Hydrogel Wound Dressings Accelerating Healing Process of Wounds in Movable Parts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Bioadhesive Performance of Hydrogel-Based Movable Wound Dressings
3. Mechanical Property of Hydrogel-Based Movable Wound Dressings
3.1. Chemical Crosslinking-Based Mechanical Property
3.2. Physical Crosslinking-Based Mechanical Property
3.3. Chemical–Physical Crosslinking-Based Mechanical Property
4. Bioactivities of Hydrogel-Based Movable Wound Dressings
4.1. Hydrogel-Based Movable Wound Dressings with Antibacterial Activity
4.1.1. Hydrogel-Based Movable Wound Dressings with Endogenous Antibacterial Capability
4.1.2. Hydrogel-Based Movable Wound Dressings Loaded with Antibiotics
4.1.3. Hydrogel-Based Movable Wound Dressings Loaded with Nanomaterials
4.2. Hydrogel-Based Movable Wound Dressings with Antioxidant Activity
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dolati, S.; Yousefi, M.; Pishgahi, A.; Nourbakhsh, S.; Pourabbas, B.; Shakouri, S.K. Prospects for the application of growth factors in wound healing. Growth Factors 2020, 38, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, L.-M. Intelligent biobased hydrogels for diabetic wound healing: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484, 149493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Sun, S.; Yang, J.; Chai, G.; Wang, N.; Ma, S.; Ding, Q.; Liu, W. Multifunctional hydrogel bioscaffolds based on polysaccharide to promote wound healing: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, S.; Ogai, K.; Mukai, K.; Sugama, J. Association of Skin Microbiome with the Onset and Recurrence of Pressure Injury in Bedridden Elderly People. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Xiang, J.; Xia, Q.; Li, K.; Lan, T.; Yu, L. Superhydrophobic cotton gauze with durably antibacterial activity as skin wound dressing. Cellulose 2019, 26, 1383–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Zhang, P.; Liu, L.; Shangguan, Y.; Cheng, X.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Hao, J.; Li, W.; Cui, J. Convergent architecting of multifunction-in-one hydrogels as wound dressings for surgical anti-infections. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 25, 100968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, S.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, C. A rapid-triggered approach towards antibacterial hydrogel wound dressing with synergic photothermal and sterilization profiles. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 138, 212873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmsjö, M.; Ingemansson, R. Green foam, black foam or gauze for NWPT: Effects on granulation tissue formation. J. Wound Care 2011, 20, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cojocaru, E.; Ghitman, J.; Pircalabioru, G.G.; Stavarache, C.; Serafim, A.; Vasile, E.; Iovu, H. Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes Based on Citric Acid-Functionalized Chitosan Containing rGO-TEPA with Potential Application in Wound Dressings. Polymers 2022, 14, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L. Emerging polymeric electrospun fibers: From structural diversity to application in flexible bioelectronics and tissue engineering. Exploration 2022, 2, 20210029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, L.I.F.; Dias, A.M.A.; Carvalho, E.; de Sousa, H.C. Recent advances on the development of wound dressings for diabetic foot ulcer treatment—A review. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 7093–7114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xiao, D.; Yu, H.; Ke, R.; Shi, S.; Tang, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sui, X.; Wang, B.; et al. Asymmetric composite wound dressing with hydrophobic flexible bandage and tissue-adhesive hydrogel for joints skin wound healing. Compos. Part B 2022, 235, 109762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamer, T.M.; Sabet, M.M.; Alhalili, Z.A.H.; Ismail, A.M.; Mohy-Eldin, M.S.; Hassan, M.A. Influence of Cedar Essential Oil on Physical and Biological Properties of Hemostatic, Antibacterial, and Antioxidant Polyvinyl Alcohol/Cedar Oil/Kaolin Composite Hydrogels. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, H.; Gao, J.; Liu, X.; Li, M.; Wu, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Tang, P. First-Aid Hydrogel Wound Dressing with Reliable Hemostatic and Antibacterial Capability for Traumatic Injuries. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2300312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Y.; Xie, Y.; Jiang, Z. Injectable and biocompatible chitosan-alginic acid hydrogels. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 14, 025010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, A.; Liao, C. Hydrogel wound dressings for diabetic foot ulcer treatment: Status-quo, challenges, and future perspectives. BMEMat 2023, 1, e12037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Shen, L.; Hong, Y. Status and future scope of hydrogels in wound healing: Synthesis, materials and evaluation. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 130, 109609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, C.; Sethu, S.; Nayak, S.; Mohan, L.; Morsi, Y.; Manivasagam, G. Suture materials—Current and emerging trends. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2016, 104, 1544–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, F.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yu, A.; Duan, B. A quaternized chitin derivatives, egg white protein and montmorillonite composite sponge with antibacterial and hemostatic effect for promoting wound healing. Compos. Part B 2022, 234, 109661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Lv, X.; Hou, Y.; Wang, K.; Ren, F.; Xu, D.; Wang, Q.; Fan, K.; Xie, C.; Lu, X. Mussel-inspired nanozyme catalyzed conductive and self-setting hydrogel for adhesive and antibacterial bioelectronics. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2676–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Lu, X.; Liu, K.; Wang, K.; Fang, L.; Weng, L.-T.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Y.; Ren, F.; Zhao, C.; et al. Mussel-Inspired Adhesive and Tough Hydrogel Based on Nanoclay Confined Dopamine Polymerization. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2561–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, H.; Qiao, X.; Jiang, T.; Fu, X.; He, Y.; Zhao, X. Agarose oligosaccharide- silver nanoparticle- antimicrobial peptide- composite for wound dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 269, 118258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Chen, Y.; Yu, X.; Yan, Y.; Liu, H.; Cui, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, X.; Meng, J.; Yang, S.; et al. Bismuth Tungstate–Silver Sulfide Z-Scheme Heterostructure Nanoglue Promotes Wound Healing through Wound Sealing and Bacterial Inactivation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 53491–53500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, A.; Khan, R.; Ul-Islam, M.; Khan, T.; Wahid, F. Bacterial cellulose-zinc oxide nanocomposites as a novel dressing system for burn wounds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 164, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Qiao, L.; Xu, H.; Guo, B. pH/Glucose Dual Responsive Metformin Release Hydrogel Dressings with Adhesion and Self-Healing via Dual-Dynamic Bonding for Athletic Diabetic Foot Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 3194–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Han, X.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q. High-strength and highly electrically conductive hydrogels for wearable strain sensor. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2021, 769, 138437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.Y.; An, S.; Cho, S.-W. Advanced Bioadhesive Hydrogels for Skin Care and Therapy. Adv. Therap. 2023, 7, 2300125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, H. Mechanoactive Nanocomposite Hydrogel to Accelerate Wound Repair in Movable Parts. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 20044–20056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lin, P.; Song, X.; Chen, K.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y. Injectable and self-healing hydrogels with tissue adhesiveness and antibacterial activity as wound dressings for infected wound healing. J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 60, 1511–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Jiang, N.; Sun, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, L. A fast UV-curable PU-PAAm hydrogel with mechanical flexibility and self-adhesion for wound healing. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 4907–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamer, T.M.; Sabet, M.M.; Omer, A.M.; Abbas, E.; Eid, A.I.; Mohy-Eldin, M.S.; Hassan, M.A. Hemostatic and antibacterial PVA/Kaolin composite sponges loaded with penicillin–streptomycin for wound dressing applications. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Ouyang, J.; She, Z.; Li, R.; Zeng, F.; Yao, Z.; Wu, S. Injectable-Hydrogel-Based Tissue Sealant for Hemostasis, Bacteria Inhibition, and Pro-Angiogenesis in Organ Bleeding Wounds and Therapeutic Outcome Monitoring Via NIR-II Optical Imaging. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, 2303997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, M.; Wu, J.; Zhu, S.; Ye, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, K.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, M.; et al. Nature-Inspired Gelatin-Based Adhesive Hydrogel: A Rapid and User-Friendly Solution for Hemostatic Applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 2304444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Jia, B.; Xu, H.; Li, Z.; Qiao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhao, X.; Guo, B. Multiple bonds crosslinked antibacterial, conductive and antioxidant hydrogel adhesives with high stretchability and rapid self-healing for MRSA infected motion skin wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Gu, Y.; Xue, P.; Xu, X. Self-Healing and Highly Stretchable Hydrogel for Interfacial Compatible Flexible Paper-Based Micro-Supercapacitor. Materials 2021, 14, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yang, J.H.; Zhou, J.; Xu, F.; Zrínyi, M.; Dussault, P.H.; Osada, Y.; Chen, Y.M. Self-healing gels based on constitutional dynamic chemistry and their potential applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 8114–8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Lopez, J.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.-C.; Niu, S.; Yan, H.; Wang, S.; Lei, T.; et al. Quadruple H-Bonding Cross-Linked Supramolecular Polymeric Materials as Substrates for Stretchable, Antitearing, and Self-Healable Thin Film Electrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 5280–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Huang, R.; Zheng, B.; Guo, W.; Li, C.; He, W.; Wei, Y.; Du, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, D.; et al. Highly Stretchable, Adhesive, Biocompatible, and Antibacterial Hydrogel Dressings for Wound Healing. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2003627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Seidi, F.; Li, C.; Wan, Z.; Jin, Y.; Song, J.; Xiao, H. Antimicrobial/Biocompatible Hydrogels Dual-Reinforced by Cellulose as Ultrastretchable and Rapid Self-Healing Wound Dressing. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, V.K.A.; Shyam, R.; Palaniappan, A.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Oh, T.-H.; Nathanael, A.J. Self-Healing Hydrogels: Preparation, Mechanism and Advancement in Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Wang, S.; Cui, L.; Li, D.; Yang, S.; Wu, J.; Meng, G.; Tian, X.; Liu, Z.; Tai, Y.; et al. Conductive Hydrogel Dressing with High Mechanical Strength for Joint Wound Healing. Macromol. Biosci. 2024, 2300528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Zhao, X.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ma, P.X.; Guo, B. Antibacterial adhesive injectable hydrogels with rapid self-healing, extensibility and compressibility as wound dressing for joints skin wound healing. Biomaterials 2018, 183, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.; Li, Z.; Pan, G.; Guo, B. Antibacterial conductive self-healable supramolecular hydrogel dressing for infected motional wound healing. Sci. China Chem. 2022, 65, 2238–2251. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, K.; Yao, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Bioinspired sequentially crosslinked nanofibrous hydrogels with robust adhesive and stretchable capability for joint wound dressing. Compos. Commun. 2021, 26, 100785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, Q.; Shao, J.; Wang, W.; Dong, X. Skin-inspired highly stretchable, tough and adhesive hydrogels for tissue-attached sensor. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, J.; Qu, J. Metal-coordinated amino acid hydrogels with ultra-stretchability, adhesion, and self-healing properties for wound healing. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 179, 111548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Kong, Y.; Shao, C.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, J.; Tao, Y.; Du, J.; Wang, H. Chitosan-based multifunctional flexible hemostatic bio-hydrogel. Acta Biomater. 2021, 136, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Hu, X.; Li, W.; Zhu, M.; Tian, J.; Li, L.; Luo, B.; Zhou, C.; Lu, L. A highly-stretchable and adhesive hydrogel for noninvasive joint wound closure driven by hydrogen bonds. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Su, J. Fabrication of physical and chemical crosslinked hydrogels for bone tissue engineering. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 12, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Wang, J.; Cong, Y.; Fu, J. Recent progress in polymer hydrogel bioadhesives. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 59, 1312–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, C.; Imani, K.B.C.; Yoon, J. Recent Advances in Design Strategies for Tough and Stretchable Hydrogels. ChemPlusChem 2021, 86, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Cheng, Y.; Jian, H.; Feng, Y.; Chang, Y.; Zheng, R.; Wu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, H. Hollow, Rough, and Nitric Oxide-Releasing Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles for Promoting Multiple Stages of Wound Healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1900256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Chang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Jian, H.; Wu, X.; Zheng, R.; Wang, L.; Ma, X.; Xu, K.; Song, P.; et al. Hierarchical Acceleration of Wound Healing through Intelligent Nanosystem to Promote Multiple Stages. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 33725–33733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konen, C.; Niederst, E. Special Issue on Disease: Mechanisms of Disease. Neuron 2019, 101, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; He, J.; Guo, B. Functional Hydrogels as Wound Dressing to Enhance Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 12687–12722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, L.; Zheng, W.; Yang, G.; Jiang, X. Rapid Fabrication of Self-Healing, Conductive, and Injectable Gel as Dressings for Healing Wounds in Stretchable Parts of the Body. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.; Zheng, W.; Prananty, D.; Li, J.; Koh, C.H.; Kang, E.-T.; Pethe, K.; Chan-Park, M.B. Polymers as advanced antibacterial and antibiofilm agents for direct and combination therapies. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Chen, Y.; Ding, M.; Fan, X.; Hu, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, W. A 4arm-PEG macromolecule crosslinked chitosan hydrogels as antibacterial wound dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wang, L.; Du, L.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Nie, J.; Ma, G. Smart Polycationic Hydrogel Dressing for Dynamic Wound Healing. Small 2022, 18, 2201620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohy Eldin, M.S.; Soliman, E.A.; Hashem, A.I.; Tamer, T.M. Antimicrobial activity of novel aminated chitosan derivatives for biomedical applications. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2012, 31, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, B. In situ and facile synthesis of silver nanoparticles on baby wipes and their applications in catalysis and SERS. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 5016–5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, B.; Xiang, G.; Jiang, T.; Zhao, X. Photodynamic Alginate Zn-MOF Thermosensitive Hydrogel for Accelerated Healing of Infected Wounds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 22830–22842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Chen, Z.; He, Y.; Lu, Q.; Chen, R.; Zhao, C.; Dong, D.; Sun, Y.; He, H. Dual light-responsive cellulose nanofibril-based in situ hydrogel for drug-resistant bacteria infected wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 297, 120042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yu, P.; Wen, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Chu, H. Nanozyme-Based Stretchable Hydrogel of Low Hysteresis with Antibacterial and Antioxidant Dual Functions for Closely Fitting and Wound Healing in Movable Parts. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2110720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wang, M.; Hu, H.; Yang, X.; Wen, B.; Wang, Z.; Jacobson, O.; Song, J.; Zhang, G.; Niu, G.; et al. Multimodal-Imaging-Guided Cancer Phototherapy by Versatile Biomimetic Theranostics with UV and γ-Irradiation Protection. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3273–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zi, Y.; Zhu, M.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Wei, H.; Li, D.; Mu, C. Effects of carboxyl and aldehyde groups on the antibacterial activity of oxidized amylose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 192, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Liu, Y.; Qin, R.; Ao, F.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Yang, M.; Liu, X. Tissue-nanoengineered hyperbranched polymer based multifunctional hydrogels as flexible “wounped treatment-health monitoring” bioelectronic implant. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 29, 101576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; He, Z.; Peng, X.; Xie, J.; Su, F.; Wei, D.-X.; Zheng, Y.; Yao, D. Injectable, Intrinsically Antibacterial Conductive Hydrogels with Self-Healing and pH Stimulus Responsiveness for Epidermal Sensors and Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 53541–53552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.; Ye, Z.; Ye, Z.; Deng, J.; Lin, J.; Wu, C.; Zhu, H. Citric acid crosslinked sphingan WL gum hydrogel films supported ciprofloxacin for potential wound dressing application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 291, 119520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
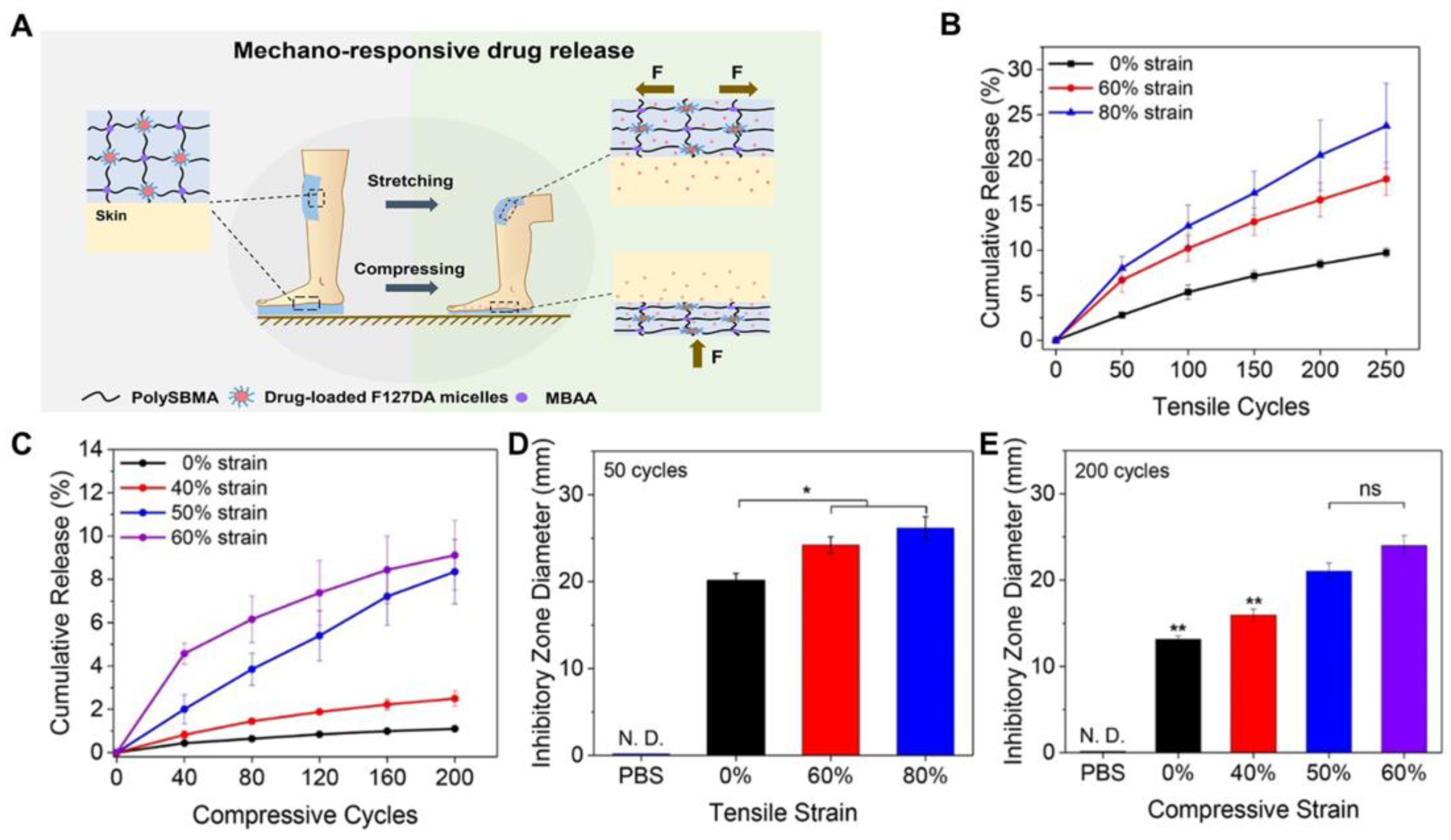
- Fang, K.; Wang, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, L.; Xu, T.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, G.; Chen, J.; Liu, D.; et al. Mechano-Responsive, Tough, and Antibacterial Zwitterionic Hydrogels with Controllable Drug Release for Wound Healing Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 52307–52318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, J.; Tang, S.; Saiding, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Cui, W. Microenvironment-Protected Exosome-Hydrogel for Facilitating Endometrial Regeneration, Fertility Restoration, and Live Birth of Offspring. Small 2021, 17, 2007235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Bi, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, R.; Wang, H.; Gu, J. Skin-inspired antibacterial conductive hydrogels customized for wireless flexible sensor and collaborative wound healing. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 14096–14107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Sun, Q.; Shi, X.; Sun, Z.; Tan, S.; Tang, B.; Chen, W.; Liang, F.; Yu, H.-D.; Huang, W. Skin-interfaced self-powered pressure and strain sensors based on fish gelatin-based hydrogel for wireless wound strain and human motion detection. Nano Energy 2023, 118, 108932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, S.B.; Thambusamy, S. Preparation of silver nanoparticles and riboflavin embedded electrospun polymer nanofibrous scaffolds for in vivo wound dressing application. Process Biochem. 2020, 88, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khansa, I.; Schoenbrunner, A.R.; Kraft, C.T.; Janis, J.E. Silver in Wound Care—Friend or Foe?: A Comprehensive Review. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2019, 7, e2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, H.; Schmid-Hempel, P. Socially transmitted gut microbiota protect bumble bees against an intestinal parasite. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19288–19292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, C.; Guo, J.; Deng, M.; Qu, X.; Huang, P.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, J. Versatile Hydrogel Dressing with Skin Adaptiveness and Mild Photothermal Antibacterial Activity for Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus-Infected Dynamic Wound Healing. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2206585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Su, Y.; Wang, C.; Lei, B.; Song, X.; Wang, W.; Wu, P.; Liu, X.; Dong, X.; Zhong, L. Injectable Tissue-Adhesive Hydrogel for Photothermal/Chemodynamic Synergistic Antibacterial and Wound Healing Promotion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 2714–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, B.; Peng, D.; Nie, X.; Wang, J.; Yu, C.-Y.; Wei, H. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Injectable Hydrogels for Wound Dressing and Localized Tumor Therapy: A Review. Adv. NanoBiomed Res. 2022, 2, 2200124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, D.; Xing, W.; Jiang, L.; Fang, J.; Zhao, C.; Ren, F.; Fang, L.; Wang, K.; Lu, X. Plant-inspired adhesive and tough hydrogel based on Ag-Lignin nanoparticles-triggered dynamic redox catechol chemistry. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Geiss, C.; Zarse, K.; Madreiter-Sokolowski, C.T.; Ristow, M. Green tea catechins EGCG and ECG enhance the fitness and lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans by complex I inhibition. Aging 2021, 13, 22629–22648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Liang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Pan, G.; Guo, B. Injectable stretchable self-healing dual dynamic network hydrogel as adhesive anti-oxidant wound dressing for photothermal clearance of bacteria and promoting wound healing of MRSA infected motion wounds. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 132039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, C.; Chang, R.; He, Y.; Guan, F.; Yao, M. Ultra-stretchable, tissue-adhesive, shape-adaptive, self-healing, on-demand removable hydrogel dressings with multiple functions for infected wound healing in regions of high mobility. Acta Biomater. 2023, 166, 224–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joorabloo, A.; Liu, T. Recent advances in reactive oxygen species scavenging nanomaterials for wound healing. Exploration 2024, 20230066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

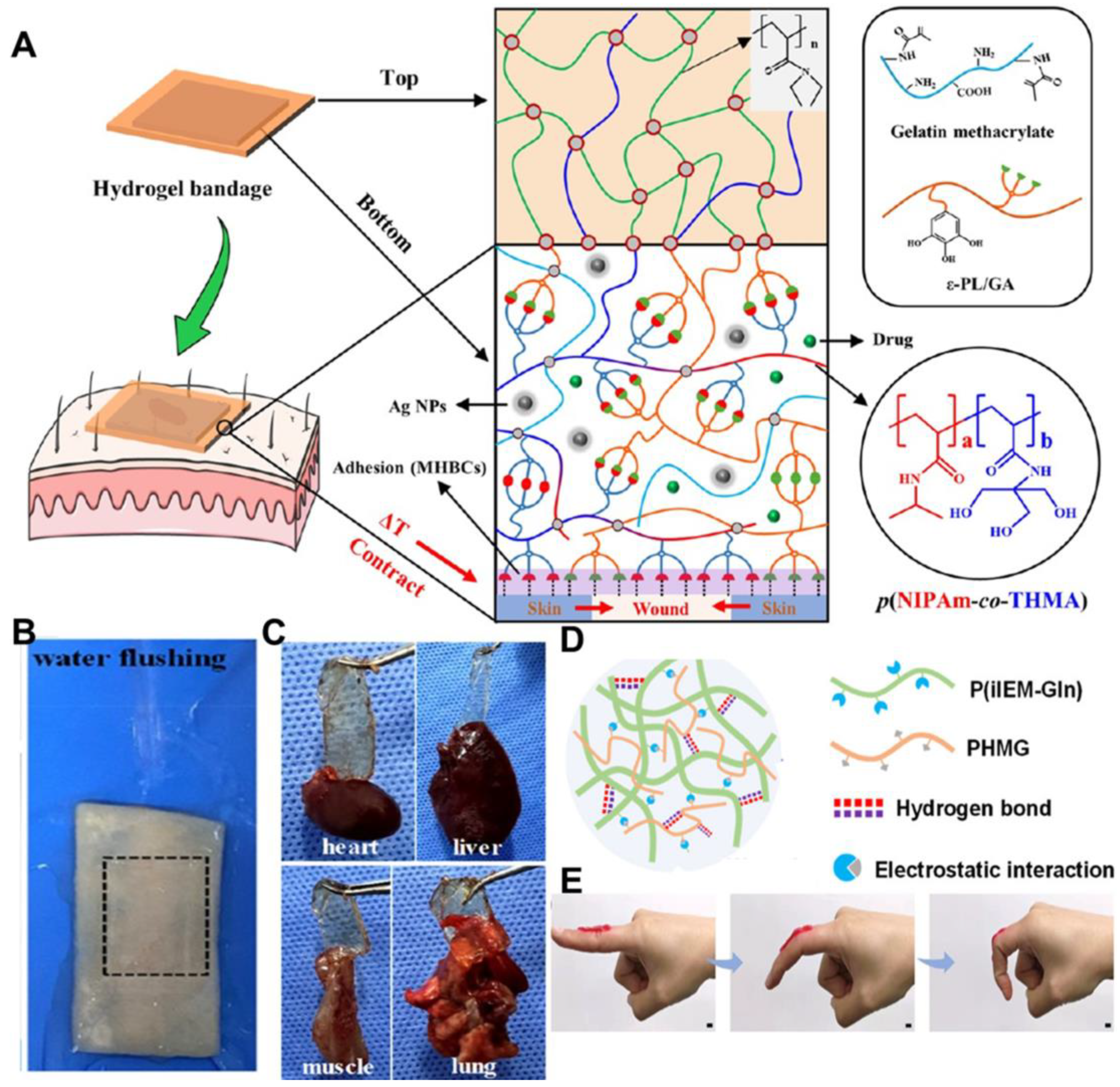
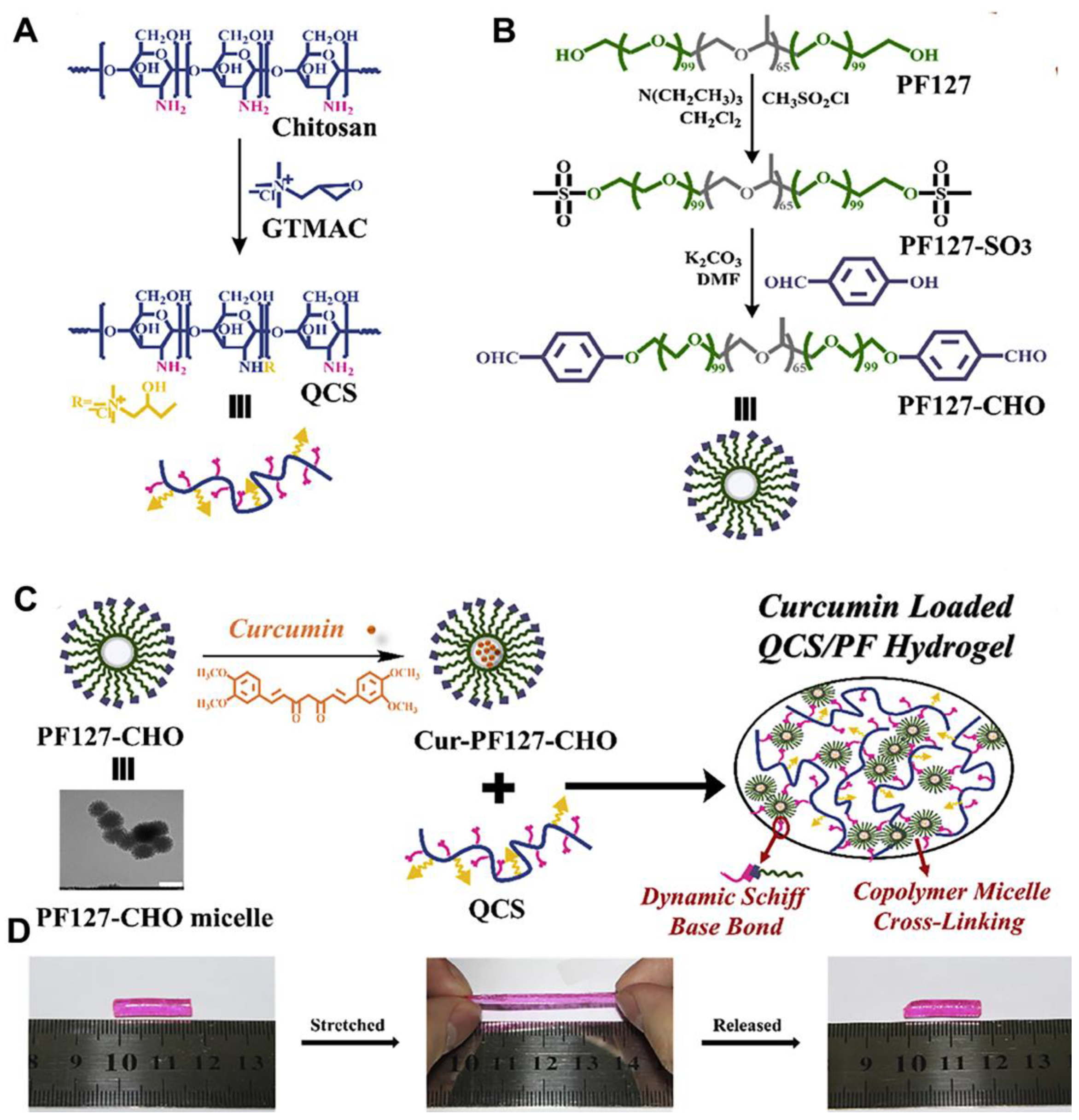
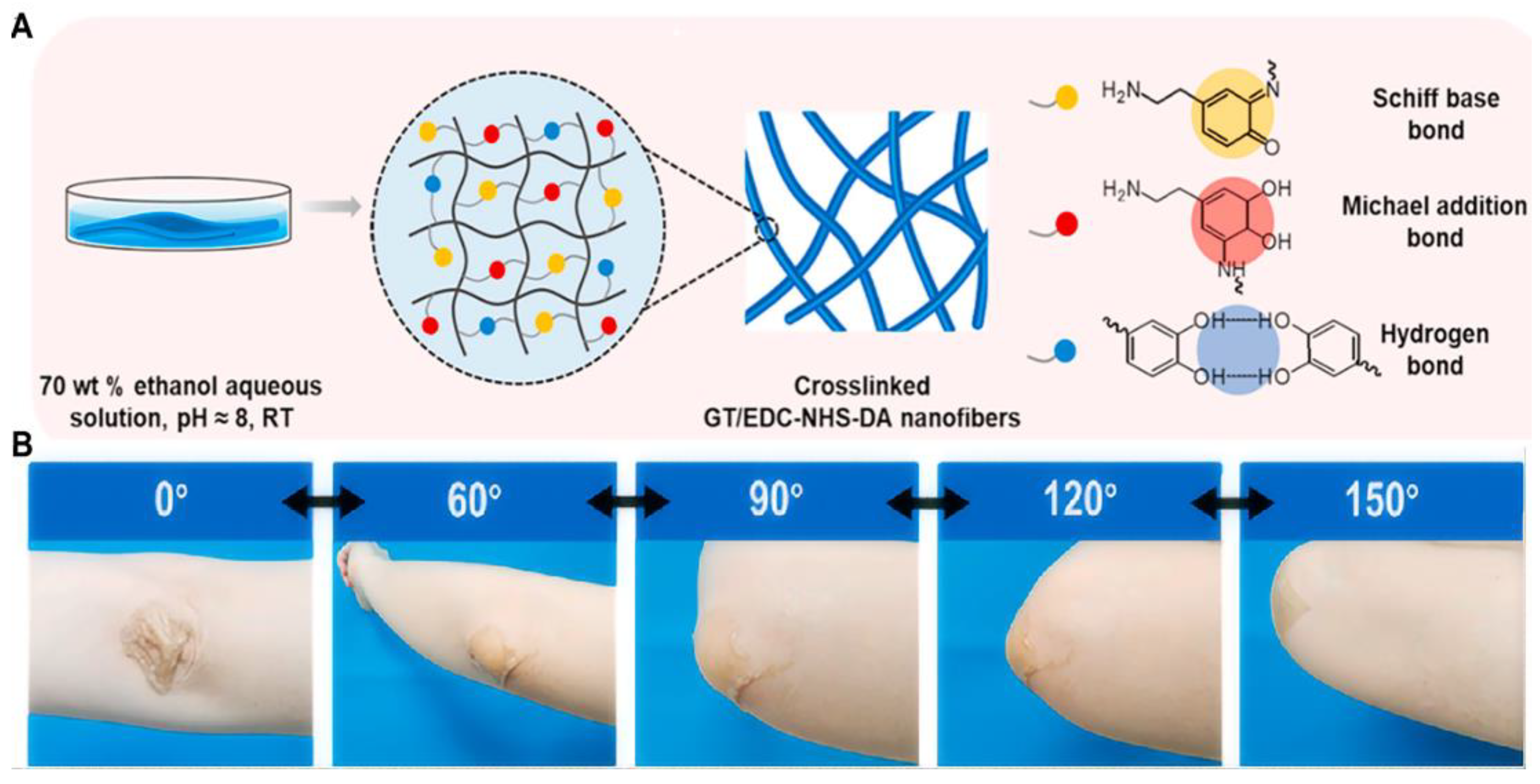

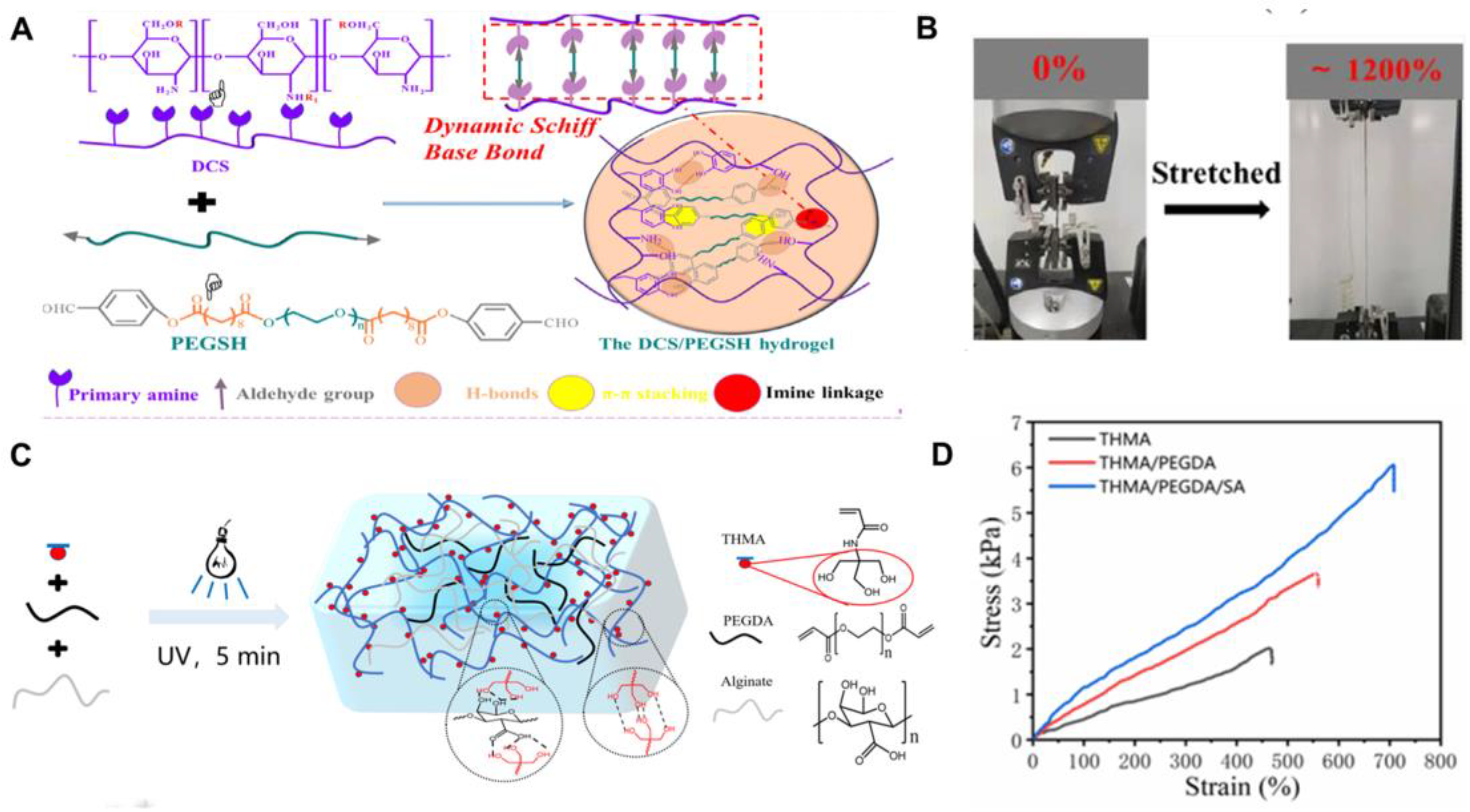



| Hydrogels | Crosslinkage | Mechanical Properties | Refs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Stress (kPa) | Tensile Strain (%) | Compressive Strain (%) | Adhesive Strength (kPa) | |||
| QCS/PF | Chemical | 9.8~25.7 | 58.2~761 | - | 6.1 ± 1.2 | [42] |
| GT-ATx/QCS/CD | Chemical | - | - | 70 | 7.75~31.5 | [43] |
| GT/EDC-NHS-DA | Chemical | 2240 | 225 | - | - | [44] |
| SMA/CNFs/PAM | Physical | 550 | 4100 | 25 | - | [45] |
| P(AM-HisMA) | Physical | 77 | 5800 | 80 | - | [46] |
| DCS-PEGSH | Chemical/ Physical | - | 1200 | 81 | 68.5 | [47] |
| THMA/PEGDA/SA | Chemical/ Physical | - | 700 | 60 | 7.5 | [48] |
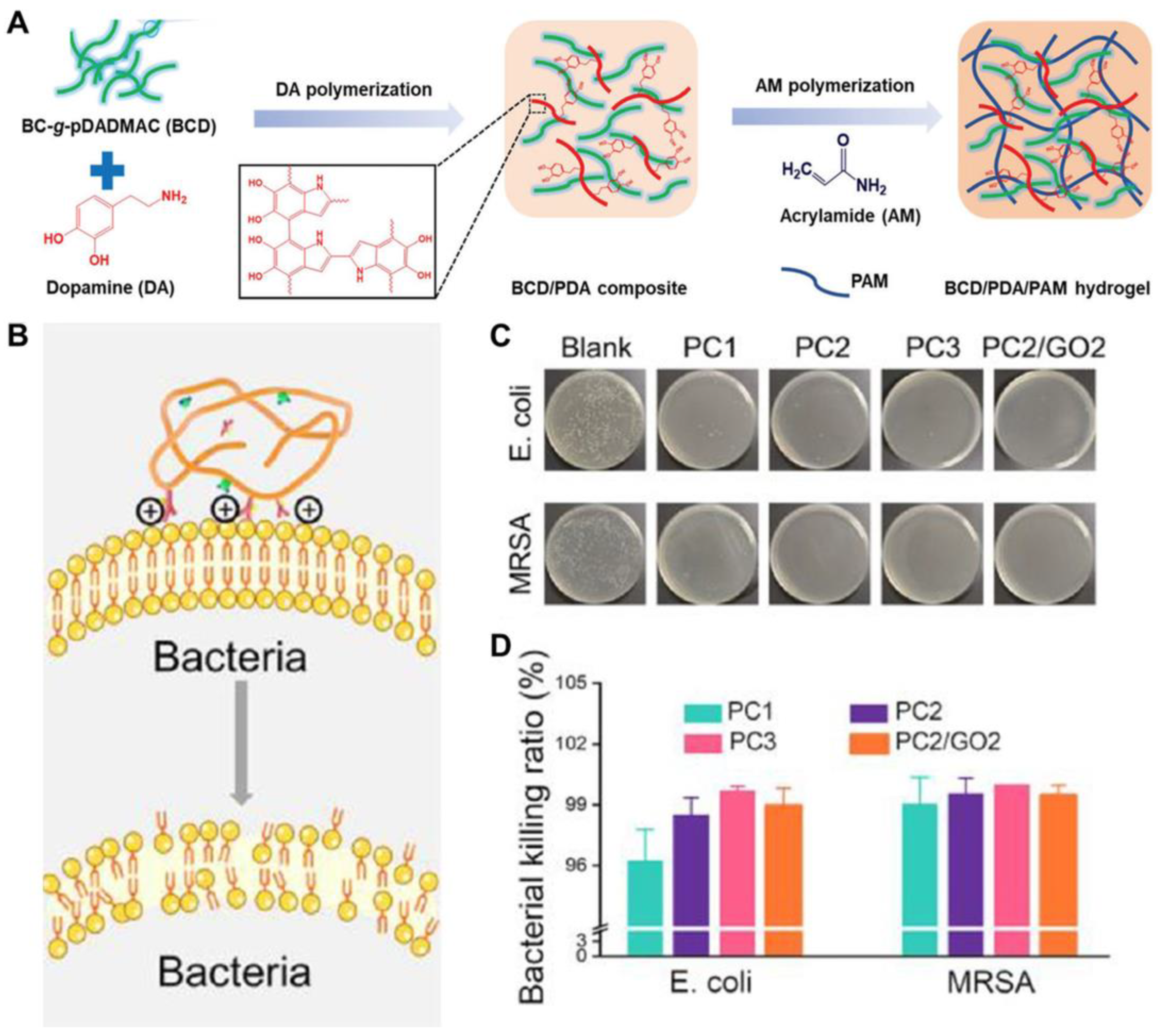
| BCD/PDA/PAM | Chemical/ Physical | 21~51 | 899~1047 | 60 | 15~20 | [38] |
| OCMC-DA/PB | Chemical/ Physical | - | 3000 | - | - | [39] |
| PAM/CMCS-RGO -Fe3+ | Chemical/ Physical | - | - | 82 | - | [41] |
| Hydrogels | Antibacterial Activity | Active Ingredients | Refs. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | S. aureus | MRSA | |||
| BCD/PDA/PAM | - | - | - | Positively charged quaternary ammonium groups | [38] |
| SA3DMC25-Gly80P7 | - | - | - | Quaternary ammonium compounds | [55] |
| QCS-PF127-CHO | >90% | >90% | - | Positively charged amino groups and quaternary ammonium groups | [42] |
| iGx/PHMGy | 92% | 93% | - | Positively charged PHMG | [56] |
| CHHCMgel | 95.4% | 94.2% | - | Chitosan aldehyde groups | [57] |
| PC | 98.9% | - | 99% | L-arginine | [22] |
| CPT | - | - | - | Chitosan/(C=N) | [58] |
| WL-CA-CIP | - | - | - | CIP | [59] |
| CS/CA/Alo | 80% | 90% | - | CS/ALO | [39] |
| F6S4.0R | - | - | - | Rifampicin | [60] |
| AM-co-SBMA | 91.25% | 99.08% | 89.22% | Ag | [25] |
| PEGSD/Zn2+ | 100% | - | 90% | Zn2+ | [27] |
| rGB/QCS/PDA-PAM | 94.6% | - | 96.6% | rGB-PTT | [61] |
| DCS-PEGSH | >95% | >95% | - | Catechol | [47] |
| HA-PEGSB-CMP | >90% | >90% | - | CMP-PTT | [62] |
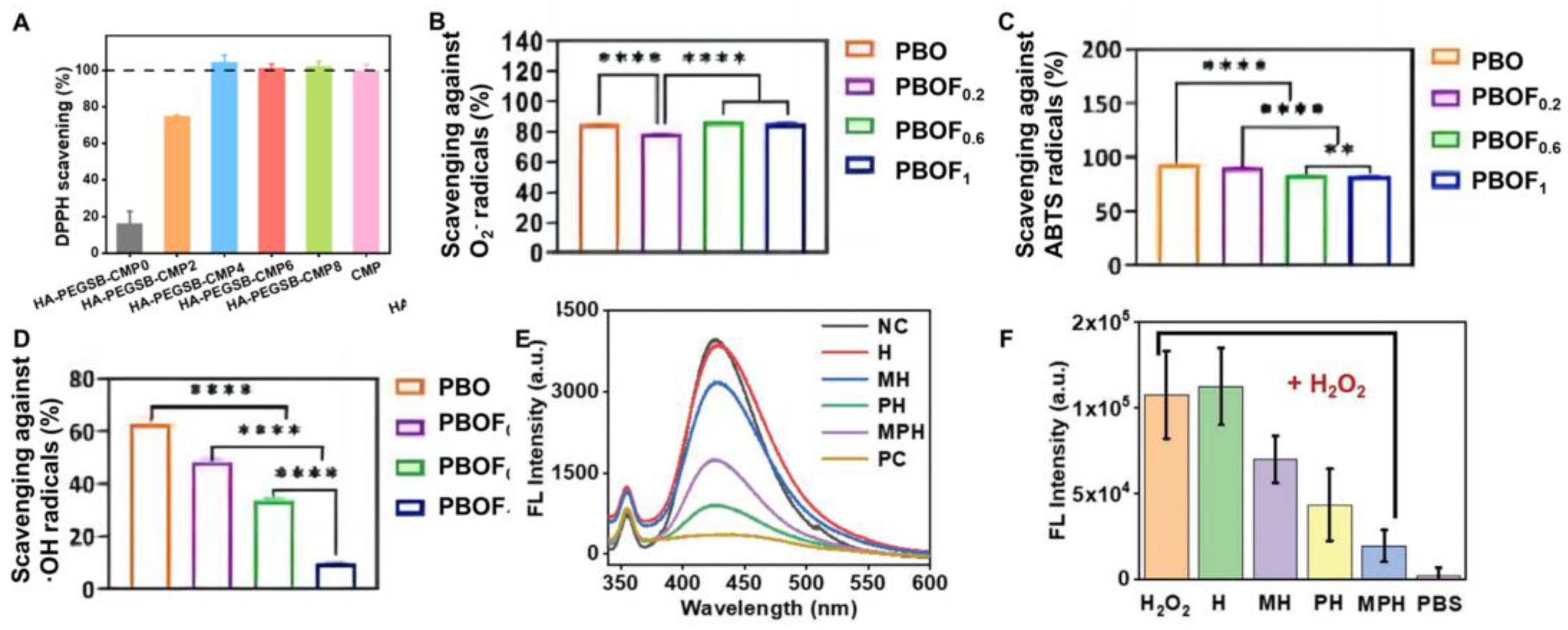
| PBOF | 99.1% | 99.4% | - | ferricion/polyphenol chelate-PTT | [63] |
| MPH | 93.9% | 99.1% | - | MoS2-PTT | [51] |
| Hydrogels | Antioxidant Activities | Active Ingredients | Refs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROS | ·OH | O2·− | |||
| QCS-PF127-CHO | >80% | - | - | Curcumin | [42] |
| PC | >100% | - | - | catechol structure | [22] |
| CS/CA/Alo | - | - | - | CS/ALO | [39] |
| PEGSD/Zn2+ | 84.5% | - | - | Catechol groups | [27] |
| DCS-PEGSH | 86% | - | - | Catechol | [47] |
| HA-PEGSB-CMP | 100% | - | - | CMP | [62] |
| Cur-QCS/PF | - | - | - | Curcumin | [42] |
| PBOF | - | 63.0% | 84% | Oligomeric procyanidin | [63] |
| MPH | - | - | - | MoS2-PDA nanozyme | [51] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, P.; Wei, L.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Ma, H.; Zhao, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, R.; Cheng, Y. Hydrogel Wound Dressings Accelerating Healing Process of Wounds in Movable Parts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6610. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126610
Yu P, Wei L, Yang Z, Liu X, Ma H, Zhao J, Liu L, Wang L, Chen R, Cheng Y. Hydrogel Wound Dressings Accelerating Healing Process of Wounds in Movable Parts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(12):6610. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126610
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Pengcheng, Liqi Wei, Zhiqi Yang, Xin Liu, Hongxia Ma, Jian Zhao, Lulu Liu, Lili Wang, Rui Chen, and Yan Cheng. 2024. "Hydrogel Wound Dressings Accelerating Healing Process of Wounds in Movable Parts" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 12: 6610. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126610
APA StyleYu, P., Wei, L., Yang, Z., Liu, X., Ma, H., Zhao, J., Liu, L., Wang, L., Chen, R., & Cheng, Y. (2024). Hydrogel Wound Dressings Accelerating Healing Process of Wounds in Movable Parts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(12), 6610. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126610






