A New One-Tube Reaction Assay for the Universal Determination of Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.) Self-(In)Compatible MGST- and S-Alleles Using Capillary Fragment Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Assay Design
2.2. Subsystem for the Detection of SI S-Alleles
2.3. Subsystem for the Identification of SC S-Alleles
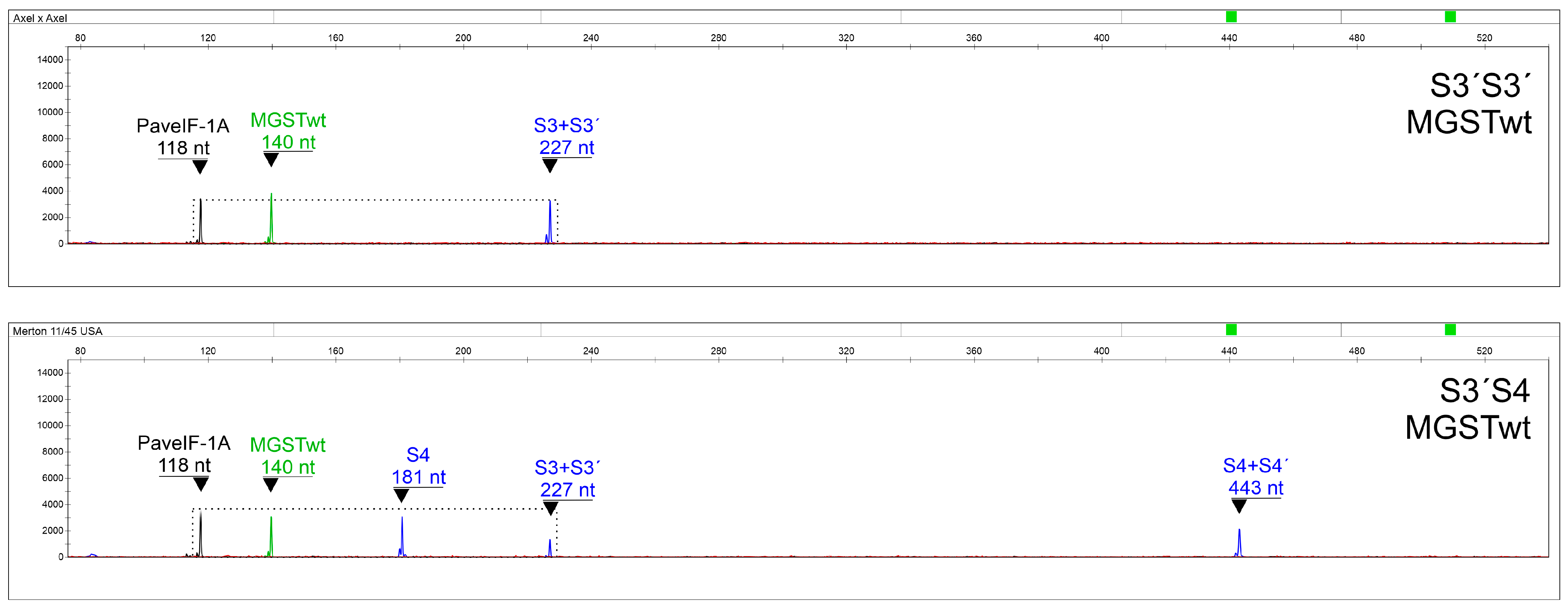
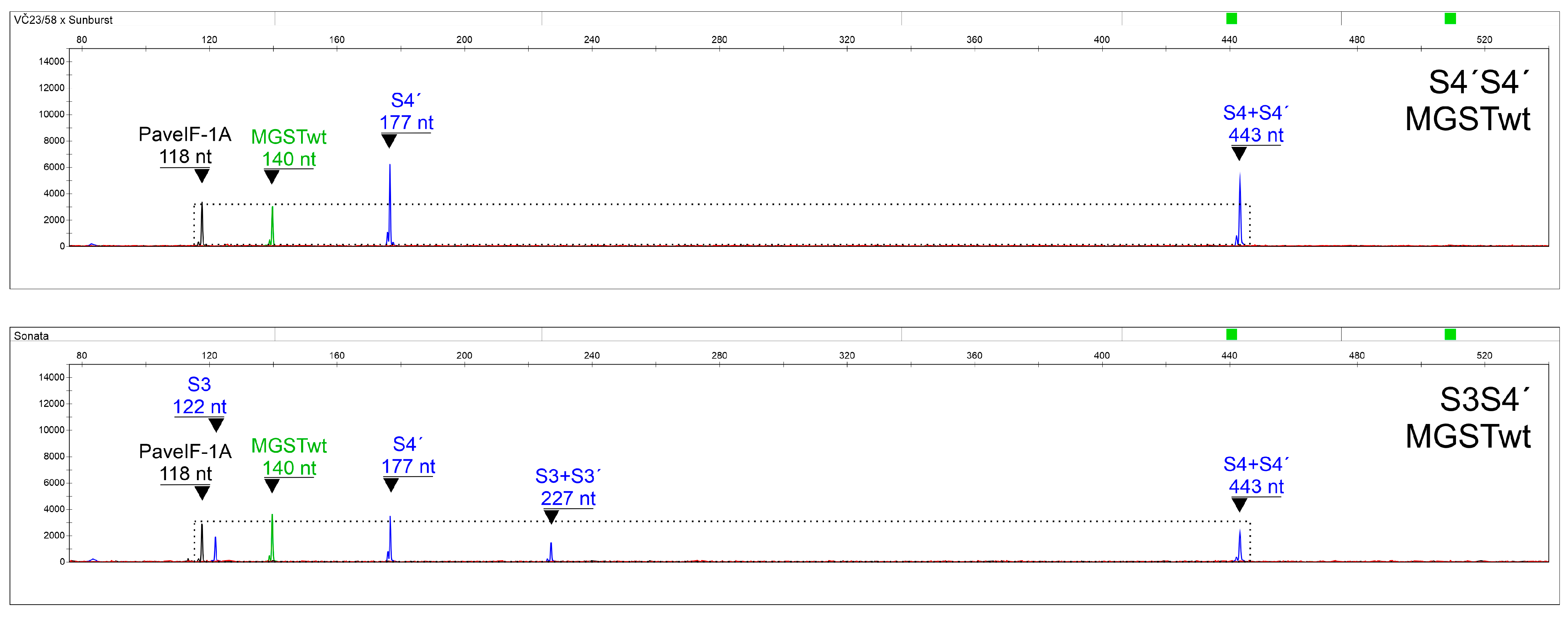
2.4. Subsystem for the Determination of MGST Alleles
2.5. Final Multiplexing and Data Interpretation
2.6. Assay Verification
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. The Assay Design Workflow
4.2. Samples, DNA Isolation
4.3. The Design of Primers and Verification
4.4. Fragment Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Nettancourt, D. Incompatibility in Angiosperms, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1977; pp. 1–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Sanz, J.V.; Zuriaga, E.; Cruz-García, F.; McClure, B.; Romero, C. Self-(In)compatibility Systems: Target Traits for Crop-Production, Plant Breeding, and Biotechnology. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crane, M.B.; Brown, A.G. Incompatibility and Sterility in the Sweet Cherry, Prunus avium L. J. Pomol. Hortic. Sci. 1938, 15, 2–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Yamane, H.; Sugiura, A.; Murayama, H.; Sassa, H.; Mori, H. Molecular Typing of S-alleles through Identification, Characterization and cDNA Cloning for S-RNases in Sweet Cherry. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1999, 124, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamane, H.; Ikeda, K.; Ushijima, K.; Sassa, H.; Tao, R. A Pollen-Expressed Gene for a Novel Protein with an F-box Motif that is Very Tightly Linked to a Gene for S-RNase in Two Species of Cherry, Prunus cerasus and P. avium. Plant Cell Physiol. 2003, 44, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schröpfer, S.; Schuster, M.; Flachowsky, H. Detection of S-alleles in a sweet cherry collection from Azerbaijan and Turkey using next generation sequencing. Acta Hortic. 2022, 1342, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, D.; Tao, R. Distinct Self-recognition in the Prunus S-RNase-based Gametophytic Self-incompatibility System. Hortic. J. 2016, 85, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsumoto, D.; Tao, R. Recognition of a wide-range of S-RNases by S locus F-box like 2, a general-inhibitor candidate in the Prunus-specific S-RNase-based self-incompatibility system. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 91, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, D.; Tao, R. Recognition of S-RNases by an S locus F-box like protein and an S haplotype-specific F-box like protein in the Prunus-specific self-incompatibility system. Plant Mol. Biol. 2019, 100, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisek, A.; Kucharska, D.; Głowacka, A.; Rozpara, E. Identification of S-haplotypes of European cultivars of sour cherry. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.; Crowe, L.K. Structure of the incompatibility gene. Heredity 1954, 8, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonneveld, T.; Tobutt, K.R.; Vaughan, S.P.; Robbins, T.P. Loss of Pollen-S Function in Two Self-Compatible Selections of Prunus avium Is Associated with Deletion/Mutation of an S Haplotype–Specific F-Box Gene. Plant Cell 2004, 17, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchese, A.; Bošković, R.I.; Caruso, T.; Raimondo, A.; Cutuli, M.; Tobutt, K.R. A new self-compatibility haplotype in the sweet cherry ’Kronio’, S5’, attributable to a pollen-part mutation in the SFB gene. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 4347–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cachi, A.M.; Wünsch, A. Characterization and mapping of non-S gametophytic self-compatibility in sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.). J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ono, K.; Akagi, T.; Morimoto, T.; W�Nsch, A.; Tao, R.; Wünsch, A. Genome Re-Sequencing of Diverse Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium) Individuals Reveals a Modifier Gene Mutation Conferring Pollen-Part Self-Compatibility. Plant Cell Physiol. 2018, 59, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bošković, R.; Tobutt, K.R. Correlation of stylar ribonuclease zymograms with incompatibility alleles in sweet cherry. Euphytica 1996, 90, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bošković, R.; Russell, K.; Tobutt, K. Inheritance of stylar ribonucleases in cherry progenies, and reassignment of incompatibility alleles to two incompatibility groups. Euphytica 1997, 95, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonneveld, T.; Robbins, T.P.; Bošković, R.; Tobutt, K.R. Cloning of six cherry self-incompatibility alleles and development of allele-specific PCR detection. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2001, 102, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonneveld, T.; Tobutt, K.R.; Robbins, T.P. Allele-specific PCR detection of sweet cherry self-incompatibility (S) alleles S1 to S16 using consensus and allele-specific primers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 107, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonneveld, T.; Robbins, T.P.; Tobutt, K.R. Improved discrimination of self-incompatibility S-RNase alleles in cherry and high throughput genotyping by automated sizing of first intron polymerase chain reaction products. Plant Breed. 2006, 125, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, S.P.; Russell, K.; Sargent, D.J.; Tobutt, K.R. Isolation of S-locus F-box alleles in Prunus avium and their application in a novel method to determine self-incompatibility genotype. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 112, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachi, A.M.; Wünsch, A.; Vilanova, A.; Guàrdia, M.; Ciordia, M.; Aletà, N. S-locus diversity and cross-compatibility of wild Prunus avium for timber breeding. Plant Breed. 2017, 136, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisek, A.; Rozpara, E.; Glowacka, A.; Kucharska, D.; Zawadzka, M. Identification of S-genotypes of sweet cherry cultivars from Central and Eastern Europe. Hort. Sci. 2015, 42, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szikriszt, B.; Doǧan, A.; Ercisli, S.; Akcay, M.E.; Hegedüs, A.; Halász, J. Molecular typing of the self-incompatibility locus of Turkish sweet cherry genotypes reflects phylogenetic relationships among cherries and other Prunus species. Tree Genet. Genomes. 2013, 9, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wünsch, A.; Hormaza, J.I. Cloning and characterization of genomic DNA sequences of four self-incompatibility alleles in sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 108, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, S.P.; Bošković, R.I.; Gisbert-Climent, A.; Russell, K.; Tobutt, K.R. Characterisation of novel S-alleles from cherry (Prunus avium L.). Tree Genet. Genomes. 2008, 4, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Watari, A.; Ushijima, K.; Yamane, H.; Hauck, N.R.; Iezzoni, A.F.; Tao, R. Molecular Markers for the Self-compatible S4’-haplotype, a Pollen-part Mutant in Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.). J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 2004, 129, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muñoz-Espinoza, C.; Espinosa, E.; Bascuñán, R.; Tapia, S.; Meneses, C.; Almeida, A. Development of a molecular marker for self-compatible S4′ haplotype in sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) using high-resolution melting. Plant Breed. 2017, 136, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, M. Self-incompatibility (S) genotypes of cultivated sweet cherries—An overview update 2020. Open Agrar. Repos. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapins, K. Stella, a self-fruitful sweet cherry. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1971, 51, 252–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, S.; Li, G.; Ye, J. Selection and validation of reference genes for quantitative RT-PCR analysis in peach fruit under different experimental conditions. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 225, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cmejlova, J.; Rejlova, M.; Paprstein, F.; Cmejla, R. A new one-tube reaction kit for the SSR genotyping of apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.). Plant Sci. 2021, 303, 110768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holušová, K.; Čmejlová, J.; Suran, P.; Čmejla, R.; Sedlák, J.; Zelený, L.; Bartoš, J. High-resolution genome-wide association study of a large Czech collection of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) on fruit maturity and quality traits. Hortic Res. 2022, 10, uhac233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peace, C.P. DNA-informed breeding of rosaceous crops: Promises, progress and prospects. Hortic. Res. 2017, 4, 17006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sebolt, A.M. Breeder profile: Nnadozie Oraguzie. RosBREED Newslett 2011, 2, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Patzak, J.; Henychová, A.; Paprštein, F.; Sedlák, J. Molecular S-genotyping of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) genetic resources. Hort. Sci. 2019, 46, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
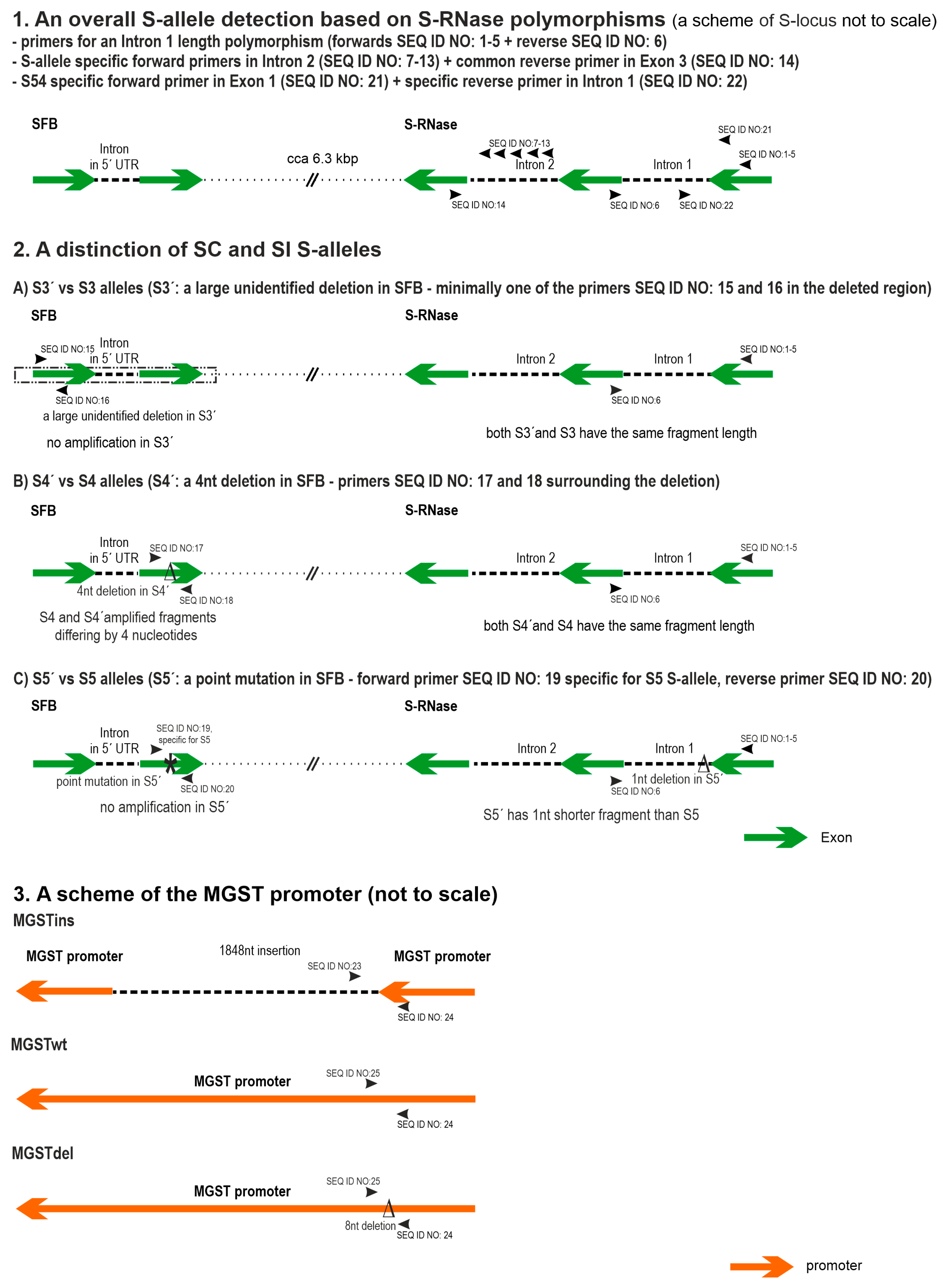
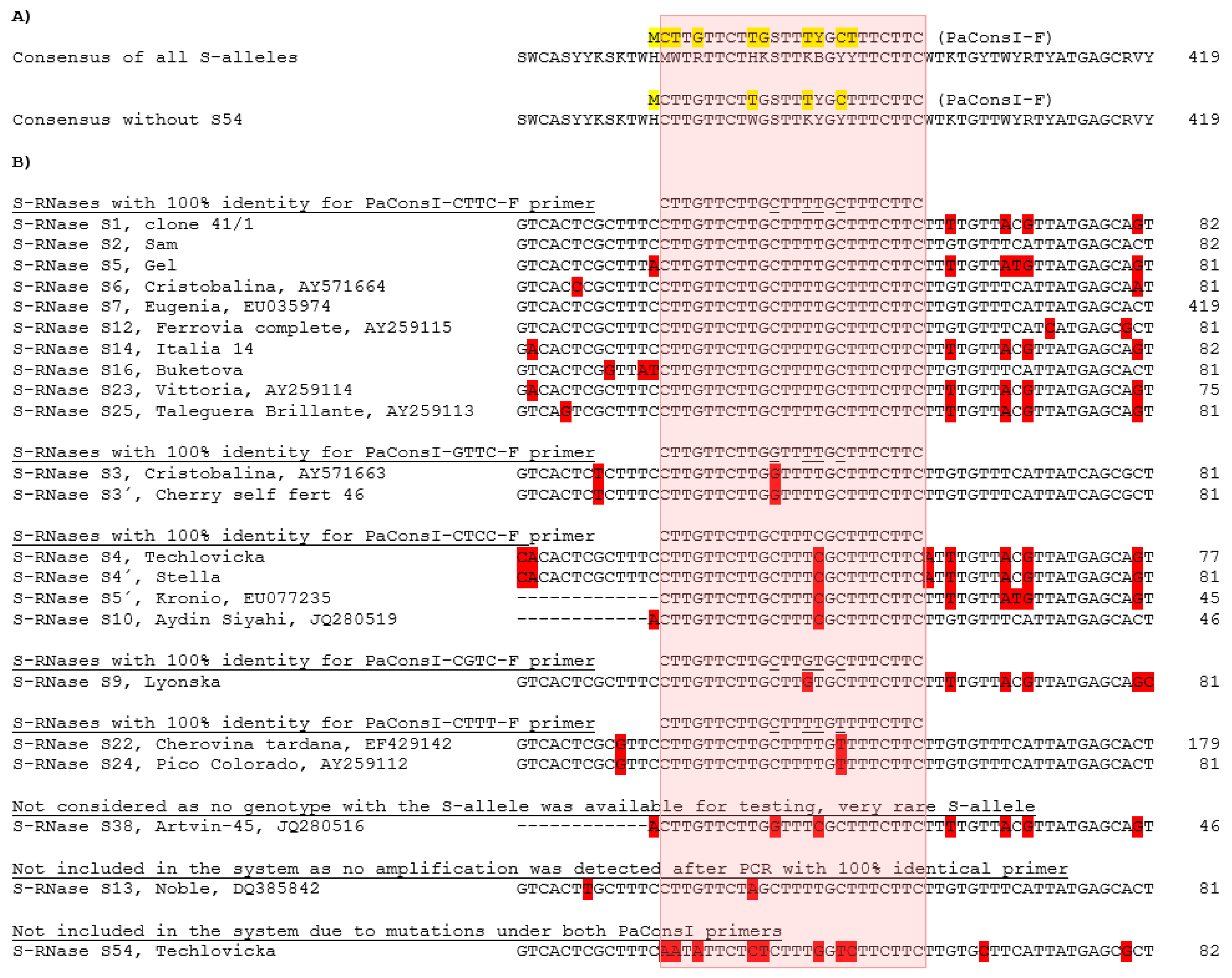
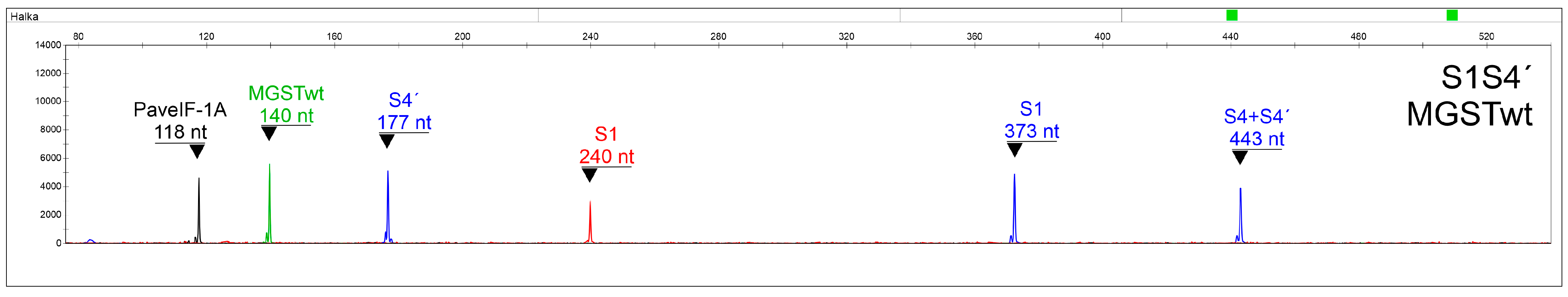
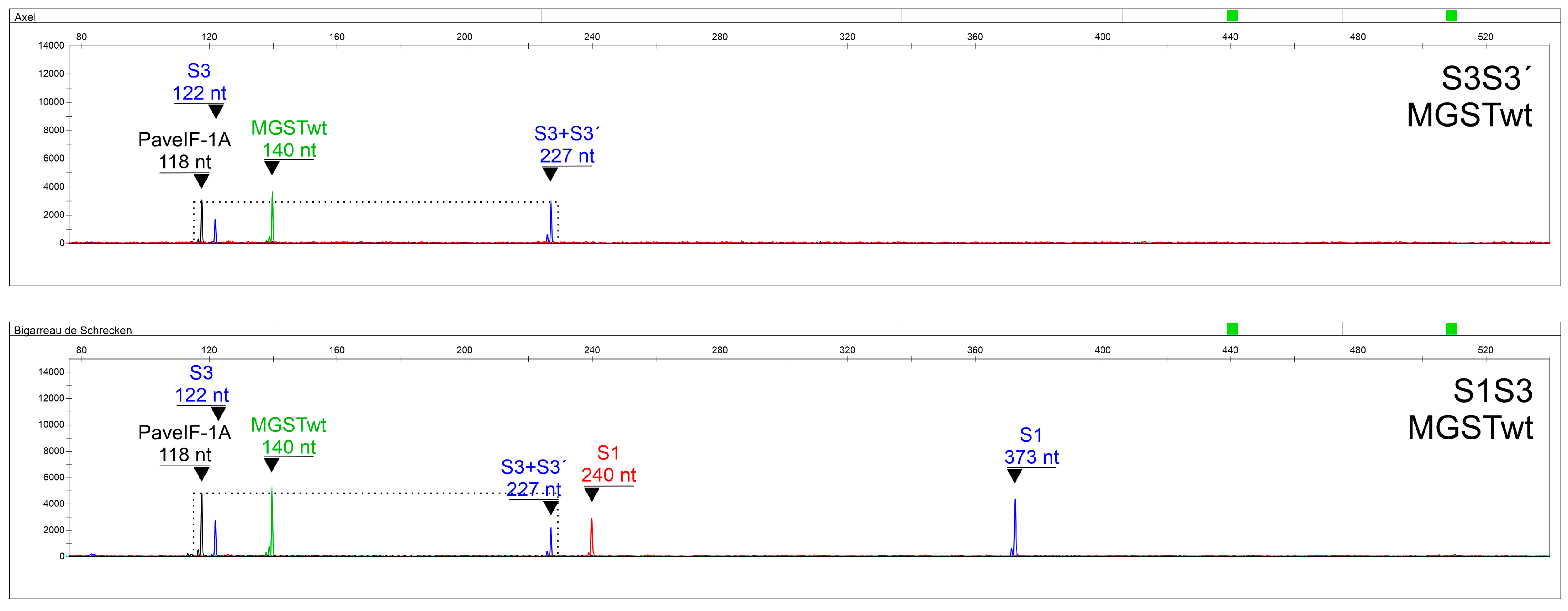

| SEQ ID NO | Primer Name | Sequence (5′->3′) | Fluorescent Label | Final Concentration (µM) | Alleles Recognized with 100% Homology | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PaConsI-CTTC-F | CTTGTTCTTGCTTTTGCTTTCTTC | 0.19 | S1, S2, S5, S6, S7, S12, S14, S16, S23, S25 S-RNase | ||
| 2 | PaConsI-GTTC-F | CTTGTTCTTGGTTTTGCTTTCTTC | 0.33 | S3, S3′ S-RNase | ||
| 3 | PaConsI-CTCC-F | CTTGTTCTTGCTTTCGCTTTCTTC | 0.18 | S4, S4′, S5′, S10 S-RNase | ||
| 4 | PaConsI-CTTT-F | CTTGTTCTTGCTTTTGTTTTCTTC | 0.5 | S22, S24 S-RNase | ||
| 5 | PaConsI-CGTC-F | CTTGTTCTTGCTTGTGCTTTCTTC | 0.22 | S9 S-RNase | ||
| 6 | PaConsI-R2 | GCCATTGTTGCACAAATTGA | FAM | 0.21 | all S-RNases with a known sequence | [20] |
| 7 | S-RNase-S1-In2-F | TGGTCTCCCTAACATGACCC | 0.175 | S1 S-RNase | ||
| 8 | S-RNase-S2-In2-F | TGAACGAAATCTCAACTCATAAATC | 0.43 | S2 S-RNase | ||
| 9 | S-RNase-S6+S24-In2-F | TCATTTTGTTTTCCACCTACCC | 0.18 | S6 and S24 S-RNase | ||
| 10 | S-RNase-S7-In2-F | TCTGTCTGGTTGTTTTGCTGG | 0.17 | S7 S-RNase | ||
| 11 | S-RNase-S9+S22-In2-F | TCTAATAATGGATCTGCTCATCTAATT | 0.7 | S9 and S22 S-RNase | ||
| 12 | S-RNase-S12-In2-F | GCTAACCCTTACATTTTGACCC | 0.25 | S12 S-RNase | ||
| 13 | S-RNase-S13-In2-F | ATATGTCTGTCTATCTATCTGTTTTCTCA | 0.4 | S13 S-RNase | ||
| 14 | S-RNases-Ex3-R | GTATCATTGCCACYTTCCACG | PET | 0.24 | most of S-RNases | |
| 15 | PaSFB3-F | CCACAATTTGAACGTCAGAAC | 0.28 | S3 SFB | [12] | |
| 16 | PaSFB3-short-R | TCTGTGTTTTCTAAAGGATGGC | FAM | 0.28 | S3 SFB | |
| 17 | PaSFB4+4′-F | TCTAGCTTTTATTCTTGCGAGG | FAM | 0.155 | S4 and S4′SFB | |
| 18 | PaSFB4+4′-R | GATCTCCTATGCCCCTAGAGAA | 0.155 | S4 and S4′SFB | ||
| 19 | PaSFB-S5-F | GCTTGGACAAAATTGACTTGTG | 0.2 | S5 SFB | ||
| 20 | PaSFB-S5+S5′-R | GATCACAATCACCCAAAGGAGG | FAM | 0.2 | S5 and S5′SFB | |
| 21 | S-RNase-S54-F | CTCTCTTTGGTCTTCTTCTTGTGC | PET | 0.17 | S54 | |
| 22 | S-RNase-S54-R | GCTTGCTGATTGTAAATAAACTGC | 0.17 | S54 | ||
| 23 | MGST-TE-in-F | ATAAATGGGTCAGTGGTGGG | 0.105 | MGSTins | ||
| 24 | MGST-TE-out-F | AAAGCCTTCAAGTGGGAAAG | 0.105 | MGSTwt, MGSTdel | ||
| 25 | MGST-TE-out-R | TTGCTTACAGGTCATTACTTACACG | VIC | 0.105 | MGSTwt, MGSTdel, MGSTins | [15] |
| 26 | PaveIF-1A-F | GCCCAAGTGCTTCGTATGCT | NED | 0.05 | only 1 allele of PaveIF-1A observed | [31] |
| 27 | PaveIF-1A-R | ATCACCGGCTGCAATCCA | 0.05 | only 1 allele of PaveIF-1A observed | [31] |
| S-allele/MGST Promoter | Length of Fragment #1 (Observed, Expected) (nt) | Length of Fragment #2 (Observed, Expected) (nt) | Number of Genotypes Described in a Reference List [29] |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | B: 373 (376/379) | R: 240 (240) | 410 |
| S2 | B: 337 (343) | R: 302 (303) | 188 |
| S3 | B: 122 (125) | B: 227 (233) | 747 |
| S3′ | B: 227 (233) | 7 | |
| S4 | B: 181 (184) | B: 443 (450) | 345 |
| S4′ | B: 177 (181) | B: 443 (450) | 76 |
| S5 | B: 83 (90) | B: 385 (392) | 149 |
| S5′ | B: 384 (391) | 3 | |
| S6 | B: 435 (442) | R: 223 (225) | 397 |
| S7 | B: 339 (340) | R: 249 (250) | 45 |
| S9 | B: 350 (355) | R: 266 (266) | 221 |
| S10 | N.D. (363) | 22 | |
| S12 | B: 338 (344) | R: 147 (148/149) | 73 |
| S13 | R: 119 (121) | 114 | |
| S14 | B: 323 (330) | 39 | |
| S16 | B: 406 (412) | 47 | |
| S21/S25 | B: 367 (374) | 5 | |
| S22 | B: 415 (421) | R: 258 (253/260) | 39 |
| S23 | N.D. (330) | 0 | |
| S24 | N.D. (421) | R: (225) | 4 |
| S28 | N.D. (367) | 0 | |
| S29 | N.D. (338) | 0 | |
| S30 | N.D. (384) | 1 | |
| S31 | N.D. (208) | 0 | |
| S34 | N.D. (377) | 0 | |
| S38 | N.D. (309) | 0 | |
| S54 | R: 172 (171) | 0 | |
| MGSTwt | G: 140 (145) | N.D. | |
| MGSTins | G: 192 (197) | N.D. | |
| MGSTdel | G: 132 (137) | N.D. | |
| PaveIF-1A | Y: 118 (120) | N.D. |
| 6-FAM (Blue) | PET (Red) | VIC (Green) | NED (Yellow) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed Length (nt) | S- Allele | Observed Length (nt) | S- Allele | Observed Length (nt) | Allele | Observed Length (nt) | Allele |
| 83 | S5 | 119 | S13 | 132 | MGSTdel | 118 | PaveIF-1A |
| 122 | S3 | 147 | S12 | 140 | MGSTwt | ||
| 177 | S4′ | 172 | S54 | 192 | MGSTins | ||
| 181 | S4′ | 223 | S6 | ||||
| 227 | S3; S3′ * | 240 | S1 | ||||
| 323 | S14/S23 ** | 249 | S7 | ||||
| 337 | S2 * | 258 | S22 | ||||
| 338 | S12 * | 265 | S9 | ||||
| 339 | S7 * | 302 | S2 | ||||
| 350 | S9 * | ||||||
| 367 | S21/S25 | ||||||
| 373 | S1 * | ||||||
| 384 | S5′ * | ||||||
| 385 | S5 * | ||||||
| 406 | S16 | ||||||
| 415 | S22 * | ||||||
| 435 | S6 * | ||||||
| 443 | S4; S4′ * | ||||||
| PaveIF-1A (Y): 118 nt/ S3 SFB (B): 122 nt | PaveIF-1A (Y): 118 nt/ S3+S3′ S-RNase (B): 227 nt | S3+S3′ S-RNase (B): 227 nt/ S3 SFB (B): 122 nt | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average ± SD | Average ± SD | Average ± SD | |
| S3S3′ | 1.75 ± 0.33 | 1.17 ± 0.21 | 1.50 ± 0.22 |
| S3Sx | 1.65 ± 0.26 | 2.12 ± 0.25 | 0.78 ± 0.15 |
| t-test (p-value) | 0.20 | 2.08 × 10−22 | 4.77 × 10−19 |
| PaveIF-1A (Y): 118 nt/S3+S3′ S-RNase (B): 227 nt | MGST (G): 140 nt/PaveIF-1A (Y): 118 nt | MGST (G): 140 nt/S3+S3′ S-RNase (B): 227 nt | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average ± SD | Average ± SD | Average ± SD | |
| S3′S3′ | 1.30 ± 0.16 | 1.14 ± 0.14 | 1.47 ± 0.16 |
| S3′Sx | 2.25 ± 0.22 | 1.10 ± 0.13 | 2.47 ± 0.27 |
| t-test (p-value) | 3.48 × 10−26 | 0.28 | 6.19 × 10−22 |
| PaveIF-1A (Y): 118 nt/ S4′(B) 177 nt | PaveIF-1A (Y): 118 nt/S4+S4′ (B): 443 nt | S4+S4′ (B): 443 nt/S4′(B) 177 nt | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average ± SD | Average ± SD | Average ± SD | |
| S4′S4′ | 0.53 ± 0.06 | 0.66 ± 0.08 | 0.81 ± 0.05 |
| S4′Sy | 1.04 ± 0.13 | 1.34 ± 0.13 | 0.78 ± 0.05 |
| t-test (p-value) | 7.44 × 10−22 | 2.76 × 10−28 | 0.052 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Čmejlová, J.; Paprštein, F.; Suran, P.; Zelený, L.; Čmejla, R. A New One-Tube Reaction Assay for the Universal Determination of Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.) Self-(In)Compatible MGST- and S-Alleles Using Capillary Fragment Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24086931
Čmejlová J, Paprštein F, Suran P, Zelený L, Čmejla R. A New One-Tube Reaction Assay for the Universal Determination of Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.) Self-(In)Compatible MGST- and S-Alleles Using Capillary Fragment Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(8):6931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24086931
Chicago/Turabian StyleČmejlová, Jana, František Paprštein, Pavol Suran, Lubor Zelený, and Radek Čmejla. 2023. "A New One-Tube Reaction Assay for the Universal Determination of Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.) Self-(In)Compatible MGST- and S-Alleles Using Capillary Fragment Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 8: 6931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24086931
APA StyleČmejlová, J., Paprštein, F., Suran, P., Zelený, L., & Čmejla, R. (2023). A New One-Tube Reaction Assay for the Universal Determination of Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.) Self-(In)Compatible MGST- and S-Alleles Using Capillary Fragment Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(8), 6931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24086931






