Studying the Roles of the Renin–Angiotensin System in Accelerating the Disease of High-Fat-Diet-Induced Diabetic Nephropathy in a db/db and ACE2 Double-Gene-Knockout Mouse Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
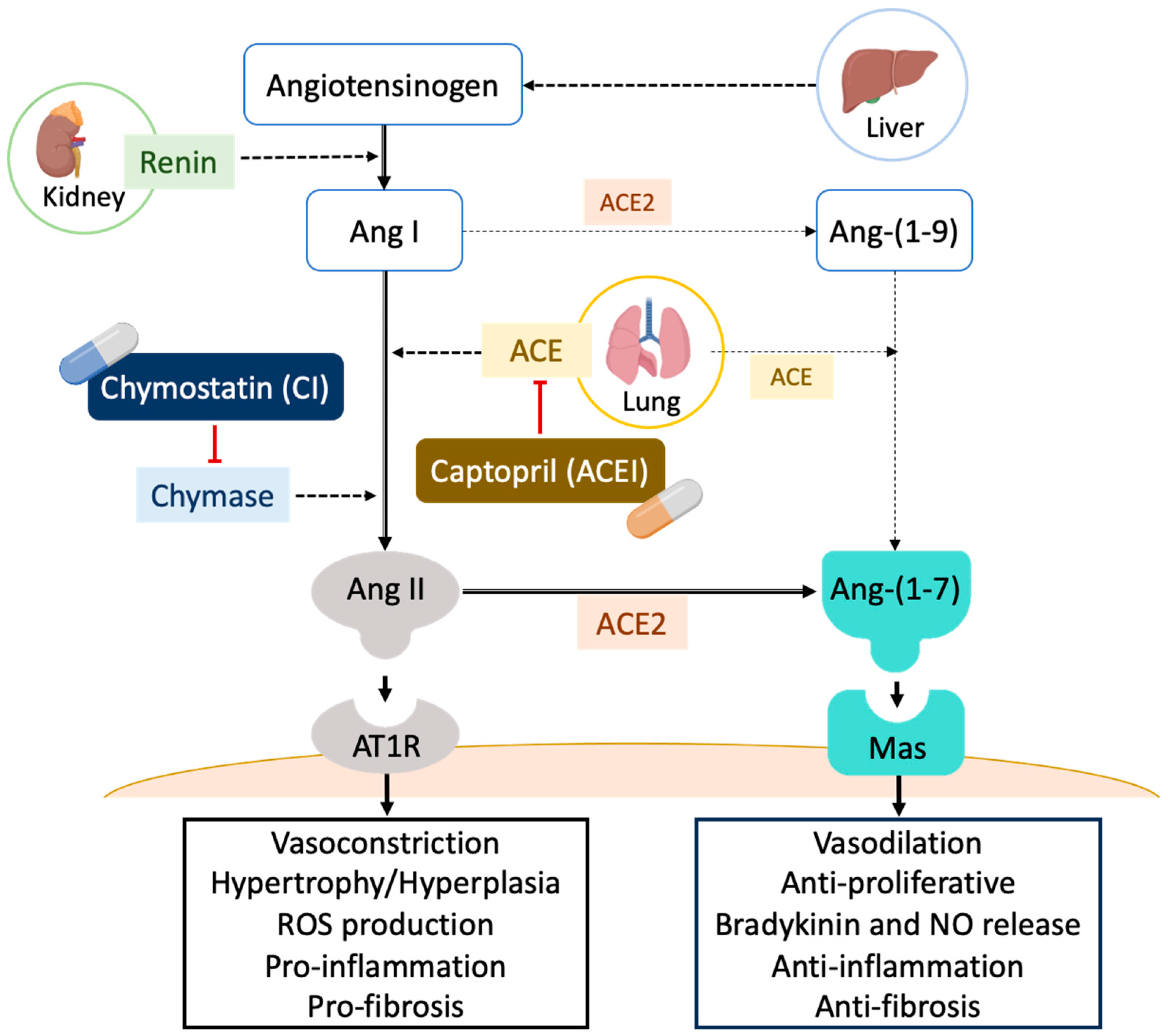
2. Results
2.1. Changes in Physical Characteristics
2.2. Changes in Biochemical Characteristics of Blood and Urine
2.3. Diabetic Nephropathy Trigged by MAPK and RAS Activation via Abnormal Production of Ang II
2.4. Histopathology of the Kidney of db/db and ACE2 KO Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Experimental Animals
4.2.1. db/db and ACE2 Double-Gene-Knockout Mice
4.2.2. Animal Model of Accelerating DN with Age and HFD Feeding
4.3. Sample Collection and Biochemical Determinations
4.4. Protein Extraction
4.5. Western Blot Assay
4.6. Histological Determination
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Lawati, J.A. Diabetes Mellitus: A Local and Global Public Health Emergency! Oman Med. J. 2017, 32, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forouhi, N.G.; Wareham, N.J. Epidemiology of diabetes. Medicine 2014, 42, 698–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldukhayel, A. Prevalence of diabetic nephropathy among Type 2 diabetic patients in some of the Arab countries. Int. J. Health Sci. 2017, 11, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.X.; Kong, J.; Yun, K. Prevalence of Diabetic Nephropathy among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in China: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 2315607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachura, A.; Khanna, I.; Krysiak, P.; Paskal, W.; Wlodarski, P. Wound Healing Impairment in Type 2 Diabetes Model of Leptin-Deficient Mice-A Mechanistic Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesch, G.H.; Lim, A.K. Recent insights into diabetic renal injury from the db/db mouse model of type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2011, 300, F301–F310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guest, P.C.; Rahmoune, H. Characterization of the db/db Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1916, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.Y.; Lin, C.H.; Huang, T.H.; Chuang, S.Y. In Vivo Rodent Models of Type 2 Diabetes and Their Usefulness for Evaluating Flavonoid Bioactivity. Nutrients 2019, 11, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L. High fat diet induced obesity model using four strainsof mice: Kunming, C57BL/6, BALB/c and ICR. Exp. Anim. 2020, 69, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Xiao, Y.; Li, L.; Xiong, X.; Han, Y.; Zhu, X.; Sun, L. The Susceptibility Genes in Diabetic Nephropathy. Kidney Dis. 2018, 4, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.; Poyan Mehr, A.; Kreutz, R. Physiology of local renin-angiotensin systems. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 747–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fyhrquist, F.; Saijonmaa, O. Renin-angiotensin system revisited. J. Intern. Med. 2008, 264, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, W.H. Studying the Roles of Chymase and Angiotensin Converting Enzyme II (ACE2) on the Pathogenesis of Nephropathy. Master’s Thesis, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.W.; Lu, L.C.; Chang, C.C.; Cho, C.C.; Hsieh, W.Y.; Tsai, C.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Lin, C.S. Imbalanced plasma ACE and ACE2 level in the uremic patients with cardiovascular diseases and its change during a single hemodialysis session. Ren. Fail. 2017, 39, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahreini, E.; Rezaei-Chianeh, Y.; Nabi-Afjadi, M. Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Intrarenal Renin-Angiotensin and Alternative Pathways in Diabetic Nephropathy—A Review. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2021, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, L.F.; Emanuele, N.; Zhang, J.H.; Brophy, M.; Conner, T.A.; Duckworth, W.; Leehey, D.J.; McCullough, P.A.; O’Connor, T.; Palevsky, P.M.; et al. Combined angiotensin inhibition for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1892–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, S.; Mehta, S.; Khwaja, A.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Ives, N.; Brettell, E.; Chadburn, M.; Cockwell, P.; Investigators, S.A.T. Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibition in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2021–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.Y.; Yap, K.; Swedberg, J.E.; Craik, D.J.; de Veer, S.J. Binding Loop Substitutions in the Cyclic Peptide SFTI-1 Generate Potent and Selective Chymase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramya, K.; Suresh, R.; Kumar, H.Y.; Kumar, B.R.P.; Murthy, N.B.S. Decades-old renin inhibitors are still struggling to find a niche in antihypertensive therapy. A fleeting look at the old and the promising new molecules. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuston, S.; Hyland, N.P. Chymase inhibition as a pharmacological target: A role in inflammatory and functional gastrointestinal disorders? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T.; Wada, A.; Tsutamoto, T.; Ohnishi, M.; Isono, T.; Kinoshita, M. Chymase inhibition prevents cardiac fibrosis and improves diastolic dysfunction in the progression of heart failure. Circulation 2003, 107, 2555–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froogh, G.; Kandhi, S.; Duvvi, R.; Le, Y.; Weng, Z.; Alruwaili, N.; Ashe, J.O.; Sun, D.; Huang, A. The contribution of chymase-dependent formation of ANG II to cardiac dysfunction in metabolic syndrome of young rats: Roles of fructose and EETs. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2020, 318, H985–H993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caughey, G.H. Update on Mast Cell Proteases as Drug Targets. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2023, 43, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takai, S.; Jin, D. Chymase as a Possible Therapeutic Target for Amelioration of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoncello, N.; Moreira, R.P.; Arita, D.Y.; Aragao, D.S.; Watanabe, I.K.; Dantas, P.S.; Santos, R.; Mattar-Rosa, R.; Yokota, R.; Cunha, T.S.; et al. Diabetic Nephropathy Induced by Increased Ace Gene Dosage Is Associated with High Renal Levels of Angiotensin (1–7) and Bradykinin. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 674047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossing, P.; Strand, J.; Avogaro, A.; Becka, M.; Kanefendt, F.; Otto, C. Effects of the chymase inhibitor fulacimstat in diabetic kidney disease-results from the CADA DIA trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 2263–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoghue, M.; Hsieh, F.; Baronas, E.; Godbout, K.; Gosselin, M.; Stagliano, N.; Donovan, M.; Woolf, B.; Robison, K.; Jeyaseelan, R.; et al. A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1–9. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, E1–E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tipnis, S.R.; Hooper, N.M.; Hyde, R.; Karran, E.; Christie, G.; Turner, A.J. A human homolog of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Cloning and functional expression as a captopril-insensitive carboxypeptidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 33238–33243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuiri, S.; Ohashi, Y. ACE and ACE2 in kidney disease. World J. Nephrol. 2015, 4, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, M.J.; Wysocki, J.; Batlle, D. ACE2 alterations in kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 2687–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, M.J.; Nangaku, M. ACE2 as therapy for glomerular disease: The devil is in the detail. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 1269–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, V.R.; Scholey, J.W. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and renal disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2018, 27, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igel, M.; Kainulainen, H.; Brauers, A.; Becker, W.; Herberg, L.; Joost, H.G. Long-term and rapid regulation of ob mRNA levels in adipose tissue from normal (Sprague Dawley rats) and obese (db/db mice, fa/fa rats) rodents. Diabetologia 1996, 39, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.J.; Ueno, M.; Nakagawa, T.; Huang, C.; Kanenishi, K.; Onodera, M.; Sakamoto, H. Oxidative damage in cerebral vessels of diabetic db/db mice. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2005, 21, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitada, M.; Ogura, Y.; Koya, D. Rodent models of diabetic nephropathy: Their utility and limitations. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2016, 9, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorowicz, A.; Buczek, E.; Mateuszuk, L.; Czarnowska, E.; Sitek, B.; Jasztal, A.; Chmura-Skirlinska, A.; Dib, M.; Steven, S.; Daiber, A.; et al. Comparison of Pulmonary and Systemic NO- and PGI(2)-Dependent Endothelial Function in Diabetic Mice. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 4036709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Seo, E.; Jun, H.S. Bavachin alleviates diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice by inhibition of oxidative stress and improvement of mitochondria function. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Forte, T.M.; Taniguchi, S.; Ishida, B.Y.; Oka, K.; Chan, L. The db/db mouse, a model for diabetic dyslipidemia: Molecular characterization and effects of Western diet feeding. Metabolism 2000, 49, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Luo, P.; Zhang, Z.; Payne, K.; Watson, S.; Wu, H.; Tan, Y.; Ding, Y.; Sun, W.; Yin, X.; et al. Zinc delays the progression of obesity-related glomerulopathy in mice via down-regulating P38 MAPK-mediated inflammation. Obesity 2016, 24, 1244–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juin, S.K.; Pushpakumar, S.; Sen, U. GYY4137 Regulates Extracellular Matrix Turnover in the Diabetic Kidney by Modulating Retinoid X Receptor Signaling. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juin, S.K.; Pushpakumar, S.; Tyagi, S.C.; Sen, U. Glucosidase inhibitor, Nimbidiol ameliorates renal fibrosis and dysfunction in type-1 diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.K.; Bailly, V.; Abichandani, R.; Thadhani, R.; Bonventre, J.V. Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1): A novel biomarker for human renal proximal tubule injury. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, H.Y.; Ford Versypt, A.N. Pathophysiology of mesangial expansion in diabetic nephropathy: Mesangial structure, glomerular biomechanics, and biochemical signaling and regulation. J. Biol. Eng. 2022, 16, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brosnihan, K.B.; Neves, L.A.; Joyner, J.; Averill, D.B.; Chappell, M.C.; Sarao, R.; Penninger, J.; Ferrario, C.M. Enhanced renal immunocytochemical expression of ANG-(1-7) and ACE2 during pregnancy. Hypertension 2003, 42, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lely, A.T.; Hamming, I.; van Goor, H.; Navis, G.J. Renal ACE2 expression in human kidney disease. J. Pathol. 2004, 204, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Wysocki, J.; William, J.; Soler, M.J.; Cokic, I.; Batlle, D. Glomerular localization and expression of Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and Angiotensin-converting enzyme: Implications for albuminuria in diabetes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 3067–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crackower, M.A.; Sarao, R.; Oudit, G.Y.; Yagil, C.; Kozieradzki, I.; Scanga, S.E.; Oliveira-dos-Santos, A.J.; da Costa, J.; Zhang, L.; Pei, Y. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is an essential regulator of heart function. Nature 2002, 417, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koitka, A.; Cooper, M.E.; Thomas, M.C.; Tikellis, C. Angiotensin converting enzyme 2 in the kidney. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2008, 35, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, Y.H.; Hsieh, W.Y.; Hsieh, J.S.; Liu, F.C.; Tsai, C.H.; Lu, L.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Wu, C.L.; Lin, C.S. Alternative Roles of STAT3 and MAPK Signaling Pathways in the MMPs Activation and Progression of Lung Injury Induced by Cigarette Smoke Exposure in ACE2 Knockout Mice. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 12, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.I.; Tsai, C.H.; Sun, Y.L.; Hsieh, W.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Lin, C.S. Instillation of particulate matter 2.5 induced acute lung injury and attenuated the injury recovery in ACE2 knockout mice. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, W.Y.; Chang, T.H.; Chang, H.F.; Chuang, W.H.; Lu, L.C.; Yang, C.W.; Lin, C.S.; Chang, C.C. Renal chymase-dependent pathway for angiotensin II formation mediated acute kidney injury in a mouse model of aristolochic acid I-induced acute nephropathy. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, S.H.; Ma, S.K.; Kim, S.W.; Bae, E.H. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and kidney diseases in the era of coronavirus disease 2019. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2021, 36, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Lin, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, T.; Wei, M.; Pan, S.; Lu, L.; Li, X.; Tian, G.; et al. Identification of the regulatory mechanism of ACE2 in COVID-19-induced kidney damage with systems genetics approach. J. Mol. Med. 2023, 101, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Bivona, B.J.; Kobori, H.; Seth, D.M.; Chappell, M.C.; Lazartigues, E.; Harrison-Bernard, L.M. Major role for ACE-independent intrarenal ANG II formation in type II diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2010, 298, F37–F48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranowska, I.; Gawrys, O.; Roszkowska-Chojecka, M.M.; Badzynska, B.; Tymecka, D.; Olszynski, K.H.; Kompanowska-Jezierska, E. Chymase Dependent Pathway of Angiotensin II Generation and Rapeseed Derived Peptides for Antihypertensive Treatment of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 658805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristovam, P.C.; Carmona, A.K.; Arnoni, C.P.; Maquigussa, E.; Pereira, L.G.; Boim, M.A. Role of chymase in diabetic nephropathy. Exp. Biol. Med. 2012, 237, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, B.; Zarbock, A.; Bellomo, R.; Legrand, M. The role of renin-angiotensin system in sepsis-associated acute kidney injury: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2023, 29, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, S.D.; Rudemiller, N.P. Immunologic Effects of the Renin-Angiotensin System. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1350–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.Y.; Yang, C.; Li, S.N. Effects of genistein on angiotensin-converting enzyme in rats. Life Sci. 2006, 79, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikary, L.; Chow, F.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J.; Stambe, C.; Dowling, J.; Atkins, R.C.; Tesch, G.H. Abnormal p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling in human and experimental diabetic nephropathy. Diabetologia 2004, 47, 1210–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, A.; Tejada, T.; Catanuto, P.; Xia, X.; Elliot, S.J.; Lenz, O.; Jauregui, A.; Saenz, M.O.; Molano, R.D.; Pileggi, A.; et al. Inhibition of C-jun N-terminal kinase improves insulin sensitivity but worsens albuminuria in experimental diabetes. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Sun, J.; Tong, Q.; Lin, Q.; Qian, L.; Park, Y.; Zheng, Y. The Role of ERK1/2 in the Development of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelzaher, W.Y.; Abdel-Gaber, S.A.; Fawzy, M.A.; Ali, A.H.; Attya, M.E.; Geddawy, A. Atorvastatin protects against cyclophosphamide-induced thyroid injury in rats via modulation of JNK/ERK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 124, 111061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.; Gao, P.; Zhao, T.; He, L.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Shui, H.; Wu, X. Calcitriol regulates angiotensin-converting enzyme and angiotensin converting-enzyme 2 in diabetic kidney disease. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2016, 43, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.Y.; Lai, C.C.; Huang, P.H.; Yang, A.H.; Chiang, S.C.; Huang, P.C.; Tseng, K.W.; Huang, C.H. Magnolol Reduces Renal Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury via Inhibition of Apoptosis. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2017, 45, 1421–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solinas, G.; Becattini, B. JNK at the crossroad of obesity, insulin resistance, and cell stress response. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.Y. Studying the Roles of Renin Angiotensin System in the Progression of High Fat Diet Induced Diabetic Nephropathy. Master’s Thesis, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Clotet, S.; Riera, M.; Pascual, J.; Soler, M.J. RAS and sex differences in diabetic nephropathy. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2016, 310, F945–F957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Li, W.; Yazdizadeh Shotorbani, P.; Dubansky, B.H.; Huang, L.; Chaudhari, S.; Wu, P.; Wang, L.A.; Ryou, M.G.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Comparison of diabetic nephropathy between male and female eNOS(-/-)db/db mice. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2019, 316, F889–F897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, R.M.; Siragy, H.M. The intrarenal renin-angiotensin system and diabetic nephropathy. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 14, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghi, C.; Omboni, S. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition: Beyond Blood Pressure Control-The Role of Zofenopril. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 4068–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, N.B.; Carpenter, A.; Dale-Harris, I.; Doree, C.; Estcourt, L.J. Interventions for chronic kidney disease in people with sickle cell disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 8, CD012380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, S.; Jin, D. Chymase Inhibitor as a Novel Therapeutic Agent for Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, W.; Bai, J.; Nie, X.; Wang, W. Chymase inhibition protects diabetic rats from renal lesions. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| 8-Week-Old ND | 12-Week-Old ND | 12-Week-Old HFD | 12-Week-Old HFD + ACEI | 12-Week-Old HFD + CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (BW) (g) | 45.4 ± 3.3 | 51.8 ± 5.1 | 64.8 ± 7.5 * | 59.6 ± 4.8 | 59.1 ± 3.6 |
| Blood glucose (mg/dL) | 256 ± 24 | 368 ± 20 *** | 620 ± 42 *** | 589 ± 44 *** | 499 ± 43 *** †† |
| Kidney weight (KW) (g) | 0.305 ± 0.037 | 0.412 ± 0.065 * | 0.545 ± 0.069 *** | 0.404 ± 0.071 * † | 0.348 ± 0.065 †† |
| KW/BW (%) | 6.54 ± 0.69 | 7.59 ± 0.56 | 7.82 ± 0.18 * | 7.40 ± 0.59 | 6.56 ± 0.81 † |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.-Y.; Lin, M.-W.; Xie, X.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Yang, C.-W.; Wu, P.-C.; Liu, D.-H.; Wu, C.-J.; Lin, C.-S. Studying the Roles of the Renin–Angiotensin System in Accelerating the Disease of High-Fat-Diet-Induced Diabetic Nephropathy in a db/db and ACE2 Double-Gene-Knockout Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010329
Chen C-Y, Lin M-W, Xie X-Y, Lin C-H, Yang C-W, Wu P-C, Liu D-H, Wu C-J, Lin C-S. Studying the Roles of the Renin–Angiotensin System in Accelerating the Disease of High-Fat-Diet-Induced Diabetic Nephropathy in a db/db and ACE2 Double-Gene-Knockout Mouse Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(1):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010329
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Cheng-Yi, Meng-Wei Lin, Xing-Yang Xie, Cheng-Han Lin, Chung-Wei Yang, Pei-Ching Wu, Dung-Huan Liu, Chih-Jen Wu, and Chih-Sheng Lin. 2024. "Studying the Roles of the Renin–Angiotensin System in Accelerating the Disease of High-Fat-Diet-Induced Diabetic Nephropathy in a db/db and ACE2 Double-Gene-Knockout Mouse Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 1: 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010329
APA StyleChen, C.-Y., Lin, M.-W., Xie, X.-Y., Lin, C.-H., Yang, C.-W., Wu, P.-C., Liu, D.-H., Wu, C.-J., & Lin, C.-S. (2024). Studying the Roles of the Renin–Angiotensin System in Accelerating the Disease of High-Fat-Diet-Induced Diabetic Nephropathy in a db/db and ACE2 Double-Gene-Knockout Mouse Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(1), 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010329






