The Acute Effects and Mechanism of Ketamine on Nicotine-Induced Neurogenic Relaxation of the Corpus Cavernosum in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
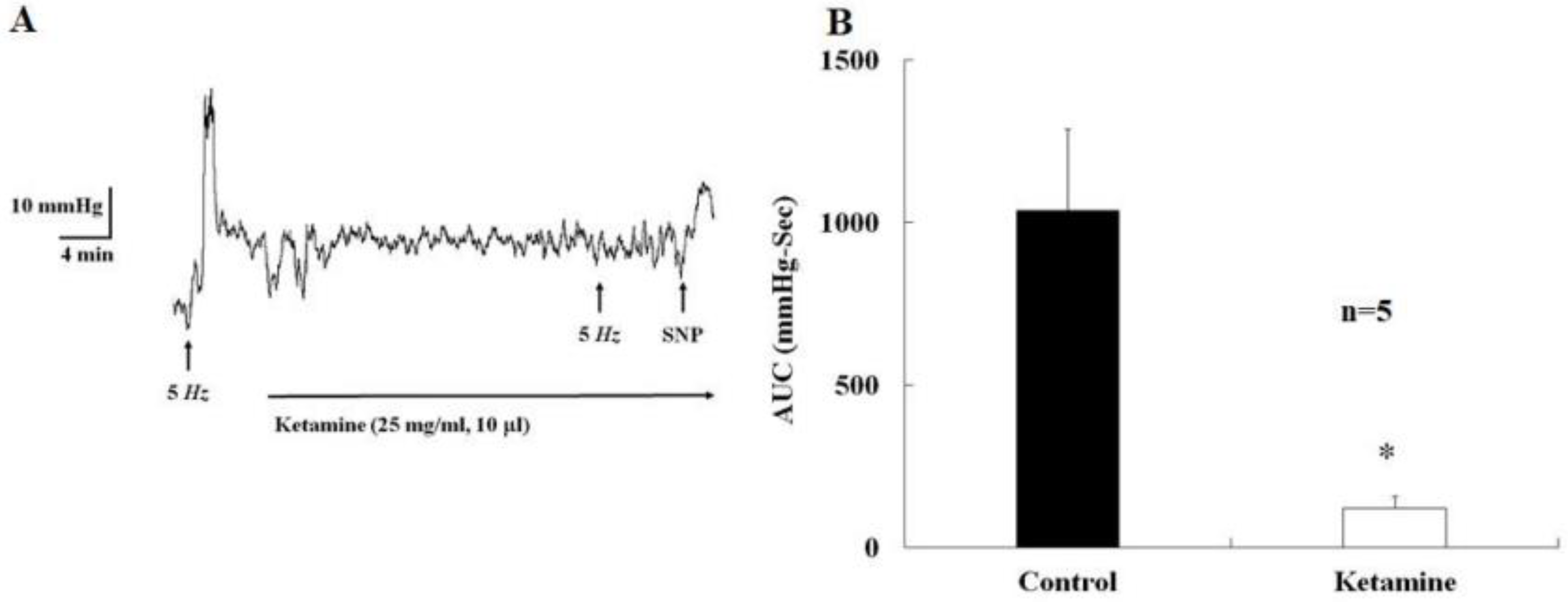
2.1. Acute Effects of Ketamine Injection on Major Pelvic Ganglion
2.2. Corpus Cavernosum Relaxation Induced by D-Serine and L-Glutamate
2.3. Effects of the N-methyl-D-aspartate Receptor Inhibitor MK-801 and Ketamine on Nicotine-Induced Relaxation
2.4. Effects of Various Drugs on Nicotine-Induced Relaxation
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Intra-Cavernosal Pressure (ICP) Measurement
4.2. Tissue Preparation
4.3. Tissue Bath Wire Myography
4.4. Chemical Denervation with 6-hydroxydopamine
4.5. Drugs
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andersson, K.E.; Hedlund, P.; Alm, P. Sympathetic pathways and adrenergic innervation of the penis. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2000, 12, S5–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lafuente-Sanchis, A.; Triguero, D.; Garcia-Pascual, A. Changes in nerve- and endothelium-mediated contractile tone of the corpus cavernosum in a mouse model of pre-mature ageing. Andrology 2014, 2, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtois, F.J.; Macdougall, J.C.; Sachs, B.D. Erectile mechanism in paraplegia. Physiol. Behav. 1993, 53, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azadzoi, K.M.; Yang, J.; Siroky, M.B. Neural regulation of sexual function in men. World J. Clin. Urol. 2013, 2, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, A.L.; Lowenstein, C.J.; Bredt, D.S.; Chang, T.S.K.; Snyder, S.H. Nitric Oxide: A Physiologic Mediator of Penile Erection. Science 1992, 257, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayashida, H.; Okamura, T.; Tomoyoshi, T.; Toda, N. Neurogenic nitric oxide mediates relaxation of canine corpus cavernosum. J. Urol. 1996, 155, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, J.; Song, G.; Feng, Y.; Pan, J.; Yang, X.; Xin, Z.; Hu, P.; Sun, T.; Liu, K.; et al. Acetyl-L-carnitine improves erectile function in bilateral cavernous nerve injury rats via promoting cavernous nerve regeneration. Andrology 2022, 10, 984–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbek, E.; Tasci, A.I.; Ilbey, Y.O.; Simsek, A.; Somay, A.; Metin, G. The effect of regular exercise on penile nitric oxide synthase expression in rats. Int. J. Androl. 2009, 33, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghir-Ghanesefat, H.; Rahimi, N.; Yarmohammadi, F.; Mokhtari, T.; Abdollahi, A.R.; Mehr, S.E.; Dehpour, A.R. The expression, localization and function of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in rat corpus cavernosum. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2017, 69, 1754–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, N.B.; Vural, I.M.; Sarioglu, Y.; Pekiner, C. Nicotine potentiates the nitrergic relaxation responses of rabbit corpus cavernosum tissue via nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 558, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, R.M.; Acker, T.M.; Zimmerman, S.S.; Katzman, B.M.; Strong, K.L.; Traynelis, S.F.; Liotta, D.C. Novel NMDA receptor modulators: An update. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2012, 22, 1337–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, H.; Haider, A.; Ametamey, S.M. N-Methyl-D-Aspartate (NMDA) receptor modulators: A patent review (2015-present). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2020, 30, 743–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, M.; Yong, X.L.H.; Roche, K.W.; Anggono, V. Regulation of NMDA glutamate receptor functions by the GluN2 subunits. J. Neurochem. 2020, 154, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Collingridge, G.L.; Singer, W. Excitatory amino acid receptors and synaptic plasticity. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1990, 11, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horak, M.; Barackova, P.; Langore, E.; Netolicky, J.; Rivas-Ramirez, P.; Rehakova, K. The Extracellular Domains of GluN Subunits Play an Essential Role in Processing NMDA Receptors in the ER. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 603715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroebel, D.; Casado, M.; Paoletti, P. Triheteromeric NMDA receptors: From structure to synaptic physiology. Curr. Opin. Physiol. 2017, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yovanno, R.A.; Chou, T.S.; Brantley, S.J.; Furukawa, H.; Lau, A.Y. Excitatory and inhibitory D-serine binding to the NMDA receptor. Elife 2022, 11, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeboah, F.; Guo, H.; Bill, A. A High-throughput Calcium-flux Assay to Study NMDA-receptors with Sensitivity to Glycine/D-serine and Glutamate. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 10, 58160. [Google Scholar]
- Faraci, F.M.; Brian, J.E., Jr. 7-Nitroindazole inhibits brain nitric oxide synthase and cerebral vasodilatation in response to N-methyl-D-aspartate. Stroke 1995, 26, 2172–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-T.; Chang, H.-H. Nitric oxide of neuronal origin mediates NMDA-induced cerebral hyperemia in rats. Neuroreport 1998, 9, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gallagher, K.; Puledda, F.; O’Daly, O.; Ryan, M.; Dancy, L.; Chowienczyk, P.J.; Zelaya, F.; Goadsby, P.J.; Shah, A.M. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase regulates regional brain perfusion in healthy humans. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 118, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudice, P.; Gemignani, A.; Raiteri, M. Evidence for functional native NMDA receptors activated by glycine or D-serine alone in the absence of glutamatergic coagonist. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1998, 10, 2934–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Hogan-Cann, A.D.; Globa, A.K.; Lu, P.; Nagy, J.I.; Bamji, S.X.; Anderson, C.M. Astrocytes drive cortical vasodilatory signaling by activating endothelial NMDA receptors. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 39, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozic, M.; Valdivielso, J.M. The potential of targeting NMDA receptors outside the CNS. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2014, 19, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, T.; Ferrini, M.; Davila, H.; Zeller, C.; Vernet, D.; Sun, J.; Lalani, R.; Burnett, A.; Rajfer, J.; González-Cadavid, N. Protein inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor are expressed in the rat and mouse penile nerves and colocalize with penile neuronal NOS. Biol. Reprod. 2003, 68, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rivera-Villaseñor, A.; Higinio-Rodríguez, F.; Nava-Gómez, L.; Vázquez-Prieto, B.; Calero-Vargas, I.; Olivares-Moreno, R.; López-Hidalgo, M. NMDA Receptor Hypofunction in the Aging-Associated Malfunction of Peripheral Tissue. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 687121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Lee, M.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Lin, M.-F. Ketamine-snorting associated cystitis. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2011, 110, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuiken, S.D.; Berg, S.J.T.V.D.; Tytgat, G.N.J.; Boeckxstaens, G.E.E. Oral S(+)-Ketamine Does Not Change Visceral Perception in Health. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2004, 49, 1745–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-H.; Huang, C.-L.; Ho, M.-C. Appetitive Motivation and Regulatory Processes in Adolescent Ketamine Users. Subst. Use Misuse 2021, 56, 1616–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.S.; Jang, M.-Y.; Lee, K.-H.; Hsu, W.-T.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, W.-S.; Chang, S.-J. Sexual and bladder dysfunction in male ketamine abusers: A large-scale questionnaire study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shehaby, D.M.; El-Mahdy, R.I.; Ahmed, A.M.; Hosny, A.; El-Rady, N.M.A. Neurobehavioral, testicular and erectile impairments of chronic ketamine administration: Pathogenesis and ameliorating effect of N-acetyl cysteine. Reprod. Toxicol. 2020, 96, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, H.-S.; Wu, Y.-N.; Liao, C.-H.; Chiueh, T.-S.; Lin, Y.-F.; Chiang, H.-S. Long-term administration of ketamine induces erectile dysfunction by decreasing neuronal nitric oxide synthase on cavernous nerve and increasing corporal smooth muscle cell apoptosis in rats. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 73670–73683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinco-Jayo, J.A.; Aguilar-Felices, E.J.; Enciso-Roca, E.C.; Arroyo-Acevedo, J.L.; Herrera-Calderon, O. Phytochemical Screening by LC-ESI-MS/MS and Effect of the Ethyl Acetate Fraction from Leaves and Stems of Jatropha macrantha Mull Arg. on Ketamine-Induced Erectile Dysfunction in Rats. Molecules 2021, 27, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-F.; Lai, S.-Y.; Kung, P.-C.; Lin, Y.-C.; Yang, H.-I.; Chen, P.-Y.; Liu, I.Y.; Lua, A.C.; Lee, T.J.-F. Inhibition by ketamine and amphetamine analogs of the neurogenic nitrergic vasodilations in porcine basilar arteries. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 305, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, A.A.; Rimmer, K.; Dyavanapalli, J.; McArthur, J.R.; Adams, D.J. Ketamine inhibits synaptic transmission and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated responses in rat intracardiac ganglia in situ. Neuropharmacology 2020, 165, 107932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezanilla, F. Voltage-gated ion channels. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 2005, 4, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, W.A.; Lenaeus, M.J.; Gamal El-Din, T.M. Structure and Pharmacology of Voltage-Gated Sodium and Calcium Channels. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 60, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schnoebel, R.; Wolff, M.; Peters, S.C.; Bräu, M.E.; Scholz, A.; Hempelmann, G.; Olschewski, H.; Olschewski, A. Ketamine impairs excitability in superficial dorsal horn neurones by blocking sodium and voltage-gated potassium currents. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 146, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, J.; Fu, B.; Wang, Y.; Yu, T. Effects of ketamine on voltage-gated sodium channels in the barrel cortex and the ventral posteromedial nucleus slices of rats. Neuroreport 2019, 30, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Fu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, T. Effect of ketamine on voltage-gated potassium channels in rat primary sensory cortex pyramidal neurons. Neuroreport 2020, 31, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellano, J.; Xelhuantzi, N.; Mirto, N.; Hernández, M.E.; Cruz, Y. Neural interrelationships of autonomic ganglia from the pelvic region of male rats. Auton. Neurosci. 2019, 217, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purinton, P.T.; Fletcher, T.F.; Bradley, W.E. Gross and light microscopic features of the pelvic plexus in the rat. Anat. Rec. 1973, 175, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aïoun, J.; Rampin, O. Anatomical evidence for glutamatergic transmission in primary sensory neurons and onto postganglionic neurons controlling penile erection in rats: An ultrastructural study with neuronal tracing and immunocytochemistry. Cell Tissue Res. 2005, 323, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanos, P.; Moaddel, R.; Morris, P.J.; Riggs, L.M.; Highland, J.N.; Georgiou, P.; Pereira, E.F.R.; Albuquerque, E.X.; Thomas, C.J.; Zarate, C.A., Jr.; et al. Ketamine and Ketamine Metabolite Pharmacology: Insights into Therapeutic Mechanisms. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 621–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Cadavid, N.F.; Ryndin, I.; Vernet, D.; Magee, T.R.; Rajfer, J. Presence of NMDA receptor subunits in the male lower urogenital tract. J. Androl. 2000, 21, 566–578. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemi, M.; Rezania, F.; Lewin, J.; Moore, K.P.; Mani, A.R. d-Serine modulates neurogenic relaxation in rat corpus cavernosum. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 1791–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papouin, T.; Ladépêche, L.; Ruel, J.; Sacchi, S.; Labasque, M.; Hanini, M.; Groc, L.; Pollegioni, L.; Mothet, J.-P.; Oliet, S.H. Synaptic and Extrasynaptic NMDA Receptors Are Gated by Different Endogenous Coagonists. Cell 2012, 150, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, H.-H.; Lee, Y.-C.; Chen, M.-F.; Kuo, J.-S.; Lee, T.J.F. Sympathetic activation increases basilar arterial blood flow in normotensive but not hypertensive rats. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2012, 302, H1123–H1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chun-Kai, H.; Hsi-Hsien, C.; Shang-Jen, C.; Stephen, Y.S.; Kuo-Feng, H. Methyl palmitate modulates the nicotine-induced increase in basilar arterial blood flow. Microcirculation 2021, 28, e12686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, T.; Ayajiki, K.; Fujioka, H.; Toda, M.; Fujimiya, M.; Toda, N. Effects of endothelial impairment by saponin on the responses to vasodilators and nitrergic nerve stimulation in isolated canine corpus cavernosum. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 127, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senbel, A.M.; Hashad, A.; Sharabi, F.M.; Daabees, T.T. Activation of muscarinic receptors inhibits neurogenic nitric oxide in the corpus cavernosum. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 65, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vural, I.M.; Fincan, G.S.O.; Koc, D.S.; Okcay, Y.; Askin, C.I.; Kibar, A.K.; Ilhan, S.O.; Sarioglu, Y. Effects of cannabinoid and vanilloid receptor antagonists on nicotine induced relaxation response enhancement in rabbit corpus cavernosum. Iran J. Basic Med. Sci. 2022, 25, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ayajiki, K.; Hayashida, H.; Okamura, T.; Toda, N. Influence of denervation on neurogenic inhibitory response of corpus cavernosum and nitric oxide synthase histochemistry. Brain Res. 1999, 825, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salonia, A.; Eardley, I.; Giuliano, F.; Hatzichristou, D.; Moncada, I.; Vardi, Y.; Wespes, E.; Hatzimouratidis, K. European As-sociation of urology. European association of Urology Guidelines on Priapism. Eur. Urol. 2014, 65, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Edvinsson, L.; Lee, T.J. Mechanism of nicotine-induced relaxation in the porcine basilar artery. Experiment 1998, 284, 790–797. [Google Scholar]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.-W.; Chao, T.-C.; Lim, L.-Y.; Chang, H.-H.; Yang, S.S.-D. The Acute Effects and Mechanism of Ketamine on Nicotine-Induced Neurogenic Relaxation of the Corpus Cavernosum in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24086976
Li M-W, Chao T-C, Lim L-Y, Chang H-H, Yang SS-D. The Acute Effects and Mechanism of Ketamine on Nicotine-Induced Neurogenic Relaxation of the Corpus Cavernosum in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(8):6976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24086976
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ming-Wei, Tze-Chen Chao, Li-Yi Lim, Hsi-Hsien Chang, and Stephen Shei-Dei Yang. 2023. "The Acute Effects and Mechanism of Ketamine on Nicotine-Induced Neurogenic Relaxation of the Corpus Cavernosum in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 8: 6976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24086976
APA StyleLi, M.-W., Chao, T.-C., Lim, L.-Y., Chang, H.-H., & Yang, S. S.-D. (2023). The Acute Effects and Mechanism of Ketamine on Nicotine-Induced Neurogenic Relaxation of the Corpus Cavernosum in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(8), 6976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24086976





