Exercise-Induced Fibroblast Growth Factor-21: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Search Strategy and Selection of Studies
2.2.1. Inclusion Criteria
- Participants:
- 2.
- Intervention:
- 3.
- Comparisons:
- 4.
- Outcomes:
- 5.
- Types of studies:
2.2.2. Exclusion Criteria
2.2.3. Strategy for Literature Search
2.2.4. Study Selection and Data Extraction
2.2.5. Quality Assessment
2.3. Strategy for Data Synthesis
3. Results
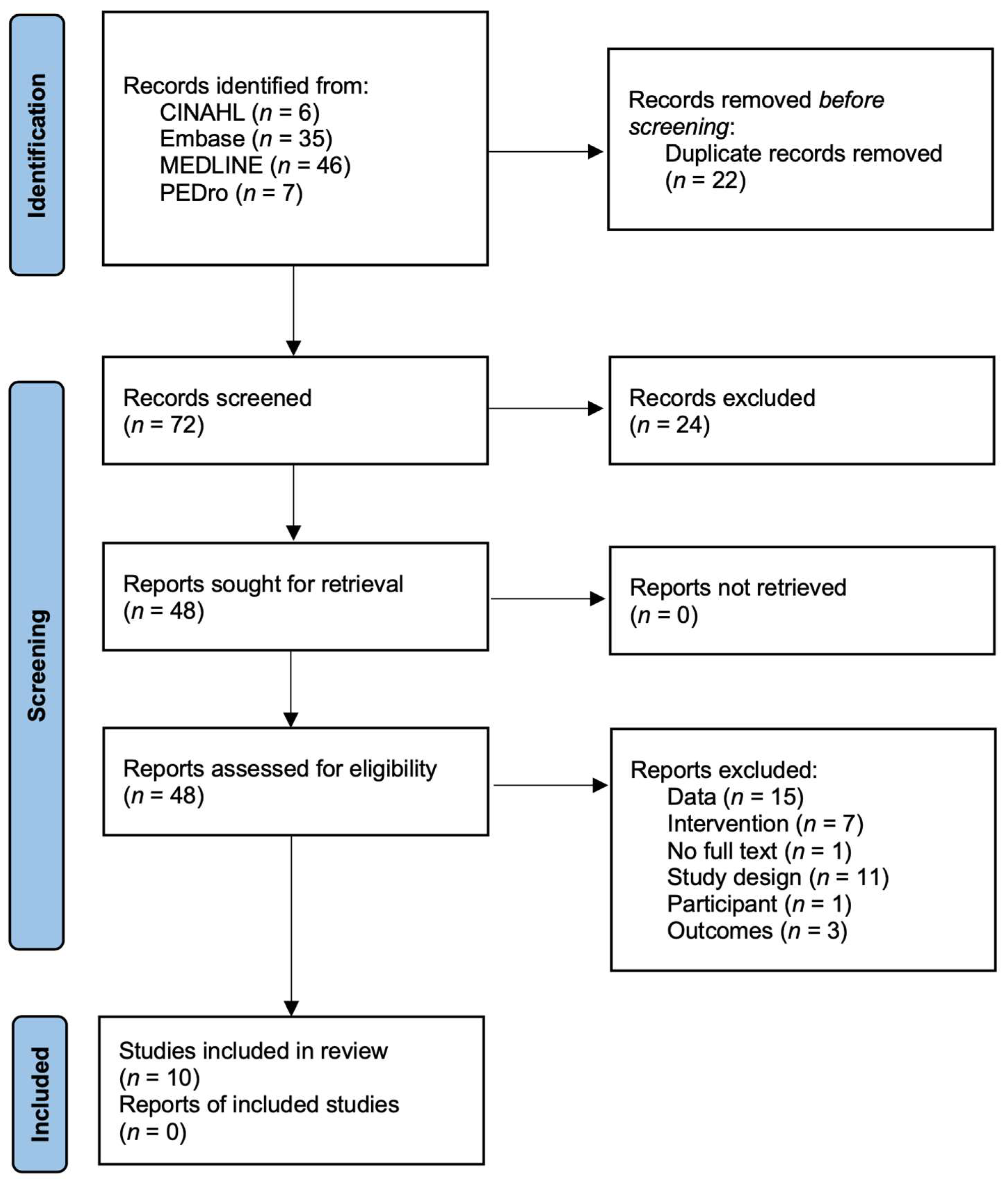
3.1. The Literature Search and Characteristics of the Included Trials
3.2. Methodological Quality Assessment of Studies on Exercise-Induced FGF-21
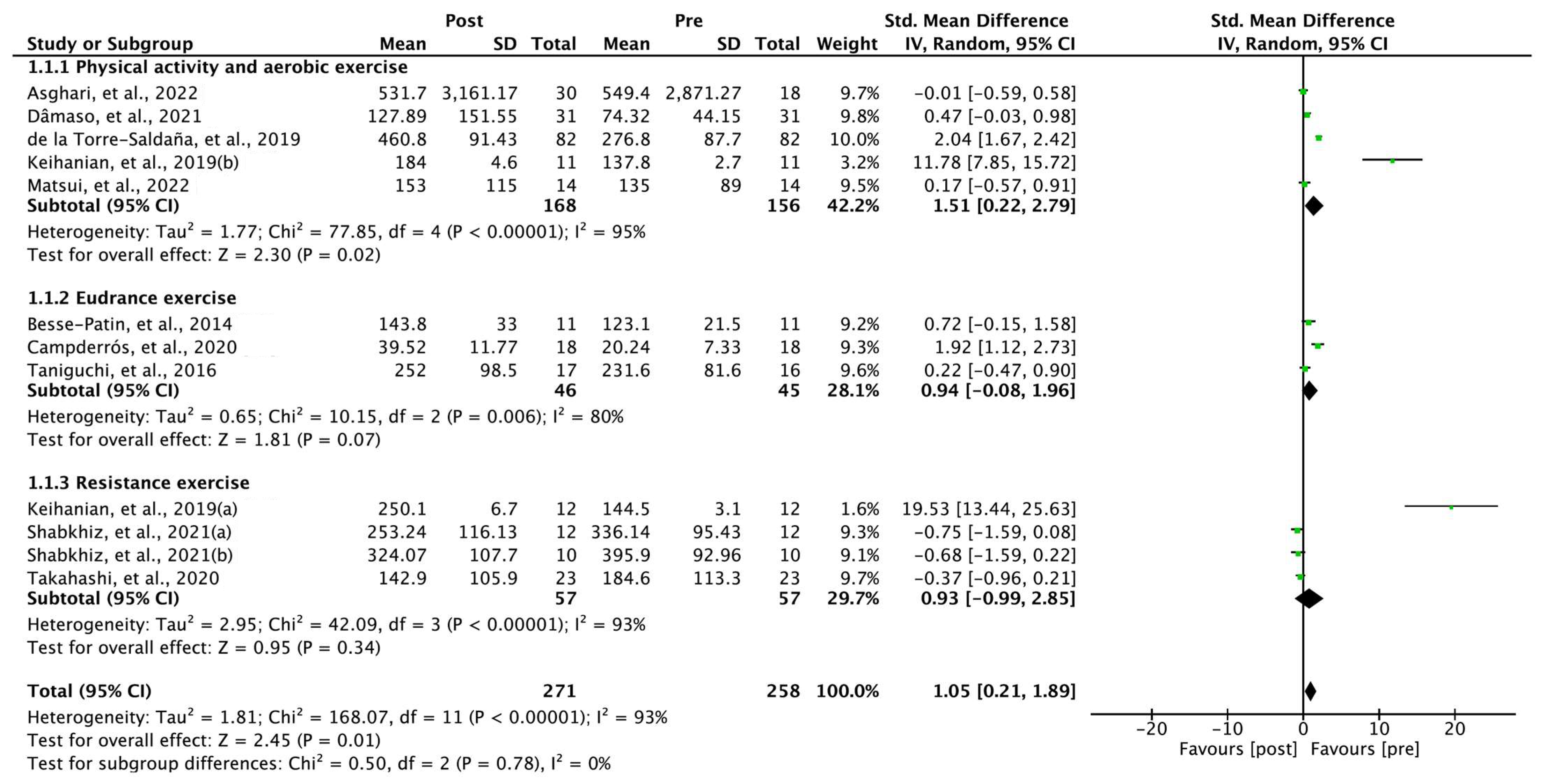
3.3. Chronic Effects of Exercise on FGF-21
3.4. Within-Group Comparisons of Exercise-Induced FGF-21
3.5. Exercise-Induced FGF-21 Levels in Comparison with Controls
3.6. Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, H.-Y.; Yong, J.K. A Study on the Regional Difference of Obesity in the Social Vulnerabilities-Focused on the Suwon City. J. Korea Cont. Assoc. 2019, 19, 682–689. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmet, P.; Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Shaw, J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature 2001, 414, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Kang, M. Effects of Built Environmental Factors on Obesity and Self-Reported Health Status in Seoul Metropolitan Area Using Spatial Regression Model. Korea Spat. Plan Rev. 2011, 68, 85–98. [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly, J.E.; Blair, S.N.; Jakicic, J.M.; Manore, M.M.; Rankin, J.W.; Smith, B.K.; American College of Sports Medicine. American College of Sports Medicine Position Stand. Appropriate Intervention Strategies for Weight Loss and Prevention of Weight Regain for Adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, 2415–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclair, E.; Liggins, R.T.; Peckett, A.J.; Teich, T.; Coy, D.H.; Vranic, M.; Riddell, M.C. Glucagon responses to exercise-induced hypoglycaemia are improved by somatostatin receptor type 2 antagonism in a rat model of diabetes. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1724–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, M.G.; Coker, R.H.; Lacy, D.B.; Zinker, B.A.; Halseth, A.E.; Wasserman, D.H. Glucagon response to exercise is critical for accelerated hepatic glutamine metabolism and nitrogen disposal. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2000, 279, E638–E645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, E.D.; Lustig, D.G.; Baheza, R.A.; Hasenour, C.M.; Lee-Young, R.S.; Donahue, E.P.; Lynes, S.E.; Swift, L.L.; Charron, M.J.; Damon, B.M.; et al. Hepatic Glucagon Action Is Essential for Exercise-Induced Reversal of Mouse Fatty Liver. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2720–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornitz, D.M.; Itoh, N. Fibroblast Growth Factors. Genome Biol. 2001, 2, reviews3005.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharitonenkov, A.; Shiyanova, T.L.; Koester, A.; Ford, A.M.; Micanovic, R.; Galbreath, E.J.; Sandusky, G.E.; Hammond, L.J.; Moyers, J.S.; Owens, R.A.; et al. FGF-21 as a novel metabolic regulator. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Nakatake, Y.; Konishi, M.; Itoh, N. Identification of a novel FGF, FGF-21, preferentially expressed in the liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Gene Struct. Expr. 2000, 1492, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostálová, I.; Haluzíková, D.; Haluzik, M. Fibroblast growth factor 21: A novel metabolic regulator with potential therapeutic properties in obesity/type 2 diabetes mellitus. Physiol. Res. 2009, 58, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharitonenkov, A.; Shanafelt, A.B. Fibroblast growth factor-21 as a therapeutic agent for metabolic diseases. Biodrugs 2008, 22, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potthoff, M.J.; Inagaki, T.; Satapati, S.; Ding, X.; He, T.; Goetz, R.; Mohammadi, M.; Finck, B.N.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Kliewer, S.A.; et al. FGF21 induces PGC-1α and regulates carbohydrate and fatty acid metabolism during the adaptive starvation response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 10853–10858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, T.; Bina, H.A.; Schneider, M.A.; Dunbar, J.D.; Hu, C.C.; Chen, Y.; Moller, D.E.; Kharitonenkov, A. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Corrects Obesity in Mice. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 6018–6027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kliewer, S.A.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Kliewer, S.A.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Fibroblast growth factor 21: From pharmacology to physiology. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 254S–257S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loyd, C.; Magrisso, I.J.; Haas, M.; Balusu, S.; Krishna, R.; Itoh, N.; Sandoval, D.A.; Perez-Tilve, D.; Obici, S.; Habegger, K.M. Fibroblast growth factor 21 is required for beneficial effects of exercise during chronic high-fat feeding. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 121, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruett, E.D.R.; Oseid, S. Effect of Exercise on Glucose and Insulin Response to Glucose Infusion. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 1970, 26, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lloyd, D.J.; Hale, C.; Stanislaus, S.; Chen, M.; Sivits, G.; Vonderfecht, S.; Hecht, R.; Li, Y.-S.; Lindberg, R.A.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Reverses Hepatic Steatosis, Increases Energy Expenditure, and Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Diabetes 2009, 58, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wente, W.; Efanov, A.M.; Brenner, M.; Kharitonenkov, A.; Koster, A.; Sandusky, G.E.; Sewing, S.; Treinies, I.; Zitzer, H.; Gromada, J. Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 Improves Pancreatic Β-Cell Function and Survival by Activation of Extracellular Signal–Regulated Kinase 1/2 and Akt Signaling Pathways. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2470–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharitonenkov, A.; Wroblewski, V.J.; Koester, A.; Chen, Y.-F.; Clutinger, C.K.; Tigno, X.T.; Hansen, B.C.; Shanafelt, A.B.; Etgen, G.J. The Metabolic State of Diabetic Monkeys Is Regulated by Fibroblast Growth Factor-21. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.S.; Clemmesen, J.O.; Secher, N.H.; Hoene, M.; Drescher, A.; Weigert, C.; Pedersen, B.K.; Plomgaard, P. Glucagon-to-insulin ratio is pivotal for splanchnic regulation of FGF-21 in humans. Mol. Metab. 2015, 4, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savović, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.C. The Cochrane Collaboration’s Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Park, J.E.; Lee, Y.J.; Seo, H.-J.; Sheen, S.-S.; Hahn, S.; Jang, B.-H.; Son, H.-J. Testing a tool for assessing the risk of bias for nonrandomized studies showed moderate reliability and promising validity. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 66, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeks, J.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G. Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. Analysing Data and Undertaking Meta-Analyses. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 241–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, S.; Tweedie, R. Trim and Fill: A Simple Funnel-Plot-Based Method of Testing and Adjusting for Publication Bias in Meta-Analysis. Biometrics 2000, 56, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campderrós, L.; Sánchez-Infantes, D.; Villarroya, J.; Nescolarde, L.; Bayès-Genis, A.; Cereijo, R.; Roca, E.; Villarroya, F. Altered Gdf15 and Fgf21 Levels in Response to Strenuous Exercise: A Study in Marathon Runners. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 550102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dâmaso, A.R.; Machado, P.P.; Rhein, S.O.; Masquio, D.C.L.; Oyama, L.M.; Boldarine, V.T.; de Oliveira, G.I.; Tock, L.; Thivel, D.; Campos, R.M.D.S. Effects of an interdisciplinary weight loss program on fibroblast growth factor 21 and inflammatory biomarkers in women with overweight and obesity. Arch. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2021, 65, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Torre-Saldaña, V.A.; Gómez-Sámano, M.Á.; Gómez-Pérez, F.J.; Rosas-Saucedo, J.; León-Suárez, A.; Grajales-Gómez, M.; Oseguera-Moguel, J.; Vega-Beyhart, A.; Cuevas-Ramos, D. Fasting Insulin and Alanine Amino Transferase, but Not Fgf21, Were Independent Parameters Related with Irisin Increment after Intensive Aerobic Exercising. Rev. Invest. Clin. 2019, 71, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keihanian, A.; Arazi, H.; Kargarfard, M. Effects of Aerobic Versus Resistance Training on Serum Fetuin-a, Fetuin-B, and Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 Levels in Male Diabetic Patients. Physiol. Int. 2019, 106, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabkhiz, F.; Khalafi, M.; Rosenkranz, S.; Karimi, P.; Moghadami, K. Resistance training attenuates circulating FGF-21 and myostatin and improves insulin resistance in elderly men with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomised controlled clinical trial. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2020, 21, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Abe, K.; Fujita, M.; Hayashi, M.; Okai, K.; Ohira, H. Simple Resistance Exercise Decreases Cytokeratin 18 and Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Levels in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Retrospective Clinical Study. Medicine 2020, 99, e20399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, M.; Kosaki, K.; Myoenzono, K.; Yoshikawa, T.; Park, J.; Kuro-o, M.; Maeda, S. Effect of Aerobic Exercise Training on Circulating Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 Response to Glucose Challenge in Overweight and Obese Men: A Pilot Study. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2022, 130, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghari, S.; Rezaei, M.; Rafraf, M.; Taghizadeh, M.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Ebadi, M. Effects of Calorie Restricted Diet on Oxidative/Antioxidative Status Biomarkers and Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Levels in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients: A Randomized, Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besse-Patin, A.; Montastier, E.; Vinel, C.; Castan-Laurell, I.; Louche, K.; Dray, C.; Daviaud, D.; Mir, L.; Marques, M.-A.; Thalamas, C.; et al. Effect of endurance training on skeletal muscle myokine expression in obese men: Identification of apelin as a novel myokine. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 38, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, H.; Tanisawa, K.; Sun, X.; Kubo, T.; Higuchi, M. Endurance exercise reduces hepatic fat content and serum fibroblast growth factor 21 levels in elderly men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Sterne, J.A.C. Assessing Risk of Bias Due to Missing Results in a Synthesis. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Cochrane: London, UK, 2019; pp. 349–374. [Google Scholar]
- Safdar, A.; Tarnopolsky, M.A. Exosomes as Mediators of the Systemic Adaptations to Endurance Exercise. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 8, a029827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennequin, G.; Sirvent, P.; Whitham, M. Role of exercise-induced hepatokines in metabolic disorders. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2019, 317, E11–E24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, R.; Tew, G.; Aning, J.J.; Gilbert, S.E.; Lewis, L.; Saxton, J.M. Effects of short-term, medium-term and long-term resistance exercise training on cardiometabolic health outcomes in adults: Systematic review with meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Takenami, E.; Iwamoto, S.; Shiraishi, N.; Kato, A.; Watanabe, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Yamada, S.; Ishii, N. Effects of low-intensity resistance training on muscular function and glycemic control in older adults with type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Investig. 2019, 10, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Choi, S.-E.; Ha, E.S.; An, S.-Y.; Kim, T.H.; Han, S.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, D.J.; Kang, Y.; Lee, K.-W. Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 Protects Human Skeletal Muscle Myotubes from Palmitate-Induced Insulin Resistance by Inhibiting Stress Kinase and Nf-Κb. Metab 2012, 61, 1142–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, Y.C.; Xu, A.; Wang, Y.; Lam, K.S.L. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 as an emerging metabolic regulator: Clinical perspectives. Clin. Endocrinol. 2013, 78, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, F.M.; Maratos-Flier, E.; Haas, J.T.; Francque, S.; Staels, B.; Kozak, L.P.; Harper, M.-E.; Waki, H.; Tontonoz, P.; Johnson, P.R.; et al. Understanding the Physiology of FGF21. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2016, 78, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchiatto, B.; de Castro, T.L.; Muller, C.R.; Azevedo-Martins, A.K.; Evangelista, F.S. Physical Exercise-Induced FGF-21 to Fight Obesity: An Update Review. Obesities 2022, 2, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domin, R.; Dadej, D.; Pytka, M.; Zybek-Kocik, A.; Ruchała, M.; Guzik, P. Effect of Various Exercise Regimens on Selected Exercise-Induced Cytokines in Healthy People. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Kim, S.H.; Min, Y.-K.; Yang, H.-M.; Lee, J.-B.; Lee, M.-S. Acute Exercise Induces FGF21 Expression in Mice and in Healthy Humans. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, S.A.; Sargeant, J.; Thackray, A.; Yates, T.; Stensel, D.J.; Aithal, G.; King, J.A. Effect of exercise intensity on circulating hepatokine concentrations in healthy men. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 44, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalafi, M.; Alamdari, K.A.; Symonds, M.E.; Nobari, H.; Carlos-Vivas, J. Impact of acute exercise on immediate and following early post-exercise FGF-21 concentration in adults: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Hormones 2020, 20, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Ramos, D.; Almeda-Valdes, P.; Meza-Arana, C.E.; Brito-Córdova, G.; Gómez-Pérez, F.J.; Mehta, R.; Oseguera-Moguel, J.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A. Exercise Increases Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 (FGF21) Levels. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapsell, L.C.; Neale, E.P. The Effect of Interdisciplinary Interventions on Risk Factors for Lifestyle Disease: A Literature Review. Health Educ. Behav. 2016, 43, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Ramos, D.; Almeda-Valdes, P.; Gómez-Pérez, F.J.; Meza-Arana, C.E.; Cruz-Bautista, I.; Arellano-Campos, O.; Navarrete-López, M.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A. Daily physical activity, fasting glucose, uric acid, and body mass index are independent factors associated with serum fibroblast growth factor 21 levels. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 163, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Lee, E.; Kim, H. Does Exercise Affect Telomere Length? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Medicina 2022, 58, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, S.; Holman, G.; Schmitz, O.; Pedersen, O. Contraction stimulates translocation of glucose transporter GLUT4 in skeletal muscle through a mechanism distinct from that of insulin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 5817–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockl, K.S.C.; Hirshman, M.F.; Brandauer, J.; Fujii, N.; Witters, L.A.; Goodyear, L.J. Skeletal Muscle Adaptation to Exercise Training: Amp-Activated Protein Kinase Mediates Muscle Fiber Type Shift. Diabetes 2007, 56, 2062–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhihetty, P.J.; Irrcher, I.; Joseph, A.-M.; Ljubicic, V.; Hood, D.A. Plasticity of Skeletal Muscle Mitochondria in Response to Contractile Activity. Exp. Physiol. 2003, 88, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arner, P.; Pettersson, A.; Mitchell, P.J.; Dunbar, J.D.; Kharitonenkov, A.; Rydén, M. FGF21 attenuates lipolysis in human adipocytes—A possible link to improved insulin sensitivity. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltiel, A.R.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature 2001, 414, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, C.; Brambilla, R.; Thomas, K.L. A Simple Role for Bdnf in Learning and Memory? Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2010, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Lee, D.; Lee, Y. The Effect of Aerobic Exercise on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) in Individuals with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trials. Phys. Ther. Rehabil. Sci. 2022, 11, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.-Y.; Formolo, D.A.; Kong, T.; Lau, S.W.-Y.; Ho, C.S.-L.; Leung, R.Y.H.; Hung, F.H.-Y.; Yau, S.-Y. Potential exerkines for physical exercise-elicited pro-cognitive effects: Insight from clinical and animal research. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2019, 147, 361–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, J.; Tselykh, T.V.; Maiorana, F.; Eriksson, O.; Do, H.T.; Mudò, G.; Korhonen, L.T.; Belluardo, N.; Lindholm, D. Fibroblast growth factor-21 enhances mitochondrial functions and increases the activity of PGC-1α in human dopaminergic neurons via Sirtuin-1. Springerplus 2014, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsuchou, H.; Pan, W.; Kastin, A.J. The fasting polypeptide FGF21 can enter brain from blood. Peptides 2007, 28, 2382–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.K.; Hallschmid, M.; Adya, R.; Kern, W.; Lehnert, H.; Randeva, H.S. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 (Fgf21) in Human Cerebrospinal Fluid: Relationship with Plasma Fgf21 and Body Adiposity. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2758–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Geng, L.; Ying, L.; Shu, L.; Ye, K.; Yang, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Jiang, X.; et al. FGF21–Sirtuin 3 Axis Confers the Protective Effects of Exercise Against Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by Governing Mitochondrial Integrity. Circulation 2022, 146, 1537–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Jia, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, N.; Guo, X.; Cao, M.; Fang, F.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; He, Q.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor-21 as a novel metabolic factor for regulating thrombotic homeostasis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Items | Besse-Patin et al., 2014 [34] | Campderrós et al., 2020 [26] | Dâmaso et al., 2021 [27] | De la Torre-Saldaña et al., 2019 [28] | Matsui et al., 2022 [32] | Takahashi et al., 2020 [31] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selection of participants | Low | Low | Low | Unclear | Low | High |
| Confounding variables | Low | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | High |
| Measurement of exposure | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Unclear |
| Blinding of outcome assessments | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | Unclear | Low |
| Incomplete outcome data | Low | Low | Low | Low | Unclear | Low |
| Selective outcome reporting | Low | Low | Low | Low | Unclear | Low |
| Study | Health Condition (n) Participants (Mean Age) | Study Design EG and/or CG | Therapeutic Intensity | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asghari et al., 2022 [33] | NAFLD (n = 60) CR (40.08 years) and CG (39.27 years) | A randomized controlled trial CR: healthy calorie-restricted diet CG: control | Healthy eating and weight control advice for12 weeks Participants in the CR group were targeted to lose a maximum of 10% of their baseline body weight through a healthy calorie-restricted diet | CR diet with moderate weight loss has some favorable effects on NAFLD but was not able to modify oxidative/antioxidative status in these patients. |
| Besse-Patin et al., 2014 [34] | Eleven obese (n = 11) Non-diabetic male subjects (35.4 years) | An interventional clinical trial Single arm: endurance training | 8-week endurance training The 45–60 min exercise sessions consisted mainly of cycling and running, 5 times a week, for 8 weeks | Exercise training upregulates muscle apelin expression in obese subjects. |
| Campderrós et al., 2020 [26] | Healthy (n = 18) Marathon runners (41.71 years) | An interventional clinical trial Single arm: marathon | 42.2-km running race Maintaining an adequate level of hydration during the race | GDF-15 and FGF-21 levels transiently increased in runners following a marathon race. |
| Dâmaso et al., 2021 [27] | Overweight and obese (n = 31) Overweight and obese women (32 years) | An interventional clinical trial Single arm: overweight and obese women | 12-week interdisciplinary weight loss program Nutritional therapy (individual nutritional consultation), physical activity (weekly videos with examples of exercise and health education information), and education for lifestyle changes | Changes in FGF-21 concentrations were different among the women participating in the weight loss program, with some having increased levels and some reduced levels. |
| De la Torre-Saldaña et al., 2019 [28] | Healthy (n = 82) Young sedentary healthy women (23 years) | An interventional clinical trial Single arm: physical activity | Maintaining daily physical activity according to a regular diet, lifestyle, and instructions for 2 weeks | Serum irisin and FGF-21 levels significantly increased after 2 weeks of supervised physical activity. |
| Keihanian et al., 2019 [29] | Type 2 diabetes mellitus (n = 34) ATG (52.4 years), RTG (52.4 years), and CG (53.0 years) | A controlled clinical trial ATG: aerobic training RTG: resistance training CG: control | Aerobic training: 30–45 min of aerobic running at 65–75% of maximum heart rate for 8 weeks Resistance training: 8 weeks of three sets of 10 repetitions maximum of leg press, bench press, knee extension, seated cable row, knee flexion, military press, and calf rise. | Aerobic and resistance exercise training led to a significant decrease in serum fetuin-A and fetuin-B levels and increased FGF-21 levels in men with type 2 diabetes mellitus. |
| Matsui, et al., 2022 [32] | Overweight and obese (n = 14) Overweight and obese men (49 years) | An interventional clinical trial Single arm: aerobic exercise | Supervised aerobic exercise training for 12 weeks (three times per week) Aerobic exercise (walking and/or jogging) was performed with moderate intensity (Borg scale: 12–14) for approximately 40–60 min. | Lowering postprandial circulating FGF21 levels may be associated with the improved glucose tolerance induced by habitual aerobic exercise in overweight and obese men. |
| Shabkhiz et al., 2021 [30] | Elderly men with and without T2D (n = 44) Elderly men without T2D (72.08 years) and with T2D (72.45 years) | A randomized controlled clinical trial EG: resistance training without and with T2D CG: normal activity without and with T2D | Resistance training: machine-based exercises (leg press, leg extension, seated leg curl, seated calf, bench press, compound row, triceps press, and bicep curl) over 12 weeks/3 sessions per week. | 12 weeks of RT induced an overall significant reduction of FGF-21 and myostatin in elderly men with and without T2D. |
| Takahashi et al., 2020 [31] | NAFLD (n = 50) EG (55.5 years) and CG (50.4 years) | A retrospective clinical study EG: resistance training CG: lifestyle counseling | Resistance training: three sets of push-ups and three sets of squats at 20–30 min per session 3 times a week for a total of 12 weeks. | Simple resistance exercise reduced CK-18 and FGF-21 levels in patients with NAFLD. |
| Taniguchi et al., 2016 [35] | Elderly men (n = 32) Elderly Japanese men (69.6 years) | A randomized crossover trial EG: endurance exercise CG: control | 5-week endurance exercise program The exercise program comprised three cycle ergometer sessions per week. The exercise time was 30 min for weeks 1 and 2 and 45 min for weeks 3–5. | A 5-week endurance exercise program decreased hepatic fat content and serum FGF21 levels without weight loss in elderly men, and exercise-induced hepatic fat reduction mediated the reduction in serum FGF21 levels. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.; Jung, J.; Park, S.; Joo, Y.; Lee, S.; Sim, J.; Choi, J.; Lee, H.; Hwang, G.; Lee, S. Exercise-Induced Fibroblast Growth Factor-21: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7284. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087284
Kim H, Jung J, Park S, Joo Y, Lee S, Sim J, Choi J, Lee H, Hwang G, Lee S. Exercise-Induced Fibroblast Growth Factor-21: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(8):7284. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087284
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyunjoong, Jihye Jung, Sungeon Park, Younglan Joo, Sangbong Lee, Jeongu Sim, Jinhyeong Choi, Hyun Lee, Gyujeong Hwang, and Seungwon Lee. 2023. "Exercise-Induced Fibroblast Growth Factor-21: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 8: 7284. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087284
APA StyleKim, H., Jung, J., Park, S., Joo, Y., Lee, S., Sim, J., Choi, J., Lee, H., Hwang, G., & Lee, S. (2023). Exercise-Induced Fibroblast Growth Factor-21: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(8), 7284. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087284









