Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor, Nivolumab, Combined with Chemotherapy Improved the Survival of Unresectable Advanced and Metastatic Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Real-World Experience
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patients’ Characteristics
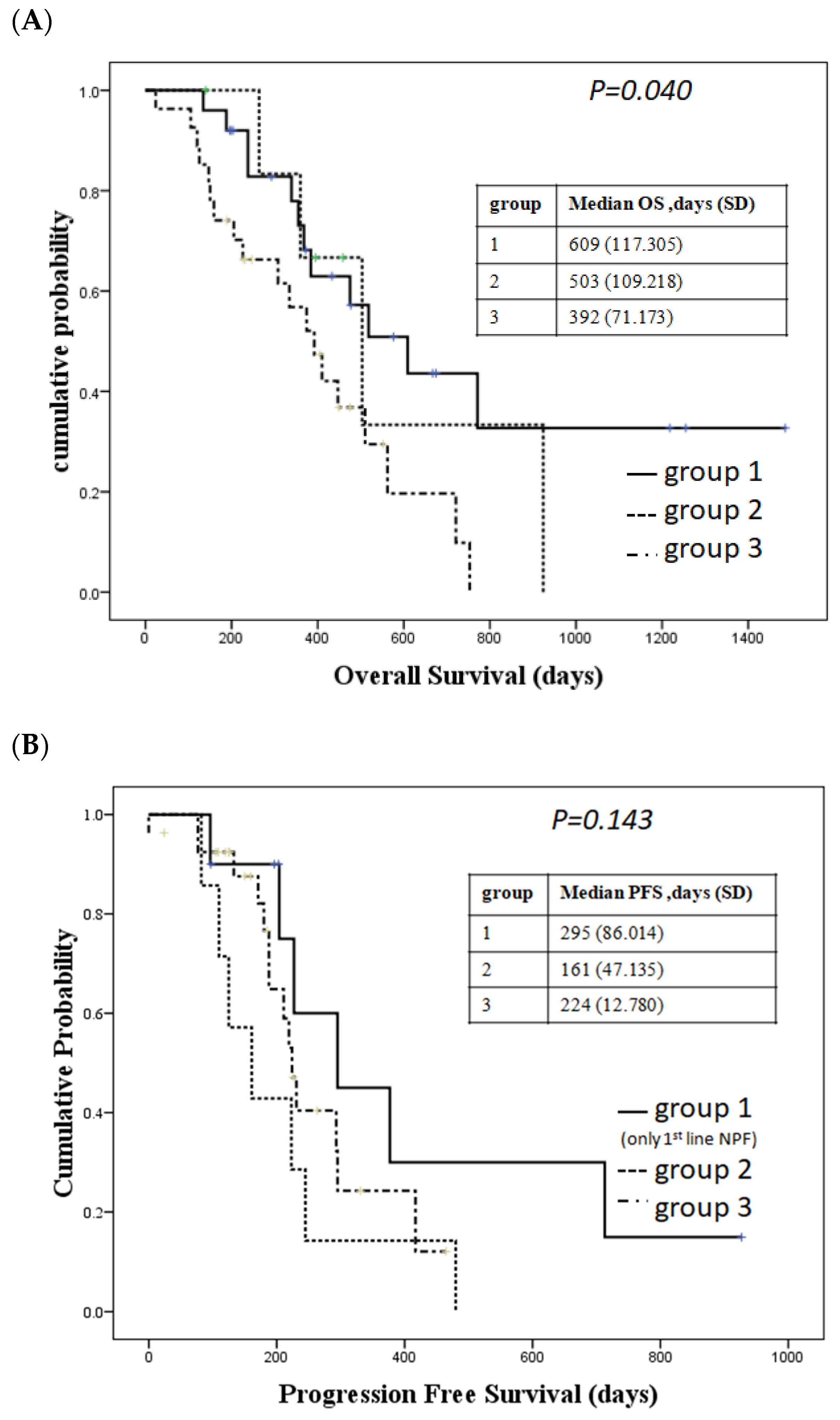
2.2. Patients Who Received Nivolumab Combined with Chemotherapy Had a Trend of Longer Overall Survival and a Better Response than Those Who Received Standard Chemotherapy with or without Radiotherapy
2.3. Liver Metastasis Influenced Dual Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Treatment Response
2.4. Program Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Expression and Treatment Response
2.5. Adverse Effects between Patients Received Nivolumab Combine with Chemotherapy and Standard Treatment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Statistics
4.3. Immunohistochemistry Stain of PD-L1
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, A.; Matsuda, T.; Ajiki, W.; Sobue, T. Trend in Incidence of Adenocarcinoma of the Esophagus in Japan, 1993–2001. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 38, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Totsuka, Y.; He, Y.; Kikuchi, S.; Qiao, Y.; Ueda, J.; Wei, W.; Inoue, M.; Tanaka, H. Epidemiology of Esophageal Cancer in Japan and China. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Li, D.; Shan, B.; Liang, D.; Shi, J.; Chen, W.; He, J. Incidence and mortality of esophagus cancer in China, 2008–2012. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 31, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islami, F.; DeSantis, C.E.; Jemal, A. Incidence Trends of Esophageal and Gastric Cancer Subtypes by Race, Ethnicity, and Age in the United States, 1997–2014. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kitagawa, Y.; Uno, T.; Oyama, T.; Kato, K.; Kato, H.; Kawakubo, H.; Kawamura, O.; Kusano, M.; Kuwano, H.; Takeuchi, H.; et al. Esophageal cancer practice guidelines 2017 edited by the Japan esophageal society: Part 2. Esophgus 2019, 16, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, Y.; Agata, Y.; Shibahara, K.; Honjo, T. Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 3887–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohigashi, Y.; Sho, M.; Yamada, Y.; Tsurui, Y.; Hamada, K.; Ikeda, N.; Mizuno, T.; Yoriki, R.; Kashizuka, H.; Yane, K.; et al. Clinical significance of programmed death-1 lignad-1 and programmed death-1 ligand-2 expression in human esophageal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 2947–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Lu, M.; Xu, B.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, J.; Wu, C. B7-H1 expression associates with tumor invasion and predicts patient’s survival in human esophageal cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 6015–6023. [Google Scholar]
- Kojima, T.; Shah, M.A.; Muro, K.; Francois, E.; Adenis, A.; Hsu, C.-H.; Doi, T.; Moriwaki, T.; Kim, S.-B.; Lee, S.-H.; et al. Randomized Phase III KEYNOTE-181 Study of Pembrolizumab Versus Chemotherapy in Advanced Esophageal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 4138–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.S.; D’Angelo, S.P.; Minor, D.; Hodi, F.S.; Gutzmer, R.; Neyns, B.; Hoeller, C.; Khushalani, N.I.; Miller, W.H.; Lao, C.D.; et al. Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma refractory or intolerant to previous chemotherapy (ATTRACTION-3): A multicentre randomized, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1506–1517. [Google Scholar]
- US Food and Drug Administration FDA Approves Pembrolizumab for Esophageal or GEJ Carcinoma. 2 March 2022. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-pembrolizumab-esophageal-or-gej-carcinoma (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Bristol Myers Squibb. US Food and Drug Administration Approves Two Opdivo® (Nivolumab)-Based Regimens as First-Line Treatments for Unresectable Advanced or Metastatic Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 27 May 2022. Available online: https://news.bms.com/news/corporate-financial/2022/U.S.-Food-and-Drug-Administration-Approves-Two-Opdivo-nivolumab-Based-Regimens-as-First-Line-Treatments-for-Unresectabke-Acvanced-or-Metastatic-Esophageal-Wquamous-Cell-Carcinoma/default.aspx (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Bristol Myers Squibb. Bristol Myers Squibb Receives European Commission Approval for Opdivo (Nivolumab) with Chemotherapy as First-Line Treatment for Patients with Unresectable Advanced, Recurrent or Metastatic Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma with Tumor Cell PD-L1 Expression ≧ 1%. 5 April 2022. Available online: https://news.bms.com/news/details/2022/Bristol-Myers-Squibb-Receives-European-Commission-Approval-for-Opdivo-nivolumab-with-Chemtherapy-as-First-Line-Treatment-for-Patients-with/default.aspx (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anderson, L.A.; Tavilla, A.; Brenner, H.; Luttmann, S.; Navarro, C.; Gavin, A.T.; Holleczek, B.; Johnston, B.T.; Cook, M.B.; Bannon, F.; et al. Survival for oesophageal, stomach and small intestine cancers in Europe 1999–2007: Results from EUROCARE-5. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 2144–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, H.; Zheng, R.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zou, X.; Wang, N.; Zhang, L.; Tang, J.; Chen, J.; Wei, K.; et al. Cancer survival in China, 2003–2005: A population-based study. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rong, L.; Liu, Y.; Hui, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Yuan, Y.; Li, W.; Guo, L.; Ying, J.; et al. PD-L1 expression and its clinicopathological correlation in advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in a Chinese population. Diagn. Pathol. 2019, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardoll, D.M. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brahmer, J.R.; Tykodi, S.S.; Chow, L.Q.M.; Hwu, W.-J.; Topalian, S.L.; Hwu, P.; Drake, C.G.; Camacho, L.H.; Kauh, J.; Odunsi, K.; et al. Safety and Activity of Anti-PD-L1 Antibody in Patients with Advanced Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharpe, A.H. Introduction to checkpoint inhibitors and cancer immunotherapy. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 276, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Topalian, S.L.; Taube, J.M.; Anders, R.A.; Pardoll, D.M. Mechanism-driven biomarkers to guide immune checkpoint blockade in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, T.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Jalal, S.I.; Saraf, S.; Lunceford, J.; Koshiji, M.; Bennouna, J. Safety and antitumor activity of the anti-programmed death-1 antibody pembrolizumab in patients with advanced esophageal cancinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kudo, T.; Hamamoto, Y.; Kato, K.; Ura, T.; Kojima, T.; Tsushima, T.; Hironaka, S.; Hara, H.; Satoh, T.; Iwasa, S.; et al. Nivolumab treatment for oesophageal squamous-cell carcinoma: An open-label, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.A.; Kojima, T.; Hochhauser, D.; Enzinger, P.; Raimbourg, J.; Hollebecque, A.; Lordick, F.; Kim, S.B.; Tajika, M.; Kim, H.T.; et al. Efficacy and safety of pembrolizumab for heavily pretreated patients with advanced, metastatic adenocarcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: The phase 2 keynote-180 study. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.-M.; Shen, L.; Shah, M.A.; Enzinger, P.; Adenis, A.; Doi, T.; Kojima, T.; Metges, J.-P.; Li, Z.; Kim, S.-B.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for first-line treatment of advanced oesophageal cancer (KEYNOTE-590): A randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet 2021, 398, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doki, Y.; Ajani, J.A.; Kato, K.; Xu, J.; Wyrwicz, L.; Motoyama, S.; Ogata, T.; Kawakami, H.; Hsu, C.-H.; Adenis, A.; et al. Nivolumab Combination Therapy in Advanced Esophageal Squamous-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, D.W.T.; Leone, A.G.; Wong, N.Z.H.; Zhao, J.J.; Tey, J.C.S.; Sundar, R.; Pietrantonio, F. Effectiveness of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Patients With Advanced Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. A meta-analysis including low PD-L1 subgroups. JAMA Oncol. 2023, 9, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Nivolumab + C/T (n = 25) | Nivolumab + ipi (n = 7) | Chemotherapy (n = 27) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (M/F) | 25 (100%)/0 | 7 (100%)/0 | 26 (96.30%)/1 (3.70%) | 0.547 |
| Age (median ± SD) | 53 ± 7.544 | 56 ± 5.090 | 59 ± 10.886 | 0.216 |
| Recurrent | 7 (28%) | 2 (28.57%) | 1 (3.70%) | 0.045 * |
| initial metastasis | 18 (72%) | 5 (71.42%) | 26 (96.30%) | |
| Stage (AJCC8) | 0.020 * | |||
| III | 2 (8%) | 0 | 2 (7.40%) | |
| IVA | 6 (24%) | 0 | 15 (55.56%) | |
| IVB | 17 (68%) | 7 (100%) | 10 (37.03%) | |
| Stage-T 0 | 5 (20%) | 3 (42.85%) | 0 | 0.075 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 (3.70%) | |
| 2 | 1 (4%) | 0 | 0 | |
| 3 | 9 (36%) | 3 (42.85%) | 8 (29.63%) | |
| 4 | 10 (40%) | 1 (14.28%) | 18 (66.67%) | |
| Stage-N 0 | 6 (24%) | 2 (28.57%) | 3 (11.11%) | 0.272 |
| 1 | 9 (36%) | 2 (28.57%) | 8 (29.63%) | |
| 2 | 5 (20%) | 0 | 11 (40.74%) | |
| 3 | 5 (20%) | 3 (42.85%) | 5 (18.52%) | |
| Stage-M 0 | 8 (32%) | 0 | 17 (62.96%) | 0.004 * |
| 1 | 17 (68%) | 7 (100%) | 10 (37.04%) | |
| ECOG | 22 (88%) | 7 (100%) | 16 (59.26%) | 0.048 * |
| 0 | 3 (12%) | 0 | 7 (25.93%) | |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 4 (14.81%) | |
| 2 | ||||
| Location | ||||
| upper | 6 (24%) | 4 (57.14%) | 11 (40.74%) | 0.788 |
| middle | 7 (28%) | 1 (14.28%) | 5 (18.52%) | |
| upper/middle | 1 (4%) | 0 | 2 (7.41%) | |
| Middle/lower | 1 (4%) | 0 | 0 | |
| lower | 9 (36%) | 2 (28.57%) | 9 (33.33%) | |
| panesophagus | 1 (4%) | 0 | 0 | |
| Metastatic site (%) | ||||
| lung | 5 (20%) | 3 (42.85%) | 3 (11.11%) | 0.154 |
| liver | 2 (8%) | 1 (14.28%) | 1 (3.70%) | 0.581 |
| bone | 5 (20%) | 0 | 2 (7.41%) | 0.219 |
| distant LN | 5 (20%) | 4 (57.14%) | 5 (18.52%) | 0.092 |
| DM (%) | 3 (12%) | 2 (28.57%) | 4 (14.81%) | 0.557 |
| Hypertension (%) | 7 (28%) | 2 (28.57%) | 4 (14.81%) | 0.470 |
| Other cancer # (%) | 4 (16%) | 1 (14.28%) | 7 (14.81%) | 0.811 |
| Hepatitis B (%) | 0 | 0 | 1 (3.70%) | 0.636 |
| Hepatitis C (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Liver cirrhosis (%) | 0 | 1 (14.28%) | 2 (7.41%) | 0.355 |
| Best Response (%) | 0.038 * | |||
| CR | 5 (20%) | 0 | 3 (11.11%) | |
| PR | 13 (52%) | 1 (14.28%) | 15 (55.56%) | |
| SD | 6 (24%) | 5 (71.42%) | 3 (11.11%) | |
| PD | 1 (4%) | 1 (14.28%) | 4 (14.81%) | |
| not measure | 2 (7.41%) | |||
| Treatment lines (%) | 0.008 * | |||
| 1 | 4 (16%) | 2 (28.57%) | 18 (66.67%) | |
| 2 | 14 (56%) | 3 (42.86%) | 8 (29.63%) | |
| 3 | 5 (20%) | 1 (14.28%) | 1 (3.70%) | |
| 4 | 1 (4%) | 0 | 0 | |
| 5 | 1 (4%) | 0 | 0 | |
| 6 | 0 | 1 (14.28%) | 0 | |
| Receive curative esophagectomy | 0 | 0 | 2 (7.41%) |
| Nivo + Chemotherapy | p-Value | Nivo + Epi | p-Value | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location (n) | Upper (6) | Upper/Middle (1) | Middle (7) | Middle/Lower (1) | Lower (9) | PANESOPHAGUS (1) | Upper (4) | Middle (1) | Lower (2) | |||
| CR (%) | 2 (33) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 (33.3) | 0 | 0.350 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.478 | |
| PR (%) | 2 (33) | 1 (100) | 4 (57) | 0 | 4 (44.4) | 0 | 1 (25) | 0 | 0 | |||
| SD (%) | 2 (33) | 0 | 1 (14) | 0 | 1 (11.1) | 1 (100) | 3 (75) | 1 (100) | 1 (50) | |||
| PD (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (11.1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (50) | |||
| NA (%) | 0 | 0 | 2 (29) | 1 (100) | 0 | 0 | ||||||
| T stage (n) | 0 (5) | 1 (0) | 2 (1) | 3 (9) | 4a (4) | 4b (6) | 0 (3) | 3 (3) | 4a (1) | |||
| CR (%) | 1 (20) | 0 | 0 | 1 (11.1) | 1 (25) | 2 (33.3) | 0.436 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.443 | |
| PR (%) | 2 (40) | 0 | 1 (100) | 5 (55.5) | 1 (25) | 3 (50) | 0 | 1 (33.3) | 0 | |||
| SD (%) | 1 (20) | 0 | 0 | 2 (22.2) | 1 (25) | 1 (16.7) | 3 (100) | 1 (33.3) | 1 (100) | |||
| PD (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (25) | 0 | 0 | 1 (33.3) | 0 | |||
| NA (%) | 1 (20) | 1 (11.1) | ||||||||||
| N stage (n) | 0 (6) | 1 (9) | 2 (5) | 3 (5) | 0 (n = 2) | 1 (n = 2) | 3 (n = 3) | |||||
| CR (%) | 2 (33.33) | 2 (22.22) | 0 | 1 (20) | 0.854 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.380 | |||
| PR (%) | 2 (33.33) | 4 (44.44) | 3 (60) | 2 (40) | 0 | 1 (50) | 0 | |||||
| SD (%) | 1 (16.67) | 2 (22.22) | 1 (20) | 1 (20) | 2 (100) | 1 (50) | 2 (66.67) | |||||
| PD (%) | 0 | 0 | 1 (20) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (33.33) | |||||
| NA (%) | 1 (16.67) | 1 (11.11) | 1 (20) | |||||||||
| M stage | 0 (8) | 1 (17) | 0 (n = 0) | 1 (n = 7) | ||||||||
| CR (%) | 2 (25) | 3 (17.65) | 0.606 | 0 | 0 | |||||||
| PR (%) | 3 (37.5) | 8 (47.06) | 1 (14.29) | |||||||||
| SD (%) | 1 (12.5) | 4 (23.53) | 5 (71.43) | |||||||||
| PD (%) | 1 (12.5) | 0 | 1 (14.29) | |||||||||
| NA (%) | 1 (12.5) | 2 (11.76) | ||||||||||
| Metastatic site (lung) (n) | N (20) | Y (5) | N (n = 4) | Y (n = 3) | ||||||||
| CR (%) | 5 (25) | 0 | 0.425 | 0 | 0 | 0.350 | ||||||
| PR (%) | 8 (40) | 3 (60) | 0 | 1 (33.33) | ||||||||
| SD (%) | 3 (15) | 2 (40) | 3 (75) | 2 (66.67) | ||||||||
| PD (%) | 1 (5) | 0 | 1 (25) | 0 | ||||||||
| NA (%) | 3 (15) | |||||||||||
| Metastatic site (liver) (n) | N (23) | Y (2) | N (n = 6) | Y (n = 1) | ||||||||
| CR (%) | 5 (21.74) | 0 | 0.464 | 0 | 0 | 0.030* | ||||||
| PR (%) | 10 (43.48) | 1 (50) | 1 (16.67) | 0 | ||||||||
| SD (%) | 5 (21.74) | 0 | 5 (83.33) | 0 | ||||||||
| PD (%) | 1 (4.35) | 0 | 0 | 1 (100) | ||||||||
| NA (%) | 2 (8.70) | 1 (50) | ||||||||||
| Metastatic site (bone) (n) | N (20) | Y (5) | N (n = 7) | Y (n = 0) | ||||||||
| CR (%) | 5 (20) | 0 | 0.425 | 0 | 0 | |||||||
| PR (%) | 8 (40) | 3 (60) | 1 (14.29) | |||||||||
| SD (%) | 3 (15) | 2 (40) | 5 (71.43) | |||||||||
| PD (%) | 1 (5) | 0 | 1 (14.29) | |||||||||
| NA (%) | 3 (15) | |||||||||||
| Metastatic site (LN) # (n) | N (20) | Y (5) | N (n = 3) | Y (n = 4) | ||||||||
| CR (%) | 2 (10) | 3 (60) | 0.080 | 0 | 0 | 0.350 | ||||||
| PR (%) | 11 (55) | 0 | 0 | 1 (25) | ||||||||
| SD (%) | 4 (20) | 1 (20) | 2 (66.67) | 3 (75) | ||||||||
| PD (%) | 1 (5) | 0 | 1 (33.33) | 0 | ||||||||
| NA (%) | 2 (10) | 1 (20) | ||||||||||
| Recurrent $ (n) | N (18) | Y (7) | 0 (n = 5) | 1 (n = 2) | ||||||||
| CR (%) | 3 (16.67) | 2 (28.57) | 0.796 | 0 | 0 | 0.571 | ||||||
| PR (%) | 9 (50) | 2 (28.57) | 1 (20) | 0 | ||||||||
| SD (%) | 3 (16.67) | 2 (28.57) | 3 (60) | 2 (100) | ||||||||
| PD (%) | 1 (5.56) | 0 | 1 (20) | 0 | ||||||||
| NA (%) | 2 (11.11) | 1 (14.29) | ||||||||||
| ECOG | 0 (22) | 1 (3) | 0 (7) | 1 (0) | ||||||||
| CR (%) | 5 (22.75) | 0 | 0.526 | 0 | ||||||||
| PR (%) | 9 (40.91) | 2 (66.67) | 1 (14.29) | |||||||||
| SD (%) | 5 (22.73) | 0 | 5 (71.43) | |||||||||
| PD (%) | 1 (4.55) | 0 | 1 (14.29) | |||||||||
| NA (%) | 2 (9.10) | 1 (33.33) | ||||||||||
| Treat line | 1st (10) | 2nd (12) | 3rd (3) | |||||||||
| CR (%) | 3 (30) | 2 (16.67) | 0 | 0.575 | ||||||||
| PR (%) | 4 (40) | 5 (41.67) | 2 (66.67) | |||||||||
| SD (%) | 2 (20) | 2 (16.67) | 1 (33.33) | |||||||||
| PD (%) | 1 (10) | 0 | 0 | |||||||||
| NA (%) | 3 (25) | |||||||||||
| All Population @ | p-Value | I/O-containing Regimen & | p-Value | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location (n) | Upper (21) | Upper/Middle (3) | Middle (13) | Middle/Lower (1) | Lower (20) | Panesophagus(1) | Upper(10) | Upper/Middle (1) | Middle (8) | Middle/Lower (1) | Lower (11) | ||
| CR (%) | 3 (14.3) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 (25) | 0 | 0.339 | 2 (20) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 (27.3) | 0.171 |
| PR (%) | 8 (38.1) | 2 (66.7) | 9 (69.2) | 0 | 10 (50) | 0 | 3 (30) | 1 (100) | 4 (50) | 0 | 4 (36.4) | ||
| SD (%) | 6 (28.6) | 0 | 4 (30.8) | 1 | 2 (10) | 1 | 5 (50) | 0 | 2 (25) | 1 | 2(18.2) | ||
| PD (%) | 2 (9.5) | 1 (33.3) | 0 | 0 | 3 (15) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (18.2) | ||
| NA (%) | 2 (9.5) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (25) | ||||||
| T stage (n) | 0 (8) | 1 (1) | 2 (1) | 3 (20) | 4a (8) | 4b (21) | 0 (8) | 2 (1) | 3 (12) | 4a (5) | 4b (6) | ||
| CR (%) | 1 (12.5) | 0 | 0 | 3 (15) | 0 | 4 (19) | 0.438 | 1 (12.5) | 0 | 1 (8.3) | 1 (20) | 2 (33.3) | 0.343 |
| PR (%) | 2 (25) | 0 | 1 (100) | 11 (55) | 6 (75) | 9(42.9) | 2 (25) | 0 | 6 (50) | 1 (20) | 3 (50) | ||
| SD (%) | 5(62.5) | 0 | 4 (20) | 1 (12.5) | 4 (19) | 4 (50) | 0 | 3 (25) | 2 (40) | 1 (16.7) | |||
| PD (%) | 0 | 1 (100) | 2 (10) | 1 (12.5) | 2 (9.5) | 0 | 0 | 1 (8.3) | 1 (20) | 0 | |||
| NA (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (9.5) | 1 (12.5) | 1 (100) | 1 (8.3) | ||||||
| N stage (n) | 0 (11) | 1 (19) | 2 (16) | 3 (13) | 0 (n = 8) | 1(n = 11) | 2(n = 5) | 3 (n = 8) | |||||
| CR (%) | 2 (18.2) | 2 (10.5) | 3 (18.75) | 1 (7.69) | 0.373 | 2 (25) | 2 (18.18) | 0 | 1 (12.5) | 0.848 | |||
| PR (%) | 3 (27.3) | 11 (57.9) | 8 (50) | 7 (53.85) | 2 (25) | 5 (45.45) | 3 (60) | 2 (25) | |||||
| SD (%) | 5 (45.5) | 5 (26.3) | 1 (6.25) | 3 (23.08) | 3 (37.5) | 3 (27.27) | 1 (20) | 3 (37.5) | |||||
| PD (%) | 1 (9.1) | 1 (5.3) | 2 (12.5) | 2(15.38) | 0 | 0 | 1 (20) | 1 (12.5) | |||||
| NA (%) | 0 | 0 | 2 (12.5) | 0 | 1 (12.5) | 1 (9.09) | 1 (12.5) | ||||||
| M stage | 0 (25) | 1 (34) | 0 (n = 8) | 1 (n = 24) | |||||||||
| CR (%) | 3 (12) | 5 (14.71) | 0.342 | 2 (25) | 3 (12.5) | 0.631 | |||||||
| PR (%) | 14 (56) | 15 (44.12) | 3 (37.5) | 9 (37.5) | |||||||||
| SD (%) | 3 (12) | 11 (32.35) | 1 (12.5) | 9 (37.5) | |||||||||
| PD (%) | 4 (16) | 2 (5.88) | 1 (12.5) | 1 (4.17) | |||||||||
| NA(%) | 1 (4) | 1 (2.94) | 1 (12.5) | 2 (8.33) | |||||||||
| Metastatic site (lung) (n) | N (48) | Y (11) | N (n = 24) | Y (n = 8) | |||||||||
| CR (%) | 7 (14.58) | 1 (9.09) | 0.554 | 5 (20.83) | 0 | 0.290 | |||||||
| PR (%) | 23 (47.92) | 6 (54.55) | 8 (33.33) | 4 (50) | |||||||||
| SD (%) | 10 (20.83) | 4 (36.36) | 6 (25) | 4 (50) | |||||||||
| PD (%) | 6 (12.5) | 0 | 2 (8.33) | 0 | |||||||||
| NA (%) | 2 (4.17) | 0 | 3 (12.5) | 0 | |||||||||
| Metastatic site (liver) (n) | N (55) | Y (4) | N (n = 29) | Y (n = 3) | |||||||||
| CR (%) | 8 (14.55) | 0 | 0.094 | 5 (17.24) | 0 | 0.113 | |||||||
| PR (%) | 28 (50.91) | 1 (25) | 11 (37.93) | 1 (33.33) | |||||||||
| SD (%) | 13 (23.64) | 1 (25) | 10 (34.48) | 0 | |||||||||
| PD (%) | 4 (7.27) | 2 (50) | 1 (3.45) | 1 (33.33) | |||||||||
| NA (%) | 2 (3.64) | 0 | 2 (6.90) | 1 (33.33) | |||||||||
| Metastatic site (bone) (n) | N (52) | Y (7) | N (n = 27) | Y (n = 5) | |||||||||
| CR (%) | 8 (15.38) | 0 | 0.303 | 5 (18.52) | 0 | 0.592 | |||||||
| PR (%) | 25 (48.08) | 4 (57.14) | 9 (33.33) | 3 (60) | |||||||||
| SD (%) | 12 (23.08) | 2 (28.57) | 8 (29.63) | 2 (40) | |||||||||
| PD (%) | 6 (11.54) | 0 | 2 (7.41) | 0 | |||||||||
| NA (%) | 1 (1.92) | 1 (14.29) | 3 (11.11) | 0 | |||||||||
| Metastatic site (LN) # (n) | N (45) | Y (14) | N (n = 23) | Y (n = 9) | |||||||||
| CR (%) | 4 (8.88) | 4 (28.57) | 0.120 | 2 (8.70) | 3 (33.33) | 0.174 | |||||||
| PR (%) | 24 (53.33) | 5 (35.71) | 11 (47.83) | 1 (11.11) | |||||||||
| SD (%) | 9 (20) | 5 (35.71) | 6 (26.09) | 4 (44.44) | |||||||||
| PD (%) | 6 (13.33) | 0 | 2 (8.70) | 0 | |||||||||
| NA (%) | 2 (4.44) | 0 | 2 (8.70) | 1 (11.11) | |||||||||
| Recurrent $ (n) | N (49) | Y (10) | N (n = 23) | Y (n = 9) | |||||||||
| CR (%) | 6 (12.24) | 2 (20) | 0.029 * | 3 (13.04) | 2 (22.22) | 0.173 | |||||||
| PR (%) | 27 (55.10)) | 2 (20) | 10 (43.48) | 2 (22.22) | |||||||||
| SD (%) | 8 (16.33) | 6 (60) | 6 (26.09) | 5 (55.55) | |||||||||
| PD (%) | 6 (12.24) | 0 | 2 (8.70) | 0 | |||||||||
| NA (%) | 2 (4.08) | 0 | 2 (8.70) | ||||||||||
| ECOG | 0 (45) | 1 (10) | 2 (4) | 0 (29) | 1 (3) | ||||||||
| CR (%) | 7 (15.56) | 0 | 1 (25) | 0.660 | 5 (17.24) | 0 | 0.338 | ||||||
| PR (%) | 21 (46.67) | 6 (60) | 2 (50) | 10 (34.48) | 2 (66.66) | ||||||||
| SD (%) | 12 (26.67) | 2 (20) | 0 | 10 (34.48) | 0 | ||||||||
| PD (%) | 4 (8.89) | 1 (10) | 1 (25) | 2 (6.70) | 0 | ||||||||
| NA (%) | 1 (2.22) | 1 (10) | 0 | 2 (6.70) | 1 (33.33) | ||||||||
| Nivolumab + C/T (n = 25) | Nivolumab + ipi (n = 7) | Chemotherapy (n = 27) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GI (all/Gr 3,4, %) | ||||
| Diarrhea | 5 (20%)/0 | 4 (57.15%)/0 | 15 (55.56%)/0 | 0.021 * |
| Constipation | 14 (56%)/0 | 6 (85.71%)/0 | 25 (92.59%)/0 | 0.842 |
| Nausea | 14 (56%))/0 | 4 (57.14%)/0 | 23 (85.19%)/0 | 0.020 * |
| Vomiting | 3 (12%)/0 | 1 (14.28%)/0 | 7 (25.93%)/0 | 0.415 |
| Skin rash (all/Gr 3,4, %) | 2 (8%)/1 (4%) | 3 (42.85%)/1 (14.28%) | 3 (11.11%)/0 | 0.112 |
| Mucositis (all/Gr 3,4, %) | 10 (40%)/3 (12%) | 3 (42.85%)/0 | 9 (33.33%)/0 | 0.463 |
| Pneumonitis (all/Gr 3,4, %) | 8 (32%)/0 | 3 (42.85%)/0 | 12 (44.44%)/2 (7.41%) | 0.628 |
| Hepatitis (all/Gr 3,4, %) | 2 (8%)/0 | 0/0 | 7 (25.93%)/3 (11.11%) | 0.304 |
| AKI (all/Gr 3,4, %) | 2 (8%)/0 | 0/1 (14.28%) | 0/0 | 0.036 * |
| Endocrine (all/Gr 3,4, %) # | 0/0 | 1 (14.28%)/0 | 0/0 | 0.044 * |
| Leukopenia (all/Gr 3,4, %) | 8 (32%)/1 (4%) | 2 (28.57%)/0 | 17 (62.92%)/7 (25.93%) | 0.102 |
| Anemia (all/Gr 3,4, %) | 10 (40%)/2 (8%) | 2 (28.57%)/1 (14.28%) | 23 (85.19%)/2 (7.41%) | 0.003 * |
| Thrombocytopenia(all/Gr 3,4, %) | 9 (36%)/2 (8%) | 0/0 | 16 (59.26%)/0 | 0.018 * |
| Fatigue(all/Gr 3,4, %) | 14 (56%)/0 | 3 (42.85%)/0 | 13 (48.15%)/0 | 0.870 |
| Nivolumab + C/T, First Line (n = 10) | Nivolumab +C/T Second Line (n = 12) | Nivolumab +C/T ≧ Third Line (n = 3) | Nivolumab + ipi (n = 7) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GI (all/Gr 3,4, %) | |||||
| Diarrhea | 3 (30%)/0 | 0/0 | 1 (33.3%)/0 | 4 (57.14%)/0 | 0.044 * |
| Constipation | 3 (30%)/0 | 4 (33.33%)/0 | 1 (33.3%)/0 | 1 (14.28%)/0 | 0.830 |
| Nausea | 7 (70%)/0 | 6 (50%)/0 | 1 (33.3%)/0 | 3 (42.86%)/0 | 0.466 |
| Vomiting | 2 (20%)/0 | 0/0 | 1 (33.3%)/0 | 1 (14.28%)/0 | 0.329 |
| Skin rash (all/Gr 3,4, %) | 1 (10%)/ 1 (10%) | 1 (8.33%)/0 | 0/0 | 3 (42.85%)/ 1 (14.28%) | 0.351 |
| Mucositis (all/Gr 3,4, %) | 4 (40%)/ 2 (20%) | 5 (41.66%)/ 1 (8.33%) | 1 (33.33%)/0 | 3 (42.85%)/0 | 0.715 |
| Pneumonia (all/Gr 3,4, %) | 3 (30%)/0 | 4 (33.33%)/0 | 1 (33.33%)/0 | 3 (42.85%)/0 | 0.930 |
| Hepatitis (all/Gr 3,4, %) | 0/0 | 1 (8.33%)/0 | 1 (33.33%)/0 | 0/0 | 0.632 |
| AKI (all/Gr 3,4, %) | 2 (20%)/0 | 0/0 | 1 (33.33%)/0 | 0/1 (14.28%) | 0.184 |
| Endocrine (all/Gr 3,4, %) # | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1 (14.28%)/0 | 0.552 |
| Leukopenia (all/Gr 3,4, %) | 1 (10%)/0 | 5 (41.66%)/1 (8.33%) | 1 (33.33%)/0 | 2 (28.57%)/0 | 0.809 |
| Anemia (all/Gr 3,4, %) | 5 (50%)/1 (10%) | 3 (25%)/0 | 1 (33.33%)/0 | 2 (28.57%)/1 (14.28%) | 0.139 |
| Thrombocytopenia (all/Gr 3,4, %) | 2 (10%)/0 | 5 (41.66%)/1 (8.33%) | 2 (66.66%)/1 (33.33%) | 0/0 | 0.190 |
| Fatigue (all/Gr 3,4, %) | 5 (50%)/0 | 6 (50%)/0 | 1 (33.33%)/0 | 3 (42.85%)/0 | 0.880 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kao, M.-W.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Hsieh, K.-C.; Lee, C.-T.; Wu, S.-C.; Yang, W.-C. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor, Nivolumab, Combined with Chemotherapy Improved the Survival of Unresectable Advanced and Metastatic Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Real-World Experience. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087312
Kao M-W, Kuo Y-H, Hsieh K-C, Lee C-T, Wu S-C, Yang W-C. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor, Nivolumab, Combined with Chemotherapy Improved the Survival of Unresectable Advanced and Metastatic Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Real-World Experience. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(8):7312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087312
Chicago/Turabian StyleKao, Ming-Wei, Yao-Hung Kuo, Kun-Chou Hsieh, Ching-Tai Lee, Shih-Chi Wu, and Wen-Chi Yang. 2023. "Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor, Nivolumab, Combined with Chemotherapy Improved the Survival of Unresectable Advanced and Metastatic Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Real-World Experience" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 8: 7312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087312
APA StyleKao, M.-W., Kuo, Y.-H., Hsieh, K.-C., Lee, C.-T., Wu, S.-C., & Yang, W.-C. (2023). Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor, Nivolumab, Combined with Chemotherapy Improved the Survival of Unresectable Advanced and Metastatic Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Real-World Experience. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(8), 7312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087312







