Increased Dentate Gyrus Excitability in the Intrahippocampal Kainic Acid Mouse Model for Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
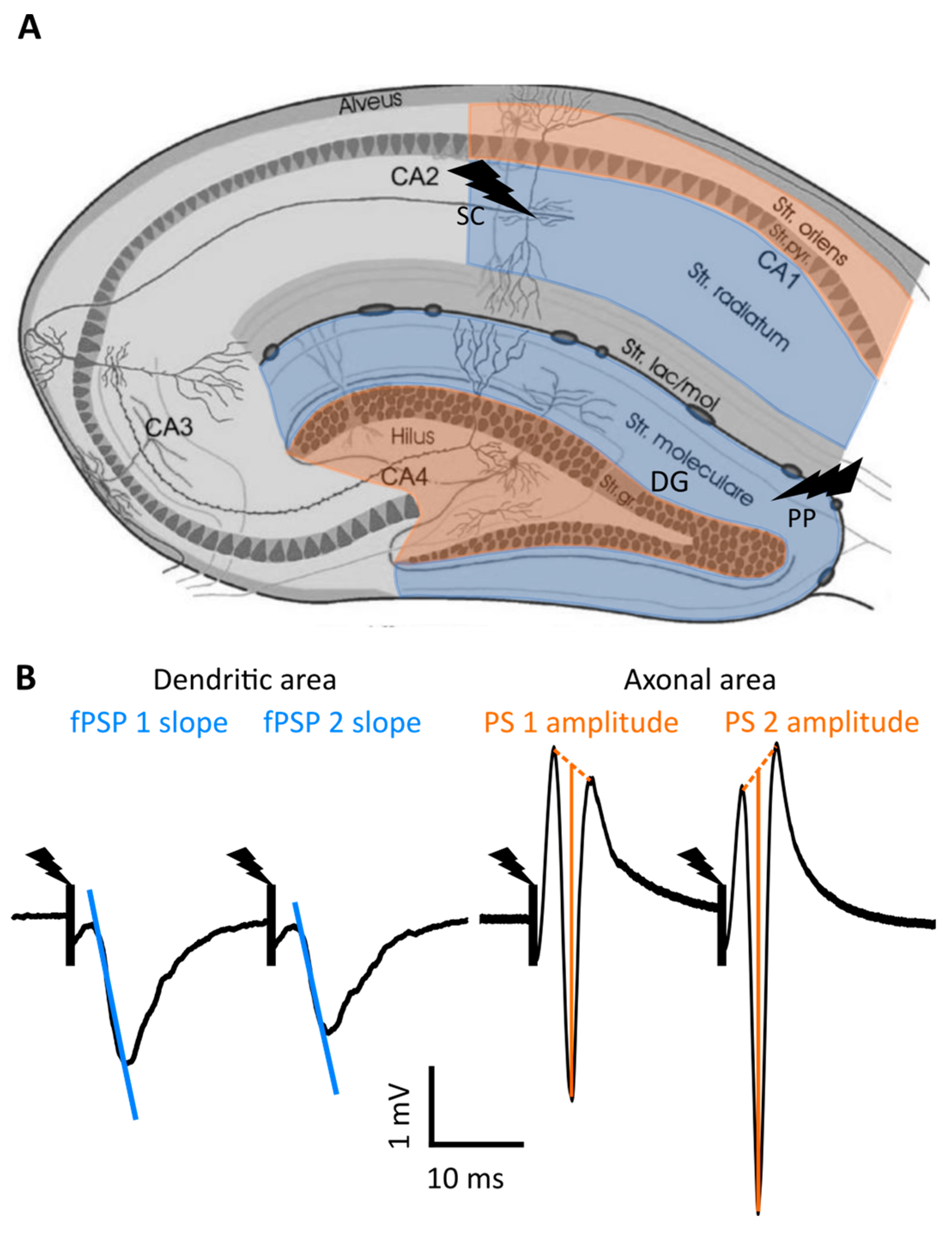
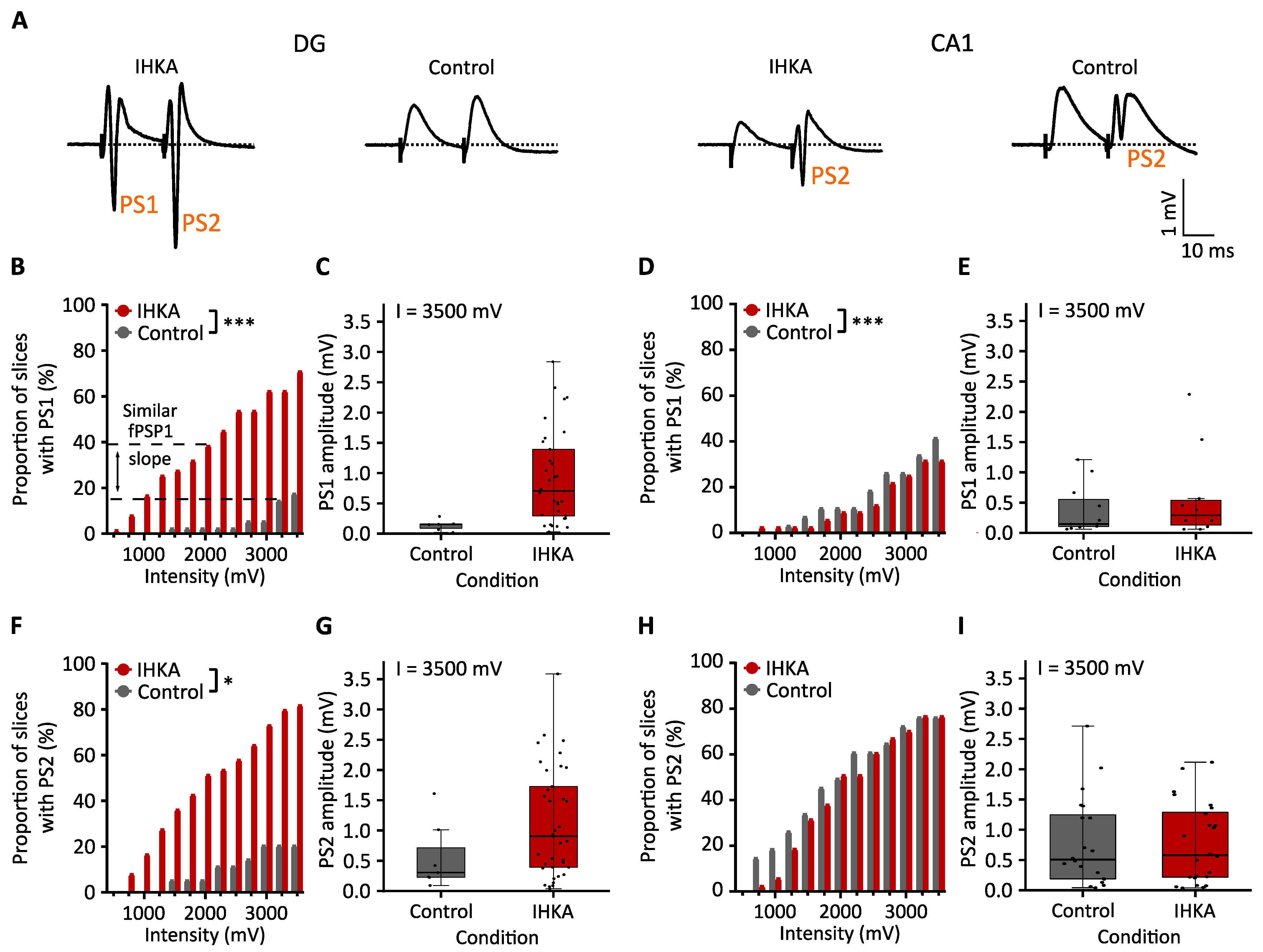
2.1. Input–Output Curve Analysis
2.1.1. fPSP Slope
2.1.2. Population Spike
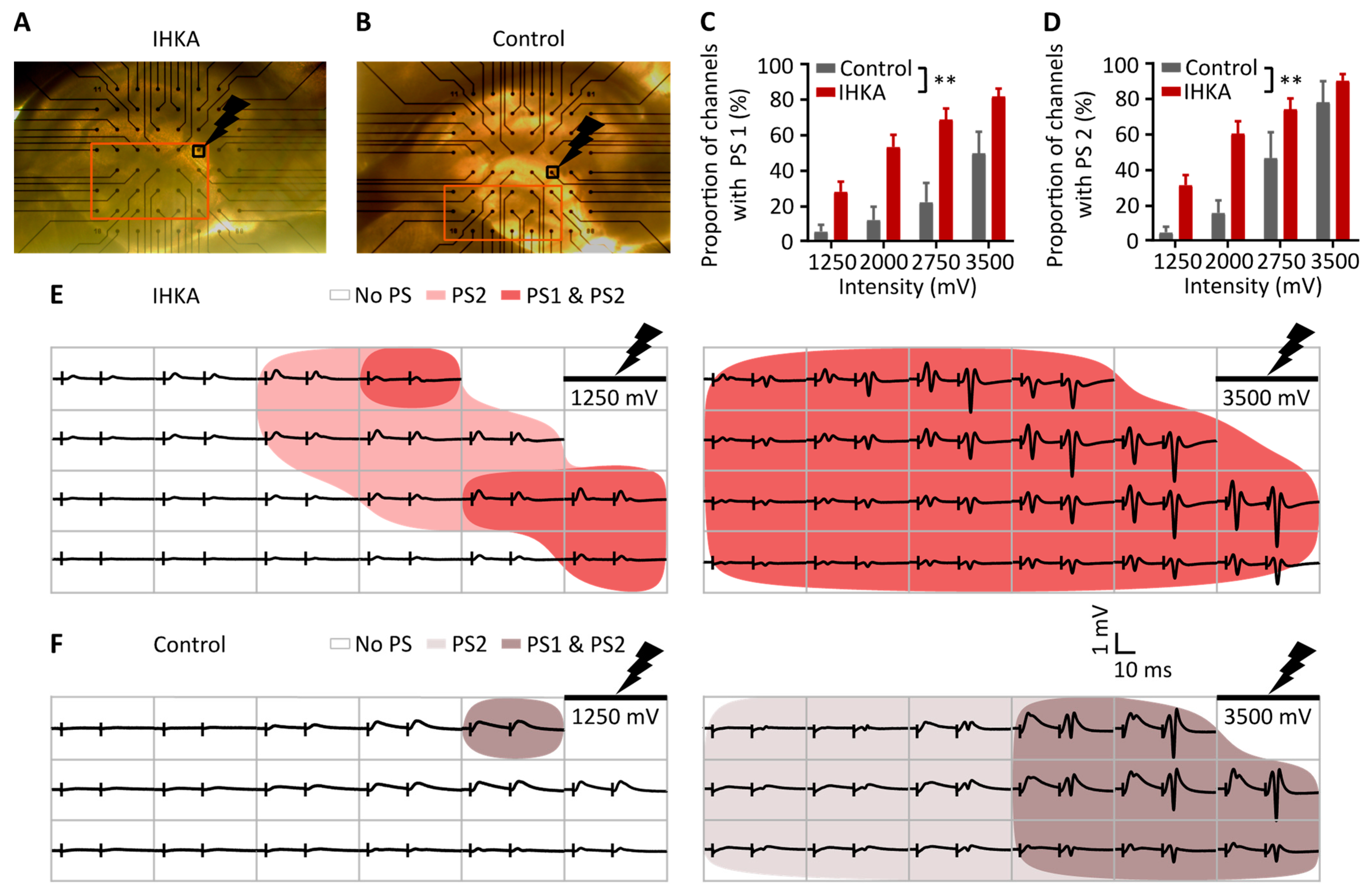
2.2. Spatial Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Intrahippocampal Kainic Acid Injection and Status Epilepticus
4.3. Cortico-Hippocampal Slice Preparation and Positioning
4.4. Electrophysiological Set-Up
4.5. CA1 and DG Evoked Potential Recording
4.6. Data Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lisgaras, C.P.; Scharfman, H.E. Robust Chronic Convulsive Seizures, High Frequency Oscillations, and Human Seizure Onset Patterns in an Intrahippocampal Kainic Acid Model in Mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2022, 166, 105637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladino, L.D.; Moien-Afshari, F.; Tellez-Zenteno, J.F. A Comprehensive Review of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. In Neurolological Disordisorders: Clinical Methods; iConcept Press Ltd.: Hong Kong, China, 2014; pp. 1–35. ISBN 978-1922227744. [Google Scholar]
- Lévesque, M.; Avoli, M. The Kainic Acid Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 37, 2887–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, K.S.; West, P.J.; Metcalf, C.S. The Current Approach of the Epilepsy Therapy Screening Program Contract Site for Identifying Improved Therapies for the Treatment of Pharmacoresistant Seizures in Epilepsy. Neuropharmacology 2020, 166, 107811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duveau, V.; Pouyatos, B.; Bressand, K.; Bouyssières, C.; Chabrol, T.; Roche, Y.; Depaulis, A.; Roucard, C. Differential Effects of Antiepileptic Drugs on Focal Seizures in the Intrahippocampal Kainate Mouse Model of Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2016, 22, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehne, J.H.; Klein, B.D.; Raeissi, S.; Sharma, S. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) Epilepsy Therapy Screening Program (ETSP). Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 1894–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Public Access to Neuroactive & Anticonvulsant Chemical Evaluations (PANAChE). Available online: https://panache.ninds.nih.gov/ (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Riban, V.; Bouilleret, V.; Pham-Lê, B.T.; Fritschy, J.M.; Marescaux, C.; Depaulis, A. Evolution of Hippocampal Epileptic Activity during the Development of Hippocampal Sclerosis in a Mouse Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Neuroscience 2002, 112, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouilleret, V.; Ridoux, V.; Depaulis, A.; Marescaux, C.; Nehlig, A.; Le Gal, G.; Salle, L.A. Recurrent Seizures and Hippocampal Sclerosis Following Intrahippocampal Kainate Injection in Adult Mice: Electroencephalography, Histopathology and Synaptic Reorganization Similar to Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Neuroscience 1999, 89, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ari, Y. Limbic Seizure and Brain Damage Produced by Kainic Acid: Mechanisms and Relevance to Human Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Neuroscience 1985, 14, 375–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharfman, H.E. Current Review The Dentate Gyrus and Temporal Lobe Epilepsy: An “Exciting” Era. Epilepsy Curr. 2019, 19, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieu, L.A.; Eugène, E.; Bonnot, A.; Cohen, I. Disrupted Co-Activation of Interneurons and Hippocampal Network after Focal Kainate Lesion. Front. Neural Circuits 2017, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Duigou, C.; Bouilleret, V.; Miles, R. Epileptiform Activities in Slices of Hippocampus from Mice after Intra-Hippocampal Injection of Kainic Acid. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 4891–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krook-Magnuson, E.; Armstrong, C.; Bui, A.; Lew, S.; Oijala, M.; Soltesz, I. In Vivo Evaluation of the Dentate Gate Theory in Epilepsy. J. Physiol. 2015, 593, 2379–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinemann, U.; Beck, H.; Dreier, J.; Ficker, E.; Stabel, J.; Zhang, C. The Dentate Gyrus as a Regulated Gate for the Propagation of Epileptiform Activity. Epilepsy Res. 1992, 7, 273–280. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, C.; Szabadics, J.; Tamás, G.; Soltesz, I. Neurogliaform Cells in the Molecular Layer of the Dentate Gyrus as Feed-Forward γ-Aminobutyric Acidergic Modulators of Entorhinal-Hippocampal Interplay. J. Comp. Neurol. 2011, 519, 1476–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Duigou, C.; Wittner, L.; Danglot, L.; Miles, R. Effects of Focal Injection of Kainic Acid into the Mouse Hippocampus In Vitro and Ex Vivo. J. Physiol. 2005, 569, 833–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.J.; Clement, E.M.; Park, I.H.; Greenfield, L.J.; Smith, B.N.; Lee, S.H. Vulnerability of Cholecystokinin-Expressing GABAergic Interneurons in the Unilateral Intrahippocampal Kainate Mouse Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 342, 113724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, M.C.; Kullmann, D.M. Optogenetic and Chemogenetic Therapies for Epilepsy. Neuropharmacology 2020, 168, 107751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerch, M.M.; Hansen, M.J.; van Dam, G.M.; Szymanski, W.; Feringa, B.L. EmergingTargetsinPhotopharmacology. Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 11140–11163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorter, J.A.; van Vliet, E.A.; Lopes da Silva, F.H. Which Insights Have We Gained from the Kindling and Post-Status Epilepticus Models? J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 260, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strange, B.A.; Witter, M.P.; Lein, E.S.; Moser, E.I. Functional Organisation of the Hippocampal Longitudinal Axis. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, D.; Wu, S.M. Foundations of Cellular Neurophysiology; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995; ISBN 0262100533. [Google Scholar]
- Kova, R.; Cs, Â.; Gutie  Rrez, R.; Kivi, A.; Schuchmann, S.; Gabriel, S.; Heinemann, U. Acute Cell Damage after Low Mg 2‡-Induced Epileptiform Activity in Organotypic Hippocampal Slice Cultures. Neuroreport 1999, 10, 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Rune, G.M. Regulation Der Expression von ADAM22 in der Molekularschicht Des Gyrus Dentatus; Universitatsklinikum Hamburg-Eppendorf: Hamburg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kernig, K.; Kirschstein, T.; Würdemann, T.; Rohde, M.; Köhling, R. The Afterhyperpolarizing Potential Following a Train of Action Potentials Is Suppressed in an Acute Epilepsy Model in the Rat Cornu Ammonis 1 Area. Neuroscience 2012, 201, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, B.; Bichler, E.; Benveniste, M. Excitatory Synaptic Transmission in Hippocampal Area CA1 Is Enhanced Then Reduced as Chronic Epilepsy Progresses. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 154, 105343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, M.C.; Yu, P.N.; Song, D.; Liu, C.Y.; Heck, C.N.; Millett, D.; Berger, T.W. An in Vitro Seizure Model from Human Hippocampal Slices Using Multi-Electrode Arrays. J. Neurosci. Methods 2015, 244, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.G.; Chen, X.F.; He, T.; Li, Z.; Chen, J. Use of Multi-Electrode Array Recordings in Studies of Network Synaptic Plasticity in Both Time and Space. Neurosci. Bull. 2012, 28, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitkänen, A.; Schwartzkroin, P.A.; Moché, S.L. (Eds.) Models of Seizures and Epilepsy, 1st ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2005; ISBN 9780128040676. [Google Scholar]
- West, P.J.; Saunders, G.W.; Billingsley, P.; Smith, M.D.; White, H.S.; Metcalf, C.S.; Wilcox, K.S. Recurrent Epileptiform Discharges in the Medial Entorhinal Cortex of Kainate-Treated Rats Are Differentially Sensitive to Antiseizure Drugs. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 2035–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharfman, H.E.; Sollas, A.L.; Berger, R.E.; Goodman, J.H. Electrophysiological Evidence of Monosynaptic Excitatory Transmission between Granule Cells after Seizure-Induced Mossy Fiber Sprouting. J. Neurophysiol. 2003, 90, 2536–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coras, R.; Blümcke, I. Clinico-Pathological Subtypes of Hippocampal Sclerosis in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy and Their Differential Impact on Memory Impairment. Neuroscience 2015, 309, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.M.; Gutekunst, C.A.; Grogan, D.P.; Pedersen, N.P.; Gross, R.E. Loss of Efferent Projections of the Hippocampal Formation in the Mouse Intrahippocampal Kainic Acid Model. Epilepsy Res. 2022, 180, 106863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuya, K.; Nitta, N.; Suzuki, F. Persistent Zinc Depletion in the Mossy Fiber Terminals in the Intrahippocampal Kainate Mouse Model of Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 1979–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharfman, H.E.; Goodman, J.H.; Sollas, A.L. Granule-Like Neurons at the Hilar/CA3 Border after Status Epilepticus and Their Synchrony with Area CA3 Pyramidal Cells: Functional Implications of Seizure-Induced Neurogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 6144–6158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendricks, W.D.; Westbrook, G.L.; Schnell, E. Early Detonation by Sprouted Mossy Fibers Enables Aberrant Dentate Network Activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 10994–10999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulter, D.A.; Carlson, G.C. Functional Regulation of the Dentate Gyrus by GABA-Mediated Inhibition. Prog. Brain Res. 2007, 163, 235–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouilleret, V.; Loup, F.; Kiener, T.; Marescaux, C.; Fritschy, J.M. Early Loss of Interneurons and Delayed Subunit-Specific Changes in GABA(A)-Receptor Expression in a Mouse Model of Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Hippocampus 2000, 10, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Sun, J.; Erisir, A.; Kapur, J. Loss of Cholecystokinin-Containing Terminals in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 62, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schmidt-Hieber, C.; Jones, P.; Bischofberger, J. Enhanced Synaptic Plasticity in Newly Generated Granule Cells of the Adult Hippocampus. Nature 2004, 429, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häussler, U.; Bielefeld, L.; Froriep, U.P.; Wolfart, J.; Haas, C.A. Septotemporal Position in the Hippocampal Formation Determines Epileptic and Neurogenic Activity in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Cereb. Cortex 2012, 22, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malenka, R.C. Postsynaptic Factors Control the Duration of Synaptic Enhancement of the Hippocampus in Area CA1. Neuron 1991, 6, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, Y.O.; Maru, E.; Ohata, H.; Takashima, I.; Kajiwara, R.; Iijima, T. Optical Recording Study of Granule Cell Activities in the Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus of Kainate-Treated Rats. J. Neurophysiol. 2000, 83, 2421–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chang, P.Y.; Taylor, P.E.; Jackson, M.B. Voltage Imaging Reveals the CA1 Region at the CA2 Border as a Focus for Epileptiform Discharges and Long-Term Potentiation in Hippocampal Slices. J. Neurophysiol. 2007, 98, 1309–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, J.; Leverton, L.K.; Naganatanahalli, L.M.; Christian-Hinman, C.A. Seizure Burden Fluctuates with the Female Reproductive Cycle in a Mouse Model of Chronic Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 334, 113492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desloovere, J.; Boon, P.; Larsen, L.E.; Merckx, C.; Goossens, M.; Van den Haute, C.; Baekelandt, V.; De Bundel, D.; Carrette, E.; Delbeke, J.; et al. Long-term Chemogenetic Suppression of Spontaneous Seizures in a Mouse Model for Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2019, 60, 2314–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desloovere, J.; Boon, P.; Larsen, L.E.; Goossens, M.-G.; Delbeke, J.; Carrette, E.; Wadman, W.; Vonck, K.; Raedt, R. Chemogenetic Seizure Control with Clozapine and the Novel Ligand JHU37160 Outperforms the Effects of Levetiracetam in the Intrahippocampal Kainic Acid Mouse Model. Neurotherapeutics 2021, 19, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziak, J.J.; Coffman, D.L.; Lanza, S.T.; Li, R.; Jermiin, L.S. Sensitivity and Specificity of Information Criteria. Brief. Bioinform. 2020, 21, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, W.H.; Bolin, J.E.; Kelley, K. Statistics in the Social and Behavioral Sciences Series Multilevel Modeling Using R; Gill, J., van der Linden, W., Heeringa, S., Long, J.S., Eds.; CRC Press (Taylor & Francis Group): Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-1-4665-1586-4. [Google Scholar]


| Excitability Measure | Group | DG | CA1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value * | Difference | Value * | Difference | ||
| Synaptic strength | |||||
| fPSP1 slope | IHKA | 0.45 mV/ms | ↑ * | 0.40 mV/ms | ns |
| Control | 0.28 mV/ms | 0.45 mV/ms | |||
| fPSP2 slope | IHKA | 0.40 mV/ms | ns | 0.52 mV/ms | ns |
| Control | 0.34 mV/ms | 0.67 mV/ms | |||
| Paired-pulse index | IHKA | 0.89 | ↓ ** | 1.49 | ns |
| Control | 1.30 | 1.33 | |||
| Neuronal output | |||||
| Prevalence of PS1 | IHKA | 71.74% | ↑ *** | 32.26% | ↓ *** |
| Control | 18.18% | 42.31% | |||
| Amplitude of PS1 | IHKA | 0.92 mV | ns | 0.59 mV | ns |
| Control | 0.14 mV | 0.38 mV | |||
| Prevalence of PS2 | IHKA | 82.61% | ↑ * | 77.42% | ns |
| Control | 21.21% | 76.92% | |||
| Amplitude of PS2 | IHKA | 1.09 mV | ns | 0.77 mV | ns |
| Control | 0.56 mV | 0.79 mV | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vergaelen, M.; Manzella, S.; Vonck, K.; Craey, E.; Spanoghe, J.; Sprengers, M.; Carrette, E.; Wadman, W.J.; Delbeke, J.; Boon, P.; et al. Increased Dentate Gyrus Excitability in the Intrahippocampal Kainic Acid Mouse Model for Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010660
Vergaelen M, Manzella S, Vonck K, Craey E, Spanoghe J, Sprengers M, Carrette E, Wadman WJ, Delbeke J, Boon P, et al. Increased Dentate Gyrus Excitability in the Intrahippocampal Kainic Acid Mouse Model for Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(1):660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010660
Chicago/Turabian StyleVergaelen, Marijke, Simona Manzella, Kristl Vonck, Erine Craey, Jeroen Spanoghe, Mathieu Sprengers, Evelien Carrette, Wytse Jan Wadman, Jean Delbeke, Paul Boon, and et al. 2024. "Increased Dentate Gyrus Excitability in the Intrahippocampal Kainic Acid Mouse Model for Temporal Lobe Epilepsy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 1: 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010660
APA StyleVergaelen, M., Manzella, S., Vonck, K., Craey, E., Spanoghe, J., Sprengers, M., Carrette, E., Wadman, W. J., Delbeke, J., Boon, P., Larsen, L. E., & Raedt, R. (2024). Increased Dentate Gyrus Excitability in the Intrahippocampal Kainic Acid Mouse Model for Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(1), 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010660






