Peripheral Branch Injury Induces Oxytocin Receptor Expression at the Central Axon Terminals of Primary Sensory Neurons
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Immunhistochemical Detection of OTR
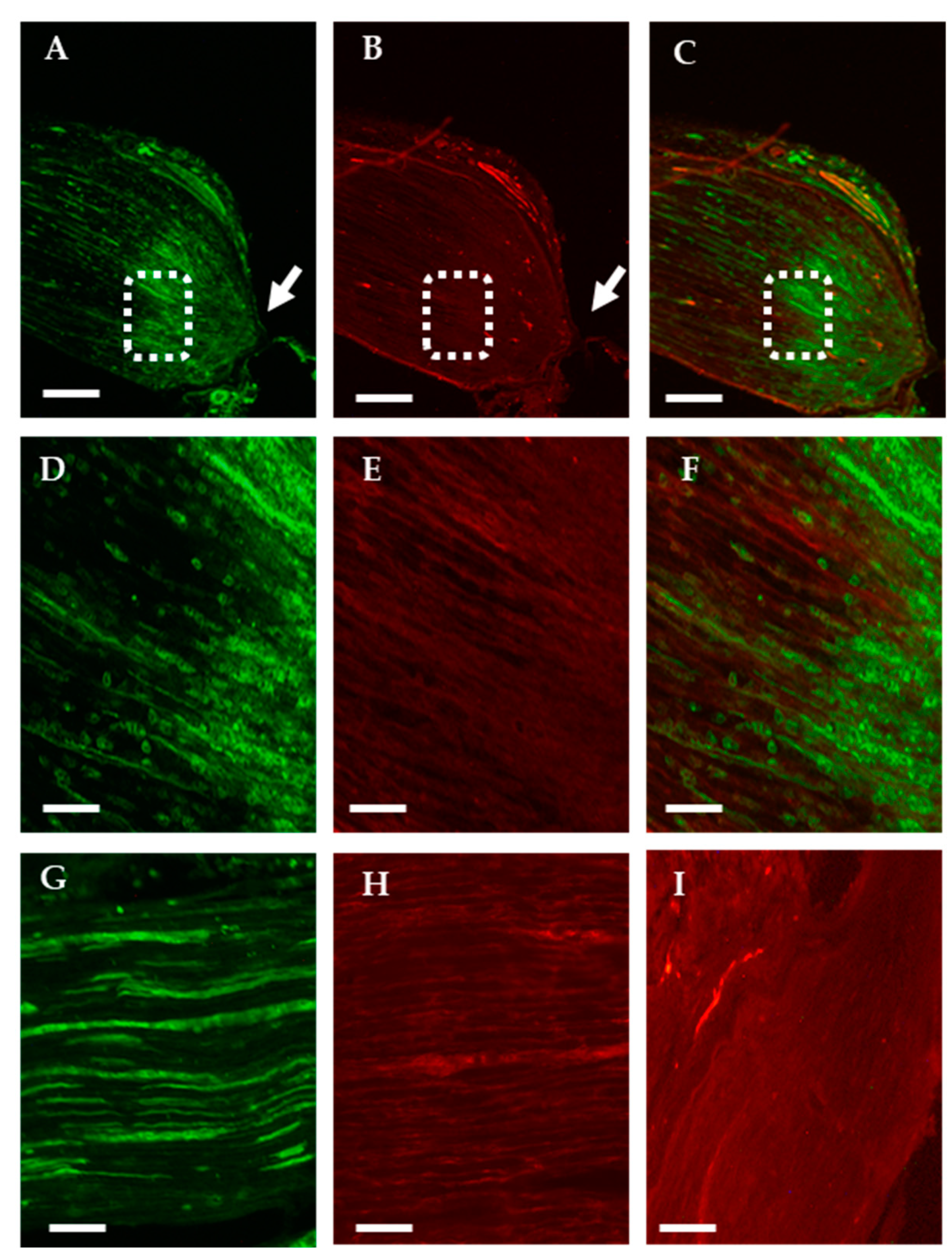
2.1.1. Analysis of the Axonal Transport of OTR
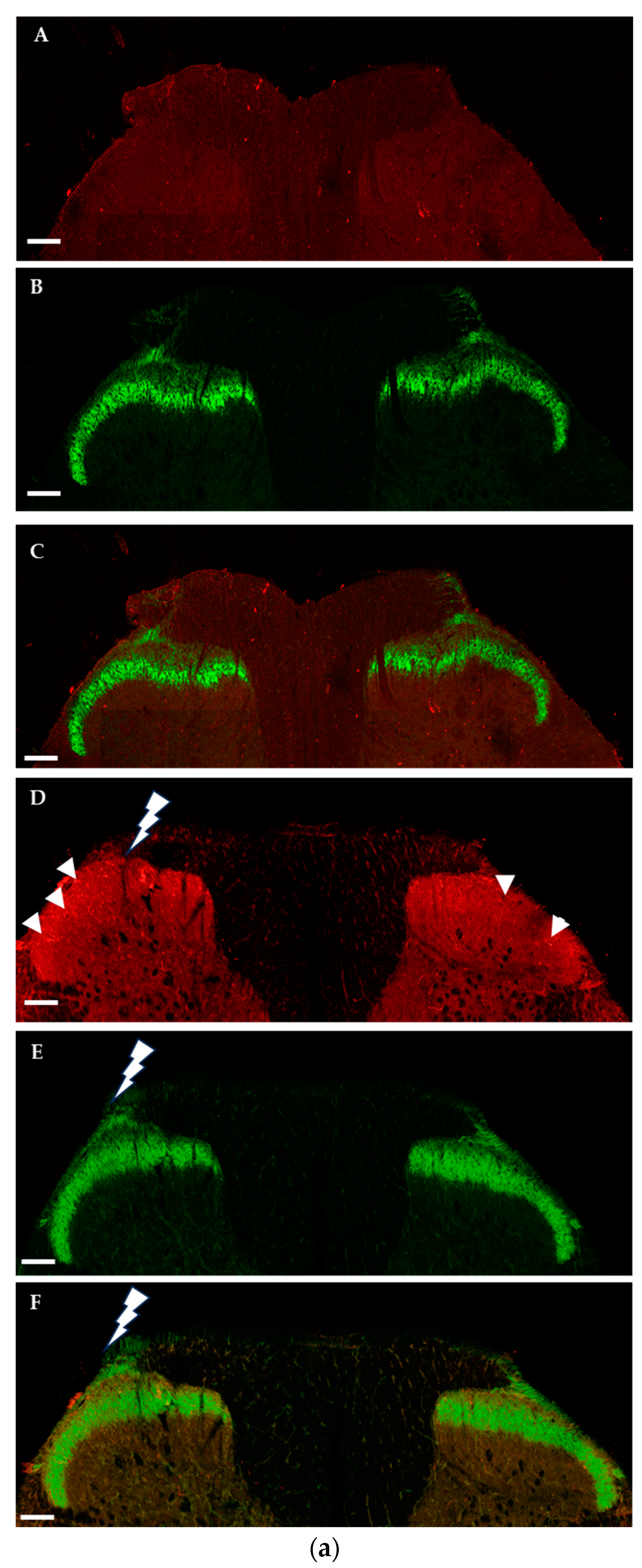
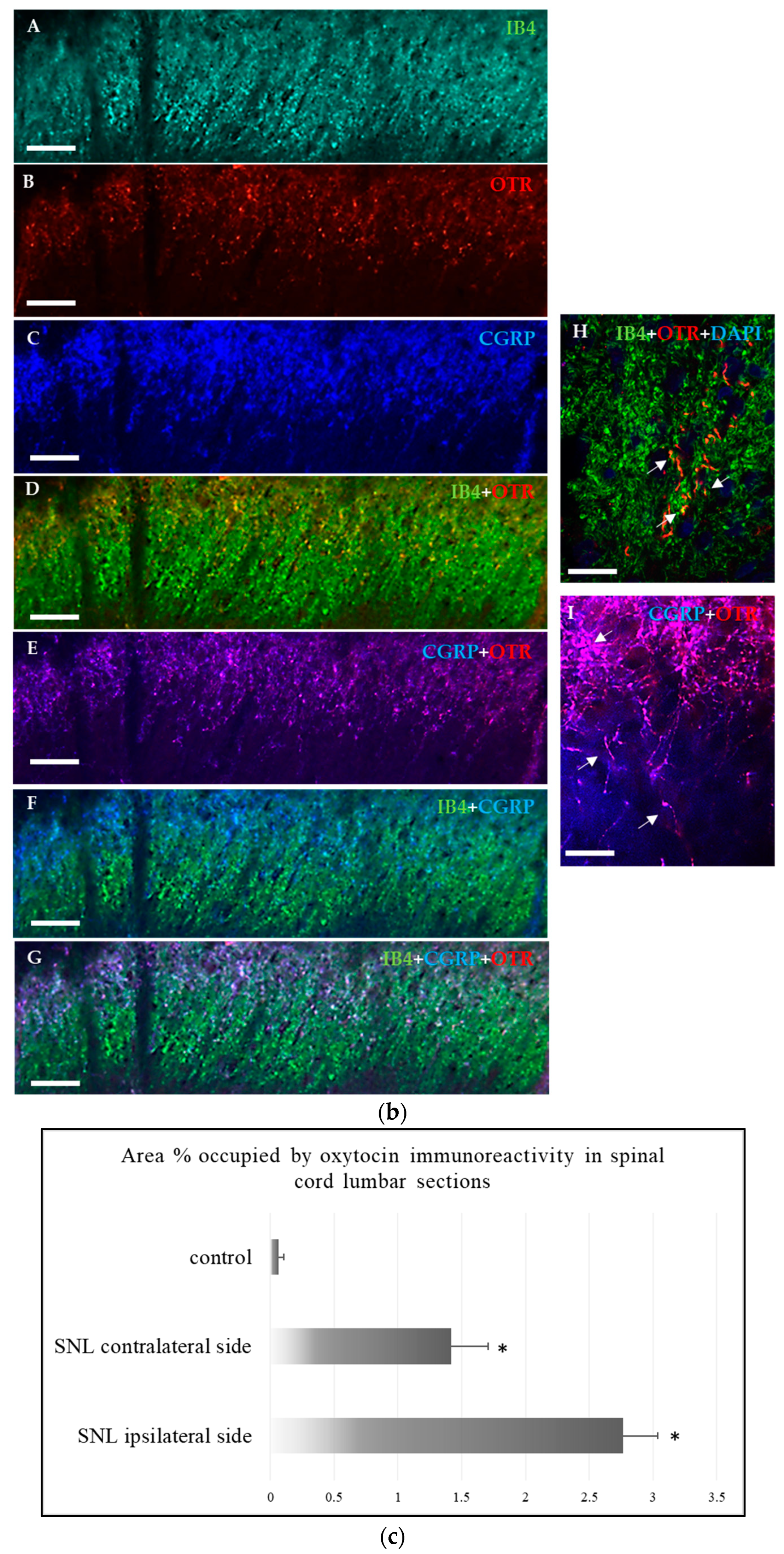
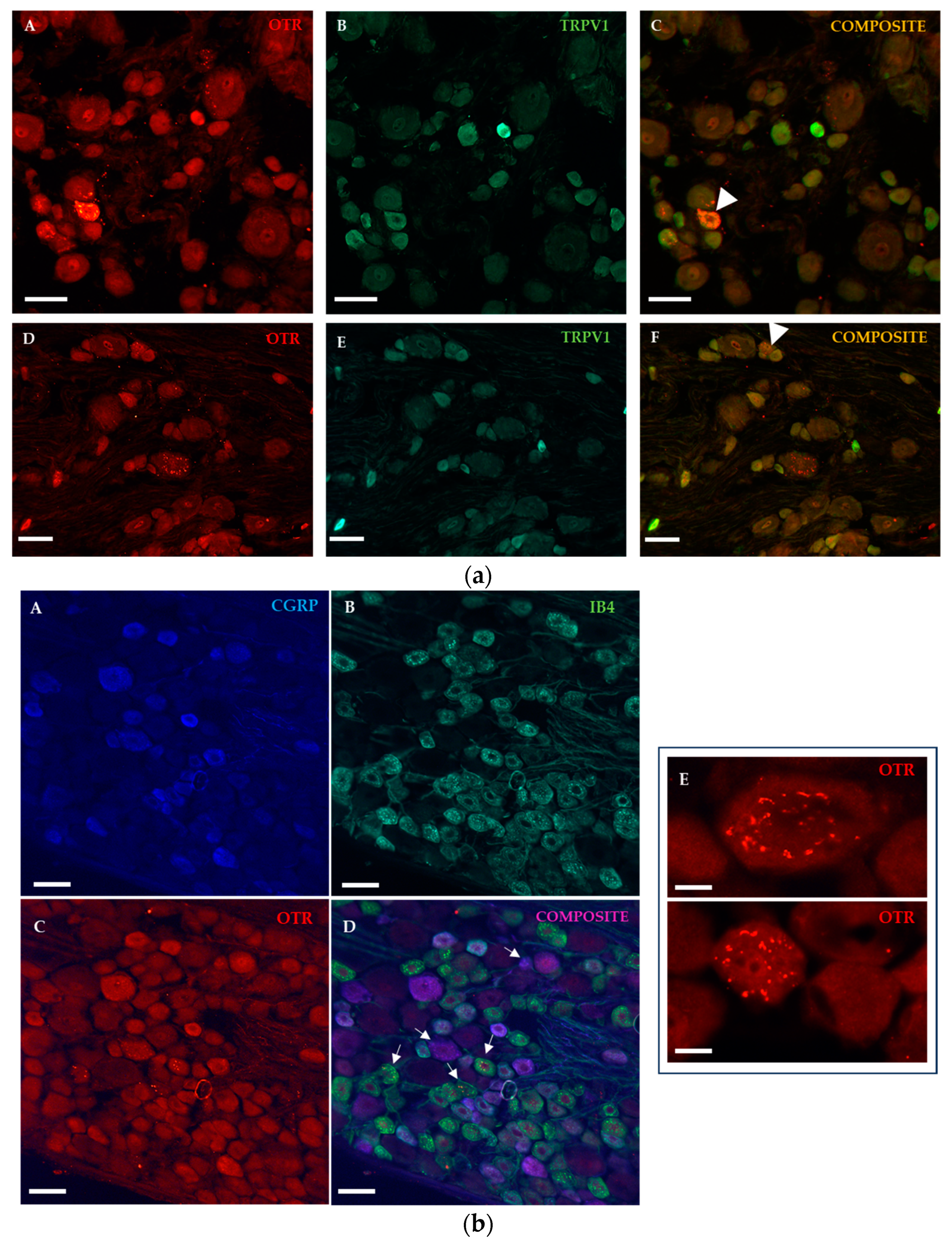
2.1.2. Immunohistochemical Detection of OTRs in the Spinal Cord and Dorsal Root Ganglia
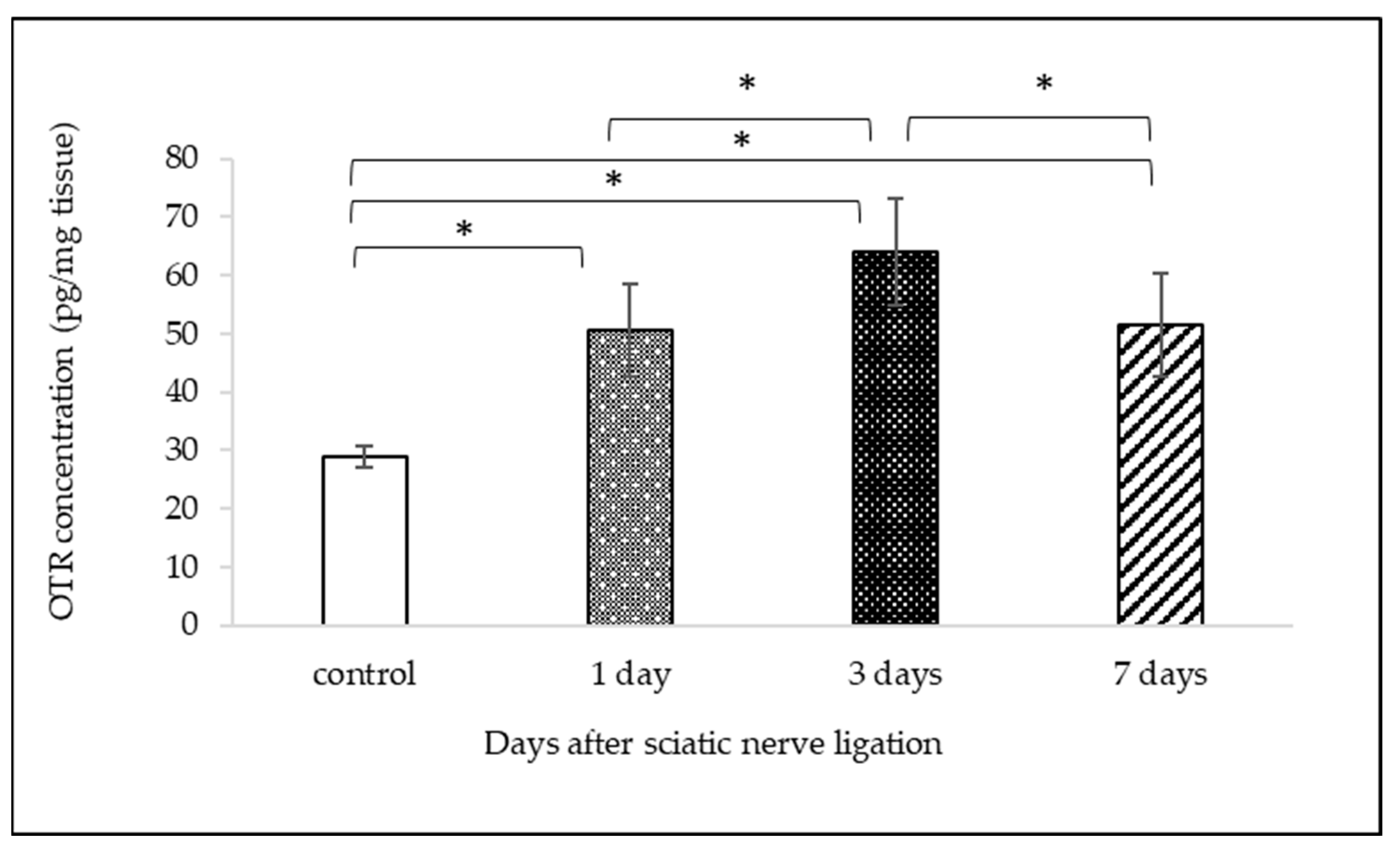
2.2. Measurement of OTR Protein Expression with ELISA
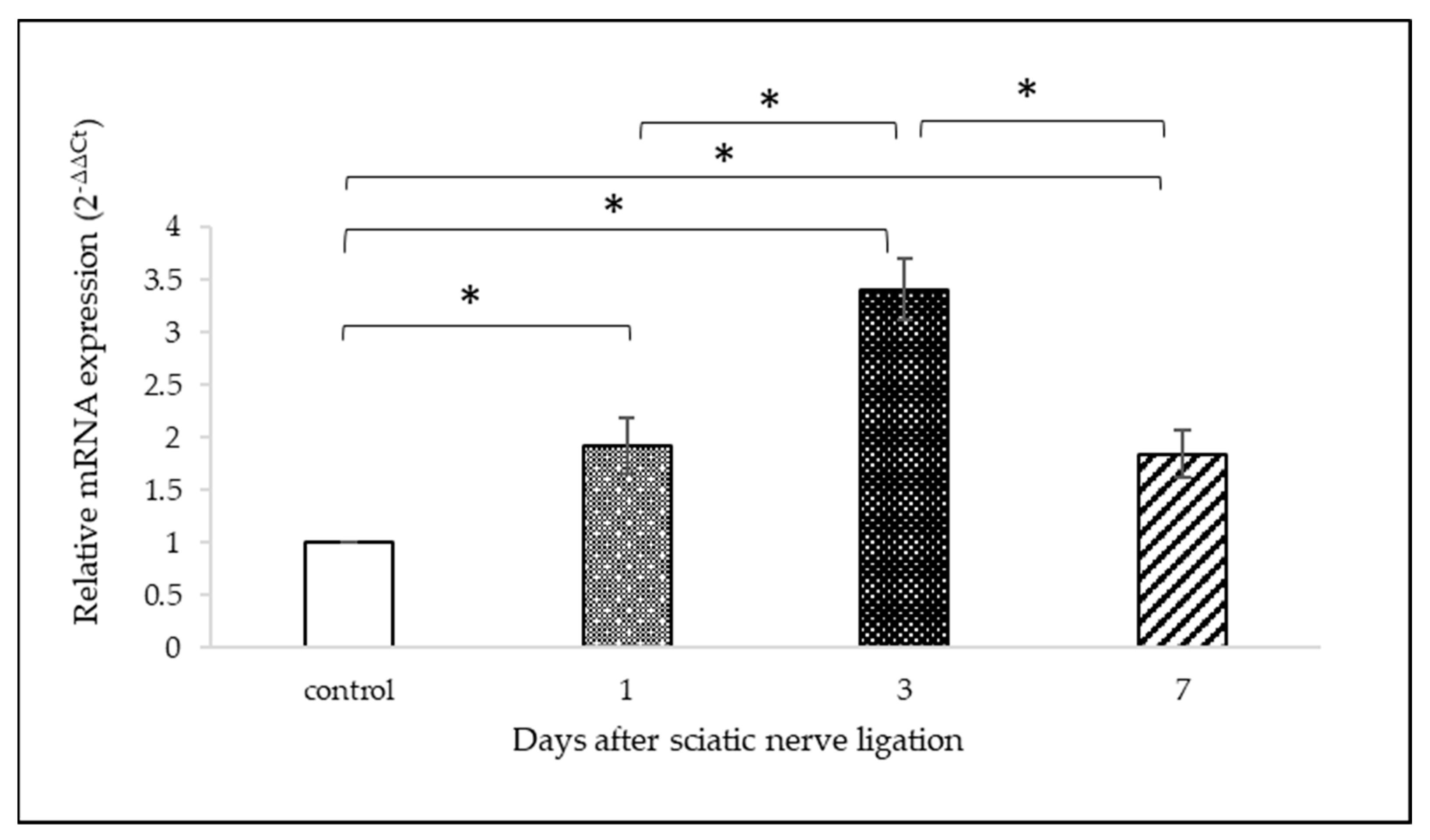
2.3. OTR mRNA Analysis with qPCR
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Peripheral Nerve Injury (PNI)
4.3. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
4.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.5. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
6.1. Choice of the Antibody
6.2. Choice of Female Rats
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaggi, A.S.; Jain, V.; Singh, N. Animal Models of Neuropathic Pain. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 25, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condés-Lara, M.; Rojas-Piloni, G.; Martínez-Lorenzana, G.; Rodríguez-Jiménez, J. Paraventricular Hypothalamic Oxytocinergic Cells Responding to Noxious Stimulation and Projecting to the Spinal Dorsal Horn Represent a Homeostatic Analgesic Mechanism. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 30, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLaTorre, S.; Rojas-Piloni, G.; Martínez-Lorenzana, G.; Rodríguez-Jiménez, J.; Villanueva, L.; Condés-Lara, M. Paraventricular Oxytocinergic Hypothalamic Prevention or Interruption of Long-Term Potentiation in Dorsal Horn Nociceptive Neurons: Electrophysiological and Behavioral Evidence. Pain 2009, 144, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condés-Lara, M.; Marina González, N.; Martínez-Lorenzana, G.; Luis Delgado, O.; José Freund-Mercier, M. Actions of Oxytocin and Interactions with Glutamate on Spontaneous and Evoked Dorsal Spinal Cord Neuronal Activities. Brain Res. 2003, 976, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condés-Lara, M.; Maie, I.A.S.; Dickenson, A.H. Oxytocin Actions on Afferent Evoked Spinal Cord Neuronal Activities in Neuropathic but Not in Normal Rats. Brain Res. 2005, 1045, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condés-Lara, M.; Rojas-Piloni, G.; Martínez-Lorenzana, G.; López-Hidalgo, M.; Rodríguez-Jiménez, J. Hypothalamospinal Oxytocinergic Antinociception Is Mediated by GABAergic and Opiate Neurons That Reduce A-Delta and C Fiber Primary Afferent Excitation of Spinal Cord Cells. Brain Res. 2009, 1247, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-López, Y.; Martínez-Lorenzana, G.; Condés-Lara, M.; Rojas-Piloni, G. Identification of Oxytocin Receptor in the Dorsal Horn and Nociceptive Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons. Neuropeptides 2013, 47, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodin, B.; Ness, T.; Robbins, M. Oxytocin—A Multifunctional Analgesic for Chronic Deep Tissue Pain. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 21, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliava, M.; Melchior, M.; Knobloch-Bollmann, H.S.; Wahis, J.; da Silva Gouveia, M.; Tang, Y.; Ciobanu, A.C.; Triana del Rio, R.; Roth, L.C.; Althammer, F.; et al. A New Population of Parvocellular Oxytocin Neurons Controlling Magnocellular Neuron Activity and Inflammatory Pain Processing. Neuron 2016, 89, 1291–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Boll, E.; Martínez-Lorenzana, G.; Condés-Lara, M.; González-Hernández, A. Oxytocin Inhibits the Rat Medullary Dorsal Horn Sp5c/C1 Nociceptive Transmission through OT but Not V1A Receptors. Neuropharmacology 2018, 129, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rash, J.A.; Aguirre-Camacho, A.; Campbell, T.S. Oxytocin and Pain: A Systematic Review and Synthesis of Findings. Clin. J. Pain 2014, 30, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.-M.; Liu, W.-Y.; Wang, C.-H.; Lin, B.-C. Central Oxytocin Enhances Antinociception in the Rat. Peptides 2007, 28, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engle, M.P.; Ness, T.J.; Robbins, M.T. Intrathecal Oxytocin Inhibits Visceromotor Reflex and Spinal Neuronal Responses to Noxious Distention of the Rat Urinary Bladder. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2012, 37, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, A.; Shinoda, M.; Katagiri, A.; Takeda, M.; Suzuki, T.; Asaka, J.; Yeomans, D.C.; Iwata, K. Oxytocin Alleviates Orofacial Mechanical Hypersensitivity Associated with Infraorbital Nerve Injury through Vasopressin-1A Receptors of the Rat Trigeminal Ganglia. Pain 2017, 158, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.-Q.; Lundeberg, T.; Yu, L.-C. Involvement of Oxytocin in Spinal Antinociception in Rats with Inflammation. Brain Res. 2003, 983, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averill, S.; Davis, D.R.; Shortland, P.J.; Priestley, J.V.; Hunt, S.P. Dynamic Pattern of Reg-2 Expression in Rat Sensory Neurons after Peripheral Nerve Injury. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 7493–7501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Reid, A.; Verkhratsky, A.; Magnaghi, V.; Faroni, A. Gene Expression Changes in Dorsal Root Ganglia Following Peripheral Nerve Injury: Roles in Inflammation, Cell Death and Nociception. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, T.; Nagarajan, R.; Milbrandt, J. Identification of Genes Induced in Peripheral Nerve after Injury. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 34131–34141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berta, T.; Perrin, F.E.; Pertin, M.; Tonello, R.; Liu, Y.-C.; Chamessian, A.; Kato, A.C.; Ji, R.-R.; Decosterd, I. Gene Expression Profiling of Cutaneous Injured and Non-Injured Nociceptors in SNI Animal Model of Neuropathic Pain. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A. Axonal Transport. In Neuroscience in the 21st Century: From Basic to Clinical; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 255–308. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, G.J.; Xie, Y.-K. A Peripheral Mononeuropathy in Rat That Produces Disorders of Pain Sensation like Those Seen in Man. Pain 1988, 33, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, P.; dos Santos, I.R.; Júnior, I.M.; Palazzo, E.; da Silva, J.A.; Machado, H.R.; Ferreira, S.H.; Maione, S.; Coimbra, N.C.; de Freitas, R.L. An Adapted Chronic Constriction Injury of the Sciatic Nerve Produces Sensory, Affective, and Cognitive Impairments: A Peripheral Mononeuropathy Model for the Study of Comorbid Neuropsychiatric Disorders Associated with Neuropathic Pain in Rats. Pain Med. 2021, 22, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.-Q.; Snider, W.D. Intracellular Control of Developmental and Regenerative Axon Growth. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 361, 1575–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosse, F.; Küry, P.; Müller, H.W. Gene Expression Profiling and Molecular Aspects in Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2001, 19, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rousselot, P.; Papadopoulos, G.; Merighi, A.; Poulain, D.A.; Theodosis, D.T. Oxytocinergic Innervation of the Rat Spinal Cord. An Electron Microscopic Study. Brain Res. 1990, 529, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrobel, L.; Schorscher-Petcu, A.; Dupré, A.; Yoshida, M.; Nishimori, K.; Tribollet, E. Distribution and Identity of Neurons Expressing the Oxytocin Receptor in the Mouse Spinal Cord. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 495, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Hernández, A.; Manzano-García, A.; Martínez-Lorenzana, G.; Tello-García, I.A.; Carranza, M.; Arámburo, C.; Condés-Lara, M. Peripheral Oxytocin Receptors Inhibit the Nociceptive Input Signal to Spinal Dorsal Horn Wide-Dynamic-Range Neurons. Pain 2017, 158, 2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, T.; Motojima, Y.; Kawasaki, M.; Ohnishi, H.; Sakai, A.; Ueta, Y. Relationship between Oxytocin and Pain Modulation and Inflammation. J. UOEH 2016, 38, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Severino, A.L.; Chen, R.; Hayashida, K.; Aschenbrenner, C.A.; Sun, H.; Peters, C.M.; Gutierrez, S.; Pan, B.; Eisenach, J.C. Plasticity and Function of Spinal Oxytocin and Vasopressin Signaling during Recovery from Surgery with Nerve Injury. Anesthesiology 2018, 129, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jójárt, J.; Jójárt, I.; Boda, K.; Gálfi, M.; Mihály, A.; B.-Baldauf, Z.; Vecsernyés, M. Distribution of Oxytocin-Immunoreactive Neuronal Elements in the Rat Spinal Cord. Acta Biol. Hung. 2009, 60, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobo, S.; Hayashida, K.; Eisenach, J.C. Oxytocin Inhibits the Membrane Depolarization-Induced Increase in Intracellular Calcium in Capsaicin Sensitive Sensory Neurons: A Peripheral Mechanism of Analgesic Action. Anesth. Analg. 2012, 114, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayar, A.; Ozcan, M.; Alcin, E.; Serhatlioglu, I.; Ozcan, S.; Kutlu, S.; Kelestimur, H. Oxytocin Activates Calcium Signaling in Rat Sensory Neurons through a Protein Kinase C-Dependent Mechanism. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juif, P.-E.; Poisbeau, P. Neurohormonal Effects of Oxytocin and Vasopressin Receptor Agonists on Spinal Pain Processing in Male Rats. Pain 2013, 154, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godínez-Chaparro, B.; Martínez-Lorenzana, G.; Rodríguez-Jiménez, J.; Manzano-García, A.; Rojas-Piloni, G.; Condés-Lara, M.; González-Hernández, A. The Potential Role of Serotonergic Mechanisms in the Spinal Oxytocin-Induced Antinociception. Neuropeptides 2016, 60, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breton, J.D.; Poisbeau, P.; Darbon, P. Antinociceptive Action of Oxytocin Involves Inhibition of Potassium Channel Currents in Lamina II Neurons of the Rat Spinal Cord. Mol. Pain 2009, 5, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breton, J.-D.; Veinante, P.; Uhl-Bronner, S.; Vergnano, A.M.; Freund-Mercier, M.J.; Schlichter, R.; Poisbeau, P. Oxytocin-Induced Antinociception in the Spinal Cord Is Mediated by a Subpopulation of Glutamatergic Neurons in Lamina I-II Which Amplify GABAergic Inhibition. Mol. Pain 2008, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.-Y.; Fujita, T.; Kumamoto, E. Synaptic Modulation and Inward Current Produced by Oxytocin in Substantia Gelatinosa Neurons of Adult Rat Spinal Cord Slices. J. Neurophysiol. 2014, 111, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Gao, F.; Li, J.; Yu, X.; Ma, X.; Zheng, W.; Cui, S.; Liu, K.; Zhang, M.; Kunze, W.; et al. Oxytocin-Induced Membrane Hyperpolarization in Pain-Sensitive Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurons Mediated by Ca2+/nNOS/NO/KATP Pathway. Neuroscience 2015, 289, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzabazis, A.; Mechanic, J.; Miller, J.; Klukinov, M.; Pascual, C.; Manering, N.; Carson, D.S.; Jacobs, A.; Qiao, Y.; Cuellar, J.; et al. Oxytocin Receptor: Expression in the Trigeminal Nociceptive System and Potential Role in the Treatment of Headache Disorders. Cephalalgia 2016, 36, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandel, E.R.; Schwartz, J.H. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Edition|AccessBiomedical Science. Available online: https://neurology.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?sectionid=59138139&bookid=1049 (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- Dalla Costa, I.; Buchanan, C.N.; Zdradzinski, M.D.; Sahoo, P.K.; Smith, T.P.; Thames, E.; Kar, A.N.; Twiss, J.L. The Functional Organization of Axonal mRNA Transport and Translation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2021, 22, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P.K.; Smith, D.S.; Perrone-Bizzozero, N.; Twiss, J.L. Axonal mRNA Transport and Translation at a Glance. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs196808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Tsai, N.-P.; Lin, Y.-P.; Loh, H.H.; Wei, L.-N. Axonal mRNA Transport and Localized Translational Regulation of κ-Opioid Receptor in Primary Neurons of Dorsal Root Ganglia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19919–19924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, P.; de Freitas, R.L.; Boccella, S.; Iannotta, M.; Belardo, C.; Mazzitelli, M.; Romano, R.; De Gregorio, D.; Coimbra, N.C.; Palazzo, E.; et al. Characterization of the Sensory, Affective, Cognitive, Biochemical, and Neuronal Alterations in a Modified Chronic Constriction Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain in Mice. J. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 98, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaertner, D.J.; Hallman, T.M.; Hankenson, F.C.; Batchelder, M.A. Chapter 10—Anesthesia and Analgesia for Laboratory Rodents. In Anesthesia and Analgesia in Laboratory Animals, 2nd ed.; Fish, R.E., Brown, M.J., Danneman, P.J., Karas, A.Z., Eds.; American College of Laboratory Animal Medicine; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 239–297. ISBN 978-0-12-373898-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hartig, S.M. Basic Image Analysis and Manipulation in ImageJ. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2013, 102, 14.15.1–14.15.12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangaru, M.L.Y.; Park, F.; Hudmon, A.; McCallum, J.B.; Hogan, Q.H. Quantification of Gene Expression after Painful Nerve Injury: Validation of Optimal Reference Genes. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 46, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.-L.; Lee, J.-N. Ovarian and Circulating Levels of Oxytocin and Arginine Vasopressin during the Estrous Cycle in the Rat. Acta Endocrinol. Nor. 1992, 126, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Target Gene | Primer Pairs (5′→3′) | Product Length | Reference Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase 6 (MAPK6) | Fw: TAAAGCCATTGACATGTGGG 1 Rev: TCGTGCACAACAGGGATAGA 1 | 129 | NM_031622.2 |
| Oxytocin receptor (OTR) | Fw: TTCTTCTGCTGCTCTGCTCGT Rev: TCATGCTGAAGATGGCTGAGA | 140 | NM_012871.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Heni, H.; Kemenesi-Gedei, P.B.; Pálvölgyi, L.; Kozma-Szeredi, I.D.; Kis, G. Peripheral Branch Injury Induces Oxytocin Receptor Expression at the Central Axon Terminals of Primary Sensory Neurons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010007
El Heni H, Kemenesi-Gedei PB, Pálvölgyi L, Kozma-Szeredi ID, Kis G. Peripheral Branch Injury Induces Oxytocin Receptor Expression at the Central Axon Terminals of Primary Sensory Neurons. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Heni, Heni, Péter Bátor Kemenesi-Gedei, Laura Pálvölgyi, Ivett Dorina Kozma-Szeredi, and Gyöngyi Kis. 2024. "Peripheral Branch Injury Induces Oxytocin Receptor Expression at the Central Axon Terminals of Primary Sensory Neurons" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010007
APA StyleEl Heni, H., Kemenesi-Gedei, P. B., Pálvölgyi, L., Kozma-Szeredi, I. D., & Kis, G. (2024). Peripheral Branch Injury Induces Oxytocin Receptor Expression at the Central Axon Terminals of Primary Sensory Neurons. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010007






