The Plastic Interplay between Lung Regeneration Phenomena and Fibrotic Evolution: Current Challenges and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Predisposing Factors
2.1. Genetic Predisposition
2.2. Surfactant Proteins
2.3. Mucin 5B
2.4. Telomerase-Related Genes
2.5. Other Genes
2.6. A-Kinase Anchoring Protein 13
2.7. Kinesin Family Member 15
2.8. Additional Loci
2.9. Inflammation
2.10. Fibroblast and Epithelial Cell Dysfunction
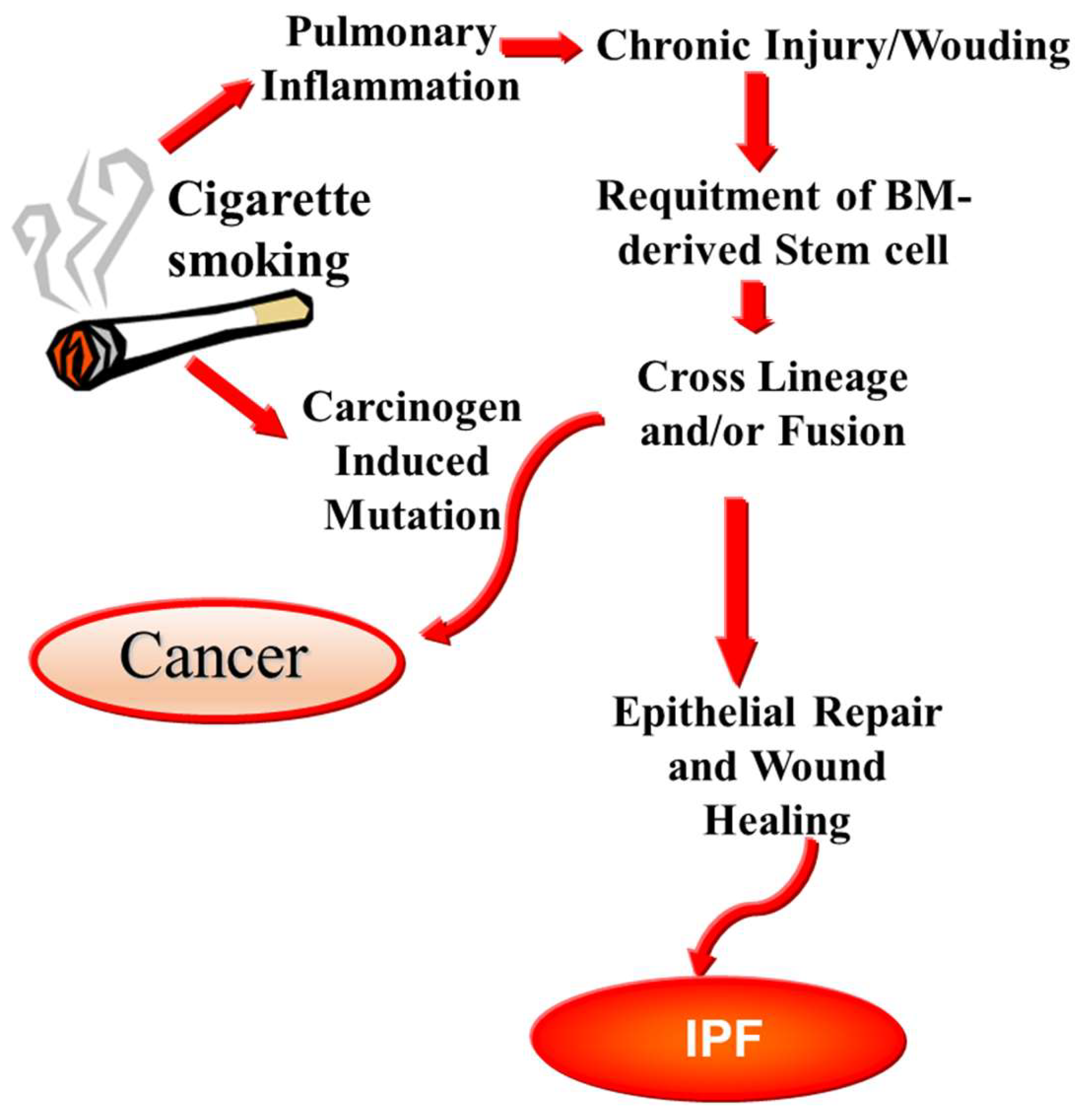
3. Progression to Fibrosis
4. Mechanisms of Fibrosis
4.1. Altered Re-Epithelialization
4.2. Cytokines, Growth Factors, and Other Molecules
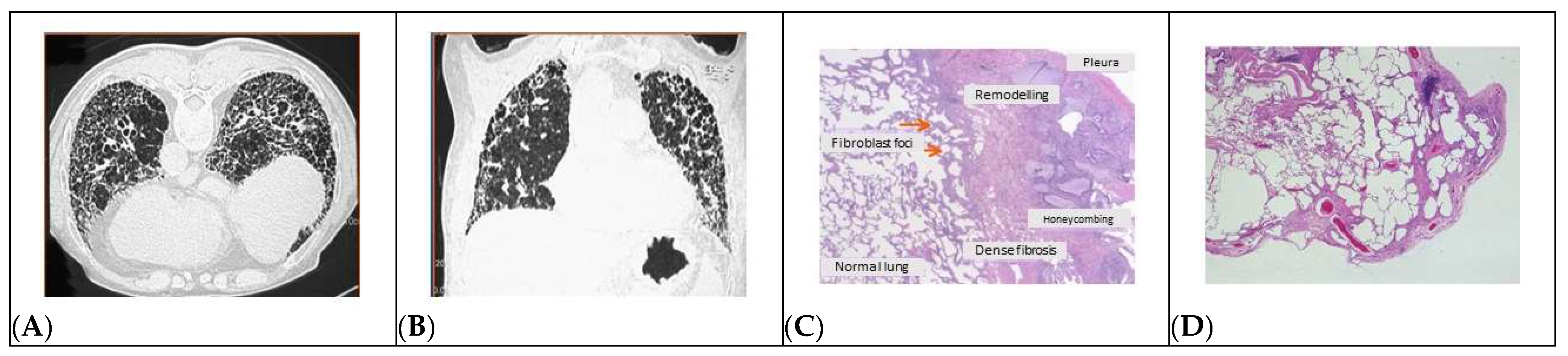
4.3. Fibrotic Foci
4.4. Mesenchymal Cells
4.5. Fibroblast Subtypes
4.6. Circulating Fibrocytes
4.7. Fibroblast Proliferation
4.8. Stem-like Phenotype and Properties of Myofibroblasts
4.9. Collagen Deposition
5. Discussion
5.1. Current Therapeutic Approaches
5.1.1. Nintedanib
5.1.2. Pirfenidone (PFD)
5.1.3. Not Only IPF
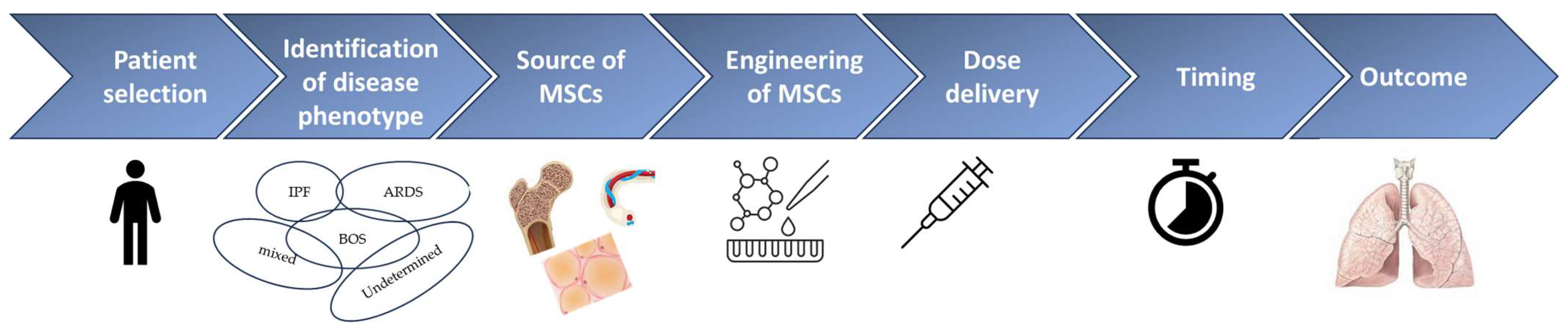
5.2. The Role of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
5.3. Senolytics and Other Drugs under Investigation
5.3.1. Pentraxins
5.3.2. Pamrevlumab
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navaratnam, V.; Fleming, K.M.; West, J.; Smith, C.J.; Jenkins, R.G.; Fogarty, A.; Hubbard, R.B. The rising incidence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in the U.K. Thorax 2011, 66, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, T.J.; Hunninghake, G.W. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzenstein, A.L.; Myers, J.L. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Clinical relevance of pathologic classification. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 157, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homer, R.J.; Elias, J.A.; Lee, C.G.; Herzog, E. Modern concepts on the role of inflammation in pulmonary fibrosis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2011, 135, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaherty, K.R.; Travis, W.D.; Colby, T.V.; Toews, G.B.; Kazerooni, E.A.; Gross, B.H.; Jain, A.; Strawderman, R.L.; Flint, A.; Lynch, J.P.; et al. Histopathologic variability in usual and nonspecific interstitial pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 1722–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cool, C.D.; Groshong, S.D.; Rai, P.R.; Henson, P.M.; Stewart, J.S.; Brown, K.K. Fibroblast foci are not discrete sites of lung injury or repair: The fibroblast reticulum. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.D.; Hua, J.; Mui, A.; O’Connor, R.; Grotendorst, G.; Khalil, N. Release of biologically active TGF-beta1 by alveolar epithelial cells results in pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2003, 285, L527–L539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degryse, A.L.; Lawson, W.E. Progress toward improving animal models for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 341, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lederer, D.J.; Martinez, F.J. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1811–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvaro Undurraga, P. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Rev. Med. Clin. Condes 2015, 26, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marshall, R.P.; McAnulty, R.J.; Laurent, G.J. The pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis: Is there a fibrosis gene? Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997, 29, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, P.K.; Moore, B.B. Viral infection and aging as cofactors for the development of pulmonary fibrosis. Expert. Rev. Respir. Med. 2010, 4, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haura, E.B. Is repetitive wounding and bone marrow-derived stem cell mediated-repair an etiology of lung cancer development and dissemination? Med. Hypotheses 2006, 67, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chilosi, M.; Carloni, A.; Rossi, A.; Poletti, V. Premature lung aging and cellular senescence in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and COPD/emphysema. Transl. Res. 2013, 162, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samarelli, A.V.; Tonelli, R.; Heijink, I.; Martin Medina, A.; Marchioni, A.; Bruzzi, G.; Castaniere, I.; Andrisani, D.; Gozzi, F.; Manicardi, L.; et al. Dissecting the Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Cause or Solution. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 692551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Mathai, S.K.; Schwartz, D.A. Genetics in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Pathogenesis, Prognosis, and Treatment. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Wang, Y. Candidate genes of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Current evidence and research. Appl. Clin. Genet. 2016, 9, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.J.; Porte, J.; Braybrooke, R.; Flores, C.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Oldham, J.M.; Guillen-Guio, B.; Ma, S.F.; Okamoto, T.; John, A.E.; et al. Genetic variants associated with susceptibility to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in people of European ancestry: A genome-wide association study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Moorsel, C.H.M.; van der Vis, J.J.; Grutters, J.C. Genetic disorders of the surfactant system: Focus on adult disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 200085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, E.; Luisetti, M.; Spialtini, L.; Coccia, P.; Rossi, A.; Donnini, M.; Cetta, G.; Salmona, M. Relationship between changes in alveolar surfactant levels and lung defence mechanisms. Respiration 1989, 55 (Suppl. S1), 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kuan, P.J.; Xing, C.; Cronkhite, J.T.; Torres, F.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; DiMaio, J.M.; Kinch, L.N.; Grishin, N.V.; Garcia, C.K. Genetic defects in surfactant protein A2 are associated with pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Moorsel, C.H.; van Oosterhout, M.F.; Barlo, N.P.; de Jong, P.A.; van der Vis, J.J.; Ruven, H.J.; van Es, H.W.; van den Bosch, J.M.; Grutters, J.C. Surfactant protein C mutations are the basis of a significant portion of adult familial pulmonary fibrosis in a dutch cohort. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossno, P.F.; Polosukhin, V.V.; Blackwell, T.S.; Johnson, J.E.; Markin, C.; Moore, P.E.; Worrell, J.A.; Stahlman, M.T.; Phillips, J.A., 3rd; Loyd, J.E.; et al. Identification of early interstitial lung disease in an individual with genetic variations in ABCA3 and SFTPC. Chest 2010, 137, 969–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullard, J.E.; Nogee, L.M. Heterozygosity for ABCA3 mutations modifies the severity of lung disease associated with a surfactant protein C gene (SFTPC) mutation. Pediatr. Res. 2007, 62, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Seidl, E.; Knoflach, K.; Gothe, F.; Forstner, M.E.; Michel, K.; Pawlita, I.; Gesenhues, F.; Sattler, F.; Yang, X.; et al. ABCA3-related interstitial lung disease beyond infancy. Thorax 2023, 78, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibold, M.A.; Wise, A.L.; Speer, M.C.; Steele, M.P.; Brown, K.K.; Loyd, J.E.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Zhang, W.; Gudmundsson, G.; Groshong, S.D.; et al. A common MUC5B promoter polymorphism and pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, C.J.; Sato, H.; Fonseca, C.; Banya, W.A.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Adamali, H.; Russell, A.M.; Denton, C.P.; Abraham, D.J.; Hansell, D.M.; et al. Mucin 5B promoter polymorphism is associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis but not with development of lung fibrosis in systemic sclerosis or sarcoidosis. Thorax 2013, 68, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leavy, O.C.; Ma, S.F.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Maher, T.M.; Oldham, J.M.; Flores, C.; Noth, I.; Jenkins, R.G.; Dudbridge, F.; Wain, L.V.; et al. Proportion of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Risk Explained by Known Common Genetic Loci in European Populations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 775–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanios, M.Y.; Chen, J.J.; Cogan, J.D.; Alder, J.K.; Ingersoll, R.G.; Markin, C.; Lawson, W.E.; Xie, M.; Vulto, I.; Phillips, J.A., 3rd; et al. Telomerase mutations in families with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiri, K.D.; Cronkhite, J.T.; Kuan, P.J.; Xing, C.; Raghu, G.; Weissler, J.C.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; Shay, J.W.; Garcia, C.K. Adult-onset pulmonary fibrosis caused by mutations in telomerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7552–7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronkhite, J.T.; Xing, C.; Raghu, G.; Chin, K.M.; Torres, F.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; Garcia, C.K. Telomere shortening in familial and sporadic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alder, J.K.; Chen, J.J.; Lancaster, L.; Danoff, S.; Su, S.C.; Cogan, J.D.; Vulto, I.; Xie, M.; Qi, X.; Tuder, R.M.; et al. Short telomeres are a risk factor for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13051–13056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Chemaly, S.; Ziegler, S.G.; Calado, R.T.; Wilson, K.A.; Wu, H.P.; Haughey, M.; Peterson, N.R.; Young, N.S.; Gahl, W.A.; Moss, J.; et al. Natural history of pulmonary fibrosis in two subjects with the same telomerase mutation. Chest 2011, 139, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Ullenbruch, M.; Young Choi, Y.; Yu, H.; Ding, L.; Xaubet, A.; Pereda, J.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.A.; Bitterman, P.B.; Henke, C.A.; et al. Telomerase and telomere length in pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogan, J.D.; Kropski, J.A.; Zhao, M.; Mitchell, D.B.; Rives, L.; Markin, C.; Garnett, E.T.; Montgomery, K.H.; Mason, W.R.; McKean, D.F.; et al. Rare variants in RTEL1 are associated with familial interstitial pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingerlin, T.E.; Murphy, E.; Zhang, W.; Peljto, A.L.; Brown, K.K.; Steele, M.P.; Loyd, J.E.; Cosgrove, G.P.; Lynch, D.; Groshong, S.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies multiple susceptibility loci for pulmonary fibrosis. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.J.; Stockwell, A.; Oldham, J.M.; Guillen-Guio, B.; Schwartz, D.A.; Maher, T.M.; Flores, C.; Noth, I.; Yaspan, B.L.; Jenkins, R.G.; et al. Genome-wide association study across five cohorts identifies five novel loci associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax 2022, 77, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Povysil, G.; Kobeissy, P.H.; Li, Q.; Wang, B.; Amelotte, M.; Jaouadi, H.; Newton, C.A.; Maher, T.M.; Molyneaux, P.L.; et al. Rare and Common Variants in KIF15 Contribute to Genetic Risk of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 206, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoghue, L.J.; Stockwell, A.D.; Neighbors, M.; Sheng, R.X.; Prabhakaran, R.; Wolters, P.J.; Lancaster, L.H.; Kropski, J.A.; Blackwell, T.S.; McCarthy, M.I.; et al. Identification of a Genetic Susceptibility Locus for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in the 16p Subtelomere Using Whole-Genome Sequencing. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 941–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, G.L. Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 1986, 89 (Suppl. S3), 115S–121S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, H.Y.; Fulmer, J.D.; Kazmierowski, J.A.; Roberts, W.C.; Frank, M.M.; Crystal, R.G. Analysis of cellular and protein content of broncho-alveolar lavage fluid from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. J. Clin. Investig. 1977, 59, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selman, M.; King, T.E.; Pardo, A.; American Thoracic Society; European Respiratory Society; American College of Chest Physicians. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Prevailing and evolving hypotheses about its pathogenesis and implications for therapy. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 134, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, C., 3rd; Boldt, J.; King, T.E., Jr.; Crouch, E.; Vartio, T.; McDonald, J.A. An immunohistochemical study of architectural remodeling and connective tissue synthesis in pulmonary fibrosis. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1989, 140, 1693–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecker, L.; Thannickal, V.J. Nonresolving fibrotic disorders: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis as a paradigm of impaired tissue regeneration. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 341, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Striker, L.J.; Hudson, L.D.; Striker, G.E. Extracellular matrix in normal and fibrotic human lungs. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1985, 131, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, B.C.; Liebler, J.M.; Luby-Phelps, K.; Nicholson, A.G.; Crandall, E.D.; du Bois, R.M.; Borok, Z. Induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in alveolar epithelial cells by transforming growth factor-beta1: Potential role in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 1321–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, N.A.H.M.; Harith, H.H.; Israf, D.A.; Tham, C.L. The differential effects of commercial specialized media on cell growth and transforming growth factor beta 1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in bronchial epithelial cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 3511–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, N.; Tager, A.M. Fibrosis of two: Epithelial cell-fibroblast interactions in pulmonary fibrosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2013, 1832, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, M.; Pardo, A. The leading role of epithelial cells in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Signal. 2020, 66, 109482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunninghake, G.W. Antioxidant therapy for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 2285–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, D.E.; Hirose, N.; Zagarella, L.; Cherniack, R.M. Prolonged monocyte accumulation in the lung during bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. A noninvasive assessment of monocyte kinetics by scintigraphy. Lab. Investig. 1992, 66, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fries, K.M.; Blieden, T.; Looney, R.J.; Sempowski, G.D.; Silvera, M.R.; Willis, R.A.; Phipps, R.P. Evidence of fibroblast heterogeneity and the role of fibroblast subpopulations in fibrosis. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1994, 72, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basset, F.; Ferrans, V.J.; Soler, P.; Takemura, T.; Fukuda, Y.; Crystal, R.G. Intraluminal fibrosis in interstitial lung disorders. Am. J. Pathol. 1986, 122, 443–461. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gabbiani, G. Evolution and clinical implications of the myofibroblast concept. Cardiovasc. Res. 1998, 38, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, N.; Xu, Y.D.; O’Connor, R.; Duronio, V. Proliferation of pulmonary interstitial fibroblasts is mediated by transforming growth factor-beta1-induced release of extracellular fibroblast growth factor-2 and phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and JNK. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 43000–43009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Königshoff, M.; Kramer, M.; Balsara, N.; Wilhelm, J.; Amarie, O.V.; Jahn, A.; Rose, F.; Fink, L.; Seeger, W.; Schaefer, L.; et al. WNT1-inducible signaling protein-1 mediates pulmonary fibrosis in mice and is upregulated in humans with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 772–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilosi, M.; Poletti, V.; Zamò, A.; Lestani, M.; Montagna, L.; Piccoli, P.; Pedron, S.; Bertaso, M.; Scarpa, A.; Murer, B.; et al. Aberrant Wnt/beta-catenin pathway activation in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 162, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.K. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Update on genetic discoveries. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2011, 8, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, N.; O’Connor, R.N.; Flanders, K.C.; Unruh, H. TGF-beta 1, but not TGF-beta 2 or TGF-beta 3, is differentially present in epithelial cells of advanced pulmonary fibrosis: An immunohistochemical study. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1996, 14, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broekelmann, T.J.; Limper, A.H.; Colby, T.V.; McDonald, J.A. Transforming growth factor beta 1 is present at sites of extracellular matrix gene expression in human pulmonary fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 6642–6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi-Wen, X.; Leask, A.; Abraham, D. Regulation and function of connective tissue growth factor/CCN2 in tissue repair, scarring and fibrosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008, 19, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atamas, S.P.; White, B. Cytokine regulation of pulmonary fibrosis in scleroderma. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003, 14, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sime, P.J.; Marr, R.A.; Gauldie, D.; Xing, Z.; Hewlett, B.R.; Graham, F.L.; Gauldie, J. Transfer of tumor necrosis factor-alpha to rat lung induces severe pulmonary inflammation and patchy interstitial fibrogenesis with induction of transforming growth factor-beta1 and myofibroblasts. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 153, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, L.A.; Lasky, J.; Lungarella, G.; Cavarra, E.; Martorana, P.; Banks, W.A.; Peschon, J.J.; Schmidts, H.L.; Brody, A.R.; Friedman, M. Upregulation of the p75 but not the p55 TNF-alpha receptor mRNA after silica and bleomycin exposure and protection from lung injury in double receptor knockout mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1999, 20, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, M.; Hubbard, R.; Meliconi, R.; Whidborne, M.; Eaton, V.; Bingle, C.; Timms, J.; Duff, G.; Facchini, A.; Pacilli, A.; et al. Increased risk of fibrosing alveolitis associated with interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene polymorphisms. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eferl, R.; Hasselblatt, P.; Rath, M.; Popper, H.; Zenz, R.; Komnenovic, V.; Idarraga, M.H.; Kenner, L.; Wagner, E.F. Development of pulmonary fibrosis through a pathway involving the transcription factor Fra-2/AP-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10525–10530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, N. Microarray analysis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2003, 29 (Suppl. S3), S32–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, K.; Gibson, K.F.; Lindell, K.O.; Richards, T.J.; Zhang, Y.; Dhir, R.; Bisceglia, M.; Gilbert, S.; Yousem, S.A.; Song, J.W.; et al. Gene expression profiles of acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, I.O.; Richards, T.J.; Konishi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Gibson, K.; Lokshin, A.E.; Lindell, K.O.; Cisneros, J.; Macdonald, S.D.; Pardo, A.; et al. MMP1 and MMP7 as potential peripheral blood biomarkers in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrove, G.P.; Brown, K.K.; Schiemann, W.P.; Serls, A.E.; Parr, J.E.; Geraci, M.W.; Schwarz, M.I.; Cool, C.D.; Worthen, G.S. Pigment epithelium-derived factor in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A role in aberrant angiogenesis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Rekhter, M.D.; Gordon, D.; Phan, S.H. Myofibroblasts and their role in lung collagen gene expression during pulmonary fibrosis. A combined immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization study. Am. J. Pathol. 1994, 145, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hecker, L.; Vittal, R.; Jones, T.; Jagirdar, R.; Luckhardt, T.R.; Horowitz, J.C.; Pennathur, S.; Martinez, F.J.; Thannickal, V.J. NADPH oxidase-4 mediates myofibroblast activation and fibrogenic responses to lung injury. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, J.C.; Thannickal, V.J. Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in pulmonary fibrosis. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 27, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, R.P.; Penney, D.P.; Keng, P.; Quill, H.; Paxhia, A.; Derdak, S.; Felch, M.E. Characterization of two major populations of lung fibroblasts: Distinguishing morphology and discordant display of Thy 1 and class II MHC. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1989, 1, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempowski, G.D.; Derdak, S.; Phipps, R.P. Interleukin-4 and interferon-gamma discordantly regulate collagen biosynthesis by functionally distinct lung fibroblast subsets. J. Cell Physiol. 1996, 167, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurton, J.; Rose, T.M.; Raghu, G.; Narayanan, A.S. Isolation of a gene product expressed by a subpopulation of human lung fibroblasts by differential display. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1999, 20, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Phillips, R.J.; Burdick, M.D.; Hong, K.; Lutz, M.A.; Murray, L.A.; Xue, Y.Y.; Belperio, J.A.; Keane, M.P.; Strieter, R.M. Circulating fibrocytes traffic to the lungs in response to CXCL12 and mediate fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, T.E.; Cowper, S.; Wu, S.P.; Bockenstedt, L.K.; Bucala, R. Circulating fibrocytes: Collagen-secreting cells of the peripheral blood. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordana, M.; Schulman, J.; McSharry, C.; Irving, L.B.; Newhouse, M.T.; Jordana, G.; Gauldie, J. Heterogeneous proliferative characteristics of human adult lung fibroblast lines and clonally derived fibroblasts from control and fibrotic tissue. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1988, 137, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Chen, Y.Y.; Rusch, V.; Rabinovitch, P.S. Differential proliferation of fibroblasts cultured from normal and fibrotic human lungs. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1988, 138, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilborn, J.; Crofford, L.J.; Burdick, M.D.; Kunkel, S.L.; Strieter, R.M.; Peters-Golden, M. Cultured lung fibroblasts isolated from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis have a diminished capacity to synthesize prostaglandin E2 and to express cyclooxygenase-2. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 1861–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, T.M.; Evans, I.C.; Bottoms, S.E.; Mercer, P.F.; Thorley, A.J.; Nicholson, A.G.; Laurent, G.J.; Tetley, T.D.; Chambers, R.C.; McAnulty, R.J. Diminished prostaglandin E2 contributes to the apoptosis paradox in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzenstein, A.L.; Myers, J.L.; Mazur, M.T. Acute interstitial pneumonia. A clinicopathologic, ultrastructural, and cell kinetic study. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1986, 10, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyalov, S.L.; Gabbiani, G.; Kapanci, Y. Rat alveolar myofibroblasts acquire alpha-smooth muscle actin expression during bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 1993, 143, 1754–1765. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iwano, M.; Plieth, D.; Danoff, T.M.; Xue, C.; Okada, H.; Neilson, E.G. Evidence that fibroblasts derive from epithelium during tissue fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; Neilson, E.G. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1776–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, B.C.; duBois, R.M.; Borok, Z. Epithelial origin of myofibroblasts during fibrosis in the lung. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2006, 3, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, G.M.; Balestro, E. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis landscapes: Looking glass from pathology to therapy. Minerva Med. 2015, 106, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Stella, G.M.; Inghilleri, S.; Pignochino, Y.; Zorzetto, M.; Oggionni, T.; Morbini, P.; Luisetti, M. Activation of oncogenic pathways in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Transl. Oncol. 2014, 7, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghatak, S.; Bogatkevic, G.S.; Atnelishvili, I.; Akter, T.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.; Hoffman, S.; Fresco, V.M.; Fucsh, J.V.; Visconti, R.P.; Markwald, R.R.; et al. Overexpression of c-MET and CD44v6 receptors contributes to autocrineTGF-β1 signaling in interstitial lung disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 7856–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.K.; Wei, Y.; Szekeres, C.; Kugler, M.C.; Wolters, P.J.; Hill, M.L.; Frank, J.A.; Brumwell, A.N.; Wheeler, S.E.; Kreidberg, J.A.; et al. Epithelial cell alpha3beta1 integrin links beta-catenin and Smad signaling to promote myofibroblast formation and pulmonary fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thannickal, V.J.; Horowitz, J.C. Evolving concepts of apoptosis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2006, 3, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandit, K.V.; Milosevic, J. MicroRNA regulatory networks in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 93, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Cui, H.; Xie, N.; Icyuz, M.; Banerjee, S.; Antony, V.B.; Abraham, E.; Thannickal, V.J.; Liu, G. miR-145 regulates myofibroblast differentiation and lung fibrosis. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 2382–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milosevic, J.; Pandit, K.; Magister, M.; Rabinovich, E.; Ellwanger, D.C.; Yu, G.; Vuga, L.J.; Weksler, B.; Benos, P.V.; Gibson, K.F.; et al. Profibrotic role of miR-154 in pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 47, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lino Cardenas, C.L.; Henaoui, I.S.; Courcot, E.; Roderburg, C.; Cauffiez, C.; Aubert, S.; Copin, M.C.; Wallaert, B.; Glowacki, F.; Dewaeles, E.; et al. miR-199a-5p Is upregulated during fibrogenic response to tissue injury and mediates TGFbeta-induced lung fibroblast activation by targeting caveolin-1. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Kumar, M.; Negi, V.; Pattnaik, B.; Prakash, Y.S.; Agrawal, A.; Ghosh, B. MicroRNA-326 regulates profibrotic functions of transforming growth factor-β in pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 50, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakhlallah, D.; Batte, K.; Wang, Y.; Cantemir-Stone, C.Z.; Yan, P.; Nuovo, G.; Mikhail, A.; Hitchcock, C.L.; Wright, V.P.; Nana-Sinkam, S.P.; et al. Epigenetic regulation of miR-17~92 contributes to the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, J.A.; Broekelmann, T.J.; Matheke, M.L.; Crouch, E.; Koo, M.; Kuhn, C., 3rd. A monoclonal antibody to the carboxyterminal domain of procollagen type I visualizes collagen-synthesizing fibroblasts. Detection of an altered fibroblast phenotype in lungs of patients with pulmonary fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 1986, 78, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, E.D.; Turner-Warwick, M.; Adelmann-Grill, B.C. Immunohistochemical study of collagen types in human foetal lung and fibrotic lung disease. Thorax 1981, 36, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, N.K.; Argent, A.C.; McAnulty, R.J.; Black, C.M.; Corrin, B.; Laurent, G.J. Collagen synthesis and degradation by systemic sclerosis lung fibroblasts. Responses to transforming growth factor-beta. Chest 1991, 99, 71S–72S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Masta, S.; Meyers, D.; Narayanan, A.S. Collagen synthesis by normal and fibrotic human lung fibroblasts and the effect of transforming growth factor-beta. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1989, 140, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selman, M.; Montaño, M.; Ramos, C.; Chapela, R. Concentration, biosynthesis and degradation of collagen in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax 1986, 41, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi-Dana, S.M.M.; Gholami, Y.; Meghdadi, M.; Fadaei, M.S.; Askari, V.R. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for COVID-19 infection. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nykänen, A.I.; Liu, M.; Keshavjee, S. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapy in Lung Transplantation. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleasants, R.; Tighe, R.M. Management of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Ann. Pharmacother. 2019, 53, 1238–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Anstrom, K.J.; King, T.E.J.; Lasky, J.A.; Martinez, F.J. Prednisone, azathioprine, and N-acetylcysteine for pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1968–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondoh, Y.; Taniguchi, H.; Yokoi, T.; Nishiyama, O.; Ohishi, T.; Kato, T.; Suzuki, K.; Suzuki, R. Cyclophosphamide and low-dose prednisolone in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and fibrosing nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 25, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzouvelekis, A.; Bouros, E.; Oikonomou, A.; Ntolios, P.; Zacharis, G.; Kolios, G.; Bouros, D. Effect and safety of mycophenolate mofetil in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Pulm. Med. 2011, 2011, 849035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabata, C.; Tabata, R.; Kadokawa, Y.; Hisamori, S.; Takahashi, M.; Mishima, M.; Nakano, T.; Kubo, H. Thalidomide prevents bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.L.; Xu, P.; Chen, H.H.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, J.; Jiang, C.; Jiang, S.; Ni, S.Z.; Xu, B.; Li, L. Thalidomide Inhibits TGF-β1-induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Alveolar Epithelial Cells via Smad-Dependent and Smad-Independent Signaling Pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wind, S.; Schmid, U.; Freiwald, M.; Marzin, K.; Lotz, R.; Ebner, T.; Stopfer, P.; Dallinger, C. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Nintedanib. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2019, 58, 1131–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hostettler, K.E.; Zhong, J.; Papakonstantinou, E.; Karakiulakis, G.; Tamm, M.; Seidel, P.; Sun, Q.; Mandal, J.; Lardinois, D.; Lambers, C.; et al. Anti-fibrotic effects of nintedanib in lung fibroblasts derived from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2014, 15, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollin, L.; Maillet, I.; Quesniaux, V.; Holweg, A.; Ryffel, B. Antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory activity of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor nintedanib in experimental models of lung fibrosis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 349, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; du Bois, R.M.; Raghu, G.; Azuma, A.; Brown, K.K.; Costabel, U.; Cottin, V.; Flaherty, K.R.; Hansell, D.M.; Inoue, Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, H.; Takeda, N.; Komuro, I. Pathophysiology and therapeutic potential of cardiac fibrosis. Inflamm. Regen. 2017, 37, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziani, F.; Varone, F.; Crea, F.; Richeldi, L. Treating heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Learning from pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimo, A.; Spitaleri, G.; Nieri, D.; Tavanti, L.M.; Meschi, C.; Panichella, G.; Lupón, J.; Pistelli, F.; Carrozzi, L.; Bayes-Genis, A.; et al. Pirfenidone for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Beyond. Card. Fail. Rev. 2022, 8, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.F.; Egan, A.M.; Shaughnessy, G.F.; Anderson, D.K.; Kottom, T.J.; Dasari, H.; Van Keulen, V.P.; Aubry, M.C.; Yi, E.S.; Limper, A.H.; et al. Antifibrotics Modify B-Cell-induced Fibroblast Migration and Activation in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 64, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swigris, J.; Fairclough, D. Pirfenidone in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 36, 695–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, T.E., Jr.; Bradford, W.Z.; Castro-Bernardini, S.; Fagan, E.A.; Glaspole, I.; Glassberg, M.K.; Gorina, E.; Hopkins, P.M.; Kardatzke, D.; Lancaster, L.; et al. A phase 3 trial of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2083–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vancheri, C.; Kreuter, M.; Richeldi, L.; Ryerson, C.J.; Valeyre, D.; Grutters, J.C.; Wiebe, S.; Stansen, W.; Quaresma, M.; Stowasser, S.; et al. Nintedanib with add-on pirfenidone in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Results of the INJOURNEY trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran-Mendoza, O.; Alharthi, B.; Clements-Baker, M. Nintedanib for Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaherty, K.R.; Wells, A.U.; Cottin, V.; Devaraj, A.; Walsh, S.L.F.; Inoue, Y.; Richeldi, L.; Kolb, M.; Tetzlaff, K.; Stowasser, S.; et al. Nintedanib in Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Highland, K.B.; Distler, O.; Kuwana, M.; Allanore, Y.; Assassi, S.; Azuma, A.; Bourdin, A.; Denton, C.P.; Distler, J.H.W.; Hoffmann-Vold, A.M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease treated with mycophenolate: A subgroup analysis of the SENSCIS trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, T.M.; Mayes, M.D.; Kreuter, M.; Volkmann, E.R.; Aringer, M.; Castellvi, I.; Cutolo, M.; Stock, C.; Schoof, N.; Alves, M.; et al. Effect of Nintedanib on Lung Function in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease: Further Analyses of a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, T.M.; Corte, T.J.; Fischer, A.; Kreuter, M.; Lederer, D.J.; Molina-Molina, M.; Axmann, J.; Kirchgaessler, K.U.; Samara, K.; Gilberg, F.; et al. Pirfenidone in patients with unclassifiable progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behr, J.; Prasse, A.; Kreuter, M.; Johow, J.; Rabe, K.F.; Bonella, F.; Bonnet, R.; Grohe, C.; Held, M.; Wilkens, H.; et al. Pirfenidone in patients with progressive fibrotic interstitial lung diseases other than idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (RELIEF): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, J.J.; Danoff, S.K.; Woodhead, F.A.; Hurwitz, S.; Maurer, R.; Glaspole, I.; Dellaripa, P.F.; Gooptu, B.; Vassallo, R.; Cox, P.G.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of pirfenidone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, N.; Sharma, S.K.; Mishra, D.; Dhooria, S.; Dhir, V.; Jain, S. Efficacy and safety of pirfenidone in systemic sclerosis-related interstitial lung disease-a randomised controlled trial. Rheumatol. Int. 2020, 40, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnerty, J.P.; Ponnuswamy, A.; Dutta, P.; Abdelaziz, A.; Kamil, H. Efficacy of antifibrotic drugs, nintedanib and pirfenidone, in treatment of progressive pulmonary fibrosis in both idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and non-IPF: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, D.F.; Roets, L.; Krasnodembskaya, A.D. The Role of Lung Resident Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in the Pathogenesis and Repair of Chronic Lung Disease. Stem Cells 2023, 41, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Castro, L.L.; Lopes-Pacheco, M.; Weiss, D.J.; Cruz, F.F.; Rocco, P.R.M. Current understanding of the immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal stromal cells. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 97, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerkic, M.; Szaszi, K.; Laffey, J.G.; Rotstein, O.; Zhang, H. Key Role of Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Interaction with Macrophages in Promoting Repair of Lung Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida-Porada, G.; Atala, A.J.; Porada, C.D. Therapeutic Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for Immunotherapy and for Gene and Drug Delivery. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 16, 204–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittenger, M.F.; Discher, D.E.; Péault, B.M.; Phinney, D.G.; Hare, J.M.; Caplan, A.I. Mesenchymal stem cell perspective: Cell biology to clinical progress. NPJ Regen. Med. 2019, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, D.M.L.W.; Wisman, M.; Noordhoek, J.A.; Nizamoglu, M.; Jonker, M.R.; de Bruin, H.G.; Arevalo Gomez, K.; Ten Hacken, N.H.T.; Pouwels, S.D.; Heijink, I.H. Paracrine Regulation of Alveolar Epithelial Damage and Repair Responses by Human Lung-Resident Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.A.; Wang, S.Y.; Yeh, C.C.; Fu, T.W.; Fu, Y.Y.; Ko, T.L.; Chiu, M.M.; Chen, T.H.; Tsai, P.J.; Fu, Y.S. Reversal of bleomycin-induced rat pulmonary fibrosis by a xenograft of human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells from Wharton’s jelly. Theranostics 2019, 9, 6646–6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zheng, R.; Chen, Q.; Shao, J.; Yu, J.; Hu, S. Mesenchymal stem cells microvesicles stabilize endothelial barrier function partly mediated by hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, F. Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapies for Pulmonary Fibrosis. DNA Cell Biol. 2022, 41, 951–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Park, J.; Liu, A.; Lee, J.; Zhang, X.; Hao, Q.; Lee, J.W. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Microvesicles Restore Protein Permeability Across Primary Cultures of Injured Human Lung Microvascular Endothelial Cells. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2018, 7, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.; Krause, D.; Deans, R.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.J.; Horwitz, E. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramireddy, A.; Brodt, C.R.; Mendizabal, A.M.; DiFede, D.L.; Healy, C.; Goyal, V.; Alansari, Y.; Coffey, J.O.; Viles-Gonzalez, J.F.; Heldman, A.W.; et al. Effects of Transendocardial Stem Cell Injection on Ventricular Proarrhythmia in Patients with Ischemic Cardiomyopathy: Results from the POSEIDON and TAC-HFT Trials. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Németh, K.; Leelahavanichkul, A.; Yuen, P.S.; Mayer, B.; Parmelee, A.; Doi, K.; Robey, P.G.; Leelahavanichkul, K.; Koller, B.H.; Brown, J.M.; et al. Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate sepsis via prostaglandin E(2)-dependent reprogramming of host macrophages to increase their interleukin-10 production. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrzejewska, A.; Dabrowska, S.; Lukomska, B.; Janowski, M. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Neurological Disorders. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2002944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zhang, H.; Hua, B.; Wang, H.; Lu, L.; Shi, S.; Hou, Y.; Zeng, X.; Gilkeson, G.S.; Sun, L. Allogenic mesenchymal stem cells transplantation in refractory systemic lupus erythematosus: A pilot clinical study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1423–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Blanc, K.; Frassoni, F.; Ball, L.; Locatelli, F.; Roelofs, H.; Lewis, I.; Lanino, E.; Sundberg, B.; Bernardo, M.E.; Remberger, M.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of steroid-resistant, severe, acute graft-versus-host disease: A phase II study. Lancet 2008, 371, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, J.; Peng, Z. The safety and efficacy of mesenchymal stromal cells in ARDS: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzouvelekis, A.; Toonkel, R.; Karampitsakos, T.; Medapalli, K.; Ninou, I.; Aidinis, V.; Bouros, D.; Glassberg, M.K. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for the Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.; Fonseca, L.; Gowda, S.; Chougule, B.; Hari, A.; Totey, S. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate early stage of bleomycin induced pulmonary fibrosis: Comparison with pirfenidone. Int. J. Stem Cells 2016, 9, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, M.A.; Laffey, J.G.; Pelosi, P.; Rocco, P.R. Mesenchymal stem cell trials for pulmonary diseases. J. Cell Biochem. 2014, 115, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Liu, P.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dai, H.; Wang, C. Therapeutic Applications of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 639657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed, M.; El-Feky, M.A.; El-Amir, M.I.; Hasan, A.S.; Tag-Adeen, M.; Urata, Y.; Goto, S.; Luo, L.; Yan, C.; Li, T.S. Immunomodulatory effect of mesenchymal stem cells: Cell origin and cell quality variations. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrenko, Y.; Vackova, I.; Kekulova, K.; Chudickova, M.; Koci, Z.; Turnovcova, K.; Kupcova Skalnikova, H.; Vodicka, P.; Kubinova, S. A Comparative Analysis of Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells derived from Different Sources, with a Focus on Neuroregenerative Potential. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periera-Simon, S.; Xia, X.; Catanuto, P.; Coronado, R.; Kurtzberg, J.; Bellio, M.; Lee, Y.S.; Khan, A.; Smith, R.; Elliot, S.J.; et al. Anti-fibrotic effects of different sources of MSC in bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in C57BL6 male mice. Respirology 2021, 26, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzouvelekis, A.; Paspaliaris, V.; Koliakos, G.; Ntolios, P.; Bouros, E.; Oikonomou, A.; Zissimopoulos, A.; Boussios, N.; Dardzinski, B.; Gritzalis, D.; et al. A prospective, non-randomized, no placebo-controlled, phase Ib clinical trial to study the safety of the adipose derived stromal cells-stromal vascular fraction in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glassberg, M.K.; Minkiewicz, J.; Toonkel, R.L.; Simonet, E.S.; Rubio, G.A.; DiFede, D.; Shafazand, S.; Khan, A.; Pujol, M.V.; LaRussa, V.F.; et al. Allogeneic Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis via Intravenous Delivery (AETHER): A Phase I Safety Clinical Trial. Chest 2017, 151, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, D.C.; Enever, D.; Ilic, N.; Sparks, L.; Whitelaw, K.; Ayres, J.; Yerkovich, S.T.; Khalil, D.; Atkinson, K.M.; Hopkins, P.M. A phase 1b study of placenta-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respirology 2014, 19, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, D.C.; Enever, D.; Lawrence, S.; Sturm, M.J.; Herrmann, R.; Yerkovich, S.; Musk, M.; Hopkins, P.M. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapy for Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction: Results of a First-in-Man Study. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 1152–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averyanov, A.; Koroleva, I.; Konoplyannikov, M.; Revkova, V.; Lesnyak, V.; Kalsin, V.; Danilevskaya, O.; Nikitin, A.; Sotnikova, A.; Kotova, S.; et al. First-in-human high-cumulative-dose stem cell therapy in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with rapid lung function decline. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2020, 9, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, M.; Midolo, M.; Bassi, G.; Malpeli, G.; Bifari, F.; Chilosi, M.; Zanotto, M.; Carusone, R.; Zanoncello, J.; Pizzolo, G.; et al. Comparison between bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells (BM-MSC) and lung mesenchymal stromal cells (Lung-MSC) for epithelial regeneration. Blood 2013, 122, 5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, K.M.; Samad, S.; Spiteri, M.A.; Forsyth, N.R. Mesenchymal stem cells promote alveolar epithelial cell wound repair in vitro through distinct migratory and paracrine mechanisms. Respir. Res. 2013, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez-Curtis, L.A.; Janowska-Wieczorek, A. Enhancing the migration ability of mesenchymal stromal cells by targeting the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 561098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardia, E.; Ch’ng, E.S.; Yahaya, B.H. Aerosol-based airway epithelial cell delivery improves airway regeneration and repair. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, e995–e1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosser, K.; Wang, J.P.; Dos Santos, C.; Walley, K.R.; Marshall, J.; Fergusson, D.A.; Winston, B.W.; Granton, J.; Watpool, I.; Stewart, D.J.; et al. Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Treatment on Systemic Cytokine Levels in a Phase 1 Dose Escalation Safety Trial of Septic Shock Patients. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Chiang, C.H.; Hung, S.C.; Chian, C.F.; Tsai, C.L.; Chen, W.C.; Zhang, H. Hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate ischemia/reperfusion-induced lung injury. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; An, G.; Wang, Y.; Liang, D.; Zhu, Z.; Lian, X.; Niu, P.; Guo, C.; Tian, L. Anti-fibrotic effects of bone morphogenetic protein-7-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2017, 102, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.W.; Theng, S.M.; Huang, T.T.; Choo, K.B.; Chen, C.M.; Kuo, H.P.; Chong, K.Y. Oncostatin M-Preconditioned Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Through Paracrine Effects of the Hepatocyte Growth Factor. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 1006–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, W.; Yue, S.; Yang, L.; Hua, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, H.; Luo, Z.; Tang, S. Pretreatment with G-CSF Could Enhance the Antifibrotic Effect of BM-MSCs on Pulmonary Fibrosis. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 1726743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, W.G.; Guo, X.C.; Wu, M.J.; Xu, Z.Y.; Jiang, J.F.; Shen, C.; Liu, H.Q. N-acetylcysteine-pretreated human embryonic mesenchymal stem cell administration protects against bleomycin-induced lung injury. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 346, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Park, J.E.; Tsagkogeorga, G.; Yanagita, M.; Koo, B.K.; Han, N.; Lee, J.H. Inflammatory Signals Induce AT2 Cell-Derived Damage-Associated Transient Progenitors that Mediate Alveolar Regeneration. Cell Stem Cell. 2020, 27, 366–382.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Confalonieri, P.; Volpe, M.C.; Jacob, J.; Maiocchi, S.; Salton, F.; Ruaro, B.; Confalonieri, M.; Braga, L. Regeneration or Repair? The Role of Alveolar Epithelial Cells in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF). Cells 2022, 11, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, T.J.; Brownfield, D.G.; Krasnow, M.A. Alveolar progenitor and stem cells in lung development, renewal and cancer. Nature 2014, 507, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treutlein, B.; Brownfield, D.G.; Wu, A.R.; Neff, N.F.; Mantalas, G.L.; Espinoza, F.H.; Desai, T.J.; Krasnow, M.A.; Quake, S.R. Reconstructing lineage hierarchies of the distal lung epithelium using single-cell RNA-seq. Nature 2014, 509, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basil, M.C.; Cardenas-Diaz, F.L.; Kathiriya, J.J.; Morley, M.P.; Carl, J.; Brumwell, A.N.; Katzen, J.; Slovik, K.J.; Babu, A.; Zhou, S.; et al. Human distal airways contain a multipotent secretory cell that can regenerate alveoli. Nature 2022, 604, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabhan, A.N.; Brownfield, D.G.; Harbury, P.B.; Krasnow, M.A.; Desai, T.J. Single-cell Wnt signaling niches maintain stemness of alveolar type 2 cells. Science 2018, 359, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Mollar, A.; Nacher, M.; Gay-Jordi, G.; Closa, D.; Xaubet, A.; Bulbena, O. Intratracheal transplantation of alveolar type II cells reverses bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillamat-Prats, R.; Gay-Jordi, G.; Xaubet, A.; Peinado, V.I.; Serrano-Mollar, A. Alveolar type II cell transplantation restores pulmonary surfactant protein levels in lung fibrosis. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2014, 33, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Mollar, A.; Gay-Jordi, G.; Guillamat-Prats, R.; Closa, D.; Hernandez-Gonzalez, F.; Marin, P.; Burgos, F.; Martorell, J.; Sánchez, M.; Arguis, P.; et al. Safety and Tolerability of Alveolar Type II Cell Transplantation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Chest 2016, 150, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galipeau, J. The mesenchymal stromal cells dilemma--does a negative phase III trial of random donor mesenchymal stromal cells in steroid-resistant graft-versus-host disease represent a death knell or a bump in the road? Cytotherapy 2013, 15, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galderisi, U.; Peluso, G.; Di Bernardo, G. Clinical Trials Based on Mesenchymal Stromal Cells are Exponentially Increasing: Where are We in Recent Years? Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2022, 18, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgoulis, V.; Adams, P.D.; Alimonti, A.; Bennett, D.C.; Bischof, O.; Bishop, C.; Campisi, J.; Collado, M.; Evangelou, K.; Ferbeyre, G.; et al. Cellular Senescence: Defining a Path Forward. Cell 2019, 179, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salama, R.; Sadaie, M.; Hoare, M.; Narita, M. Cellular senescence and its effector programs. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Cui, X.; Wang, Q.; Fang, C.; Tan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yi, K.; Yang, C.; You, H.; Shang, R.; et al. RUNX1 contributes to the mesenchymal subtype of glioblastoma in a TGFβ pathway-dependent manner. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilbey, A.; Terry, A.; Cameron, E.R.; Neil, J.C. Oncogene-induced senescence: An essential role for Runx. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 2333–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguma, Y.; Alessio, N.; Aprile, D.; Dezawa, M.; Peluso, G.; Di Bernardo, G.; Galderisi, U. Meta-analysis of senescent cell secretomes to identify common and specific features of the different senescent phenotypes: A tool for developing new senotherapeutics. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, M.J.; White, T.A.; Iijima, K.; Haak, A.J.; Ligresti, G.; Atkinson, E.J.; Oberg, A.L.; Birch, J.; Salmonowicz, H.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Cellular senescence mediates fibrotic pulmonary disease. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomas, N.J.; Watts, K.L.; Akram, K.M.; Forsyth, N.R.; Spiteri, M.A. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Immunohistochemical analysis provides fresh insights into lung tissue remodelling with implications for novel prognostic markers. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2012, 5, 58–71. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Tchkonia, T.; Pirtskhalava, T.; Gower, A.C.; Ding, H.; Giorgadze, N.; Palmer, A.K.; Ikeno, Y.; Hubbard, G.B.; Lenburg, M.; et al. The Achilles’ heel of senescent cells: From transcriptome to senolytic drugs. Aging Cell. 2015, 14, 644–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampel, H.; Lista, S.; Neri, C.; Vergallo, A. Time for the systems-level integration of aging: Resilience enhancing strategies to prevent Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2019, 181, 101662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justice, J.N.; Nambiar, A.M.; Tchkonia, T.; LeBrasseur, N.K.; Pascual, R.; Hashmi, S.K.; Prata, L.; Masternak, M.M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Musi, N.; et al. Senolytics in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Results from a first-in-human, open-label, pilot study. EBioMedicine 2019, 40, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nambiar, A.; Kellogg, D., 3rd; Justice, J.; Goros, M.; Gelfond, J.; Pascual, R.; Hashmi, S.; Masternak, M.; Prata, L.; LeBrasseur, N.; et al. Senolytics dasatinib and quercetin in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Results of a phase I, single-blind, single-center, randomized, placebo-controlled pilot trial on feasibility and tolerability. EBioMedicine 2023, 90, 104481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohmann, M.S.; Habiel, D.M.; Coelho, A.L.; Verri, W.A., Jr.; Hogaboam, C.M. Quercetin Enhances Ligand-induced Apoptosis in Senescent Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Fibroblasts and Reduces Lung Fibrosis In Vivo. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 60, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyanov, V.; Kim, G.J.; Hayes, W.; Du, S.; Ganguly, B.J.; Sy, O.; Lee, S.K.; Bogatkevich, G.S.; Schieven, G.L.; Schiopu, E.; et al. Novel lung imaging biomarkers and skin gene expression subsetting in dasatinib treatment of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkt, W.; Bueno, M.; Mora, A.L.; Lagares, D. Senotherapeutics: Targeting senescence in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 101, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecker, L.; Logsdon, N.J.; Kurundkar, D.; Kurundkar, A.; Bernard, K.; Hock, T.; Meldrum, E.; Sanders, Y.Y.; Thannickal, V.J. Reversal of persistent fibrosis in aging by targeting Nox4-Nrf2 redox imbalance. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 231ra47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, A.; Gilpin, S.E.; Ask, K.; Cox, G.; Cook, D.; Gauldie, J.; Margetts, P.J.; Farkas, L.; Dobranowski, J.; Boylan, C.; et al. Circulating fibrocytes are an indicator of poor prognosis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillingh, M.R.; van den Blink, B.; Moerland, M.; van Dongen, M.G.; Levi, M.; Kleinjan, A.; Wijsenbeek, M.S.; Lupher, M.L., Jr.; Harper, D.M.; Getsy, J.A.; et al. Recombinant human serum amyloid P in healthy volunteers and patients with pulmonary fibrosis. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 26, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Blink, B.; Dillingh, M.R.; Ginns, L.C.; Morrison, L.D.; Moerland, M.; Wijsenbeek, M.; Trehu, E.G.; Bartholmai, B.J.; Burggraaf, J. Recombinant human pentraxin-2 therapy in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Safety, pharmacokinetics and exploratory efficacy. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; van den Blink, B.; Hamblin, M.J.; Brown, A.W.; Golden, J.A.; Ho, L.A.; Wijsenbeek, M.S.; Vasakova, M.; Pesci, A.; Antin-Ozerkis, D.E.; et al. Effect of Recombinant Human Pentraxin 2 vs Placebo on Change in Forced Vital Capacity in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2018, 319, 2299–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, D.S.; Grossfeld, D.; Renna, H.A.; Agarwala, P.; Spiegler, P.; DeLeon, J.; Reiss, A.B. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Current and future treatment. Clin. Respir. J. 2022, 16, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richeldi, L.; Fernández Pérez, E.R.; Costabel, U.; Albera, C.; Lederer, D.J.; Flaherty, K.R.; Ettinger, N.; Perez, R.; Scholand, M.B.; Goldin, J.; et al. Pamrevlumab, an anti-connective tissue growth factor therapy, for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (PRAISE): A phase 2, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Phase 3 Trial | |
|---|---|
| Molecule | Study Design |
| Anlotinib | A phase 2 and 3 trial in China is evaluating 1-year outcomes of once-daily oral anlotinib for treatment of IPF/progressive fibrosis–interstitial lung disease (PF-ILDS) (NCT05828953). Anlotinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) that targets four factors: vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGR), fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR), platelet-derived growth factor receptors (PDGFR), and c-kit. It is approved in China as a third-line therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). |
| BI 101550 | Enrollment in the FIBRONEER-IPF trial commenced in autumn 2022 (NCT05321069), with completion scheduled for 2024. BI 1015550 is an oral phosphodiesterase 4B (PDE4B) inhibitor. FIBRONEER-ILD is a separate phase 3 trial in fibrosing idiopathic lung disease (NCT05321082). In both trials, the primary endpoint is the absolute change from baseline in FVC at week 52. |
| BMS-986278 | Results of a phase 2 trial showed that twice-daily treatment with oral BMS-986278 60 mg over 26 weeks reduced the rate of decline in ppFVC by 69% vs. placebo. The phase 3 ALOFT trial has been approved but has not yet started recruiting patients (NCT06003426). BMS-986278 is a lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 (LPA1) antagonist. |
| Lansoprazole | Commonly used to treat and prevent gastrointestinal problems like stomach ulcers and esophagitis, this oral proton pump inhibitor (PPI) is the focus of a trial in the United Kingdom evaluating if PPIs can slow the progression of IPF (NCT04965298). |
| N-acetylcysteine (NAC) | The PRECISIONS trial is evaluating the effect of NAC plus standard-of care treatment in IPF patients who have the TOLLIP rs3750910 TT genotype (NCT04300920). Participants receive 600 mg NAC orally or matched placebo three times daily for 24 months. Trial completion is scheduled for 2025. |
| Treprostinil | Already approved to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension and pulmonary hypertension associated with interstitial lung disease, inhaled treprostinil is the subject of the TETON 1 and 2 trials evaluating its impact on ppFVC after 52 weeks of treatment (NCT04708782, NCT05255991). |
| Phase 2 Trial | |
| Molecule | Study Design |
| Bexotegrast (PLN-74809) | (PLN-74809) is an oral, small-molecule, dual-selective inhibitor of alphav/beta6 and alphav/beta1 (NCT04396756). |
| BBT-877 | Described as a potent autotaxin (ATX) inhibitor, BBT-877 demonstrated its ability to inhibit lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) production by as much as 90% (NCT05483907). |
| CC-90001 | It is an oral, once-daily c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor. JNKs have been implicated in the underlying mechanisms of fibrosis, including epithelial cell death, inflammation and polarization of profibrotic macrophages, fibroblast activation, and collagen production (NCT03142191). |
| C21 | C21 targets the underlying fibrosis in IPF by stimulating the protective arm of the renin–angiotensin system. It also has an upstream effect by promoting alveolar repair, by which it can reduce fibrosis formation, stabilize disease, and increase lung capacity (NCT04533022). |
| CSL312 (garadacimab) | It is a humanized anti-FXIIa monoclonal antibody administrated intravenously (NCT05130970). |
| Cudetaxestat | It is a noncompetitive autotaxin inhibitor (NCT05373914). |
| Bersiposocin/DWN12088 | Bersiposocin/DWN12088, an inhibitor of prolyl-tRNA synthetase 1 (PARS1), is suspected to control the pathologic accumulation of collagen containing high amounts of proline in fibrotic diseases (NCT05389215). |
| ENV-101 | ENV-101 is a small-molecule inhibitor of the Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway, which plays a key role in IPF. This agent was originally developed to target Hh-driven cancers (NCT04968574). |
| GKT137831 (setanaxib) | It inhibits nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase (NOX) isoforms (NCT03865927). |
| HZN-825 | HZN-825 is a lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 (LPAR1) antagonist (NCT05032066). |
| Ifetroban | It is a potent and selective thromboxane–prostanoid receptor(TPr) antagonist, exhibits a high affinity for TPr in platelets, vascular and airway smooth muscle, and fibroblasts, and lacks agonistic activity (NCT05571059). |
| INS018_055 | It is a small-molecule, oral antifibrotic candidate notable for being the first entirely AI-generated drug to enter phase 2 trials. Trial enrollment started in October (NCT05975983,NCT05983920). |
| Jaktinib dihydrochloride mono- hydrate | It is an oral JAK1, JAK2, and JAK3 inhibitor (NCT04312594). |
| Leramistat | It is an anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) agent (NCT05951296). |
| LTP001 | It is an oral, selectively deuterated form of pirfenidone designed to retain the antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory activity of pirfenidone with a differentiated pharmacokinetic profile (NCT05497284, NCT05321420). |
| ME-015 (suplatast tosilate) | It aims to stabilize ion channels in the neuronal endings in the lungs that mediate IPF-related cough (NCT05983471). |
| Nalbuphine | It is a small-molecule, dual-mechanism treatment for chronic cough in IPF and acts as both a mu opioid receptor antagonist and a kappa opioid receptor agonist (NCT05964335). The CANAL trial, completed last year, is evaluating an extended-release formulation (NCT04030026). |
| NP-120 (ifenprodil) | It is a small-molecule N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist that specifically targets the NMDA-type subunit 2B (GluN2B) (NCT04318704). |
| Orvepitant | It is a selective antagonist for the NK1 receptor and is being evaluated to treat IPF-related cough (NCT05815089). |
| RXC007 (zelasudil) | It is a coiled-coil-containing protein kinase 2 (ROCK2) selective inhibitor and was granted FDA orphan drug designation in August 2023 (NCT05570058). |
| Saracatinib | It is a selective Src kinase inhibitor originally developed for oncological indications (NCT04598919). |
| SHR-1906 | For intravenous treatment, it inhibits the binding of a target protein to a variety of cytokines and growth factors, affects downstream signaling pathways, and reduces cell proliferation and migration (NCT05722964). |
| TTI-101 | It is an oral, small-molecule inhibitor of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT3), which has been found to accumulate in the lungs of IPF patients (NCT05671835). |
| VAY736 (lanalumab) | It is a BAFF-R inhibitor (NCT03287414). |
| Vixarelimab | It is a human monoclonal oncastatin M receptor beta antibody (NCT05785624). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lettieri, S.; Bertuccio, F.R.; del Frate, L.; Perrotta, F.; Corsico, A.G.; Stella, G.M. The Plastic Interplay between Lung Regeneration Phenomena and Fibrotic Evolution: Current Challenges and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010547
Lettieri S, Bertuccio FR, del Frate L, Perrotta F, Corsico AG, Stella GM. The Plastic Interplay between Lung Regeneration Phenomena and Fibrotic Evolution: Current Challenges and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(1):547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010547
Chicago/Turabian StyleLettieri, Sara, Francesco R. Bertuccio, Lucia del Frate, Fabio Perrotta, Angelo G. Corsico, and Giulia M. Stella. 2024. "The Plastic Interplay between Lung Regeneration Phenomena and Fibrotic Evolution: Current Challenges and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 1: 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010547
APA StyleLettieri, S., Bertuccio, F. R., del Frate, L., Perrotta, F., Corsico, A. G., & Stella, G. M. (2024). The Plastic Interplay between Lung Regeneration Phenomena and Fibrotic Evolution: Current Challenges and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(1), 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010547






