Uptake of Tropheryma whipplei by Intestinal Epithelia
Abstract
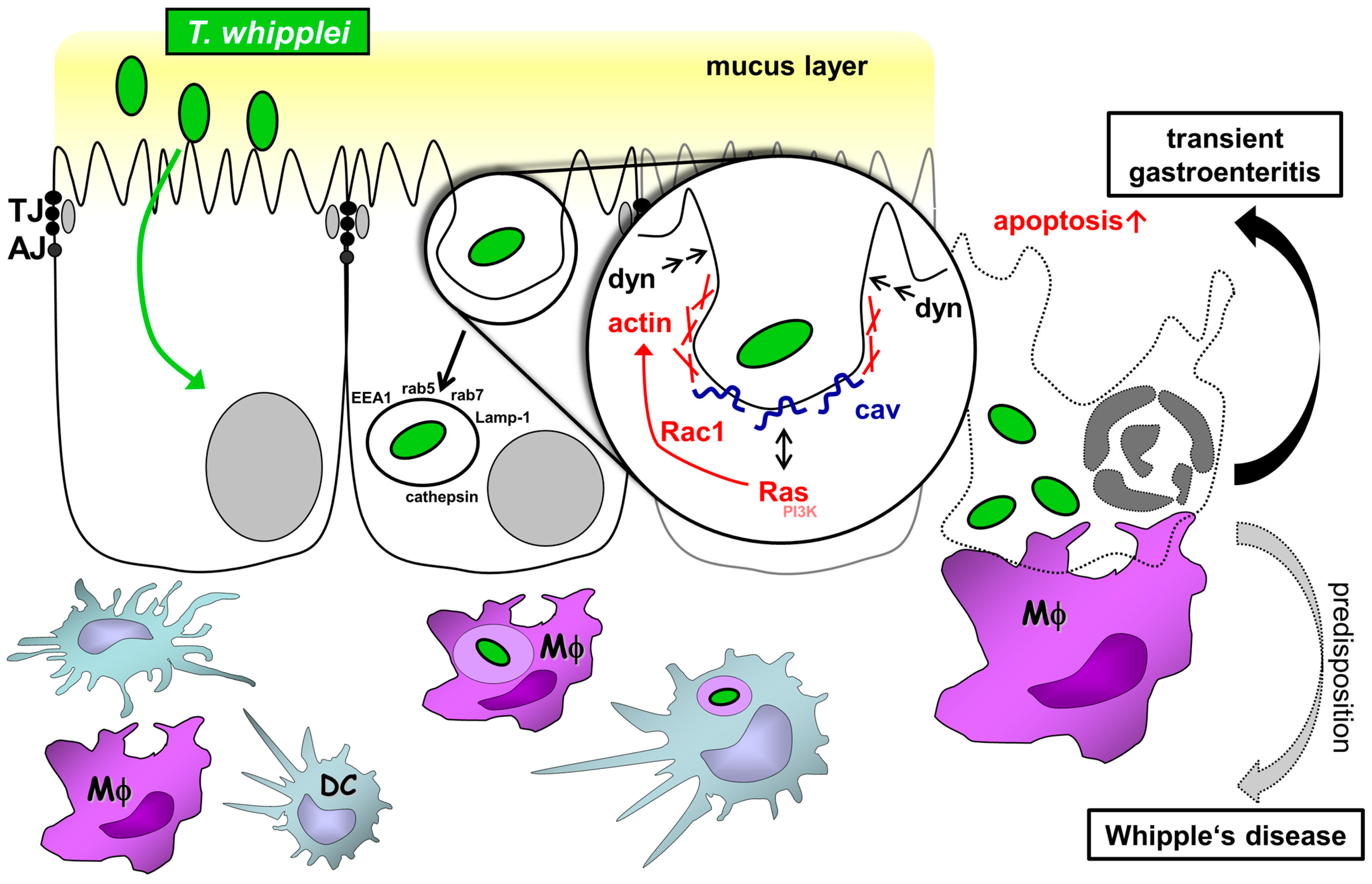
1. Introduction
2. Results
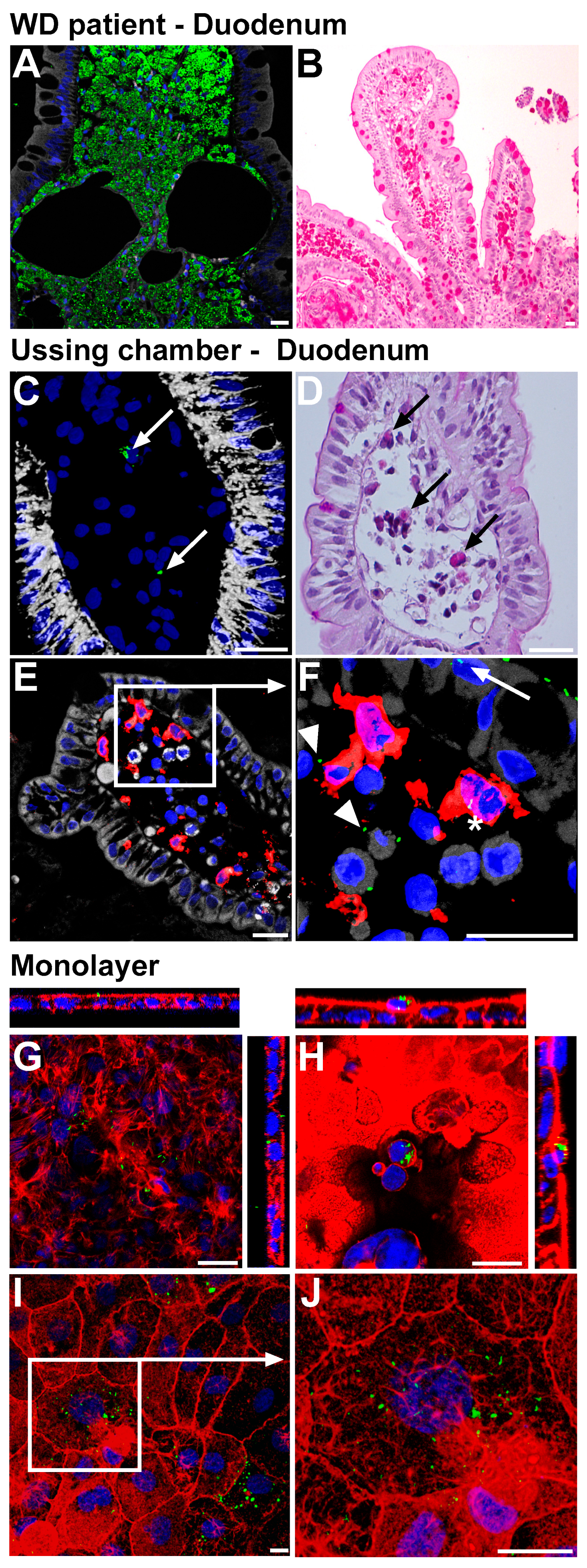
2.1. Establishment of Epithelial Models for Translocation of T. whipplei
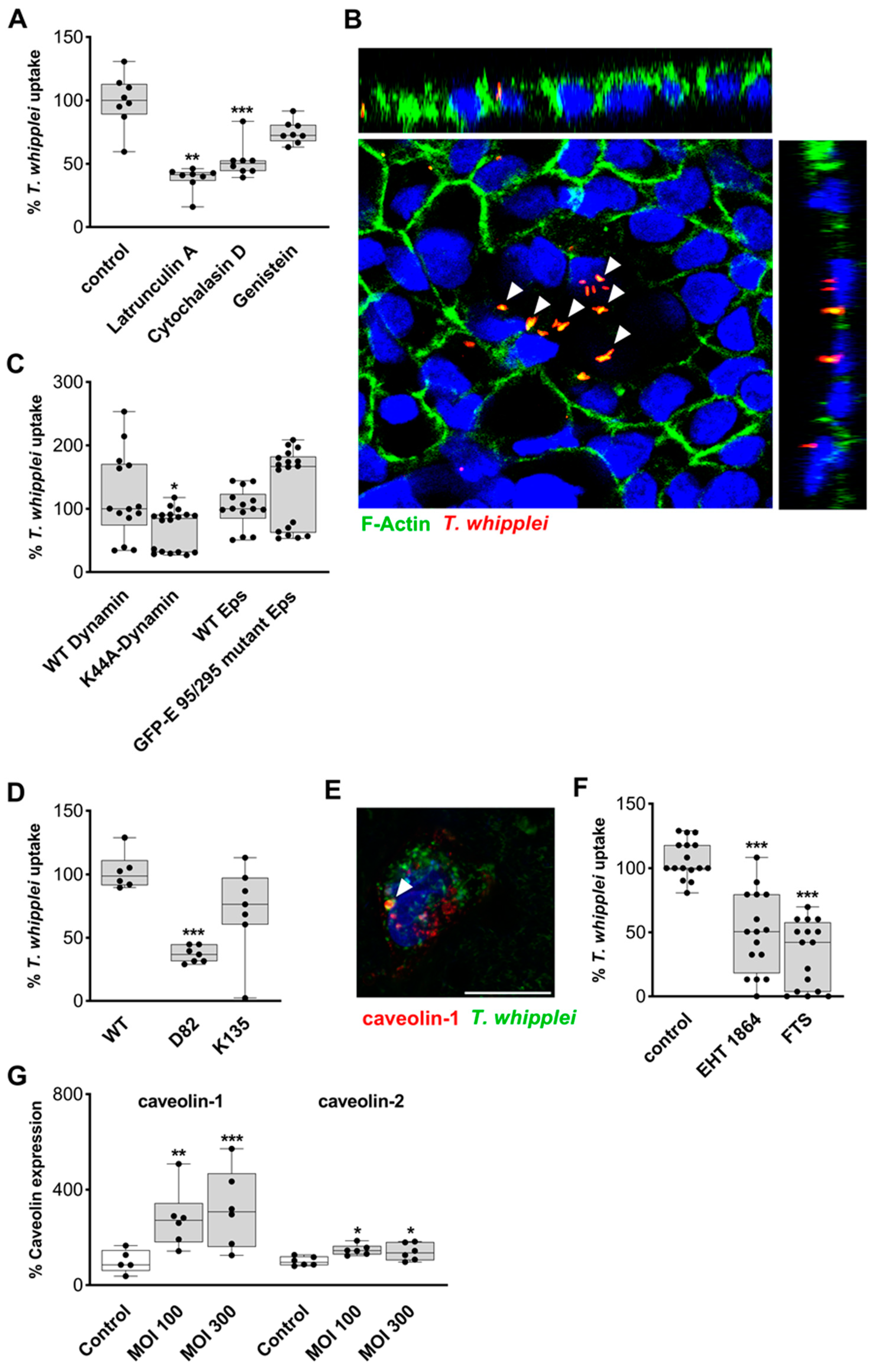
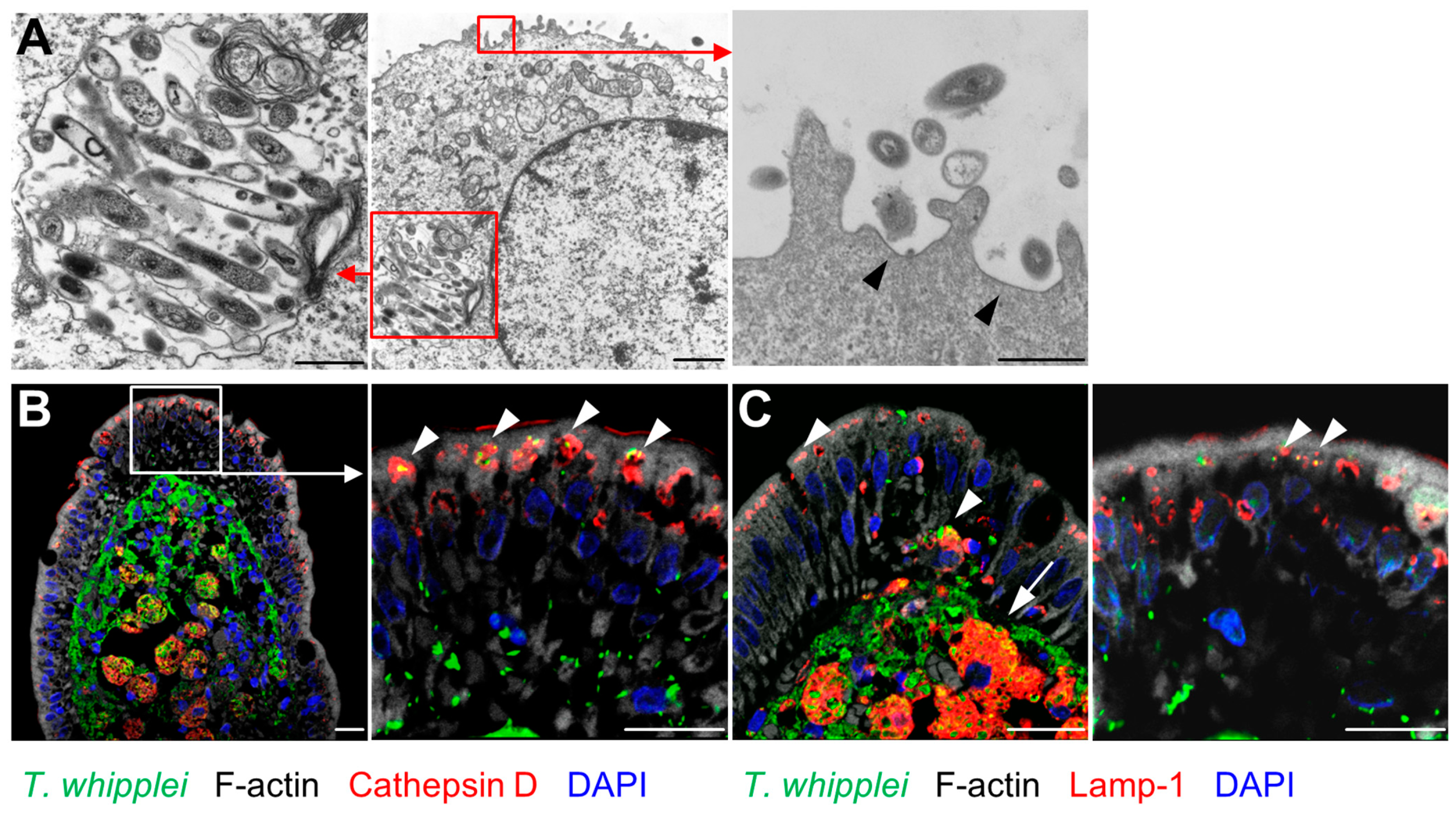
2.2. Mechanism of Transepithelial Passage of T. whipplei
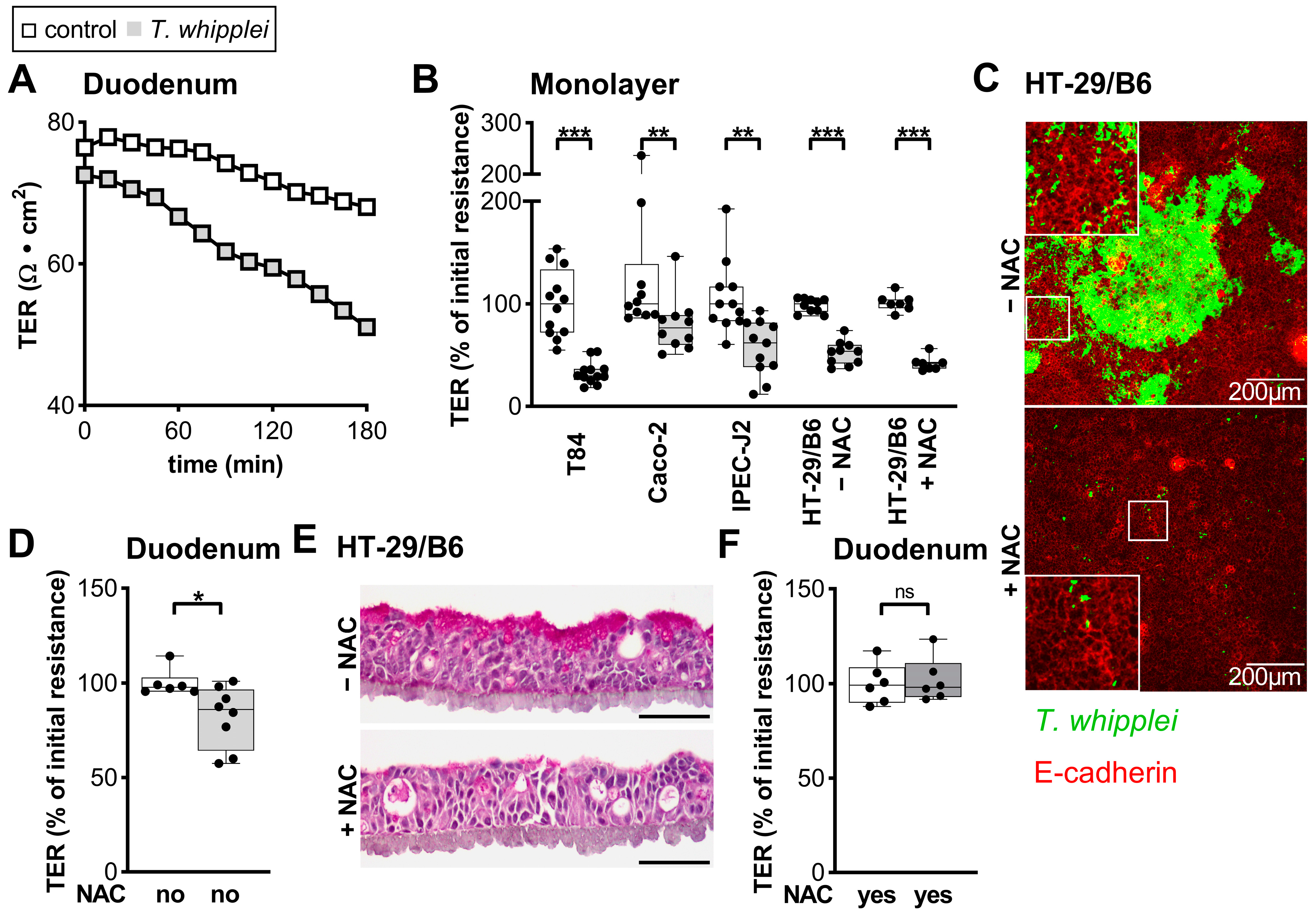
2.3. Epithelial Barrier in T. whipplei Infection
2.4. Epithelial Apoptosis Due to T. whipplei Exposure
2.5. Uptake of Apoptotic, T.-whipplei-Bearing Intestinal Epithelial Cells by Macrophages
3. Discussion
3.1. Transcellular Route of T. whipplei
3.2. Mechanism of Endocytic Uptake
3.3. Barrier Defect Caused by T. whipplei
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Constructs
4.3. Bacterial Strains and Preparations
4.4. Cell Culture and Transfection
4.5. Inhibition of Endocytic T. whipplei Uptake
4.6. T. whipplei Translocation in a Caco-2/Macrophage Coculture Model
4.7. Immunostaining and Confocal Microscopy
4.8. Electron Microscopy
4.9. Live Cell Microscopy
4.10. Analysis of Barrier Function of Small Intestinal Mucosae
4.11. Purification of the Intracellular Compartment Containing T. whipplei
4.12. Western Blotting
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marth, T.; Schneider, T. Whipple disease. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2008, 24, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, T.; Moos, V.; Loddenkemper, C.; Marth, T.; Fenollar, F.; Raoult, D. Whipple’s disease: New aspects of pathogenesis and treatment. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2008, 8, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geelhaar-Karsch, A.; Schinnerling, K.; Conrad, K.; Friebel, J.; Allers, K.; Schneider, T.; Moos, V. Evaluation of arginine metabolism for the analysis of M1/M2 macrophage activation in human clinical specimens. Inflamm. Res. 2013, 62, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moos, V.; Feurle, G.E.; Schinnerling, K.; Geelhaar, A.; Friebel, J.; Allers, K.; Moter, A.; Kikhney, J.; Loddenkemper, C.; Kühl, A.A.; et al. Immunopathology of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in Whipple’s disease. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 2354–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinnerling, K.; Moos, V.; Geelhaar, A.; Allers, K.; Loddenkemper, C.; Friebel, J.; Conrad, K.; Kühl, A.A.; Erben, U.; Schneider, T. Regulatory T cells in patients with Whipple’s disease. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 4061–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinnerling, K.; Geelhaar-Karsch, A.; Allers, K.; Friebel, J.; Conrad, K.; Loddenkemper, C.; Kühl, A.A.; Erben, U.; Ignatius, R.; Moos, V.; et al. Role of dendritic cells in the pathogenesis of Whipple’s disease. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoult, D.; Fenollar, F.; Rolain, J.M.; Minodier, P.; Bosdure, E.; Li, W.; Garnier, J.M.; Richet, H. Tropheryma whipplei in children with gastroenteritis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenollar, F.; Minodier, P.; Boutin, A.; Laporte, R.; Brémond, V.; Noël, G.; Miramont, S.; Richet, H.; Benkouiten, S.; Lagier, J.C.; et al. Tropheryma whipplei associated with diarrhoea in young children. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagier, J.C.; Fenollar, F.; Raoult, D. Acute infections caused by Tropheryma whipplei. Future Microbiol. 2017, 12, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinnemeier, C.D.; Klupp, E.M.; Krumkamp, R.; Rolling, T.; Fischer, N.; Owusu-Dabo, E.; Addo, M.M.; Adu-Sarkodie, Y.; Käsmaier, J.; Aepfelbacher, M.; et al. Tropheryma whipplei in children with diarrhoea in rural Ghana. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 65.e1–65.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautret, P.; Benkouiten, S.; Parola, P.; Brouqui, P.; Memish, Z.; Raoult, D. Occurrence of Tropheryma whipplei during diarrhea in Hajj pilgrims: A PCR analysis of paired rectal swabs. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2014, 12, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makka, S.; Papadogiannaki, I.; Voulgari-Kokota, A.; Georgakopoulou, T.; Koutantou, M.; Angelakis, E. Tropheryma whipplei Intestinal Colonization in Migrant Children, Greece. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 1926–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, L.; Pomari, E.; Leonardi, M.; La Marca, G.; Pajola, B.; Mazzi, C.; Piubelli, C.; Beltrame, A. Tropheryma whipplei, Helicobacter pylori, and Intestinal Protozoal Co-Infections in Italian and Immigrant Populations: A Cross-Sectional Study. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoult, D.; Birg, M.L.; La Scola, B.; Fournier, P.E.; Enea, M.; Lepidi, H.; Roux, V.; Piette, J.C.; Vandenesch, F.; Vital-Durand, D.; et al. Cultivation of the bacillus of Whipple’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoult, D.; La Scola, B.; Lecocq, P.; Lepidi, H.; Fournier, P.E. Culture and immunological detection of Tropheryma whippelii from the duodenum of a patient with Whipple disease. JAMA 2001, 285, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, M.A.; Hirst, B.H.; Jepson, M.A. M-cell surface beta1 integrin expression and invasin-mediated targeting of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis to mouse Peyer’s patch M cells. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, M.A.; Jepson, M.A.; Simmons, N.L.; Hirst, B.H. Preferential interaction of Salmonella typhimurium with mouse Peyer’s patch M cells. Res. Microbiol. 1994, 145, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-del Portillo, F.; Finlay, B.B. Salmonella invasion of nonphagocytic cells induces formation of macropinosomes in the host cell. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 4641–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounier, J.; Vasselon, T.; Hellio, R.; Lesourd, M.; Sansonetti, P.J. Shigella flexneri enters human colonic Caco-2 epithelial cells through the basolateral pole. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansonetti, P.J.; Arondel, J.; Cantey, J.R.; Prevost, M.C.; Huerre, M. Infection of rabbit Peyer’s patches by Shigella flexneri: Effect of adhesive or invasive bacterial phenotypes on follicle-associated epithelium. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 2752–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, M.; Gunzel, D.; Buergel, N.; Richter, J.F.; Troeger, H.; May, C.; Fromm, A.; Sorgenfrei, D.; Daum, S.; Bojarski, C.; et al. Cell polarity-determining proteins Par-3 and PP-1 are involved in epithelial tight junction defects in coeliac disease. Gut 2012, 61, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelkmans, L.; Puntener, D.; Helenius, A. Local actin polymerization and dynamin recruitment in SV40-induced internalization of caveolae. Science 2002, 296, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmerah, A.; Bayrou, M.; Cerf-Bensussan, N.; Dautry-Varsat, A. Inhibition of clathrin-coated pit assembly by an Eps15 mutant. J. Cell Sci. 1999, 112 Pt 9, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Luetterforst, R.; Harding, A.; Apolloni, A.; Etheridge, M.; Stang, E.; Rolls, B.; Hancock, J.F.; Parton, R.G. Dominant-negative caveolin inhibits H-Ras function by disrupting cholesterol-rich plasma membrane domains. Nat. Cell Biol. 1999, 1, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.S.; Shin, M.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, K.S.; Choy, H.E.; Cho, K.A. Caveolin-1 mediates Salmonella invasion via the regulation of SopE-dependent Rac1 activation and actin reorganization. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinze, C.; Boucrot, E. Local actin polymerization during endocytic carrier formation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2018, 46, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, C.M.; Pots, H.; Gueho, A.; Vines, J.H.; Munn, C.J.; Phillips, B.A.; Gilsbach, B.; Traynor, D.; Nikolaev, A.; Soldati, T.; et al. Coordinated Ras and Rac Activity Shapes Macropinocytic Cups and Enables Phagocytosis of Geometrically Diverse Bacteria. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 2912–2926.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreusel, K.M.; Fromm, M.; Schulzke, J.D.; Hegel, U. Cl- secretion in epithelial monolayers of mucus-forming human colon cells (HT-29/B6). Am. J. Physiol. 1991, 261, C574–C582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissner, D.; Schumann, M.; Batra, A.; Kredel, L.I.; Kuhl, A.A.; Erben, U.; May, C.; Schulzke, J.D.; Siegmund, B. Monocyte and M1 Macrophage-induced Barrier Defect Contributes to Chronic Intestinal Inflammation in IBD. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soderholm, J.D.; Streutker, C.; Yang, P.C.; Paterson, C.; Singh, P.K.; McKay, D.M.; Sherman, P.M.; Croitoru, K.; Perdue, M.H. Increased epithelial uptake of protein antigens in the ileum of Crohn’s disease mediated by tumour necrosis factor alpha. Gut 2004, 53, 1817–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, J.R. Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niess, J.H.; Brand, S.; Gu, X.; Landsman, L.; Jung, S.; McCormick, B.A.; Vyas, J.M.; Boes, M.; Ploegh, H.L.; Fox, J.G.; et al. CX3CR1-mediated dendritic cell access to the intestinal lumen and bacterial clearance. Science 2005, 307, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rescigno, M.; Urbano, M.; Valzasina, B.; Francolini, M.; Rotta, G.; Bonasio, R.; Granucci, F.; Kraehenbuhl, J.P.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P. Dendritic cells express tight junction proteins and penetrate gut epithelial monolayers to sample bacteria. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Spreeuwel, J.P.; Duursma, G.C.; Meijer, C.J.; Bax, R.; Rosekrans, P.C.; Lindeman, J. Campylobacter colitis: Histological immunohistochemical and ultrastructural findings. Gut 1985, 26, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carayol, N.; Tran Van Nhieu, G. The inside story of Shigella invasion of intestinal epithelial cells. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a016717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, H.K.; Parry, C.M.; van der Poll, T.; Wiersinga, W.J. Host–Pathogen Interaction in Invasive Salmonellosis. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Tall, B.D.; Curtis, S.K.; Kopecko, D.J. Enhanced microscopic definition of Campylobacter jejuni 81-176 adherence to, invasion of, translocation across, and exocytosis from polarized human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 5294–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucker, R.; Schulz, E.; Gunzel, D.; Bojarski, C.; Lee, I.F.; John, L.J.; Wiegand, S.; Janssen, T.; Wieler, L.H.; Dobrindt, U.; et al. alpha-Haemolysin of Escherichia coli in IBD: A potentiator of inflammatory activity in the colon. Gut 2014, 63, 1893–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troeger, H.; Richter, J.F.; Beutin, L.; Gunzel, D.; Dobrindt, U.; Epple, H.J.; Gitter, A.H.; Zeitz, M.; Fromm, M.; Schulzke, J.D. Escherichia coli alpha-haemolysin induces focal leaks in colonic epithelium: A novel mechanism of bacterial translocation. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2530–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweitzer, S.M.; Hinshaw, J.E. Dynamin undergoes a GTP-dependent conformational change causing vesiculation. Cell 1998, 93, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinchen, J.M.; Doukoumetzidis, K.; Almendinger, J.; Stergiou, L.; Tosello-Trampont, A.; Sifri, C.D.; Hengartner, M.O.; Ravichandran, K.S. A pathway for phagosome maturation during engulfment of apoptotic cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pentecost, M.; Kumaran, J.; Ghosh, P.; Amieva, M.R. Listeria monocytogenes internalin B activates junctional endocytosis to accelerate intestinal invasion. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Argudo, I.; Jepson, M.A. Salmonella translocates across an in vitro M cell model independently of SPI-1 and SPI-2. Microbiology 2008, 154, 3887–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parton, R.G.; Simons, K. The multiple faces of caveolae. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friebel, J.; Weithauser, A.; Witkowski, M.; Rauch, B.H.; Savvatis, K.; Dörner, A.; Tabaraie, T.; Kasner, M.; Moos, V.; Bösel, D.; et al. Protease-activated receptor 2 deficiency mediates cardiac fibrosis and diastolic dysfunction. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 3318–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shutes, A.; Onesto, C.; Picard, V.; Leblond, B.; Schweighoffer, F.; Der, C.J. Specificity and mechanism of action of EHT 1864, a novel small molecule inhibitor of Rac family small GTPases. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 35666–35678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, L.; Kloog, Y. A Ras inhibitor tilts the balance between Rac and Rho and blocks phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent glioblastoma cell migration. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11709–11717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egami, Y.; Taguchi, T.; Maekawa, M.; Arai, H.; Araki, N. Small GTPases and phosphoinositides in the regulatory mechanisms of macropinosome formation and maturation. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, J.; Mendoza, P.; Ortiz, R.; Diaz, N.; Leyton, L.; Stupack, D.; Quest, A.F.; Torres, V.A. Rab5 is required in metastatic cancer cells for Caveolin-1-enhanced Rac1 activation, migration and invasion. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 2401–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghigo, E.; Barry, A.O.; Pretat, L.; Al Moussawi, K.; Desnues, B.; Capo, C.; Kornfeld, H.; Mege, J.L. IL-16 promotes T. whipplei replication by inhibiting phagosome conversion and modulating macrophage activation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghigo, E.; Capo, C.; Aurouze, M.; Tung, C.H.; Gorvel, J.P.; Raoult, D.; Mege, J.L. Survival of Tropheryma whipplei, the agent of Whipple’s disease, requires phagosome acidification. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 1501–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottola, G.; Boucherit, N.; Trouplin, V.; Oury Barry, A.; Soubeyran, P.; Mege, J.L.; Ghigo, E. Tropheryma whipplei, the agent of Whipple’s disease, affects the early to late phagosome transition and survives in a Rab5- and Rab7-positive compartment. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoult, D.; Ogata, H.; Audic, S.; Robert, C.; Suhre, K.; Drancourt, M.; Claverie, J.M. Tropheryma whipplei Twist: A human pathogenic Actinobacteria with a reduced genome. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 1800–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coureuil, M.; Mikaty, G.; Miller, F.; Lecuyer, H.; Bernard, C.; Bourdoulous, S.; Dumenil, G.; Mege, R.M.; Weksler, B.B.; Romero, I.A.; et al. Meningococcal type IV pili recruit the polarity complex to cross the brain endothelium. Science 2009, 325, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, N.; Nishizawa, H.; Kitao, S.; Deguchi, S.; Nakamura, T.; Fujimoto, A.; Shikata, M.; Gotoh, N. Pseudomonas aeruginosa injects type III effector ExoS into epithelial cells through the function of type IV pili. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorvel, L.; Al Moussawi, K.; Ghigo, E.; Capo, C.; Mege, J.L.; Desnues, B. Tropheryma whipplei, the Whipple’s disease bacillus, induces macrophage apoptosis through the extrinsic pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2010, 1, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuhan, R.; Koutsouris, A.; Savkovic, S.D.; Hecht, G. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli-induced myosin light chain phosphorylation alters intestinal epithelial permeability. Gastroenterology 1997, 113, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, H.L.; Nielsen, H.; Ejlertsen, T.; Engberg, J.; Gunzel, D.; Zeitz, M.; Hering, N.A.; Fromm, M.; Schulzke, J.D.; Bucker, R. Oral and fecal Campylobacter concisus strains perturb barrier function by apoptosis induction in HT-29/B6 intestinal epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, N.A.; Richter, J.F.; Krug, S.M.; Gunzel, D.; Fromm, A.; Bohn, E.; Rosenthal, R.; Bucker, R.; Fromm, M.; Troeger, H.; et al. Yersinia enterocolitica induces epithelial barrier dysfunction through regional tight junction changes in colonic HT-29/B6 cell monolayers. Lab. Investig. 2011, 91, 310–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epple, H.J.; Friebel, J.; Moos, V.; Troeger, H.; Krug, S.M.; Allers, K.; Schinnerling, K.; Fromm, A.; Siegmund, B.; Fromm, M.; et al. Architectural and functional alterations of the small intestinal mucosa in classical Whipple’s disease. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 1542–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friebel, J.; Schinnerling, K.; Geelhaar-Karsch, A.; Allers, K.; Schneider, T.; Moos, V. Intestinal barrier dysfunction mediates Whipple’s disease immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS). Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2022, 10, e622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mankertz, J.; Schulzke, J.D. Altered permeability in inflammatory bowel disease: Pathophysiology and clinical implications. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 23, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemka, A.; Clyne, M.; Shanahan, F.; Tompkins, T.; Corcionivoschi, N.; Bourke, B. Probiotic colonization of the adherent mucus layer of HT29MTXE12 cells attenuates Campylobacter jejuni virulence properties. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 2812–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumann, M.; Nakagawa, T.; Mantey, S.A.; Howell, B.; Jensen, R.T. Function of non-visual arrestins in signaling and endocytosis of the gastrin-releasing peptide receptor (GRP receptor). Biochem. Pharm. 2008, 75, 1170–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepidi, H.; Fenollar, F.; Gerolami, R.; Mege, J.-L.; Bonzi, M.-F.; Chappuis, M.; Sahel, J.; Raoult, D. Whipple’s disease: Immunospecific and quantitative immunohistochemical study of intestinal biopsy specimens. Hum. Pathol. 2003, 34, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moos, V.; Schmidt, C.; Geelhaar, A.; Kunkel, D.; Allers, K.; Schinnerling, K.; Loddenkemper, C.; Fenollar, F.; Moter, A.; Raoult, D.; et al. Impaired immune functions of monocytes and macrophages in Whipple’s disease. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutrave, S.; Kikhney, J.; Schmidt, J.; Petrich, A.; Wiessner, A.; Kursawe, L.; Gebhardt, M.; Kertzscher, U.; Gabel, G.; Goubergrits, L.; et al. Effect of daptomycin and vancomycin on Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms: An in vitro assessment using fluorescence in situ hybridization. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, R.S.; Bundey, R.A.; Insel, P.A. Nitric oxide inhibition of adenylyl cyclase type 6 activity is dependent upon lipid rafts and caveolin signaling complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 19846–19853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Friebel, J.; Schinnerling, K.; Weigt, K.; Heldt, C.; Fromm, A.; Bojarski, C.; Siegmund, B.; Epple, H.-J.; Kikhney, J.; Moter, A.; et al. Uptake of Tropheryma whipplei by Intestinal Epithelia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6197. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076197
Friebel J, Schinnerling K, Weigt K, Heldt C, Fromm A, Bojarski C, Siegmund B, Epple H-J, Kikhney J, Moter A, et al. Uptake of Tropheryma whipplei by Intestinal Epithelia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(7):6197. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076197
Chicago/Turabian StyleFriebel, Julian, Katina Schinnerling, Kathleen Weigt, Claudia Heldt, Anja Fromm, Christian Bojarski, Britta Siegmund, Hans-Jörg Epple, Judith Kikhney, Annette Moter, and et al. 2023. "Uptake of Tropheryma whipplei by Intestinal Epithelia" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 7: 6197. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076197
APA StyleFriebel, J., Schinnerling, K., Weigt, K., Heldt, C., Fromm, A., Bojarski, C., Siegmund, B., Epple, H.-J., Kikhney, J., Moter, A., Schneider, T., Schulzke, J. D., Moos, V., & Schumann, M. (2023). Uptake of Tropheryma whipplei by Intestinal Epithelia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(7), 6197. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076197






