Anti-Cancer and Anti-Proliferative Potential of Cannabidiol: A Cellular and Molecular Perspective
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Endocannabinoid System and Cancer
3. Anti-Cancer and Anti-Proliferation Mechanisms of CBD in Cancer
3.1. Breast Cancer
3.2. Lung Cancer
3.3. Prostate Cancer
3.4. Glioma
4. Overview of Anti-Cancer Capabilities of CBD in Other Cancers
5. CBD and THC: Why One, Not the Other, or Both?
6. Concluding Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seltzer, E.S.; Watters, A.K.; Mackenzie, D.; Granat, L.M.; Zhang, D. Cannabidiol (CBD) as a Promising Anti-Cancer Drug. Cancers 2020, 12, 3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomko, A.M.; Whynot, E.G.; Ellis, L.D.; Dupré, D.J. Anti-Cancer Potential of Cannabinoids, Terpenes, and Flavonoids Present in Cannabis. Cancers 2020, 12, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shaughnessy, W.B. On the Preparations of the Indian Hemp, or Gunjah: Cannabis Indica Their Effects on the Animal System in Health, and their Utility in the Treatment of Tetanus and other Convulsive Diseases. Prov. Med. J. Retrosp. Med. Sci. 1843, 5, 363–369. [Google Scholar]
- Hinz, B.; Ramer, R. Cannabinoids as anticancer drugs: Current status of preclinical research. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 127, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechoulam, R.; Shvo, Y. Hashish—I: The structure of Cannabidiol. Tetrahedron 1963, 19, 2073–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.; Merlin, M. Cannabis: Evolution and Ethnobotany. Plant Ecol. Evol. 2013, 147, 149. [Google Scholar]
- Motadi, L.R.; Jantjies, Z.E.; Moleya, B. Cannabidiol and Cannabis Sativa as a potential treatment in vitro prostate cancer cells silenced with RBBp6 and PC3 xenograft. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 4039–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tramèr, M.R.; Carroll, D.; Campbell, F.A.; Reynolds, D.J.M.; Moore, R.A.; McQuay, H.J. Cannabinoids for control of chemotherapy induced nausea and vomiting: Quantitative systematic review. BMJ 2001, 323, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, S.J.; Lichtman, A.H.; Piomelli, D.; Parker, L.A. Cannabinoids and Cancer Chemotherapy-Associated Adverse Effects. JNCI Monogr. 2021, 2021, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moela, P.; Choene, M.S.; Motadi, L.R. Silencing RBBP6 (Retinoblastoma Binding Protein 6) sensitises breast cancer cells MCF7 to staurosporine and camptothecin-induced cell death. Immunobiology 2014, 219, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukhele, S.T.; Motadi, L.R. Cannabidiol rather than Cannabis sativa extracts inhibit cell growth and induce apoptosis in cervical cancer cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A.; Kuzontkoski, P.M.; Groopman, J.E.; Prasad, A. Cannabidiol induces programmed cell death in breast cancer cells by coordinating the cross-talk between apoptosis and autophagy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Hudson, J.B.; Adomat, H.; Guns, E.; Cox, M.E.; Sharma, M. In Vitro Anticancer Activity of Plant-Derived Cannabidiol on Prostate Cancer Cell Lines. Pharmacol. Pharm. 2014, 5, 806–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainz-Cort, A.; Müller-Sánchez, C.; Espel, E. Anti-proliferative and cytotoxic effect of cannabidiol on human cancer cell lines in presence of serum. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śledziński, P.; Zeyland, J.; Słomski, R.; Nowak, A. The current state and future perspectives of cannabinoids in cancer biology. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’hooghe, M.; Willekens, B.; Delvaux, V.; D’haeseleer, M.; Guillaume, D.; Laureys, G.; Nagels, G.; Vanderdonckt, P.; Van Pesch, V.; Popescu, V. Sativex® (nabiximols) cannabinoid oromucosal spray in patients with resistant multiple sclerosis spasticity: The Belgian experience. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, F.; Chisari, C.G.; Fernández, Ó.; Sarroca, J.; Ferrer-Picón, E.; Hernández Vicente, F.; Silvan, C.V. A real-world evidence study of nabiximols in multiple sclerosis patients with resistant spasticity: Analysis in relation to the newly described ‘spasticity-plus syndrome’. Eur. J. Neurol. 2022, 29, 2744–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.M.; Maeng, K.; Lee, K.H.; Hong, S.H. Combined treatment with the Cox-2 inhibitor niflumic acid and PPARγ ligand ciglitazone induces ER stress/caspase-8-mediated apoptosis in human lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2011, 300, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, M.; Carracedo, A.; Salanueva, Í.J.; Hernández-Tiedra, S.; Lorente, M.; Egia, A.; Vazquez, P.; Blazquez, C.; Torres, S.; Garcia, S.; et al. Cannabinoid action induces autophagy-mediated cell death through stimulation of ER stress in human glioma cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1359–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motadi, L.R.; Moleya, B.N. The Antitumor Activity of Cannabis Sativa/CBD in Prostate Cancer pc3 Cells. Appl. Med. Res. 2022, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, W.; Hegde, V.L.; Singh, N.P.; Sisco, D.; Grant, S.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol-Induced Apoptosis in Jurkat Leukemia T Cells Is Regulated by Translocation of Bad to Mitochondria. Mol. Cancer Res. 2006, 4, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, R.; Mortuza, A.; Blumenthal, E.; Mustafa, A. Effects of cannabidiol (CBD) on the inhibition of melanoma cells in vitro. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2021, 42, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massi, P.; Solinas, M.; Cinquina, V.; Parolaro, D. Cannabidiol as potential anticancer drug. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 75, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javid, F.A.; Phillips, R.M.; Afshinjavid, S.; Verde, R.; Ligresti, A. Cannabinoid pharmacology in cancer research: A new hope for cancer patients? Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 775, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, J.; Hohmann, A.G. The endocannabinoid system and cancer: Therapeutic implication. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 1447–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamat, J.M.; Abbott, K.L.; Flannery, P.C.; Ledbetter, E.L.; Pondugula, S.R. Interplay between the Cannabinoid System and microRNAs in Cancer. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 9995–10000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laezza, C.; Pagano, C.; Navarra, G.; Pastorino, O.; Proto, M.C.; Fiore, D.; Piscopo, C.; Gazzerro, P.; Bifulco, M. The Endocannabinoid System: A Target for Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bifulco, M.; Laezza, C.; Pisanti, S.; Gazzerro, P. Cannabinoids and cancer: Pros and cons of an antitumour strategy. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 148, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amantini, C.; Mosca, M.; Nabissi, M.; Lucciarini, R.; Caprodossi, S.; Arcella, A.; Giangaspero, F.; Santoni, G. Capsaicin-induced apoptosis of glioma cells is mediated by TRPV1 vanilloid receptor and requires p38 MAPK activation. J. Neurochem. 2007, 102, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, L.V.; Al-Refae, K.; Wölk, G.; Bonatz, G.; Altmüller, J.; Becker, C.; Gisselmann, G.; Hatt, H. Expression and functionality of TRPV1 in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Targets Ther. 2016, 8, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, S.; Fischer, O.M.; Ullrich, A. Cannabinoids Induce Cancer Cell Proliferation via Tumor Necrosis Factor α-Converting Enzyme (TACE/ADAM17)-Mediated Transactivation of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 1943–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, V.N.; Wu, J.; Hei, T.K.; Ivanov, V.N.; Wu, J.; Hei, T.K. Regulation of human glioblastoma cell death by combined treatment of cannabidiol, γ-radiation and small molecule inhibitors of cell signaling pathways. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 74068–74095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramer, R.; Bublitz, K.; Freimuth, N.; Merkord, J.; Rohde, H.; Haustein, M.; Borchert, P.; Schmuhl, E.; Linnebacher, M.; Hinz, B. Cannabidiol inhibits lung cancer cell invasion and metastasis via intercellular adhesion molecule-1. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 1535–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haustein, M.; Ramer, R.; Linnebacher, M.; Manda, K.; Hinz, B. Cannabinoids increase lung cancer cell lysis by lymphokine-activated killer cells via upregulation of ICAM-1. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 92, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, E.; Cavic, M.; Krivokuca, A.; Casadó, V.; Canela, E. The endocannabinoid system as a target in cancer diseases: Are we there yet? Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, K. Cannabidiol (CBD) in Cancer Management. Cancers 2022, 14, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heider, C.G.; Itenberg, S.A.; Rao, J.; Ma, H.; Wu, X. Mechanisms of Cannabidiol (CBD) in Cancer Treatment: A Review. Biology 2022, 11, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertwee, R.G. Inverse agonism and neutral antagonism at cannabinoid CB1 receptors. Life Sci. 2005, 76, 1307–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, Y.Y.; Kim, S.R.; Kim, D.Y.; Chae, S.W.; Song, J.J. Cannabidiol enhances cytotoxicity of anti-cancer drugs in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qin, Y.; Pan, Z.; Li, M.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Qu, G.; Zhou, L.; Xu, M.; Zheng, Q.; et al. Cannabidiol Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Cell Apoptosis in Human Gastric Cancer SGC-7901 Cells. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhelyazkova, M.; Kirilov, B.; Momekov, G. The pharmacological basis for application of cannabidiol in cancer chemotherapy. Pharmacia 2020, 67, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.F.; Teixeira, N.; Correia-Da-silva, G.; Amaral, C. Cannabinoids in Breast Cancer: Differential Susceptibility According to Subtype. Molecules 2021, 27, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisogno, T.; Hanuš, L.; De Petrocellis, L.; Tchilibon, S.; Ponde, D.E.; Brandi, I.; Moriello, A.S.; Davis, J.B.; Mechoulam, R.; Di Marzo, V. Molecular targets for cannabidiol and its synthetic analogues: Effect on vanilloid VR1 receptors and on the cellular uptake and enzymatic hydrolysis of anandamide. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 134, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligresti, A.; Moriello, A.S.; Starowicz, K.; Matias, I.; Pisanti, S.; De Petrocellis, L.; Laezza, C.; Portella, G.; Bifulco, M.; Di Marzo, V. Antitumor Activity of Plant Cannabinoids with Emphasis on the Effect of Cannabidiol on Human Breast Carcinoma. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 318, 1375–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeele, F.V.; Lotteau, S.; Ducreux, S.; Dubois, C.; Monnier, N.; Hanna, A.; Gkika, D.; Romestaing, C.; Noyer, L.; Flourakis, M.; et al. TRPV1 variants impair intracellular Ca2+ signaling and may confer susceptibility to malignant hyperthermia. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehning, D.; Patterson, R.L.; Snyder, S.H. Apoptosis and Calcium: New Roles for Cytochrome c and Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Cell Cycle 2004, 3, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, G.; Zubair, S.; Tayubi, I.A.; Dahms, H.U.; Madar, I.H. Towards the early detection of ductal carcinoma (a common type of breast cancer) using biomarkers linked to the PPAR(γ) signaling pathway. Bioinformation 2019, 15, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, T.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Yang, K.; Xie, F.; Liao, Z.; Wei, P. PPAR-γ Modulators as Current and Potential Cancer Treatments. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 737776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, R.; Kawamura, R.; Singer, E.; Pakdel, A.; Sarma, P.; Judkins, J.; Elwakeel, E.; Dayal, S.; Martinez-Martinez, E.; Amere, M.; et al. Targeting multiple cannabinoid anti-tumour pathways with a resorcinol derivative leads to inhibition of advanced stages of breast cancer. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 4464–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaz, M.; Nasser, M.W.; Ravi, J.; Wani, N.A.; Ahirwar, D.K.; Zhao, H.; Oghumu, S.; Satoskar, A.R.; Shilo, K.; Carson, W.E.; et al. Modulation of the tumor microenvironment and inhibition of EGF/EGFR pathway: Novel anti-tumor mechanisms of Cannabidiol in breast cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 906–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milian, L.; Mata, M.; Alcacer, J.; Oliver, M.; Sancho-Tello, M.; de Llano, J.J.M.; Camps, C.; Galbis, J.; Carretero, J.; Carda, C. Cannabinoid receptor expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Effectiveness of tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol inhibiting cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vitro. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, S.; Ishibashi, T.; Kokura, M.; Fujimoto, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Shidara, S.; Kurppa, K.J.; Pape, J.; Caton, J.; Morgan, P.R.; et al. RAF1–MEK/ERK pathway-dependent ARL4C expression promotes ameloblastoma cell proliferation and osteoclast formation. J. Pathol. 2022, 256, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffarel, M.M.; Andradas, C.; Pérez-Gómez, E.; Guzmán, M.; Sánchez, C. Cannabinoids: A new hope for breast cancer therapy? Cancer Treat. Rev. 2012, 38, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraguas-Sánchez, A.I.; Martín-Sabroso, C.; Torres-Suárez, A.I. Insights into the effects of the endocannabinoid system in cancer: A review. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 2566–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Harpe, A.; Beukes, N.; Frost, C.L. CBD activation of TRPV1 induces oxidative signaling and subsequent ER stress in breast cancer cell lines. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramer, R.; Rohde, A.; Merkord, J.; Rohde, H.; Hinz, B. Decrease of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 may contribute to the anti-invasive action of cannabidiol on human lung cancer cells. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 2162–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramer, R.; Heinemann, K.; Merkord, J.; Rohde, H.; Salamon, A.; Linnebacher, M.; Hinz, B. COX-2 and PPAR-γ confer cannabidiol-induced apoptosis of human lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Multhoff, G. Repurposing Cannabidiol as a Potential Drug Candidate for Anti-Tumor Therapies. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elrod, H.A.; Sun, S.Y. PPARγ and apoptosis in cancer. PPAR Res. 2008, 2008, 704165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malenczyk, K.; Keimpema, E.; Piscitelli, F.; Calvigioni, D.; Björklund, P.; Mackie, K.; Di Marzo, V.; Hokfelt, T.G.M.; Dobrzyn, A.; Harkany, T. Fetal endocannabinoids orchestrate the organization of pancreatic islet microarchitecture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E6185–E6194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, I.V.d.A.; Bellozi, P.M.Q.; Batista, E.M.; Vilela, L.R.; Brandão, I.L.; Ribeiro, F.M.; Moraes, F.M.D.; Moreira, F.A.; de Oliveira, A.C.P. Cannabidiol anticonvulsant effect is mediated by the PI3Kγ pathway. Neuropharmacology 2020, 176, 108156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheratta, A.; Thayyullathil, F.; Pallichankandy, S.; Subburayan, K.; Alakkal, A.; Galadari, S. Prostate apoptosis response-4 and tumor suppression: It’s not just about apoptosis anymore. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, L.; Miguel, A.; Díaz-Laviada, I. Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol induces apoptosis in human prostate PC-3 cells via a receptor-independent mechanism. FEBS Lett. 1999, 458, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nithipatikom, K.; Endsley, M.P.; Isbell, M.A.; Falck, J.R.; Iwamoto, Y.; Hillard, C.J.; Campbell, W.B. 2-ArachidonoylglycerolA Novel Inhibitor of Androgen-Independent Prostate Cancer Cell Invasion. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 8826–8830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarfaraz, S.; Afaq, F.; Adhami, V.M.; Malik, A.; Mukhtar, H. Cannabinoid receptor agonist-induced apoptosis of human prostate cancer cells LNCaP proceeds through sustained activation of ERK1/2 leading to G 1 cell cycle arrest. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 39480–39491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.; Jamshidi, N.; Zomer, R.; Piva, T.J.; Mantri, N. Cannabinoids and Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review of Animal Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco, G.; Sánchez, C.; Guzmán, M. Towards the use of cannabinoids as antitumour agents. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, S.; Lorente, M.; Rodríguez-Fornés, F.; Hernández-Tiedra, S.; Salazar, M.; García-Taboada, E.; Barcia, J.; Guzman, M.; Velasco, G. A Combined Preclinical Therapy of Cannabinoids and Temozolomide against Glioma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.A.; Dalgleish, A.G.; Liu, W.M. The combination of cannabidiol and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol enhances the anticancer effects of radiation in an orthotopic murine glioma model. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 2955–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Valero, I.; Torres, S.; Salazar-Roa, M.; García-Taboada, E.; Hernández-Tiedra, S.; Guzmán, M.; Sepulveda, J.M.; Velasco, G.; Lorente, M. Optimization of a preclinical therapy of cannabinoids in combination with temozolomide against glioma. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 157, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio-Blanco, J.; Sebastián, V.; Benoit, J.P.; Torres-Suárez, A.I. Lipid nanocapsules decorated and loaded with cannabidiol as targeted prolonged release carriers for glioma therapy: In vitro screening of critical parameters. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 134, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carracedo, A.; Gironella, M.; Lorente, M.; Garcia, S.; Guzmán, M.; Velasco, G.; Iovanna, J.L. Cannabinoids Induce Apoptosis of Pancreatic Tumor Cells via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress–Related Genes. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 6748–6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vara, D.; Salazar, M.; Olea-Herrero, N.; Guzmán, M.; Velasco, G.; Díaz-Laviada, I. Anti-tumoral action of cannabinoids on hepatocellular carcinoma: Role of AMPK-dependent activation of autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, V.N.; Wu, J.; Wang, T.J.C.; Hei, T.K. Inhibition of ATM kinase upregulates levels of cell death induced by cannabidiol and Ɣ-irradiation in human glioblastoma cells. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 825–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Sun, M.M.; Zhang, G.G.; Yang, J.; Chen, K.S.; Xu, W.W.; Li, B. Targeting PI3K/Akt signal transduction for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennessy, B.T.; Smith, D.L.; Ram, P.T.; Lu, Y.; Mills, G.B. Exploiting the PI3K/AKT Pathway for Cancer Drug Discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 988–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Vogt, P.K.; Rommel, C. PI3K: From the Bench to the Clinic and Back. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2010, 347, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, E.C.; Celestino, J.; Dai, C.; Schaefer, L.; Sawaya, R.E.; Fuller, G.N. Combined activation of Ras and Akt in neural progenitors induces glioblastoma formation in mice. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabissi, M.; Morelli, M.B.; Amantini, C.; Liberati, S.; Santoni, M.; Ricci-Vitiani, L.; Pallini, R.; Santoni, G. Cannabidiol stimulates Aml-1a-dependent glial differentiation and inhibits glioma stem-like cells proliferation by inducing autophagy in a TRPV2-dependent manner. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 1855–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, R.A.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR Signaling in Growth, Metabolism, and Disease. Cell 2017, 168, 960–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckerdt, F.D.; Bell, J.B.; Gonzalez, C.; Oh, M.S.; Perez, R.E.; Mazewski, C.; Fischietti, M.; Goldman, S.; Nakano, I.; Platanias, M.C. Combined PI3Kα-mTOR Targeting of Glioma Stem Cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solinas, M.; Massi, P.; Cinquina, V.; Valenti, M.; Bolognini, D.; Gariboldi, M.; Monti, E.; Rubino, T.; Parolaro, D. Cannabidiol, a Non-Psychoactive Cannabinoid Compound, Inhibits Proliferation and Invasion in U87-MG and T98G Glioma Cells through a Multitarget Effect. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laub, V.; Devraj, K.; Elias, L.; Schulte, D. Bioinformatics for wet-lab scientists: Practical application in sequencing analysis. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, B.; Carracedo, A.; Diez-Zaera, M.; Gómez del Pulgar, T.; Guzmán, M.; Velasco, G. The CB2 cannabinoid receptor signals apoptosis via ceramide-dependent activation of the mitochondrial intrinsic pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2006, 312, 2121–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramer, R.; Wendt, F.; Wittig, F.; Schäfer, M.; Boeckmann, L.; Emmert, S.; Hinz, B. Impact of Cannabinoid Compounds on Skin Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dika, E.; Scarfì, F.; Ferracin, M.; Broseghini, E.; Marcelli, E.; Bortolani, B.; Campione, E.; Riefolo, M.; Ricci, C.; Lambertini, M. Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merhavi-Shoham, E.; Itzhaki, O.; Markel, G.; Schachter, J.; Besser, M.J. Adoptive Cell Therapy for Metastatic Melanoma. Cancer J. 2017, 23, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.B.; Einhorn, L.H.; Meyers, M.L.; Saxman, S.; Destro, A.N.; Panageas, K.S.; Begg, C.B.; Agarwala, S.S.; Schuchter, L.M.; Ernstoff, M.S.; et al. Phase III multicenter randomized trial of the Dartmouth regimen versus dacarbazine in patients with metastatic melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 2745–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhao, H.; Fang, X.; Li, H. Cannabinoid receptor 2 is upregulated in melanoma. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2012, 8, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blázquez, C.; Carracedo, A.; Barrado, L.; José Real, P.; Luis Fernández-Luna, J.; Velasco, G.; Malumbres, M.; Guzman, M. Cannabinoid receptors as novel targets for the treatment of melanoma. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 2633–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmerman, E.; Qin, X.; Yu, J.C.; Baban, B. Cannabinoids as a Potential New and Novel Treatment for Melanoma: A Pilot Study in a Murine Model. J. Surg. Res. 2019, 235, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, J.L.; Hill, D.S.; McKee, C.S.; Hernandez-Tiedra, S.; Lorente, M.; Lopez-Valero, I.; Anagnostou, M.E.; Babatunde, F.; Corazzari, M.; Redfern, C.P.F.; et al. Exploiting cannabinoid-induced cytotoxic autophagy to drive melanoma cell death. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richtig, G.; Kienzl, M.; Rittchen, S.; Roula, D.; Eberle, J.; Sarif, Z.; Pichler, M.; Hoefler, G.; Heinemann, A. Cannabinoids Reduce Melanoma Cell Viability and Do Not Interfere with Commonly Used Targeted Therapy in Metastatic Melanoma In Vivo and In Vitro. Biology 2023, 12, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviello, G.; Romano, B.; Borrelli, F.; Capasso, R.; Gallo, L.; Piscitelli, F.; Di Marzo, V.; Izzo, A.A. Chemopreventive effect of the non-psychotropic phytocannabinoid cannabidiol on experimental colon cancer. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 90, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Yun, H.K.; Jeong, Y.A.; Jo, M.J.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, J.L.; Kim, D.Y.; Park, S.H.; Kim, B.R.; Na, Y.J.; et al. Cannabidiol-induced apoptosis is mediated by activation of Noxa in human colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2019, 447, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juknat, A.; Pietr, M.; Kozela, E.; Rimmerman, N.; Levy, R.; Gao, F.; Coppola, G.; Geschwind, D.; Vogel, Z. Microarray and Pathway Analysis Reveal Distinct Mechanisms Underlying Cannabinoid-Mediated Modulation of LPS-Induced Activation of BV-2 Microglial Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naya, N.; Kelly, J.; Corna, G.; Golino, M.; Abbate, A.; Toldo, S. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Action of Cannabidiol. Molecules 2023, 28, 5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maayah, Z.H.; Takahara, S.; Ferdaoussi, M.; Dyck, J.R.B. The Molecular Mechanisms that Underpin the Biological Benefits of Full-spectrum Cannabis Extract in the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain and Inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Morrison, P.D.; Fusar-Poli, P.; Martin-Santos, R.; Borgwardt, S.; Wintonbrown, T.T.; Nosarti, C.; Carroll, C.M.O.; Seal, M.L.; Allen, P.; et al. Opposite Effects of Δ-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol and Cannabidiol on Human Brain Function and Psychopathology. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
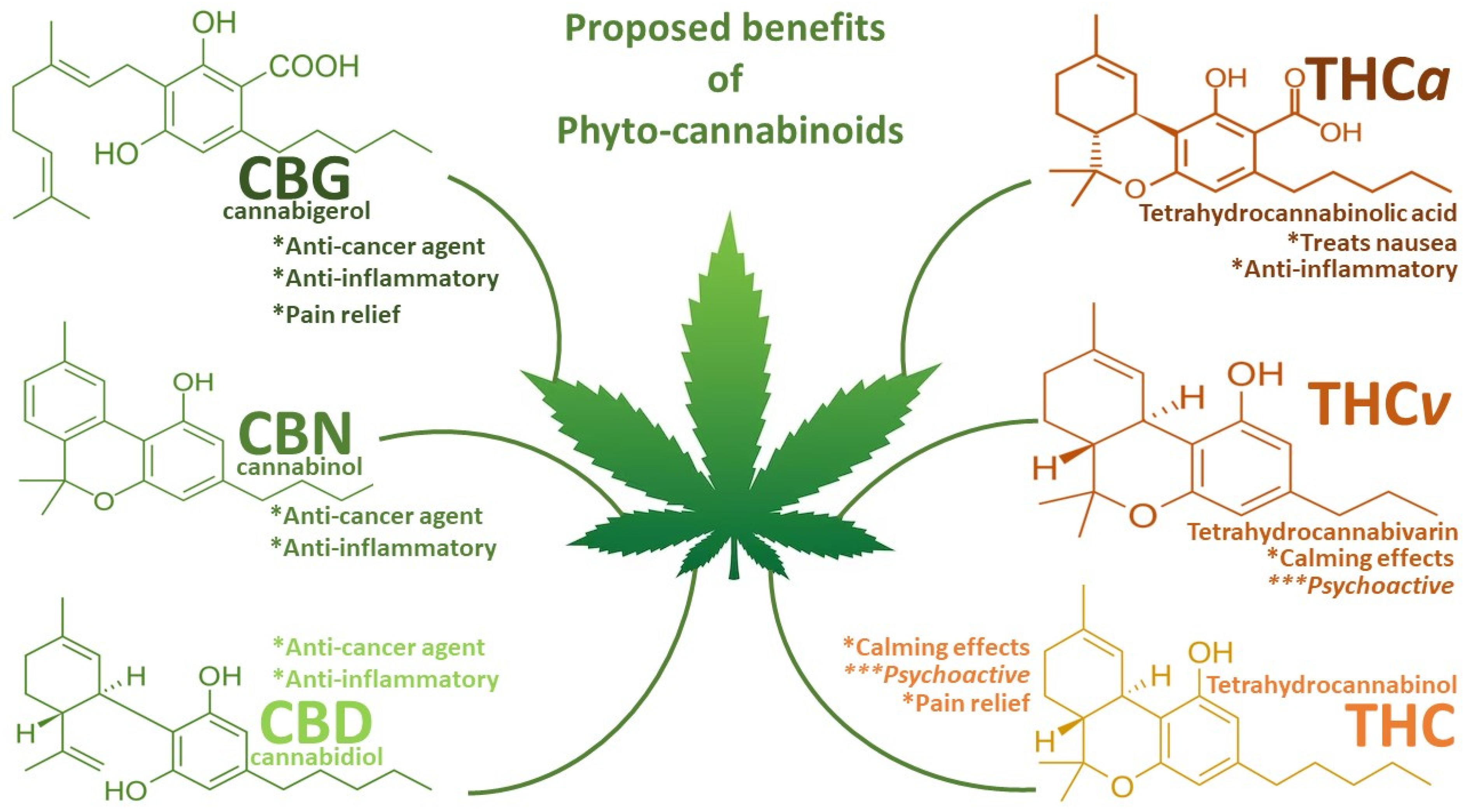
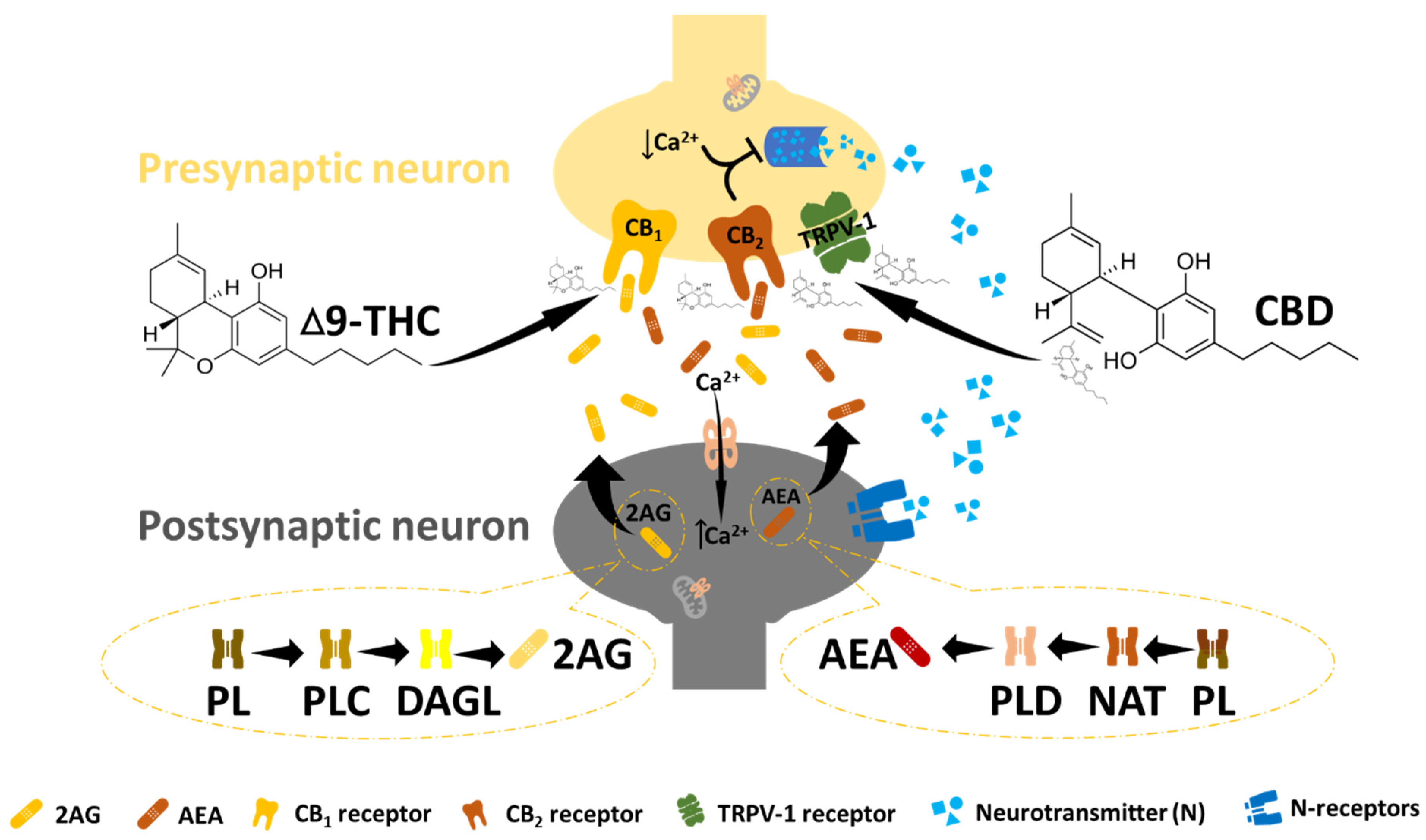
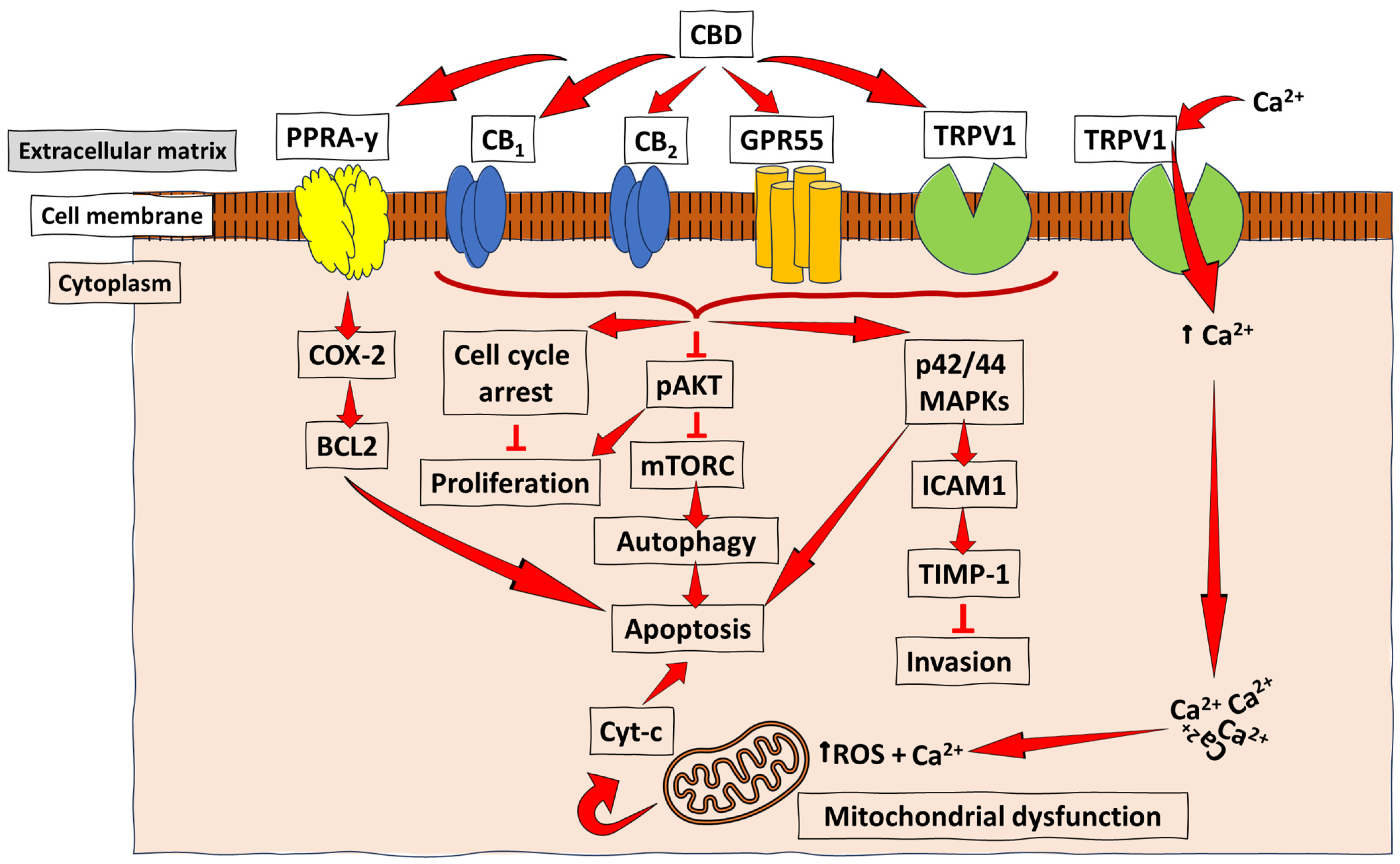

| Cancer | Receptor | Molecular Cell Signalling | In Vitro/Vivo Effect on Cancer Cells | Autophagy Apoptosis | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cervical | ND | ↑ p53, caspase3/7 and bax ↓ ATP levels | ↓ Proliferation | Apoptosis | [11] |
| Breast | ND | ↓ RBBP6 expression ↑ p53 gene expression | ↓ Cell growth ↓ Cellular proliferation | Apoptosis | [10] |
| Lung | ND | ↑ caspase-9/-3 ↑ caspase-8/Bid/Bax ↑ ER stress responses | ↓ Tumour cell growth ↓ Cellular proliferation | Apoptosis | [18] |
| Breast | Receptor- Independent | ↓ AKT and mTOR signalling ↑ Reactive oxygen species (ROS) ↑ ER stress responses | ↑ Cytotoxicity ↓ Tumour cell migration | Autophagy Apoptosis | [12] |
| Pancreatic | CB2 | ↑ Ceramide synthesis ↑ ER stress ↑ p8–TRIB3 induction ↑ AKT inhibition | ↑ Antitumor action ↓ Tumour cell growth ↓ Cellular proliferation | Autophagy Apoptosis | [19] |
| Colon | ND | ↑ Mitochondrial Ca2+ ↑ ER stress responses | ↓ Cellular proliferation ↑ Cytotoxicity | ND | [14] |
| Prostate | ND | ↑ Caspase3/7 activity ↓ RBBP6 ↑ p53; bax mRNA expression ↓ Bcl2 gene expression | ↓ Cellular proliferation ↓ Tumour cell growth | Apoptosis | [20] |
| Prostate | CB1, CB2 | ↓ PSA, VEGF, ↓ Chemokine IL-6 and IL-8. ↓ CB1, CB2 on cancer cells ↓ Pro-inflammatory cytokines | ↑ Anti-inflammatory ↑ Cytotoxicity ↓ Cancer cell growth | Autophagy | [13] |
| Leukaemia | CB2 | ↑ ER stress ↑ p8–TRIB3 induction | ND | Autophagy Apoptosis | [21] |
| Melanoma | CB2 | ↑ p8–TRIB3 induction ↓ AKT and mTOR signalling | ↓ Cell growth ↓ Cell viability, ↓ Invasion ↓ Metastasis ↓ Proliferation | Autophagy Apoptosis | [22] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mashabela, M.D.; Kappo, A.P. Anti-Cancer and Anti-Proliferative Potential of Cannabidiol: A Cellular and Molecular Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115659
Mashabela MD, Kappo AP. Anti-Cancer and Anti-Proliferative Potential of Cannabidiol: A Cellular and Molecular Perspective. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(11):5659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115659
Chicago/Turabian StyleMashabela, Manamele Dannies, and Abidemi Paul Kappo. 2024. "Anti-Cancer and Anti-Proliferative Potential of Cannabidiol: A Cellular and Molecular Perspective" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 11: 5659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115659
APA StyleMashabela, M. D., & Kappo, A. P. (2024). Anti-Cancer and Anti-Proliferative Potential of Cannabidiol: A Cellular and Molecular Perspective. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(11), 5659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115659






