Genetic Background Influence on Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity: Frequency-Dependent Variations between an Inbred and an Outbred Mice Strain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
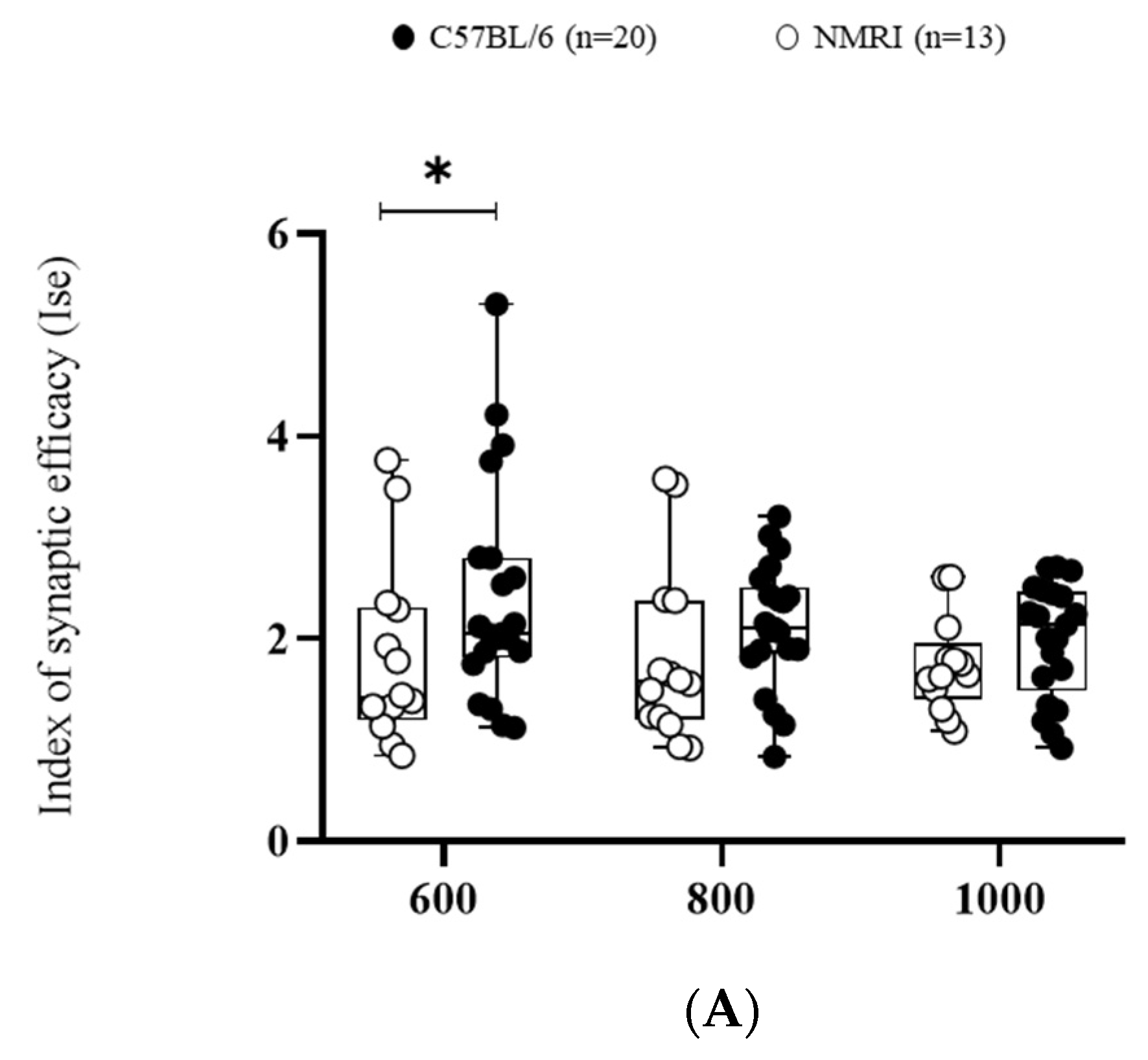
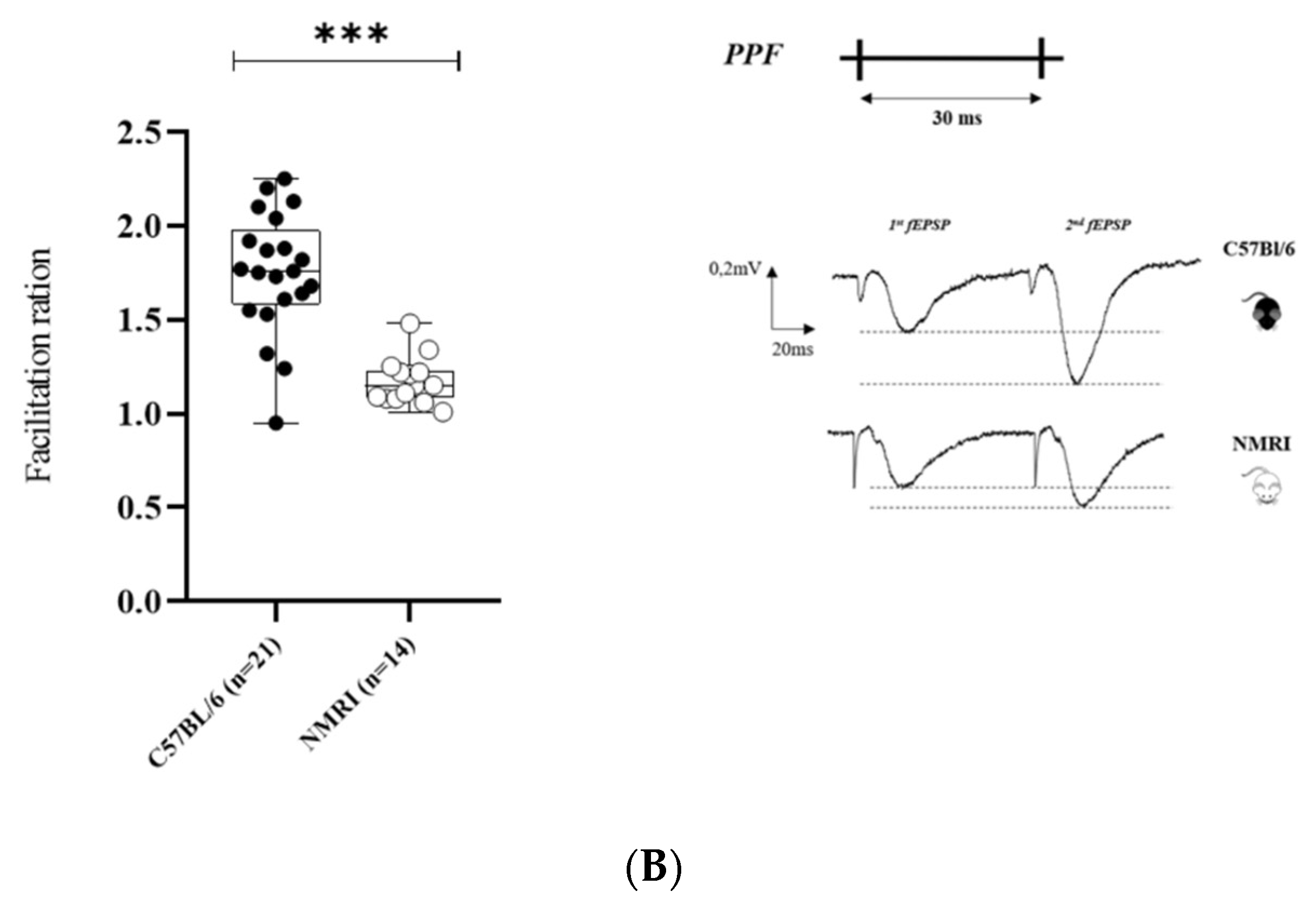
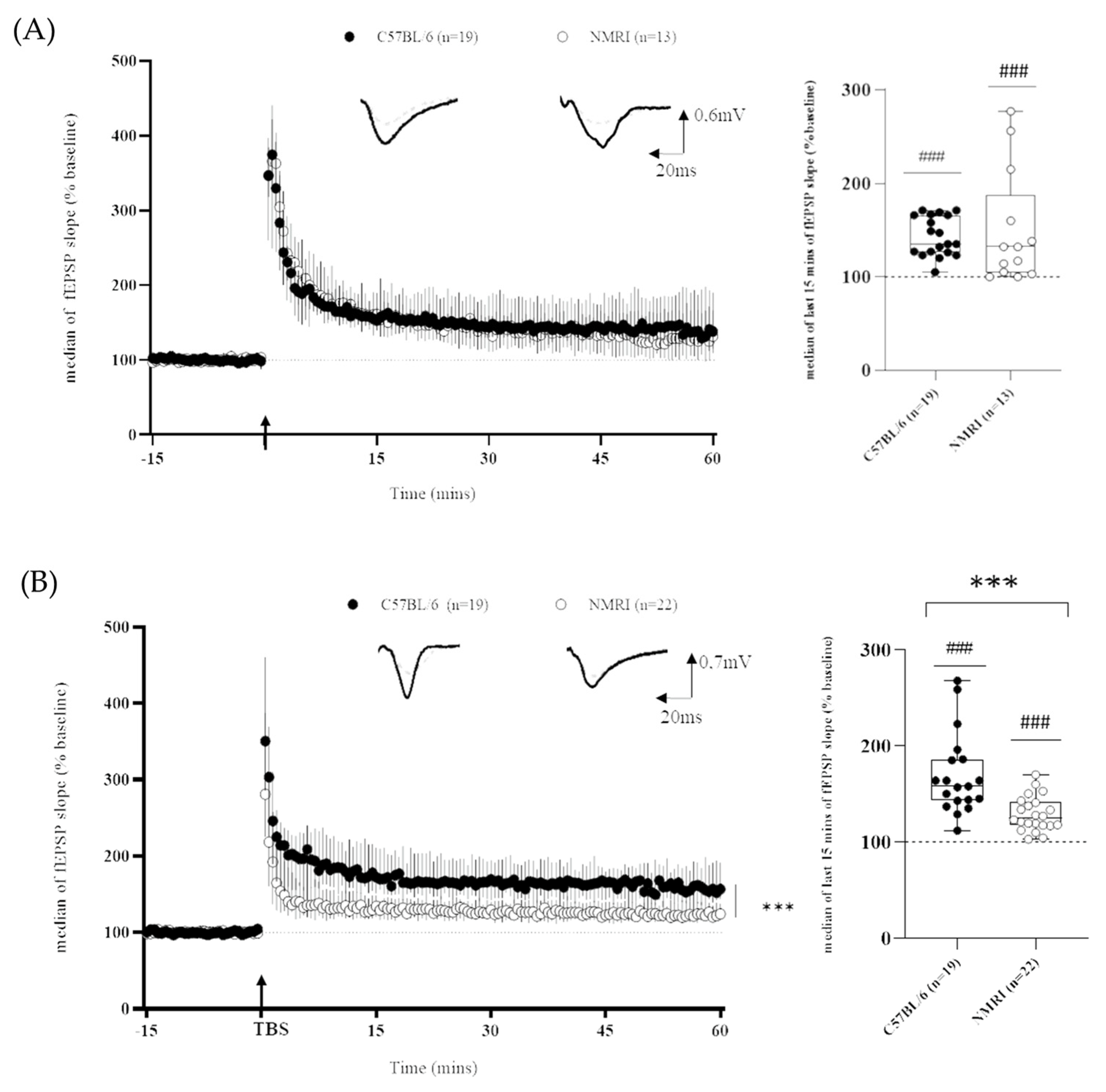
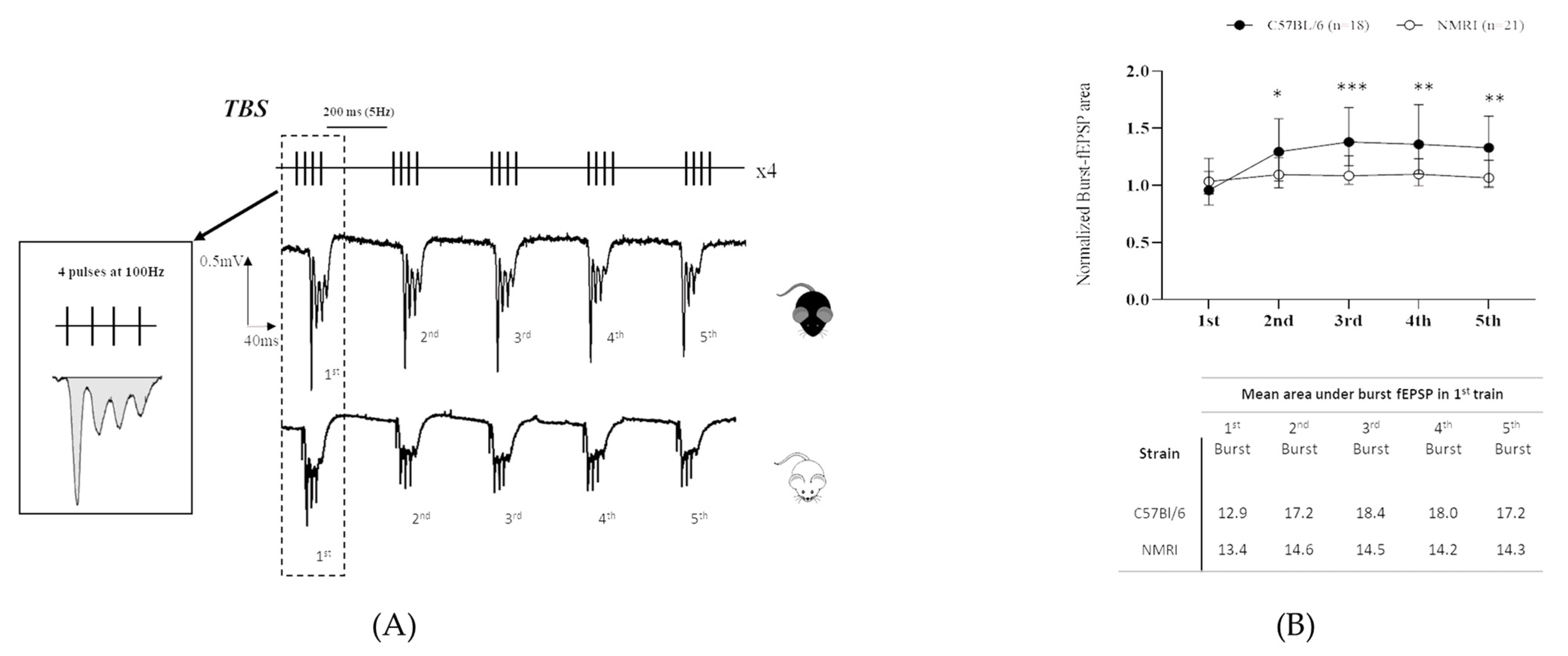
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
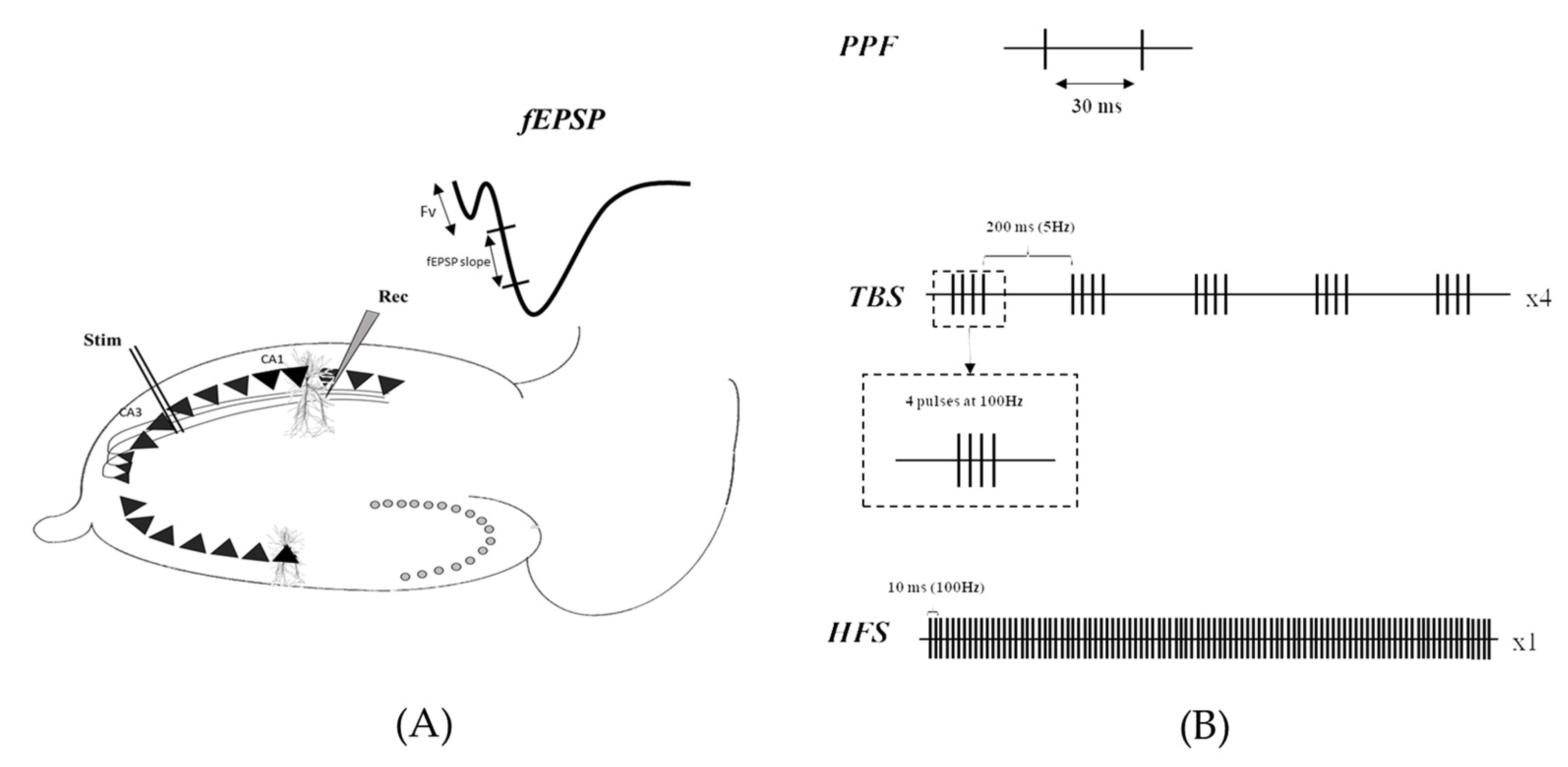
4.1. Animals
4.2. Electrophysiological Recordings
4.3. Data Analyses
4.4. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bliss, T.V.P.; Collingridge, G.L. A Synaptic Model of Memory: Long-Term Potentiation in the Hippocampus. Nature 1993, 361, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bliss, T.V.P.; Lømo, T. Long-Lasting Potentiation of Synaptic Transmission in the Dentate Area of the Anaesthetized Rabbit Following Stimulation of the Perforant Path. J. Physiol. 1973, 232, 331–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartzkroin, P.A.; Wester, K. Long-Lasting Facilitation of a Synaptic Potential Following Tetanization in Thein Vitro Hippocampal Slice. Brain Res. 1975, 89, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoll, R.A. A Brief History of Long-Term Potentiation. Neuron 2017, 93, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larson, J.; Munkácsy, E. Theta-Burst LTP. Brain Res. 2015, 1621, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bragin, A.; Jando, G.; Nadasdy, Z.; Hetke, J.; Wise, K.; Buzsaki, G. Gamma (40–100 Hz) Oscillation in the Hippocampus of the Behaving Rat. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Keefe, J.; Recce, M.L. Phase Relationship between Hippocampal Place Units and the EEG Theta Rhythm. Hippocampus 1993, 3, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tort, A.B.L.; Kramer, M.A.; Thorn, C.; Gibson, D.J.; Kubota, Y.; Graybiel, A.M.; Kopell, N.J. Dynamic Cross-Frequency Couplings of Local Field Potential Oscillations in Rat Striatum and Hippocampus during Performance of a T-Maze Task. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20517–20522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, P.V. Strain-Dependent Differences in LTP and Hippocampus-Dependent Memory in Inbred Mice. Learn. Mem. 2000, 7, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azkona, G.; Sanchez-Pernaute, R. Mice in Translational Neuroscience: What R We Doing? Prog. Neurobiol. 2022, 217, 102330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freret, T.; Lelong-Boulouard, V.; Lecouflet, P.; Hamidouche, K.; Dauphin, F.; Boulouard, M. Co-Modulation of an Allosteric Modulator of Nicotinic Receptor-Cholinesterase Inhibitor (Galantamine) and a 5-HT4 Receptor Agonist (RS-67333): Effect on Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficit in the Mouse. Psychopharmacology 2017, 234, 2365–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Tuohimaa, P. Contrasting Grooming Phenotypes in Three Mouse Strains Markedly Different in Anxiety and Activity (129S1, BALB/c and NMRI). Behav. Brain Res. 2005, 160, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Festing, M.F.W. International Index of Laboratory Animals: Giving the Location and Status of over 7000 Stocks of Laboratory Animals throughout the World, 6th ed.; Festing: Leicester, UK, 1993; ISBN 978-0-9520975-0-1. [Google Scholar]
- Festing, M.F.W. Inbred Strains in Biomedical Research; Macmillan Education: London, UK, 1979; ISBN 978-1-349-03818-3. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama, S.; Namgung, U.; Routtenberg, A. Long-Term Potentiation Persistence Greater in C57BL/6 than DBA/2 Mice: Predicted on Basis of Protein Kinase C Levels and Learning Performance. Brain Res. 1997, 763, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlai, R. Hippocampal LTP and Memory in Mouse Strains: Is There Evidence for a Causal Relationship? Hippocampus 2002, 12, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liljequist, S. Genetic Differences in the Effects of Competitive and Non-Competitive NMDA Receptor Antagonists on Locomotor Activity in Mice. Psychopharmacology 1991, 104, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Kwon, J.; Sohn, J.-W.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.; Ho, W.-K. MGluR5-Dependent Modulation of Dendritic Excitability in CA1 Pyramidal Neurons Mediated by Enhancement of Persistent Na+ Currents: MGluR5-Induced Short-Term Plasticity of Dendritic Excitability. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 4141–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golding, N.L.; Jung, H.Y.; Mickus, T.; Spruston, N. Dendritic Calcium Spike Initiation and Repolarization Are Controlled by Distinct Potassium Channel Subtypes in CA1 Pyramidal Neurons. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 8789–8798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, H.; Tsubokawa, H.; Tsukada, M.; Aihara, T. Frequency-Dependent Signal Processing in Apical Dendrites of Hippocampal CA1 Pyramidal Cells. Neuroscience 2014, 278, 194–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredens, K. Genetic Variation in the Histoarchitecture of the Hippocampal Region of Mice. Anat. Embryol. 1981, 161, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwegler, H.; Crusio, W.E.; Lipp, H.-P.; Heimrich, B. Water-Maze Learning in the Mouse Correlates with Variation in Hippocampal Morphology. Behav. Genet. 1988, 18, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwegler, H.; Boldyreva, M.; Pyrlik-Göhlmann, M.; Linke, R.; Wu, J.; Zilles, K. Genetic Variation in the Morphology of the Septo-Hippocampal Cholinergic and GABAergic System in Mice. I. Cholinergic and GABAergic Markers. Hippocampus 1996, 6, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolls, E.T. Information Representation, Processing, and Storage in the Brain: Analysis at the Single Neuron Level. In The Neural and Molecular Bases of Learning; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1987; pp. 503–540. [Google Scholar]
- Rolls, E.T.; Kesner, R.P. A Computational Theory of Hippocampal Function, and Empirical Tests of the Theory. Prog. Neurobiol. 2006, 79, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, D.K.; Corfman, T.P. An Overview of Neurobiological Comparisons in Mouse Strains. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1980, 4, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stäubli, U.; Scafidi, J.; Chun, D. GABAB Receptor Antagonism: Facilitatory Effects on Memory Parallel Those on LTP Induced by TBS but Not HFS. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 4609–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klapdor, K.; Van Der Staay, F.J. The Morris Water-Escape Task in Mice: Strain Differences and Effects of Intra-Maze Contrast and Brightness. Physiol. Behav. 1996, 60, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salari, A.-A.; Samadi, H.; Homberg, J.R.; Kosari-Nasab, M. Small Litter Size Impairs Spatial Memory and Increases Anxiety-like Behavior in a Strain-Dependent Manner in Male Mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vicens, P.; Bernal, M.C.; Carrasco, M.C.; Redolat, R. Previous Training in the Water Maze. Physiol. Behav. 1999, 67, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicens, P.; Redolat, R.; Carrasco, M.C. Effects of Early Spatial Training on Water Maze Performance: A Longitudinal Study in Mice. Exp. Gerontol. 2002, 37, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.G.M.; Anderson, E.; Lynch, G.S.; Baudry, M. Selective Impairment of Learning and Blockade of Long-Term Potentiation by an N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Antagonist, AP5. Nature 1986, 319, 774–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.; Butcher, S.P.; Morris, R.G. The NMDA Receptor Antagonist D-2-Amino-5-Phosphonopentanoate (D-AP5) Impairs Spatial Learning and LTP in Vivo at Intracerebral Concentrations Comparable to Those That Block LTP In Vitro. J. Neurosci. 1992, 12, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberty, Y.; Gower, A.J. Arm Width and Brightness Modulation of Spontaneous Behaviour of Two Strains of Mice Tested in the Elevated Plus-Maze. Physiol. Behav. 1996, 59, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölscher, C. Synaptic Plasticity and Learning and Memory: LTP and Beyond. J. Neurosci. Res. 1999, 58, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiri, N.; Sun, M.-K.; Segal, Z.; Alkon, D.L. Memory and Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) Dissociated: Normal Spatial Memory despite CA1 LTP Elimination with Kv1.4 Antisense. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 15037–15042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lecouflet, P.; Roux, C.M.; Potier, B.; Leger, M.; Brunet, E.; Billard, J.-M.; Schumann-Bard, P.; Freret, T. Interplay between 5-HT4 Receptors and GABAergic System within CA1 Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity. Cereb. Cortex 2021, 31, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickenden, A.D. Overview of Electrophysiological Techniques. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2000, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, W.W.; Collingridge, G.L. The LTP Program: A Data Acquisition Program for on-Line Analysis of Long-Term Potentiation and Other Synaptic Events. J. Neurosci. Methods 2001, 108, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolotto, Z.A.; Amici, M.; Anderson, W.W.; Isaac, J.T.R.; Collingridge, G.L. Synaptic Plasticity in the Hippocampal Slice Preparation. Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. 2011, 54, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmazer-Hanke, D.M. Morphological Correlates of Emotional and Cognitive Behaviour: Insights from Studies on Inbred and Outbred Rodent Strains and Their Crosses. Behav. Pharmacol. 2008, 19, 403–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Zootechnical Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Strain | C57BL6/Rj | NMRI | |
| Genetics | Inbred | Outbred | |
| Coat | Black | White (albino) | |
| Litter size at birth | 6.53 | 14.8 | Janvier Labs 2011 data |
| Median life span (months) | 27–31 | 17 | Gower & Lamberty, 1993 |
| Spatial behavioral performance (Morris water maze) | |||
| Learning rate | C57BL6 vs. NMRI | ||
| Escape latency | No difference | Klapdor et al., 1996; Salari et al., 2018 | |
| C57BL6 < NMRI | Vicens et al., 1999; Vicens et al., 2002 | ||
| Memory performance | C57BL6 vs. NMRI | ||
| Time spent in target quadrant | No difference | Vicens et al., 2002; Salari et al., 2018; Klapdor et al., 1996; Vicens et al., 1999 | |
| Platform crossing | No difference | Salari et al., 2018; Klapdor et al., 1996 | |
| (Ex vivo) hippocampal synaptic plasticity | |||
| HFS-LTP | C57BL6 | NMRI | |
| Magnitude (%) | 143 (+/−4) | 149 (+/−18) | No difference |
| Coefficient of variation (%) | 12% | 41% | C57BL/6 < NMRI |
| TBS-LTP | C57BL6 | NMRI | |
| Magnitude (%) | 169 (+/−10) | 127 (+/−4) | C57BL/6 > NMRI |
| Coefficient of variation (%) | 26% | 14% | C57BL/6 > NMRI |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roux, C.M.; Lecouflet, P.; Billard, J.-M.; Esneault, E.; Leger, M.; Schumann-Bard, P.; Freret, T. Genetic Background Influence on Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity: Frequency-Dependent Variations between an Inbred and an Outbred Mice Strain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054304
Roux CM, Lecouflet P, Billard J-M, Esneault E, Leger M, Schumann-Bard P, Freret T. Genetic Background Influence on Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity: Frequency-Dependent Variations between an Inbred and an Outbred Mice Strain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(5):4304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054304
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoux, Candice M., Pierre Lecouflet, Jean-Marie Billard, Elise Esneault, Marianne Leger, Pascale Schumann-Bard, and Thomas Freret. 2023. "Genetic Background Influence on Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity: Frequency-Dependent Variations between an Inbred and an Outbred Mice Strain" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 5: 4304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054304
APA StyleRoux, C. M., Lecouflet, P., Billard, J.-M., Esneault, E., Leger, M., Schumann-Bard, P., & Freret, T. (2023). Genetic Background Influence on Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity: Frequency-Dependent Variations between an Inbred and an Outbred Mice Strain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(5), 4304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054304






