Abstract
Cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channels (CNGCs) are channel proteins for calcium ions, and have been reported to play important roles in regulating survival and environmental response of various plants. However, little is known about how the CNGC family works in Gossypium. In this study, 173 CNGC genes, which were identified from two diploid and five tetraploid Gossypium species, were classified into four groups by phylogenetic analysis. The collinearity results demonstrated that CNGC genes are integrally conservative among Gossypium species, but four gene losses and three simple translocations were detected, which is beneficial to analyzing the evolution of CNGCs in Gossypium. The various cis-acting regulatory elements in the CNGCs’ upstream sequences revealed their possible functions in responding to multiple stimuli such as hormonal changes and abiotic stresses. In addition, expression levels of 14 CNGC genes changed significantly after being treated with various hormones. The findings in this study will contribute to understanding the function of the CNGC family in cotton, and lay a foundation for unraveling the molecular mechanism of cotton plants’ response to hormonal changes.
1. Introduction
Cyclic nucleotide gated channel (CNGC) protein is one of the calcium ion conduction pathways and widely exists in animals and plants. Plant CNGCs are members of the “P-loop” superfamily of cation channels, which is found in all prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells [1]. P-loop channels, which emerged early in evolution, have evolved into channels that conduct various cations and serve a wide range of functions in cells [2]. The calcium ion (Ca2+) is an important secondary messenger that modulates multiple signaling pathways in plants. Calcium signal transduction is the main mechanism for plants to receive and respond to endogenous and exogenetic stimuli, such as hormones [3], pathogens [4], salt stress [5], optical signals [6] and circadian rhythm [7]. As cation channel proteins, CNGCs have been reported to mediate the accumulation of Ca2+ in cytosol and the conversion of external optical and odor signals into bioelectrical signals [8,9]. For example, AtCNGC1 contributes to Ca2+ uptake into plants [10], while AtCNGC3 functions as a Na+ uptake and a K+ uptake mechanism and is required for cellular homeostasis [11]. Furthermore, CNGCs are also involved in plant development and disease resistance [12,13]. Silencing of both TaCNGC14 and TaCNGC16 enhances wheat resistance against Pst [14].
With the identification of the first CNGC (HVCBT1) in barley, a series of gene family members have been identified in plants in recent years, such as Arabidopsis, rice, pear, tobacco, Chinese cabbage, Brassica napus, Brassica oleracea, tomato, maize and wheat [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. Based on the gene structure, the CNGC family could be classified into four groups (group I–IV), and group IV can be further subdivided into “IV-A and IV-B” [15]. It was reported that different groups of tomato CNGC genes play distinguishable roles in disease resistance and abiotic stress responses [22]. In plants, the CNGC consists of six transmembrane (TM) domains and a pore region located in the middle of the fifth and sixth TM domains. The cyclic nucleotide binding domain (CNBD) is a highly conserved domain with a phosphate binding cassette (PBC) and a “hinge” region [22]. A specific motif of plant CNGC ([LIMV0]-X(2)-[GSANCR]-X-[FVIYASCL]-XGX(0,1)-X(0,1)-[EDAQGH]-L-[LIVFA]-X-[WRCMLS0]-X-[LMSIQAFT0]-X(7,37)-[SAC]-X(9)-[VTIALMS]-X(0,1)-[EQDN]-[AGSVT]-[FYL]-X-[LIVF]) located in the PBC and “hinge” region of CNBD and existed uniquely in the plant CNGC, and this motif has been treated as a criterion to identify the CNGC gene family in plants [22,24].
CNGCs are involved in different signaling pathways associated with the response to biotic and abiotic stress, including salt, drought, cold, plant nutrition and calcium homeostasis and pathogen infection. In this study, CNGC families of Gossypium species were identified. The chromosome location and synteny among species of CNGCs, along with their gene structure, domain composition and cis-acting regulatory elements, were further analyzed. Moreover, the expression levels of Gossypium CNGC genes among tissues and in response to hormones and oxidative stress were quantitated to understand their potential functions. These findings will be beneficial to understanding the function of the CNGC family in cotton, and lay a foundation for unraveling the molecular mechanism of cotton plants’ response to hormonal changes.
2. Results
2.1. CNGC Identification in Seven Gossypium Species
A total of 17, 14, 28, 28, 29, 28 and 29 genes were identified in Gossypium arboreum, Gossypium raimondii, Gossypium barbadense, Gossypium darwinii, Gossypium hirsutum, Gossypium tomentosum and Gossypium mustelinum, respectively. Based on their chromosomal location, CNGC genes were named GaCNGC1 to GaCNGC17 in G. arboreum, GbCNGC1 to GbCNGC28 in G. barbadense, GdCNGC1 to GdCNGC28 in G. darwinii, GhCNGC1 to GhCNGC29 in G. hirsutum, GrCNGC1 to GrCNGC14 in G. raimondii, GtCNGC1 to GtCNGC28 in G. tomentosum and GmCNGC1 to GmCNGC29 in G. mustelinum. The protein size of CNGCs ranged from 517 (aa) to 769 (aa). The theoretical isoelectric point (PI) of most CNGC proteins was greater than eight, with the exception of six Gossypium CNGC genes (GbCNGC19, GdCNGC19, GhCNGC19, GmCNGC20, GrCNGC12, GtCNGC19) that have a theoretical PI of 6.53 and five Gossypium CNGC genes (GaCNGC4, GbCNGC6, GdCNGC6, GmCNGC7 and GtCNGC6) with a theoretical PI of 7.52 (Table S1). These findings indicated that the number of CNGCs varies slightly between species, which may have been caused by the loss or duplication of genes during the evolution of Gossypium. Furthermore, the Gossypium CNGC proteins are a good source of fundamental amino acids.
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of the CNGC Family
In order to investigate the genetic evolutionary relationship of CNGCs, a neighbor-joining tree was constructed using the maximum likelihood (ML) method with a total of 209 CNGC proteins, including 20 from Arabidopsis [15], 16 from rice [16] and 173 from Gossypium species. (Figure 1). As a result, these CNGCs were unevenly classified into four groups, and group IV was further divided into subgroup IVa and subgroup IVb. Group I included four GaCNGCs, six GbCNGCs, six GdCNGCs, six GhCNGCs, six GmCNGCs, three GrCNGCs, six GtCNGCs, six AtCNGCs and three OsCNGCs. Group II included three GaCNGCs, four GbCNGCs, five GdCNGCs, five GhCNGCs, six GmCNGCs, three GrCNGCs, five GtCNGCs, five AtCNGCs and three OsCNGCs. Group III contained 6 GaCNGCs, 12 GbCNGCs, 12 GdCNGCs, 12 GhCNGCs, 12 GmCNGCs, 6 GrCNGCs, 12 GtCNGCs, 5 AtCNGCs and 5 OsCNGCs. Group III has 82 CNGCs, which is the largest branch of the four CNGC groups. Group IVb contained four GaCNGCs, five GbCNGCs, five GdCNGCs, six GhCNGCs, five GmCNGCs, two GrCNGCs, five GtCNGCs, two AtCNGCs and three OsCNGCs. However, no CNGCs from Gossypium were contained in group IVa, indicating the peculiarity of cotton species.
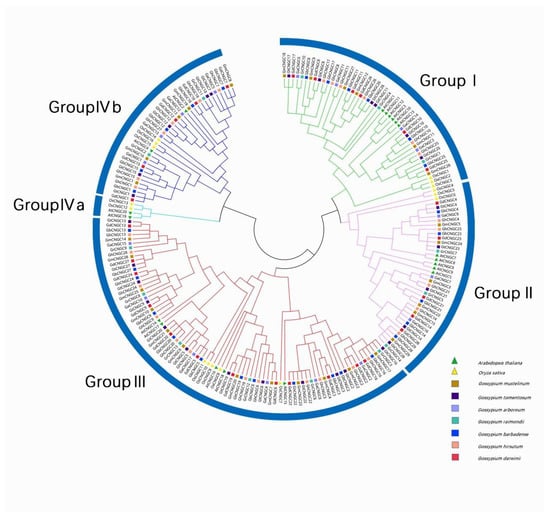
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree of 9 species including Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa, G. arboreum, G. barbadense, G. darwinii, G. hirsutum, G. raimondii, G. tomentosum, G. mustelinum.
2.3. Chromosomal Distribution and Synteny Analysis of Gossypium CNGCs
The chromosomal distribution of Gossypium CNGC genes is shown in Figure 2 and Figure S1. For diploid species, G. arboreum and G. raimondii, CNGC genes were located on eight chromosomes. For five allotetraploid species, CNGC genes were located on 17 chromosomes in G. hirsutum, and spread on 16 chromosomes in the other four allotetraploid species. CNGCs are unevenly distributed on chromosomes in Gossypium. In allotetraploid species, most chromosomes contained only one CNGC gene, while chromosomes At05 and Dt04 contained six and five CNGCs, respectively.
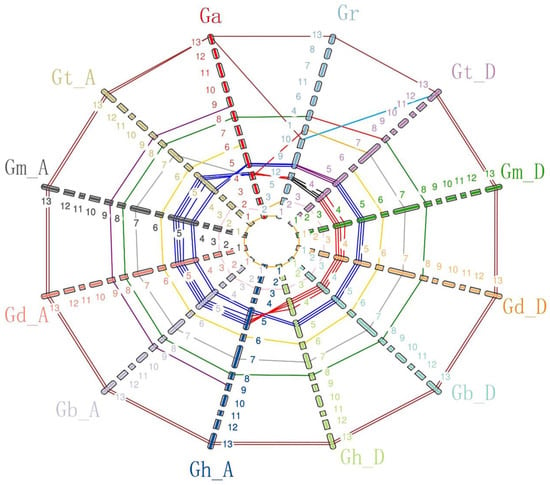
Figure 2.
Analysis of Gossypium CNGCs for synteny. Ga: G. arboreum, Gr: G. raimondii, Gt_D: G. tomentosum Dt subgenome, Gm_D: G. mustelinum Dt subgenome, Gd_D: G. darwinii Dt subgenome, Gb_D: G. barbadense Dt subgenome, Gh_D: G. hirsutum Dt subgenome, Gh_A: G. hirsutum At subgenome, Gb_A: G. barbadense At subgenome, Gd_A: G. darwinii At subgenome, Gm_A: G. mustelinum Dt subgenome, Gt_A: G. tomentosum Dt subgenome. 1–13 represent Chromosome1 to Chromosome13, and different colors represent different chromosomes.
The synteny analysis of Gossypium CNGCs showed that the CNGC genes were well distributed on the homologous chromosome except for the CNGC gene on the reciprocal translocation chromosomes At4 and At5 in allotetraploid species. Meanwhile, three simple translocations and two deletions existed in Gossypium. The CNGC gene located on chromosome At7 or Dt7 of allotetraploid species was simply translocated on chromosome 4 of G. arboretum, and one CNGC gene located on chromosome At3 or Dt3 of allotetraploid species was simply translocated on chromosome 2 of G. arboretum. One CNGC gene located on chromosome At13 or Dt13 of allotetraploid species was simply translocated on chromosome 10 of G. raimondii. The CNGC gene existed in chromosome At9 of allotetraploids, but it was absent in the Dt subgenome and G. raimondii. The CNGC gene occurred on chromosomes At6 and Dt6 of tetraploid species or on chromosome 6 of G. arboretum, but it was absent in G. raimondii.
2.4. Genic Structure and Motif Composition Analysis
To further reveal the phylogenetic relationships of CNGCs, the gene structure of CNGCs was visualized by TBtools based on genome annotation files from each species (Figure 3). The results showed that Gossypium CNGCs had slightly different but similar structural characteristics. The majority of Gossypium CNGC genes contained seven exons. In addition, there were 13 genes (GaCNGC4, GbCNGC6, GtCNGC6, GdCNGC6, GmCNGC7, GaCNGC4, GhCNGC6, GrCNGC12, GhCNGC19, GbCNGC19, GmCNGC20, GdCNGC19, GtCNGC19) and 9 genes (GaCNGC11, GaCNGC12, GbCNGC12, GdCNGC12, GmCNGC12, GhCNGC12, GtCNGC12, GaCNGC14, GhCNGC18) that had 6 and 8 exons, respectively. Additionally, the last exons of genes in group III were longer than all the other exons. The similar genic structure of CNGC genes indicated their evolutionary conservation [25]. However, there were a few CNGC members with different genic structures, which suggested that independent evolutionary events occurred in them.
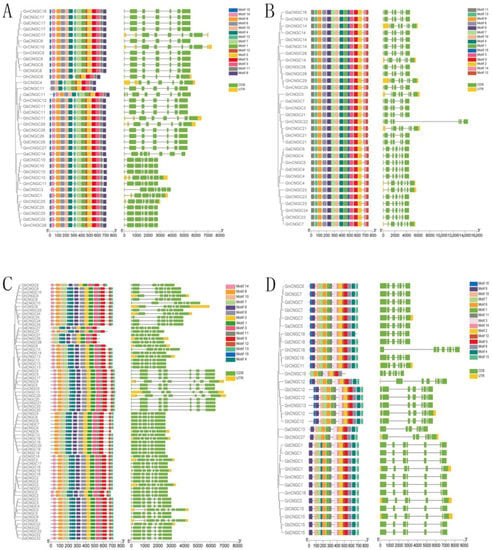
Figure 3.
Phylogenetically aligned conserved motifs and gene structure analysis of CNGC genes in seven Gossypium species. (A) Group I; (B) group II; (C) group III; (D) group IVb.
A total of 15 conserved motifs, labeled motif 1 to motif 15, were identified in Gossypium CNGCs (Figure 3). Motif 5, which belongs to the cyclic nucleotide-binding domain (CNBD), was the conserved domain contained in all the Gossypium CNGC genes. The majority of CNGCs contained all 15 motifs, with different arrangements in each group. However, there were a few CNGCs with fewer than 15 motifs, indicating that motif deletions occurred in them during evolution. GmCNGC19, with only 10 motifs, was the one with the fewest motifs. These findings demonstrated that most CNGC genes were conserved, with a few exceptions being due to evolutionary variation.
2.5. Domain Composition and Conserved Motif at the PBC and Hinge Region of CNB Domain of CNGC Proteins in Plants
Plant CNGCs are composed of three main domains including the TM /ITP domain, CNB domain and calmodulin-binding (CaMB) domain, with the latter two domains usually overlapping partially [12]. The CNB domain ([LI]-X(2)-[GS]-X-[FYIVS]-X-G-X(0,1)-[DE]-LL-X(8,25)-[SA]-X(9)-[VLIT]-E-X-F-X-[IL]), which contained a PBC region and a “hinge” region, was the distinguishing feature of the CNGC protein [24]. To investigate the CNB domain of Gossypium CNGCs, protein sequences of the PBC and “hinge” regions from rice and Arabidopsis were used as controls, and the PBC and “hinge” region of 173 CNGC proteins in cotton were then aligned. As a result, individual CNB motifs for each group were created as follows: [LI]-X-A-G-D-F-C-G-[ED]-X-LL-X(25)-E-A-F-A-L for group I, L-K-E-G-D-F-C-G-E-E-LL-X(25)-E-A-F-A-L for group II, [LI]-X-P-G-D-F-C-G-E-E-LL-X(25)-E-A-F-A-L for group III and [LI]-X(2)-G-X-F-X-G-D-E-LL-X(25)-E-A-F-G-L for group IVb (Figure 4).
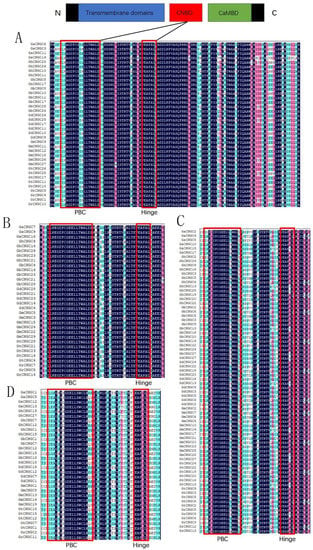
Figure 4.
Multiple alignments of CNGC proteins in cotton. (A) Group I; (B) group II; (C) group III; (D) group IVb.
2.6. Prediction of Cis-Acting Regulatory Elements
To determine the preliminary function of the GhCNGCs, 2000 bp sequences in the upstream region were cropped in order to analyze the cis-acting elements in the potential promoter regions. The results revealed that the cis-acting elements of the GhCNGC genes from the same clade were similar, which was consistent with their genetic structure and phylogenetic relationships (Figure 5). A variety of cis-elements of GhCNGCs were related to various exogenous stimuli, such as abscisic acid responsiveness elements, anaerobic induction elements, auxin-responsive elements, defense and stress responsiveness elements, gibberellin-responsive elements, MeJA-responsive elements and salicylic acid responsiveness elements. These elements, which are crucial for plants to respond abiotic stress [26], suggested that abiotic stressors might regulate the expression of GhCNGCs.
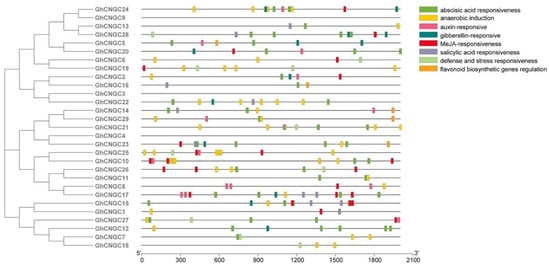
Figure 5.
Cis-acting element analysis of GhCNGC genes.
2.7. Expression Profiling of CNGC Family in G. hirsutum
To explore the biological functions of the CNGC family, the transcriptome of G. hirsutum was analyzed to investigate the expression profiles of GhCNGCs in various tissues, including fiber, calycle, leaf, petal, pistil, root, stamen, stem, torus and ovule (Figure 6). The results revealed that most CNGCs were expressed in almost all tissues, but the dominantly expressed tissues were diverse for different genes. In detail, GhCNGC12 and GhCNGC18 were highly expressed in calycle, petal, stamen and ovule. GhCNGC14 and GhCNGC29 were highly expressed in the stem and torus. GhCNGC6 and GhCNGC19 were highly expressed in the stamen. GhCNGC14 and GhCNGC10 were highly expressed in the petal. Additionally, 16 GhCNGC genes were highly expressed in the leaf. These findings suggested that the main functional tissues of different GhCNGCs might be distinct.
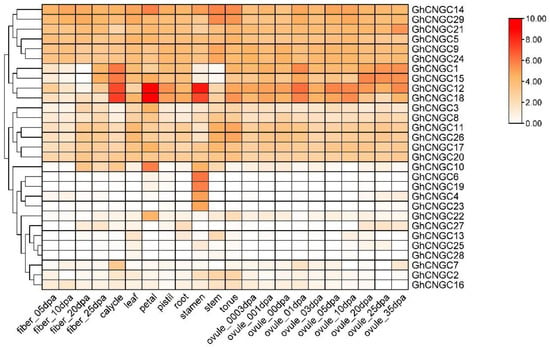
Figure 6.
Expression patterns of GhCNGC genes: a heatmap of GhCNGC genes in fiber developmental stages, calycle, leaf, petal, pistil, root, stamen, stem, torus and ovule developmental stages.
2.8. Response of GhCNGCs to Oxidative Stress and Hormones
To investigate whether GhCNGCs were regulated by oxidative stress or hormones, the expression levels of GhCNGCs were analyzed using qRT-PCR. For GhCNGCs distributed on homologous chromosomes, only the one on the At subgenome was analyzed. In total, the expression levels of 15 GhCNGCs were qualified, and 14 of them, with the exception for GhCNGC6, showed significant expression changes in response to various stimuli (Figure 7). GhCNGC6 was not expressed in either the CK or treatment assays. Most of the other GhCNGCs were significantly upregulated in response to exogenous stimuli. For instance, the IAA, SA, MeJA, GA, ABA, ETH and H2O2 treatments significantly upregulated 2, 8, 6, 13, 11, 10 and 2 GhCNGCs, respectively. Additionally, five, four, two, one and seven GhCNGCs were significantly downregulated by the IAA, SA, MeJA, ETH and H2O2 treatments, respectively. Furthermore, GhCNGC10 was significantly regulated by all the treatments. These findings supported the hypothesis that CNGCs in cotton respond to changes in oxidative stress and hormone levels.
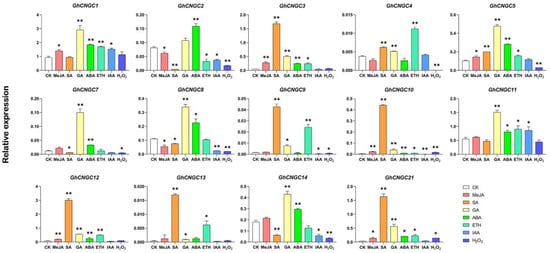
Figure 7.
The relative expression levels of selected CNGC genes under control condition (water), abscisic acid (ABA, 100 μM), salicylic acid (SA, 1 mM), methyl jasmonate (MeJA, 100 μM), auxin (IAA, 5 μM), gibberellin (GA 0.5 μM), ethylene (ETH, 200 μM) and H2O2 (100 mM). All statistical tests were two-tailed Student’s t-tests at the 0.05 and 0.01 levels, and the p-values are given by the symbols * (p < 0.05) and ** (p < 0.01), respectively.
3. Discussion
In this study, 173 CNGC genes from seven Gossypium species, together with 20 AtCNGCs [15] and 16 OsCNGCs [16], from a total of 209 CNGCs were used to construct a phylogenetic tree, and the CNGC genes were classed into five groupings after examination. However, group IVa CNGC genes did not exist in Gossypium, and it was similar to maize [22]. This finding supported that group IVa CNGC genes were more ancient in the evolution of green plants [22]. In addition, four gene losses and three simple translocations were identified in seven Gossypium species. The first gene loss was found on chromosome At05 of allotetraploid Gossypium species, but this gene could be found in two diploid species and the Dt subgenome of tetraploid species. This finding indicated that the gene loss on chromosome At05 of allotetraploid species occurred during the formation of the reciprocal translocation on chromosomes At4 and At5 in allotetraploid species. The second gene loss was found on chromosome Dt09 of allotetraploid species and G. raimondii, but this gene could be found on chromosome At9 in allotetraploid species. The gene loss on chromosome Dt9 in allotetraploid species occurred in G. raimondii before the merging of the two diploid species.
In the previous study, CNGC genes were identified and characterized in several species, including 20, 16, 21, 35, 30, 61, 26, 18, 12, 16, 16 and 14 CNGC genes in Arabidopsis, rice, pear, tobacco, Chinese cabbage, Brassica napus, Brassica oleracea, tomato, maize and subgenomes A, B, D of wheat, respectively [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. In the present study, 17 and 14 CNGC genes were identified in diploid Gossypium species G. arboretum and G. raimondii, respectively. The number of CNGC genes in the At subgenome or Dt subgenome was also inconstant compared with other species. The difference in CNGC number might have resulted from the evolution and domestication of different species. In addition, allotetraploid Gossypium was formed after hybridization between the A genome and D genome and chromosome doubling [27]. Theoretically, the number of CNGC genes in allotetraploid species was double that of diploid species. However, all allotetraploid species had fewer CNGC genes than the sum of the two diploid Gossypium species. This phenomenon might be due to the ongoing process of gene loss in allotetraploid species [28].
Sequence alignment analysis showed that CNGC genes possessed a highly conserved motif. In this study, 173 Gossypium CNGC genes from 2 diploid and 5 allotetraploid Gossypium species were classified into 4 groups (I-IV). The motifs for the four groups were [LI]-X-A-G-D-F-C-G-[ED]-X-LL-X(25)-E-A-F-A-L, L-K-E-G-D-F-C-G-E-E-LL-X(25)-E-A-F-A-L, [LI]-X-P-G-D-F-C-G-E-E-LL-X(25)-E-A-F-A-L and [LI]-X(2)-G-X-F-X-G-D-E-LL-X(25)-E-A-F-G-L, respectively. Subsequently, the sequence structure of Gossypium, [LI]-X(2)-G-X-F-X-G-[ED]-X-L-L-X(25)-E-A-F-[AG]-L, was obtained. Additionally, the conserved motif of Gossypium was similar to other species with a slight difference, such as wheat ([LI]-X(2)-[GS]-X-[FCV]-X-G-[ED]-E-L-L-[TGS]-W-X-[LF]-X(7,17)-[LFR]-[PL]-X-[SA]-X(2)-[TS]-X(6)-[VAT]-[EQ]-X-F-X-L-X-[AS]-X-[DE]-[LV]) and rice ([LI]-X(2)-[GS]-X-[FV]-X-G-[DE]-ELL-X-W-X(12,22)-SA-X(2)-T-X(7)-[EQ]-AF-X-L) [14,16]. The CNGC genes from different species had a highly conserved sequence, so they might possess similar functions.
The previous study showed that the CNGC genes were involved in biotic and abiotic stress in plants, for example, the expression of BrCNGC7 was downregulated under temperature stress but upregulated under salt and osmotic stress [19]. OsCNGC6 responds to stress and plant defense-related functions in rice [16]. BoCNGC genes from phylogenetic groups I and IV were particularly sensitive to cold stress and infections with bacterial pathogens [21]. Four genes (BnaC03g31050D, BnaC03g31720D, BnaA05g01380D and BnaC04g01250D) from group I and two genes (BnaCnng45430D and BnaA03g34680D) from group IVa were all strongly induced by SA and infection of S. sclerotiorum [20]. VIGS analysis demonstrates that SlCNGC17 and SlCNGC18 play a role in resistance to P. aphanidermatum [22]. TaCNGC14 and TaCNGC16 play a negative role in wheat resistance against pathogens [29]. Notable performances were exhibited by group I and IV NtabCNGC genes against black shank [18]. In this study, the response of GhCNGC genes to hormone treatment indicated that the GhCNGC genes were regulated by several hormones, for example, twelve GhCNGC genes were induced by SA treatment. The previous study showed that SA plays crucial roles in plant defense against pathogens [30]. In addition, AtCNGC2 and AtCNGC6 have been reported as having a key role in stress response [31,32,33]. In this study, GhCNGC2 and GhCNGC7/18 were identified as homologous genes of AtCNGC2. GhCNGC4/23, GhCNGC14/29 and GhCNGC21 were homologous genes of AtCNGC6. These findings suggest the putative roles of these GhCNGC genes may be involved in biotic and abiotic stress through hormone signaling pathways.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Growth and Treatments
CCRI 35, a G. hirsutum cultivar, was planted in potting soil at 25 °C in a culture room with a 16 h light/8 h dark cycle to determine the responses of GhCNGCs to oxidative stress and hormones. As treatment assays, abscisic acid (ABA, 100 μM), salicylic acid (SA, 1 mM), methyl jasmonate (MeJA, 100 μM), auxin (IAA, 5 μM), gibberellin (GA, 0.5 μM), ethylene (ETH, 200 μM) and H2O2 (100 mM) were sprayed individually onto cotton leaves. The control assay was performed with pure water. To prepare these treating solutions, the corresponding powder was dissolved to the desired concentration in deionized water. For powder that was difficult to dissolve in water, ethanol (ABA, IAA, SA) or methanol (GA) was added as a hydrotropic agent. After being treated for 10 h, leaf samples were flash frozen by liquid nitrogen and then stored at −80 °C until further experiments were performed.
4.2. Gene Identification and Characterization Analysis
Genome sequences of seven Gossypium species, including G. arboreum, G. raimondii, G. barbadense, G. darwinii, G. hirsutum, G. tomentosum and G. mustelinum, were downloaded from NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 1 September 2022). The protein sequences of 20 Arabidopsis CNGCs and 16 rice CNGCs were downloaded from the Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR10) database (http://www.arabidopsis.org/) (accessed on 5 September 2022) and Rice Genome Annotation Project (RGAP) database (http://rice.plantbiology.msu.edu/) (accessed on 7 September 2022), respectively. AtCNGC amino acid sequences were used as queries in local Basic Local Alignment Search Tool protein (BLASTP) [34] (e-value of 1 × 10−10) searches to identify potential CNGC proteins in seven Gossypium species. In addition, the HMM profiles of the CNB domain (PF00027) from the Pfam database (http://pfam.xfam.org, [35] (accessed on 7 September 2022)) was used to search the cotton protein database using HMMER 3.0 (http://hmmer.janelia.org/, accessed on 8 September 2022) [36]. The intersection of results from BLASTP and HMMER was selected. In addition, the Simple Modular Architecture Research Tool (SMART) (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/, accessed on 11 September 2022) [37] and InterPro (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/, accessed on 11 September 2022) [38] were utilized to confirm the domains of selected proteins.
4.3. Analysis of Gossypium CNGC Protein Features and Chromosomal Localization
Protein features, including the number of amino acids, molecular weight, theoretical isoelectric point (PI), instability index, aliphatic index and grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY), were analyzed by ExPASy (https://web.expasy.org/protparam/, accessed on 9 September 2022) [29]. Additionally, locations of CNGCs were obtained from genomic annotation. TBtools [39] was used to display the locations of genes on chromosomes. In addition, JCVI (https://www.cnpython.com/pypi/jcvi, accessed on 10 September 2022) was used to display the synteny of Gossypium CNGCs in seven different cotton species.
4.4. Analysis of Protein Motifs, Gene Structures and Cis-Acting Regulatory Elements
Protein sequences of the CNGCs were uploaded to MEME (https://meme-suite.org/meme/tools/meme, accessed on 12 September 2022) to identify conserved motifs with the parameters of 15 motifs. The motifs of Gossypium CNGCs were displayed by TBtools [39].
For promoter analysis, 2000 bp sequences at the upstream of the start codon (ATG) of GhCNGC genes were obtained as potential promoter regions. PlantCARE was used to search promoter regions for cis-acting regulatory elements. The cis-acting regulatory elements in the promoter regions of CNGC genes were classified on the basis of their responses to different hormones and abiotic factors.
4.5. Phylogenetic Analysis and Multiple Sequence Alignment
CNGC protein sequences from Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa, G. arboreum, G. barbadense, G. darwinii, G. hirsutum, G. raimondii, G. tomentosum and G. mustelinum were aligned using the MUSCLE program in MEGA 7.0 with default settings [40]. The alignment was further used to construct the neighbor-joining (NJ) tree with the following parameters: 1000 bootstrap replicates, Poisson model, uniform rates and pairwise deletion. The conserved domains were aligned and shaded with DNAMAN software.
4.6. Transcriptome Analysis of CNGC Genes in Different Tissues
RNA-seq data of the G. hirsutum cultivar TM-1 [28] were downloaded from NCBI (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 1 September 2022). These data were used to analyze the expression of GhCNGC genes in eight different tissues (calycle, leaf, petal, pistil, root, stamen, stem, torus) and at different fiber and ovule developmental stages.
4.7. RNA Isolation and qPCR
Total RNA was extracted from treated leaves using a plant RNA kit (boer, ChongQing, China) according to the manufacturer’s instruction. First strand cDNA was synthesized from 1 µg of total RNA using the PrimerScriptTM RT reagent kit with gDNA Eraser (Takara, Japan). The cDNA samples were diluted five times in sterile water before storing at −20 °C. The program for the qRT-PCR was as follows: 5 min at 95 °C, 40 cycles of 5 s at 95 °C and 30 s at 62 °C, 30 s at 95 °C. qRT-PCR was performed in a total volume of 20 μL (0.4 μL each primer (10 μM), 4 μL cDNA, 10 μL SYBR Green Master mix (2×), and 5.2 μL ddH2O) in three technological replicates on a QTOWER Real Time PCR System (Analytik Jena, Germany), and the relative expression of the genes was calculated using the 2−ΔCt method [41]. GhACTIN was used as the internal standard.
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Data for quantification analyses were presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) with three biological replicates. GraphPad Prism 8.0.2 (https://www.graphpad.com, accessed on 19 September 2022) was utilized to perform significance tests [42]. All statistical tests were two-tailed Student’s t-tests at the 0.05 and 0.01 levels, and the p-values are given by the symbols * (p < 0.05) and ** (p < 0.01), respectively.
5. Conclusions
In this study, 173 CNGC genes were identified from two diploid and five tetraploid Gossypium species. The domain organization, chromosomal location, evolutionary relationships, promoter cis-elements and expression profiles of the Gossypium CNGC gene family were then thoroughly examined. The collinearity data demonstrated that four gene losses and three simple translocations occurred during the evolution of Gossypium. Furthermore, the expression of 14 CNGC genes varied significantly after being treated with different hormones and H2O2. The findings in this study will lay a foundation for unraveling the molecular mechanism of cotton plants’ response to hormonal and exogenous changes.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms24054617/s1.
Author Contributions
Z.Z.: designed and supervised the experiments and contributed to the final editing of manuscript, L.C.: data curation, writing—original draft. W.W.: formal analysis, methodology. H.H.: formal analysis. P.Y.: data curation. X.S.: software, visualization. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 31871670).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The genome data of the Gossypium and RNA-Seq data can be found in the NCBI (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ward, J.M.; Mäser, P.; Schroeder, J.I. Plant ion channels: Gene families, physiology, and functional genomics analyses. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2009, 71, 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhorov, B.S.; Tikhonov, D.B. Potassium, sodium, calcium and glutamate-gated channels: Pore architecture and ligand action. J. Neurochem. 2004, 88, 782–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jammes, F.; Hu, H.-C.; Villiers, F.; Bouten, R.; Kwak, J.M. Calcium-permeable channels in plant cells. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 4262–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Z.; Verma, R.; Gehring, C.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ryan, C.A.; Berkowitz, G.A. Ca2+ signaling by plant Arabidopsis thaliana Pep peptides depends on AtPepR1, a receptor with guanylyl cyclase activity, and cGMP-activated Ca2+ channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21193–21198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tracy, F.E.; Gilliham, M.; Dodd, A.N.; Webb, A.A.; Tester, M. NaCl-induced changes in cytosolic free Ca2+ in Arabidopsis thaliana are heterogeneous and modified by external ionic composition. Plant Cell Environ. 2008, 31, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, A.; Sakai, T.; Okada, K. Phot1 and phot2 mediate blue light-induced transient increases in cytosolic Ca2+ differently in Arabidopsis leaves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8583–8588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodd, A.N.; Gardner, M.J.; Hotta, C.T.; Hubbard, K.E.; Dalchau, N.; Love, J.; Assie, J.M.; Robertson, F.C.; Jakobsen, M.K.; Goncalves, J.; et al. The Arabidopsis circadian clock incorporates a cADPR-based feedback loop. Science 2007, 318, 1789–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, C.C.Y.; Christopher, D.A. The group IV-A cyclic nucleotide-gated channels, CNGC19 and CNGC20, localize to the vacuole membrane in Arabidopsis thaliana. Aob Plants 2013, 5, plt012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalakis, S.; Becirovic, E.; Biel, M. Retinal Cyclic Nucleotide-Gated Channels: From Pathophysiology to Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Ali, R.; Berkowitz, G.A. Characterization of plant phenotypes associated with loss-of-function of AtCNGC1, a plant cyclic nucleotide gated cation channel. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2006, 44, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobert, A.; Park, G.; Amtmann, A.; Sanders, D.; Maathuis, F.J.M. Arabidopsis thaliana cyclic nucleotide gated channel 3 forms a non-selective ion transporter involved in germination and cation transport. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, K.; Moeder, W.; Yoshioka, K. Biological roles of cyclic-nucleotide-gated ion channels in plants: What we know and don’t know about this 20 member ion channel family. Botany 2009, 87, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFalco, T.A.; Marshall, C.; Munro, K.; Kang, H.-G.; Moeder, W.; Ikura, M.; Snedden, W.A.; Yoshioka, K. Multiple Calmodulin-Binding Sites Positively and Negatively Regulate Arabidopsis Cyclic Nucleotide-Gated Channel12. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 1738–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Islam, M.A.; Lin, H.; Ji, C.; Duan, Y.; Liu, P.; Zeng, Q.; Day, B.; Kang, Z.; Guo, J. Genome-Wide Identification of Cyclic Nucleotide-Gated Ion Channel Gene Family in Wheat and Functional Analyses of TaCNGC14 and TaCNGC16. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäser, P.; Thomine, S.; Schroeder, J.I.; Ward, J.M.; Hirschi, K.; Sze, H.; Talke, I.N.; Amtmann, A.; Maathuis, F.J.; Sanders, D.; et al. Phylogenetic relationships within cation transporter families of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 1646–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, Z.; Kakar, K.U.; Saand, M.A.; Shu, Q.Y. Cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel gene family in rice, identification, characterization and experimental analysis of expression response to plant hormones, biotic and abiotic stresses. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Yin, H.; Gu, J.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, H.; Wei, S.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J. Genomic characterization, phylogenetic comparison and differential expression of the cyclic nucleotide-gated channels gene family in pear (Pyrus bretchneideri Rehd.). Genomics 2015, 105, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, Z.; Kakar, K.U.; Ullah, R.; Yu, S.; Zhang, J.; Shu, Q.-Y.; Ren, X.-L. Genome-wide identification, evolution and expression analysis of cyclic nucleotide-gated channels in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Genomics 2019, 111, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Yang, S.; Ren, J.; Ye, X.; Jiang, X.; Liu, Z. Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of the cyclic nucleotide-gated channel gene family in Chinese cabbage. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Kang, Y.; Ren, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Xie, P.; Liao, L.; Wang, W.; Qian, L.; Guan, M.; et al. Identification and expression analysis of BnaCNGC family gene in the response to phytohormones, abiotic and biotic stresses in Brassica napus. J. Plant Interact. 2021, 16, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakar, K.U.; Nawaz, Z.; Kakar, K.; Ali, E.; Almoneafy, A.A.; Ullah, R.; Ren, X.-L.; Shu, Q.-Y. Comprehensive genomic analysis of the CNGC gene family in Brassica oleracea: Novel insights into synteny, structures, and transcript profiles. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saand, M.A.; Xu, Y.-P.; Munyampundu, J.-P.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.-R.; Cai, X.-Z. Phylogeny and evolution of plant cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel (CNGC) gene family and functional analyses of tomato CNGCs. DNA Res. 2015, 22, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, L.; Qiao, X. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the CNGC gene family in maize. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelman, A.K.; Dawe, A.; Gehring, C.; Berkowitz, G.A. Evolutionary and structural perspectives of plant cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channels. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Guo, C.; Shan, H.; Kong, H. Divergence of duplicate genes in exon-intron structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popko, J.; Hänsch, R.; Mendel, R.-R.; Polle, A.; Teichmann, T. The role of abscisic acid and auxin in the response of poplar to abiotic stress. Plant Biol. 2010, 12, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Wu, Z.; Percy, R.G.; Bai, M.; Li, Y.; Frelichowski, J.E.; Hu, J.; Wang, K.; Yu, J.Z.; Zhu, Y. Genome sequence of Gossypium herbaceum and genome updates of Gossypium arboreum and Gossypium hirsutum provide insights into cotton A-genome evolution. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Fang, L.; Guan, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Saski, C.A.; Scheffler, B.E.; Stelly, D.M.; et al. Sequencing of allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. acc. TM-1) provides a resource for fiber improvement. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Gattiker, A.; Hoogland, C.; Ivanyi, I.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loake, G.; Grant, M. Salicylic acid in plant defence—The players and protagonists. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kang, Y.; Ma, C.L.; Miao, R.Y.; Wu, C.L.; Long, Y.; Ge, T.; Wu, Z.; Hou, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. CNGC2 Is a Ca2+ Influx Channel That Prevents Accumulation of Apoplastic Ca2+ in the Leaf. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 1342–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Han, X.; Wu, J.; Zheng, S.; Shang, Z.; Sun, D.; Zhou, R.; Li, B. A heat-activated calcium-permeable channel—Arabidopsis cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel 6—Is involved in heat shock responses. Plant J. 2012, 70, 1056–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kugler, A.; Köhler, B.; Palme, K.; Wolff, P.; Dietrich, P. Salt-dependent regulation of a CNG channel subfamily in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 2009, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Tate, J.; Mistry, J.; Coggill, P.C.; Sammut, S.J.; Hotz, H.-R.; Ceric, G.; Forslund, K.; Eddy, S.R.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L.; et al. The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D281–D288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, A.; Birney, E.; Durbin, R.; Eddy, S.; Finn, R.D.; Sonnhammer, E. Pfam 3.1: 1313 multiple alignments and profile HMMs match the majority of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. 20 years of the SMART protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D493–D496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paysan-Lafosse, T.; Blum, M.; Chuguransky, S.; Grego, T.; Pinto, B.L.; Salazar, G.A.; Bileschi, M.L.; Bork, P.; Bridge, A.; Colwell, L.; et al. InterPro in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D418–D427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.H.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant. 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkman, S.J.; Roscoe, E.M.; Bourret, J.C. Comparing self-directed methods for training staff to create graphs using Graphpad Prism. J. Appl. Behav. Anal. 2019, 52, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).