NRF2 Plays a Crucial Role in the Tolerogenic Effect of Ethyl Pyruvate on Dendritic Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
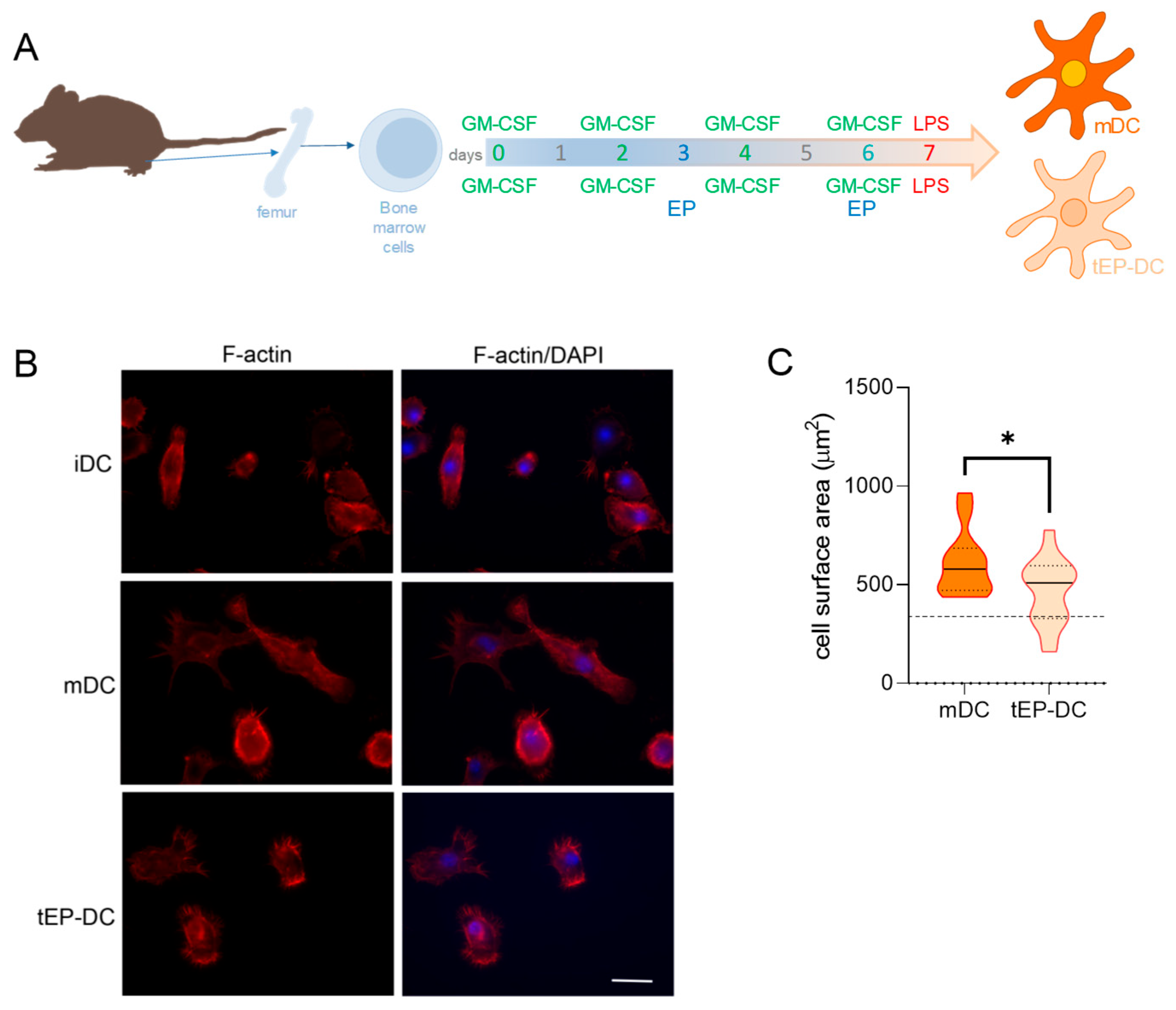
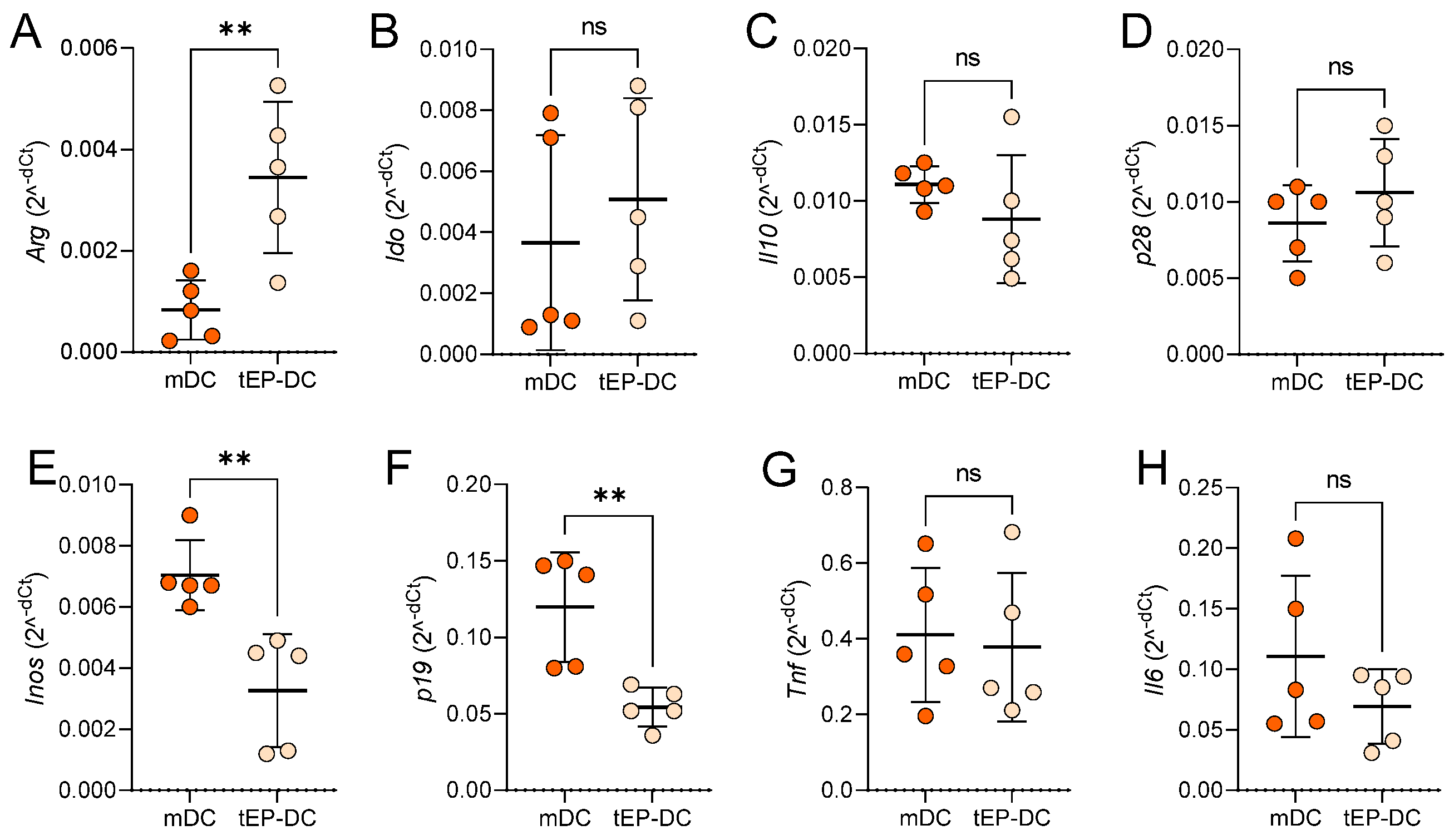
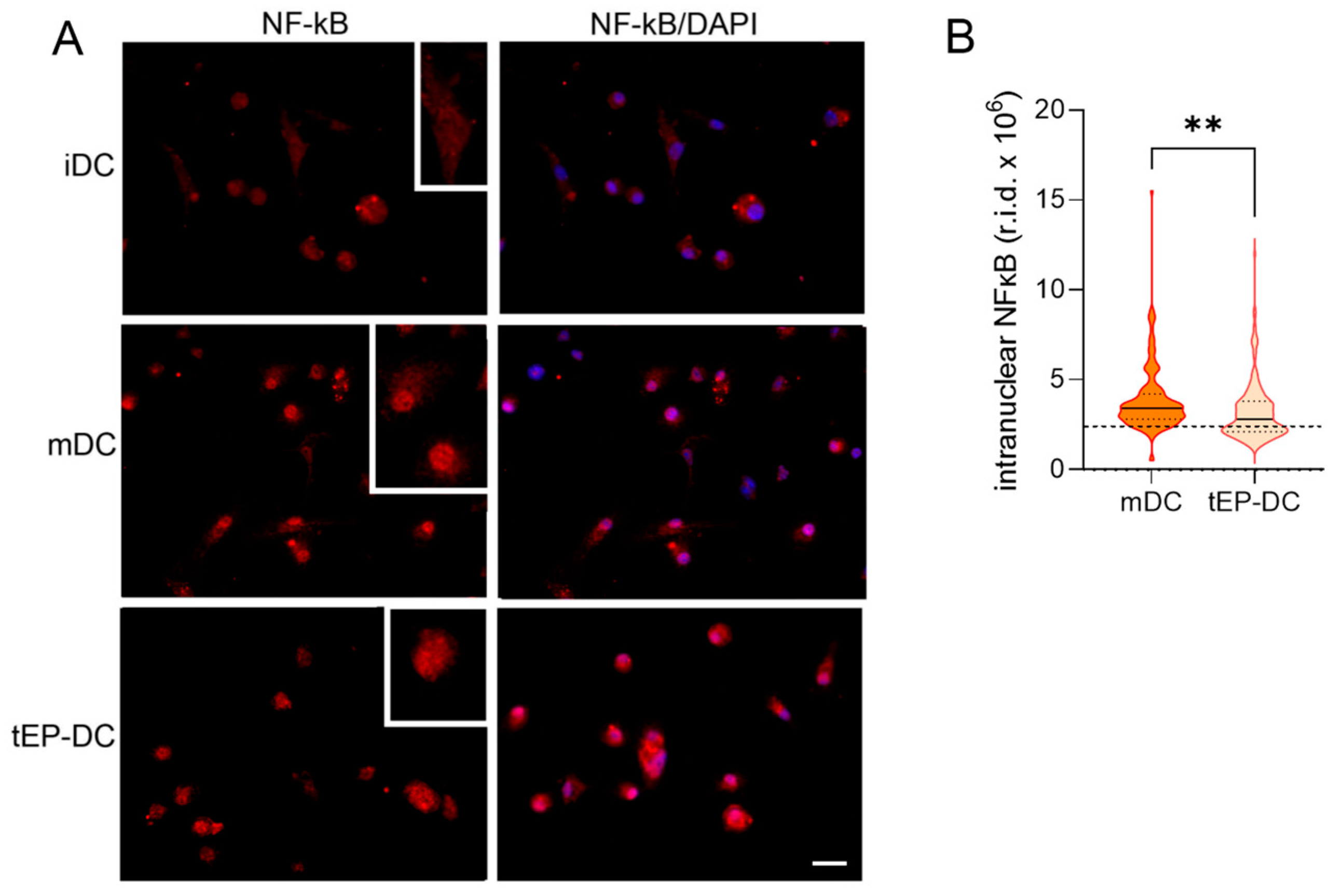
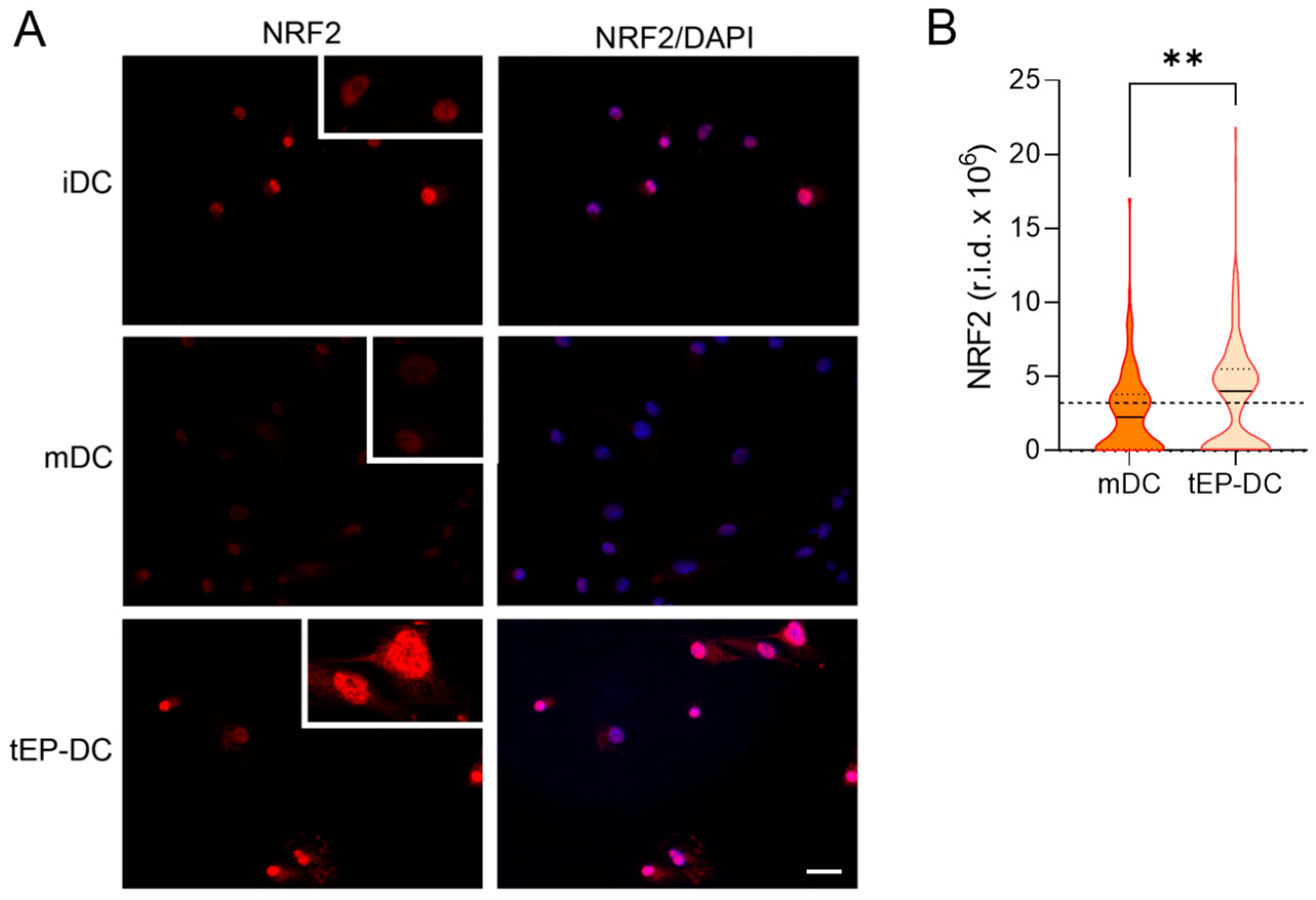
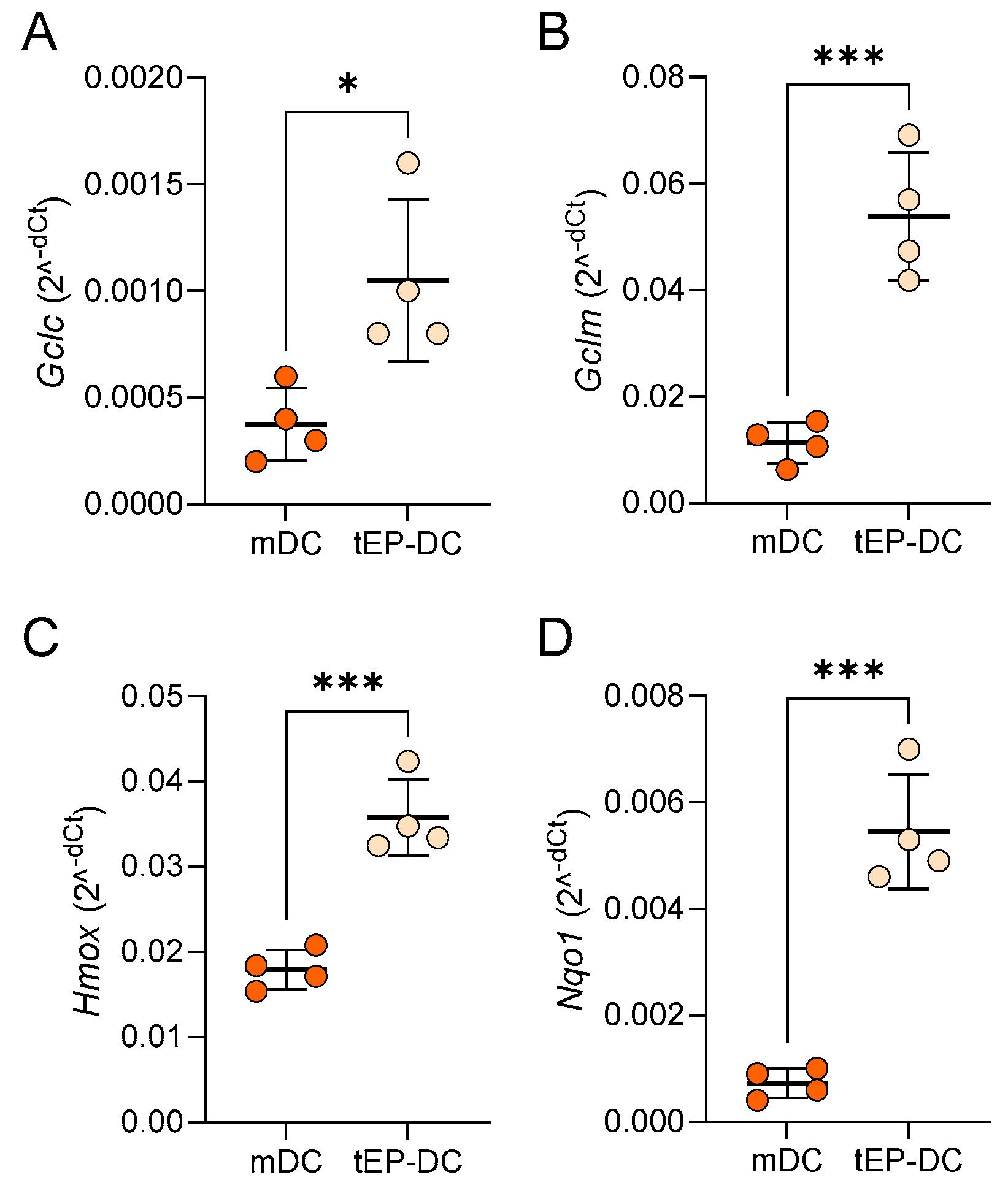
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bone-Marrow-Derived Dendritic Cells
4.2. Phalloidin Staining
4.3. Immunofluorescent Labeling for NF-κB, NRF2, NQO1, and HO-1
4.4. Reverse Transcription−Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.5. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albrecht, P.; Bouchachia, I.; Goebels, N.; Henke, N.; Hofstetter, H.H.; Issberner, A.; Kovacs, Z.; Lewerenz, J.; Lisak, D.; Maher, P.; et al. Effects of dimethyl fumarate on neuroprotection and immunomodulation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koprivica, I.; Djedovic, N.; Stojanović, I.; Miljković, Đ. Ethyl pyruvate, a versatile protector in inflammation and autoimmunity. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 71, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Koprivica, I.; Vujičić, M.; Gajić, D.; Saksida, T.; Stojanović, I. Ethyl Pyruvate Stimulates Regulatory T Cells and Ameliorates Type 1 Diabetes Development in Mice. Front. Immunol. 2019, 9, 3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miljković, D.; Blaževski, J.; Petković, F.; Djedović, N.; Momčilović, M.; Stanisavljević, S.; Jevtić, B.; Mostarica Stojković, M.; Spasojević, I. A comparative analysis of multiple sclerosis-relevant anti-inflammatory properties of ethyl pyruvate and dimethyl fumarate. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 2493–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djedović, N.; Stanisavljevic, S.; Jevtić, B.; Momčilović, M.; Lavrnja, I.; Miljković, D. Anti-encephalitogenic effects of ethyl pyruvate are reflected in the central nervous system and the gut. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djedovic, N.; Mansilla, M.J.; Jevtić, B.; Navarro-Barriuso, J.; Saksida, T.; Martínez-Cáceres, E.M.; Miljković, Ð. Ethyl Pyruvate Induces Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakhtoura, M.; Chain, R.W.; Sato, P.Y.; Qiu, C.C.; Lee, M.H.; Meissler, J.J.; Eisenstein, T.K.; Koch, W.J.; Caricchio, R.; Gallucci, S. Ethyl Pyruvate Modulates Murine Dendritic Cell Activation and Survival Through Their Immunometabolism. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozic, I.; Savic, D.; Laketa, D.; Bjelobaba, I.; Milenkovic, I.; Pekovic, S.; Nedeljkovic, N.; Lavrnja, I. Benfotiamine attenuates inflammatory response in LPS stimulated BV-2 microglia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, S.; Qin, J.; Bennett, C.; Qian, S.; Fung, J.J.; Hamilton, T.A.; Lu, L. All-trans retinoic acid induces arginase-1 and inducible nitric oxide synthase-producing dendritic cells with T cell inhibitory function. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 5098–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Panfili, E.; Mondanelli, G.; Orabona, C.; Bianchi, R.; Gargaro, M.; Fallarino, F.; Puccetti, P.; Grohmann, U.; Volpi, C.; Belladonna, M.L. IL-35Ig-expressing dendritic cells induce tolerance via Arginase 1. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3757–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jang, H.J.; Kim, Y.M.; Tsoyi, K.; Park, E.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Joe, Y.; Chung, H.T.; Chang, K.C. Ethyl pyruvate induces heme oxygenase-1 through p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation by depletion of glutathione in RAW 264.7 cells and improves survival in septic animals. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2012, 17, 878–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital, A.L.; Gonçalo, M.; Cruz, M.T.; Figueiredo, A.; Duarte, C.B.; Lopes, M.C. Dexamethasone prevents granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-induced nuclear factor-kappaB activation, inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and nitric oxide production in a skin dendritic cell line. Mediat. Inflamm. 2003, 12, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambhir, V.; Kim, J.; Siddiqui, S.; Taylor, M.; Byford, V.; Petrof, E.O.; Jones, G.; Basta, S. Influence of 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3 on TLR4-induced activation of antigen presenting cells is dependent on the order of receptor engagement. Immunobiology 2011, 216, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, K.; Treacy, O.; Gerlach, J.Q.; Annuk, H.; Lohan, P.; Cabral, J.; Joshi, L.; Ryan, A.E.; Ritter, T. Regulating Immunogenicity and Tolerogenicity of Bone Marrow-Derived Dendritic Cells through Modulation of Cell Surface Glycosylation by Dexamethasone Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppmann, B.; Lesley, R.; Blom, B.; Timans, J.C.; Xu, Y.; Hunte, B.; Vega, F.; Yu, N.; Wang, J.; Singh, K.; et al. Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity 2000, 13, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, X.; Ma, Y.; Hua, S. IL-23 and dendritic cells: What are the roles of their mutual attachment in immune response and immunotherapy? Cytokine 2019, 120, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, A.; Fabri, M. Vitamin D regulates cytokine patterns secreted by dendritic cells to promote differentiation of IL-22-producing T cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartels, L.E.; Jørgensen, S.P.; Bendix, M.; Hvas, C.L.; Agnholt, J.; Agger, R.; Dahlerup, J.F. 25-Hydroxy vitamin D3 modulates dendritic cell phenotype and function in Crohn’s disease. Inflammopharmacology 2013, 21, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderheyde, N.; Verhasselt, V.; Goldman, M.; Willems, F. Inhibition of human dendritic cell functions by methylprednisolone. Transplantation 1999, 67, 1342–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woltman, A.M.; de Fijter, J.W.; Kamerling, S.W.; Paul, L.C.; Daha, M.R.; van Kooten, C. The effect of calcineurin inhibitors and corticosteroids on the differentiation of human dendritic cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 30, 1807–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozkova, D.; Horvath, R.; Bartunkova, J.; Spisek, R. Glucocorticoids severely impair differentiation and antigen presenting function of dendritic cells despite upregulation of Toll-like receptors. Clin. Immunol. 2006, 120, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toebak, M.J.; de Rooij, J.; Moed, H.; Stoof, T.J.; von Blomberg, B.M.; Bruynzeel, D.P.; Scheper, R.J.; Gibbs, S.; Rustemeyer, T. Differential suppression of dendritic cell cytokine production by anti-inflammatory drugs. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 158, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouaaz, F.; Arron, J.; Zheng, Y.; Choi, Y.; Beg, A.A. Dendritic cell development and survival require distinct NF-kappaB subunits. Immunity 2002, 16, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, S.; Bondeson, J.; Foxwell, B.M.; Brennan, F.M.; Feldmann, M. Effective antigen presentation by dendritic cells is NF-kappaB dependent: Coordinate regulation of MHC, co-stimulatory molecules and cytokines. Int. Immunol. 2001, 13, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander Lugt, B.; Riddell, J.; Khan, A.A.; Hackney, J.A.; Lesch, J.; DeVoss, J.; Weirauch, M.T.; Singh, H.; Mellman, I. Transcriptional determinants of tolerogenic and immunogenic states during dendritic cell maturation. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 779–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, N.; Maldonado, M.L.L.; Bachman, L.A.; McKean, D.J.; Kumar, R.; Griffin, M.D. Distinctive dendritic cell modulation by vitamin D(3) and glucocorticoid pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 297, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Craig, T.; Xing, N.; Bachman, L.A.; Paya, C.V.; Weih, F.; McKean, D.J.; Kumar, R.; Griffin, M.D. Direct transcriptional regulation of RelB by 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and its analogs: Physiologic and therapeutic implications for dendritic cell function. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 49378–49385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.K.; Wu, X.L.; He, X.J.; Li, B.; Hu, Y.X. Dexamethasone impairs the differentiation and maturation of murine dendritic cells by Toll-like receptor 4-nuclear factor-kappaB pathway. Chin. Med. J. 2010, 123, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dáňová, K.; Klapetková, A.; Kayserová, J.; Šedivá, A.; Špíšek, R.; Jelínková, L.P. NF-κB, p38 MAPK, ERK1/2, mTOR, STAT3 and increased glycolysis regulate stability of paricalcitol/dexamethasone-generated tolerogenic dendritic cells in the inflammatory environment. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 14123–14138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaguarnera, L.; Marsullo, A.; Zorena, K.; Musumeci, G.; di Rosa, M. Vitamin D3 regulates LAMP3 expression in monocyte derived dendritic cells. Cell Immunol. 2017, 311, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Gallo, D.J.; Baust, J.J.; Uchiyama, T.; Watkins, S.K.; Delude, R.L.; Fink, M.P. Ethyl pyruvate modulates inflammatory gene expression in mice subjected to hemorrhagic shock. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2002, 283, G212–G221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Han, X.; Delude, R.L.; Fink, M.P. Ethyl pyruvate ameliorates acute alcohol-induced liver injury and inflammation in mice. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2003, 142, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Uchiyama, T.; Alber, S.M.; Han, X.; Watkins, S.K.; Delude, R.L.; Fink, M.P. Ethyl pyruvate ameliorates distant organ injury in a murine model of acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 32, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchiyama, T.; Delude, R.L.; Fink, M.P. Dose-dependent effects of ethyl pyruvate in mice subjected to mesenteric ischemia and reperfusion. Care Med. 2003, 29, 2050–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Kellum, J.A.; Kaldas, H.; Fink, M.P. Evidence that glutathione depletion is a mechanism responsible for the anti-inflammatory effects of ethyl pyruvate in cultured lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 308, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeang, H.; Hamdam, J.M.; Al-Huseini, L.; Sethu, S.; Djouhri, L.; Walsh, J.; Kitteringham, N.; Park, B.K.; Goldring, C.E.; Sathish, J.G. Loss of transcription factor nuclear factor-erythroid 2 (NF-E2) p45-related factor-2 (Nrf2) leads to dysregulation of immune functions, redox homeostasis, and intracellular signaling in dendritic cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 10556–10564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.J.; Gupta, A.; Kao, W.M.; Almudallal, O.; Letterio, J.J.; Pareek, T.K. Nrf2-mediated metabolic reprogramming of tolerogenic dendritic cells is protective against aplastic anemia. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 94, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poss, K.D.; Tonegawa, S. Reduced stress defense in heme oxygenase 1-deficient cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 10925–10930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauveau, C.; Rémy, S.; Royer, P.J.; Hill, M.; Tanguy-Royer, S.; Hubert, F.X.; Tesson, L.; Brion, R.; Beriou, G.; Gregoire, M.; et al. Heme oxygenase-1 expression inhibits dendritic cell maturation and proinflammatory function but conserves IL-10 expression. Blood 2005, 106, 1694–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chora, A.A.; Fontoura, P.; Cunha, A.; Pais, T.F.; Cardoso, S.; Ho, P.P.; Lee, L.Y.; Sobel, R.A.; Steinman, L.; Soares, M.P. Heme oxygenase-1 and carbon monoxide suppress autoimmune neuroinflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.F.; Braun, A.; Brusko, T.M.; Joseph, R.; Bolisetty, S.; Wasserfall, C.H.; Atkinson, M.A.; Agarwal, A.; Kapturczak, M.H. Suppression by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells is dependent on expression of heme oxygenase-1 in antigen-presenting cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, A.; Waschbisch, A.; Kuhbandner, K.; Bayas, A.; Lee, D.H.; Duscha, A.; Haghikia, A.; Gold, R.; Linker, R.A. The NRF2 pathway as potential biomarker for dimethyl fumarate treatment in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2018, 5, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hull, T.D.; Agarwal, A.; George, J.F. The mononuclear phagocyte system in homeostasis and disease: A role for heme oxygenase-1. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 1770–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deramaudt, T.B.; da Silva, J.L.; Remy, P.; Kappas, A.; Abraham, N.G. Negative regulation of human heme oxygenase in microvessel endothelial cells by dexamethasone. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1999, 222, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratschmar, D.V.; Calabrese, D.; Walsh, J.; Lister, A.; Birk, J.; Appenzeller-Herzog, C.; Moulin, P.; Goldring, C.E.; Odermatt, A. Suppression of the Nrf2-dependent antioxidant response by glucocorticoids and 11β-HSD1-mediated glucocorticoid activation in hepatic cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Haldar, C. Melatonin modulates glucocorticoid receptor mediated inhibition of antioxidant response and apoptosis in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2016, 436, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, P.; Xin, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. Nrf2 suppresses the function of dendritic cells to facilitate the immune escape of glioma cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 360, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, P.; Kaur, G.; Tandon, A.; Sharma, A.; Bhatnagar, A. Altered redox regulation by Nrf2-Keap1 system in dendritic cells of systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Lupus 2020, 29, 1544–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, A.; Waschbisch, A.; Knippertz, I.; Zinser, E.; Berg, J.; Jörg, S.; Kuhbandner, K.; David, C.; Pi, J.; Bayas, A.; et al. Role of Nuclear Factor (Erythroid-Derived 2)-Like 2 Signaling for Effects of Fumaric Acid Esters on Dendritic Cells. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medzhitov, R.; Horng, T. Transcriptional control of the inflammatory response. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stanisavljević, S.; Stegnjaić, G.; Jevtić, B.; Dimitrijević, M.; Miljković, Đ.; Lavrnja, I.; Nikolovski, N. NRF2 Plays a Crucial Role in the Tolerogenic Effect of Ethyl Pyruvate on Dendritic Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25116195
Stanisavljević S, Stegnjaić G, Jevtić B, Dimitrijević M, Miljković Đ, Lavrnja I, Nikolovski N. NRF2 Plays a Crucial Role in the Tolerogenic Effect of Ethyl Pyruvate on Dendritic Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(11):6195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25116195
Chicago/Turabian StyleStanisavljević, Suzana, Goran Stegnjaić, Bojan Jevtić, Mirjana Dimitrijević, Đorđe Miljković, Irena Lavrnja, and Neda Nikolovski. 2024. "NRF2 Plays a Crucial Role in the Tolerogenic Effect of Ethyl Pyruvate on Dendritic Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 11: 6195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25116195
APA StyleStanisavljević, S., Stegnjaić, G., Jevtić, B., Dimitrijević, M., Miljković, Đ., Lavrnja, I., & Nikolovski, N. (2024). NRF2 Plays a Crucial Role in the Tolerogenic Effect of Ethyl Pyruvate on Dendritic Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(11), 6195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25116195







