Irradiation-Induced Dysbiosis: The Compounding Effect of High-Fat Diet on Metabolic and Immune Functions in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Whole Body Metabolic Profile
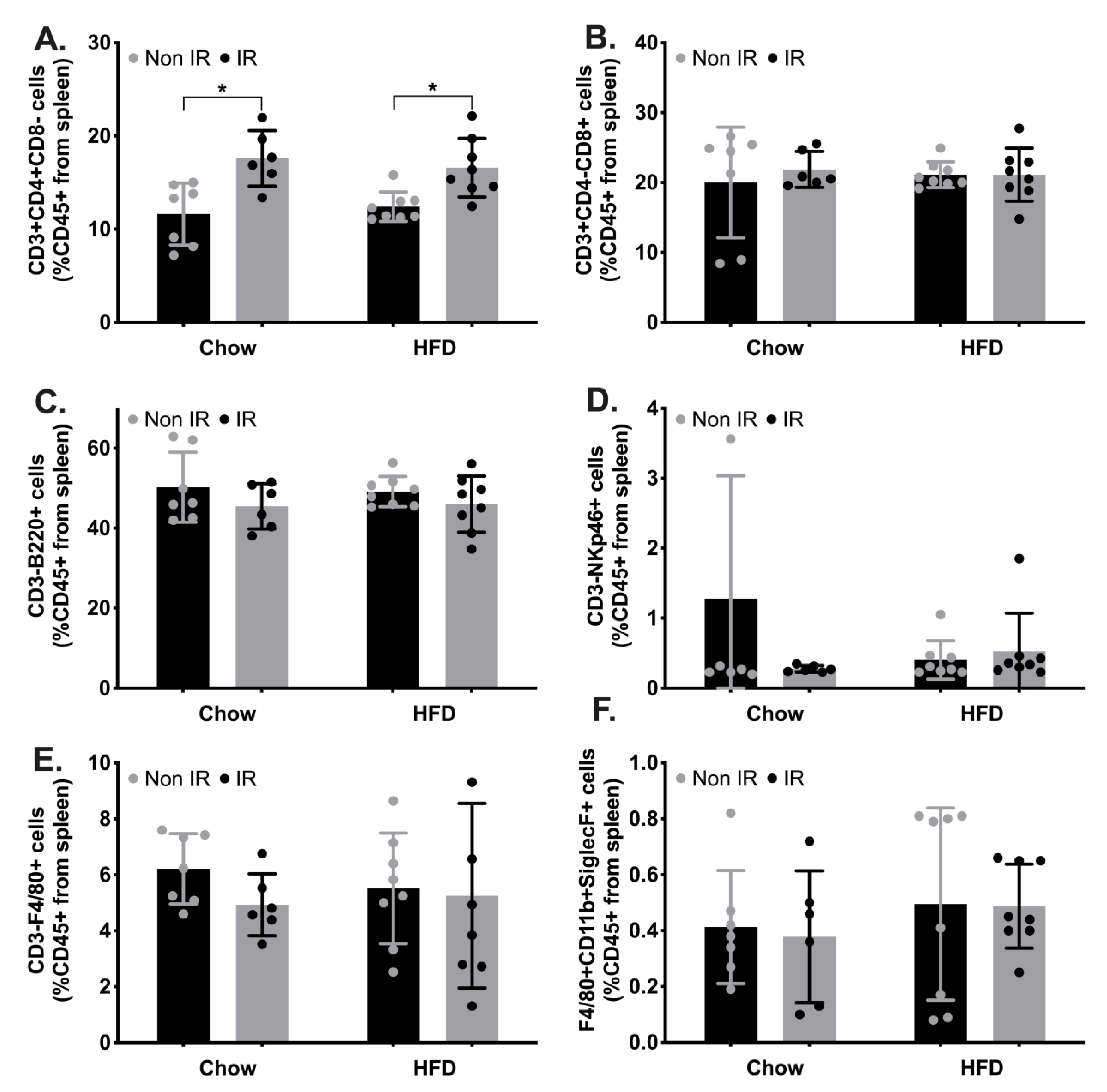
2.2. Effect of Irradiation and Diet on Systemic Inflammation and Immune Cell Profiles
2.3. Innate and Adaptive Immune Cell Phenotypic Profiles
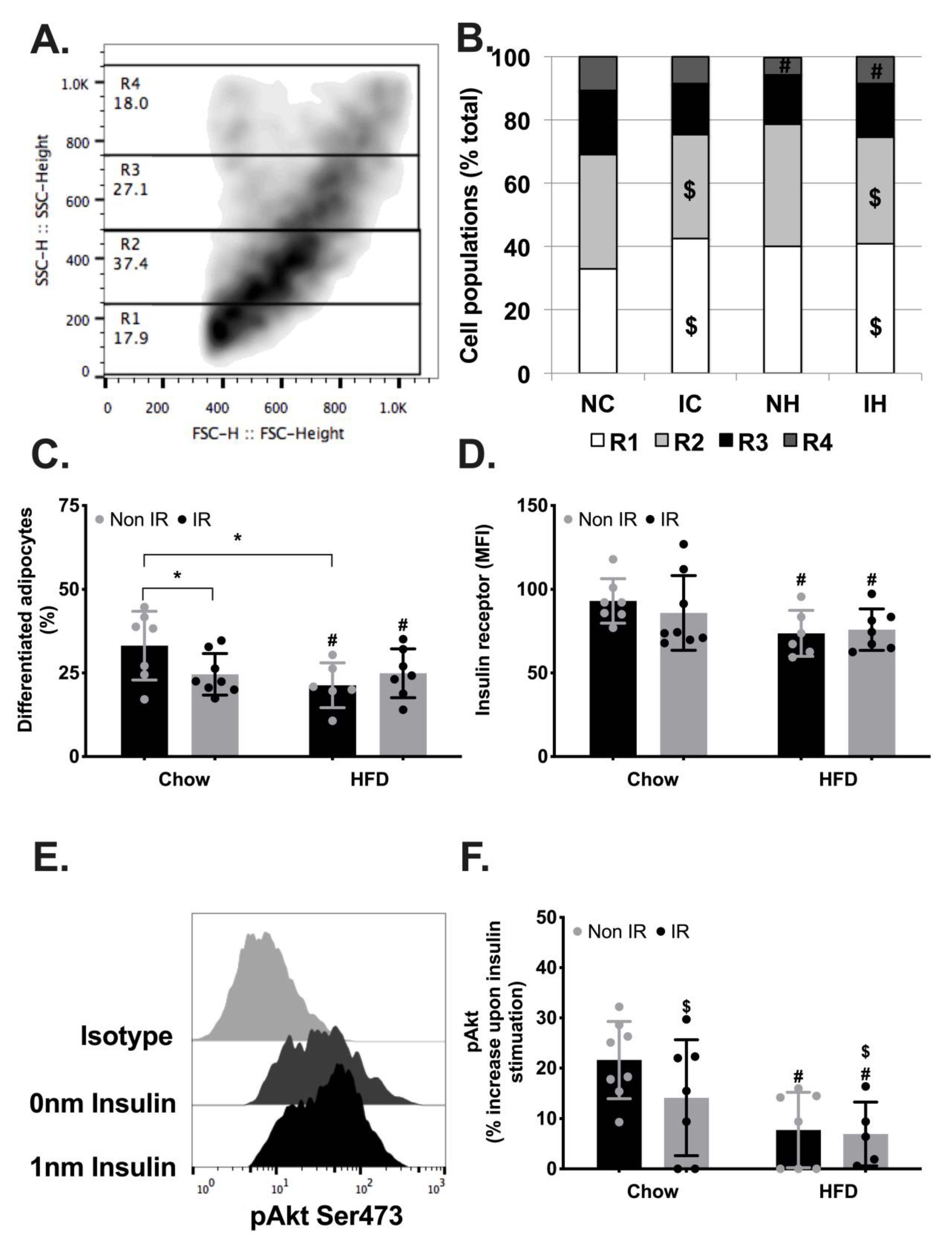
2.4. Immune Activation in Adipose Tissue
2.5. Adipose Tissue Metabolic Functions
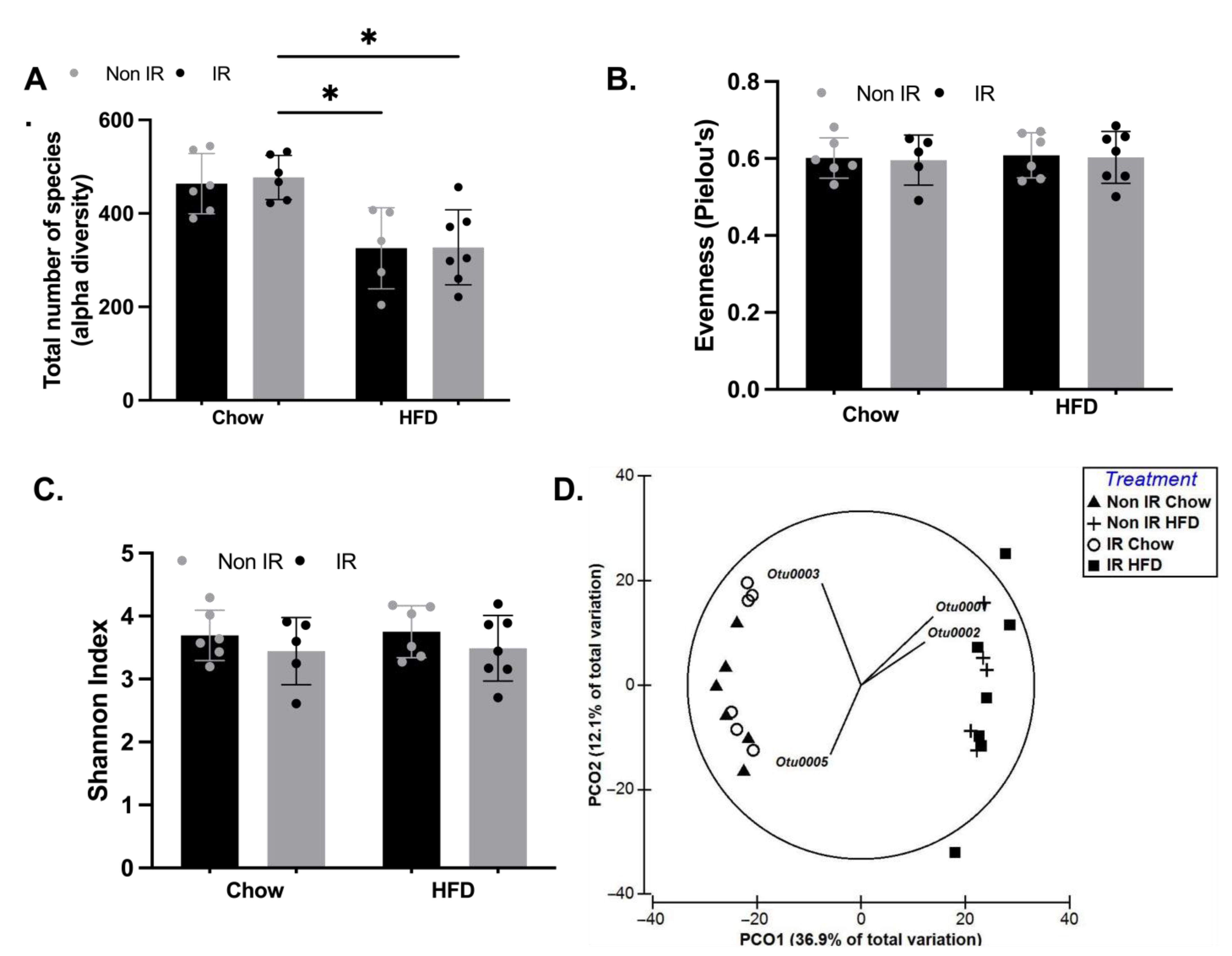
2.6. Effect of Irradiation and Diet on Gut Microbiota Diversity and Profile
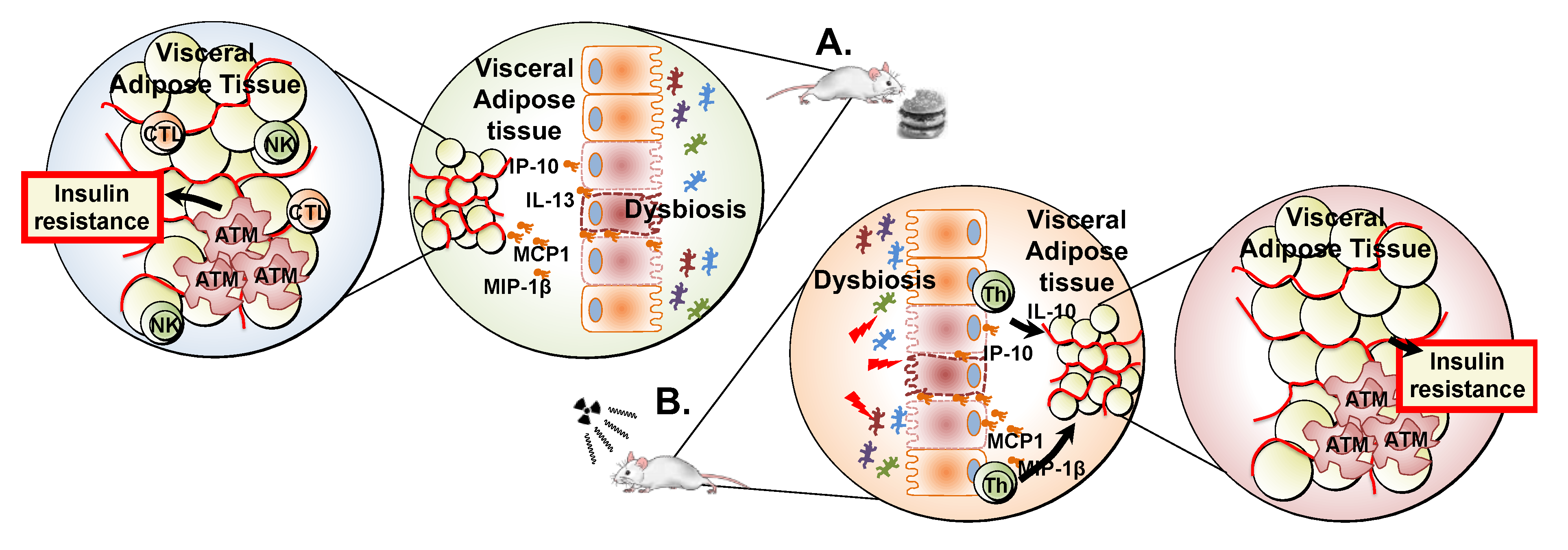
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Procedure
4.2. Extraction of DNA from Stool
4.3. Cytokine Multiplex Assay
4.4. Spleen Immune Cell Profiling
4.5. Adipose Tissue Metabolic Functions and Immune Cells Infiltration
4.6. Raw Data and Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Botta, L.; Gatta, G.; Capocaccia, R.; Stiller, C.; Cañete, A.; Maso, L.D.; Innos, K.; Mihor, A.; Erdmann, F.; Spix, C.; et al. Long-term survival and cure fraction estimates for childhood cancer in Europe (EUROCARE-6): Results from a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 1525–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennati, E.; Girolami, F.; Spaziani, G.; Calabri, G.B.; Favre, C.; Parrini, I.; Lucà, F.; Tamburini, A.; Favilli, S. Cardio-Oncology in Childhood: State of the Art. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 24, 1765–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, M.M.; Ness, K.K.; Gurney, J.G.; Mulrooney, D.A.; Chemaitilly, W.; Krull, K.R.; Green, D.M.; Armstrong, G.T.; Nottage, K.A.; Jones, K.E.; et al. Clinical ascertainment of health outcomes among adults treated for childhood cancer. JAMA 2013, 309, 2371–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meacham, L.R.; Sklar, C.A.; Li, S.; Liu, Q.; Gimpel, N.; Yasui, Y.; Whitton, J.A.; Stovall, M.; Robison, L.L.; Oeffinger, K.C. Diabetes mellitus in long-term survivors of childhood cancer. Increased risk associated with radiation therapy: A report for the childhood cancer survivor study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeffinger, K.C.; Mertens, A.C.; Sklar, C.A.; Kawashima, T.; Hudson, M.M.; Meadows, A.T.; Friedman, D.L.; Marina, N.; Hobbie, W.; Kadan-Lottick, N.S.; et al. Chronic health conditions in adult survivors of childhood cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 1572–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, N.M.; Kee, A.; Coster, A.C.; Lucas, C.; Bould, S.; Daniel, S.; Weir, J.M.; Mellett, N.A.; Barbour, J.; Meikle, P.J.; et al. Irradiation impairs mitochondrial function and skeletal muscle oxidative capacity: Significance for metabolic complications in cancer survivors. Metabolism 2020, 103, 154025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, K.A.; Cohn, R.; Steinbeck, K.S.; Johnston, K.; Walker, J.L. Hyperinsulinemia, impaired glucose tolerance, and diabetes mellitus in survivors of childhood cancer: Prevalence and risk factors. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 4401–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, S.; Nylander, V.; Ingerslev, L.R.; Zhong, L.; Fabre, O.; Clifford, B.; Johnston, K.; Cohn, R.J.; Barres, R.; Simar, D. T cell epigenetic remodeling and accelerated epigenetic aging are linked to long-term immune alterations in childhood cancer survivors. Clin. Epigenet. 2018, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, E.J.; Simmons, J.H.; Roth, C.L.; Baker, K.S.; Hoffmeister, P.A.; Sanders, J.E.; Friedman, D.L. Increased cardiometabolic traits in pediatric survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with total body irradiation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010, 16, 1674–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckhed, F.; Ding, H.; Wang, T.; Hooper, L.V.; Koh, G.Y.; Nagy, A.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J.I. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15718–15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhu, F.; Chen, Z.; Li, D.; Li, B. Regulation of Metabolism Across Different Subsets of T Cells in Cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1011, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Chi, M.M.; Scull, B.P.; Rigby, R.; Schwerbrock, N.M.J.; Magness, S.; Jobin, C.; Lund, P.K. High-fat diet: Bacteria interactions promote intestinal inflammation which precedes and correlates with obesity and insulin resistance in mouse. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; Amar, J.; Iglesias, M.A.; Poggi, M.; Knauf, C.; Bastelica, D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Fava, F.; Tuohy, K.M.; Chabo, C.; et al. Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, Y.Y.; Ha, C.W.Y.; Campbell, C.R.; Mitchell, A.J.; Dinudom, A.; Oscarsson, J.; Cook, D.I.; Hunt, N.H.; Caterson, I.D.; Holmes, A.J.; et al. Increased gut permeability and microbiota change associate with mesenteric fat inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in diet-induced obese mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, Y.Y.; Ha, C.W.Y.; Storlien, L.H.; Hoffmann, J.M.A.; Oscarsson, J.; Dinudom, A.; Mather, T.J.; Cook, D.I.; Hunt, N.H.; Caterson, I.D.; et al. Effects of dietary fat profile on gut permeability and microbiota and their relationships with metabolic changes in mice. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2015, 23, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Boerma, M.; Fu, Q.; Hauer-Jensen, M. Significance of endothelial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of early and delayed radiation enteropathy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 3047–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stringer, A.; Gibson, R.; Bowen, J.; Keefe, D. Chemotherapy-induced modifications to gastrointestinal microflora: Evidence and implications of change. Curr. Drug Metab. 2009, 10, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerassy-Vainberg, S.; Blatt, A.; Danin-Poleg, Y.; Gershovich, K.; Sabo, E.; Nevelsky, A.; Daniel, S.; Dahan, A.; Ziv, O.; Dheer, R.; et al. Radiation induces proinflammatory dysbiosis: Transmission of inflammatory susceptibility by host cytokine induction. Gut 2018, 67, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeComte, V.; Kaakoush, N.O.; Maloney, C.A.; Raipuria, M.; Huinao, K.D.; Mitchell, H.M.; Morris, M.J. Changes in gut microbiota in rats fed a high fat diet correlate with obesity-associated metabolic parameters. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylander, V.; Ingerslev, L.R.; Andersen, E.; Fabre, O.; Garde, C.; Rasmussen, M.; Citirikkaya, K.; Bæk, J.; Christensen, G.L.; Aznar, M.; et al. Ionizing Radiation Potentiates High-Fat Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance and Reprograms Skeletal Muscle and Adipose Progenitor Cells. Diabetes 2016, 65, 3573–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, F.; Masetti, R.; Andreozzi, L.; Zama, D.; Fabi, M.; Meli, M.; Prete, A.; Lanari, M. The Role of Nutrition in Primary and Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Damage in Childhood Cancer Survivors. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Wakefield, C.E.; Fleming, C.A.K.; Gawthorne, R.; Tapsell, L.C.; Cohn, R.J. Dietary intake after treatment in child cancer survivors. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2012, 58, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goddard, E.; Cohen, J.; Bramley, L.; Wakefield, C.E.; Beck, E.J. Dietary intake and diet quality in children receiving treatment for cancer. Nutr. Rev. 2019, 77, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meacham, W.D.; Antoon, J.W.; Burow, M.E.; Struckhoff, A.P.; Beckman, B.S. Sphingolipids as determinants of apoptosis and chemoresistance in the MCF-7 cell model system. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2009, 234, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Ishikawa, M.; Inoue, N.; Yamada, N.; Shimano, H. Abdominal Irradiation Ameliorates Obesity in ob/ob Mice. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2007, 40, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machate, D.J.; Figueiredo, P.S.; Marcelino, G.; Guimarães, R.D.C.A.; Hiane, P.A.; Bogo, D.; Pinheiro, V.A.Z.; de Oliveira, L.C.S.; Pott, A. Fatty Acid Diets: Regulation of Gut Microbiota Composition and Obesity and Its Related Metabolic Dysbiosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poglio, S.; Galvani, S.; Bour, S.; André, M.; Prunet-Marcassus, B.; Pénicaud, L.; Casteilla, L.; Cousin, B. Adipose tissue sensitivity to radiation exposure. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, G.; Wuest, M.; Tang, X.; Dufour, J.; Zhao, Y.; Curtis, J.M.; McMullen, T.P.W.; Murray, D.; Wuest, F.; Brindley, D.N. Repeated Fractions of X-Radiation to the Breast Fat Pads of Mice Augment Activation of the Autotaxin-Lysophosphatidate-Inflammatory Cycle. Cancers 2019, 11, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Wang, F.; Yuan, J.; Li, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Tang, J.; Huang, T.; et al. Effects of dietary fat on gut microbiota and faecal metabolites, and their relationship with cardiometabolic risk factors: A 6-month randomised controlled-feeding trial. Gut 2019, 68, 1417–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, S.; Manabe, I.; Nagasaki, M.; Eto, K.; Yamashita, H.; Ohsugi, M.; Otsu, M.; Hara, K.; Ueki, K.; Sugiura, S.; et al. CD8+ effector T cells contribute to macrophage recruitment and adipose tissue inflammation in obesity. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuerer, M.; Herrero, L.; Cipolletta, D.; Naaz, A.; Wong, J.; Nayer, A.; Lee, J.; Goldfine, A.B.; Benoist, C.; Shoelson, S.; et al. Lean, but not obese, fat is enriched for a unique population of regulatory T cells that affect metabolic parameters. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sell, H.; Habich, C.; Eckel, J. Adaptive immunity in obesity and insulin resistance. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, D.E.; Stöckli, J.; Birnbaum, M.J. The aetiology and molecular landscape of insulin resistance. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 751–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stienstra, R.; Joosten, L.A.; Koenen, T.; van Tits, B.; van Diepen, J.A.; van den Berg, S.A.; Rensen, P.C.N.; Voshol, P.J.; Fantuzzi, G.; Hijmans, A.; et al. The inflammasome-mediated caspase-1 activation controls adipocyte differentiation and insulin sensitivity. Cell Metab. 2010, 12, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, H.; Gholami, A.M.; Berry, D.; Desmarchelier, C.; Hahne, H.; Loh, G.; Mondot, S.; Lepage, P.; Rothballer, M.; Walker, A.; et al. High-fat diet alters gut microbiota physiology in mice. ISME J. 2014, 8, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, M.A.; Hoffmann, C.; Sherrill–Mix, S.A.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Hamady, M.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Knight, R.; Ahima, R.S.; Bushman, F.; Wu, G.D. High-fat diet determines the composition of the murine gut microbiome independently of obesity. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1716–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisanz, J.E.; Upadhyay, V.; Turnbaugh, J.A.; Ly, K.; Turnbaugh, P.J. Meta-Analysis Reveals Reproducible Gut Microbiome Alterations in Response to a High-Fat Diet. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, D.M.; Volpe, G.E.; Duffalo, C.; Bhalchandra, S.; Tai, A.K.; Kane, A.V.; Wanke, C.A.; Ward, H.D. Intestinal microbiota, microbial translocation, and systemic inflammation in chronic HIV infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 211, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaakoush, N.O. Insights into the Role of Erysipelotrichaceae in the Human Host. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Lyu, W.; Ren, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, S.; Yang, H.; Xiao, Y. Allobaculum Involves in the Modulation of Intestinal ANGPTLT4 Expression in Mice Treated by High-Fat Diet. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 690138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Palombaro, M.; Pulcini, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M. Nutritional Interventions Targeting Gut Microbiota during Cancer Therapies. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-H.; Chen, S.-Y.; Wiesner, R.J.; Huang, Y.-F. Simple flow cytometric method used to assess lipid accumulation in fat cells. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetzels, S.; Bijnen, M.; Wijnands, E.; Biessen, E.A.; Schalkwijk, C.G.; Wouters, K. Characterization of Immune Cells in Human Adipose Tissue by Using Flow Cytometry. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, e57319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the MiSeq Illumina sequencing platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Chow Diet | High-Fat Diet | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non IR | IR | Non IR | IR | Irradiation (p-Value) | Diet (p-Value) | Interaction (p-Value) | |
| Body weight (g) | 29.8 ± 2.4 | 26.0 ± 1.3 | 43.4 ± 6.2 | 37.7 ± 5.4 | 0.028 * | <0.0001 * | 0.616 |
| Body Fat (g) | 4.7 ± 0.8 | 3.8 ± 0.5 | 17.7 ± 4.0 | 13.8 ± 2.9 | 0.053 | <0.0001 * | 0.200 |
| Blood Glucose (mM/L) | 8.4 ± 1.9 | 9.4 ± 1.2 | 12.8 ± 1.5 | 13.1 ± 2.4 | 0.418 | <0.0001 * | 0.682 |
| Insulin (µU/L) | 10.5 ± 3.1 | 10.9 ± 4.4 | 16.0 ± 8.7 | 11.8 ± 4.2 | 0.459 | 0.214 | 0.355 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Clifford, B.K.; Amorim, N.M.L.; Kaakoush, N.O.; Boysen, L.; Tedla, N.; Goldstein, D.; Hardeman, E.C.; Simar, D. Irradiation-Induced Dysbiosis: The Compounding Effect of High-Fat Diet on Metabolic and Immune Functions in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065631
Clifford BK, Amorim NML, Kaakoush NO, Boysen L, Tedla N, Goldstein D, Hardeman EC, Simar D. Irradiation-Induced Dysbiosis: The Compounding Effect of High-Fat Diet on Metabolic and Immune Functions in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(6):5631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065631
Chicago/Turabian StyleClifford, Briana K., Nadia M. L. Amorim, Nadeem O. Kaakoush, Lykke Boysen, Nicodemus Tedla, David Goldstein, Edna C. Hardeman, and David Simar. 2023. "Irradiation-Induced Dysbiosis: The Compounding Effect of High-Fat Diet on Metabolic and Immune Functions in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 6: 5631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065631
APA StyleClifford, B. K., Amorim, N. M. L., Kaakoush, N. O., Boysen, L., Tedla, N., Goldstein, D., Hardeman, E. C., & Simar, D. (2023). Irradiation-Induced Dysbiosis: The Compounding Effect of High-Fat Diet on Metabolic and Immune Functions in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(6), 5631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065631






