Differential Expression of ATM, NF-KB, PINK1 and Foxo3a in Radiation-Induced Basal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
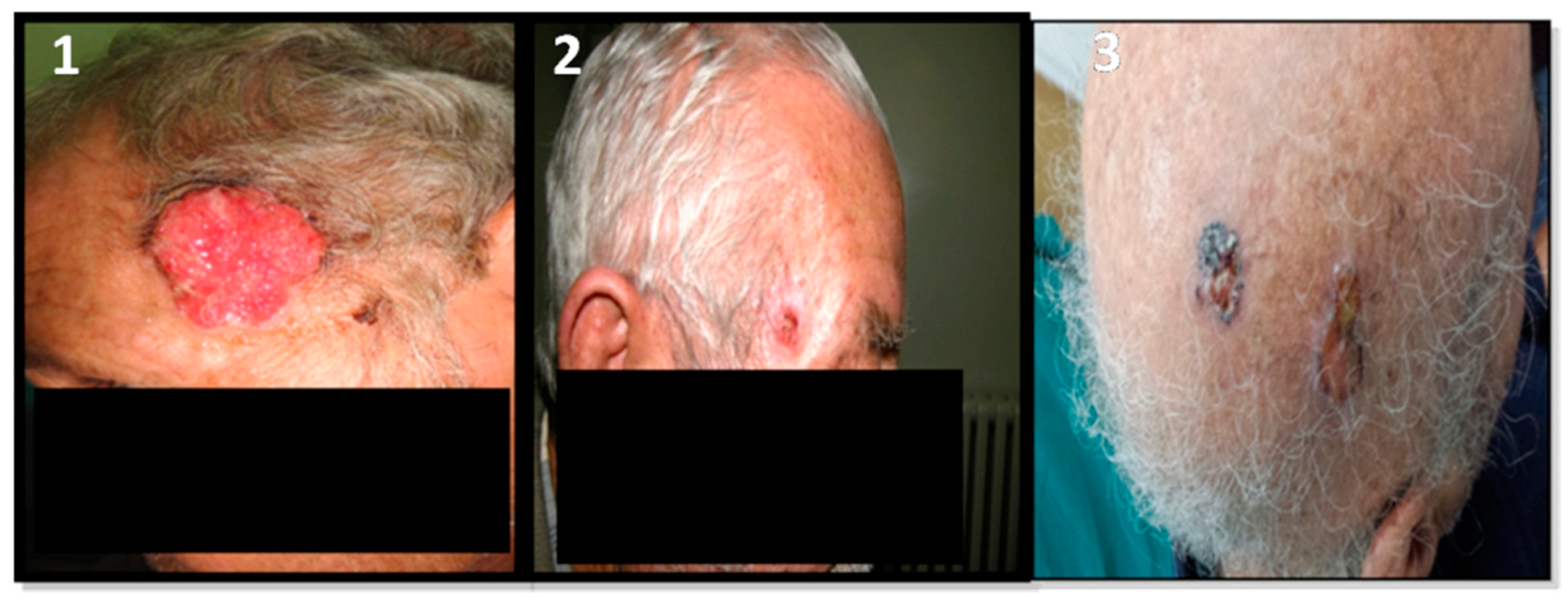
2.1. Clinical Features of BCC Patients
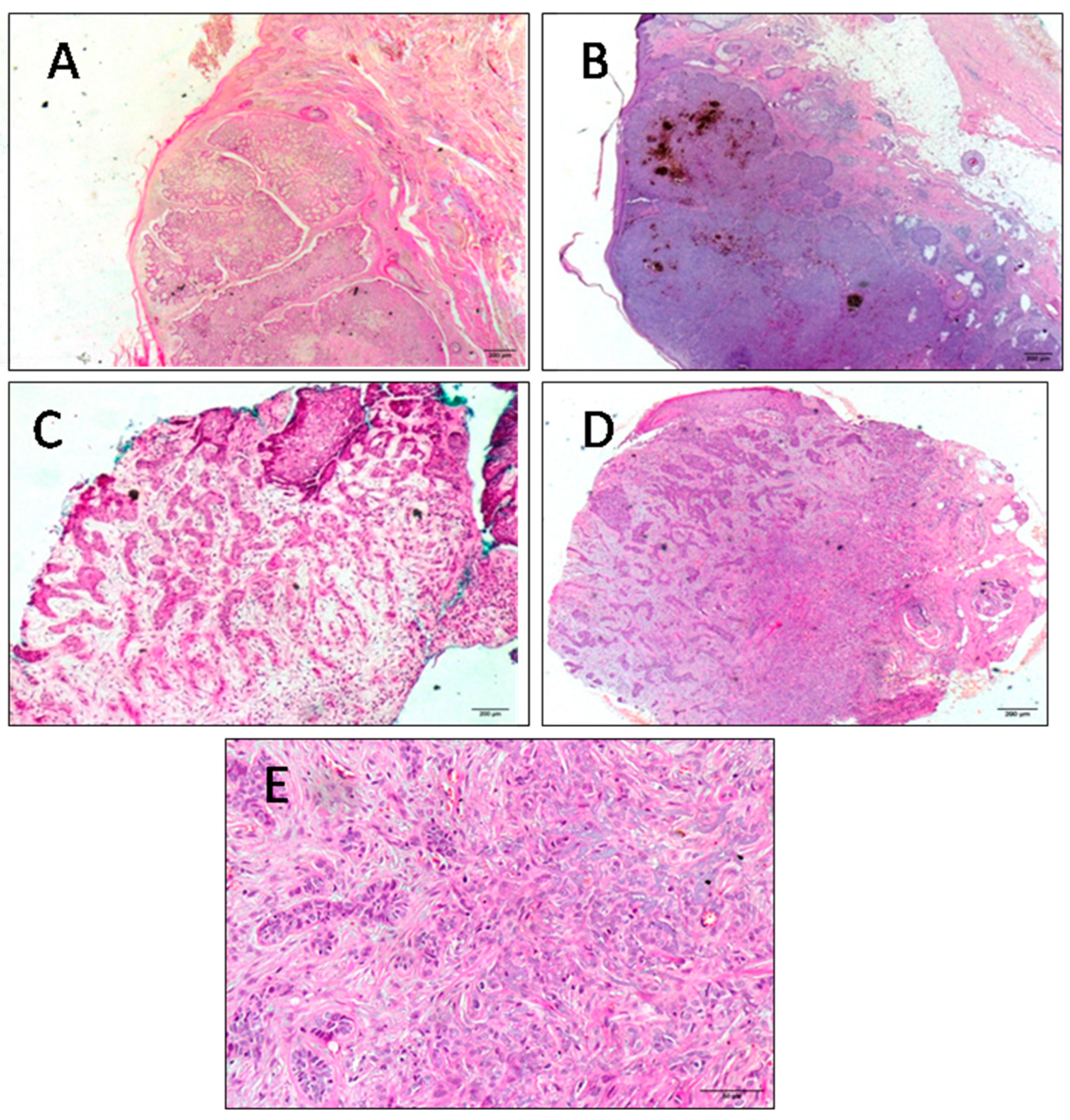
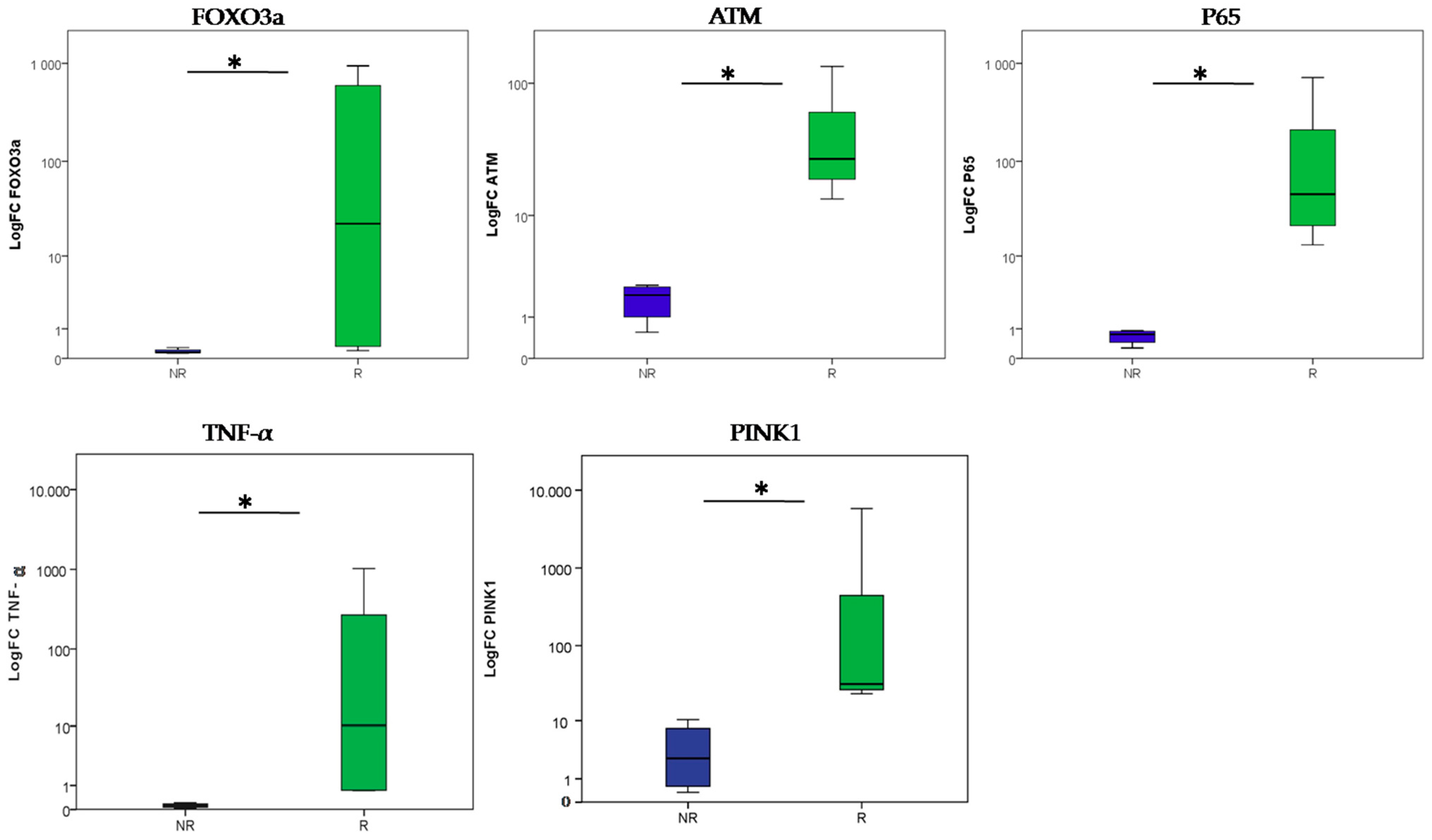
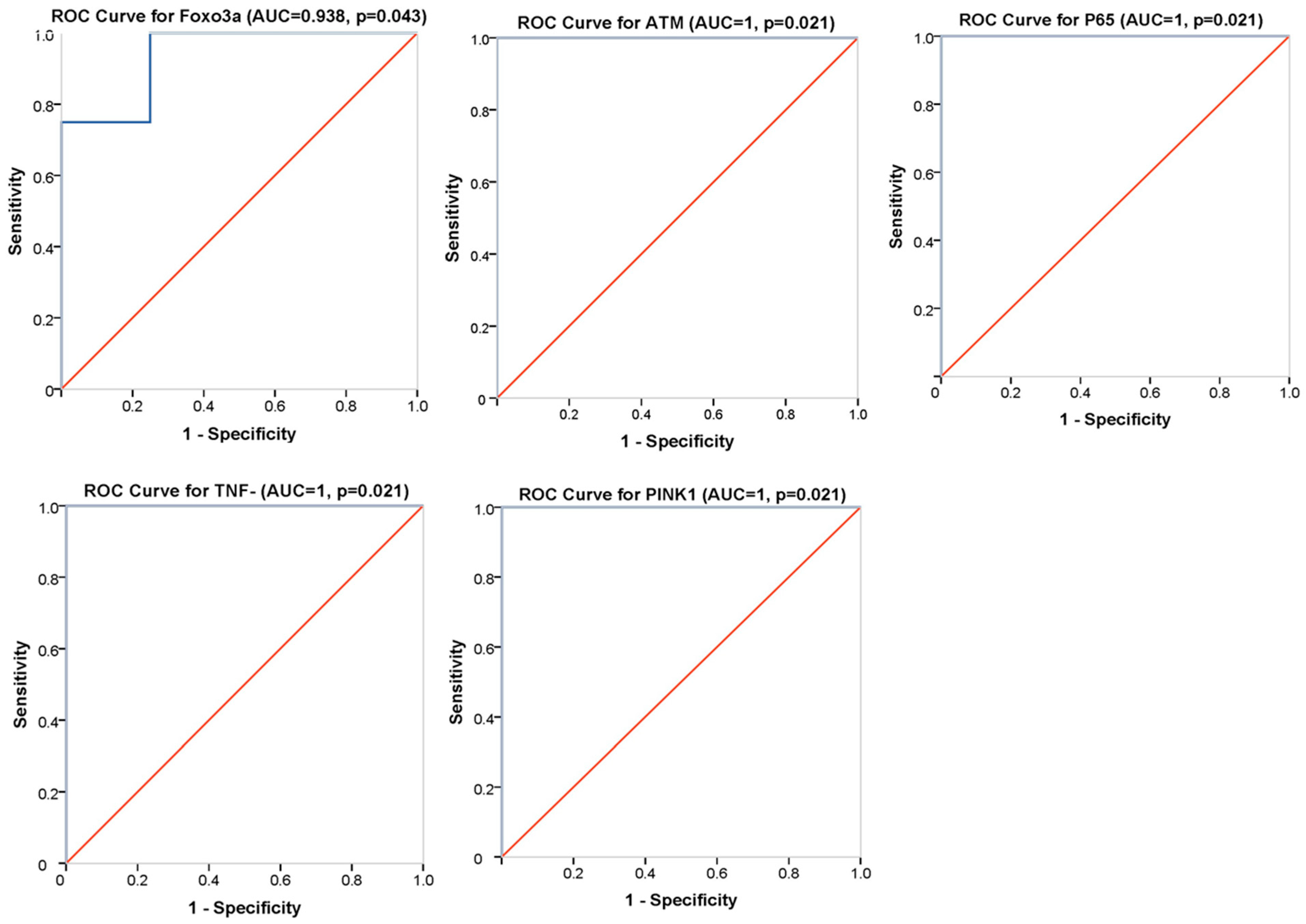
2.2. Molecular Analysis
2.3. Bioinformatic Analysis
3. Discussion
- -
- Clinical features of radio-induced BCC and non-radio-induced BCC
- -
- Gene expression analysis to decipher radio-induced BCC carcinogenesis mechanisms
- -
- ATM-NF-kB signaling and PINK1-mediated mitophagy in response to irradiation
- -
- Biomarkers of radio-induced BCC
- -
- miRNA regulators in BCC radiation carcinogenesis
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human Specimens and Sample Collection
4.2. Gene Expression Analysis
4.2.1. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
4.2.2. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.3. Statistical Analysis
4.4. Bioinformatic Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fania, L.; Didona, D.; Morese, R.; Campana, I.; Coco, V.; Di Pietro, F.R.; Ricci, F.; Pallotta, S.; Candi, E.; Abeni, D.; et al. Basal Cell Carcinoma: From Pathophysiology to Novel Therapeutic Approaches. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Cancer Observatory. Estimated Number of New Cases in 2020, World, Both Sexes, All Ages. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/online-analysis-table (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- McKeown, S.R.; Hatfield, P.; Prestwich, R.J.; Shaffer, R.E.; Taylor, R.E. Radiotherapy for benign disease; assessing the risk of radiation-induced cancer following exposure to intermediate dose radiation. Br. J. Radiol. 2015, 88, 20150405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ron, E.; Modan, B.; Preston, D.; Alfandary, E.; Stovall, M.; Boice, J.D., Jr. Radiation-induced skin carcinomas of the head and neck. Radiat. Res. 1991, 125, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichter, M.D.; Karagas, M.R.; Mott, L.A.; Spencer, S.K.; Stukel, T.A.; Greenberg, E.R. Therapeutic ionizing radiation and the incidence of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. The New Hampshire Skin Cancer Study Group. Arch. Dermatol. 2000, 136, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ekmekçi, P.; Bostanci, S.; Anadolu, R.; Erdem, C.; Gürgey, E. Multiple basal cell carcinomas developed after radiation therapy for tinea capitis: A case report. Dermatol. Surg. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Dermatol. Surg. 2001, 27, 667–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour, S.E.; Kalantar-Hormozi, A.; Motamed, S.; Moosavizadeh, S.M.; Shahverdiani, R. Basal cell carcinoma of scalp in patients with history of childhood therapeutic radiation: A retrospective study and comparison to nonirradiated patients. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2006, 57, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsness, S.L.; Freites-Martinez, A.; Marchetti, M.A.; Navarrete-Dechent, C.; Lacouture, M.E.; Tonorezos, E.S. Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer in Childhood and Young Adult Cancer Survivors Previously Treated With Radiotherapy. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. JNCCN 2019, 17, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oshinsky, S.; Baum, S.; Huszar, M.; Debby, A.; Barzilai, A. Basal cell carcinoma induced by therapeutic radiation for tinea capitis-clinicopathological study. Histopathology 2018, 73, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilla, X.; Parmentier, L.; King, B.; Bezrukov, F.; Kaya, G.; Zoete, V.; Seplyarskiy, V.B.; Sharpe, H.J.; McKee, T.; Letourneau, A.; et al. Genomic analysis identifies new drivers and progression pathways in skin basal cell carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, A.; Chaudhary, S.C.; Rana, M.; Elmets, C.A.; Athar, M. Basal cell carcinoma pathogenesis and therapy involving hedgehog signaling and beyond. Mol. Carcinog. 2017, 56, 2543–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardoso, J.C.; Ribeiro, I.P.; Caramelo, F.; Tellechea, O.; Barbosa de Melo, J.; Marques Carreira, I. Basal cell carcinomas of the scalp after radiotherapy for tinea capitis in childhood: A genetic and epigenetic study with comparison with basal cell carcinomas evolving in chronically sun-exposed areas. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 1126–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessone, A.; Amariglio, N.; Weissman, O.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Liran, A.; Stavrou, D.; Haik, J.; Orenstein, A.; Winkler, E. Radiotherapy-induced basal cell carcinomas of the scalp: Are they genetically different? Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2012, 36, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Athar, M. Ionizing Radiation Exposure and Basal Cell Carcinoma Pathogenesis. Radiat. Res. 2016, 185, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fleenor, C.J.; Higa, K.; Weil, M.M.; DeGregori, J. Evolved Cellular Mechanisms to Respond to Genotoxic Insults: Implications for Radiation-Induced Hematologic Malignancies. Radiat. Res. 2015, 184, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lesluyes, T.; Baud, J.; Perot, G.; Charon-Barra, C.; You, A.; Valo, I.; Bazille, C.; Mishellany, F.; Leroux, A.; Renard-Oldrini, S. Genomic and transcriptomic comparison of post-radiation versus sporadic sarcomas. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 1786–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maenhaut, C.; Detours, V.; Dom, G.; Handkiewicz-Junak, D.; Oczko-Wojciechowska, M.; Jarzab, B. Gene expression profiles for radiation-induced thyroid cancer. Clin. Oncol. R Coll. Radiol. 2011, 23, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Saenko, V.; Yamashita, S.; Mitsutake, N. Radiation-Induced Thyroid Cancers: Overview of Molecular Signatures. Cancers 2019, 11, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thiagarajan, A.; Iyer, N. Radiation-induced sarcomas of the head and neck. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 5, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detours, V.; Wattel, S.; Venet, D.; Hutsebaut, N.; Bogdanova, T.; Tronko, M.D.; Dumont, J.E.; Franc, B.; Thomas, G.; Maenhaut, C. Absence of a specific radiation signature in post-Chernobyl thyroid cancers. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Story, M.; Legerski, R. Cellular responses to ionizing radiation damage. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2001, 49, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; You, L.; Xue, J.; Lu, Y. Ionizing Radiation-Induced Cellular Senescence in Normal, Non-transformed Cells and the Involved DNA Damage Response: A Mini Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averbeck, D.; Rodriguez-Lafrasse, C. Role of Mitochondria in Radiation Responses: Epigenetic, Metabolic, and Signaling Impacts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, M.; Motevaseli, E.; Shirazi, A.; Geraily, G.; Rezaeyan, A.; Norouzi, F.; Rezapoor, S.; Abdollahi, H. Mechanisms of inflammatory responses to radiation and normal tissues toxicity: Clinical implications. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2018, 94, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzam, E.I.; Jay-Gerin, J.; Pain, D. Ionizing radiation-induced metabolic oxidative stress and prolonged cell injury. Cancer Lett. 2012, 327, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Classen, F.; Kranz, P.; Riffkin, H.; Pompsch, M.; Wolf, A.; Göpelt, K.; Baumann, M.; Baumann, J.; Brockmeier, U.; Metzen, E. Autophagy induced by ionizing radiation promotes cell death over survival in human colorectal cancer cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 374, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, A.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Di, C.; Sun, C. microRNA expression and biogenesis in cellular response to ionizing radiation. DNA Cell Biol. 2014, 33, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Cui, J.; Gong, Y.; Wei, S.; Wei, Y.; Yi, L. MicroRNA: A novel implication for damage and protection against ionizing radiation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 15584–15596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Wang, Z. MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Ionizing Radiation Injury. Front Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 861451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.Q.; To, N.H.; Zadigue, P.; Kerbrat, S.; De La Taille, A.; Le Gouvello, S.; Belkacemi, Y. Ionizing radiation-induced cellular senescence promotes tissue fibrosis after radiotherapy. A review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2018, 129, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Cao, K.; Xia, Y.; Li, Y.; Hou, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Chang, L.; Li, W. Cellular senescence in ionizing radiation (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkouteren, J.A.C.; Ramdas, K.H.R.; Wakkee, M.; Nijsten, T. Epidemiology of basal cell carcinoma: Scholarly review. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basset-Seguin, N.; Herms, F. Update in the Management of Basal Cell Carcinoma. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2020, 100, adv00140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, C.; Maturo, M.G.; Di Nardo, L.; Ciciarelli, V.; Gutiérrez García-Rodrigo, C.; Fargnoli, M.C. Understanding the Molecular Genetics of Basal Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shore, R.E.; Moseson, M.; Xue, X.; Tse, Y.; Harley, N.; Pasternack, B.S. Skin cancer after X-ray treatment for scalp ringworm. Radiat. Res. 2002, 157, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, N.; Sharma, A.; Singh, C.; Pandia, K.; Gupta, A. Adenoid basal cell carcinoma: A rare variant and a diagnostic dilemma. Clin. Dermatol. Rev. 2021, 5, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarallo, M.; Cigna, E.; Frati, R.; Delfino, S.; Innocenzi, D.; Fama, U.; Corbianco, A.; Scuderi, N. Metatypical basal cell carcinoma: A clinical review. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 27, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conforti, C.; Pizzichetta, M.A.; Vichi, S.; Toffolutti, F.; Serraino, D.; Di Meo, N.; Giuffrida, R.; Deinlein, T.; Giacomel, J.; Rosendahl, C.; et al. Sclerodermiform basal cell carcinomas vs. other histotypes: Analysis of specific demographic, clinical and dermatoscopic features. J. Eur. Acad Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, B.; Badri, T.; Steele, R.B. Basal Cell Carcinoma; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Peris, K.; Fargnoli, M.C.; Garbe, C.; Kaufmann, R.; Bastholt, L.; Seguin, N.B.; Bataille, V.; Marmol, V.D.; Dummer, R.; Harwood, C.A.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of basal cell carcinoma: European consensus-based interdisciplinary guidelines. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 118, 10–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grob, J.J.; Gaudy-Marqueste, C.; Guminski, A.; Malvehy, J.; Basset-Seguin, N.; Bertrand, B.; Fernandez-Penas, P.; Kaufmann, R.; Zalaudek, I.; Fargnoli, M.C.; et al. Position statement on classification of basal cell carcinomas. Part 2: EADO proposal for new operational staging system adapted to basal cell carcinomas. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 2149–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaraa, I.; Ben Taazayet, S.; Zribi, H.; Chelly, I.; El Euch, D.; Trojjet, S.; Mokni, M.; Haouet, S.; Ben Osman, A. Cutaneous carcinoma induced by radiotherapy: A report of 31 cases. Tunis. Med. 2013, 91, 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno, T.; Tokuoka, S.; Kishikawa, M.; Nakashima, E.; Mabuchi, K.; Iwamoto, K.S. Molecular basis of basal cell carcinogenesis in the atomic-bomb survivor population: p53 and PTCH gene alterations. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 2286–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pazzaglia, S.; Mancuso, M.; Tanori, M.; Atkinson, M.J.; Merola, P.; Rebessi, S.; Di Majo, V.; Covelli, V.; Hahn, H.; Saran, A. Modulation of patched-associated susceptibility to radiation induced tumorigenesis by genetic background. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3798–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaudhary, S.C.; Tang, X.; Arumugam, A.; Li, C.; Srivastava, R.K.; Weng, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Kim, A.L.; McKay, K.; et al. Shh and p50/Bcl3 signaling crosstalk drives pathogenesis of BCCs in Gorlin syndrome. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 36789–36814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naruke, Y.; Nakashima, M.; Suzuki, K.; Kondo, H.; Hayashi, T.; Soda, M.; Sekine, I. Genomic instability in the epidermis induced by atomic bomb (A-bomb) radiation: A long-lasting health effect in A-bomb survivors. Cancer 2009, 115, 3782–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boaventura, P.; Pereira, D.; Mendes, A.; Batista, R.; da Silva, A.F.; Guimarães, I.; Honavar, M.; Teixeira-Gomes, J.; Lopes, J.M.; Máximo, V.; et al. Mitochondrial D310 D-Loop instability and histological subtypes in radiation-induced cutaneous basal cell carcinomas. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2014, 73, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, A. Activation of DNA damage response signaling in mammalian cells by ionizing radiation. Free Radic. Res. 2021, 55, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.B.; Chung, Y.M.; Takahashi, Y.; Xu, Z.; Hu, M.C. Functional interaction between FOXO3a and ATM regulates DNA damage response. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yalcin, S.; Zhang, X.; Luciano, J.P.; Mungamuri, S.K.; Marinkovic, D.; Vercherat, C.; Sarkar, A.; Grisotto, M.; Taneja, R.; Ghaffari, S. Foxo3 is essential for the regulation of ataxia telangiectasia mutated and oxidative stress-mediated homeostasis of hematopoietic stem cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25692–25705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, R.R.; Maslov, A.Y.; Lee, M.; Wilner, S.E.; Levy, M.; Vijg, J. FOXO3a acts to suppress DNA double-strand break-induced mutations. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarrade, S.; Bhardwaj, T.; Flegal, M.; Bertrand, L.; Velegzhaninov, I.; Moskalev, A.; Klokov, D. Histone H2AX is involved in FoxO3a-mediated transcriptional responses to ionizing radiation to maintain genome stability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 29996–30014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trémezaygues, L.; Seifert, M.; Vogt, T.; Tilgen, W.; Reichrath, J. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 modulates effects of ionizing radiation (IR) on human keratinocytes: In vitro analysis of cell viability/proliferation, DNA-damage and -repair. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 121, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warters, R.L.; Packard, A.T.; Kramer, G.F.; Gaffney, D.K.; Moos, P.J. Differential gene expression in primary human skin keratinocytes and fibroblasts in response to ionizing radiation. Radiat. Res. 2009, 172, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhu, L.; Wang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Xiong, N.; Bao, H.; Jin, W. Ionizing radiation promotes CCL27 secretion from keratinocytes through the cross talk between TNF-α and ROS. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2016, 31, e21868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, T.; Shimada, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Okino, A. DNA Damage Response After Ionizing Radiation Exposure in Skin Keratinocytes Derived from Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, M.; Hong, D.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, X. The Paradoxical Role of Cellular Senescence in Cancer. Front Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 722205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimura, T. ATM-Mediated Mitochondrial Radiation Responses of Human Fibroblasts. Genes 2021, 12, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, W.W.-Y.; Banati, R. Effects of ionizing radiation on mitochondria. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, K.; Qi, F.; Kobayashi, J. Potential relationship between the biological effects of low-dose irradiation and mitochondrial ROS production. J. Radiat. Res. 2018, 59 (Suppl. S2), ii91–ii97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawamura, K.; Qi, F.; Kobayashi, J. Lead (Pb) induced ATM-dependent mitophagy via PINK1/Parkin pathway. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 291, 92–100. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, A.; Stellrecht, C.M.; Vangapandu, H.V.; Ayres, M.; Kaipparettu, B.A.; Park, J.H.; Balakrishnan, K.; Burks, J.K.; Pandita, T.K.; Hittelman, W.N. Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated interacts with Parkin and induces mitophagy independent of kinase activity. Evidence from mantle cell lymphoma. Haematologica 2021, 106, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, Y.; Qiu, Q.; Gu, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y. ATM mediates spermidine-induced mitophagy via PINK1 and Parkin regulation in human fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shimura, T.; Kobayashi, J.; Komatsu, K.; Kunugita, N. Severe mitochondrial damage associated with low-dose radiation sensitivity in ATM- and NBS1-deficient cells. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Xie, W.; Mak, T.W.; You, H. FOXO3a-dependent regulation of Pink1 (Park6) mediates survival signaling in response to cytokine deprivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5153–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaurasia, M.; Bhatt, A.N.; Das, A.; Dwarakanath, B.S.; Sharma, K. Radiation-induced autophagy: Mechanisms and consequences. Free Radic. Res. 2016, 50, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Zaharieva, E.K.; Sasatani, M.; Kobayashi, J. Possible relationship between mitochondrial changes and oxidative stress under low dose-rate irradiation. Redox Rep. 2021, 26, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mito, J.K.; Qian, X.; Jo, V.Y.; Doyle, L.A. MYC expression has limited utility in the distinction of undifferentiated radiation-associated sarcomas from sporadic sarcomas and sarcomatoid carcinoma. Histopathology 2020, 77, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boerma, M.; Davis, C.M.; Jackson, I.L.; Schaue, D.; Williams, J.P. All for one, though not one for all: Team players in normal tissue radiobiology. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2022, 98, 346–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Kusunoki, Y.; Hakoda, M.; Morishita, Y.; Kubo, Y.; Maki, M.; Kasagi, F.; Kodama, K.; Macphee, D.G.; Kyoizumi, S. Radiation dose-dependent increases in inflammatory response markers in A-bomb survivors. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2003, 79, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Morishita, Y.; Khattree, R.; Misumi, M.; Sasaki, K.; Hayashi, I.; Yoshida, K.; Kajimura, J.; Kyoizumi, S.; Imai, K.; et al. Evaluation of systemic markers of inflammation in atomic-bomb survivors with special reference to radiation and age effects. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 4765–4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukherjee, S.; Laiakis, E.C.; Fornace, A.J., Jr.; Amundson, S.A. Impact of inflammatory signaling on radiation biodosimetry: Mouse model of inflammatory bowel disease. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Furukawa, K.; Morishita, Y.; Hayashi, I.; Kato, N.; Yoshida, K.; Kusunoki, Y.; Kyoizumi, S.; Ohishi, W. Intracellular reactive oxygen species level in blood cells of atomic bomb survivors is increased due to aging and radiation exposure. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 171, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuu-Matsuyama, M.; Shichijo, K.; Okaichi, K.; Kurashige, T.; Kondo, H.; Miura, S.; Nakashima, M. Effect of age on the sensitivity of the rat thyroid gland to ionizing radiation. J. Radiat. Res. 2015, 56, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kraemer, A.; Anastasov, N.; Angermeier, M.; Winkler, K.; Atkinson, M.J.; Moertl, S. MicroRNA-mediated processes are essential for the cellular radiation response. Radiat. Res. 2011, 176, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatkowska, M.; Krupa, R. Regulation of DNA Damage Response and Homologous Recombination Repair by microRNA in Human Cells Exposed to Ionizing Radiation. Cancers 2020, 12, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rzeszowska-Wolny, J.; Hudy, D.; Biernacki, K.; Ciesielska, S.; Jaksik, R. Involvement of miRNAs in cellular responses to radiation. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2022, 98, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iizuka, D.; Imaoka, T.; Nishimura, M.; Kawai, H.; Suzuki, F.; Shimada, Y. Aberrant microRNA expression in radiation-induced rat mammary cancer: The potential role of miR-194 overexpression in cancer cell proliferation. Radiat. Res. 2013, 179, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.S.; Choi, Y.E.; Hwang, S.J.; Han, Y.H.; Park, M.J.; Bae, I.H. IL-4, a direct target of miR-340/429, is involved in radiation-induced aggressive tumor behavior in human carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 86836–86856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, P.; Sun, M.; Gao, F.; Liu, C.; Cai, J. Down regulation of miR200c promotes radiation-induced thymic lymphoma by targeting BMI1. J. Cell Biochem. 2014, 115, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, N.; Tang, Q.; Sheng, H.; Long, S.; Wu, W. MicroRNA-24 in Cancer: A Double Side Medal With Opposite Properties. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 553714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, R.; Xu, T.; Wu, W.; Zhang, R.; Wang, C.; Huang, H.; Calin, C.A.; Yang, H.; et al. Hsa-miR-24-3p increases nasopharyngeal carcinoma radiosensitivity by targeting both the 3’UTR and 5’UTR of Jab1/CSN5. Oncogene 2016, 35, 6096–6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lal, A.; Kim, H.H.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Kuwano, Y.; Pullmann, R., Jr.; Srikantan, S.; Subrahmanyam, R.; Martindale, J.L.; Yang, X.; Ahmed, F.; et al. p16(INK4a) translation suppressed by miR-24. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khorsandi, S.E.; Salehi, S.; Cortes, M.; Vilca-Melendez, H.; Menon, K.; Srinivasan, P.; Prachalias, A.; Jassem, W.; Heaton, N. An in silico argument for mitochondrial microRNA as a determinant of primary non function in liver transplantation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oladejo, A.O.; Li, Y.; Imam, B.H.; Ma, X.; Shen, W.; Wu, X.; Jiang, W.; Yang, J.; Lv, Y.; Ding, X.; et al. MicroRNA miR-24-3p Mediates the Negative Regulation of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Endometrial Inflammatory Response by Targeting TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 6 (TRAF6). J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 807–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Tang, S.; Nie, X.; Zhou, Z.; Ruan, G.; Han, W.; Zhu, Z.; Ding, C. Decreased miR-214-3p activates NF-κB pathway and aggravates osteoarthritis progression. EBioMedicine 2021, 65, 103283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, M.; Jinnin, M.; Wang, Z.; Hirano, A.; Tomizawa, Y.; Kira, T.; Igata, T.; Masuguchi, S.; Fukushima, S.; Ihn, H. The expression of miR-124 increases in aged skin to cause cell senescence and it decreases in squamous cell carcinoma. Biosci. Trends 2017, 10, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saleh, A.D.; Savage, J.E.; Cao, L.; Soule, B.P.; Ly, D.; DeGraff, W.; Harris, C.C.; Mitchell, J.B.; Simone, N.L. Cellular stress induced alterations in microRNA let-7a and let-7b expression are dependent on p53. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.; Lan, J.; Ge, J.; Nie, Q.; Guo, L.; Qiu, Y.; Mao, Q. MiR-26a enhances the radiosensitivity of glioblastoma multiforme cells through targeting of ataxia-telangiectasia mutated. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 320, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Ng, W.L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Mo, Y.Y.; Mao, H.; Hao, C.; Olson, J.J.; Curran, W.J.; et al. Targeting DNA-PKcs and ATM with miR-101 sensitizes tumors to radiation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmings, K.E.; Riches-Suman, K.; Bailey, M.A.; O’Regan, D.J.; Turner, N.A.; Porter, K.E. Role of MicroRNA-145 in DNA Damage Signalling and Senescence in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells of Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Cells 2021, 10, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Gao, Y. The p53/miR-145a Axis Promotes Cellular Senescence and Inhibits Osteogenic Differentiation by Targeting Cbfb in Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Front Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 609186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand, M.; Hessam, S.; Amur, S.; Skrygan, M.; Bromba, M.; Stockfleth, E.; Gambichler, T.; Bechara, F.G. Expression of oncogenic miR-17-92 and tumor suppressive miR-143-145 clusters in basal cell carcinoma and cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 86, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Scheiber, M.N.; Neumann, C.; Calin, G.A.; Zhou, D. MicroRNA regulation of ionizing radiation-induced premature senescence. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 81, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rivetti di Val Cervo, P.; Lena, A.M.; Nicoloso, M.; Rossi, S.; Mancini, M.; Zhou, H.; Saintigny, G.; Dellambra, E.; Odorisio, T.; Mahé, C.; et al. p63-microRNA feedback in keratinocyte senescence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaudhry, M.A.; Omaruddin, R.A.; Brumbaugh, C.D.; Tariq, M.A.; Pourmand, N. Identification of radiation-induced microRNA transcriptome by next-generation massively parallel sequencing. J. Radiat. Res. 2013, 54, 808–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naito, Y.; Oue, N.; Pham, T.T.; Yamamoto, M.; Fujihara, M.; Ishida, T.; Mukai, S.; Sentani, K.; Sakamoto, N.; Hida, E.; et al. Characteristic miR-24 Expression in Gastric Cancers among Atomic Bomb Survivors. Pathobiology 2015, 82, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

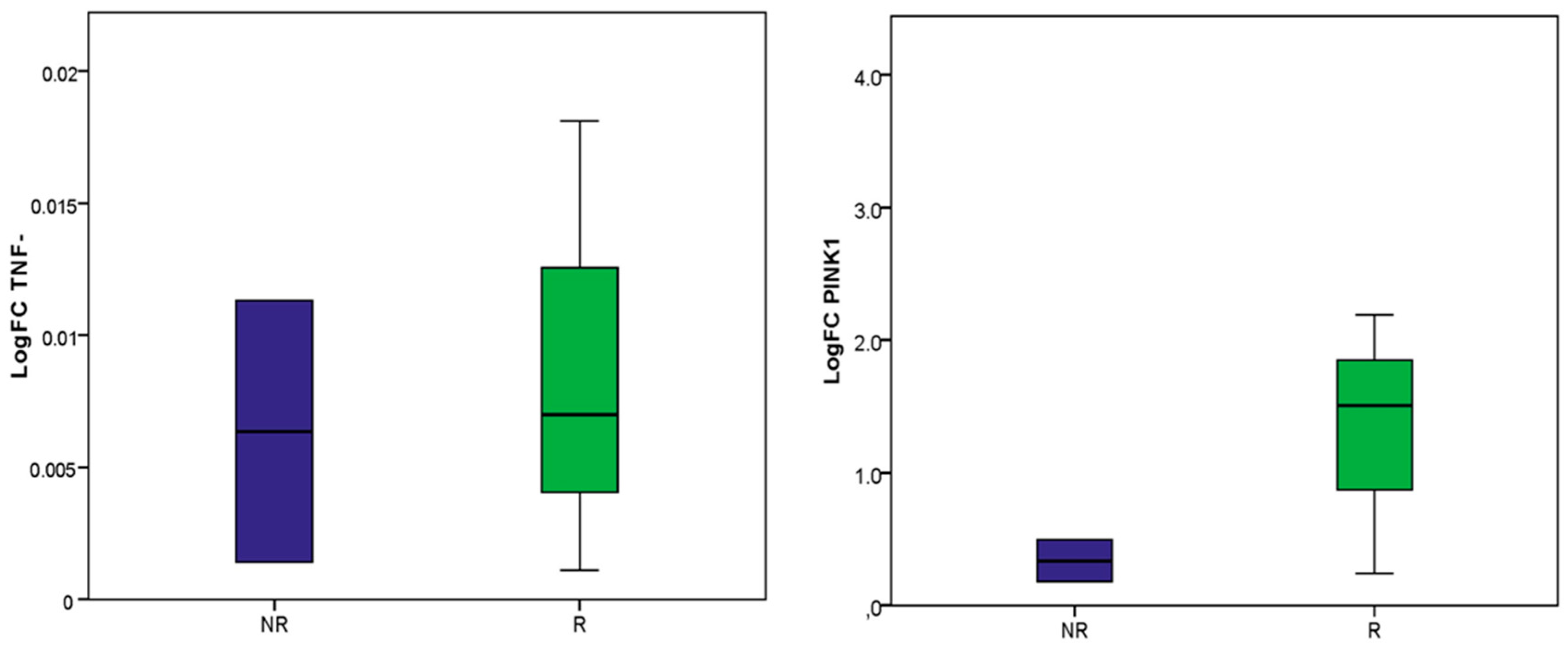
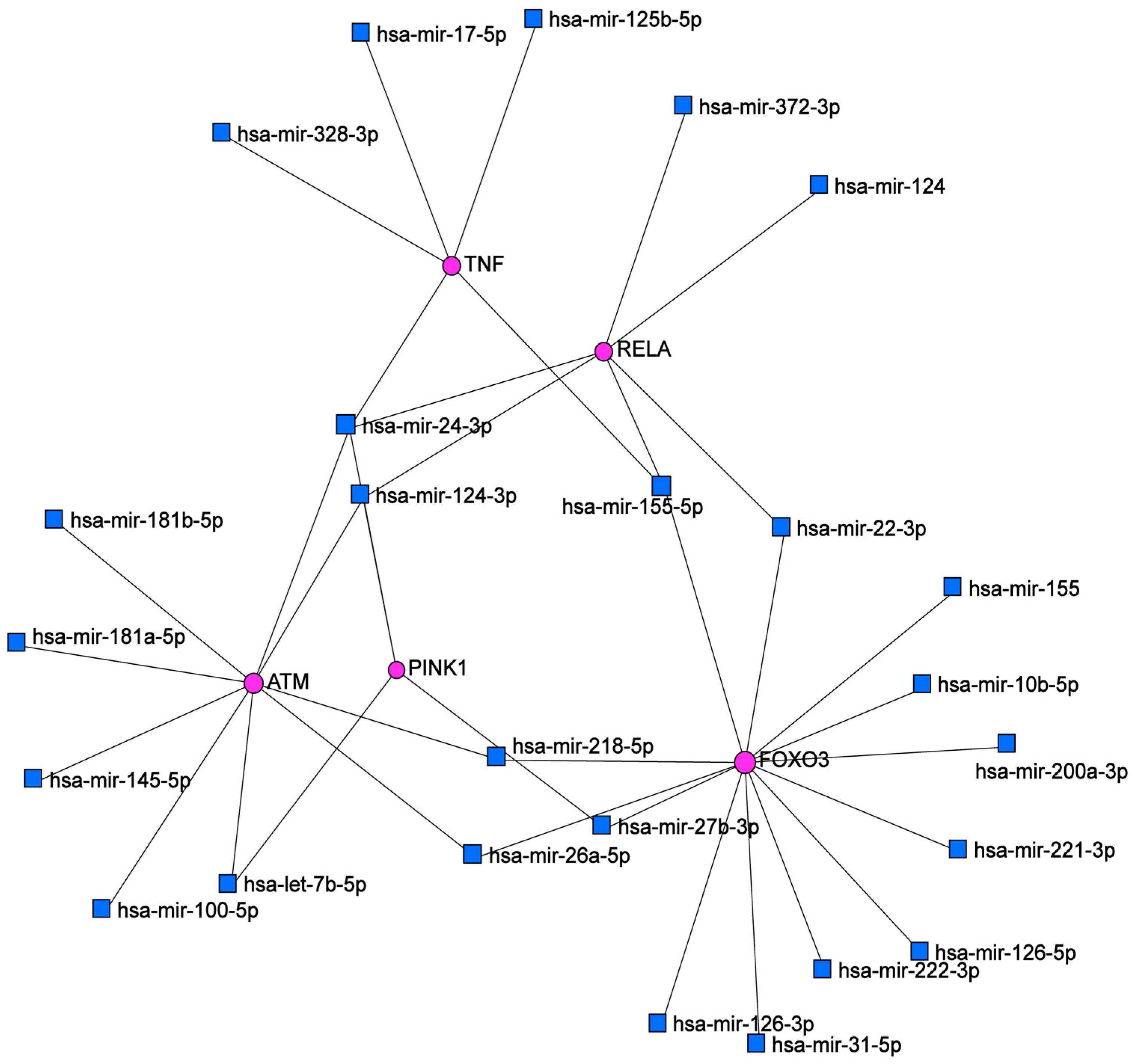
| Patient | Gender | Ethnicity | Age | History of Radiotherapy | Histology | Tumor Size | Multifocality | Tumor Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCC2 | M | Tunisia | 60 | Yes | Adenoid | 3 cm | Yes (n = 7) | Temporal region of the face |
| BCC4 | M | Tunisia | 60 | Yes | Adenoid | 3 cm | Yes (n = 2) | Temporal region of the face |
| BCC5 | M | Tunisia | 79 | No | Adenoid | 1 cm | Yes (n = 3) | Temporal region of the face |
| BCC8 | M | Tunisia | 85 | Yes | Nodular | 2.5 cm | No | Scalp |
| BCC12 | F | Tunisia | 63 | No | Nodular | 3 cm | Yes (n = 2) | Ala of nose |
| BCC16 | M | Tunisia | 40 | No | Nodular | 3 cm | No | Ala of nose |
| BCC19 | M | Tunisia | 80 | No | Nodular | 3 cm | No | Cheek |
| BCC22 | M | Tunisia | 60 | Yes | Nodular | 2 cm | Yes (n = 2) | Scalp |
| Node | Degree |
|---|---|
| FOXO3a | 13 |
| ATM | 9 |
| RELA | 6 |
| TNF | 5 |
| hsa-mir-24-3p | 4 |
| PINK1 | 4 |
| hsa-mir-124-3p | 3 |
| hsa-mir-155-5p | 3 |
| hsa-mir-26a-5p | 2 |
| hsa-mir218-5p | 2 |
| hsa-mir-27b-3p | 2 |
| hsa-mir-22b-3p | 2 |
| hsa-mir-22b | 2 |
| hsa-mir-let-7b-5p | 3 |
| Gene | Sequence (5’-3’) | Length | Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FOXO3a | F: CGGACAAACGGCTCACTCT R: GGACCCGCATGAATCGACTAT | 19 21 | 61.9 61.7 |
| ATM | F: GCACGAAGTGCCTCCAATTC R: ACATTCTGGCACGCTTTGG | 21 19 | 61.1 61.4 |
| TNF-α | F: CCTCTCTCTAATCAGCCCTCTG R: GAGGACCTGGGAGTAGATGAG | 22 21 | 62.1 62.8 |
| PINK1 | F: CCCAAGCAACTAGCCCCTC R: GGCAGCACATCAGGGTAGTC | 19 20 | 64.5 63.1 |
| P65 | F: ATGTGGAGATCATTGAGCAGC R: CCTGGTCCTGTGTAGCCATT | 21 20 | 60 60.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jenni, R.; Chikhaoui, A.; Nabouli, I.; Zaouak, A.; Khanchel, F.; Hammami-Ghorbel, H.; Yacoub-Youssef, H. Differential Expression of ATM, NF-KB, PINK1 and Foxo3a in Radiation-Induced Basal Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087181
Jenni R, Chikhaoui A, Nabouli I, Zaouak A, Khanchel F, Hammami-Ghorbel H, Yacoub-Youssef H. Differential Expression of ATM, NF-KB, PINK1 and Foxo3a in Radiation-Induced Basal Cell Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(8):7181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087181
Chicago/Turabian StyleJenni, Rim, Asma Chikhaoui, Imen Nabouli, Anissa Zaouak, Fatma Khanchel, Houda Hammami-Ghorbel, and Houda Yacoub-Youssef. 2023. "Differential Expression of ATM, NF-KB, PINK1 and Foxo3a in Radiation-Induced Basal Cell Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 8: 7181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087181
APA StyleJenni, R., Chikhaoui, A., Nabouli, I., Zaouak, A., Khanchel, F., Hammami-Ghorbel, H., & Yacoub-Youssef, H. (2023). Differential Expression of ATM, NF-KB, PINK1 and Foxo3a in Radiation-Induced Basal Cell Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(8), 7181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087181






