Soybean Mosaic Virus 6K1 Interactors Screening and GmPR4 and GmBI1 Function Characterization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
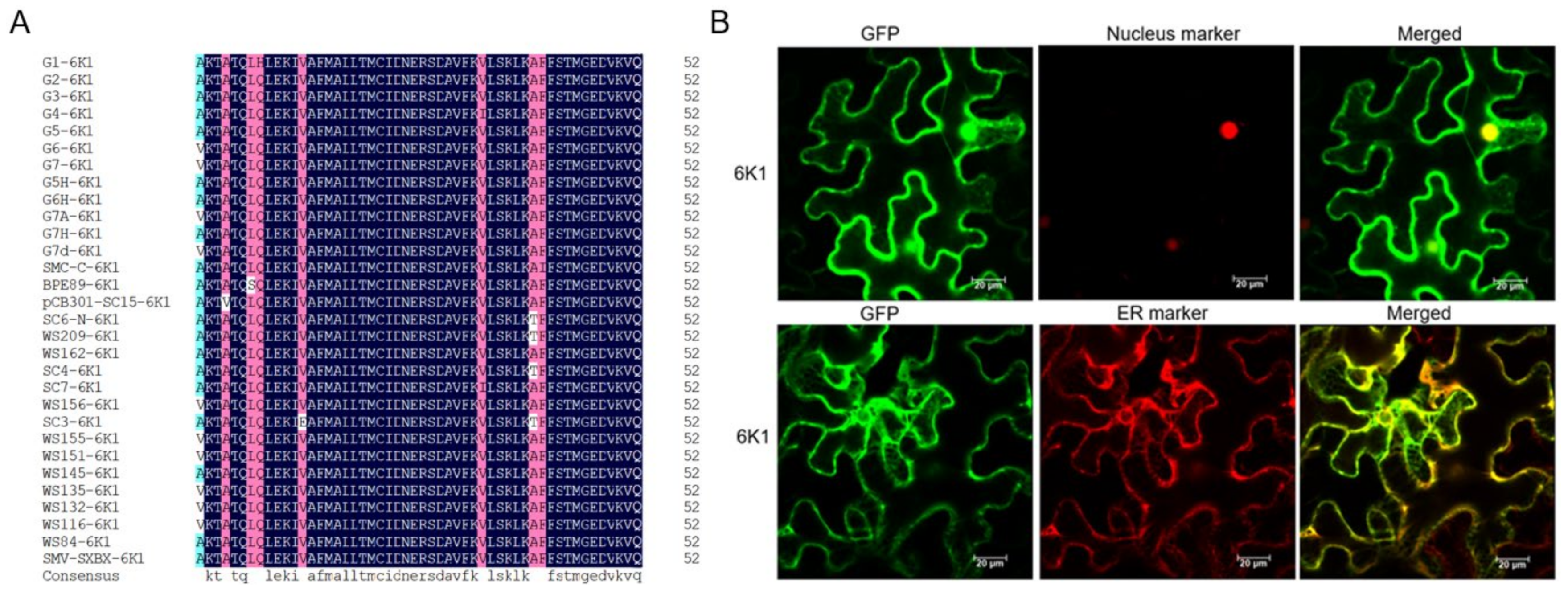
2.1. 6K1 Localizes to Nucleus, ER and Cytoplasm
2.2. Evaluation of the pBT3-STE-6K1 Bait Vector
2.3. Screening of Soybean Proteins Interacting with SMV-6K1
2.4. Protein-Protein Interaction Networks of SMV-6K1 Interactors
2.5. Subcellular Localization and BiFC Analyses of GmPR4 and GmBI1
2.6. Expression Analyses of GmPR4 and GmBI1 by qRT-PCR
2.7. Transient Overexpression of GmPR4 and GmBI1 Reduced SMV Accumulation in N. benthamiana
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials, Virus Strains and Soybean cDNA Library
4.2. Gene Cloning, Vector Construction and Primers
4.3. Bioinformatic Analysis
4.4. Yeast Two-Hybrid (Y2H) Assay
4.5. Localization and Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation (BiFC) Assays
4.6. Stress Treatments, Quantitative RT-PCR and ELISA
4.7. Agrobacterium-Mediated Transient Overexpression
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hill, J.; Bailey, T.; Benner, H.; Tachibana, H.; Durand, D. Soybean mosaic virus: Effects of primary disease incidence on yield and seed quality. Plant Dis. 1987, 71, 237–239. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer, T.W.; Peyyala, R.; Ren, Q.X.; Ghabrial, S.A. Increased soybean pubescence density: Yield and soybean mosaic virus resistance effects. Crop Sci. 2003, 43, 2071–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urcuqui-Inchima, S.; Haenni, A.L.; Bernardi, F. Potyvirus proteins: A wealth of functions. Virus Res. 2001, 74, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, K.I.; Eskelin, K.; Lõhmus, A.; Mäkinen, K. Molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying potyvirus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 1415–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hajimorad, M.R.; Domier, L.L.; Tolin, S.A.; Whitham, S.A.; Saghai Maroof, M.A. Soybean mosaic virus: A successful potyvirus with a wide distribution but restricted natural host range. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, K.; Yang, Q.H.; Zhi, H.J.; Gai, J.Y. Identification and Distribution of Soybean mosaic virus Strains in Southern China. Plant Dis. 2010, 94, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, T.; Karthikeyan, A.; Wang, L.; Zong, T.; Wang, T.; Yin, J.; Hu, T.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; Cui, Y.; et al. Digs out and characterization of the resistance gene accountable to soybean mosaic virus in soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, accepted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.K.; Goodman, R.M. Strains of soybean mosaic virus: Classification based on virulence in resistant soybean cultivars. Phytopathology 1979, 69, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riechmann, J.L.; Laín, S.; García, J.A. Highlights and prospects of potyvirus molecular biology. J. Gen. Virol. 1992, 73, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, B.Y.; Miller, W.A.; Atkins, J.F.; Firth, A.E. An overlapping essential gene in the Potyviridae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5897–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dolja, V.V.; Haldeman, R.; Robertson, N.L.; Dougherty, W.G.; Carrington, J.C. Distinct functions of capsid protein in assembly and movement of tobacco etch potyvirus in plants. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 1482–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, I.G.; Haenni, A.; Bernardi, F. Potyviral HC-Pro: A multifunctional protein. J. Gen. Virol. 1996, 77, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, O.; Dunnington, S.W.; Gotow, L.F.; Pirone, T.P.; Hellmann, G.M. Variations in the VPg protein allow a potyvirus to overcome va gene resistance in tobacco. Virology 1997, 237, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, R.H.; Hajimorad, M.R. Mutational analysis of the putative pipo of soybean mosaic virus suggests disruption of PIPO protein impedes movement. Virology 2010, 400, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrington, J.C.; Jensen, P.E.; Schaad, M.C. Genetic evidence for an essential role for potyvirus CI protein in cell-to-cell movement. Plant J. 1998, 14, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spetz, C.; Valkonen, J.P. Potyviral 6K2 protein long-distance movement and symptom-induction functions are independent and host-specific. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2004, 17, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaad, M.C.; Lellis, A.D.; Carrington, J.C. VPg of tobacco etch potyvirus is a host genotype-specific determinant for long-distance movement. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 8624–8631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klein, P.G.; Klein, R.R.; Rodríguez-Cerezo, E.; Hunt, A.G.; Shaw, J.G. Mutational analysis of the tobacco vein mottling virus genome. Virology 1994, 204, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Wang, A. Biogenesis of cytoplasmic membranous vesicles for plant potyvirus replication occurs at endoplasmic reticulum exit sites in a COPI- and COPII-dependent manner. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 12252–12264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, T.; Huang, T.S.; McNeil, J.; Laliberté, J.F.; Hong, J.; Nelson, R.S.; Wang, A. Sequential recruitment of the endoplasmic reticulum and chloroplasts for plant potyvirus replication. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suehiro, N.; Natsuaki, T.; Watanabe, T.; Okuda, S. An important determinant of the ability of Turnip mosaic virus to infect Brassica spp. and/or Raphanus sativus is in its P3 protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 2087–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauchemin, C.; Boutet, N.; Laliberté, J.F. Visualization of the interaction between the precursors of VPg, the viral protein linked to the genome of turnip mosaic virus, and the translation eukaryotic initiation factor iso 4E in Planta. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, W.; Shi, Y.; Dai, Z.; Wang, A. The RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase NIb of Potyviruses Plays Multifunctional, Contrasting Roles during Viral Infection. Viruses 2020, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jenner, C.E.; Wang, X.; Tomimura, K.; Ohshima, K.; Ponz, F.; Walsh, J.A. The dual role of the potyvirus P3 protein of Turnip mosaic virus as a symptom and avirulence determinant in brassicas. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2003, 16, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eggenberger, A.L.; Hajimorad, M.R.; Hill, J.H. Gain of virulence on Rsv1-genotype soybean by an avirulent Soybean mosaic virus requires concurrent mutations in both P3 and HC-Pro. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2008, 21, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Hajimorad, M.R.; Eggenberger, A.L.; Tsang, S.; Whitham, S.A.; Hill, J.H. Cytoplasmic inclusion cistron of Soybean mosaic virus serves as a virulence determinant on Rsv3-genotype soybean and a symptom determinant. Virology 2009, 391, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, J.; Wang, L.; Jin, T.; Nie, Y.; Liu, H.; Qiu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; et al. A cell wall-localized NLR confers resistance to Soybean mosaic virus by recognizing viral-encoded cylindrical inclusion protein. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 1881–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltermann, A.; Maiss, E. Detection of 6K1 as a mature protein of 6 kDa in plum pox virus-infected Nicotiana benthamiana. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 2381–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.Y.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y.H.; Chen, J.P. The ‘6K1′ protein of a strain of Soybean mosaic virus localizes to the cell periphery. Arch. Virol. 2007, 152, 1547–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Wang, A. Plum Pox Virus 6K1 Protein Is Required for Viral Replication and Targets the Viral Replication Complex at the Early Stage of Infection. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 5119–5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geng, C.; Yan, Z.Y.; Cheng, D.J.; Liu, J.; Tian, Y.P.; Zhu, C.X.; Wang, H.Y.; Li, X.D. Tobacco vein banding mosaic virus 6K2 Protein Hijacks NbPsbO1 for Virus Replication. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.X.; Howell, S.H. Endoplasmic reticulum protein quality control and its relationship to environmental stress responses in plants. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 2930–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gayral, M.; Arias Gaguancela, O.; Vasquez, E.; Herath, V.; Flores, F.J.; Dickman, M.B.; Verchot, J. Multiple ER-to-nucleus stress signaling pathways are activated during Plantago asiatica mosaic virus and Turnip mosaic virus infection in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2020, 103, 1233–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.; Shine, M.B.; Cui, X.; Chen, X.; Ma, N.; Kachroo, P.; Zhi, H.; Kachroo, A. The Potyviral P3 Protein Targets Eukaryotic Elongation Factor 1A to Promote the Unfolded Protein Response and Viral Pathogenesis. Plant Physiol. 2016, 172, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delaney, T.P.; Uknes, S.; Vernooij, B.; Friedrich, L.; Weymann, K.; Negrotto, D.; Gaffney, T.; Gut-Rella, M.; Kessmann, H.; Ward, E.; et al. A central role of salicylic Acid in plant disease resistance. Science 1994, 266, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryals, J.A.; Neuenschwander, U.H.; Willits, M.G.; Molina, A.; Steiner, H.Y.; Hunt, M.D. Systemic Acquired Resistance. Plant Cell 1996, 8, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Han, K.; Peng, J.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, L.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Lin, L.; Chen, J.; Yan, F. NbALD1 mediates resistance to turnip mosaic virus by regulating the accumulation of salicylic acid and the ethylene pathway in Nicotiana benthamiana. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 20, 990–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Love, A.J.; Laval, V.; Geri, C.; Laird, J.; Tomos, A.D.; Hooks, M.A.; Milner, J.J. Components of Arabidopsis defense- and ethylene-signaling pathways regulate susceptibility to Cauliflower mosaic virus by restricting long-distance movement. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2007, 20, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casteel, C.L.; De Alwis, M.; Bak, A.; Dong, H.; Whitham, S.A.; Jander, G. Disruption of Ethylene Responses by Turnip mosaic virus Mediates Suppression of Plant Defense against the Green Peach Aphid Vector. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 128–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, F.; Jiang, L.; Chen, C.; Wu, L.; Liu, Z. Different Pathogen Defense Strategies in Arabidopsis: More than Pathogen Recognition. Cells 2018, 7, 252. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Meng, D.; Jin, T.; Zhou, X. HC-Pro viral suppressor from tobacco vein banding mosaic virus interferes with DNA methylation and activates the salicylic acid pathway. Virology 2016, 497, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bera, S.; Arena, G.D.; Ray, S.; Flannigan, S.; Casteel, C.L. The Potyviral Protein 6K1 Reduces Plant Proteases Activity during Turnip mosaic virus Infection. Viruses 2022, 14, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosque, G.; Folch-Fortuny, A.; Picó, J.; Ferrer, A.; Elena, S.F. Topology analysis and visualization of Potyvirus protein-protein interaction network. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A. Dissecting the molecular network of virus-plant interactions: The complex roles of host factors. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2015, 53, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howell, S.H. Endoplasmic reticulum stress responses in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2013, 64, 477–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez, F.; Rodrigo, G.; Aragonés, V.; Ruiz, M.; Lodewijk, I.; Fernández, U.; Elena, S.F.; Daròs, J.A. Interaction network of tobacco etch potyvirus NIa protein with the host proteome during infection. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luan, H.; Liao, W.; Niu, H.; Cui, X.; Chen, X.; Zhi, H. Comprehensive Analysis of Soybean Mosaic Virus P3 Protein Interactors and Hypersensitive Response-Like Lesion-Inducing Protein Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Cheng, G.; Yang, Z.; Wang, T.; Xu, J. Identification of Sugarcane Host Factors Interacting with the 6K2 Protein of the Sugarcane Mosaic Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, C.J.; Shin, R.; Park, J.M.; Lee, G.J.; Yoo, T.H.; Paek, K.H. A hot pepper cDNA encoding a pathogenesis-related protein 4 is induced during the resistance response to tobacco mosaic virus. Mol. Cells 2001, 11, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.; Xiao, B.; Xiong, L. Identification of a cluster of PR4-like genes involved in stress responses in rice. J. Plant Physiol. 2011, 168, 2212–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Jiao, Y.T.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhang, N.; Wang, B.B.; Liu, R.Q.; Yin, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, G.T. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated VvPR4b editing decreases downy mildew resistance in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, M.; Van Zaanen, W.; Koornneef, A.; Korzelius, J.P.; Dicke, M.; Van Loon, L.C.; Pieterse, C.M. Herbivore-induced resistance against microbial pathogens in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubois, M.; Van den Broeck, L.; Inzé, D. The Pivotal Role of Ethylene in Plant Growth. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plett, J.M.; Khachane, A.; Ouassou, M.; Sundberg, B.; Kohler, A.; Martin, F. Ethylene and jasmonic acid act as negative modulators during mutualistic symbiosis between Laccaria bicolor and Populus roots. New Phytol. 2014, 202, 270–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, H.J.; Kim, H.R.; Xu, C.; Bailly-Maitre, B.; Krajewska, M.; Krajewski, S.; Banares, S.; Cui, J.; Digicaylioglu, M.; Ke, N.; et al. BI-1 regulates an apoptosis pathway linked to endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol. Cell 2004, 15, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, K.S.; Clements, A.; Williams, A.C.; Berger, C.N.; Frankel, G. Bax inhibitor 1 in apoptosis and disease. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2391–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, N.; Lam, E. BAX inhibitor-1 modulates endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated programmed cell death in Arabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 3200–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramiro, D.A.; Melotto-Passarin, D.M.; Barbosa Mde, A.; Santos, F.D.; Gomez, S.G.; Massola Júnior, N.S.; Lam, E.; Carrer, H. Expression of Arabidopsis Bax Inhibitor-1 in transgenic sugarcane confers drought tolerance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 1826–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Çakır, B.; Tumer, N.E. Arabidopsis Bax Inhibitor-1 inhibits cell death induced by pokeweed antiviral protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb. Cell 2015, 2, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, P.; de Torres Zabala, M.; Grant, M. AtBI-1, a plant homologue of Bax inhibitor-1, suppresses Bax-induced cell death in yeast and is rapidly upregulated during wounding and pathogen challenge. Plant J. 2000, 21, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaguancela, O.A.; Zúñiga, L.P.; Arias, A.V.; Halterman, D.; Flores, F.J.; Johansen, I.E.; Wang, A.; Yamaji, Y.; Verchot, J. The IRE1/bZIP60 Pathway and Bax Inhibitor 1 Suppress Systemic Accumulation of Potyviruses and Potexviruses in Arabidopsis and Nicotiana benthamiana Plants. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2016, 29, 750–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Tang, C.; Huang, X.; Li, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, G.; Sun, Y.; Han, D.; Kang, Z. Wheat BAX inhibitor-1 contributes to wheat resistance to Puccinia striiformis. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 4571–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Babaeizad, V.; Imani, J.; Kogel, K.H.; Eichmann, R.; Hückelhoven, R. Over-expression of the cell death regulator BAX inhibitor-1 in barley confers reduced or enhanced susceptibility to distinct fungal pathogens. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 118, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebulski, J.; Malouin, J.; Pinches, N.; Cascio, V.; Austriaco, N. Yeast Bax inhibitor, Bxi1p, is an ER-localized protein that links the unfolded protein response and programmed cell death in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wang, S.; Han, S.; Xie, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. Plant Bax Inhibitor-1 interacts with ATG6 to regulate autophagy and programmed cell death. Autophagy 2017, 13, 1161–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Earley, K.W.; Haag, J.R.; Pontes, O.; Opper, K.; Juehne, T.; Song, K.; Pikaard, C.S. Gateway-compatible vectors for plant functional genomics and proteomics. Plant J. 2006, 45, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuhashi, N.; Shimada, T.; Mano, S.; Nishimura, M.; Hara-Nishimura, I. Characterization of organelles in the vacuolar-sorting pathway by visualization with GFP in tobacco BY-2 cells. Plant Cell Physiol. 2000, 41, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, J.; Liu, H.; Xiang, W.; Jin, T.; Guo, D.; Wang, L.; Zhi, H. Discovery of the Agrobacterium growth inhibition sequence in virus and its application to recombinant clone screening. AMB Express 2019, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Protein Name | Gene | Function Description | Function Classification | Identification of Interaction 1 | Subcellular Location 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GmBI1-1 | Glyma.01g205200 | Inhibitor of apoptosis-promoting Bax1 | Defense-related | + | ER |
| GmPR3 | Glyma.02G042500 | Chitin recognition protein, PR3 | Defense-related | + | Extra |
| GmPR4 | Glyma.03g247500 | Barwin family, chitinase-related | Defense-related | + | Extra |
| GmDFP | Glyma.04g009400 | Dehydrin family protein | Defense-related | + | N |
| GmPFCP-1 | Glyma.04g027600 | Papain family cysteine protease | Defense-related | + | Extra |
| GmBI1–2 | Glyma.05g064700 | Inhibitor of apoptosis-promoting Bax1 | Defense-related | + | ER |
| GmMT2A | Glyma.07g132000 | Metallothionein | Defense-related | + | Ch, N |
| GmERG4 | Glyma.08g224200 | Ergosterol biosynthesis ERG4/ERG24 family | Defense-related | + | PM |
| GmTLP | Glyma.10g061000 | Thaumatin family | Defense-related | + | Extra |
| GmBI1-3 | Glyma.11g037700 | Inhibitor of apoptosis-promoting Bax1 | Defense-related | + | ER |
| GmELP | Glyma.11g154900 | Extensin-like protein repeat | Defense-related | + | Extra |
| GmALIP | Glyma.12g150500 | Aluminium induced protein | Defense-related | − | Cyto, N, Ch |
| GmMBF1 | Glyma.12g129100 | Multiprotein bridging factor 1 | Defense-related | + | N, Mito |
| GmCYSB-1 | Glyma.13g071800 | Cysteine protease inhibitors | Defense-related | + | Cyto |
| GmBI1-4 | Glyma.13g211300 | Inhibitor of apoptosis-promoting Bax1 | Defense-related | + | ER |
| GmCYSB-2 | Glyma.13g189500 | Cysteine protease inhibitors | Defense-related | + | V |
| GmPFCP-2 | Glyma.14g085800 | Papain family cysteine protease | Defense-related | + | Cyto, N |
| GmPR1 | Glyma.15g062400 | Cysteine-rich secretory protein family | Defense-related | + | Extra |
| GmPSK | Glyma.17g233500 | Phytosulfokine precursor protein | Defense-related | + | Ch, Extra |
| GmTPT1 | Glyma.07g201300 | Triose-phosphate Transporter family | Transport-related | + | Ch |
| GmZIP | Glyma.08g328000 | ZIP Zinc transporter | Transport-related | + | PM |
| GmTPT2 | Glyma.13g175100 | Triose-phosphate Transporter family | Transport-related | + | Ch, Mito |
| GmMIP-1 | Glyma.13g325900 | Major intrinsic protein | Transport-related | + | PM |
| GmMIP-2 | Glyma.19G181300 | Major intrinsic protein | Transport-related | + | PM |
| GmRD | Glyma.03G245100 | Rubredoxin | Metabolism-related | + | Ch, N |
| GmPSBR-1 | Glyma.08g173700 | Photosystem II 10 kDa polypeptide PsbR | Metabolism-related | + | Ch |
| GmP4Hc | Glyma.11g080700 | Prolyl 4-hydroxylase alpha subunit | Metabolism-related | + | Ch |
| GmPSBR-2 | Glyma.15g253700 | Photosystem II 10 kDa polypeptide PsbR | Metabolism-related | + | Ch |
| GmUBC | Glyma.17g032800 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme | Metabolism-related | + | G |
| GmRPS8–1 | Glyma.03G086400 | 40S ribosomal protein S8 | DNA Binding | − | Ch, N |
| GmRRM | Glyma.11g117600 | RNA recognition protein | DNA Binding | − | N |
| GmEF1 | Glyma.13g073200 | Elongation factor 1 beta/delta chain | DNA binding | − | Cyto, N |
| GmRPL18A | Glyma.13g261500 | 60S ribosomal protein L18A | DNA Binding | + | PM |
| GmRPL34 | Glyma.13g209500 | 60S ribosomal protein L34 | DNA Binding | + | Mito |
| GmRPS8-2 | Glyma.16g087700 | 40S ribosomal protein S8 | DNA Binding | − | Cyto, N |
| GmEIF5A | Glyma.17g103100 | Translation initiation factor 5A (eIF-5A) | DNA Binding | + | Cyto |
| GmUP1 | Glyma.04g111000 | Unknown protein | Unknown | + | Ch |
| GmUP2 | Glyma.08g183000 | Unknown protein | Unknown | + | Extra, Ch |
| GmPMP | Glyma.04G167300 | Predicted membrane protein | Membrane-related | − | PM |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, T.; Luan, H.; Wang, L.; Ren, R.; Sun, L.; Yin, J.; Liu, H.; Jin, T.; Li, B.; Li, K.; et al. Soybean Mosaic Virus 6K1 Interactors Screening and GmPR4 and GmBI1 Function Characterization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065304
Hu T, Luan H, Wang L, Ren R, Sun L, Yin J, Liu H, Jin T, Li B, Li K, et al. Soybean Mosaic Virus 6K1 Interactors Screening and GmPR4 and GmBI1 Function Characterization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(6):5304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065304
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Ting, Hexiang Luan, Liqun Wang, Rui Ren, Lei Sun, Jinlong Yin, Hui Liu, Tongtong Jin, Bowen Li, Kai Li, and et al. 2023. "Soybean Mosaic Virus 6K1 Interactors Screening and GmPR4 and GmBI1 Function Characterization" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 6: 5304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065304
APA StyleHu, T., Luan, H., Wang, L., Ren, R., Sun, L., Yin, J., Liu, H., Jin, T., Li, B., Li, K., & Zhi, H. (2023). Soybean Mosaic Virus 6K1 Interactors Screening and GmPR4 and GmBI1 Function Characterization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(6), 5304. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065304






