Vitamin D and Sulforaphane Decrease Inflammatory Oxidative Stress and Restore the Markers of Epithelial Integrity in an In Vitro Model of Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
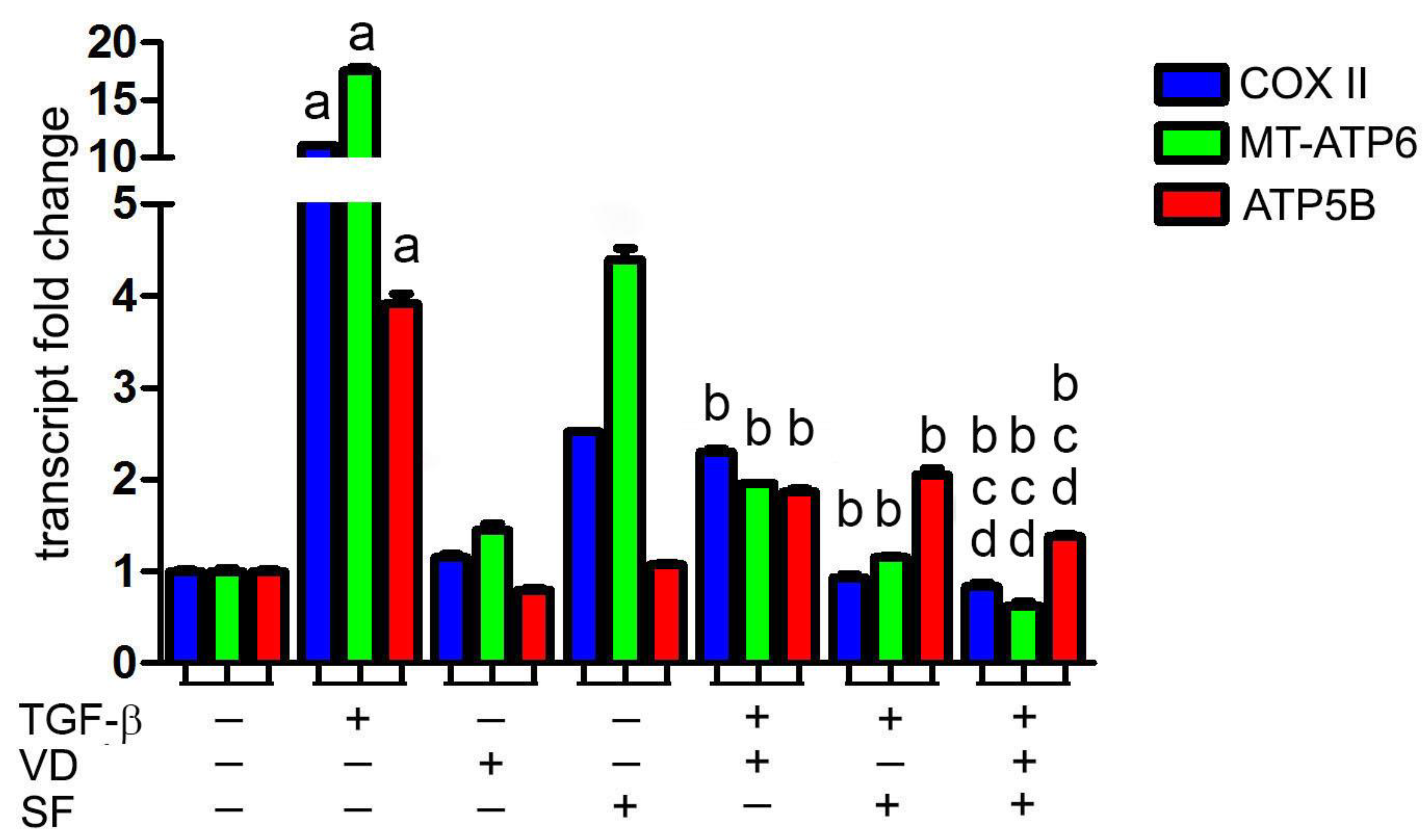
2.1. Sulforaphane Potentiates the Antioxidant Activity of Vitamin D on TGF-β Dependent ROS Production
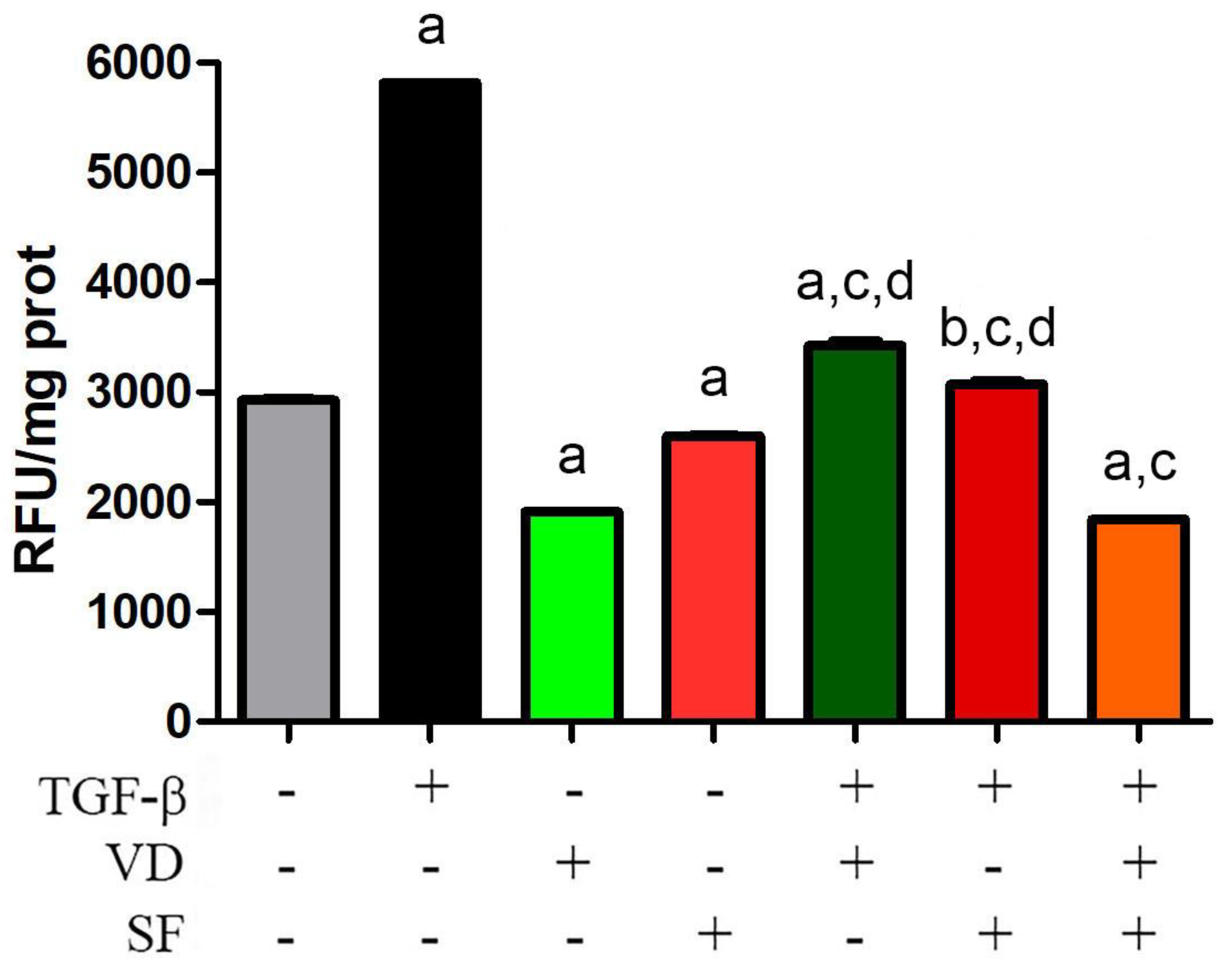
2.2. Vitamin D and Sulforaphane Decrease the Respiratory Burst Triggered by TGF-β Stimulation
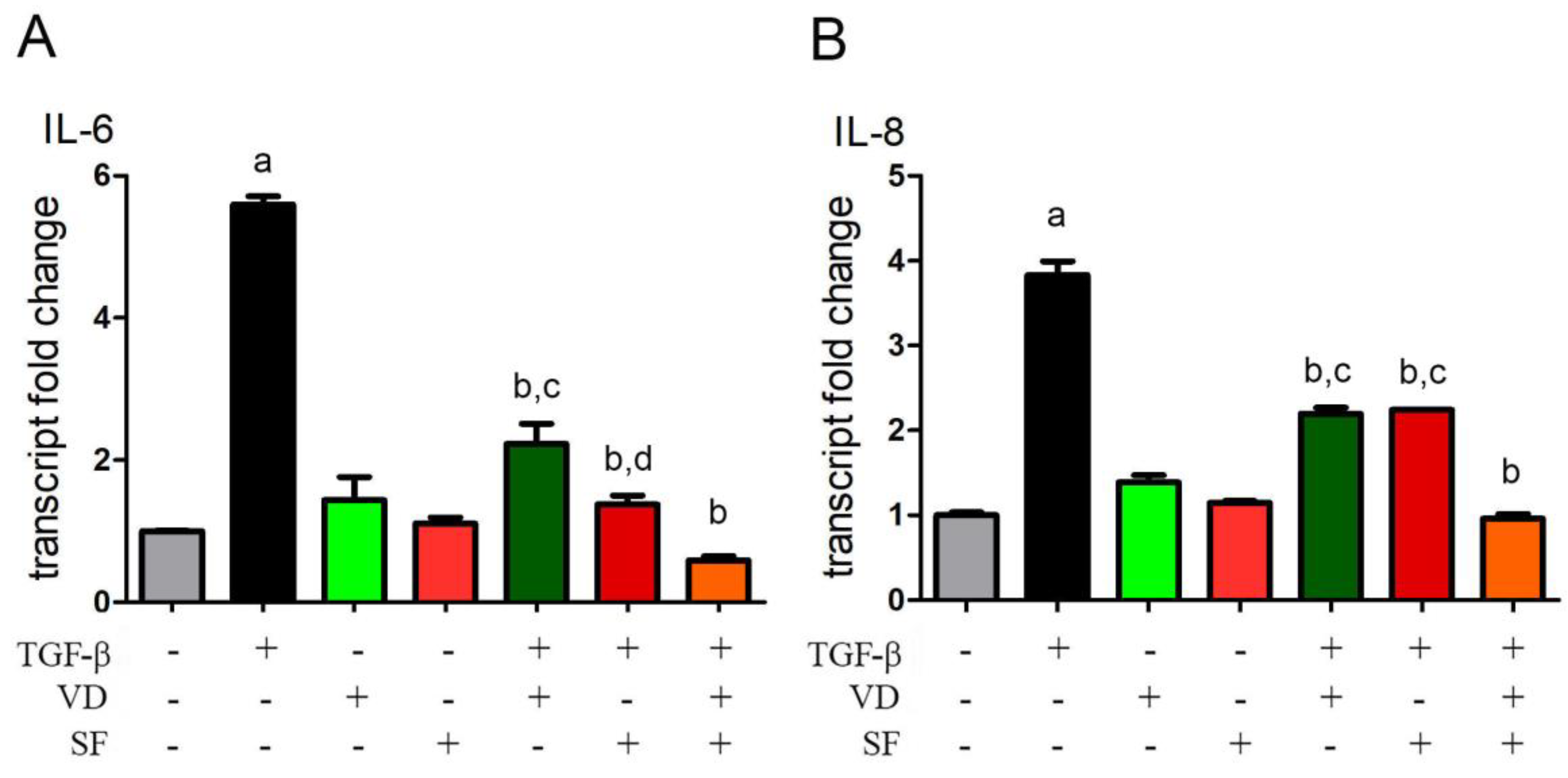
2.3. Vitamin D and Sulforaphane Reduce the Transcription Levels of IL-6 and IL-8 Induced by TGF-β
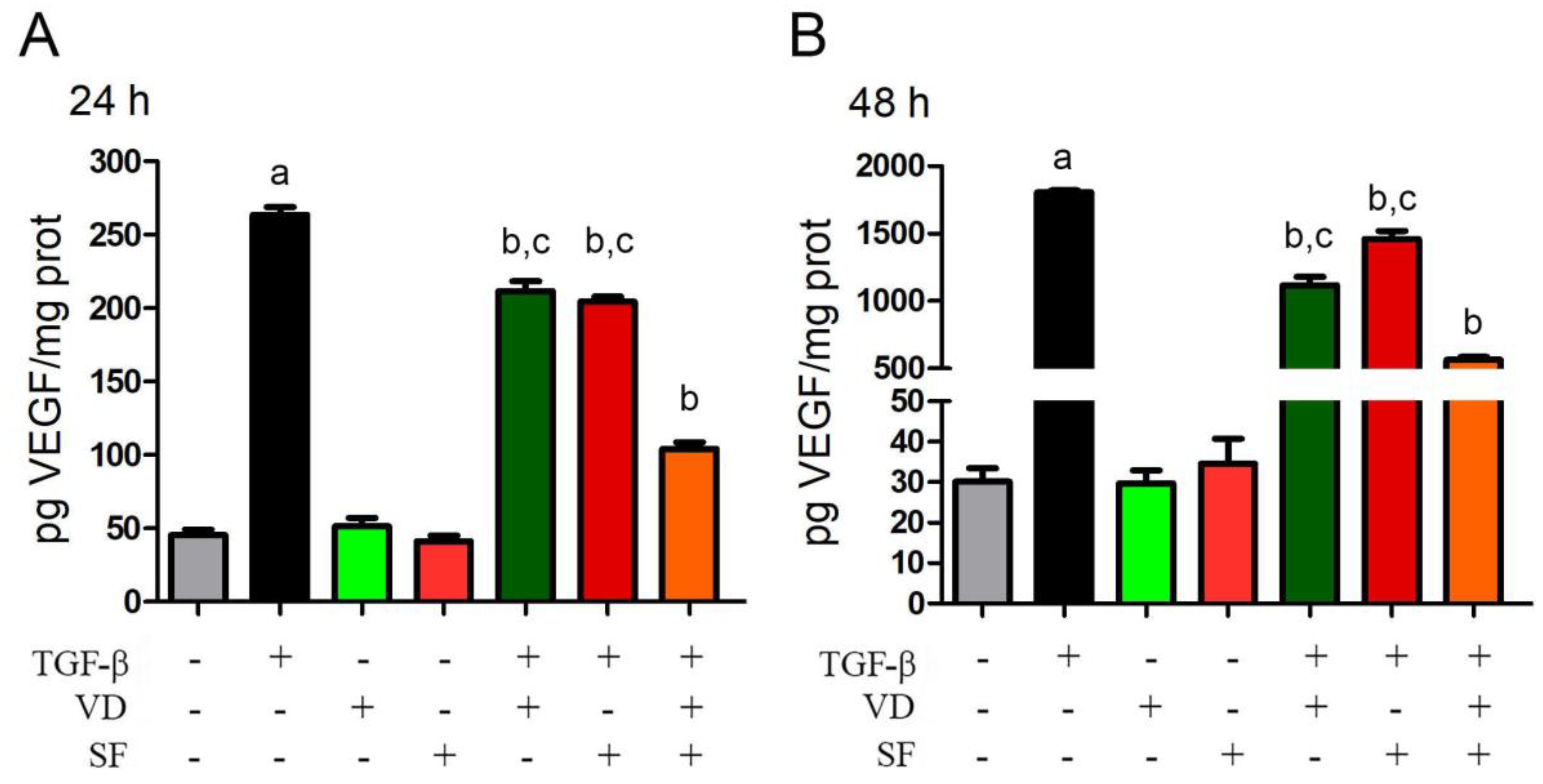
2.4. TGF-β-Induced VEGF Secretion Is Abated by Vitamin D and Sulforaphane
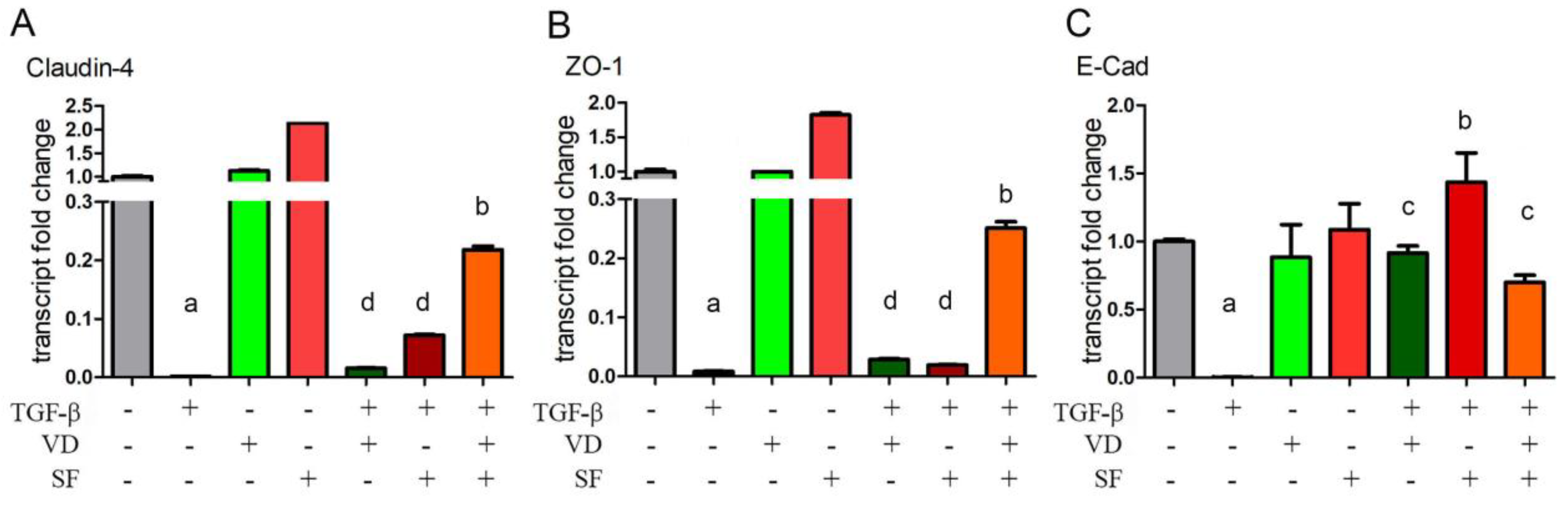
2.5. Epithelium Integrity and Differentiation Are Enhanced by Vitamin D and Sulforaphane Treatment
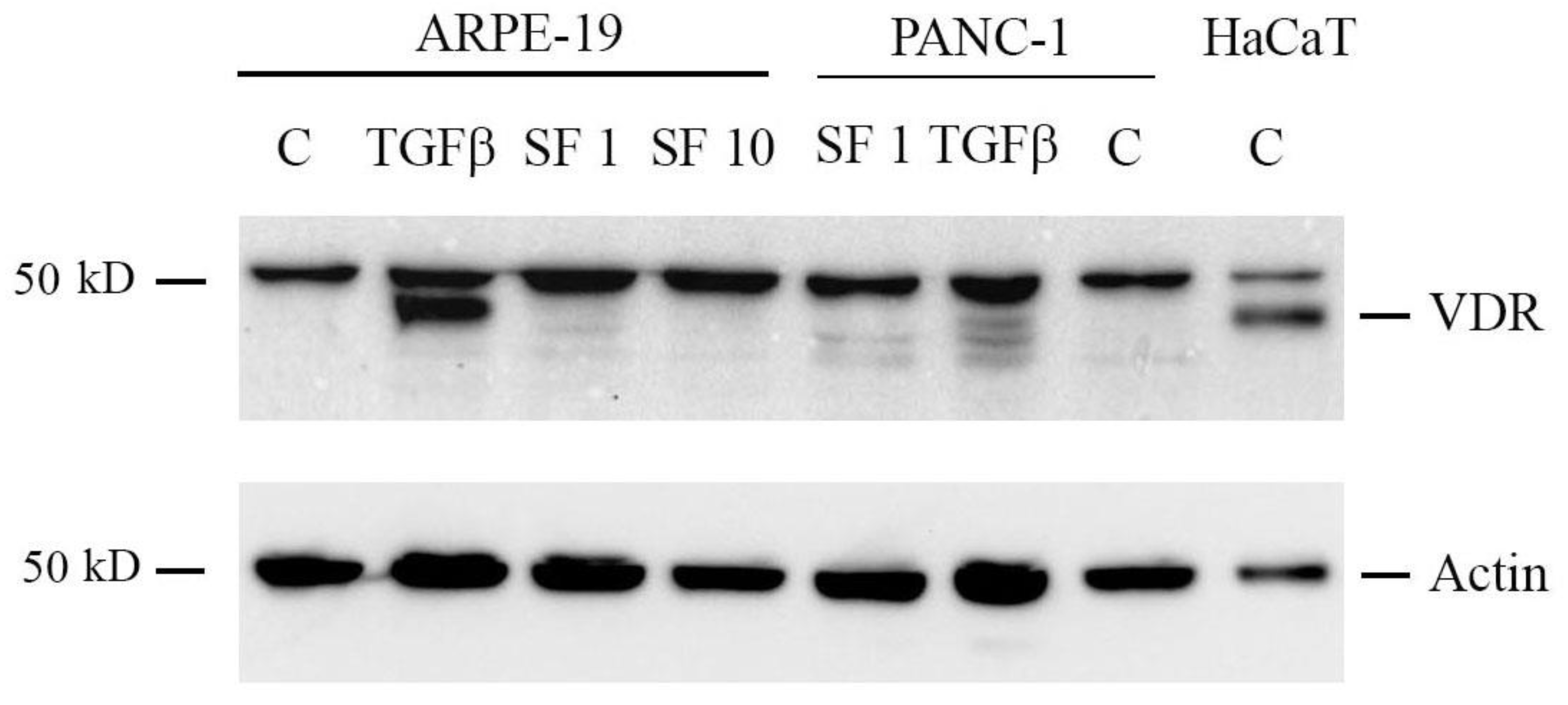
2.6. Sulforaphane Does Not Induce VDR Expression
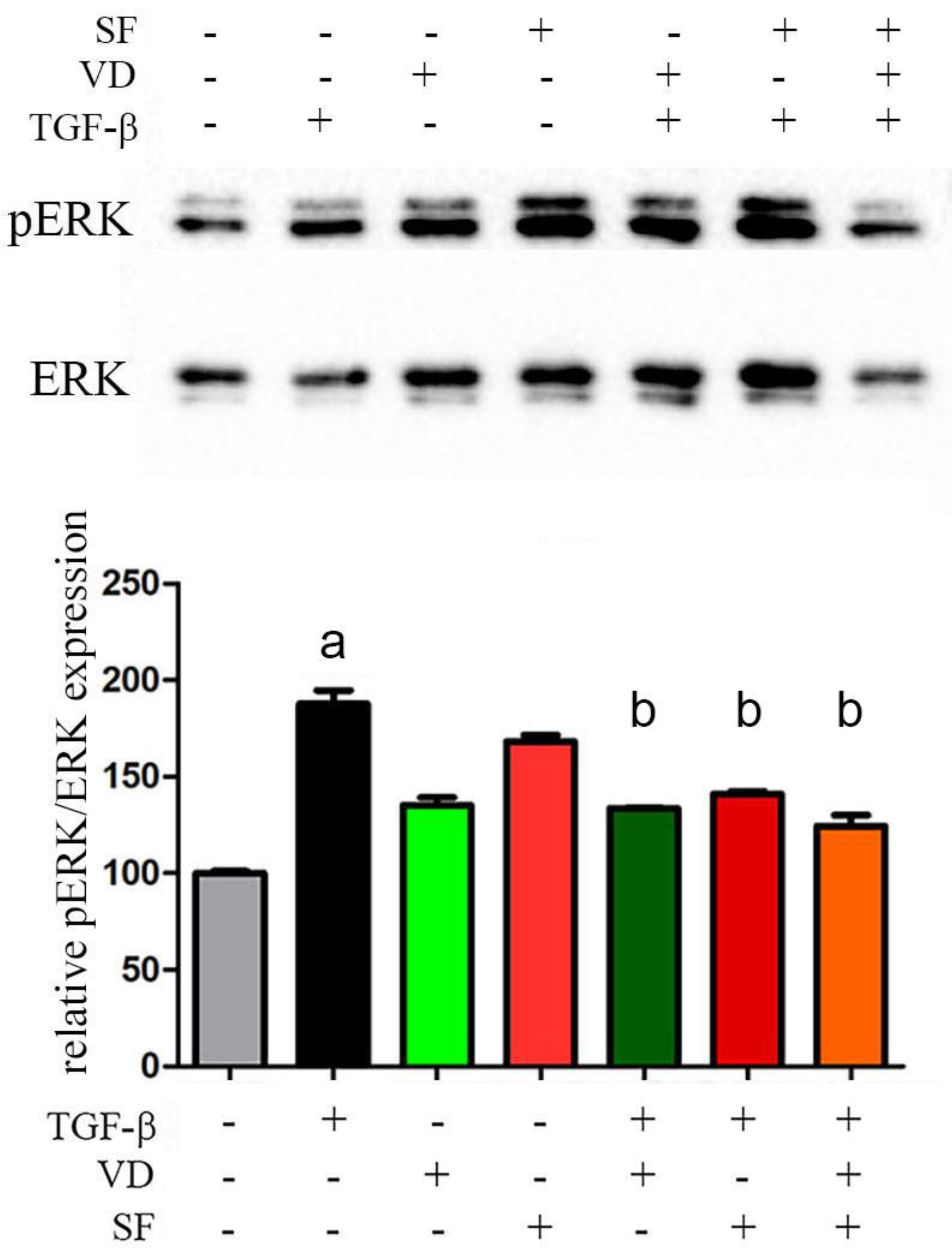
2.7. The Activity of Vitamin D and Sulforaphane Is Mediated by pERK 1/2 Signaling Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Treatments
4.2. Western Blotting Analysis
4.3. Measurement of Intracellular ROS production
4.4. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.5. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Quantification
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gehrs, K.M.; Anderson, D.H.; Johnson, L.V.; Hageman, G.S. Age-Related Macular Degeneration--Emerging Pathogenetic and Therapeutic Concepts. Ann. Med. 2006, 38, 450–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyawahare, H.; Shinde, P. Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Cureus 2022, 14, e29583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadziahmetovic, M.; Malek, G. Age-Related Macular Degeneration Revisited: From Pathology and Cellular Stress to Potential Therapies. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 612812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasiak, J.; Chojnacki, J.; Szczepanska, J.; Fila, M.; Chojnacki, C.; Kaarniranta, K.; Pawlowska, E. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate, an Active Green Tea Component to Support Anti-VEGFA Therapy in Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorusupudi, A.; Nelson, K.; Bernstein, P.S. The Age-Related Eye Disease 2 Study: Micronutrients in the Treatment of Macular Degeneration. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushwah, N.; Bora, K.; Maurya, M.; Pavlovich, M.C.; Chen, J. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasiak, J. Senescence in the Pathogenesis of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 789–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macchioni, L.; Chiasserini, D.; Mezzasoma, L.; Davidescu, M.; Orvietani, P.L.; Fettucciari, K.; Salviati, L.; Cellini, B.; Bellezza, I. Crosstalk between Long-Term Sublethal Oxidative Stress and Detrimental Inflammation as Potential Drivers for Age-Related Retinal Degeneration. Antioxidants 2020, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bressler, S.B. Introduction: Understanding the Role of Angiogenesis and Antiangiogenic Agents in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmology 2009, 116, S1–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Lin, S.; Copland, D.A.; Dick, A.D.; Liu, J. Cellular Senescence in the Aging Retina and Developments of Senotherapies for Age-Related Macular Degeneration. J. Neuroinflammation 2021, 18, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, F.; Campbell, M. The Blood–Retina Barrier in Health and Disease. FEBS J. 2023, 290, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauppinen, A.; Paterno, J.J.; Blasiak, J.; Salminen, A.; Kaarniranta, K. Inflammation and Its Role in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 1765–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, N.J.Y.; Chan, E.J.J.; Cheung, C. Choroidal Neovascularization: Mechanisms of Endothelial Dysfunction. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somasundaran, S.; Constable, I.J.; Mellough, C.B.; Carvalho, L.S. Retinal Pigment Epithelium and Age-related Macular Degeneration: A Review of Major Disease Mechanisms. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2020, 48, 1043–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joussen, A.M.; Ricci, F.; Paris, L.P.; Korn, C.; Quezada-Ruiz, C.; Zarbin, M. Angiopoietin/Tie2 Signalling and Its Role in Retinal and Choroidal Vascular Diseases: A Review of Preclinical Data. Eye 2021, 35, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibuya, M. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and Its Receptor (VEGFR) Signaling in Angiogenesis: A Crucial Target for Anti- and Pro-Angiogenic Therapies. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Yu, T.; Li, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhang, J.; Wen, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, X.; Li, X.; Li, F.; et al. Sulforaphane Enhances the Ability of Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cell against Oxidative Stress, and Its Effect on Gene Expression Profile Evaluated by Microarray Analysis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2013, 2013, 413024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.Y.; Lou, W.J.; Zhang, D.Y.; Sun, S.Y. ROS Plays a Role in the Neonatal Rat Intestinal Barrier Damages Induced by Hyperoxia. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 8819195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finger, C.E.; Moreno-Gonzalez, I.; Gutierrez, A.; Moruno-Manchon, J.F.; McCullough, L.D. Age-Related Immune Alterations and Cerebrovascular Inflammation. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, D.A.; Pearson, C.I. Angiogenesis in the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Joint and Lung Diseases. Arthritis Res. 2001, 3, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heloterä, H.; Kaarniranta, K. A Linkage between Angiogenesis and Inflammation in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Cells 2022, 11, 3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.; Liu, P.; Shang, K.; Ma, Y. Application and Mechanism of Anti-VEGF Drugs in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 943915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzara, F.; Longo, A.M.; Giurdanella, G.; Lupo, G.; Platania, C.B.M.; Rossi, S.; Drago, F.; Anfuso, C.D.; Bucolo, C. Vitamin D3 Preserves Blood Retinal Barrier Integrity in an in Vitro Model of Diabetic Retinopathy. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 971164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsalem, J.A.; Patel, D.; Susarla, R.; Coca-Prados, M.; Bland, R.; Walker, E.A.; Rauz, S.; Wallace, G.R. Characterization of Vitamin D Production by Human Ocular Barrier Cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 2140–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantell, D.J.; Owens, P.E.; Bundred, N.J.; Mawer, E.B.; Canfield, A.E. 1 Alpha,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D(3) Inhibits Angiogenesis in Vitro and in Vivo. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, M.; Recalde, S.; González-Zamora, J.; Bilbao-Malavé, V.; Sáenz de Viteri, M.; Bezunartea, J.; Moreno-Orduña, M.; Belza, I.; Barrio-Barrio, J.; Fernandez-Robredo, P.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidative Synergistic Effect of Vitamin D and Nutritional Complex on Retinal Pigment Epithelial and Endothelial Cell Lines against Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layana, A.G.; Minnella, A.M.; Garhöfer, G.; Aslam, T.; Holz, F.G.; Leys, A.; Silva, R.; Delcourt, C.; Souied, E.; Seddon, J.M. Vitamin D and Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.-N.; Zhang, X.-J.; Ling, X.-T.; Bui, C.H.-T.; Wang, Y.-M.; Ip, P.; Chu, W.-K.; Chen, L.-J.; Tham, C.C.; Yam, J.C.; et al. Vitamin D and Ocular Diseases: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlberg, C.; Haq, A. The Concept of the Personal Vitamin D Response Index. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 175, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-W.; Friso, S. Epigenetics: A New Bridge between Nutrition and Health. Adv. Nutr. 2010, 1, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apprato, G.; Fiz, C.; Fusano, I.; Bergandi, L.; Silvagno, F. Natural Epigenetic Modulators of Vitamin D Receptor. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Wang, Y.-H.; Zhou, H.-Y.; Cui, K.-M. Sulforaphane Alleviates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Injury in ARPE-19 Cells by Repressing the PWRN2/NF-kB Pathway. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2022, 44, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Sung, B.; Kang, Y.J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Yoon, J.-H.; Im, E.; Kim, N.D. Sulforaphane Inhibits Hypoxia-Induced HIF-1α and VEGF Expression and Migration of Human Colon Cancer Cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 2226–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Atkinson, S.J.; Akbareian, S.E.; Zhou, Z.; Munsterberg, A.; Robinson, S.D.; Bao, Y. Sulforaphane Exerts Anti-Angiogenesis Effects against Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Inhibition of STAT3/HIF-1α/VEGF Signalling. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-B.; Liu, P.-P.; Zheng, H.; Yang, X.-X.; Yang, C.-C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. Inhibition of TGF-Β2-Induced Migration and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in ARPE-19 by Sulforaphane. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 14, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Chou, H.-C.; Ho, Y.-J.; Chang, S.-J.; Liao, E.-C.; Wei, Y.-S.; Lin, M.-W.; Wang, Y.-S.; Chien, Y.-A.; Yu, X.-R.; et al. Characterization of TGF-β by Induced Oxidative Stress in Human Trabecular Meshwork Cells. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaarniranta, K.; Pawlowska, E.; Szczepanska, J.; Jablkowska, A.; Blasiak, J. Role of Mitochondrial DNA Damage in ROS-Mediated Pathogenesis of Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wei, T.-T.; Cai, J.; Xie, T.-H.; Yao, Y.; Zhu, L. Smurf1: A Possible Therapeutic Target in Dry Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Exp. Eye Res. 2023, 233, 109549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starkov, A.A. The Role of Mitochondria in Reactive Oxygen Species Metabolism and Signaling. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1147, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailloux, R.J. An Update on Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species Production. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricca, C.; Aillon, A.; Viano, M.; Bergandi, L.; Aldieri, E.; Silvagno, F. Vitamin D Inhibits the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by a Negative Feedback Regulation of TGF-β Activity. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 187, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppner, M.C.; McKillop-Smith, S.; Forrester, J.V. TGF-Beta and IL-1 Beta Act in Synergy to Enhance IL-6 and IL-8 mRNA Levels and IL-6 Production by Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. Immunology 1995, 84, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Planck, S.R.; Dang, T.T.; Graves, D.; Tara, D.; Ansel, J.C.; Rosenbaum, J.T. Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells Secrete Interleukin-6 in Response to Interleukin-1. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1992, 33, 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Elner, V.M.; Strieter, R.M.; Elner, S.G.; Baggiolini, M.; Lindley, I.; Kunkel, S.L. Neutrophil Chemotactic Factor (IL-8) Gene Expression by Cytokine-Treated Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Pathol. 1990, 136, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.-H.; Ojha, U.; Lee, Y.M. Pathological Angiogenesis and Inflammation in Tissues. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2021, 44, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyfuss, J.L.; Giordano, R.J.; Regatieri, C.V. Ocular Angiogenesis. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 2015, 892043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Age-Related Macular Degeneration: From Basic Science to Therapy. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, P.A.; McCarty, J.H.; Guerrero, P.A.; McCarty, J.H. TGF-β Activation and Signaling in Angiogenesis; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-953-51-3024-6. [Google Scholar]
- Narimatsu, T.; Ozawa, Y.; Miyake, S.; Kubota, S.; Hirasawa, M.; Nagai, N.; Shimmura, S.; Tsubota, K. Disruption of Cell-Cell Junctions and Induction of Pathological Cytokines in the Retinal Pigment Epithelium of Light-Exposed Mice. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 4555–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obert, E.; Strauss, R.; Brandon, C.; Grek, C.; Ghatnekar, G.; Gourdie, R.; Rohrer, B. Targeting The Tight Junction Protein, Zonula Occludens-1, With The Connexin 43 Mimetic Peptide, αCT1, Reduces VEGF-Dependent RPE Pathophysiology. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consiglio, M.; Destefanis, M.; Morena, D.; Foglizzo, V.; Forneris, M.; Pescarmona, G.; Silvagno, F. The Vitamin D Receptor Inhibits the Respiratory Chain, Contributing to the Metabolic Switch That Is Essential for Cancer Cell Proliferation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiz, C.; Apprato, G.; Ricca, C.; Aillon, A.; Bergandi, L.; Silvagno, F. TGF Beta Induces Vitamin D Receptor and Modulates Mitochondrial Activity of Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarev, E.; Cantor, C.; Zhavoronkov, A.; Buzdin, A.; Aliper, A.; Csoka, A.B. Pathway Activation Profiling Reveals New Insights into Age-Related Macular Degeneration and Provides Avenues for Therapeutic Interventions. Aging 2014, 6, 1064–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, R.; Harris, A.; Kheradiya, N.S.; Winston, D.M.; Ciulla, T.A.; Wirostko, B. Age-Related Macular Degeneration and the Aging Eye. Clin. Interv. Aging 2008, 3, 473–482. [Google Scholar]
- Fabre, M.; Mateo, L.; Lamaa, D.; Baillif, S.; Pagès, G.; Demange, L.; Ronco, C.; Benhida, R. Recent Advances in Age-Related Macular Degeneration Therapies. Molecules 2022, 27, 5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral de Guimaraes, T.A.; Daich Varela, M.; Georgiou, M.; Michaelides, M. Treatments for Dry Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Therapeutic Avenues, Clinical Trials and Future Directions. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 106, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scondotto, G.; Sultana, J.; Vadalà, M.; Avitabile, T.; Cillino, S.; Foti, S.S.; Labbate, L.; Longo, A.; Mirabelli, E.; Puzo, M.R.; et al. Assessment of Intravitreal Anti-VEGF Drugs and Dexamethasone for Retinal Diseases in Real World Setting: A Multi-Centre Prospective Study from Southern Italy. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 32, 3064–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhu, N.; Ji, A. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Faricimab and Other Anti-VEGF Therapy for Age-Related Macular Degeneration and Diabetic Macular Edema: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Medicine 2023, 102, e36370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, S.; Komati, R.; Eichenbaum, D.A.; Hariprasad, I.; Ciulla, T.A.; Hariprasad, S.M. Current and Upcoming Anti-VEGF Therapies and Dosing Strategies for the Treatment of Neovascular AMD: A Comparative Review. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2019, 4, e000398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, H.; Sun, R.; Liu, C.; Luo, Y.; Fu, S.; Ying, Y. Emerging Roles of Transforming Growth Factor β Signaling in Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2019, 51, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosi, G.M.; Orlandini, M.; Galvagni, F. The Controversial Role of TGF-β in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, Z.-M.; Elner, S.G.; Elner, V.M. Regulation of VEGF mRNA Expression and Protein Secretion by TGF-Β2 in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2007, 84, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Mandal, A.K.; Son, Y.-O.; Pratheeshkumar, P.; Wise, J.T.F.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, X.; Chen, Z. Roles of ROS, Nrf2, and Autophagy in Cadmium-Carcinogenesis and Its Prevention by Sulforaphane. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 353, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.; Luong, L.; Naase, H.; Vives, M.; Jakaj, G.; Finch, J.; Boyle, J.; Mulholland, J.W.; Kwak, J.; Pyo, S.; et al. Sulforaphane Pretreatment Prevents Systemic Inflammation and Renal Injury in Response to Cardiopulmonary Bypass. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 148, 690–697.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Yan, X. Sulforaphane Protects Rabbit Corneas against Oxidative Stress Injury in Keratoconus through Activation of the Nrf-2/HO-1 Antioxidant Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Talalay, P. Powerful and Prolonged Protection of Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells, Keratinocytes, and Mouse Leukemia Cells against Oxidative Damage: The Indirect Antioxidant Effects of Sulforaphane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 15221–15226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortorella, S.M.; Royce, S.G.; Licciardi, P.V.; Karagiannis, T.C. Dietary Sulforaphane in Cancer Chemoprevention: The Role of Epigenetic Regulation and HDAC Inhibition. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2015, 22, 1382–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, M.; Reynders, V.; Loitsch, S.; Steinhilber, D.; Schröder, O.; Stein, J. The Dietary Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Sulforaphane Induces Human β-Defensin-2 in Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Immunology 2008, 125, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günzel, D.; Yu, A.S.L. Claudins and the Modulation of Tight Junction Permeability. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 525–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanshahi, M.; Anderson, P.H.; Sylvester, C.L.; Stringer, A.M. Highlight Article: Current Evidence for Vitamin D in Intestinal Function and Disease. Exp. Biol. Med. 2019, 244, 1040–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, T.; Araki, S.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Watanabe, Y. Oxidative Stress Orchestrates MAPK and Nitric-Oxide Synthase Signal. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvagno, F.; Consiglio, M.; Foglizzo, V.; Destefanis, M.; Pescarmona, G. Mitochondrial Translocation of Vitamin D Receptor Is Mediated by the Permeability Transition Pore in Human Keratinocyte Cell Line. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergandi, L.; Apprato, G.; Silvagno, F. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Combined Phycocyanin and Palmitoylethanolamide in Human Lung and Prostate Epithelial Cells. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricca, C.; Aillon, A.; Bergandi, L.; Alotto, D.; Castagnoli, C.; Silvagno, F. Vitamin D Receptor Is Necessary for Mitochondrial Function and Cell Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergandi, L.; Flutto, T.; Valentini, S.; Thedy, L.; Pramotton, R.; Zenato, S.; Silvagno, F. Whey Derivatives and Galactooligosaccharides Stimulate the Wound Healing and the Function of Human Keratinocytes through the NF-kB and FOXO-1 Signaling Pathways. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bergandi, L.; Palladino, G.; Meduri, A.; De Luca, L.; Silvagno, F. Vitamin D and Sulforaphane Decrease Inflammatory Oxidative Stress and Restore the Markers of Epithelial Integrity in an In Vitro Model of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6404. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126404
Bergandi L, Palladino G, Meduri A, De Luca L, Silvagno F. Vitamin D and Sulforaphane Decrease Inflammatory Oxidative Stress and Restore the Markers of Epithelial Integrity in an In Vitro Model of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(12):6404. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126404
Chicago/Turabian StyleBergandi, Loredana, Giulia Palladino, Alessandro Meduri, Laura De Luca, and Francesca Silvagno. 2024. "Vitamin D and Sulforaphane Decrease Inflammatory Oxidative Stress and Restore the Markers of Epithelial Integrity in an In Vitro Model of Age-Related Macular Degeneration" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 12: 6404. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126404
APA StyleBergandi, L., Palladino, G., Meduri, A., De Luca, L., & Silvagno, F. (2024). Vitamin D and Sulforaphane Decrease Inflammatory Oxidative Stress and Restore the Markers of Epithelial Integrity in an In Vitro Model of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(12), 6404. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126404






