GFAP as Astrocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Cargo in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients—A Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Baseline Features of the Study Population
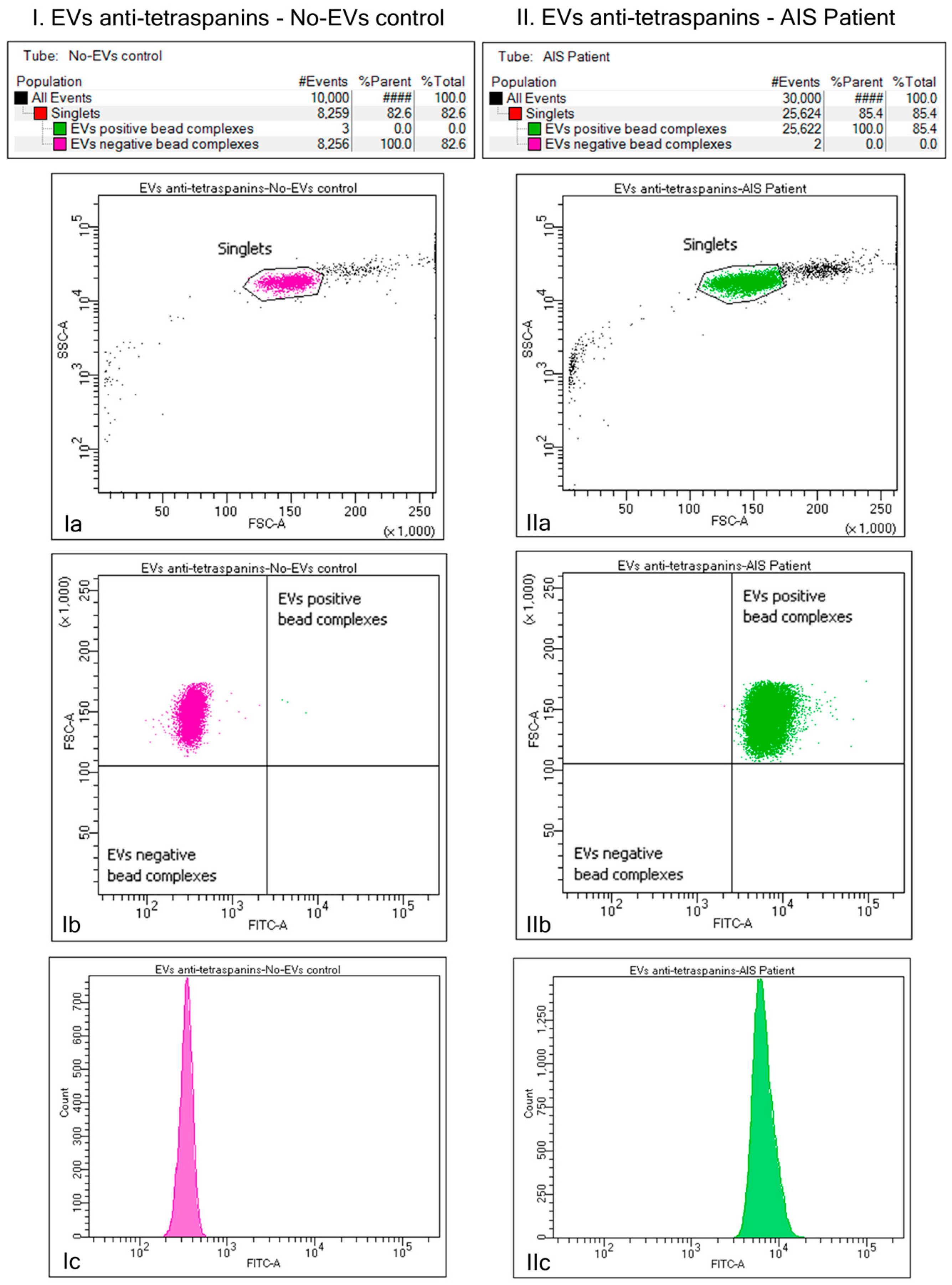
2.2. Identification of the Plasma EVs via Bead–Antibody–EVs–FITC Complexes and Flow Cytometry Analysis of Beads-Captured EVs
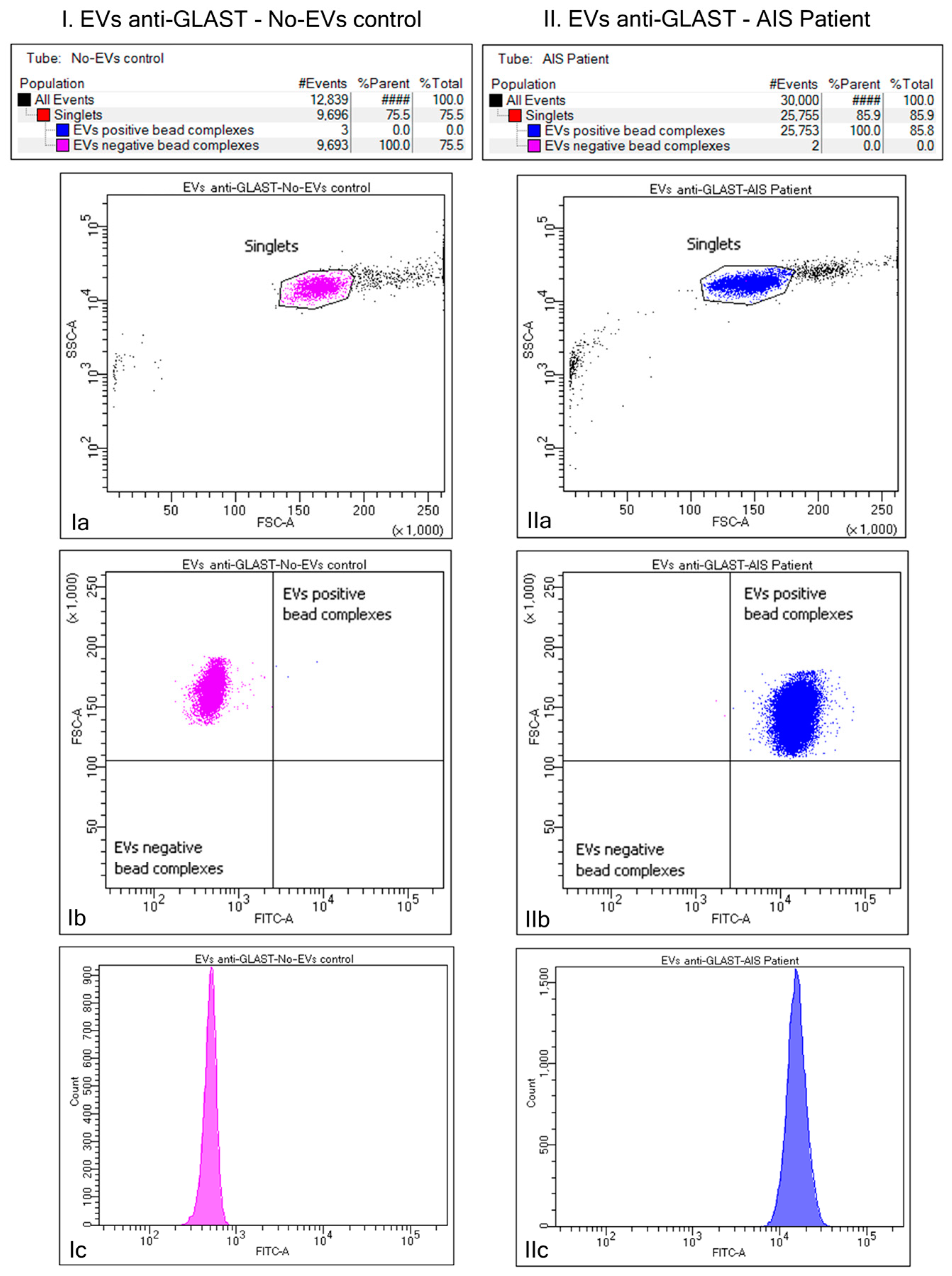
2.3. Purification of ADEV Subpopulation via Bead–Antibody–EVs–FITC Complexes and Flow Cytometry Analysis of Beads-Captured EVs
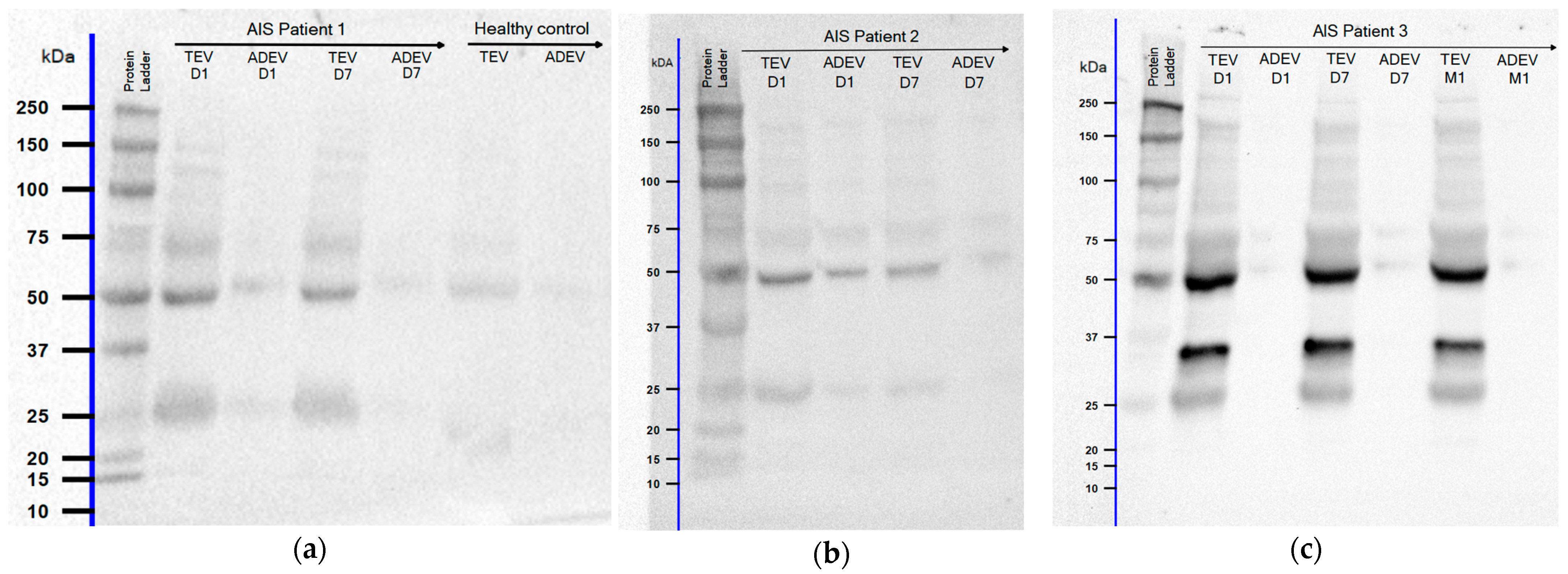
2.4. Western Blot Analyses of EV GFAP Levels
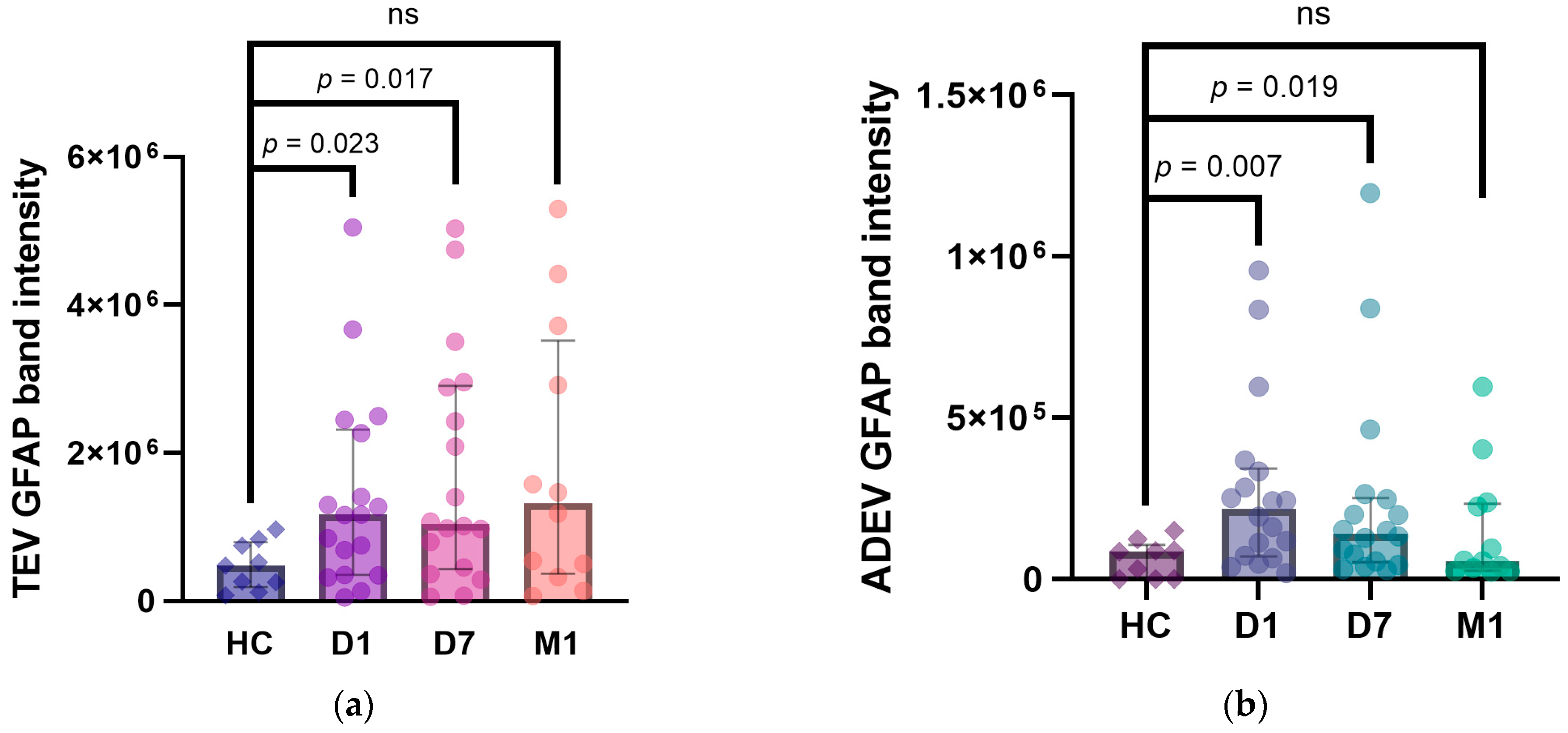
2.5. Temporal Profile of EV GFAP
2.6. Correlations between EV GFAP and Stroke Severity (NIHSS)/Outcome (mRS)
3. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
4. Materials and Methods
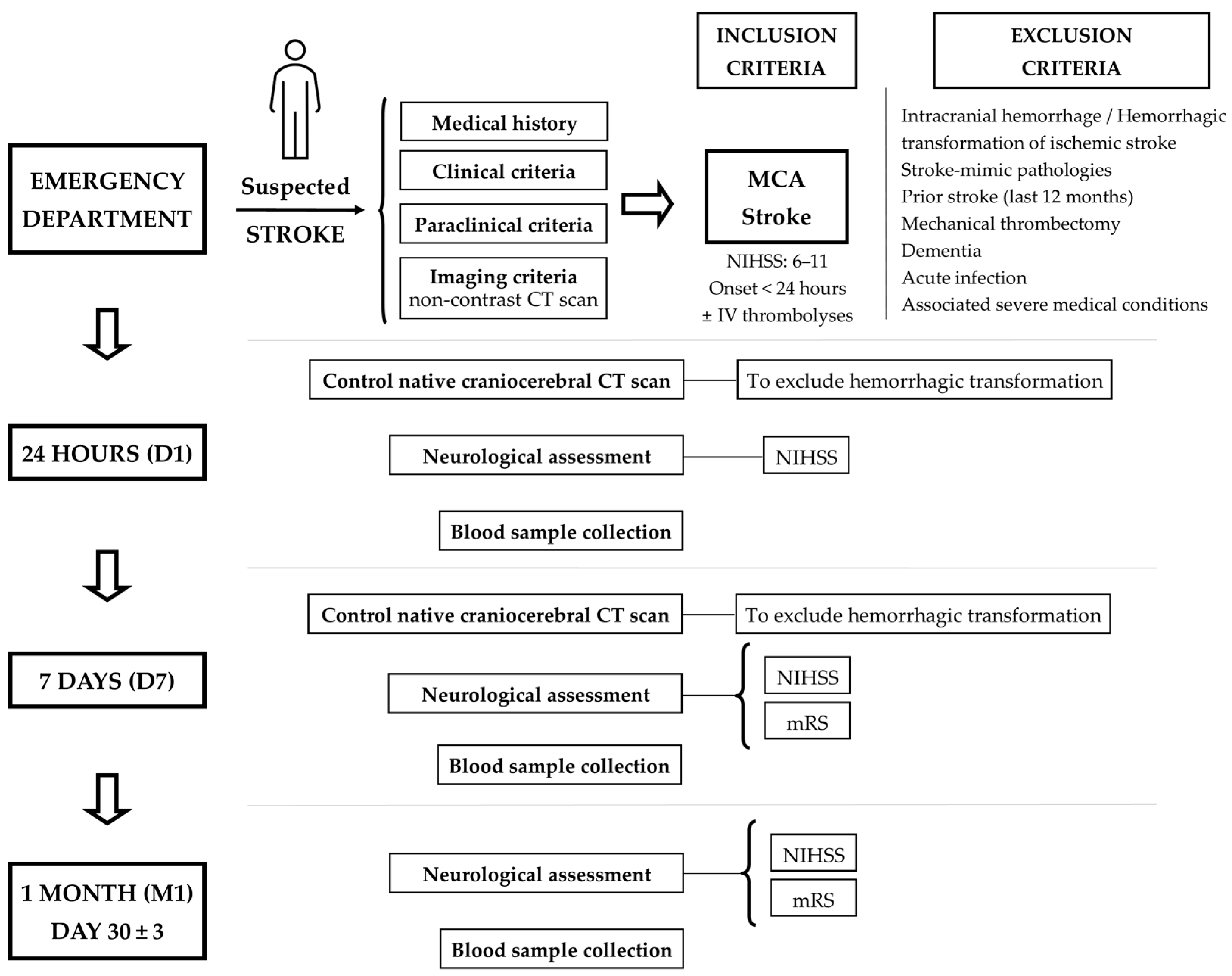
4.1. Patients Enrolled and Study Design
4.2. Blood Collection
4.3. Isolation and Identification of EVs from Plasma Samples
4.4. Purification of ADEV Subpopulation via Bead–Antibody–EVs–FITC Complexes and Flow Cytometry Analysis of Beads-Captured EVs
4.5. Western Blot Analyses
4.6. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| aa | amino acids |
| ACSA-1 | astrocyte cell surface antigen-1 |
| ADEVs | astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles |
| AIS | acute ischemic stroke |
| ALS | amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| BBB | blood–brain barrier |
| BDPs | breakdown products |
| BWB | Bead Wash Buffer |
| cat. no. | catalog number |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| CSF | cerebrospinal fluid |
| CT | computed tomography |
| d | standardized difference |
| e.g. | for example |
| EVs | extracellular vesicles |
| FITC | fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| FSC | forward scatter |
| GFAP | glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| GLAST | glutamate aspartate transporter |
| HC | healthy controls |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| IS | ischemic stroke |
| IV | intravenous |
| kDa | kilodaltons |
| MCA | middle cerebral artery |
| min | minutes |
| mRS | modified Rankin Scale |
| NIHSS | National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale |
| ns | not significant |
| NVU | neurovascular unit |
| PVDF | polyvinylidene difluoride |
| RT | room temperature |
| SCI | spinal cord injury |
| SD | standard deviation |
| SDS | sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| sec | seconds |
| TBI | traumatic brain injury |
| TEVs | total extracellular vesicles |
| vs. | versus |
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Brainin, M.; Norrving, B.; Martins, S.; Sacco, R.L.; Hacke, W.; Fisher, M.; Pandian, J.; Lindsay, P. World Stroke Organization (WSO): Global Stroke Fact Sheet 2022. Int. J. Stroke 2022, 17, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigin, V.L.; Stark, B.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Roth, G.A.; Bisignano, C.; Abady, G.G.; Abbasifard, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abedi, V.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Stroke and Its Risk Factors, 1990–2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 795–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jickling, G.C.; Sharp, F.R. Biomarker Panels in Ischemic Stroke. Stroke J. Cereb. Circ. 2015, 46, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, V.; Guada, L.; Yavagal, D.R. Global Epidemiology of Stroke and Access to Acute Ischemic Stroke Interventions. Neurology 2021, 97 (Suppl. S2), S6–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinichenko, S.G.; Pushchin, I.I.; Matveeva, N.Y. Neurotoxic and Cytoprotective Mechanisms in the Ischemic Neocortex. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2023, 128, 102230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.J. Astrocyte Heterogeneity in the Adult Central Nervous System. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, H.L.; Kersch, C.N.; Woltjer, R.L.; Neuwelt, E.A. The Translational Significance of the Neurovascular Unit. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steliga, A.; Kowiański, P.; Czuba, E.; Waśkow, M.; Moryś, J.; Lietzau, G. Neurovascular Unit as a Source of Ischemic Stroke Biomarkers-Limitations of Experimental Studies and Perspectives for Clinical Application. Transl. Stroke Res. 2020, 11, 553–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürer, G.; Gursoy-Ozdemir, Y.; Erdemli, E.; Can, A.; Dalkara, T. Astrocytes Are More Resistant to Focal Cerebral Ischemia than Neurons and Die by a Delayed Necrosis. Brain Pathol. 2009, 19, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collyer, E.; Blanco-Suarez, E. Astrocytes in Stroke-Induced Neurodegeneration: A Timeline. Front. Mol. Med. 2023, 3, 1240862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Yang, G.Y.; Zhang, Z. Crosstalk of Astrocytes and Other Cells during Ischemic Stroke. Life 2022, 12, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekny, M.; Pekna, M. Reactive Gliosis in the Pathogenesis of CNS Diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1862, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middeldorp, J.; Hol, E.M. GFAP in Health and Disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 93, 421–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofroniew, M.V.; Vinters, H.V. Astrocytes: Biology and Pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 7–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tykhomyrov, A.; Pavlova, A.S.; Nedzvetsky, V.S. Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP): On the 45th Anniversary of Its Discovery. Neurophysiology 2016, 48, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Asperen, J.V.; Robe, P.A.J.T.; Hol, E.M. GFAP Alternative Splicing and the Relevance for Disease—A Focus on Diffuse. ASN Neuro 2022, 14, 17590914221102065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimfarth, L.; Passos, F.R.S.; Monteiro, B.S.; Araújo, A.A.d.S.; Quintans Júnior, L.J.; Quintans, J.d.S.S. Serum Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Is a Body Fluid Biomarker: A Valuable Prognostic for Neurological Disease—A Systematic Review. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 107, 108624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foerch, C.; Niessner, M.; Back, T.; Bauerle, M.; De Marchis, G.M.; Ferbert, A.; Grehl, H.; Hamann, G.F.; Jacobs, A.; Kastrup, A.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Plasma Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein for Differentiating Intracerebral Hemorrhage and Cerebral Ischemia in Patients with Symptoms of Acute Stroke. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janigro, D.; Mondello, S.; Posti, J.P.; Unden, J. GFAP and S100B: What You Always Wanted to Know and Never Dared to Ask. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 835597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Gao, G.; Feng, J.; Jin, Y.; Wang, C.; Mao, Q.; Jiang, J. Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein as a Biomarker in Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Patients: A Prospective Cohort Study. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, M.; Tsuruta, R.; Kaneko, T.; Kasaoka, S.; Yagi, T.; Todani, M.; Fujita, M.; Izumi, T.; Maekawa, T. Serum Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Is a Highly Specific Biomarker for Traumatic Brain Injury in Humans Compared with S-100B and Neuron-Specific Enolase. J. Trauma 2010, 69, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Bodegraven, E.J.; Sluijs, J.A.; Tan, A.K.; Robe, P.A.J.T.; Hol, E.M. New GFAP Splice Isoform (GFAPµ) Differentially Expressed in Glioma Translates into 21 KDa N-Terminal GFAP Protein. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tichy, J.; Spechtmeyer, S.; Mittelbronn, M.; Hattingen, E.; Rieger, J.; Senft, C.; Foerch, C. Prospective Evaluation of Serum Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP) as a Diagnostic Marker for Glioblastoma. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2016, 126, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, N.; Mishra, K.; Kumar, B.C.A.; Singh, D.; Subberwal, M. Clinical Utility of Serum Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein in Glial Neoplasm. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2022, 13, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunkhorst, R.; Pfeilschifter, W.; Foerch, C. Astroglial Proteins as Diagnostic Markers of Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage-Pathophysiological Background and Clinical Findings. Transl. Stroke Res. 2010, 1, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabezas, J.A.; Bustamante, A.; Giannini, N.; Pecharroman, E.; Katsanos, A.H.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Rozanski, M.; Audebert, H.; Mondello, S.; Llombart, V.; et al. Discriminative Value of Glial Fibrillar Acidic Protein (GFAP) as a Diagnostic Tool in Acute Stroke. Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis. J. Investig. Med. 2020, 68, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florijn, B.W.; Leontien van der Bent, M.; Nguyen, T.M.T.; Quax, P.H.A.; Wermer, M.J.H.; Yaël Nossent, A.; Kruyt, N.D. Non-Coding RNAs versus Protein Biomarkers to Diagnose and Differentiate Acute Stroke: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2023, 32, 107388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, E.; Kim, H.; Cho, B.; Lee, J.J.; Shin, S.; Oh, E.J.; Chae, H. Plasma Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein and N-Terminal Pro B-Type Natriuretic Peptide: Potential Biomarkers to Differentiate Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, L.P.; Khatter, H.; Ramanathan, S.; Sapehia, S.; Devi, K.; Kaliyaperumal, A.; Bal, D.; Sebastian, I.; Kakarla, R.; Singhania, A.; et al. Serum GFAP for Stroke Diagnosis in Regions with Limited Access to Brain Imaging (BE FAST India). Eur. Stroke J. 2021, 6, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Misra, S.; Yadav, A.K.; Sagar, R.; Verma, B.; Grover, A.; Prasad, K. Role of Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein as a Biomarker in Differentiating Intracerebral Haemorrhage from Ischaemic Stroke and Stroke Mimics: A Meta-Analysis. Biomarkers 2020, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Montaner, J.; Ramiro, L.; Arora, R.; Talwar, P.; Nath, M.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, P.; Pandit, A.K.; Mohania, D.; et al. Blood Biomarkers for the Diagnosis and Differentiation of Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Stroke 2020, 15, 704–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, L.A.; Lucarelli, T.; Penny-Dimri, J.C.; McInnes, M.D.F.; Mondello, S.; Bustamante, A.; Montaner, J.; Foerch, C.; Kwan, P.; Davis, S.; et al. Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein for the Early Diagnosis of Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Test Accuracy. Int. J. Stroke 2019, 14, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.H.; Lin, X.L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Shi, S.L. Serum Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein as a Biomarker for Differentiating Intracerebral Hemorrhage and Ischemic Stroke in Patients with Symptoms of Acute Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 34, 1887–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmielewska, N.; Szyndler, J.; Makowska, K.; Wojtyna, D.; Maciejak, P.; Płaźnik, A. Looking for Novel, Brain-Derived, Peripheral Biomarkers of Neurological Disorders. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2018, 52, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Geng, J. Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein as a Prognostic Marker of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2018, 37, 1048–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, M.; Silva, I.; Gabriel, D.; Simrén, J.; Carneiro, A.; Ribeiro, S.; Dória, H.M.; Varela, R.; Aires, A.; Minta, K.; et al. Early Plasma Biomarker Dynamic Profiles Are Associated with Acute Ischemic Stroke Outcomes. Eur. J. Neurol. 2022, 29, 1630–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafarzadeh-Esfehani, R.; Soudyab, M.; Parizadeh, S.M.; Jaripoor, M.E.; Nejad, P.S.; Shariati, M.; Nabavi, A.S. Circulating Exosomes and Their Role in Stroke. Curr. Drug Targets 2020, 21, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, L.M.; Wang, M.Z. Overview of Extracellular Vesicles, Their Origin, Composition, Purpose, and Methods for Exosome Isolation and Analysis. Cells 2019, 8, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.M.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological Properties of Extracellular Vesicles and Their Physiological Functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, K.B.; Gudbergsson, J.M.; Skov, M.N.; Pilgaard, L.; Moos, T.; Duroux, M. A Comprehensive Overview of Exosomes as Drug Delivery Vehicles—Endogenous Nanocarriers for Targeted Cancer Therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1846, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollen-Bittle, N.; Roseborough, A.D.; Wang, W.; Wu, J.-L.D.; Whitehead, S.N. Mechanisms and Biomarker Potential of Extracellular Vesicles in Stroke. Biology 2022, 11, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, H.; Drummen, G.P.C.; Mathivanan, S. Focus on Extracellular Vesicles: Introducing the Next Small Big Thing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, S.; Massoumi, H.; Tewari, D.; Roy, A.; Chaudhuri, M.; Jazayerli, C.; Krishan, A.; Singh, M.; Soleimani, M.; Karaca, E.E.; et al. Cell Type-Specific Extracellular Vesicles and Their Impact on Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, A.; Fan, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, N.; Tang, Y. Astrocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Ischemic Stroke: Therapeutic Potential and Prospective. Aging Dis. 2023, 15, 1227–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwardson, M.A.; Mitsuhashi, M.; Van Epps, D. Elevation of Astrocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles over the First Month Post-Stroke in Humans. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Yang, J.; Hou, Y.; Shi, X.; Liu, K. Prediction of Clinical Progression in Nervous System Diseases: Plasma Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP). Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetzl, E.J.; Schwartz, J.B.; Abner, E.L.; Jicha, G.A.; Kapogiannis, D. High Complement Levels in Astrocyte-Derived Exosomes of Alzheimer’s Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, C.N.; Goetzl, E.J.; Schwartz, J.B.; Elahi, F.M.; Rissman, R.A. Complement Protein Levels in Plasma Astrocyte-Derived Exosomes Are Abnormal in Conversion from Mild Cognitive Impairment to Alzheimer’s Disease Dementia. Alzheimer’s Dement. Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2019, 11, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetzl, E.J.; Mustapic, M.; Kapogiannis, D.; Eitan, E.; Lobach, I.V.; Goetzl, L.; Schwartz, J.B.; Miller, B.L. Cargo Proteins of Plasma Astrocyte-Derived Exosomes in Alzheimer’s Disease. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 3853–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueras-Ortiz, C.J.; Mahairaki, V.; Delgado-Peraza, F.; Das, D.; Avgerinos, K.; Eren, E.; Hentschel, M.; Goetzl, E.J.; Mattson, M.P.; Kapogiannis, D. Astrocyte- and Neuron-Derived Extracellular Vesicles from Alzheimer’s Disease Patients Effect Complement-Mediated Neurotoxicity. Cells 2020, 9, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmichi, T.; Mitsuhashi, M.; Tatebe, H.; Kasai, T.; Ali El-Agnaf, O.M.; Tokuda, T. Quantification of Brain-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Plasma as a Biomarker to Diagnose Parkinson’s and Related Diseases. Park. Relat. Disord. 2019, 61, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xia, K.; Chen, L.; Fan, D. Increased Interleukin-6 Levels in the Astrocyte-Derived Exosomes of Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpakowski, P.; Ksiazek-Winiarek, D.; Czpakowska, J.; Kaluza, M.; Milewska-Jedrzejczak, M.; Glabinski, A. Astrocyte-Derived Exosomes Differentially Shape T Cells’ Immune Response in MS Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.E.; Winston-Gray, C.; Barlow, J.W.; Rissman, R.A.; Jeste, D.V. Plasma Levels of Neuron- and Astrocyte-Derived Exosomal Amyloid Beta1-42, Amyloid Beta1-40, and Phosphorylated Tau Levels in Schizophrenia Patients and Non-Psychiatric Comparison Subjects: Relationships with Cognitive Functioning and Psychopathology. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 532624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranganathan, M.; Rahman, M.; Ganesh, S.; D’Souza, D.C.; Skosnik, P.D.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Pathania, S.; Mohanakumar, T. Analysis of Circulating Exosomes Reveals a Peripheral Signature of Astrocytic Pathology in Schizophrenia. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 23, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, C.N.; Romero, H.K.; Ellisman, M.; Nauss, S.; Julovich, D.A.; Conger, T.; Hall, J.R.; Campana, W.; O’Bryant, S.E.; Nievergelt, C.M.; et al. Assessing Neuronal and Astrocyte Derived Exosomes from Individuals with Mild Traumatic Brain Injury for Markers of Neurodegeneration and Cytotoxic Activity. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetzl, E.J.; Srihari, V.H.; Guloksuz, S.; Ferrara, M.; Tek, C.; Heninger, G.R. Neural Cell-Derived Plasma Exosome Protein Abnormalities Implicate Mitochondrial Impairment in First Episodes of Psychosis. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Sun, C.; Xue, S.; Leng, B.; Sun, H.; Shen, T.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Shang, X.; Zhang, J. Complement Protein Levels in Serum Astrocyte-Derived Exosomes Are Associated with Cognitive Impairment in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. J. Clin. Sleep. Med. 2023, 19, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Liu, Y.; Chi, H.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, Q.; Li, M.; Yao, R.; Sun, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J. Complement Proteins in Serum Astrocyte-Derived Exosomes Are Associated with Mild Cognitive Impairment in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Neurosci. Lett. 2023, 810, 137318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helman, G.; Takanohashi, A.; Hagemann, T.L.; Perng, M.D.; Walkiewicz, M.; Woidill, S.; Sase, S.; Cross, Z.; Du, Y.; Zhao, L.; et al. Type II Alexander Disease Caused by Splicing Errors and Aberrant Overexpression of an Uncharacterized GFAP Isoform. Hum. Mutat. 2020, 41, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galea, E.; Dupouey, P.; Feinstein, D.L. Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein MRNA Isotypes: Expression In Vitro and In Vivo. J. Neurosci. Res. 1995, 41, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelenika, D.; Grima, B.; Brenner, M.; Pessac, B. A Novel Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein MRNA Lacking Exon 1. Mol. Brain Res. 1995, 30, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roelofs, R.F.; Fischer, D.F.; Houtman, S.H.; Sluijs, J.A.; Van Haren, W.; Van Leeuwen, F.W.; Hol, E.M. Adult Human Subventricular, Subgranular, and Subpial Zones Contain Astrocytes with a Specialized Intermediate Filament Cytoskeleton. Glia 2005, 52, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clairembault, T.; Kamphuis, W.; Leclair-Visonneau, L.; Rolli-Derkinderen, M.; Coron, E.; Neunlist, M.; Hol, E.M.; Derkinderen, P. Enteric GFAP Expression and Phosphorylation in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurochem. 2014, 130, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, K.K.W. Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein: From Intermediate Filament Assembly and Gliosis to Neurobiomarker. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamphuis, W.; Middeldorp, J.; Kooijman, L.; Sluijs, J.A.; Kooi, E.J.; Moeton, M.; Freriks, M.; Mizee, M.R.; Hol, E.M. Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Isoform Expression in Plaque Related Astrogliosis in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 492–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, T.; Yuan, J. Cross-Talk between Two Cysteine Protease FamiliesActivation of Caspase-12 by Calpain in Apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 150, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Arja, R.D.; Zhu, T.; Sarkis, G.A.; Patterson, R.L.; Romo, P.; Rathore, D.S.; Moghieb, A.; Abbatiello, S.; Robertson, C.S.; et al. Characterization of Calpain and Caspase-6-Generated Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Breakdown Products Following Traumatic Brain Injury and Astroglial Cell Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zoltewicz, J.S.; Mondello, S.; Newsom, K.J.; Yang, Z.; Yang, B.; Kobeissy, F.; Guingab, J.; Glushakova, O.; Robicsek, S.; et al. Human Traumatic Brain Injury Induces Autoantibody Response against Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein and Its Breakdown Products. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 92698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susie Zoltewicz, J.; Scharf, D.; Yang, B.; Chawla, A.; Newsom, K.J.; Fang, L. Characterization of Antibodies That Detect Human GFAP after Traumatic Brain Injury. Biomark. Insights 2012, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Kato, T.; Yamauchi, M.; Ando, M.; Honda, M.; Nagata, Y. Increases in Fragmented Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Levels in the Spinal Cords of Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Neurochem. Res. 1998, 23, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokobori, S.; Zhang, Z.; Moghieb, A.; Mondello, S.; Gajavelli, S.; Dietrich, W.D.; Bramlett, H.; Hayes, R.L.; Wang, M.; Wang, K.K.W.; et al. Acute Diagnostic Biomarkers for Spinal Cord Injury: Review of the Literature and Preliminary Research Report. World Neurosurg. 2015, 83, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, N.H.; Messing, A.; Perng, M.D. Characterization of a Panel of Monoclonal Antibodies Recognizing Specific Epitopes on GFAP. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.H.; Hagemann, T.L.; Quinlan, R.A.; Messing, A.; Perng, M.D. Caspase Cleavage of GFAP Produces an Assembly-Compromised Proteolytic Fragment That Promotes Filament Aggregation. ASN Neuro 2013, 5, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouser, P.E.; Head, E.; Ha, K.H.; Rohn, T.T. Caspase-Mediated Cleavage of Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein within Degenerating Astrocytes of the Alzheimer’s Disease Brain. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middeldorp, J.; Kamphuis, W.; Sluijs, J.A.; Achoui, D.; Leenaars, C.H.C.; Feenstra, M.G.P.; Tijn, P.; Fischer, D.F.; Berkers, C.; Ovaa, H.; et al. Intermediate Filament Transcription in Astrocytes Is Repressed by Proteasome Inhibition. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 2710–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Yue, Z.; Talloczy, Z.; Hagemann, T.; Cho, W.; Messing, A.; Sulzer, D.I.; Goldman, J.E. Autophagy Induced by Alexander Disease-Mutant GFAP Accumulation Is Regulated by P38/MAPK and MTOR Signaling Pathways. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 1540–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Z.X.; Liu, Z. Biomarkers and the Outcomes of Ischemic Stroke. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1171101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, M.T.; Wallesch, C.W.; Goertler, M. Release of Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Is Related to the Neurovascular Status in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Eur. J. Neurol. 2006, 13, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, F.; Haberer, I.; Sitzer, M.; Foerch, C. Characterisation of the Diagnostic Window of Serum Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein for the Differentiation of Intracerebral Haemorrhage and Ischaemic Stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2009, 27, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, M.; Vos, P.; Wunderlich, M.T.; De Bruijn, C.H.M.M.; Lamers, K.J.B. Release of Glial Tissue-Specific Proteins after Acute Stroke: A Comparative Analysis of Serum Concentrations of Protein S-100B and Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein. Stroke 2000, 31, 2670–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luger, S.; Jæger, H.S.; Dixon, J.; Bohmann, F.O.; Schaefer, J.H.; Richieri, S.P.; Larsen, K.; Hov, M.R.; Bache, K.G.; Foerch, C. Diagnostic Accuracy of Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein and Ubiquitin Carboxy-Terminal Hydrolase-L1 Serum Concentrations for Differentiating Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage from Ischemic Stroke. Neurocritical Care 2020, 33, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, F.; Rossi, D.; Ricciardi, A.; Morasso, C.; Brambilla, L.; Albasini, S.; Vanna, R.; Fassio, C.; Begenisic, T.; Loi, M.; et al. Quantification and Prospective Evaluation of Serum NfL and GFAP as Blood-Derived Biomarkers of Outcome in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2023, 43, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, Y.; Tateishi, N.; Shimoda, T.; Satoh, S.; Ogitani, E.; Fujita, S. Relationship between S100β and GFAP Expression in Astrocytes during Infarction and Glial Scar Formation after Mild Transient Ischemia. Brain Res. 2004, 1021, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amalia, L. Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP): Neuroinflammation Biomarker in Acute Ischemic Stroke. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 7501–7506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puspitasari, V.; Gunawan, P.Y.; Wiradarma, H.D.; Hartoyo, V. Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Serum Level as a Predictor of Clinical Outcome in Ischemic Stroke. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujol-Calderón, F.; Zetterberg, H.; Portelius, E.; Löwhagen Hendén, P.; Rentzos, A.; Karlsson, J.E.; Höglund, K.; Blennow, K.; Rosengren, L.E. Prediction of Outcome After Endovascular Embolectomy in Anterior Circulation Stroke Using Biomarkers. Transl. Stroke Res. 2022, 13, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurell, A.; Rosengren, L.E.; Karlsson, B.; Olsson, J.E.; Zbornikova, V.; Haglid, K.G. Determination of S-100 and Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Concentrations in Cerebrospinal Fluid after Brain Infarction. Stroke 1991, 22, 1254–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouns, R.; De Vil, B.; Cras, P.; De Surgeloose, D.; Mariën, P.; De Deyn, P.P. Neurobiochemical Markers of Brain Damage in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanos, A.H.; Makris, K.; Stefani, D.; Koniari, K.; Gialouri, E.; Lelekis, M.; Chondrogianni, M.; Zompola, C.; Dardiotis, E.; Rizos, I.; et al. Plasma Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein in the Differential Diagnosis of Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2017, 48, 2586–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungblut, M.; Tiveron, M.C.; Barral, S.; Abrahamsen, B.; Knöbel, S.; Pennartz, S.; Schmitz, J.; Perraut, M.; Pfrieger, F.W.; Stoffel, W.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of Living Primary Astroglial Cells Using the New GLAST-Specific Monoclonal Antibody ACSA-1. Glia 2012, 60, 894–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, U.V.; Hediger, M.A. Distribution of the Glutamate Transporters GLT-1 (SLC1A2) and GLAST (SLC1A3) in Peripheral Organs. Anat. Embryol. 2006, 211, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, H.P.; Davis, P.H.; Leira, E.C.; Chang, K.C.; Bendixen, B.H.; Clarke, W.R.; Woolson, R.F.; Hansen, M.D. Baseline NIH Stroke Scale Score Strongly Predicts Outcome after Stroke: A Report of the Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST). Neurology 1999, 53, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, J.L.; Marotta, C.A. Outcomes Validity and Reliability of the Modified Rankin Scale: Implications for Stroke Clinical Trials: A Literature Review and Synthesis. Stroke 2007, 38, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ExoQuick® ULTRA EV Isolation System|System Biosciences. Available online: https://www.systembio.com/products/exosome-research/exosome-isolation/exoquick-ultra/serum-and-plasma-0/the-purest-and-highest-yielding-ev-isolation-system (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Basic Exo-Flow Capture Kit|System Biosciences. Available online: https://www.systembio.com/basic-exo-flow-capture-kit (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Iwata, J.; Nishikaze, O. New Micro-Turbidimetric Method for Determination of Protein in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Urine. Clin. Chem. 1979, 25, 1317–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwardson, M.A.; Fernandez, S.J. Recruiting Control Participants into Stroke Biomarker. Transl. Stroke Res. 2020, 11, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | AIS Patients (n = 18) | Healthy Controls (n = 9) | d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prior vascular risk factors, n (%) | Hypertension | 18 (100%) | 6 (66.6%) | 1 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 9 (50%) | 4 (44.4%) | 0.11 | |
| Hyperlipidemia | 4 (22.2%) | 2 (22.2%) | 0.00 | |
| Atrial fibrillation | 3 (16.6%) | 1 (11.1%) | 0.16 | |
| Smoking habit | 3 (16.6%) | 2 (22.2%) | 0.14 | |
| Pre-stroke treatment, n (%) | Antiplatelet agents | 9 (50%) | N.A. | N.A. |
| Anticoagulants | 1 (5.5%) | N.A. | N.A. | |
| Statins | 1 (5.5%) | N.A. | N.A. | |
| Acute stroke treatment, n (%) | IV thrombolysis | 9 (50%) | N.A. | N.A. |
| NIHSS, median, min–max | D1 | 7.5 (6–11) | N.A. | N.A. |
| D7 | 5.5 (1–10) | N.A. | N.A. | |
| M1 (n = 12) | 2 (1–7) | N.A. | N.A. | |
| Etiological diagnosis (TOAST classification), n (%) | Large artery atherosclerosis | 14 (77.7%) | N.A. | N.A. |
| Cardioembolism | 4 (22.3%) | N.A. | N.A. | |
| Small artery occlusion | 0 | N.A. | N.A. | |
| Injured hemisphere, n (%) | Left | 11 (61.1%) | N.A. | N.A. |
| mRS, D7, n (%) | 1–2 | 3 (16.7%) | N.A. | N.A. |
| 3–5 | 15 (83.3%) | N.A. | N.A. | |
| mRS, M1 (n = 12), n (%) | 1–2 | 9 (75%) | N.A. | N.A. |
| 3–5 | 3 (25%) | N.A. | N.A. | |
| EV GFAP/Time Points | Scales/Time Points | r | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEV GFAP | D1 | NIHSS | D1 | 0.47 | 0.049 * |
| D7 | 0.45 | 0.057 | |||
| M1 | 0.24 | 0.435 | |||
| mRS | D7 | 0.48 | 0.043 * | ||
| M1 | 0.30 | 0.355 | |||
| D7 | NIHSS | D1 | 0.50 | 0.031 * | |
| D7 | 0.345 | 0.160 | |||
| M1 | 0.34 | 0.276 | |||
| mRS | D7 | 0.15 | 0.548 | ||
| M1 | 0.40 | 0.203 | |||
| M1 | NIHSS | D1 | 0.40 | 0.189 | |
| D7 | 0.15 | 0.619 | |||
| M1 | 0.42 | 0.164 | |||
| mRS | D7 | 0.15 | 0.638 | ||
| M1 | 0.37 | 0.235 | |||
| ADEV GFAP | D1 | NIHSS | D1 | 0.16 | 0.501 |
| D7 | 0.30 | 0.220 | |||
| M1 | 0.18 | 0.569 | |||
| mRS | D7 | 0.58 | 0.010 * | ||
| M1 | 0.10 | 0.789 | |||
| D7 | NIHSS | D1 | 0.07 | 0.779 | |
| D7 | 0.212 | 0.398 | |||
| M1 | 0.29 | 0.350 | |||
| mRS | D7 | 0.57 | 0.013 * | ||
| M1 | 0.13 | 0.706 | |||
| M1 | NIHSS | D1 | 0.17 | 0.581 | |
| D7 | −0.19 | 0.535 | |||
| M1 | 0.06 | 0.841 | |||
| mRS | D7 | 0.27 | 0.389 | ||
| M1 | −0.03 | 0.961 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Forró, T.; Manu, D.R.; Băjenaru, O.-L.; Bălașa, R. GFAP as Astrocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Cargo in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients—A Pilot Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115726
Forró T, Manu DR, Băjenaru O-L, Bălașa R. GFAP as Astrocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Cargo in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients—A Pilot Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(11):5726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115726
Chicago/Turabian StyleForró, Timea, Doina Ramona Manu, Ovidiu-Lucian Băjenaru, and Rodica Bălașa. 2024. "GFAP as Astrocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Cargo in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients—A Pilot Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 11: 5726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115726
APA StyleForró, T., Manu, D. R., Băjenaru, O.-L., & Bălașa, R. (2024). GFAP as Astrocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Cargo in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients—A Pilot Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(11), 5726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115726







