Abstract
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the largest family of transmembrane receptors and play important roles in many physiological processes. As a representative group of protozoa, ciliates represent the highest stage of eukaryotic cell differentiation and evolution in terms of their reproductive mode, two-state karyotype, and extremely diverse cytogenesis patterns. GPCRs have been poorly reported in ciliates. In this study, we identified 492 GPCRs in 24 ciliates. Using the existing classification system for animals, GPCRs in ciliates can be assigned to four families, including families A, B, E, and F. Most (377 members) belong to family A. The number of GPCRs is extremely different in different ciliates; the Heterotrichea ciliates usually have more GPCRs than other ciliates. Parasitic or symbiotic ciliates usually have only a few GPCRs. Gene/genome duplication events seem to play important roles in the expansion of the GPCR superfamily in ciliates. GPCRs in ciliates displayed seven typical domain organizations. GPCRs in an ortholog group are common and conserved in all ciliates. The gene expression analysis of the members in this conserved ortholog group in the model ciliate, Tetrahymena thermophila, suggested that these GPCRs play important roles in the life cycle of ciliates. In summary, this study provides the first comprehensive genome-wide identification of GPCRs in ciliates, improving our understanding of the evolution and function of GPCR in ciliates.
1. Introduction
GPCRs play important roles in signal transduction and responses to extracellular stimuli. They also function in the regulation of cellular metabolism, hormone secretion, behavior and mood regulation, immune activity, and sensory activities, thereby playing important roles in the growth, development, and reproduction of organisms [1]. Scientists have designed several systems to classify the GPCR superfamily using different features, such as the clans, ligands to which they bind, and physiological and structural aspects. One popular system is using clans which classify the GPCRs into six families [2,3]: A (rhodopsin-like), B (secretin receptor family), C (metabotropic glutamate/pheromone), D (fungal mating pheromone receptors), E (cyclic AMP receptors), and F (frizzled/smoothed). This classification system was mainly designed to cover all vertebrate and invertebrate GPCRs. Although the sequence similarities among GPCRs have largely diverged, previous studies suggested that this superfamily may have originated and diversified in early eukaryotic evolution [4,5]. Due to their important roles, GPCRs have been widely identified and studied in many species, especially in model organisms. In humans, nearly 900 GPCRs have been identified. While 813 of these can be classified into four families, others cannot be assigned to A–F families at all. In Drosophila, more than 100 encoded proteins were originally considered to be GPCRs and have been classified into four families. With the rapid development of high-throughput sequencing technology, the genomes of more and more organisms have been sequenced successfully. The whole genome identification of GPCR has also been performed in multiple organisms, including Homo sapiens [6], Gallus gallus [7], Rattus rattus [8], Mus musculus [9], Anopheles gambiae [10], Caenorhabditis elegans [11], and Drosophila melanogaster [12].
Although GPCRs have been widely studied in multicellular organisms, little is known regarding their presence in unicellular organisms. Yeasts seem to encode a surprisingly small number of GPCRs. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Saccharomyces pombe, only three and nine GPCRs were found, respectively. An interesting question asks what might be the number and functions of GPCRs in unicellular organisms. The structural difference of GPCRs usually means a difference in function. In addition, the presence or absence of a certain type of GPCR in an organism may lead to functional differences between different organisms. A good example is the opsin receptors, which are designed to detect light and can be found in any animal [13,14]. However, the structure and number of opsin receptors varied considerably in Crustacea and led to differences in spectral sensitivity in Crustacean eyes, which are linked to ecological habitat and vitality [15]. Considering that GPCRs may have originated from the early evolution of eukaryotes, there may be some structural and functional differences in GPCRs between unicellular and multicellular organisms. In addition, the unique life cycle of unicellular organisms also suggests novel GPCRs in these organisms [16].
Ciliates are an important group of unicellular eukaryotes, common almost anywhere where water is present. In the microbial food webs of water bodies, ciliates have important functions because of their ecological responsiveness to various environmental stimuli [17,18,19]. In addition, some facultative and obligate parasitic ciliates cause widespread concern because they often lead to host diseases [20]. In general, ciliate cells as a whole need to respond and adapt to changes in the environment. Their GPCRs function in response to external stimuli and therefore play an important role in their life cycles. In ciliates, previous studies in Tetrahymena thermophila showed chemosensory responses to many different stimuli. As free-living organisms, Tetrahymena cells are able to change the speed and direction of their swimming and respond to different chemorepellents and chemoattractants [21,22,23,24]. The ability to respond to different chemicals allows these cells to swim away from hazardous areas and towards preferred locations in the water environment. In Paramecium, the chemoattractants also change their swimming speed. Intracellular electrophysiological measurements in Tetrahymena and Paramecium showed that they are generally similar. Therefore, these ciliates may incorporate sensory function and membrane potential changes to generate responses. Many sensory reception processes in eukaryotes usually involve the ligand activation of a G protein-coupled receptor [25,26]. Several studies have demonstrated that canonical GPCRs exist in ciliates, but the composition and function of GPCRs in ciliates are not yet clear [27,28,29]. In addition, ciliates exhibit diverse cell sizes, living environments, and life styles. Their GPCRs may vary significantly among different species.
In this study, we collected the genome data of ciliates in public databases, including ciliates from the Hymenostomatida [30], Euplotida [31], Sporadotrichida [32], Philasterida [33], Peniculida [34], and Sessilida and Heterotrichida [35]. We performed whole-genome identifications of GPCRs in these ciliates. The comprehensive identification of the GPCRs in ciliates will help us to understand the diversification and functions of the GPCRs in unicellular organisms.
2. Results
2.1. Identification of GPCRs in Ciliates
A total of 526 GPCRs were identified in the genomes of 24 ciliates and three outgroups. Table 1 shows the classification of 526 GPCRs based on the domain annotations. In general, the rhodopsin family is the largest GPCR family in the ciliates, with a total of 377 members.

Table 1.
Distribution of GPCRs in different protein domain categories.
We also attempted to annotate the GPCRs based on the A-F classification system used in animals. Protein domain annotations and BLASTP search results were used to assign the GPCRs into A–F families. For BLAST searches, all the GPCRs were BLASTP searched against the GPCRdb using an e-value cut-off of 1 × 10−5, and the A–F families were assigned based on the top hit in GPCRdb. Of the 526 GPCRs, 499 (94.8%) could be classified in families, and the rest of the GPCRs were labeled Unknown (Supplementary Table S1). In those 27 species, we found the GPCRs could be assigned to the A, B, E, and F families.
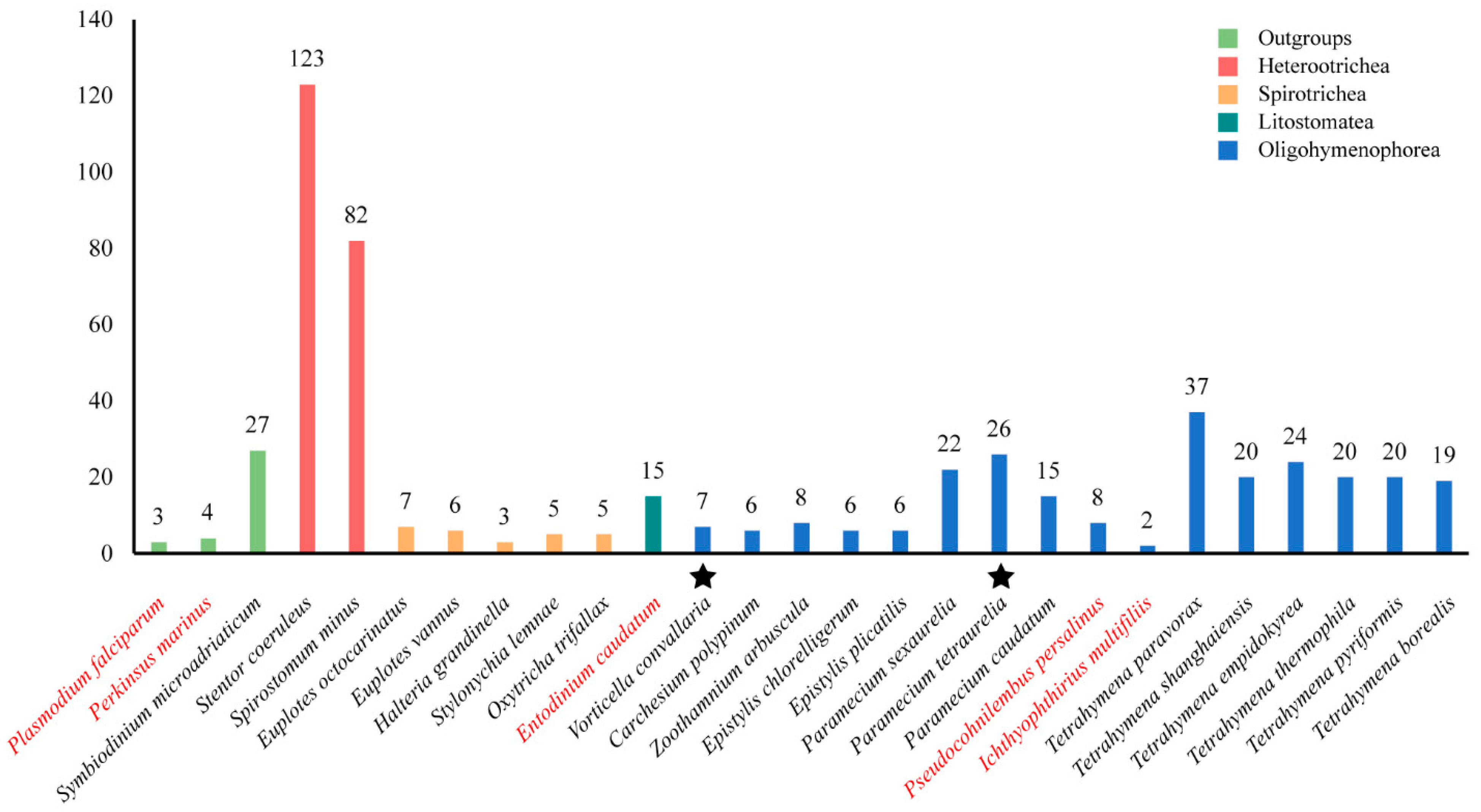
Figure 1 shows the number of GPCRs in different ciliate species. It seems that the number of GPCRs differs greatly in different species. Stentor coeruleus has the largest number of GPCRs with 123 members. The Ichthyophthirius multifiliis has the smallest number of GPCRs with only two members. In general, the class Heterotrichea ciliates, including S. coeruleus and Spirostomum minus, is shown to have the most GPCRs, followed by Oligohymenophorea (Tetrahymena, Paramecium, Epistylis, Carchesium, Vorticella, Zoothamnium), Spirotrichea (Euplotes, Halteria, Oxytricha and Stylonychia), and Litostomatea (Entodinium). Another interesting result was that the number of GPCRs identified in free-living ciliates was higher than that in parasitic or symbiotic ciliates, such as the fish obligate parasite I. multifiliis and the rumen anaerobic ciliate Entodinium caudatum.
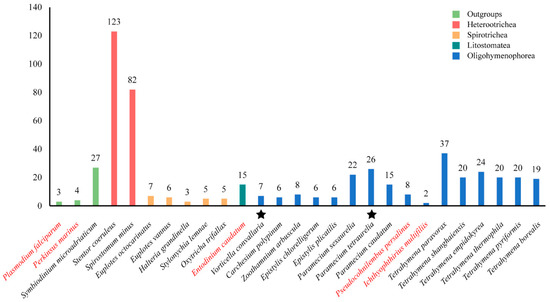
Figure 1.
The number of GPCRs in 24 ciliates and three outgroups. Different colors represent different species. Red: parasitic and symbiotic species; black: free-living species. Stars indicate that the species have been shown to undergo genome duplication.
2.2. Distribution GPCR Families in Ciliates
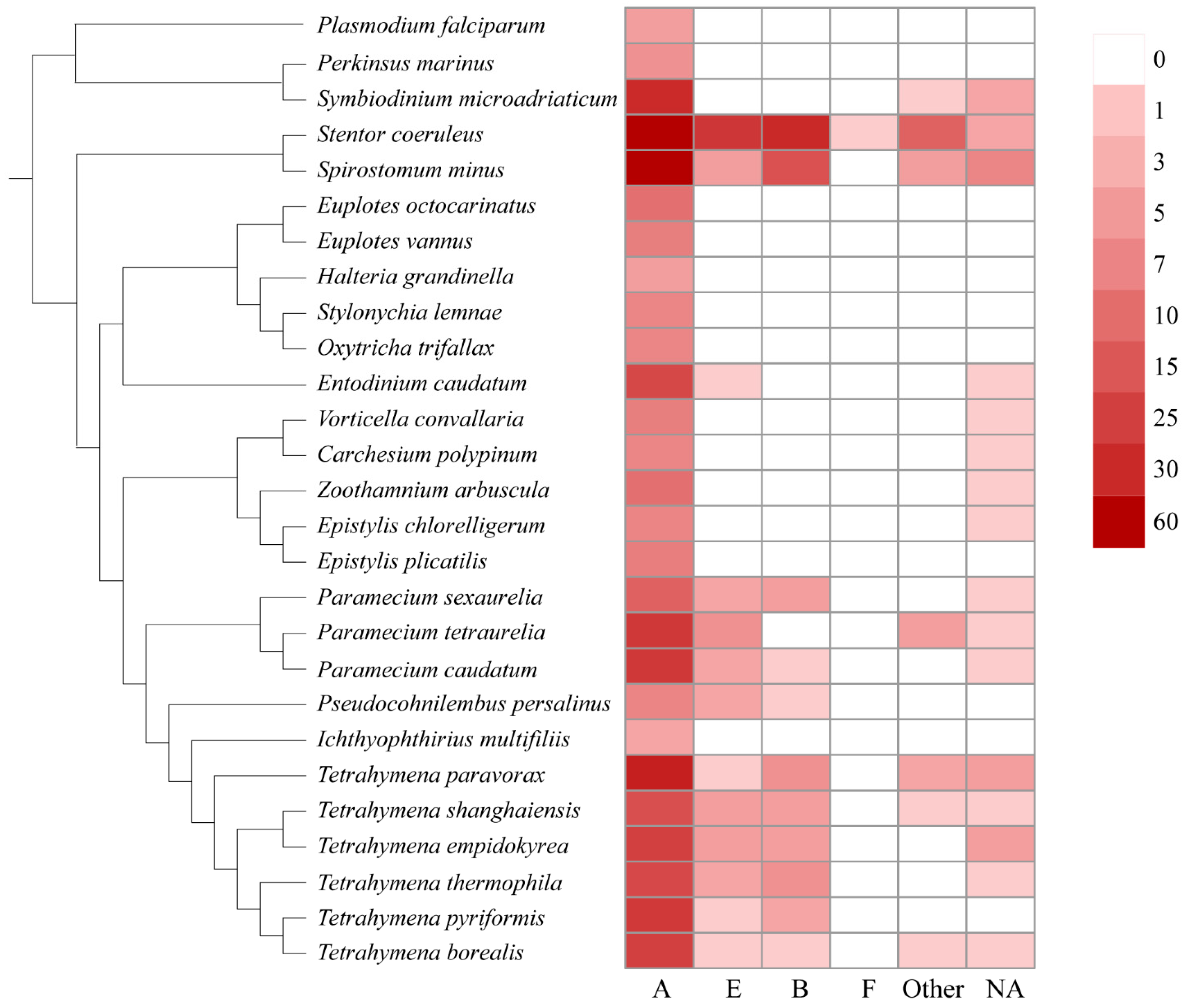
In this study, we also assigned the GPCRs to the existing classification system, e.g., the A–F families. As shown in Figure 2, the family A is the largest GPCR family in general, followed by families E, B, and F. No GPCRs belonging to families C and D were found in ciliates. Family A GPCRs seem to be most important in ciliates because they make up the largest GPCR family of all the ciliates (Figure 2). Family B and E GPCRs were mainly identified in Paramecium, Tetrahymena, Stentor, and Spirostomum.
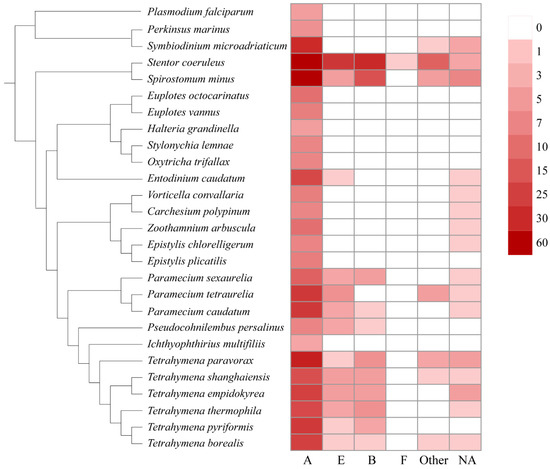
Figure 2.
Distribution of different GPCR families in ciliates.
Previous studies showed that family A rhodopsin-like GPCRs are the largest subfamily of G protein-coupled receptors and make up about half of all GPCRs, including hormones, neurotransmitters, and light receptors [36]. In general, rhodopsin-like GPCRs family members are complex and difficult to classify based on single characteristics, such as structure, function, and expression distribution, but most of these proteins transduce extracellular signals through coupled guanine nucleotide-binding (G) proteins [37]. These signals can be light, smells, ions, hormones, etc. In ciliates, family A GPCRs also had transmembrane-protein-GPR107-GPR108-like (IPR009637), phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate-5-kinase (IPR023610), archaeal-bacterial-fungal-rhodopsins (IPR001425), intimal-thickness-related-receptor-IRP (IPR019336), and GPCR-rhodopsin-like-7TM domain (IPR017452). In previous studies, these domains were considered to play the role of retrograde transport in trans-Golgi networks [38,39], the phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate precursor in the phosphoinositide signaling pathway [40], light-dependent ion transport and sensory functions [41,42], and intimal thickening in mice and transduce extracellular signals.
Family B GPCRs have been widely identified in animals [43] but not in plants, fungi, or prokaryotes. In ciliates, family B GPCRs are mainly distributed in Stentor, Paramecium, and Tetrahymena. Family B GPCRs are mainly secretory, adherent, and responsible for both maintaining homeostasis and regulating behavior [44] such as glucose homeostasis, learning and memory, and stress-related autonomic, neuroendocrine, and behavioral function [45,46].
Family E GPCRs mainly consist of cyclic AMP receptor (CAR) proteins [47,48]. The cAMP receptors belong to the cell-surface receptor family. These receptors are usually involved in chemotaxis, aggregation, and morphogenetic movement [49]. In ciliates, family E GPCRs are mainly distributed in class Heterotrichida, Peniculida, and Hymenostomatida. An interesting phenomenon is that the distribution of family E GPCRs in ciliates coincides with the speed of swimming or the strength of the locomotion ability of ciliates [50]. Paramecium and Stentor have strong swimming ability, and a large number of family E GPCRs have been identified in their genomes. In contrast, ciliates in Sessilida and Spirotrichea had relatively weak swimming ability, and few or no family E GPCRs were identified in them.
Neither family C nor family D GPCRs were identified in all ciliates. Only one family, F GPCR, was identified in all the ciliates. Family D GPCRs were only identified and involved in fungi mating [51]. Family C and F are metabotropic glutamate receptors and frizzled and smoothened receptors, respectively. Family C GPCRs were reported to function in the central nervous system and in regulating Ca2+ homeostasis, while family F GPCRs are mainly involved in ontogeny and tissue homeostasis [52,53,54]. Our results suggest that these GPCR families are lacking in ciliates.
2.3. Protein Domain Architectures of GPCRs in Ciliates
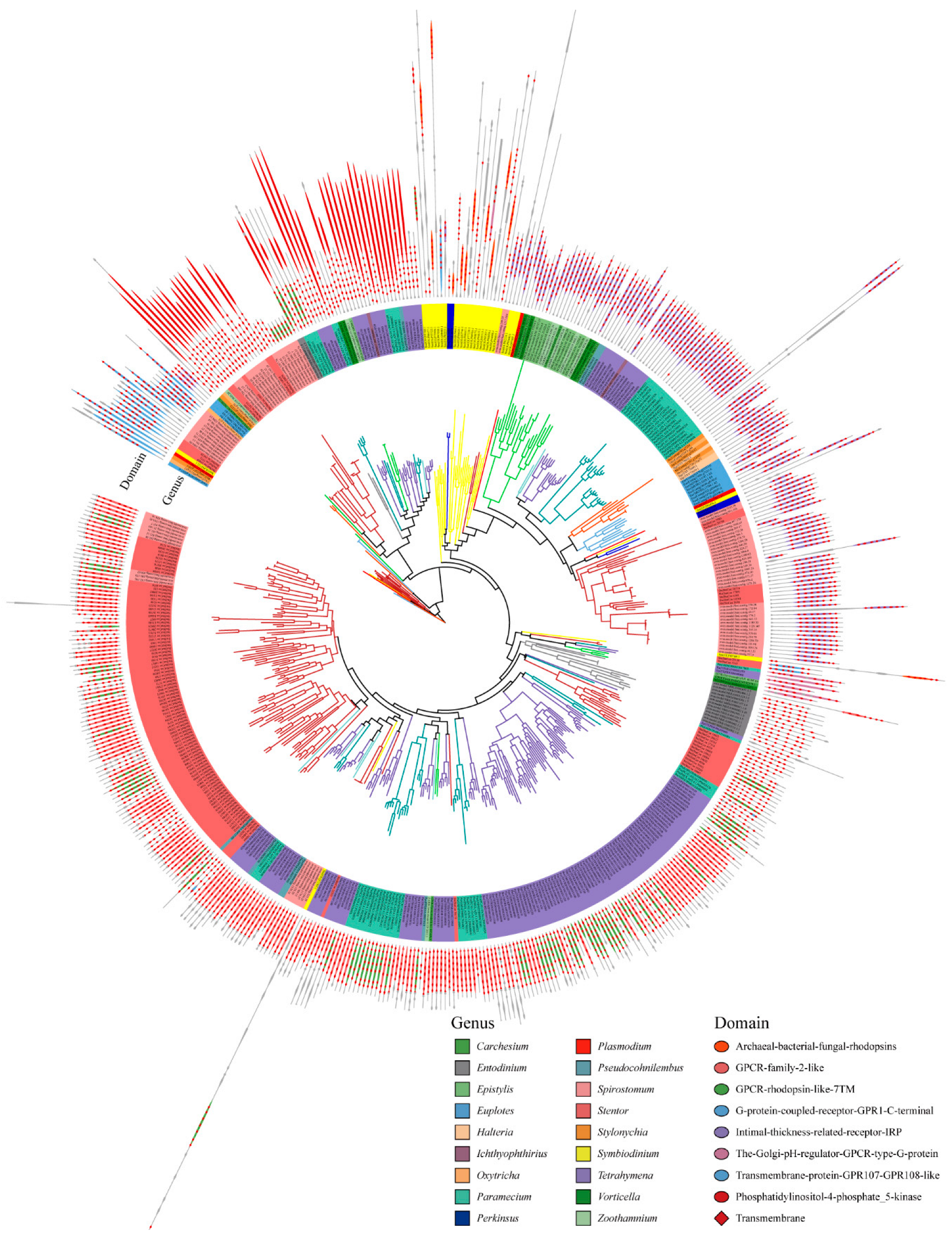
We used the maximum likelihood method to construct a phylogenetic tree of GPCRs, and the domain organizations of each protein was assigned (Figure 3). The GPCRs in ciliates showed seven typical domain organizations: Types 1 to 7. These include Type 1, which represents the 5-8TMs + archaeal-bacterial-fungal rhodopsin (IPR001425); Type 2: 4-7TMs + GPCR family 2-like (IPR017981); Type 3: 3-8TMs + GPCR rhodopsin-like 7TM (IPR017452); Type 4: 6-7TMs + G protein-coupled receptor GPR1 C-terminal (IPR022596); Type 5: 3-8TMs + intimal thickness related receptor (IPR019336); Type 6: 3-8TMs + the Golgi pH regulator-GPCR-type G protein (IPR015672); and Type 7: 5-8TMs + transmembrane protein GPR107-GPR108-like (IPR009637). In addition, some GPCR also have accessory domains, e.g., phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase (IPR023610).
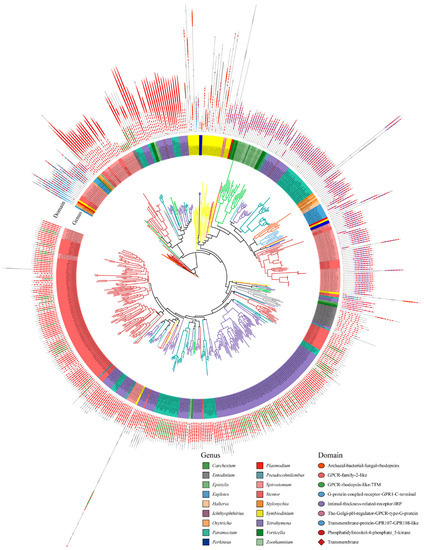
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic tree and domain architectures of the GPCRs in ciliates.
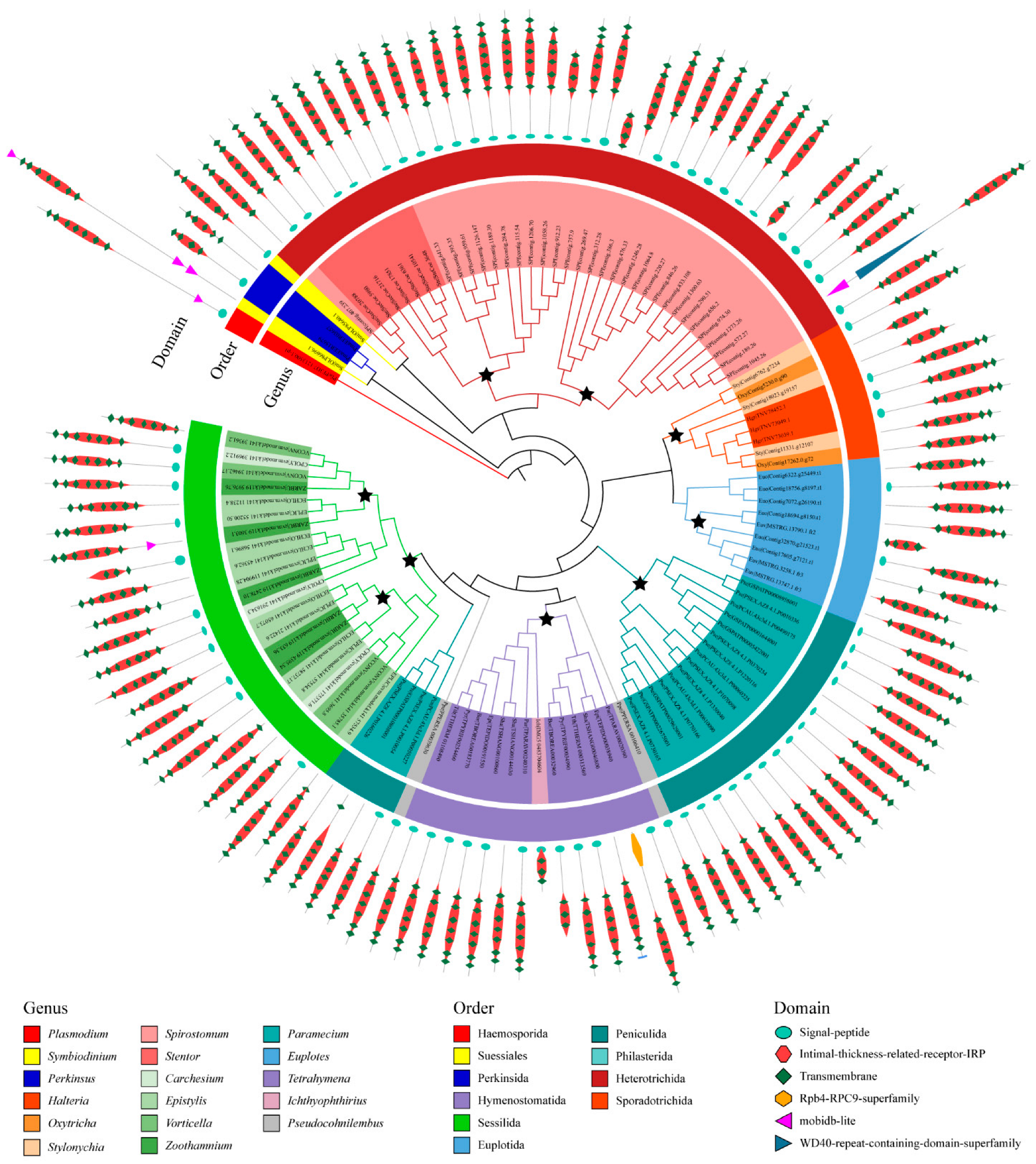
We also divided the 526 GPCRs into ortholog groups using the OrthoFinder, and 84 ortholog groups were identified (Table S1, Figure S1). In general, the ortholog groups are lineage-specific (Figure S1). Among these 84 ortholog groups, only one was seen to exist in all ciliate species, suggesting that this ortholog group included the most common and conserved GPCRs in ciliates and may be involved in certain fundamental functions. In this conserved ortholog group, 115 GPCRs belonged to family A GPCRs and contained a protein domain PF10192. GPCRs in this ortholog group were similar in length and domain architecture. These GPCRs have an average length of 400 amino acids and usually have six to seven transmembrane helices. The phylogenetic analysis of GPCRs in this ortholog group suggested that many gene duplication events occurred (Figure 4). Most of the duplication events of GPCR genes commonly took place in the species or genus. For example, the ortholog group of GPCR is divided into several distinct branches in Spirostomum minus, and the GPCR is divided into two distinct categories in the genus Tetrahymena. Therefore, gene/genome duplication events seem to play important roles regarding the expansion of the GPCR superfamily in ciliates.
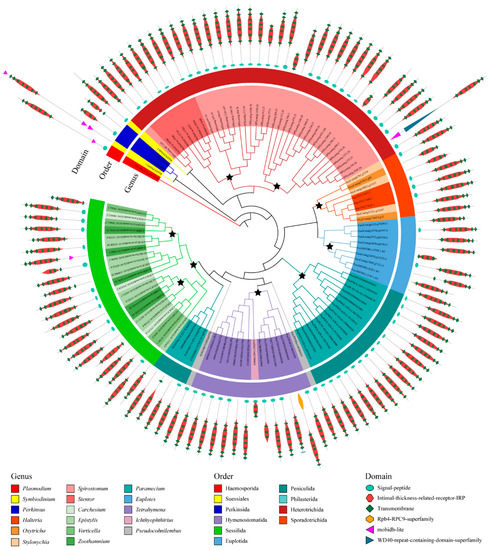
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic tree of GPCRs in the most conserved ortholog group. Stars indicate the duplicate on events of GPCR genes.
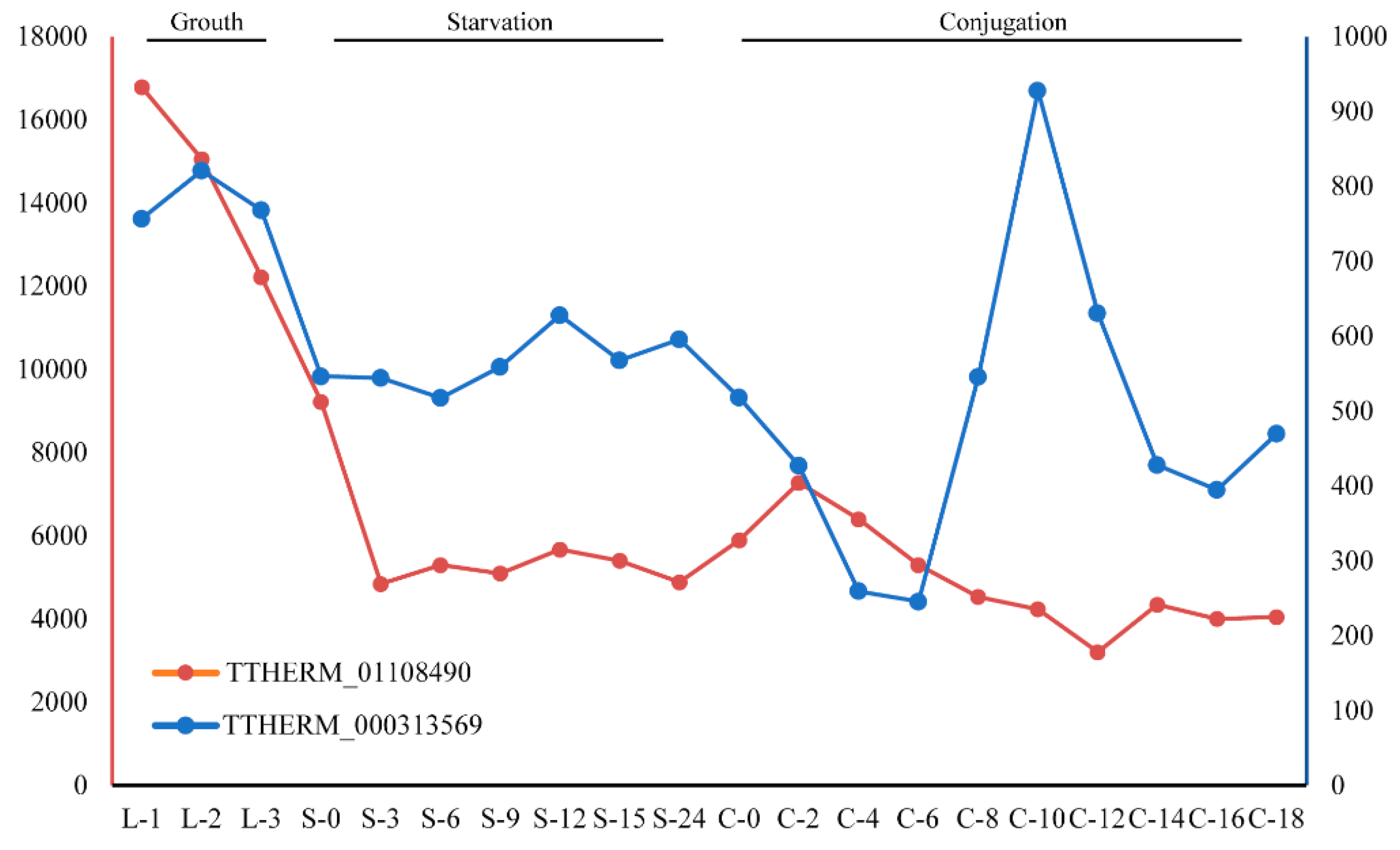
The InterProScan annotation of these GPCRs demonstrated that most have the signal peptide and are annotated as intimal thickness related receptor (ITR, IPR019336). In mice, ITRs are usually expressed in vascular smooth muscle cells. ITR knockout mice were shown to be resistant to experimental intimal thickening, suggesting that ITRs play key roles in signal receiving in vascular smooth muscle cells [55]. ITRs usually have a domain with seven transmembrane alpha helices and belong to the rhodopsin-like GPCR superfamily [56]. This type of receptor could respond to many extracellular signals, such as hormones and lipid messengers. In the model ciliate, Tetrahymena thermophila, two genes belong to this ortholog group: TTHERM_01108490 and TTHERM_000313569. Gene expression analysis for these two genes showed that TTHERM_01108490 genes have high expression levels in all three stages (growth, starvation and conjugation) in the Tetrahymena life cycle, but especially in growth (Figure 5). The gene TTHERM_000313569, although displaying a relatively lower expression level than TTHERM_01108490, was also expressed in all three stages in the Tetrahymena life cycle. This result suggested that GPCRs in this ortholog group may play important roles in the life cycle of ciliates.
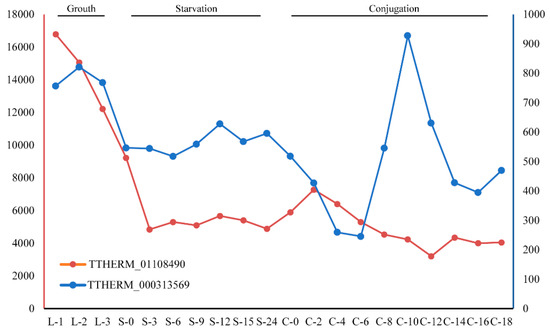
Figure 5.
Expression levels of gene TTHERM_01108490 and TTHERM_000313569 at different stages of the life cycle in Tetrahymena thermophila.
3. Discussions
3.1. High Variation of the Number of GPCR in Ciliates
Previous studies have shown significant differences in the number of GPCRs in multicellular animals. However, in ciliates, the number of GPCRs identified in different species can still differ by one to two orders of magnitude, which is very interesting. We speculate that three main factors affect the number of GPCR in ciliates. First, the large number of GPCRs in Heterotrichea ciliates may be related to the size and complexity of their cells. S. coeruleus is a large ciliate that is 0.5 to 2 mm in length. S. minus is 0.6 to 0.7 mm in length. These giant cells have complex cellular structures [57,58,59,60,61], and the large number of GPCRs may support their responses to the environment. Second, the number of GPCRs may be related to the lifestyle of ciliates. In this study, the result is similar to the finding in the Apicomplexa parasite, of which only several GPCRs have been characterized [62], and may reflect the relatively stable environments of these species encountered in its life cycle. Third, the number of GPCRs in ciliates may be related to gene/genome repetition events. Early studies demonstrated that the sequence similarity is minimal among distant GPCR proteins; thus, the origins of GPCRs between families were thought to be uncorrelated [63]. The identification and classification of GPCRs indicated a common evolutionary origin for all groups, and they may have arisen from a single ancestor through gene duplications. A study of Caenorhabditis elegans, Drosophila melanogaster, and Anopheles gambiae also suggested that GPCRs have ancient origins. Different GPCR members may have evolved through gene/genome duplications and in tandem with increasing organismal complexity [64]. Therefore, we investigated the relationship between the predicted proteome size and the number of GPCRs in ciliates. The effect of gene/genome repetition events and the number of GPCRs was positively correlated (R = 0.520, p = 0.005) (Figure S2, Table S2). Among the ciliates investigated in this study, genome duplication events have been reported in Vorticella convallaria and the Paramecium tetraurelia; the numbers of GPCRs identified in these two species are higher than those in other ciliates in the same order. These results suggested that gene/genome duplications may play important roles in the expansion of the GPCR superfamily.
3.2. Clues for the Function of GPCRs in Ciliates
The GPCRs are the largest family of transmembrane receptors, and most belong to the Family A GPCRs [3]. The rhodopsin receptor family, which is composed of Family A GPCRs, can be further divided into several subclasses, such as amines, peptides, proteins, lipids, sensory subclasses, and others. These play a crucial role in signal transduction [65]. Family A GPCRs are highly differentiated among species. However, in ciliates, an ortholog group of GPCRs was found that showed significant homology between species, making it the most common and conserved group among GPCRs. This ortholog group of GPCRs may be involved in regulating the cell life cycle, sexual partner recognition, and finding food [66]. In the model ciliate, Tetrahymena thermophila, there are two genes belonging to this ortholog group that have high expression levels in the growth or conjugation in the life cycle of Tetrahymena. Therefore, they may be involved in recognizing certain pheromones released during cellular mating. Despite the lack of clear functional annotations for many of the identified putative GPCRs, some of these genes have been classified as responsive to pheromones based on their gene ontology (GO) annotations. In particular, a gene in Paramecium and Stylonychia was annotated as the G protein-coupled receptor 180 (GPR180) [67,68]. Although its function has not yet been verified in ciliates, it has been shown to play a crucial role in signal transduction during gametogenesis in Plasmodium. In another study, the knockout of GPR180 had no observable impact on the blood development stage, but it did impair the formation of gametes [69]. This finding further confirms our conjecture that this class of GPCR may play an important role in the growth cycle or the mating of ciliates. However, more experimental data are needed to understand the detailed molecular functions of such GPCRs in ciliates.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ciliate Genome Data Collection
To identify the GPCRs of ciliates, we collected the genome data of 24 ciliates, and the dataset was derived from four sources. Of the collected ciliates, the data for Ichthyophthirius multifiliis, Tetrahymena borealis, Tetrahymena empidokyrea, Tetrahymena paravorax, Tetrahymena pyriformis, Tetrahymena shanghaiensis, Tetrahymena thermophila, Euplotes octocarinatus, Euplotes vannus, Stentor coeruleus, Oxytricha trifallax, and Stylonychia lemnae were obtained from Ciliates.org (https://ciliates.org/landing/ (accessed on 12 October 2022)). The data for Entodinium caudatum, Carchesium polypinum, Halteria grandinella, Pseudocohnilembus persalinus, and Spirostomum minus were retrieved from NCBI (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (accessed on 12 October 2022)). The data for Paramecium caudatum, Paramecium sexaurelia, and Parameciium tetraurelia were obtained from ParameciumDB (https://paramecium.i2bc.paris-saclay.fr/ (accessed on 12 October 2022)). Further ciliate data, including data for Epistylis chlorelligerum, Epistylis plicatilis, Vorticella convallara, and Zoothamnium arbuscula can be accessed through the National Genomics Data Center (https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/ (accessed on 12 October 2022)). This dataset covers four classes, eight orders, twelve families, and fifteen genera. In addition, we also identified the GPCRs in three non-ciliates species (used as outgroups), including Perkinsus marinus, Symbiodinium microadriaticum, and Plasmodium falciparum. These data were also obtained from NCBI (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (accessed on 17 October 2022)).
4.2. Identification of Putative GPCR Genes
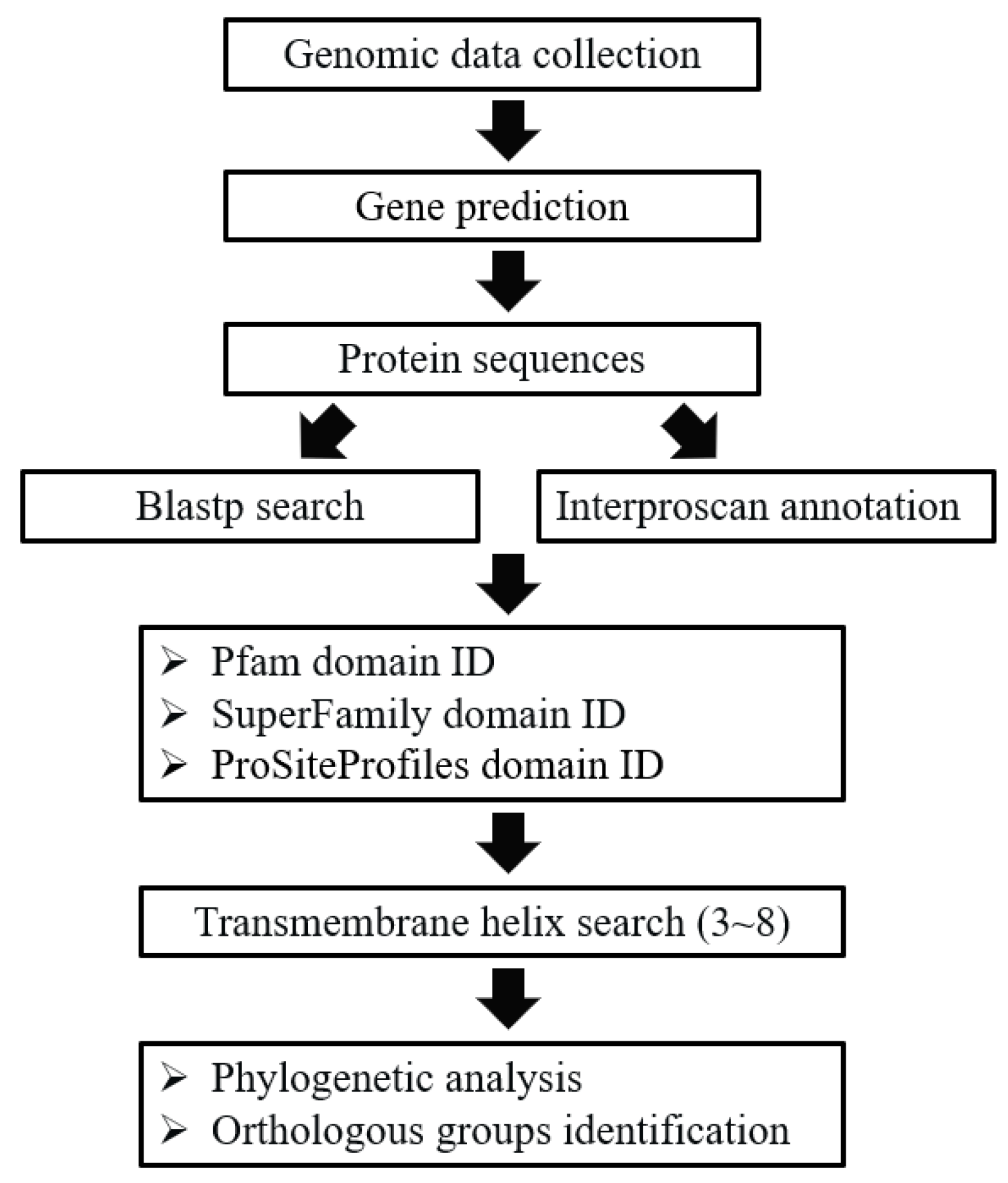
In general, the GPCRs in ciliates were identified through a combination of BLAST and HMM searches. The procedure of GPCRs identification was described in Figure 6. To perform the BLAST searches, the GPCRs previously reported in Bombyx mori [70], Caenorhabditis elegans [71], Drosophila melanogaster [12], Homo sapiens [6], Mus musculus [9], Arabidopsis thaliana [72], and Tetrahymena thermophila [55] were collected and used as the seeds for BLASTP searches. To identify putative GPCRs sequences from protein sequences in collected genomes, BLASTP (version 2.6.0+) searches were first performed with a cut-off e-value of 1e-05 in order to search for all GPCRs candidates [73]. To identify putative GPCRs that lack significant sequence similarity to known GPCRs which may have been missed in the BLAST searches, more sensitive searches based on hidden Markov models (HMM) were performed using the InterProScan program [74,75], and protein domains were annotated. We used four independent domain annotations to screen the GPCRs in the collected genomes, including the Pfam domain, the Superfamily database, the PROSITE profiles database, and transmembrane helix information. For the Pfam domain, the proteins with 7TM_1/Rhodopsin (PF00001), 7TM_2/Adhesion (PF00002), 7TM_3/Glutamate (PF00003), Frizzled (PF01534), Ocular_alb (PF02101), Dicty_CAR (PF05462), Lung_7-TM_R (PF06814), GPCRsRhopsn4 (PF10192), Git3 (PF11710), GPR_Gpa2_C (PF11970), or ABA_GPCRs (PF12430) were selected as putative GPCRs; for the Superfamily database, Family A G protein-coupled receptor-like (SSF81321) was used; for the PROSITE profile database, G_PROTEIN_RECEP_F1_2 (PS50262) was used. All the candidates based on BLAST searches and protein domain annotation were combined. Finally, we used the transmembrane helix information (TMHMM [76]) to screen the GPCRs by requiring a protein to have three to eight transmembrane helices.
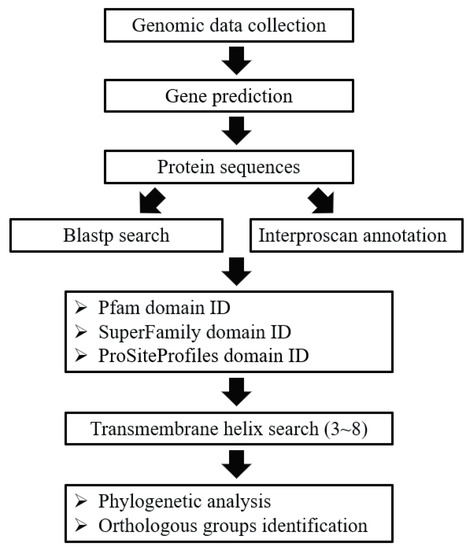
Figure 6.
Pipeline used to identify GPCRs in ciliates.
4.3. Identification of Ortholog Groups of GPCRs
To investigate the relationship of GPCRs in different ciliates, ortholog groups were identified using the predicted proteomes through the OrthoFinder (version 2.5.4) software (https://github.com/davidemms/OrthoFinder (accessed on 23 October 2022)). For phylogenetic analysis, multiple sequence alignment was performed using MAFFT (version 7.310) with E-INS_I parameter [77]. The most suitable substitution model was determined based on the Bayesian Information Criteria and Akaike Information Criteria [78]. The phylogenetic trees were constructed using RAxML (version 8.2.11) with the LG + G + F substitution model, and the reliability of the tree topology was evaluated with 1000 bootstraps [79]. The GPCR protein sequences, which were used for phylogenetic analysis, are provided in the Supplementary File S1.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms24043869/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.X. and W.M.; methodology, S.L., P.Z. and J.X.; formal analysis, S.L. and P.Z.; writing, original draft preparation, S.L. and J.X.; writing, review, and editing, S.L., J.X. and W.M.; supervision, J.X. and W.M.; and funding acquisition, J.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31872221).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article or Supplementary Material.
Acknowledgments
We thank Kai Chen, Guangying Wang, Jing Zhang, and Siyu Gu (Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences) for their assistance in data analysis. The bioinformatics analysis was performed using the computing resources of the Wuhan Branch of the Supercomputing Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest related to this research.
References
- Dorsam, R.T.; Gutkind, J.S. G-protein-coupled receptors and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelini, S.; Urbanek, M.; Dean, M.; Goldman, D. Polymorphism and genetic mapping of the human oxytocin receptor gene on chromosome 3. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1995, 60, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolakowski, L.F., Jr. GCRDb: A G-protein-coupled receptor database. Recept. Channels 1994, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perez, D.M. The evolutionarily triumphant G-protein-coupled receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 63, 1202–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strotmann, R.; Schröck, K.; Böselt, I.; Stäubert, C.; Russ, A.; Schöneberg, T. Evolution of GPCR: Change and continuity. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 331, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassilatis, D.K.; Hohmann, J.G.; Zeng, H.; Li, F.; Ranchalis, J.E.; Mortrud, M.T.; Brown, A.; Rodriguez, S.S.; Weller, J.R.; Wright, A.C.; et al. The G protein-coupled receptor repertoires of human and mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4903–4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagerström, M.C.; Hellström, A.R.; Gloriam, D.E.; Larsson, T.P.; Schiöth, H.B.; Fredriksson, R. The G protein-coupled receptor subset of the chicken genome. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2006, 2, e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloriam, D.E.; Fredriksson, R.; Schiöth, H.B. The G protein-coupled receptor subset of the rat genome. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnadóttir, T.K.; Gloriam, D.E.; Hellstrand, S.H.; Kristiansson, H.; Fredriksson, R.; Schiöth, H.B. Comprehensive repertoire and phylogenetic analysis of the G protein-coupled receptors in human and mouse. Genomics 2006, 88, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.A.; Fox, A.N.; Pitts, R.J.; Kent, L.B.; Tan, P.L.; Chrystal, M.A.; Cravchik, A.; Collins, F.H.; Robertson, H.M.; Zwiebel, L.J. G protein-coupled receptors in Anopheles gambiae. Science 2002, 298, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frooninckx, L.; Van Rompay, L.; Temmerman, L.; Van Sinay, E.; Beets, I.; Janssen, T.; Husson, S.J.; Schoofs, L. Neuropeptide GPCRs in C. elegans. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metpally, R.P.; Sowdhamini, R. Cross genome phylogenetic analysis of human and Drosophila G protein-coupled receptors: Application to functional annotation of orphan receptors. BMC Genom. 2005, 6, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terakita, A. The opsins. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baylor, D. How photons start vision. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieb, S.M.; Cortesi, F.; Sueess, L.; Carleton, K.L.; Salzburger, W.; Marshall, N.J. Why UV vision and red vision are important for damselfish (Pomacentridae): Structural and expression variation in opsin genes. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 1323–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Hoogen, J.; Govers, F. GPCR-bigrams: Enigmatic signaling components in oomycetes. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azam, F.; Fenchel, T.; Field, J.G.; Gray, J.S.; Thingstad, T.F. The Ecological Role of Water-Column Microbes in the Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1983, 10, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corliss, J.O. Chapter 4-Phylum Ciliophora: General Description and Overview of the Major Groups. In The Ciliated Protozoa, 2nd ed.; Corliss, J.O., Ed.; Pergamon: Berlin, Germany, 1979; pp. 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, D.T. The Biology and Ecology of Tintinnid Ciliates: Models for Marine Plankton. Estuaries Coasts 2014, 37, 240–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Lin, X.; Song, W. Ciliate Atlas: Species Found in the South China Sea; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Leick, V.; Koppelhus, U.; Rosenberg, J. Cilia-mediated oriented chemokinesis in Tetrahymena thermophila. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1994, 41, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, J.T.; Hennessey, T.M. Chemorepellents in Paramecium and Tetrahymena. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1995, 42, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennessey, T.M. Responses of the ciliates Tetrahymena and Paramecium to external ATP and GTP. Purinergic Signal. 2005, 1, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lampert, T.J.; Coleman, K.D.; Hennessey, T.M. Chemoattraction to lysophosphatidic acid does not require a change in membrane potential in Tetrahymena thermophila. Cell Biol. Int. 2011, 35, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagerström, M.C.; Schiöth, H.B. Structural diversity of G protein-coupled receptors and significance for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Hsueh, Y.P.; Heitman, J. Magnificent seven: Roles of G protein-coupled receptors in extracellular sensing in fungi. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 1010–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, M.J.; Sherman, T.G.; Wood, D.C. Partial cloning of putative G-proteins modulating mechanotransduction in the ciliate stentor. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2001, 48, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaud, F.L.; Colon, I.; Lebron, J.; Ortiz, N.; Rodriguez, F.; Cadilla, C. A novel opioid mechanism seems to modulate phagocytosis in Tetrahymena. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1995, 42, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ondarza, J.; Symington, S.B.; Van Houten, J.L.; Clark, J.M. G-protein modulators alter the swimming behavior and calcium influx of Paramecium tetraurelia. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2003, 50, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Duan, L.; Cheng, T.; Qiao, Y.; Stover, N.A.; Gao, S. The completed macronuclear genome of a model ciliate Tetrahymena thermophila and its application in genome scrambling and copy number analyses. Sci. China. Life Sci. 2020, 63, 1534–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, F.; Zheng, W.; Krock, T.J.; Stover, N.A.; Lu, C.; Katz, L.A.; Song, W. Genome analyses of the new model protist Euplotes vannus focusing on genome rearrangement and resistance to environmental stressors. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 19, 1292–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Sánchez, D.; Mayén-Estrada, R.; Luo, X.; Hu, X. A New Subspecies of Oxytricha granulifera (Hypotrichia: Oxytrichidae) from Mexico, with Notes on its Morphogenesis and Phylogenetic Position. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2018, 65, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, G.; Cheng, J.; Tian, M.; Pan, X.; Warren, A.; Jiang, C.; Yuan, D.; Miao, W. Genome of the facultative scuticociliatosis pathogen Pseudocohnilembus persalinus provides insight into its virulence through horizontal gene transfer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaiz, O.; Meyer, E.; Sperling, L. ParameciumDB 2019: Integrating genomic data across the genus for functional and evolutionary biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D599–D605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slabodnick, M.M.; Ruby, J.G.; Reiff, S.B.; Swart, E.C.; Gosai, S.; Prabakaran, S.; Witkowska, E.; Larue, G.E.; Fisher, S.; Freeman, R.M., Jr.; et al. The Macronuclear Genome of Stentor coeruleus Reveals Tiny Introns in a Giant Cell. Curr. Biol. CB 2017, 27, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Zhou, Q.; Labroska, V.; Qin, S.; Darbalaei, S.; Wu, Y.; Yuliantie, E.; Xie, L.; Tao, H.; Cheng, J.; et al. G protein-coupled receptors: Structure- and function-based drug discovery. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilger, D.; Masureel, M.; Kobilka, B.K. Structure and dynamics of GPCR signaling complexes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, A.J. Human GPR107 and murine Gpr108 are members of the LUSTR family of proteins found in both plants and animals, having similar topology to G-protein coupled receptors. DNA Seq. J. DNA Seq. Mapp. 2007, 18, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafesse, F.G.; Guimaraes, C.P.; Maruyama, T.; Carette, J.E.; Lory, S.; Brummelkamp, T.R.; Ploegh, H.L. GPR107, a G-protein-coupled receptor essential for intoxication by Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A, localizes to the Golgi and is cleaved by furin. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 24005–24018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulga, Y.V.; Anderson, R.A.; Topham, M.K.; Epand, R.M. Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase isoforms exhibit acyl chain selectivity for both substrate and lipid activator. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 35953–35963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oesterhelt, D.; Tittor, J. Two pumps, one principle: Light-driven ion transport in halobacteria. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1989, 14, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanck, A.; Oesterhelt, D.; Ferrando, E.; Schegk, E.S.; Lottspeich, F. Primary structure of sensory rhodopsin I, a prokaryotic photoreceptor. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 3963–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povey, S.; Lovering, R.; Bruford, E.; Wright, M.; Lush, M.; Wain, H. The HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC). Hum. Genet. 2001, 109, 678–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmar, A.J. Family-B G-protein-coupled receptors. Genome Biology 2001, 2, reviews3013.3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, K.; Li, C.; Perrin, M.H.; Blount, A.; Kunitake, K.; Donaldson, C.; Vaughan, J.; Reyes, T.M.; Gulyas, J.; Fischer, W.; et al. Identification of urocortin III, an additional member of the corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) family with high affinity for the CRF2 receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 7570–7575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamen, F.; Persson, K.; Bertrand, G.; Rodriguez-Henche, N.; Puech, R.; Bockaert, J.; Ahrén, B.; Brabet, P. PAC1 receptor-deficient mice display impaired insulinotropic response to glucose and reduced glucose tolerance. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 105, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, J.M.; Ginsburg, G.T.; Kimmel, A.R. The cAMP receptor CAR4 regulates axial patterning and cellular differentiation during late development of Dictyostelium. Genes Dev. 1994, 8, 2086–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.L.; Saxe, C.L., 3rd; Gollop, R.; Kimmel, A.R.; Devreotes, P.N. Identification and targeted gene disruption of cAR3, a cAMP receptor subtype expressed during multicellular stages of Dictyostelium development. Genes Dev. 1993, 7, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxe, C.L., 3rd; Ginsburg, G.T.; Louis, J.M.; Johnson, R.; Devreotes, P.N.; Kimmel, A.R. CAR2, a prestalk cAMP receptor required for normal tip formation and late development of Dictyostelium discoideum. Genes Dev. 1993, 7, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, K.Y.; Jékely, G. Origins of eukaryotic excitability. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 376, 20190758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, T.Y.; Liou, S.R.; Vilgalys, R. The genetic structure and diversity of the A and B mating-type genes from the tropical oyster mushroom, Pleurotus djamor. Fungal Genet. Biol. FG B 2004, 41, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanot, P.; Brink, M.; Samos, C.H.; Hsieh, J.C.; Wang, Y.; Macke, J.P.; Andrew, D.; Nathans, J.; Nusse, R. A new member of the frizzled family from Drosophila functions as a Wingless receptor. Nature 1996, 382, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Struhl, G. In vivo evidence that Patched and Smoothened constitute distinct binding and transducing components of a Hedgehog receptor complex. Development 1998, 125, 4943–4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, Y.; Masu, M.; Ishii, T.; Shigemoto, R.; Nakanishi, S. A family of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Neuron 1992, 8, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampert, T.J.; Coleman, K.D.; Hennessey, T.M. A knockout mutation of a constitutive GPCR in Tetrahymena decreases both G-protein activity and chemoattraction. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukada, S.; Iwai, M.; Nishiu, J.; Itoh, M.; Tomoike, H.; Horiuchi, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Tanaka, T. Inhibition of experimental intimal thickening in mice lacking a novel G-protein-coupled receptor. Circulation 2003, 107, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Patthy, L. Genome evolution and the evolution of exon-shuffling–a review. Gene 1999, 238, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyne, R.S. Genomics: Stentor’s Trumpet Sounds Anew. Curr. Biol. CB 2017, 27, R146–R148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dehal, P.; Satou, Y.; Campbell, R.K.; Chapman, J.; Degnan, B.; De Tomaso, A.; Davidson, B.; Di Gregorio, A.; Gelpke, M.; Goodstein, D.M.; et al. The draft genome of Ciona intestinalis: Insights into chordate and vertebrate origins. Science 2002, 298, 2157–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, X. Evolutionary patterns of gene families generated in the early stage of vertebrates. J. Mol. Evol. 2000, 51, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, P.W. Gene duplication: Past, present and future. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 1999, 10, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, A.; Doerig, C. Editorial: Heading Against Parasitic Resistance: A Screen for Next Generation Drugs Against Targets of cAMP- or cGMP-regulated Pathways. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 727978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.C.; Pinto, V.C.; Vieira, F.A.; Clark, M.S.; Power, D.M. Evolution of secretin family GPCR members in the metazoa. BMC Evol. Biol. 2006, 6, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, S.P.; Yong, P. The evolution of gene duplicates. Adv. Genet. 2002, 46, 451–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Yan, W.; McCorvy, J.D.; Cheng, J. Biased Ligands of G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs): Structure-Functional Selectivity Relationships (SFSRs) and Therapeutic Potential. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 9841–9878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csaba, G.; Kovács, P. Pheromone and insulin induced chemotaxis in Tetrahymena. Microbios 1993, 76, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Jung, S.; Beh, L.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Landweber, L.F. Combinatorial DNA Rearrangement Facilitates the Origin of New Genes in Ciliates. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 2859–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aury, J.M.; Jaillon, O.; Duret, L.; Noel, B.; Jubin, C.; Porcel, B.M.; Ségurens, B.; Daubin, V.; Anthouard, V.; Aiach, N.; et al. Global trends of whole-genome duplications revealed by the ciliate Paramecium tetraurelia. Nature 2006, 444, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.P.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, D.; Hong, M.; He, L.; Chen, L.; Yao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, G.; et al. A G-Protein-Coupled Receptor Modulates Gametogenesis via PKG-Mediated Signaling Cascade in Plasmodium berghei. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0015022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Sun, P.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; Deng, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, G.; Chen, X.; Zhou, N. The G protein-coupled receptors in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Long, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, C.; Ma, D.K. GPCR signaling regulates severe stress-induced organismic death in Caenorhabditis elegans. Aging Cell 2022, 22, e13735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josefsson, L.G.; Rask, L. Cloning of a putative G-protein-coupled receptor from Arabidopsis thaliana. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 249, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.; Zaretskaya, I.; Raytselis, Y.; Merezhuk, Y.; McGinnis, S.; Madden, T.L. NCBI BLAST: A better web interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W5–W9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quevillon, E.; Silventoinen, V.; Pillai, S.; Harte, N.; Mulder, N.; Apweiler, R.; Lopez, R. InterProScan: Protein domains identifier. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W116–W120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wistrand, M.; Käll, L.; Sonnhammer, E.L. A general model of G protein-coupled receptor sequences and its application to detect remote homologs. Protein Sci. A Publ. Protein Soc. 2006, 15, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, G. Estimating the Dimension of a Model. Ann. Stat. 1978, 6, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).