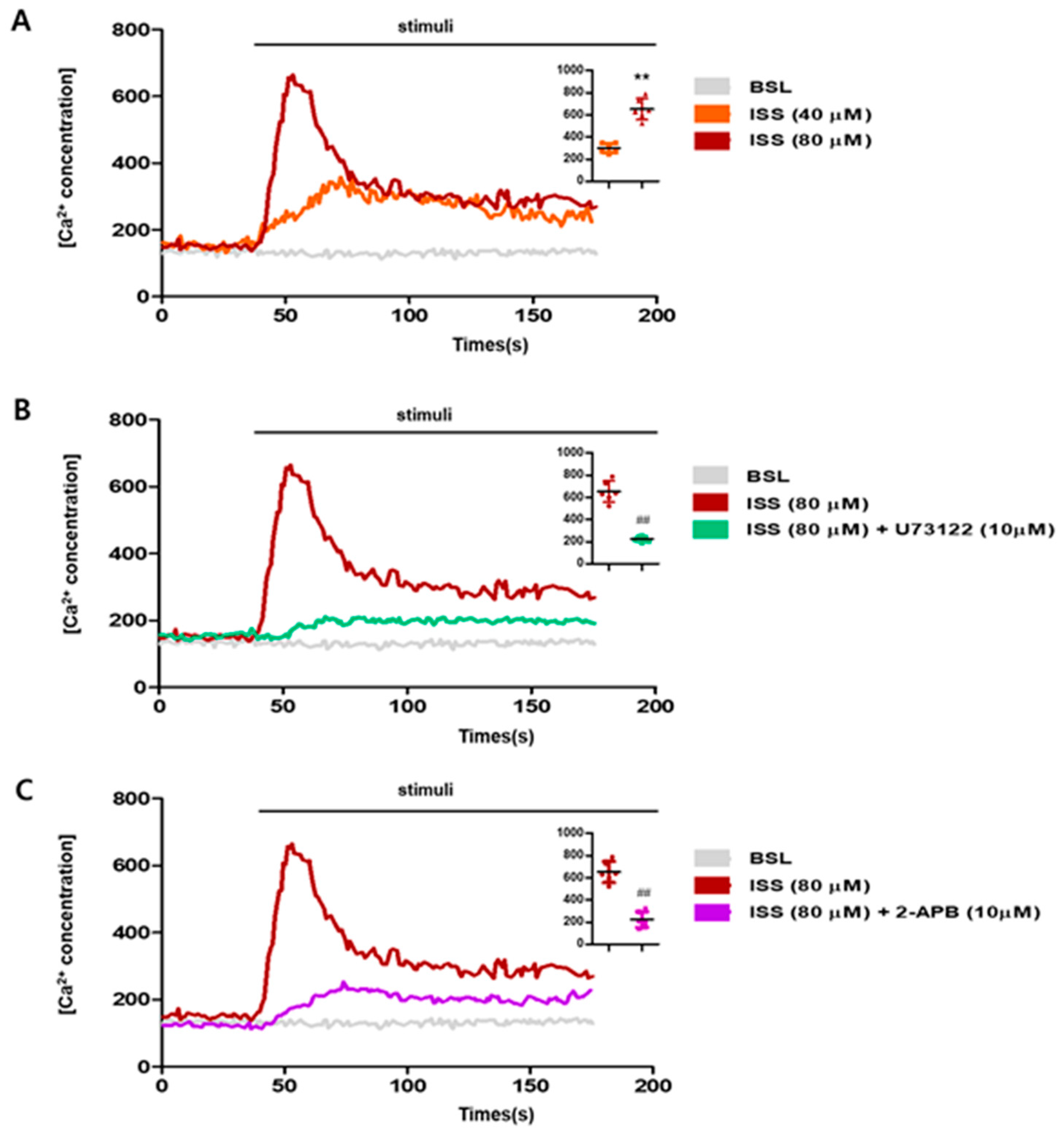
2.1. ISS Activates NCI-H716 Cells via the Phospholipase C Pathway
2.2. Profiling the Expression of hTAS2R Genes
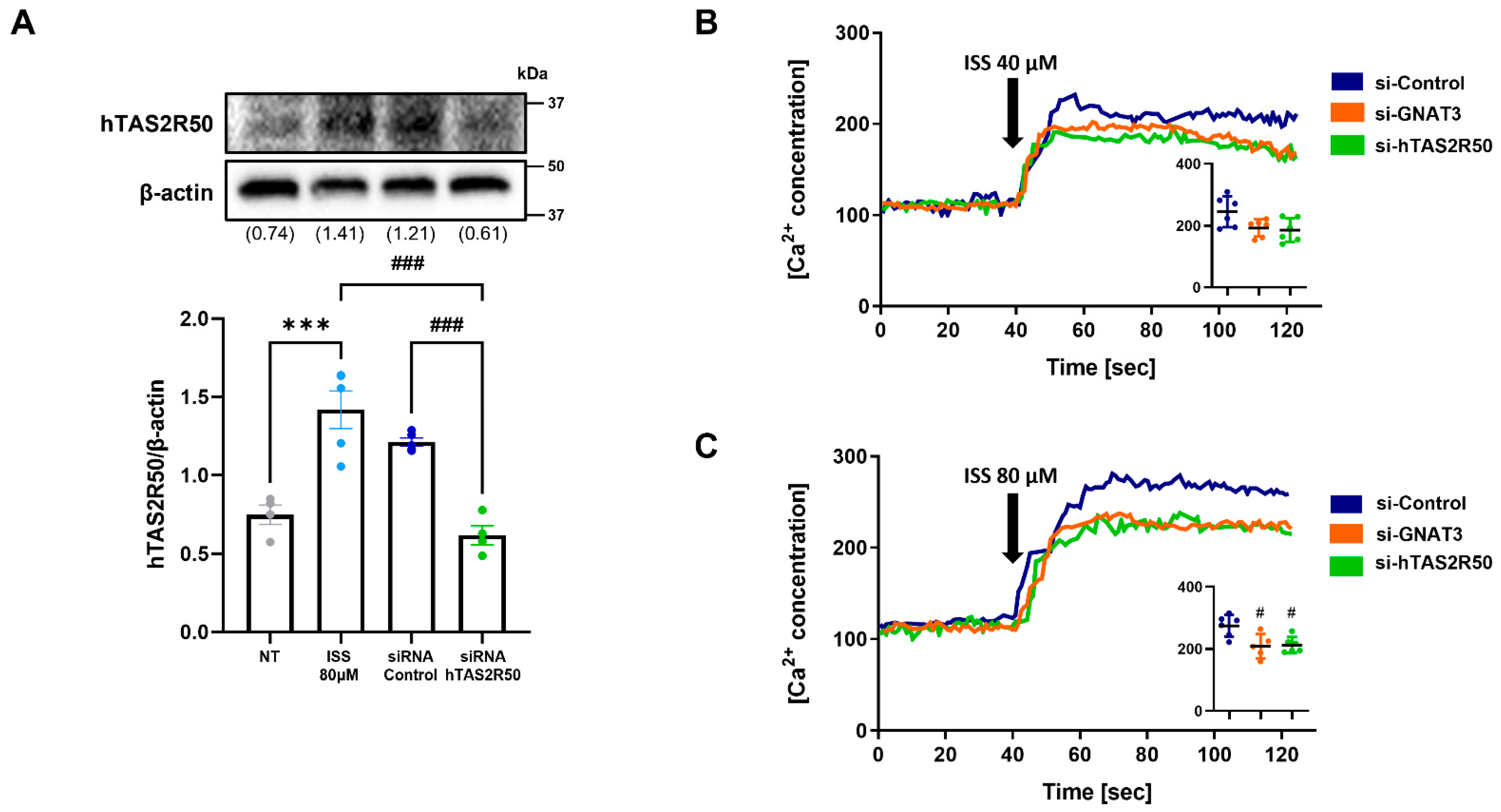
2.3. hTAS2R50 Knockdown Suppresses the Isosinensetin-Mediated Phospholipase C Pathway
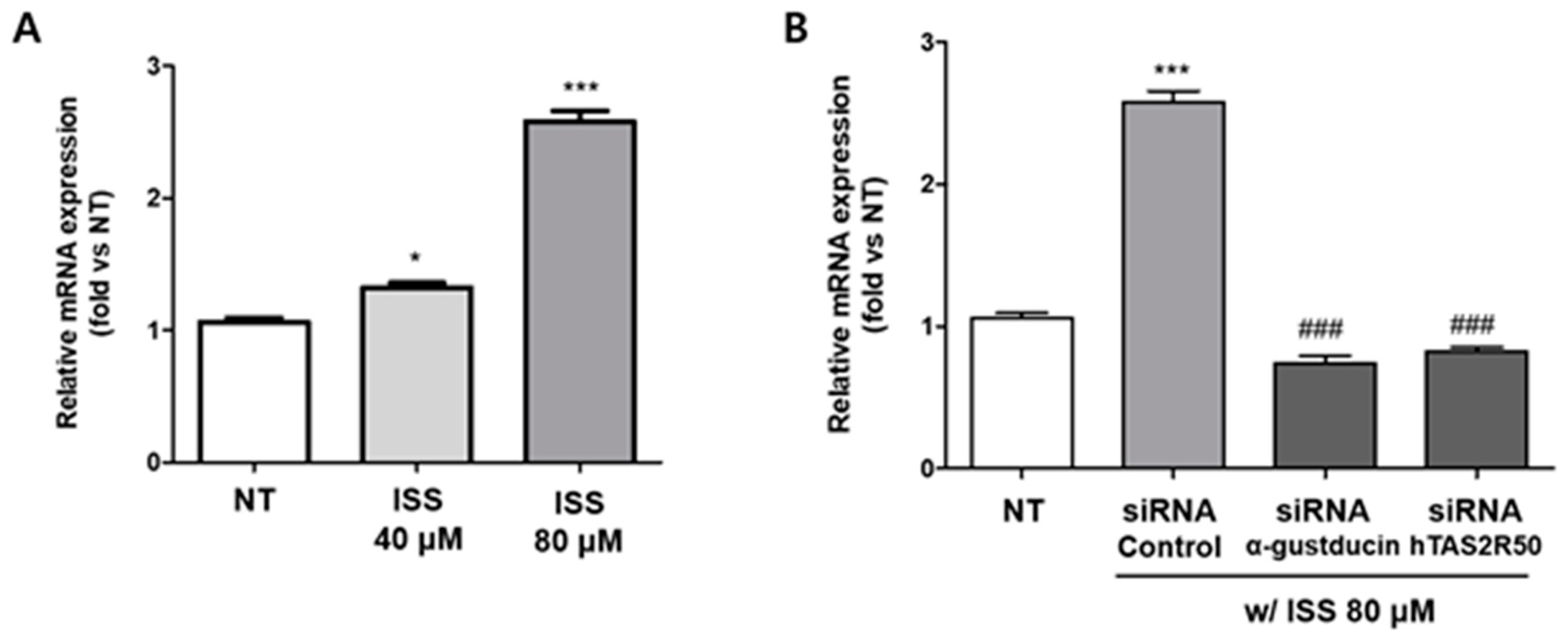
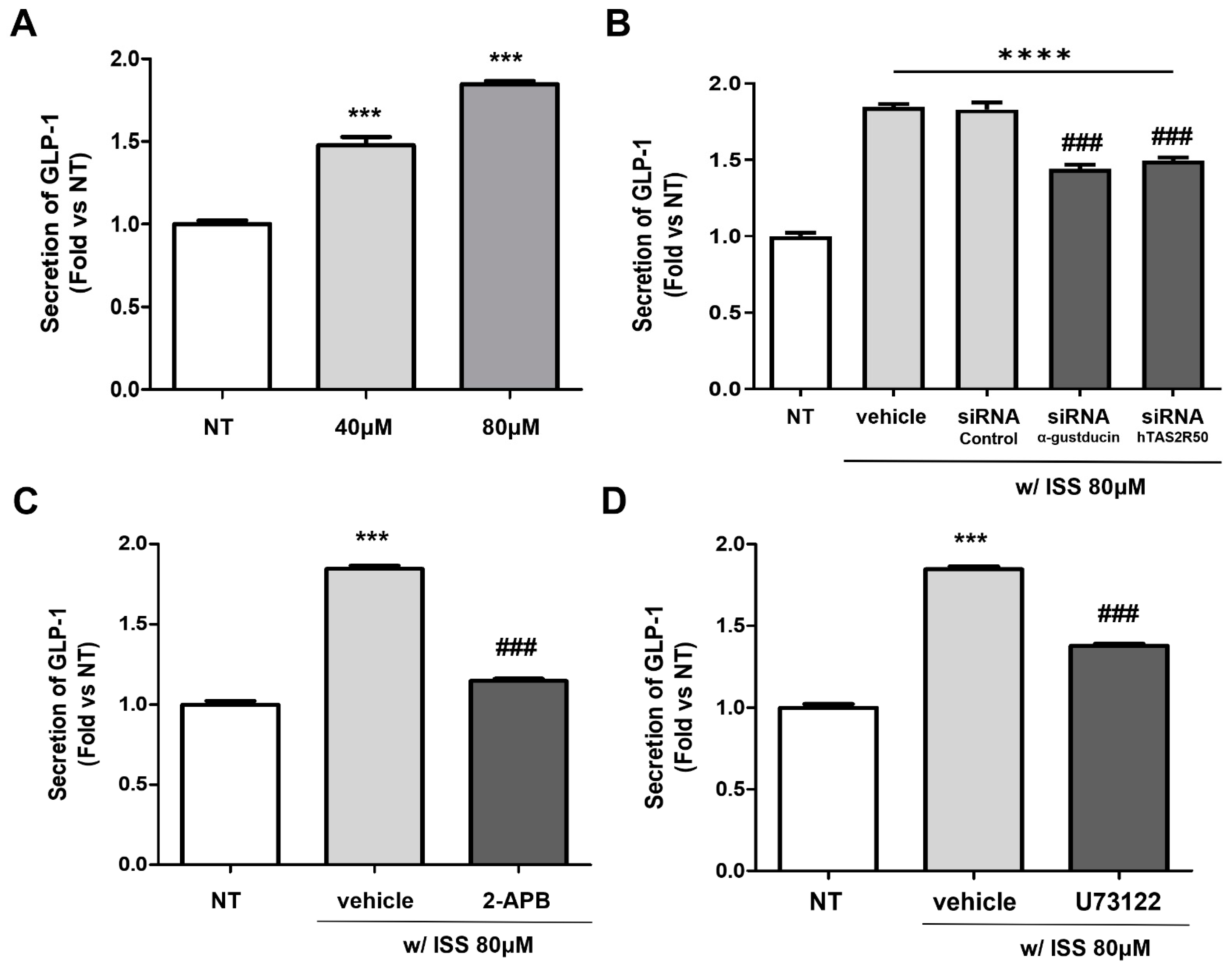
2.4. Isosinensetin Stimulates the Secretion of Proglucagon-Encoding GLP-1
2.5. Isosinensetin Stimulates hTAS2R50 and Induces GLP-1 Secretion
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. MTT Assay
4.4. Calcium Imaging
4.5. Real-Time PCR
4.6. Western Blot
4.7. siRNA Preparation and Transfection
4.8. GLP-1 ELISA
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ISS | Isosinensetin |
| 2-APB | 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-[2H]-tetrazolium bromide |
| TAS2Rs | Bitter taste receptors |
| GLP-1 | glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| GPCRs | G-protein-coupled receptors |
| PDE | phosphodiesterase |
| PLCβ2 | phospholipase Cβ2 |
| IP3 | inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate |
| DAG | diacylglycerol |
| DPP-4 | dipeptidyl peptidase-4 |
| BF | Bupleurum falcatum L. |
| DB | denatonium benzoate |
References
- Chandrashekar, J.; Hoon, M.A.; Ryba, N.J.; Zuker, C.S. The receptors and cells for mammalian taste. Nature 2006, 444, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Vrontakis, M.; Parkinson, F.; Chelikani, P. Functional bitter taste receptors are expressed in brain cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 406, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.J.; Kofonow, J.M.; Rosen, P.L.; Siebert, A.P.; Chen, B.; Doghramji, L.; Xiong, G.; Adappa, N.D.; Palmer, J.N.; Kennedy, D.W.; et al. Bitter and sweet taste receptors regulate human upper respiratory innate immunity. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozengurt, E. Taste receptors in the gastrointestinal tract. I. Bitter taste receptors and alpha-gustducin in the mammalian gut. Am. J. Physiol. 2006, 291, G171–G177. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, H.J.; Kokrashvili, Z.; Theodorakis, M.J.; Carlson, O.D.; Kim, B.J.; Zhou, J.; Kim, H.H.; Xu, X.; Chan, S.L.; Juhaszova, M.; et al. Gut-expressed gustducin and taste receptors regulate secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15069–15074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.V.; Rozengurt, N.; Yang, M.; Young, S.H.; Sinnett-Smith, J.; Rozengurt, E. Expression of bitter taste receptors of the T2R family in the gastrointestinal tract and enteroendocrine STC-1 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2392–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, J.M.; Margolskee, R.F. Taste cells of the gut and gastrointestinal chemosensation. Mol. Interv. 2008, 8, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandi, S.; Bromke, M.; Hübner, S.; Voigt, A.; Boehm, U.; Meyerhof, W.; Behrens, M. A subset of mouse colonic goblet cells expresses the bitter taste receptor Tas2r131. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, S.; Laermans, J.; Verhulst, P.J.; Thijs, T.; Tack, J.; Depoortere, I. Bitter taste receptors and α-gustducin regulate the secretion of ghrelin with functional effects on food intake and gastric emptying. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2094–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dotson, C.D.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H.; Shin, Y.K.; Vigues, S.; Ott, S.H.; Elson, A.E.; Choi, H.J.; Shaw, H.; Egan, J.M.; et al. Bitter taste receptors influence glucose homeostasis. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeruzal-Świątecka, J.; Fendler, W.; Pietruszewska, W. Clinical Role of Extraoral Bitter Taste Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pronin, A.N.; Tang, H.; Connor, J.; Keung, W. Identification of ligands for two human bitter T2R receptors. Chem. Senses 2004, 29, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, G.; Hoon, M.A.; Chandrashekar, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ryba, N.J.; Zuker, C.S. Mammalian sweet taste receptors. Cell 2001, 106, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.T.; Gannon, K.S.; Margolskee, R.F. Transduction of bitter and sweet taste by gustducin. Nature 1996, 381, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggio, L.L.; Drucker, D.J. Biology of incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2131–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, J.J. The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 1409–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, P.E.; El-Kholy, W.; Riedel, M.J.; Salapatek, A.M.; Light, P.E.; Wheeler, M.B. The multiple actions of GLP-1 on the process of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Diabetes 2002, 51 (Suppl. 3), S434–S442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J.; Sherman, S.I.; Gorelick, F.S.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Sherwin, R.S.; Buse, J.B. Incretin-based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: Evaluation of the risks and benefits. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Zhang, C.H. Extraoral bitter taste receptors in health and disease. J. Gen. Physiol. 2017, 149, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H. Variation in the TAS2R38 Bitterness Receptor Gene Was Associated with Food Consumption and Obesity Risk in Koreans. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, D.A.; Wang, W.C.; McIlmoyle, E.L.; Robinett, K.S.; Schillinger, R.M.; An, S.S.; Sham, J.S.; Liggett, S.B. Bitter taste receptors on airway smooth muscle bronchodilate by localized calcium signaling and reverse obstruction. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassin-Delyle, S.; Abrial, C.; Fayad-Kobeissi, S.; Brollo, M.; Faisy, C.; Alvarez, J.C.; Naline, E.; Devillier, P. The expression and relaxant effect of bitter taste receptors in human bronchi. Respir. Res. 2013, 14, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liggett, S.B. Bitter taste receptors on airway smooth muscle as targets for novel bronchodilators. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2013, 17, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.J.; Xiong, G.; Kofonow, J.M.; Chen, B.; Lysenko, A.; Jiang, P.; Abraham, V.; Doghramji, L.; Adappa, N.D.; Palmer, J.N.; et al. T2R38 taste receptor polymorphisms underlie susceptibility to upper respiratory infection. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 4145–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, H.W.; Lee, K.B.; Kim, K.S.; Yang, H.J.; Choi, E.K.; Shin, M.H.; Park, Y.S.; Na, Y.C.; Ahn, K.S.; Jang, Y.P.; et al. A bitter herbal medicine Gentiana scabra root extract stimulates glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion and regulates blood glucose in db/db mouse. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 172, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.S.; Jung Yang, H.; Lee, I.S.; Kim, K.H.; Park, J.; Jeong, H.S.; Kim, Y.; Seok Ahn, K.; Na, Y.C.; Jang, H.J. The aglycone of ginsenoside Rg3 enables glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion in enteroendocrine cells and alleviates hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetic mice. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, I.S.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, Y.; An, E.J.; Jang, H.J. Cucurbitacin B Induces Hypoglycemic Effect in Diabetic Mice by Regulation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Alpha and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 via Bitter Taste Receptor Signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Liang, J.; Gu, F.; Du, D.; Chen, F. Berberine activates bitter taste responses of enteroendocrine STC-1 cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 447, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, I.S.; Jeong, H.S.; Kim, Y.; Jang, H.J. GLP-1 secretion is stimulated by 1,10-phenanthroline via colocalized T2R5 signal transduction in human enteroendocrine L cell. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 468, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.S.; Egan, J.M.; Jang, H.J. Denatonium induces secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 through activation of bitter taste receptor pathways. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 2117–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerhof, W.; Batram, C.; Kuhn, C.; Brockhoff, A.; Chudoba, E.; Bufe, B.; Appendino, G.; Behrens, M. The molecular receptive ranges of human TAS2R bitter taste receptors. Chem. Senses 2010, 35, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, M.; Su, X.; Su, X.; Chen, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Z.; Li, C.; Lu, X. Identification of novel compounds for human bitter taste receptors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2014, 84, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, M.H.; Choi, E.K.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, K.H.; Jang, Y.P.; Ahn, K.S.; Chung, W.S.; Cha, N.H.; Jang, H.J. Hexane Fractions of Bupleurum falcatum L. Stimulates Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Secretion through G β γ -Mediated Pathway. Evid. Based Complement Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 982165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, M.H.; Matsumoto, T.; Kiyohara, H.; Yamada, H. B-cell proliferation activity of pectic polysaccharide from a medicinal herb, the roots of Bupleurum falcatum L. and its structural requirement. Immunology 1999, 97, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Wong, J.H.; Fu, M.; Ng, T.B.; Liu, Z.K.; Wang, C.R.; Li, N.; Qiao, W.T.; Wen, T.Y.; Liu, F. Isolation of adenosine, iso-sinensetin and dimethylguanosine with antioxidant and HIV-1 protease inhibiting activities from fruiting bodies of Cordyceps militaris. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.S.; Kang, S.I.; Yoon, S.A.; Ko, H.C.; Kim, S.J. Sinensetin attenuates LPS-induced inflammation by regulating the protein level of IκB-α. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2012, 76, 847–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Hao, G.; Zhang, Q.; Hua, W.; Wang, M.; Zhou, W.; Zong, S.; Huang, M.; Wen, X. Berberine induces GLP-1 secretion through activation of bitter taste receptor pathways. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 97, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, M.; Peluso, I.; Raguzzini, A. Flavonoids as anti-inflammatory agents. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2010, 69, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawser Hossain, M.; Abdal Dayem, A.; Han, J.; Yin, Y.; Kim, K.; Kumar Saha, S.; Yang, G.M.; Choi, H.Y.; Cho, S.G. Molecular Mechanisms of the Anti-Obesity and Anti-Diabetic Properties of Flavonoids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariri, B.M.; McMahon, D.B.; Chen, B.; Freund, J.R.; Mansfield, C.J.; Doghramji, L.J.; Adappa, N.D.; Palmer, J.N.; Kennedy, D.W.; Reed, D.R.; et al. Flavones modulate respiratory epithelial innate immunity: Anti-inflammatory effects and activation of the T2R14 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 8484–8497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensterle, M.; Rizzo, M. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 and Taste Perception: From Molecular Mechanisms to Potential Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Lee, I.S.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, Y.; An, E.J.; Jang, H.J. GI inflammation Increases Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter Sglt1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, M.; Brockhoff, A.; Batram, C.; Kuhn, C.; Appendino, G.; Meyerhof, W. The human bitter taste receptor hTAS2R50 is activated by the two natural bitter terpenoids andrographolide and amarogentin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9860–9866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Forward | Reverse | |
|---|---|---|
| hTAS2R1 | GCCCCATGCCTTTATTGTTA | GAGGTGAGACTCTAGCATTT |
| hTAS2R3 | AGTGAGGAGTTCTATGTAT | TGACCAGAATCCCAGTGTG |
| hTAS2R4 | GTGGTTTCTTTGGTCTTGAG | CCTACATGAGCTTCCGTCTG |
| hTAS2R5 | TCGCTTGAAGACAGATTACG | GAGAAATTCAACCACTGCCA |
| hTAS2R7 | ACTCCATCAACTAGA | ACCCAGTCCATGCAGTTAC |
| hTAS2R8 | TTAACCTGTTTGCAATTGTC | TGGCTCTCATGAACTTCT |
| hTAS2R9 | CTGTCATTTTCCCATCAAGC | GGGTCTCTATGGAACAAAAG |
| hTAS2R10 | CATTTCCCTTTGGAGACACA | ATGAGCTTCTGTGTTGGAGT |
| hTAS2R13 | AGGAGCAGAAAAAGGAGAAG | GTGAAGATACTCGGCAGCAGGG |
| hTAS2R14 | CCTCACTGCTTTGGCAATCT | ACACACACCAGCTTCCGAAT |
| hTAS2R16 | CCAGGAAGACACTTTGGAGT | TGACTTGCAGCCATTCTCTCTG |
| hTAS2R19 | CGAACCATTTCAGCATGTGG | CCCCAACAGTATCACCAGAA |
| hTAS2R20 | AGATGCGACCAAAAGAAATT | CACCTGCCACAAAACTGAAA |
| hTAS2R30 | TTCAGCTATCCTTCAACCCA | GCCCCTCTTGTGAATCTATG |
| hTAS2R31 | CAGCACCAAGGTCCACATAA | GTAAACGGCACATAACAAGA |
| hTAS2R38 | TGGCAACCAGGTCTTTAGAT | ACTCCAGGACTGAAATGAAC |
| hTAS2R39 | ATTACTGGATTGATACCCTGGC | TGTTTTCTTAGTGGAGTTGGAGG |
| hTAS2R40 | TGCCGGCCACTCAGTACAA | ACCGCTTCCAGGCTCTTCTC |
| hTAS2R41 | CCATGCAGAACGACTTTTAC | TTGAGGTTGCTGAAGATGAG |
| hTAS2R42 | ACTGGTAAACTGCTCTGAAGG | ATGTGAAGCAAGTCCCACTAG |
| hTAS2R43 | GACCACGAACCCACCTG | ACAAATGTAACCACTACCAG |
| hTAS2R45 | CCTTTGCTGACCAAATTGTCACT | TAATAATAACACCCAGAGCAAACCAA |
| hTAS2R46 | GACCACGAACCCACCTG | ACAAATGTAACCACTACCAG |
| hTAS2R50 | GTTGTCATGGTTAGCAAGGC | GAGTTGAGAGTTTCAGGTCT |
| hTAS2R60 | ACGGAGCTACTGTGAGAAAT | CGGAATCCTGAGGTTGTAAG |
| GAPDH | CCACTGCCGCATCCTCTTCC | CTCGTTGCCAATAGTGATGAC |
| GNAT3 | AGAGCAAGGAGTCAGCCAAAAG | CGCTCAGCATCCTCCTGAA |
| Proglucagon | AATCTTGCCACCAGGGACTT | AGTGACTGGCACGAGATGTT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-H.; Ko, H.M.; Jee, W.; Kim, H.; Chung, W.-S.; Jang, H.-J. Isosinensetin Stimulates Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Secretion via Activation of hTAS2R50 and the Gβγ-Mediated Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043682
Lee S-H, Ko HM, Jee W, Kim H, Chung W-S, Jang H-J. Isosinensetin Stimulates Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Secretion via Activation of hTAS2R50 and the Gβγ-Mediated Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(4):3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043682
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seung-Hyeon, Hyun Min Ko, Wona Jee, Hyungsuk Kim, Won-Seok Chung, and Hyeung-Jin Jang. 2023. "Isosinensetin Stimulates Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Secretion via Activation of hTAS2R50 and the Gβγ-Mediated Signaling Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 4: 3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043682
APA StyleLee, S.-H., Ko, H. M., Jee, W., Kim, H., Chung, W.-S., & Jang, H.-J. (2023). Isosinensetin Stimulates Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Secretion via Activation of hTAS2R50 and the Gβγ-Mediated Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(4), 3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043682








