Genome-Wide Identification and Multi-Stress Response Analysis of the DABB-Type Protein-Encoding Genes in Brassica napus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
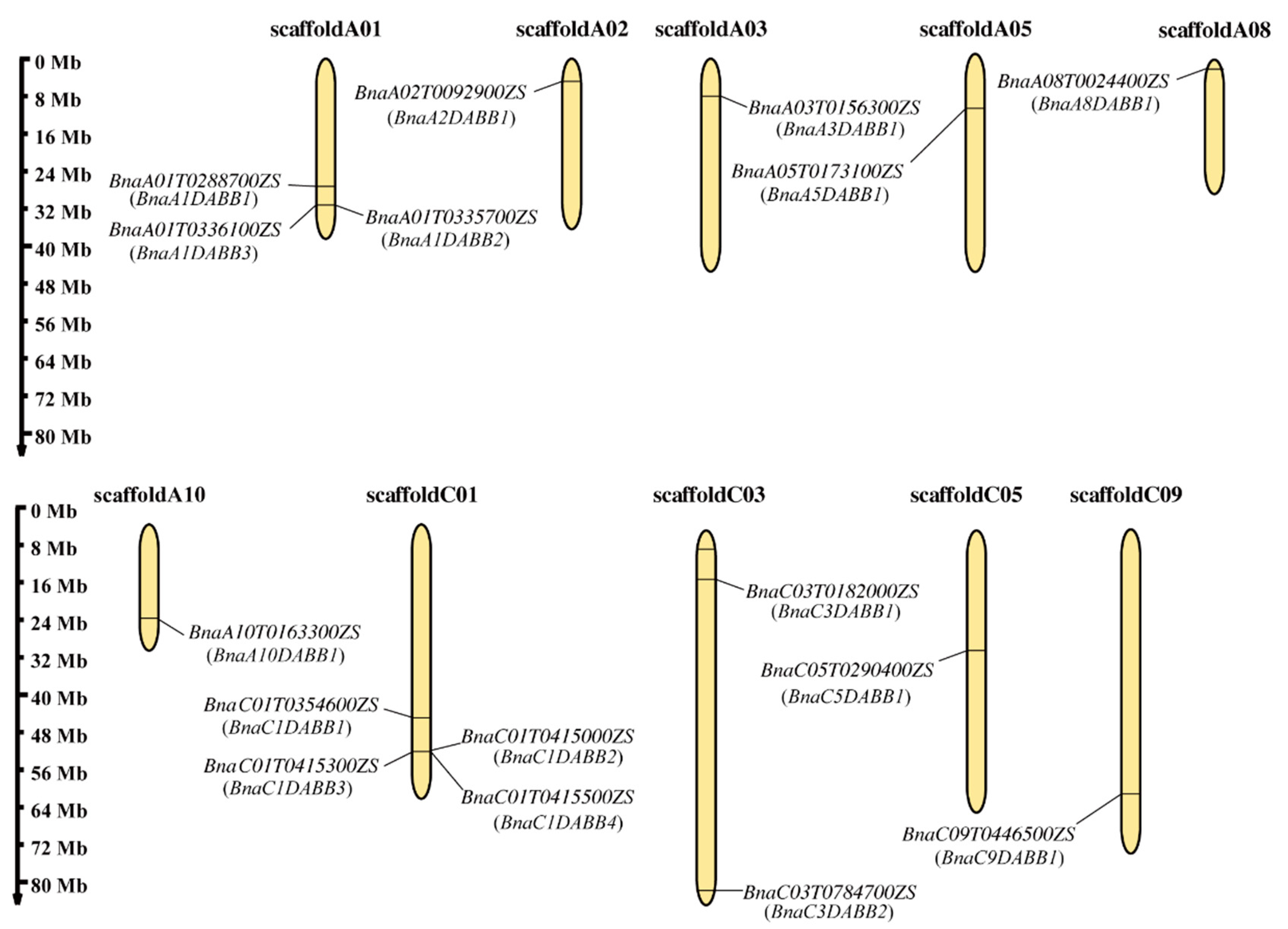
2.1. Identification, Chromosomal and Subcellular Localization of DABBs in B. napus
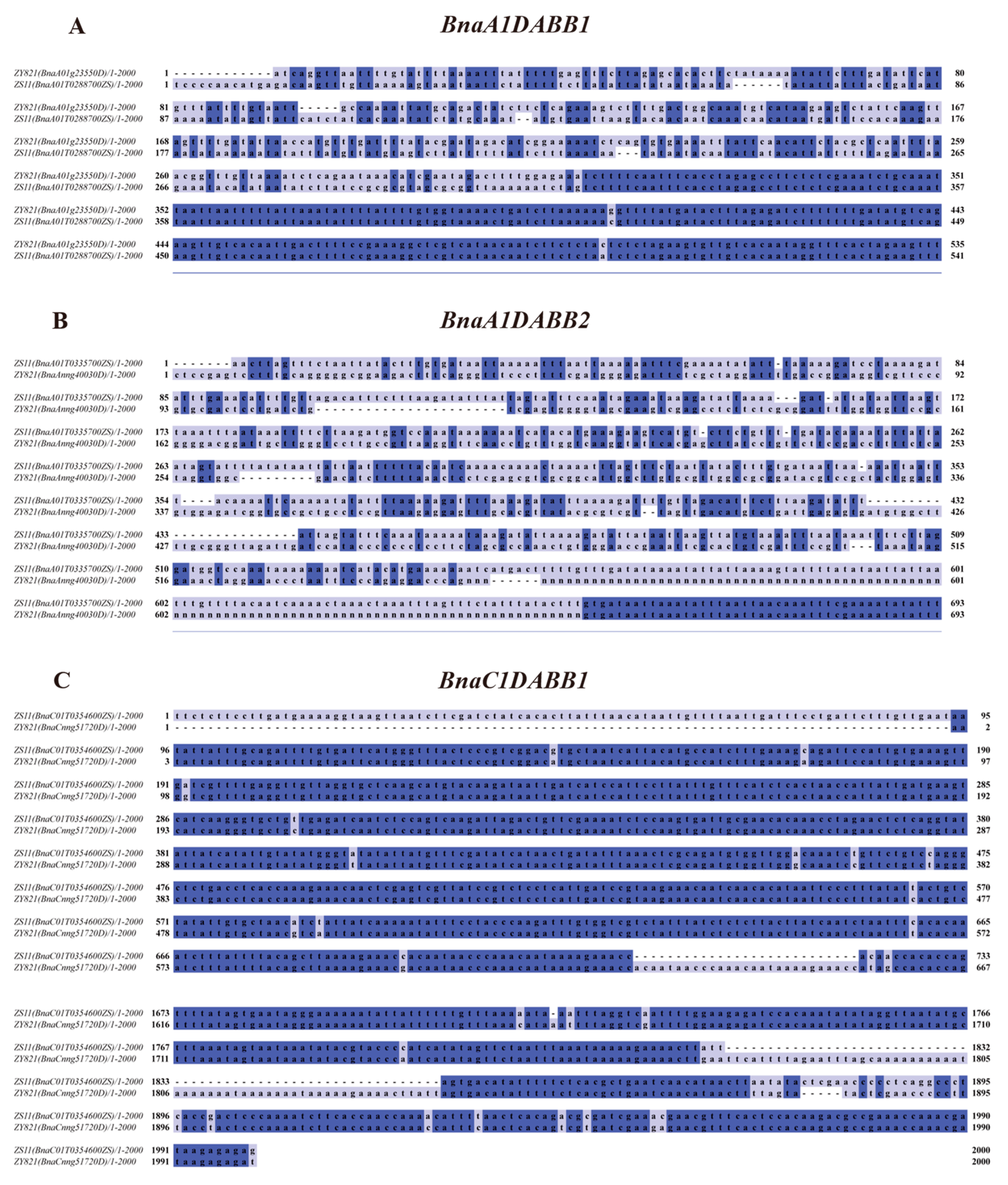
2.2. Analysis of Formation and Evolution of The BnaDABB Members in B. napus
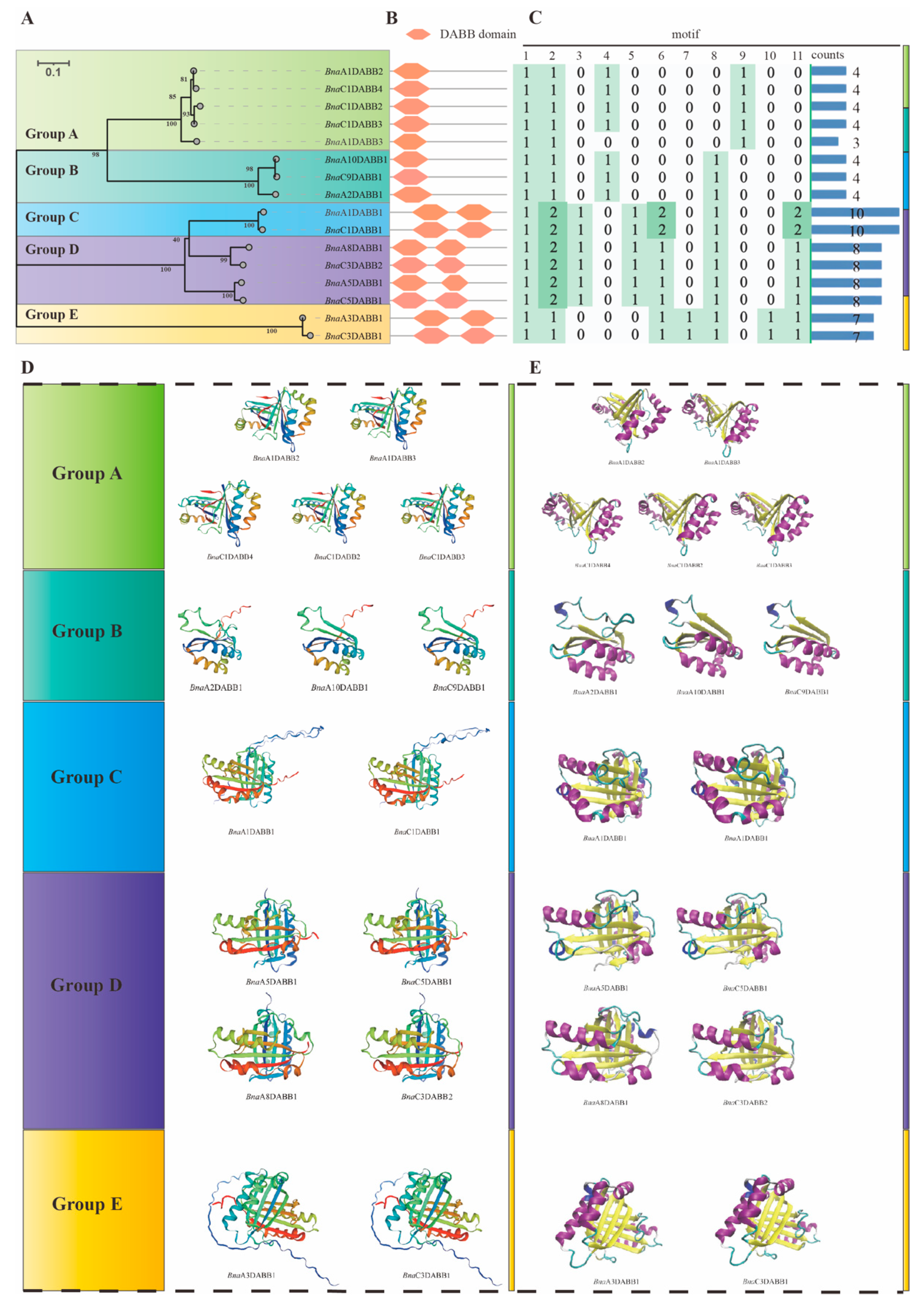
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis and Biochemical Properties Calculation of BnaDABBs
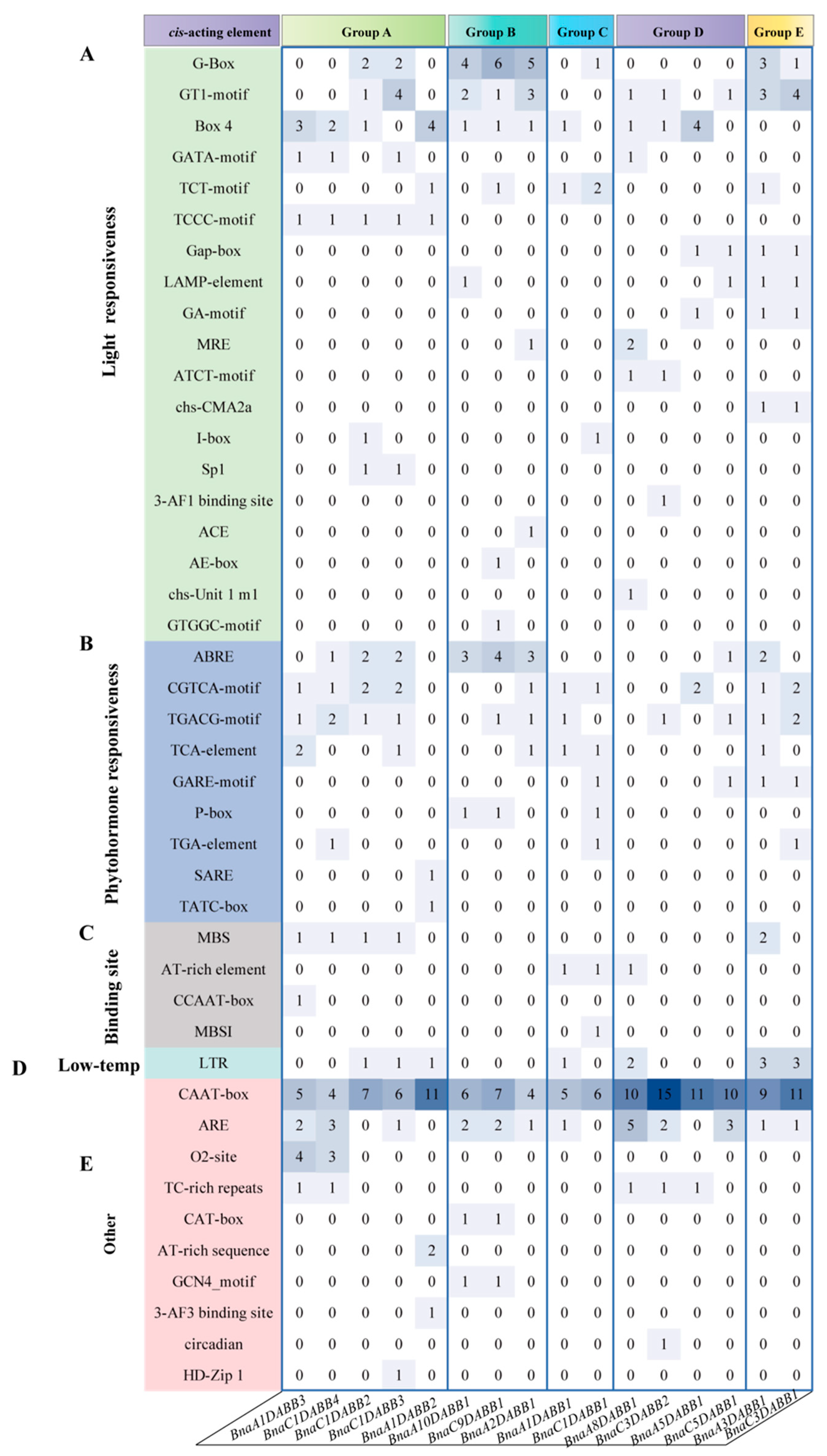
2.4. Analysis of Cis-Elements and Expression Patterns of BnaDABBs
2.5. Expression Profiling of BnaDABBs under Plant Hormones Treatment
2.6. Expression Profiling of BnaDABB Genes under Abiotic Stresses Treatment
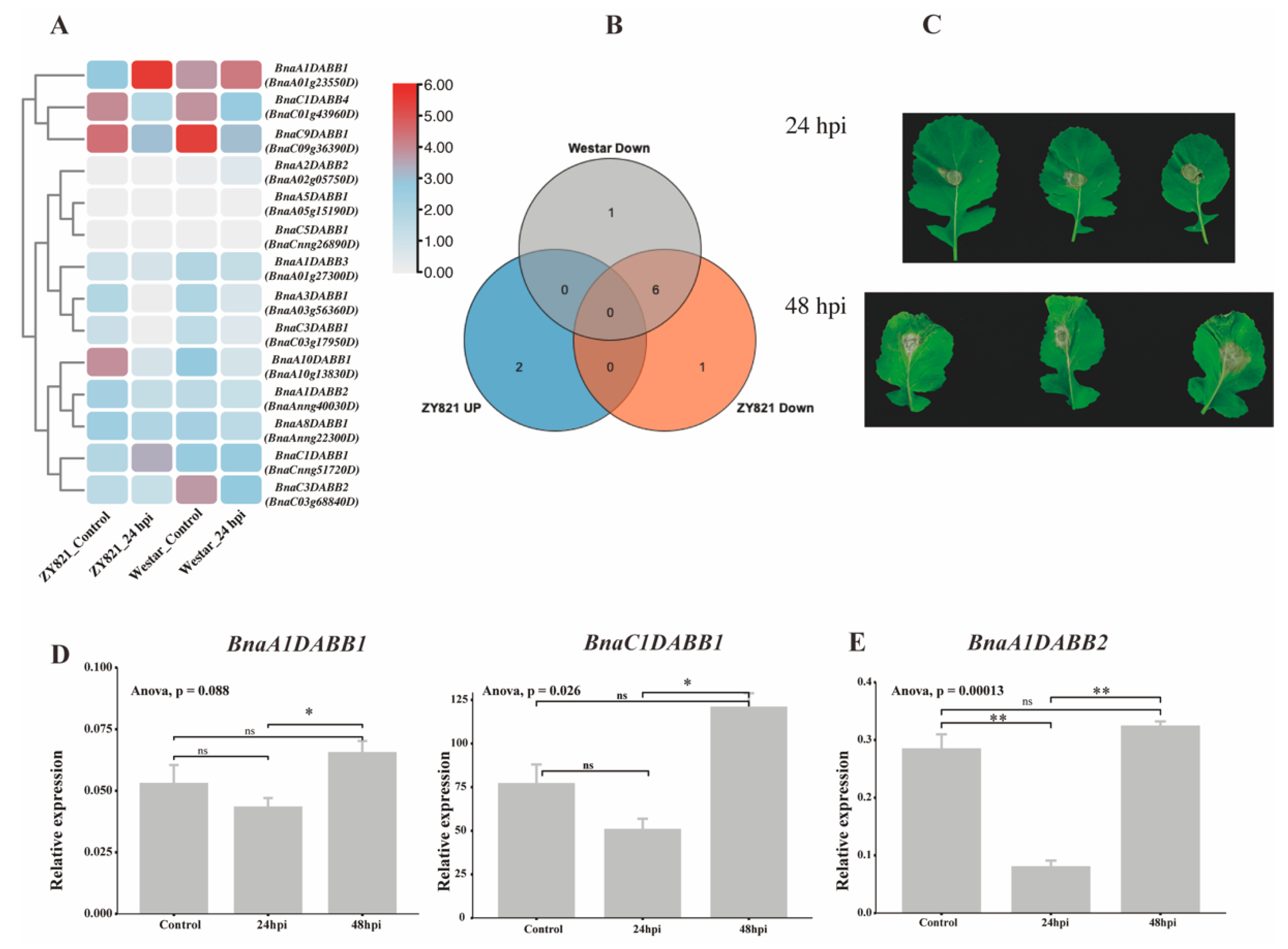
2.7. Expression Profiling of BnaDABBs during Infection by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Fungal Strains and Culture Conditions
4.2. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.3. Identification of DABB Genes in B. napus and Related Species
4.4. Chromosomal Location, Subcellular Localization and Collinearity Analysis of BnaDABB Genes
4.5. Phylogenetic Analysis and Biochemical Properties Calculation
4.6. Analysis of Cis-Element, Expression Patterns and Abiotic Stress
4.7. RNA Extraction and RT–qPCR Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neik, T.X.; Amas, J.; Barbetti, M.; Edwards, D.; Batley, J. Understanding Host-Pathogen Interactions in Brassica napus in the Omics Era. Plants 2020, 9, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesi, N.; Delourme, R.; Bregeon, M.; Falentin, C.; Renard, M. Genetic and molecular approaches to improve nutritional value of Brassica napus L. seed. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2008, 331, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.N.; Li, T.; Guo, X.J.; Li, M.; Liu, X.Y.; Cao, J.; Tan, X.L. Sclerotinia Stem Rot Resistance in Rapeseed: Recent Progress and Future Prospects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 2965–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neik, T.X.; Barbetti, M.J.; Batley, J. Current Status and Challenges in Identifying Disease Resistance Genes in Brassica napus. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolton, M.D.; Thomma, B.P.; Nelson, B.D. Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib.) de Bary: Biology and molecular traits of a cosmopolitan pathogen. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2006, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, J.; Lin, Y.; Fu, Y.; Xie, J.; Li, B.; Bian, X.; Feng, Y.; Liang, W.; Tang, Q.; et al. Editing homologous copies of an essential gene affords crop resistance against two cosmopolitan necrotrophic pathogens. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 2349–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.R.; Lee, S.S.; Park, S.C.; Kang, J.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, K.O.; Lee, S.Y. Functional characterization of pathogen-responsive protein AtDabb1 with an antifungal activity from Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1784, 1918–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.C.; Lee, J.R.; Shin, S.O.; Park, Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Hahm, K.S. Characterization of a heat-stable protein with antimicrobial activity from Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 362, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagne, S.J.; Stout, J.M.; Liu, E.; Boubakir, Z.; Clark, S.M.; Page, J.E. Identification of olivetolic acid cyclase from Cannabis sativa reveals a unique catalytic route to plant polyketides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12811–12816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Matsui, T.; Kodama, T.; Mori, T.; Zhou, X.; Taura, F.; Noguchi, H.; Abe, I.; Morita, H. Structural basis for olivetolic acid formation by a polyketide cyclase from Cannabis sativa. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 1088–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Buchwaldt, L.; Rimmer, S.R.; Sharpe, A.; McGregor, L.; Bekkaoui, D.; Hegedus, D. Patterns of differential gene expression in Brassica napus cultivars infected with Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2009, 10, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, I.J.; Tong, C.; Becker, M.G.; Mao, X.; Huang, J.; de Kievit, T.; Fernando, W.G.D.; Liu, S.; Belmonte, M.F. RNA sequencing of Brassica napus reveals cellular redox control of Sclerotinia infection. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 5079–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifbarghi, S.; Borhan, M.H.; Wei, Y.; Coutu, C.; Robinson, S.J.; Hegedus, D.D. Changes in the Sclerotinia sclerotiorum transcriptome during infection of Brassica napus. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Chen, B.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, F.; Xie, T.; Xu, K.; Gao, G.; Yan, G.; Li, H.; Li, L.; et al. Genomic selection and genetic architecture of agronomic traits during modern rapeseed breeding. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinke, D.W.; Cherry, J.M.; Dean, C.; Rounsley, S.D.; Koornneef, M. Arabidopsis thaliana: A model plant for genome analysis. Science 1998, 282, 662+679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Wei, Y.; Xiao, D.; Gong, K.; Sun, P.; Ren, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wu, T.; Yang, Q.; Li, X.; et al. Brassica carinata genome characterization clarifies U’s triangle model of evolution and polyploidy in Brassica. Plant Physiol. 2021, 186, 388–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, A.K.; Parmar, N.; Singh, K.H.; Nanjundan, J. Current achievements and future prospects of genetic engineering in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern & Coss.). Planta 2020, 252, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaz, R.; Ahmed, I.; Sizmaz, O.; Ahsan, U. Use of Camelina sativa and By-Products in Diets for Dairy Cows: A Review. Animals 2022, 12, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waadt, R.; Seller, C.A.; Hsu, P.K.; Takahashi, Y.; Munemasa, S.; Schroeder, J.I. Plant hormone regulation of abiotic stress responses. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 680–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, Y.S.; Sintaha, M.; Cheung, M.Y.; Lam, H.M. Plant Hormone Signaling Crosstalks between Biotic and Abiotic Stress Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Pelah, D.; Alergand, T.; Shoseyov, O.; Altman, A. Characterization of SP1, a stress-responsive, boiling-soluble, homo-oligomeric protein from aspen. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Zhao, R.; Sheng, J.; Shen, L. SlERF2 Is Associated with Methyl Jasmonate-Mediated Defense Response against Botrytis cinerea in Tomato Fruit. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9923–9932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boratyn, G.M.; Schaffer, A.A.; Agarwala, R.; Altschul, S.F.; Lipman, D.J.; Madden, T.L. Domain enhanced lookup time accelerated BLAST. Biol. Direct 2012, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L.; Tosatto, S.C.E.; Paladin, L.; Raj, S.; Richardson, L.J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D412–D419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddy, S.R. Accelerated Profile HMM Searches. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 7, e1002195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Lu, S.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; Thanki, N.; Yamashita, R.A.; et al. The conserved domain database in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D384–D388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Khedkar, S.; Bork, P. SMART: Recent updates, new developments and status in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D458–D460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, S.; Wei, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, D.; Jia, Y.; Luo, C.; Lin, Y.; Liang, C.; Hu, Y.; et al. BnIR: A multi-omics database with various tools for Brassica napus research and breeding. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Aluko, O.O.; Wu, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, G. MG2C: A user-friendly online tool for drawing genetic maps. Mol. Hortic. 2021, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.C.; Shen, H.B. Plant-mPLoc: A top-down strategy to augment the power for predicting plant protein subcellular localization. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Debarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, F.; Pearce, M.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Basutkar, P.; Lee, J.; Edbali, O.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Kolesnikov, A.; Lopez, R. Search and sequence analysis tools services from EMBL-EBI in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W276–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, M.R.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Sanchez, J.C.; Williams, K.L.; Appel, R.D.; Hochstrasser, D.F. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999, 112, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Dehais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouze, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | Name | Gene ID | Molecular Weight | Theoretical pI | Instability Index | Aliphatic Index | Grand Average of Hydropathicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | BnaA1DABB2 | BnaA01T0335700ZS | 11,213.85 | 5.46 | 19 | 93.43 | −0.297 |
| A | BnaA1DABB3 | BnaA01T0336100ZS | 12,142.96 | 5.41 | 26.72 | 95.61 | −0.103 |
| A | BnaC1DABB2 | BnaC01T0415000ZS | 12,142.96 | 5.42 | 24.86 | 94.67 | −0.123 |
| A | BnaC1DABB3 | BnaC01T0415300ZS | 12,147.98 | 5.26 | 25.83 | 95.61 | −0.106 |
| A | BnaC1DABB4 | BnaC01T0415500ZS | 12,115.94 | 5.41 | 27.42 | 95.61 | −0.077 |
| B | BnaA2DABB1 | BnaA02T0092900ZS | 13,701.93 | 8.76 | 35.92 | 82.07 | −0.146 |
| B | BnaA10DABB1 | BnaA10T0163300ZS | 12,321.08 | 5.22 | 22.95 | 85.95 | 0.109 |
| B | BnaC9DABB1 | BnaC09T0446500ZS | 12,351.11 | 5.22 | 23.72 | 85.95 | 0.105 |
| C | BnaA1DABB1 | BnaA01T0288700ZS | 29,132.53 | 7.14 | 45.9 | 98.52 | 0.051 |
| C | BnaC1DABB1 | BnaC01T0354600ZS | 29,343.92 | 7.14 | 48.98 | 99.93 | 0.054 |
| D | BnaA5DABB1 | BnaA05T0173100ZS | 22,568.01 | 4.85 | 33.16 | 107.33 | 0.073 |
| D | BnaA8DABB1 | BnaA08T0024400ZS | 22,540.81 | 5.17 | 30.86 | 101.67 | −0.085 |
| D | BnaC3DABB2 | BnaC03T0784700ZS | 22,363.70 | 5.49 | 28.18 | 101.7 | −0.087 |
| D | BnaC5DABB1 | BnaC05T0290400ZS | 22,643.11 | 5.12 | 34.97 | 108.3 | 0.046 |
| E | BnaA3DABB1 | BnaA03T0156300ZS | 31,777.88 | 5.51 | 31.24 | 77.61 | −0.286 |
| E | BnaC3DABB1 | BnaC03T0182000ZS | 31,751.78 | 5.4 | 35.77 | 79.36 | −0.286 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Wang, K.; Xia, Q.; Xia, S. Genome-Wide Identification and Multi-Stress Response Analysis of the DABB-Type Protein-Encoding Genes in Brassica napus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5721. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115721
Wang S, Wang K, Xia Q, Xia S. Genome-Wide Identification and Multi-Stress Response Analysis of the DABB-Type Protein-Encoding Genes in Brassica napus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(11):5721. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115721
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Siyi, Kunmei Wang, Qi Xia, and Shitou Xia. 2024. "Genome-Wide Identification and Multi-Stress Response Analysis of the DABB-Type Protein-Encoding Genes in Brassica napus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 11: 5721. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115721
APA StyleWang, S., Wang, K., Xia, Q., & Xia, S. (2024). Genome-Wide Identification and Multi-Stress Response Analysis of the DABB-Type Protein-Encoding Genes in Brassica napus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(11), 5721. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115721






