Rheumatic Immune-Related Adverse Events due to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors—A 2023 Update
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Immune-Related Adverse Events (irAEs)
2.1. Mechanisms of Action of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICIs)
2.2. Mechanisms of irAEs
3. Rheumatic irAEs
3.1. Autoimmune-Disease-like Symptoms Due to ICIs
3.2. Arthritis
3.3. Myositis
3.4. Vasculitis
3.5. Myalgia (Polymyalgia Rheumatica)
3.6. Sicca Symptoms (Sjögren Syndrome)
3.7. Skin Rash (Psoriasis)
3.8. Skin Sclerosis (Systemic Sclerosis)
3.9. Lupus-like Disease
4. A Potential Strategy to Identify Patients at Risk of Rheumatic irAEs
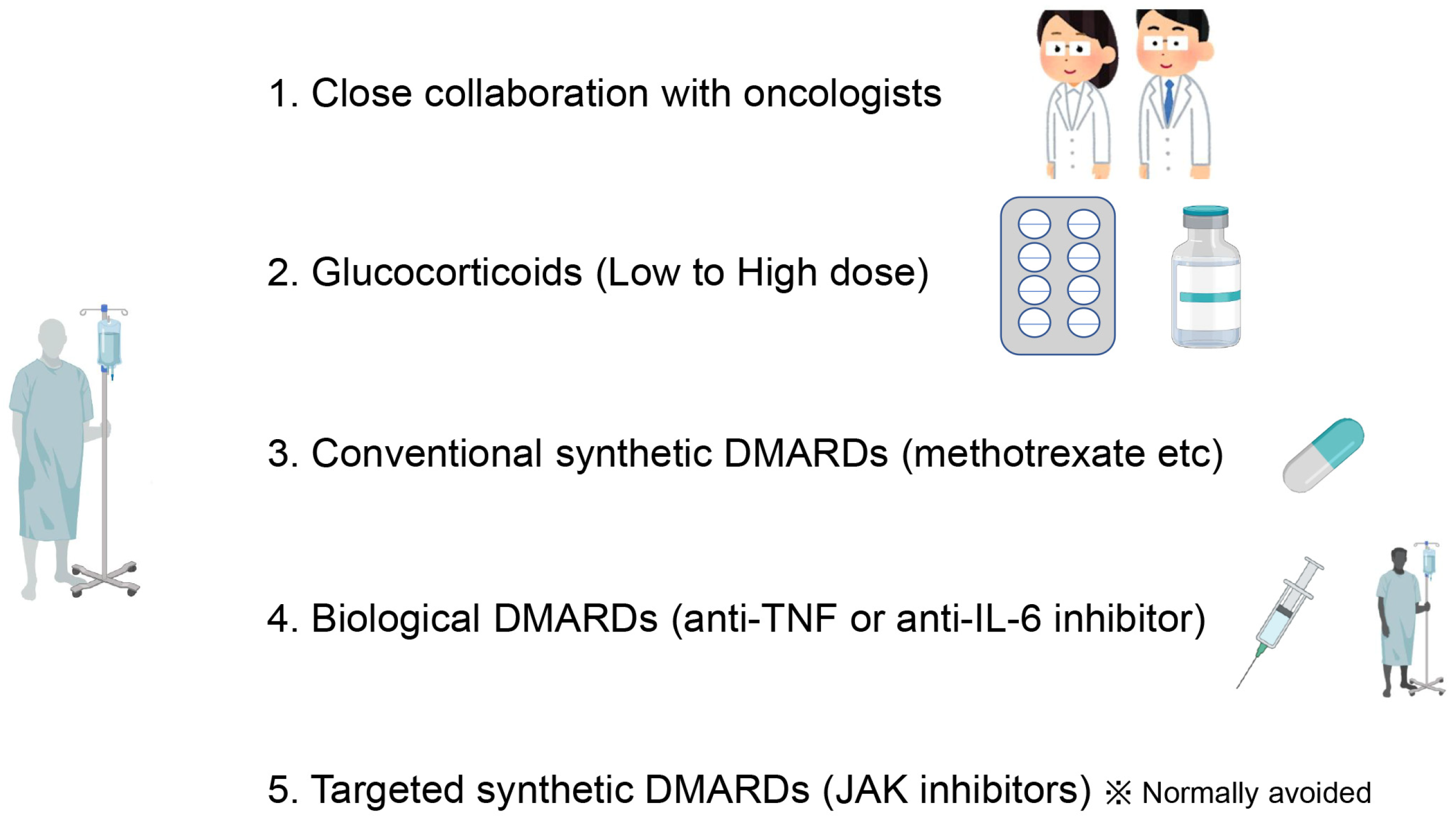
5. Optimal Management of Rheumatic irAEs
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I.B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewé, R.B.M.; Bergstra, S.A.; Kerschbaumer, A.; Sepriano, A.; Aletaha, D.; Caporali, R.; Edwards, C.J.; Hyrich, K.L.; Pope, J.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2022 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhal, L.; Lwin, M.N.; Holroyd, C.; Edwards, C.J. Rheumatoid arthritis in the elderly: Characteristics and treatment considerations. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Y.; Dai, X.; Xu, D.; Liang, J.; Yu, Y.; Cao, H.; Chen, W.; Lin, J. Features and Outcomes of Elderly Rheumatoid Arthritis: Does the Age of Onset Matter? A Comparative Study From a Single Center in China. Rheumatol. Ther. 2021, 8, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, K.; Ito, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Nishitani, K.; Murakami, K.; Tanaka, M.; Yamamoto, W.; Mimori, T.; Matsuda, S. Elderly onset of early rheumatoid arthritis is a risk factor for bone erosions, refractory to treatment: KURAMA cohort. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targońska-Stępniak, B.; Grzechnik, K.; Kolarz, K.; Gągoł, D.; Majdan, M. Systemic Inflammatory Parameters in Patients with Elderly-Onset Rheumatoid Arthritis (EORA) and Young-Onset Rheumatoid Arthritis (YORA)—An Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, T.A.; Thompson, A.; Gandhi, K.K.; Hochberg, M.C.; Suissa, S. Incidence of malignancy in adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; You, Z.; Tu, H.; He, P.; Li, J.; Gao, R.; Liu, Z.; Xi, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. Cancer risks in rheumatoid arthritis patients who received immunosuppressive therapies: Will immunosuppressants work? Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1050876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huss, V.; Bower, H.; Wadstrom, H.; Frisell, T.; Askling, J.; The ARTIS Group. Short- and longer-term cancer risks with biologic and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs as used against rheumatoid arthritis in clinical practice. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoos, A. Development of immuno-oncology drugs—From CTLA4 to PD1 to the next generations. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, D.R.; Krummel, M.F.; Allison, J.P. Enhancement of antitumor immunity by CTLA-4 blockade. Science 1996, 271, 1734–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pardoll, D.M. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, R.; Zhang, H.; Berry, G.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. Immune checkpoint dysfunction in large and medium vessel vasculitis. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2017, 312, H1052–H1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hodi, F.S.; O’Day, S.J.; McDermott, D.F.; Weber, R.W.; Sosman, J.A.; Haanen, J.B.; Gonzalez, R.; Robert, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Hassel, J.C.; et al. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korman, A.J.; Garrett-Thomson, S.C.; Lonberg, N. The foundations of immune checkpoint blockade and the ipilimumab approval decennial. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 509–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraehenbuehl, L.; Weng, C.-H.; Eghbali, S.; Wolchok, J.D.; Merghoub, T. Enhancing immunotherapy in cancer by targeting emerging immunomodulatory pathways. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postow, M.A.; Sidlow, R.; Hellmann, M.D. Immune-Related Adverse Events Associated with Immune Checkpoint Blockade. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnell, E.P.; Mooradian, M.J.; Baruch, E.N.; Yilmaz, M.; Reynolds, K.L. Immune-Related Adverse Events (irAEs): Diagnosis, Management, and Clinical Pearls. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 22, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poto, R.; Troiani, T.; Criscuolo, G.; Marone, G.; Ciardiello, F.; Tocchetti, C.G.; Varricchi, G. Holistic Approach to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Related Adverse Events. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 804597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkona, S.; Diamandis, E.P.; Blasutig, I.M. Cancer immunotherapy: The beginning of the end of cancer? BMC Med. 2016, 14, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baumeister, S.H.; Freeman, G.J.; Dranoff, G.; Sharpe, A.H. Coinhibitory Pathways in Immunotherapy for Cancer. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 34, 539–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchbinder, E.I.; Desai, A. CTLA-4 and PD-1 Pathways: Similarities, Differences, and Implications of Their Inhibition. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 39, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolchok, J.D.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Gonzalez, R.; Rutkowski, P.; Grob, J.-J.; Cowey, C.L.; Lao, C.D.; Wagstaff, J.; Schadendorf, D.; Ferrucci, P.F.; et al. Overall Survival with Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Habsi, M.; Chamoto, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Nomura, N.; Zhang, B.; Sugiura, Y.; Sonomura, K.; Maharani, A.; Nakajima, Y.; Wu, Y.; et al. Spermidine activates mitochondrial trifunctional protein and improves antitumor immunity in mice. Science 2022, 378, eabj3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Chamoto, K.; Saeki, S.; Hatae, R.; Ikematsu, Y.; Sakai, K.; Ando, N.; Sonomura, K.; Kojima, S.; Taketsuna, M.; et al. Combination bezafibrate and nivolumab treatment of patients with advanced non–small cell lung cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabq0021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cejuela, M.; Vethencourt, A.; Pernas, S. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Novel Immunotherapy Approaches for Breast Cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 24, 1801–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Yi, C.; Zhu, H. Predictive biomarkers of colon cancer immunotherapy: Present and future. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1032314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langouo Fontsa, M.; Padonou, F.; Willard-Gallo, K. Biomarkers and immunotherapy: Where are we? Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2022, 34, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobashi, T.; Baratto, L.; Reddy, S.A.; Srinivas, S.; Toriihara, A.; Hatami, N.; Yohannan, T.K.; Mittra, E. Predicting Response to Immunotherapy by Evaluating Tumors, Lymphoid Cell-Rich Organs, and Immune-Related Adverse Events Using FDG-PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2019, 44, e272–e279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyhan, A.A.; Carini, C. Insights and Strategies of Melanoma Immunotherapy: Predictive Biomarkers of Response and Resistance and Strategies to Improve Response Rates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Mayer, A.T.; Nobashi, T.W.; Gambhir, S.S. ICOS Is an Indicator of T-cell–Mediated Response to Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 3023–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matson, V.; Fessler, J.; Bao, R.; Chongsuwat, T.; Zha, Y.; Alegre, M.-L.; Luke, J.J.; Gajewski, T.F. The commensal microbiome is associated with anti-PD-1 efficacy in metastatic melanoma patients. Science 2018, 359, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.A.; Thomas, A.M.; Bolte, L.A.; Björk, J.R.; de Ruijter, L.K.; Armanini, F.; Asnicar, F.; Blanco-Miguez, A.; Board, R.; Calbet-Llopart, N.; et al. Cross-cohort gut microbiome associations with immune checkpoint inhibitor response in advanced melanoma. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Mazón, I.; Sánchez-Bilbao, L.; Martín-Varillas, J.L.; García-Castaño, A.; Delgado-Ruiz, M.; Piña, I.B.; Hernández, J.L.; Castañeda, S.; Llorca, J.; González-Gay, M.A.; et al. Immune-related adverse events in patients with solid-organ tumours treated with immunotherapy: A 3-year study of 102 cases from a single centre. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Kartolo, A.; Yeung, C.; Hopman, W.; Baetz, T. Long-Term Toxicities of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor (ICI) in Melanoma Patients. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 7953–7963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granito, A.; Muratori, L.; Lalanne, C.; Quarneti, C.; Ferri, S.; Guidi, M.; Lenzi, M.; Muratori, P. Hepatocellular carcinoma in viral and autoimmune liver diseases: Role of CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in the immune microenvironment. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 2994–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Lee, H.J., Jr.; Farmer, J.R.; Reynolds, K.L. Mechanisms Driving Immune-Related Adverse Events in Cancer Patients Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2021, 23, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangan, B.L.; McAlister, R.; Balko, J.M.; Johnson, D.B.; Moslehi, J.J.; Gibson, A.; Phillips, E.J. Evolving insights into the mechanisms of toxicity associated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 86, 1778–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoja, L.; Day, D.; Chen, T.W.-W.; Siu, L.L.; Hansen, A.R. Tumour- and class-specific patterns of immune-related adverse events of immune checkpoint inhibitors: A systematic review. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2377–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotwal, A. Hypophysitis from immune checkpoint inhibitors: Challenges in diagnosis and management. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2021, 28, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobashi, T.W.; Nishimoto, Y.; Kawata, Y.; Yutani, H.; Nakamura, M.; Tsuji, Y.; Yoshida, A.; Sugimoto, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Alam, I.S.; et al. Clinical and radiological features of immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis in lung cancer and non-lung cancers. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20200409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.C.; Zappasodi, R. A decade of checkpoint blockade immunotherapy in melanoma: Understanding the molecular basis for immune sensitivity and resistance. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carthon, B.C.; Wolchok, J.D.; Yuan, J.; Kamat, A.; Tang, D.S.N.; Sun, J.; Ku, G.; Troncoso, P.; Logothetis, C.J.; Allison, J.P.; et al. Preoperative CTLA-4 blockade: Tolerability and immune monitoring in the setting of a presurgical clinical trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 2861–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ng Tang, D.; Shen, Y.; Sun, J.; Wen, S.; Wolchok, J.D.; Yuan, J.; Allison, J.P.; Sharma, P. Increased frequency of ICOS+CD4 T cells as a pharmacodynamic biomarker for anti-CTLA-4 therapy. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2013, 1, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romano, E.; Kusio-Kobialka, M.; Foukas, P.G.; Baumgaertner, P.; Meyer, C.; Ballabeni, P.; Michielin, O.; Weide, B.; Romero, P.; Speiser, D.E. Ipilimumab-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity of regulatory T cells ex vivo by nonclassical monocytes in melanoma patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 6140–6145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, A.; Subudhi, S.K.; Blando, J.; Scutti, J.; Vence, L.; Wargo, J.; Allison, J.P.; Ribas, A.; Sharma, P. Anti-CTLA-4 Immunotherapy Does Not Deplete FOXP3(+) Regulatory T Cells (Tregs) in Human Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, A.C.; Orlowski, R.J.; Xu, X.; Mick, R.; George, S.M.; Yan, P.K.; Manne, S.; Kraya, A.A.; Wubbenhorst, B.; Dorfman, L.; et al. A single dose of neoadjuvant PD-1 blockade predicts clinical outcomes in resectable melanoma. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, T.; Togashi, Y.; Tay, C.; Ha, D.; Sasaki, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Sato, E.; Fukuoka, S.; Tada, Y.; Tanaka, A.; et al. PD-1+ regulatory T cells amplified by PD-1 blockade promote hyperprogression of cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 9999–10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumagai, S.; Togashi, Y.; Kamada, T.; Sugiyama, E.; Nishinakamura, H.; Takeuchi, Y.; Vitaly, K.; Itahashi, K.; Maeda, Y.; Matsui, S.; et al. The PD-1 expression balance between effector and regulatory T cells predicts the clinical efficacy of PD-1 blockade therapies. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 1346–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.B.; Balko, J.M.; Compton, M.L.; Chalkias, S.; Gorham, J.; Xu, Y.; Hicks, M.; Puzanov, I.; Alexander, M.R.; Bloomer, T.L.; et al. Fulminant Myocarditis with Combination Immune Checkpoint Blockade. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Galdos, F.X.; Lee, D.; Waliany, S.; Huang, Y.V.; Ryan, J.; Dang, K.; Neal, J.W.; Wakelee, H.A.; Reddy, S.A.; et al. Identification of Pathogenic Immune Cell Subsets Associated With Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Myocarditis. Circulation 2022, 146, 316–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groha, S.; Alaiwi, S.A.; Xu, W.; Naranbhai, V.; Nassar, A.H.; Bakouny, Z.; El Zarif, T.; Saliby, R.M.; Wan, G.; Rajeh, A.; et al. Germline variants associated with toxicity to immune checkpoint blockade. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2584–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.A.; Watson, R.A.; Tong, O.; Ye, W.; Nassiri, I.; Gilchrist, J.J.; de Los Aires, A.V.; Sharma, P.K.; Koturan, S.; Cooper, R.A.; et al. IL7 genetic variation and toxicity to immune checkpoint blockade in patients with melanoma. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2592–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, J.T.; Durum, S.K.; Seddon, B. Flip the coin: IL-7 and IL-7R in health and disease. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 1584–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winer, H.; Rodrigues, G.O.; Hixon, J.A.; Aiello, F.B.; Hsu, T.C.; Wachter, B.T.; Li, W.; Durum, S.K. IL-7: Comprehensive review. Cytokine 2022, 160, 156049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzidionysiou, K.; Liapi, M.; Tsakonas, G.; Gunnarsson, I.; Catrina, A. Treatment of rheumatic immune-related adverse events due to cancer immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors-is it time for a paradigm shift? Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 1687–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tivol, E.A.; Borriello, F.; Schweitzer, A.N.; Lynch, W.P.; Bluestone, J.A.; Sharpe, A.H. Loss of CTLA-4 leads to massive lymphoproliferation and fatal multiorgan tissue destruction, revealing a critical negative regulatory role of CTLA-4. Immunity 1995, 3, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waterhouse, P.; Penninger, J.M.; Timms, E.; Wakeham, A.; Shahinian, A.; Lee, K.P.; Thompson, C.B.; Griesser, H.; Mak, T.W. Lymphoproliferative Disorders with Early Lethality in Mice Deficient in Ctla-4. Science 1995, 270, 985–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, H.; Nose, M.; Hiai, H.; Minato, N.; Honjo, T. Development of lupus-like autoimmune diseases by disruption of the PD-1 gene encoding an ITIM motif-carrying immunoreceptor. Immunity 1999, 11, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishimura, H.; Okazaki, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Nakatani, K.; Hara, M.; Matsumori, A.; Sasayama, S.; Mizoguchi, A.; Hiai, H.; Minato, N.; et al. Autoimmune dilated cardiomyopathy in PD-1 receptor-deficient mice. Science 2001, 291, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, R.; Hashimoto, M. Elucidation of disease mechanisms underlying rheumatic immune-related adverse events may lead to novel therapeutic strategies for autoimmune diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 81, e262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, P.; Deng, X.; Hu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, K.; Qin, K.; Huang, Y.; Ba, X.; Yan, J.; et al. Rheumatic Manifestations and Diseases From Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 762247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardoscia, L.; Pasinetti, N.; Triggiani, L.; Cozzi, S.; Sardaro, A. Biological Bases of Immune-Related Adverse Events and Potential Crosslinks With Immunogenic Effects of Radiation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 746853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- June, C.H.; Warshauer, J.T.; Bluestone, J.A. Is autoimmunity the Achilles’ heel of cancer immunotherapy? Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Esfahani, K.; Miller, W.H., Jr. Reversal of Autoimmune Toxicity and Loss of Tumor Response by Interleukin-17 Blockade. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1989–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmstroem, R.B.; Nielsen, O.H.; Jacobsen, S.; Riis, L.B.; Theile, S.; Bjerrum, J.T.; Vilmann, P.; Johansen, J.S.; Boisen, M.K.; Eefsen, R.H.L.; et al. COLAR: Open-label clinical study of IL-6 blockade with tocilizumab for the treatment of immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced colitis and arthritis. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e005111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, L.C.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd. Expert Perspective: Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Rheumatologic Complications. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narváez, J.; Juarez-López, P.; Lluch, J.; Palmero, R.; del Muro, X.G.; Nolla, J.; Domenech, E.D. Rheumatic immune-related adverse events in patients on anti-PD-1 inhibitors: Fasciitis with myositis syndrome as a new complication of immunotherapy. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 1040–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, P.; Cappelli, L.C. Treatment of rheumatic adverse events of cancer immunotherapy. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 101805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.; Ennis, D.; Hudson, M.; Ye, C.; Saltman, A.; Himmel, M.; Rottapel, R.; Pope, J.; Hoa, S.; Tisseverasinghe, A.; et al. Rheumatic immune-related adverse events associated with cancer immunotherapy: A nationwide multi-center cohort. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zeng, L.; Shen, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Mao, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Yao, W. Diagnosis and Treatment of Rheumatic Adverse Events Related to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 2640273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Zhou, J.; Xu, D.; Zeng, X. Rheumatic immune-related adverse events induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, M.C.; Becker, J.-C.; Schiff, M.; Luggen, M.; Sherrer, Y.; Kremer, J.; Birbara, C.; Box, J.; Natarajan, K.; Nuamah, I.; et al. Abatacept for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibition. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1114–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okazaki, S.; Watanabe, R.; Harigae, H.; Fujii, H. Better Retention of Abatacept Is Associated with High Rheumatoid Factor: A Five-Year Follow-Up Study of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2020, 250, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kremer, J.M.; Westhovens, R.; Leon, M.; Di Giorgio, E.; Alten, R.; Steinfeld, S.; Russell, A.; Dougados, M.; Emery, P.; Nuamah, I.F.; et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis by selective inhibition of T-cell activation with fusion protein CTLA4Ig. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1907–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingel, H.; Brunner-Weinzierl, M.C. CTLA-4 (CD152): A versatile receptor for immune-based therapy. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 42, 101298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostine, M.; Finckh, A.; Bingham, C.O.; Visser, K.; Leipe, J.; Schulze-Koops, H.; Choy, E.H.; Benesova, K.; Radstake, T.; Cope, A.P.; et al. EULAR points to consider for the diagnosis and management of rheumatic immune-related adverse events due to cancer immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jespersen, M.S.; Fano, S.; Stenor, C.; Moller, A.K. A case report of immune checkpoint inhibitor-related steroid-refractory myocarditis and myasthenia gravis-like myositis treated with abatacept and mycophenolate mofetil. Eur. Heart J. Case Rep. 2021, 5, ytab342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chan, J.; Brinc, D.; Gandhi, S.; Izenberg, A.; Delgado, D.; Abdel-Qadir, H.; Wintersperger, B.J.; Thavendiranathan, P. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Associated Myocarditis With Persistent Troponin Elevation Despite Abatacept and Prolonged Immunosuppression. JACC Cardio Oncol. 2020, 2, 800–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, J.E.; Allenbach, Y.; Vozy, A.; Brechot, N.; Johnson, D.B.; Moslehi, J.J.; Kerneis, M. Abatacept for Severe Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Associated Myocarditis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2377–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhir, R.; Burel, S.L.; Dunogeant, L.; Marabelle, A.; Hollebecque, A.; Besse, B.; Leary, A.; Voisin, A.L.; Pontoizeau, C.; Coutte, L.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis and polymyalgia rheumatica occurring after immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1747–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappelli, L.C.; Gutierrez, A.K.; Baer, A.N.; Albayda, J.; Manno, R.L.; Haque, U.; Lipson, E.J.; Bleich, K.B.; Shah, A.A.; Naidoo, J.; et al. Inflammatory arthritis and sicca syndrome induced by nivolumab and ipilimumab. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Jaquith, J.M.; McCarthy-Fruin, K.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Crowson, C.; Davis, J.M., 3rd; Thanarajasingam, U.; Zeng, H. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced inflammatory arthritis: A novel clinical entity with striking similarities to seronegative rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 3631–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobashi, T.; Mittra, E. PD-1 Blockade–induced Inflammatory Arthritis. Radiology 2018, 289, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ponce, A.; Frade-Sosa, B.; Sarmiento-Monroy, J.C.; Sapena, N.; Ramírez, J.; Azuaga, A.B.; Morlà, R.; Ruiz-Esquide, V.; Cañete, J.D.; Sanmartí, R.; et al. Imaging Findings in Patients with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Arthritis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pundole, X.; Abdel-Wahab, N.; Suarez-Almazor, M.E. Arthritis risk with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy for cancer. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2019, 31, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M.D.; Crowson, C.; Kottschade, L.A.; Finnes, H.D.; Markovic, S.N.; Thanarajasingam, U. Rheumatic Syndromes Associated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Single-Center Cohort of Sixty-One Patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cappelli, L.C.; Bingham, C.O.; Forde, P.M.; Anagnostou, V.; Brahmer, J.; Lipson, E.J.; Mammen, J.; Schollenberger, M.; Shah, A.A.; Darrah, E. Anti-RA33 antibodies are present in a subset of patients with immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced inflammatory arthritis. RMD Open 2022, 8, e002511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, R.; Luksik, A.S.; Garzon-Muvdi, T.; Hung, A.L.; Kim, E.S.; Wu, A.; Xia, Y.; Belcaid, Z.; Gorelick, N.; Choi, J.; et al. Contrasting impact of corticosteroids on anti-PD-1 immunotherapy efficacy for tumor histologies located within or outside the central nervous system. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1500108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naidoo, J.; Cappelli, L.C.; Forde, P.M.; Marrone, K.A.; Lipson, E.J.; Hammers, H.J.; Sharfman, W.H.; Le, D.T.; Baer, A.N.; Shah, A.A.; et al. Inflammatory Arthritis: A Newly Recognized Adverse Event of Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Oncologist 2017, 22, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Xia, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Martin, V.; Li, Q.; Lin, S.; Chen, J.; Calmette, J.; Lu, M.; et al. Stress–glucocorticoid–TSC22D3 axis compromises therapy-induced antitumor immunity. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1428–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Ishikawa, Y.; Fujiwara, M.; Yukawa, H.; Yanagihara, T.; Takei, S.; Arioka, H.; Kita, Y. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced refractory polyarthritis rapidly improved by sarilumab and monitoring with joint ultrasonography: A case report. Medicine 2022, 101, e28428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, A.; Williams, S.G.; Yao, L.; Maharjan, S.; Strauss, J.; Sharon, E.; Thomas, A.; Apolo, A.B.; Gourh, P.; Hasni, S.A.; et al. Use of Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Identify Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Inflammatory Arthritis. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e200032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.T.; Tayar, J.; Trinh, V.A.; Suarez-Almazor, M.; Garcia, S.; Hwu, P.; Johnson, D.H.; Uemura, M.; Diab, A. Successful treatment of arthritis induced by checkpoint inhibitors with tocilizumab: A case series. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 2061–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroud, C.R.; Hegde, A.; Cherry, C.; Naqash, A.R.; Sharma, N.; Addepalli, S.; Cherukuri, S.; Parent, T.; Hardin, J.; Walker, P. Tocilizumab for the management of immune mediated adverse events secondary to PD-1 blockade. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2019, 25, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draghi, A.; Borch, T.H.; Radic, H.D.; Chamberlain, C.A.; Gokuldass, A.; Svane, I.M.; Donia, M. Differential effects of corticosteroids and anti-TNF on tumor-specific immune responses: Implications for the management of irAEs. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 1408–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente, F.; Belkhir, R.; Henry, J.; Nguyen, C.D.; Pham, T.; Germain, V.; Gavand, P.E.; Labadie, C.; Briere, C.; Lauret, A.; et al. Use of a bDMARD or tsDMARD for the management of inflammatory arthritis under checkpoint inhibitors: An observational study. RMD Open 2022, 8, e002612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benesova, K.; Kraus, F.V.; Carvalho, R.; Lorenz, H.; Hörth, C.H.; Günther, J.; Klika, K.D.; Graf, J.; Diekmann, L.; Schank, T.; et al. Distinct immune-effector and metabolic profile of CD8+ T cells in patients with autoimmune polyarthritis induced by therapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 1730–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ytterberg, S.R.; Bhatt, D.L.; Mikuls, T.R.; Koch, G.G.; Fleischmann, R.; Rivas, J.L.; Germino, R.; Menon, S.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. Cardiovascular and Cancer Risk with Tofacitinib in Rheumatoid Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, G.C.; Gainor, J.F.; Altan, M.; Kravets, S.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Gedmintas, L.; Azimi, R.; Rizvi, H.; Riess, J.W.; Hellmann, M.D.; et al. Safety of Programmed Death-1 Pathway Inhibitors Among Patients With Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Preexisting Autoimmune Disorders. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1905–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tison, A.; Garaud, S.; Chiche, L.; Cornec, D.; Kostine, M. Immune-checkpoint inhibitor use in patients with cancer and pre-existing autoimmune diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaçais, L.; Dalle, S.; Dereure, O.; Trabelsi, S.; Dalac, S.; Legoupil, D.; Montaudié, H.; Arnault, J.-P.; De Quatrebarbes, J.; Saiag, P.; et al. Risk of irAEs in patients with autoimmune diseases treated by immune checkpoint inhibitors for stage III or IV melanoma: Results from a matched case-control study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allenbach, Y.; Anquetil, C.; Manouchehri, A.; Benveniste, O.; Lambotte, O.; Lebrun-Vignes, B.; Spano, J.-P.; Ederhy, S.; Klatzmann, D.; Rosenzwajg, M.; et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced myositis, the earliest and most lethal complication among rheumatic and musculoskeletal toxicities. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelopoulou, F.; Bogdanos, D.; Dimitroulas, T.; Sakkas, L.; Daoussis, D. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced musculoskeletal manifestations. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagomi, Y.; Tajiri, K.; Shimada, S.; Li, S.; Inoue, K.; Murakata, Y.; Murata, M.; Sakai, S.; Sato, K.; Ieda, M. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Related Myositis Overlapping With Myocarditis: An Institutional Case Series and a Systematic Review of Literature. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 884776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, N.; Maeda, A.; Takase-Minegishi, K.; Kirino, Y.; Sugiyama, Y.; Namkoong, H.; Horita, N.; Yoshimi, R.; Nakajima, H.; YCU irAE Working Group. Incidence and Distinct Features of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Related Myositis From Idiopathic Inflammatory Myositis: A Single-Center Experience With Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 803410. [Google Scholar]
- Seki, M.; Uruha, A.; Ohnuki, Y.; Kamada, S.; Noda, T.; Onda, A.; Ohira, M.; Isami, A.; Hiramatsu, S.; Hibino, M.; et al. Inflammatory myopathy associated with PD-1 inhibitors. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 100, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoussis, D.; Kraniotis, P.; Liossis, S.N.; Solomou, A. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced myo-fasciitis. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isa, M.; Hongo, Y.; Sakamoto, N.; Yamazaki, K.; Takazaki, H.; Asakuma, J.; Ikewaki, K.; Suzuki, K. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related myositis and myocarditis with multiple myositis-specific/−associated antibodies. J. Neurol. Sci. 2023, 444, 120528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, A.M.; Gajdos, P.; Eymard, B.; Tranchant, C.; Warter, J.M.; Gomez, L.; Bourquin, C.; Bach, J.F.; Garchon, H.J. Anti-titin antibodies in myasthenia gravis: Tight association with thymoma and heterogeneity of nonthymoma patients. Arch. Neurol. 2001, 58, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soman, B.; Dias, M.C.; Rizvi, S.A.J.; Kardos, A. Myasthenia gravis, myositis and myocarditis: A fatal triad of immune-related adverse effect of immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment. BMJ Case Rep. 2022, 15, e251966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmer, J.R.; Lacchetti, C.; Schneider, B.J.; Atkins, M.B.; Brassil, K.J.; Caterino, J.M.; Chau, I.; Ernstoff, M.S.; Gardner, J.M.; Ginex, P.; et al. Management of Immune-Related Adverse Events in Patients Treated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1714–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. Immunology of Giant Cell Arteritis. Circ. Res. 2023, 132, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daxini, A.; Cronin, K.; Sreih, A.G. Vasculitis associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors-a systematic review. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 2579–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, R.; Berry, G.J.; Liang, D.H.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. Cellular Signaling Pathways in Medium and Large Vessel Vasculitis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 587089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; Bacon, P.A.; Basu, N.; Cid, M.C.; Ferrario, F.; Flores-Suarez, L.F.; Gross, W.L.; Guillevin, L.; Hagen, E.C.; et al. 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, B.L.; Gedmintas, L.; Todd, D.J. Drug-associated polymyalgia rheumatica/giant cell arteritis occurring in two patients after treatment with ipilimumab, an antagonist of ctla-4. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 768–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narala, R.; Reddy, S.A.; Mruthyunjaya, P. Giant cell arteritis manifesting as retinal arterial occlusion and paracentral acute middle maculopathy in a patient on pembrolizumab for metastatic uveal melanoma. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case Rep. 2020, 20, 100891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomer, C.H.; Annabathula, R.V.; Aggarwal, V.; Upadhya, B.; Lycan, T.W. A Case Report of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Aortitis Treated with Tocilizumab. Case Rep. Immunol. 2022, 2022, 7971169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, D.; Eslamian, G.; Poon, D.; Crabb, S.; Jones, R.; Sankey, P.; Kularatne, B.; Linch, M.; Josephs, D. Immune checkpoint inhibitor induced large vessel vasculitis. BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e233496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mort, J.; Maheshwari, S.; Basu, N.; Dillon, P.; Brady, K.; Bear, H.; Millard, T. A Rare Case of Large-Vessel Vasculitis following Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy and Pegfilgrastim. Case Rep. Oncol. Med. 2022, 2022, 7295305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkaid, S.; Berger, M.; Nouvier, M.; Picard, C.; Dalle, S. A case of Schönlein-Henoch purpura induced by immune checkpoint inhibitor in a patient with metastatic melanoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 139, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaoka-Takatori, A.; Ishii, M.; Hayama, K.; Obinata, D.; Yamaguchi, K.; Takahashi, S.; Fujita, H. A Case of IgA Vasculitis During Nivolumab Therapy for Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 14, 1885–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibille, A.; Alfieri, R.; Malaise, O.; Detrembleur, N.; Pirotte, M.; Louis, R.; Duysinx, B. Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis in a Patient on Programmed Death-1 Inhibitor for Advanced Non-small-cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, W.; Cusnir, I.; Habib, S.; Smylie, M.; Solez, K.; Yacyshyn, E. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Rheumatology 2021, 60, e190–e191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, A.; Groh, M.; Lorillon, G.; Le Pendu, C.; Maillet, J.; Arangalage, D.; Tazi, A.; Lebbe, C.; Baroudjian, B.; Delyon, J. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss) induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ak, T.; Durmus, R.B.; Onel, M. Cutaneous vasculitis associated with molecular tergeted therapies: Systematic review of the literature. Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 42, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panian, J.; Pan, E.; Shi, V.; Hinds, B.; McKay, R.R. Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis Induced by Immune Checkpoint Inhibition in a Patient With Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. Oncology 2022, 36, 316–320. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, J.E.; Manouchehri, A.; Moey, M.; Lebrun-Vignes, B.; Bastarache, L.; Pariente, A.; Gobert, A.; Spano, J.P.; Balko, J.M.; Bonaca, M.P.; et al. Cardiovascular toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: An observational, retrospective, pharmacovigilance study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Watanabe, R.; Berry, G.J.; Vaglio, A.; Liao, Y.J.; Warrington, K.J.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. Immunoinhibitory checkpoint deficiency in medium and large vessel vasculitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E970–E979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, R.; Maeda, T.; Zhang, H.; Berry, G.J.; Zeisbrich, M.; Brockett, R.; Greenstein, A.E.; Tian, L.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. MMP (Matrix Metalloprotease)-9–Producing Monocytes Enable T Cells to Invade the Vessel Wall and Cause Vasculitis. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 700–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, D.; Karabayas, M.; Basu, N.; Cid, M.C.; Goel, R.; Goodyear, C.S.; Grayson, P.C.; McAdoo, S.P.; Mason, J.C.; Owen, C.; et al. Large-vessel vasculitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2022, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, F.; Lew, A.M.; Xu, Y. Self-Tolerance of Vascular Tissues Is Broken Down by Vascular Dendritic Cells in Response to Systemic Inflammation to Initiate Regional Autoinflammation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 823853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, B.; Hua, F.; Dolff, S.; Jun, C.; Cai, X.; Specker, C.; Feldkamp, T.; Kribben, A.; Cohen Tervaert, J.W.; Witzke, O. Aberrant expression of the negative costimulator PD-1 on T cells in granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeisbrich, M.; Chevalier, N.; Sehnert, B.; Rizzi, M.; Venhoff, N.; Thiel, J.; Voll, R.E. CMTM6-Deficient Monocytes in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis Fail to Present the Immune Checkpoint PD-L1. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 673912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, R.; Berry, G.J.; Liang, D.H.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. Pathogenesis of Giant Cell Arteritis and Takayasu Arteritis-Similarities and Differences. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2020, 22, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, K.; Nevares, A.; Tamaki, H. A Spotlight on Drug-Induced Vasculitis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2022, 24, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Brom, R.R.; Abdulahad, W.H.; Rutgers, A.; Kroesen, B.J.; Roozendaal, C.; de Groot, D.J.; Schroder, C.P.; Hospers, G.A.; Brouwer, E. Rapid granulomatosis with polyangiitis induced by immune checkpoint inhibition. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 1143–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mamlouk, O.; Lin, J.S.; Abdelrahim, M.; Tchakarov, A.S.; Glass, W.F.; Selamet, U.; Buni, M.; Abdel-Wahab, N.; Abudayyeh, A. Checkpoint inhibitor-related renal vasculitis and use of rituximab. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulfken, L.M.; Becker, J.C.; Hayajneh, R.; Wagner, A.D.; Schaper-Gerhardt, K.; Flatt, N.; Grimmelmann, I.; Gutzmer, R. Case Report: Sustained Remission Due to PD-1-Inhibition in a Metastatic Melanoma Patient With Depleted B Cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 733961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laamech, R.; Terrec, F.; Emprou, C.; Toffart, A.C.; Pierret, T.; Naciri-Bennani, H.; Rostaing, L.; Noble, J. Efficacy of Plasmapheresis in Nivolumab-Associated ANCA Glomerulonephritis: A Case Report and Pathophysiology Discussion. Case Rep. Nephrol. Dial. 2021, 11, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, R.; Hashimoto, M. Perspectives of JAK Inhibitors for Large Vessel Vasculitis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 881705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Watanabe, R.; Berry, G.J.; Tian, L.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. Inhibition of JAK-STAT Signaling Suppresses Pathogenic Immune Responses in Medium and Large Vessel Vasculitis. Circulation 2018, 137, 1934–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Matteson, E.L.; Castaneda, S. Polymyalgia rheumatica. Lancet 2017, 390, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, R.; Goronzy, J.J.; Berry, G.; Liao, Y.J.; Weyand, C.M. Giant Cell Arteritis: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Management. Curr. Treat. Options Rheumatol. 2016, 2, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okazaki, S.; Watanabe, R.; Kondo, H.; Kudo, M.; Harigae, H.; Fujii, H. High Relapse Rate in Patients with Polymyalgia Rheumatica despite the Combination of Immunosuppressants and Prednisolone: A Single Center Experience of 89 patients. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2020, 251, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvarani, C.; Cantini, F.; Hunder, G.G. Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant-cell arteritis. Lancet 2008, 372, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betrains, A.E.; Blockmans, D.E. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Associated Polymyalgia Rheumatica/Giant Cell Arteritis Occurring in a Patient After Treatment With Nivolumab. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 27, S555–S556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, C.; Cappelli, L.C.; Kostine, M.; Kirchner, E.; Braaten, T.; Calabrese, L. Polymyalgia rheumatica-like syndrome from checkpoint inhibitor therapy: Case series and systematic review of the literature. RMD Open 2019, 5, e000906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, N.; Couette, N.; van Binsbergen, W.H.; Weinmann, S.C.; Jivanelli, B.; Shea, B.; Bass, A.R.; Benesova, K.; Bingham, C.O.; Calabrese, C.; et al. Identification of outcome domains in immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced inflammatory arthritis and polymyalgia rheumatica: A scoping review by the OMERACT irAE working group. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2023, 58, 152110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, I.E.; Sharma, A.; Turesson, C.; Mohammad, A.J. An update on polymyalgia rheumatica. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 292, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fremont, G.M.; Belkhir, R.; Henry, J.; Voisin, A.L.; Lambotte, O.; Besson, F.L.; Mariette, X.; Nocturne, G. Features of polymyalgia rheumatica–like syndrome after immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Der Geest, K.S.M.; Sandovici, M.; Rutgers, A.; Hiltermann, T.J.N.; Oosting, S.F.; Slart, R.H.J.; Brouwer, E. Management of immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced polymyalgia rheumatica. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, e263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Geest, K.S.M.; Sandovici, M.; Rutgers, A.; Hiltermann, T.J.N.; Oosting, S.F.; Slart, R.; Brouwer, E. Imaging in immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced polymyalgia rheumatica. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, e210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dasgupta, B.; Cimmino, M.; Maradit-Kremers, H.; Schmidt, W.; Schirmer, M.; Salvarani, C.; Bachta, A.; Dejaco, C.; Duftner, C.; Jensen, H.S.; et al. 2012 provisional classification criteria for polymyalgia rheumatica: A European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology collaborative initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreira, A.; Loquai, C.; Pföhler, C.; Kähler, K.C.; Knauss, S.; Heppt, M.V.; Gutzmer, R.; Dimitriou, F.; Meier, F.; Mitzel-Rink, H.; et al. Myositis and neuromuscular side-effects induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors. Eur J Cancer 2019, 106, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, R.I. Sjogren’s syndrome. Lancet 2005, 366, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbelo, P.D.; Ferre, E.M.N.; Chaturvedi, A.; Chiorini, J.A.; Alevizos, I.; Lionakis, M.S.; Warner, B.M. Profiling Autoantibodies against Salivary Proteins in Sicca Conditions. J. Dent. Res. 2019, 98, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, C.; Kirchner, E.; Kontzias, A.; Velcheti, V.; Calabrese, L.H. Rheumatic immune-related adverse events of checkpoint therapy for cancer: Case series of a new nosological entity. RMD Open 2017, 3, e000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mavragani, C.P.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Sicca syndrome following immune checkpoint inhibition. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 217, 108497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, B.M.; Baer, A.N.; Lipson, E.J.; Allen, C.; Hinrichs, C.; Rajan, A.; Pelayo, E.; Beach, M.; Gulley, J.L.; Madan, R.A.; et al. Sicca Syndrome Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy. Oncologist 2019, 24, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pringle, S.; Wang, X.; Vissink, A.; Bootsma, H.; Kroese, F.G.M. Checkpoint inhibition-induced sicca: A type II interferonopathy? Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38 (Suppl. S126), 253–260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jfri, A.; Leung, B.; Said, J.T.; Semenov, Y.; Le Boeuf, N.R. Prevalence of Inverse Psoriasis Subtype with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Immunother. Adv. 2022, 2, ltac016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.H.; Patel, A.B.; Uemura, M.I.; Trinh, V.A.; Jackson, N.; Zobniw, C.M.; Tetzlaff, M.T.; Hwu, P.; Curry, J.L.; Diab, A. IL17A Blockade Successfully Treated Psoriasiform Dermatologic Toxicity from Immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarguren, A.M.; Enrique, E.A.; Diana, P.L.; Ana, C.; Pedro, H.P. Apremilast for immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced psoriasis: A case series. JAAD Case Rep. 2021, 11, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, O.; Pinotti, G.; Gueli, R.; Grigioni, E.; De Santis, M.; Ceribelli, A.; Selmi, C. Psoriatic arthritis induced by anti-PD1 and treated with apremilast: A case report and review of the literature. Immunotherapy 2020, 12, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Takeda, Y.; Sugiyama, H. Systemic Psoriasiform Dermatitis Appeared after the Administration of Pembrolizumab. Intern. Med. 2020, 59, 871–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halle, B.R.; Warner, A.B.; Zaman, F.Y.; Haydon, A.; Bhave, P.; Dewan, A.K.; Ye, F.; Irlmeier, R.; Mehta, P.; Kurtansky, N.R.; et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with pre-existing psoriasis: Safety and efficacy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e003066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tan, K.; Zheng, J.; Li, J.; Cui, H. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in the Treatment of Patients With Cancer and Preexisting Psoriasis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 934093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, N.S.; Wetter, D.A.; Wieland, C.N.; Shenoy, N.K.; Markovic, S.N.; Thanarajasingam, U. Scleroderma Induced by Pembrolizumab: A Case Series. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 1158–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terrier, B.; Humbert, S.; Preta, L.-H.; Delage, L.; Razanamahery, J.; Laurent-Roussel, S.; Mestiri, R.; Beaudeau, L.; Legendre, P.; Goupil, F.; et al. Risk of scleroderma according to the type of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, L.; Mertz, P.; Gavand, P.-E.; Martin, T.; Chasset, F.; Tebacher-Alt, M.; Lambert, A.; Muller, C.; Sibilia, J.; Lebrun-Vignes, B.; et al. Drug-induced systemic lupus: Revisiting the ever-changing spectrum of the disease using the WHO pharmacovigilance database. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michot, J.-M.; Fusellier, M.; Champiat, S.; Velter, C.; Baldini, C.; Voisin, A.-L.; Danlos, F.-X.; El Dakdouki, Y.; Annereau, M.; Mariette, X.; et al. Drug-induced lupus erythematosus following immunotherapy with anti-programmed death-(ligand) 1. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raschi, E.; Antonazzo, I.C.; Poluzzi, E.; De Ponti, F. Drug-induced systemic lupus erythematosus: Should immune checkpoint inhibitors be added to the evolving list? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fadel, F.; El Karoui, K.; Knebelmann, B. Anti-CTLA4 antibody-induced lupus nephritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 211–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campochiaro, C.; Farina, N.; Tomelleri, A.; Ferrara, R.; Viola, S.; Lazzari, C.; De Luca, G.; Raggi, D.; Bulotta, A.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; et al. Autoantibody positivity predicts severity of rheumatic immune-related adverse events to immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 103, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granito, A.; Muratori, L.; Tovoli, F.; Muratori, P. Diagnostic role of anti-dsDNA antibodies: Do not forget autoimmune hepatitis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granito, A.; Muratori, P.; Muratori, L.; Pappas, G.; Cassani, F.; Worthington, J.; Guidi, M.; Ferri, S.; De Molo, C.; Lenzi, M.; et al. Antinuclear antibodies giving the ‘multiple nuclear dots’ or the ‘rim-like/membranous’ patterns: Diagnostic accuracy for primary biliary cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 24, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, F.; Hogan, S.; Menzies, A.M.; Dummer, R.; Long, G.V. Interleukin-6 blockade for prophylaxis and management of immune-related adverse events in cancer immunotherapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 157, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Ruiz, E.; Minute, L.; Otano, I.; Alvarez, M.; Ochoa, M.C.; Belsue, V.; De Andrea, C.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Marquez-Rodas, I.; et al. Prophylactic TNF blockade uncouples efficacy and toxicity in dual CTLA-4 and PD-1 immunotherapy. Nature 2019, 569, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Incidence | Treatment | |
|---|---|---|
| Arthritis | Up to 5% | 1. NSAIDs, 2. Glucocorticoids, 3. DMARDs |
| Myositis | <1% | 1. Glucocorticoids, 2. DMARDs, 3. PE, 4. IVIg |
| Vasculitis | <1% | 1. Glucocorticoids, 2. CYC, 3. RTX, 4. TCZ |
| Myalgia | Up to 5% | 1. Glucocorticoids, 2. DMARDs, 3. TCZ |
| Sicca symptom | Rare | 1. Glucocorticoids |
| Skin rash (psoriasis) | Up to 3% | 1. Glucocorticoids, 2. DMARDs |
| Skin sclerosis | Rare | 1. Glucocorticoids, 2. CYC, 3. DMARDs |
| Lupus-like disease | Rare | 1. Glucocorticoids, 2. CYC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dang, Q.M.; Watanabe, R.; Shiomi, M.; Fukumoto, K.; Nobashi, T.W.; Okano, T.; Yamada, S.; Hashimoto, M. Rheumatic Immune-Related Adverse Events due to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors—A 2023 Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065643
Dang QM, Watanabe R, Shiomi M, Fukumoto K, Nobashi TW, Okano T, Yamada S, Hashimoto M. Rheumatic Immune-Related Adverse Events due to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors—A 2023 Update. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(6):5643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065643
Chicago/Turabian StyleDang, Quang Minh, Ryu Watanabe, Mayu Shiomi, Kazuo Fukumoto, Tomomi W. Nobashi, Tadashi Okano, Shinsuke Yamada, and Motomu Hashimoto. 2023. "Rheumatic Immune-Related Adverse Events due to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors—A 2023 Update" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 6: 5643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065643
APA StyleDang, Q. M., Watanabe, R., Shiomi, M., Fukumoto, K., Nobashi, T. W., Okano, T., Yamada, S., & Hashimoto, M. (2023). Rheumatic Immune-Related Adverse Events due to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors—A 2023 Update. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(6), 5643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065643







