Serum Caspase-3 Levels as a Predictive Molecular Biomarker for Acute Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Description of the Study Population
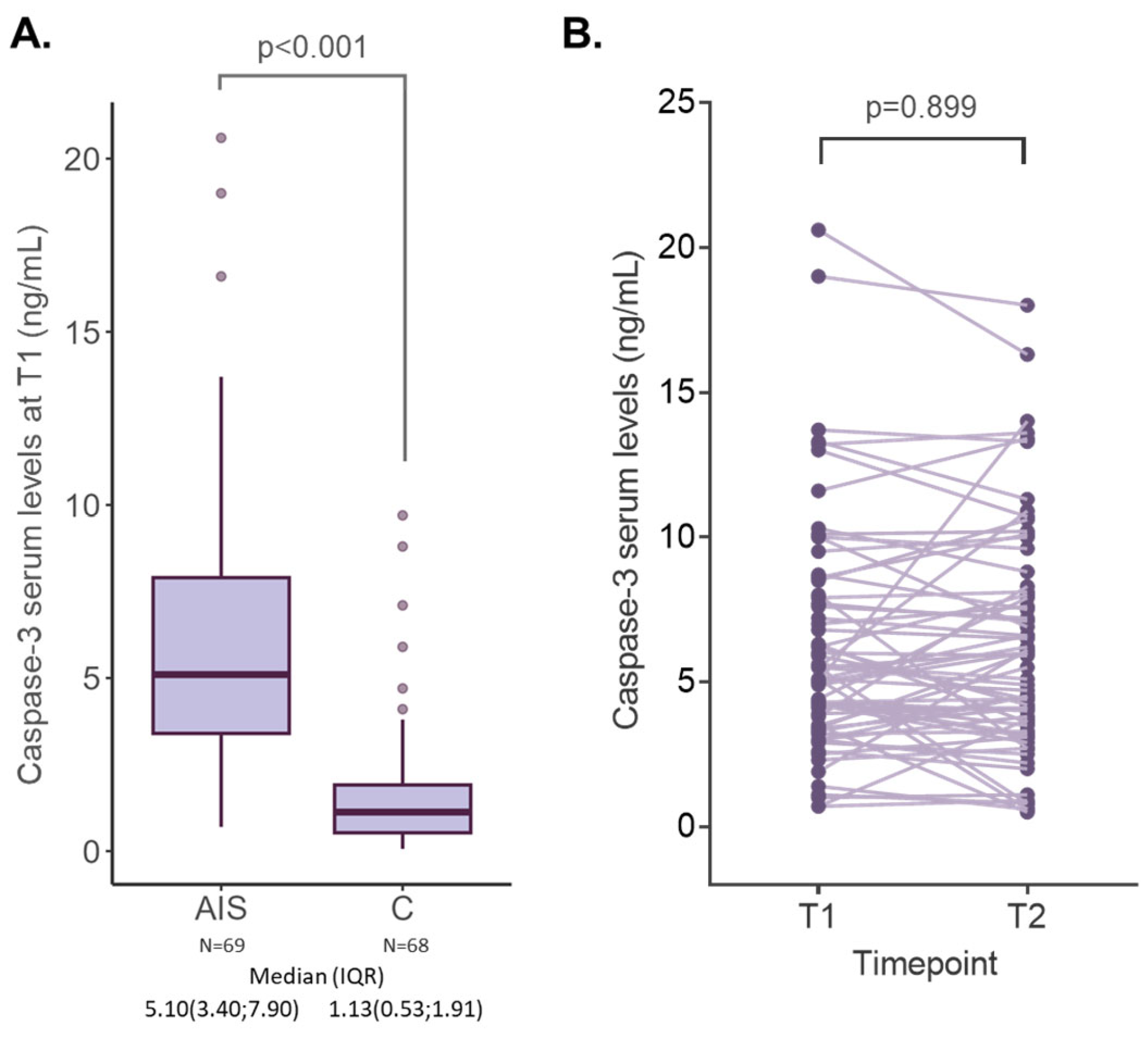
2.2. Caspase-3 Serum Levels in AIS and Control Subjects
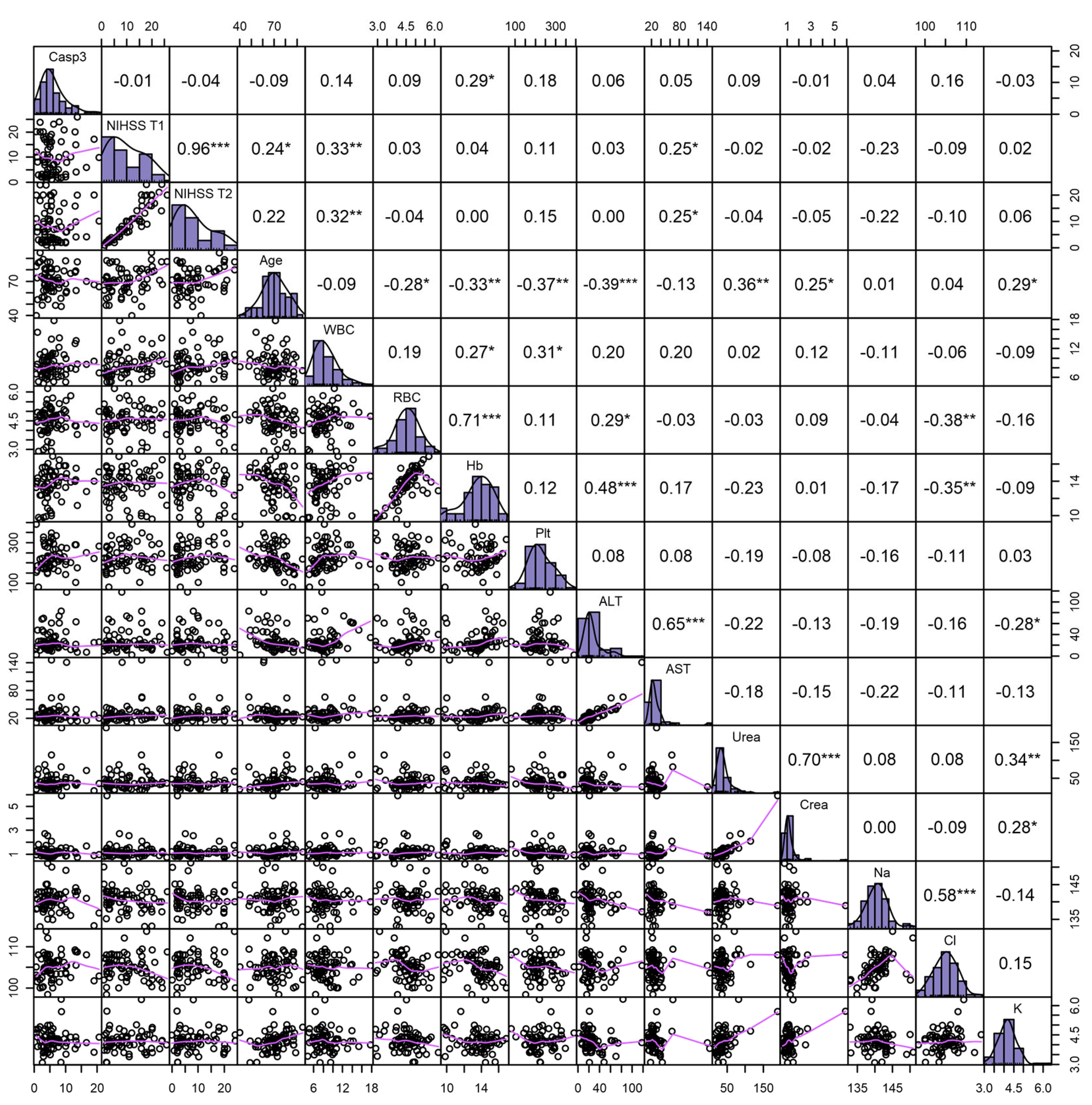
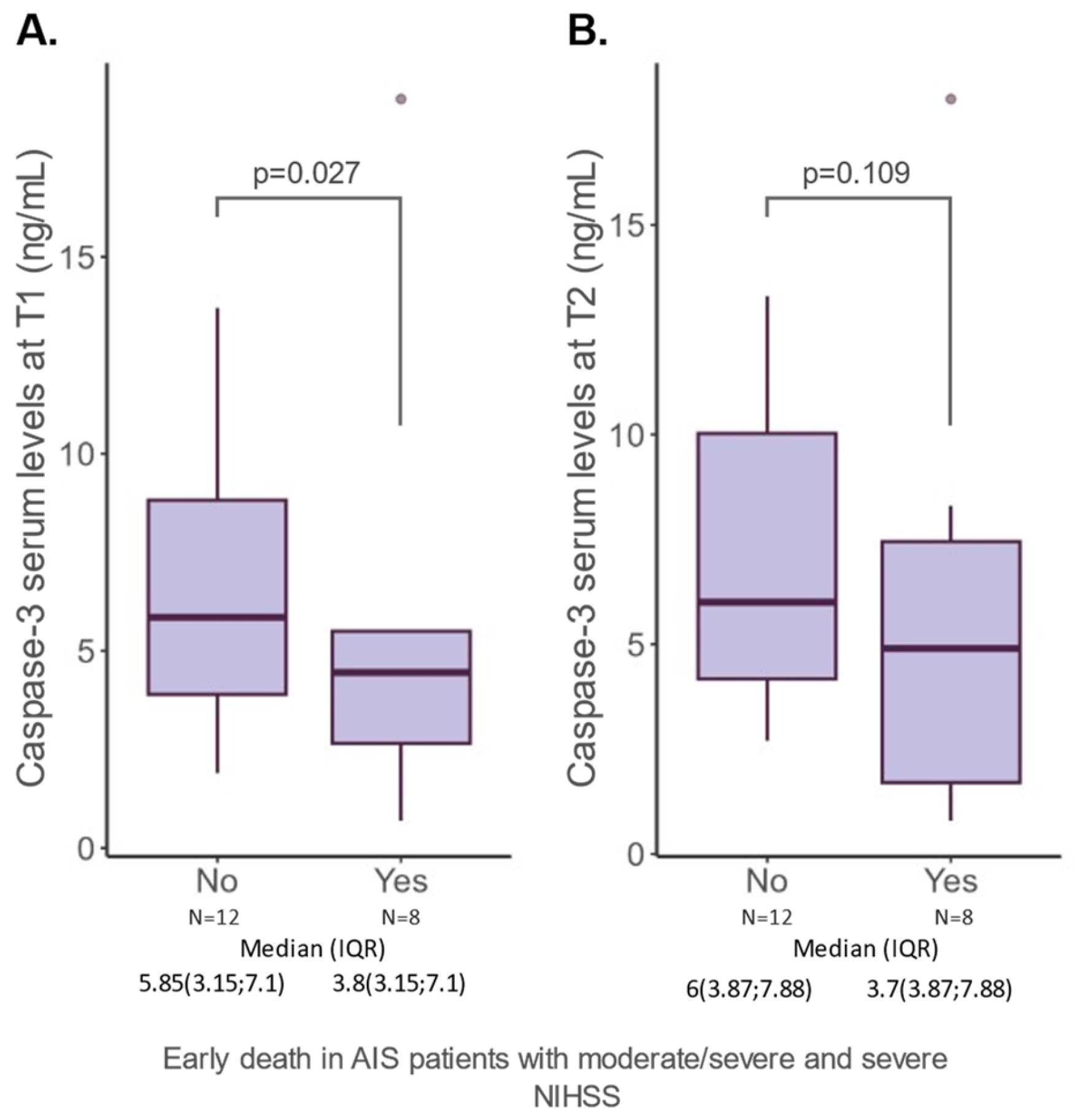
2.3. Caspase-3 Serum Levels and Features of AIS Patients
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Patients’ Selection
4.3. Patient Data Collection
4.4. Blood Work and Caspase-3 Dosing
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsao, C.W.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Alonso, A.; Beaton, A.Z.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Boehme, A.K.; Buxton, A.E.; Carson, A.P.; Commodore-Mensah, Y.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2022 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022, 145, e153–e639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, N.; Harada, M.; Uno, M.; Matsubara, S.; Nagahiro, S.; Nishitani, H. Evaluation of Initial Diffusion-Weighted Image Findings in Acute Stroke Patients Using a Semiquantitative Score. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2009, 8, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.-A.; Kim, J.; Kim, O.-J.; Kim, J.-K.; Kim, N.-K.; Song, J.; Oh, S.-H. Limited Clinical Value of Multiple Blood Markers in the Diagnosis of Ischemic Stroke. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotgiu, S.; Zanda, B.; Marchetti, B.; Fois, M.L.; Arru, G.; Pes, G.M.; Salaris, F.S.; Arru, A.; Pirisi, A.; Rosati, G. Inflammatory Biomarkers in Blood of Patients with Acute Brain Ischemia. Eur. J. Neurol. 2006, 13, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, R.; Soriano, M.; Blomgren, K.; Hagberg, H.; Wybrecht, R.; Therese, M.; Hoefer, S.; Adam, G.; Niederhauser, O.; Kemp, J.A.; et al. Role of Caspase-3 Activation in Cerebral Ischemia-Induced Neurodegeneration in Adult and Neonatal Brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2002, 22, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalini, S.; Dorstyn, L.; Dawar, S.; Kumar, S. Old, New and Emerging Functions of Caspases. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobeica, C.; Niculet, E.; Craescu, M.; Parapiru, E.-L.; Musat, C.L.; Dinu, C.; Chiscop, I.; Nechita, L.; Debita, M.; Stefanescu, V.; et al. CREST syndrome in systemic sclerosis patients—Is dystrophic calcinosis a key element to a positive diagnosis? J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 3387–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaner, J.; Mendioroz, M.; Ribó, M.; Delgado, P.; Quintana, M.; Penalba, A.; Chacón, P.; Molina, C.; Fernández-Cadenas, I.; Rosell, A.; et al. A Panel of Biomarkers Including Caspase-3 and D-Dimer May Differentiate Acute Stroke from Stroke-Mimicking Conditions in the Emergency Department. J. Intern. Med. 2011, 270, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, G.; Beer, R.; Intemann, D.; Krajewski, S.; Reed, J.C.; Engelhardt, K.; Pike, B.R.; Hayes, R.L.; Wang, K.K.; Schmutzhard, E.; et al. Temporal and Spatial Profile of Bid Cleavage after Experimental Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2002, 22, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S.; Ma, X.; Kong, J. BNIP3 Upregulation and EndoG Translocation in Delayed Neuronal Death in Stroke and in Hypoxia. Stroke 2007, 38, 1606–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaner, J.; Perea-Gainza, M.; Delgado, P.; Ribó, M.; Chacón, P.; Rosell, A.; Quintana, M.; Palacios, M.E.; Molina, C.A.; Alvarez-Sabín, J. Etiologic Diagnosis of Ischemic Stroke Subtypes with Plasma Biomarkers. Stroke 2008, 39, 2280–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, A.; Hayashi, T.; Okuno, S.; Ferrand-Drake, M.; Chan, P.H. Overexpression of Copper/Zinc Superoxide Dismutase in Transgenic Mice Protects against Neuronal Cell Death after Transient Focal Ischemia by Blocking Activation of the Bad Cell Death Signaling Pathway. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 1710–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodhe, J.; Burguillos, M.A.; de Pablos, R.M.; Kavanagh, E.; Persson, A.; Englund, E.; Deierborg, T.; Venero, J.L.; Joseph, B. Spatio-Temporal Activation of Caspase-8 in Myeloid Cells upon Ischemic Stroke. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2016, 4, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Guillamon, M. Caspase-3 Is Related to Infarct Growth after Human Ischemic Stroke. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 430, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Iluţ, S.; Vesa, Ş.C.; Văcăraș, V.; Mureșanu, D.-F. Predictors of Short-Term Mortality in Patients with Ischemic Stroke. Medicina 2023, 59, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rost, N.S.; Bottle, A.; Lee, J.; Randall, M.; Middleton, S.; Shaw, L.; Thijs, V.; Rinkel, G.J.E.; Hemmen, T.M.; The Global Comparators Stroke GOAL Collaborators; et al. Stroke Severity Is a Crucial Predictor of Outcome: An International Prospective Validation Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wafa, H.A.; Wolfe, C.D.A.; Emmett, E.; Roth, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Wang, Y. Burden of Stroke in Europe. Stroke 2020, 51, 2418–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Dai, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhu, X.; Cai, P.; Wang, L.; Sun, C.; Hu, C.; Zheng, P.; Zhao, B. Caspase-3 Modulates Regenerative Response After Stroke. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, R.; Zong, N.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y. Neuronal Death Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategy in Ischemic Stroke. Neurosci. Bull. 2022, 38, 1229–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glushakova, O.Y.; Glushakov, A.A.; Wijesinghe, D.S.; Valadka, A.B.; Hayes, R.L.; Glushakov, A.V. Prospective Clinical Biomarkers of Caspase-Mediated Apoptosis Associated with Neuronal and Neurovascular Damage Following Stroke and Other Severe Brain Injuries: Implications for Chronic Neurodegeneration. Brain Circ. 2017, 3, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Colbourne, F.; Sun, P.; Zhao, Z.; Buchan, A.M. Caspase Inhibitors Reduce Neuronal Injury After Focal but Not Global Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. Stroke 2000, 31, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, T.; Fujimura, M.; Noshita, N.; Kim, G.W.; Saito, A.; Hayashi, T.; Narasimhan, P.; Maier, C.M.; Chan, P.H. Neuronal Death/Survival Signaling Pathways in Cerebral Ischemia. Neurotherapeutics 2004, 1, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, J.R.; Blessing, R.; White, W.D.; Grocott, H.P.; Newman, M.F.; Laskowitz, D.T. Novel Diagnostic Test for Acute Stroke. Stroke 2004, 35, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asahi, M.; Hoshimaru, M.; Uemura, Y.; Tokime, T.; Kojima, M.; Ohtsuka, T.; Matsuura, N.; Aoki, T.; Shibahara, K.; Kikuchi, H. Expression of Interleukin-1β Converting Enzyme Gene Family and Bcl-2 Gene Family in the Rat Brain Following Permanent Occlusion of the Middle Cerebral Artery. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1997, 17, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namura, S.; Zhu, J.; Fink, K.; Endres, M.; Srinivasan, A.; Tomaselli, K.J.; Yuan, J.; Moskowitz, M.A. Activation and Cleavage of Caspase-3 in Apoptosis Induced by Experimental Cerebral Ischemia. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 3659–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Wu, A.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Xu, F. Correlation between Neuronal Injury and Caspase-3 after Focal Ischemia in Human Hippocampus. Chin. Med. J. 2004, 117, 1507–1512. [Google Scholar]
- Fink, K.; Zhu, J.; Namura, S.; Shimizu-Sasamata, M.; Endres, M.; Ma, J.; Dalkara, T.; Yuan, J.; Moskowitz, M.A. Prolonged Therapeutic Window for Ischemic Brain Damage Caused by Delayed Caspase Activation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1998, 18, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troy, C.M.; Akpan, N.; Jean, Y.Y. Chapter 7—Regulation of Caspases in the Nervous System: Implications for Functions in Health and Disease. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science; Di Cera, E., Ed.; Proteases in Health and Disease; Academic Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; Volume 99, pp. 265–305. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, E.D.; Wells, J.A. Caspase Substrates and Cellular Remodeling. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2011, 80, 1055–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldadah, B.A.; Faden, A.I. Caspase Pathways, Neuronal Apoptosis, and CNS Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2000, 17, 811–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gafuroğulları, S.; İşler, Y.; Kaya, H.; Yüksel, M.; Sır, Z.N.; Nennicioglu, Y. Can Caspase 3 Activity Determine Stroke Duration? Eurasian J. Crit. Care 2021, 3, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Linfante, I.; Llinas, R.H.; Schlaug, G.; Chaves, C.; Warach, S.; Caplan, L.R. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale in the Acute Phase of Posterior-Circulation Stroke. Arch. Neurol. 2001, 58, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustamante, A.; López-Cancio, E.; Pich, S.; Penalba, A.; Giralt, D.; García-Berrocoso, T.; Ferrer-Costa, C.; Gasull, T.; Hernández-Pérez, M.; Millan, M.; et al. Blood Biomarkers for the Early Diagnosis of Stroke. Stroke 2017, 48, 2419–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manabat, C.; Han, B.H.; Wendland, M.; Derugin, N.; Fox, C.K.; Choi, J.; Holtzman, D.M.; Ferriero, D.M.; Vexler, Z.S. Reperfusion Differentially Induces Caspase-3 Activation in Ischemic Core and Penumbra after Stroke in Immature Brain. Stroke 2003, 34, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, H.P.; Bendixen, B.H.; Kappelle, L.J.; Biller, J.; Love, B.B.; Gordon, D.L.; Marsh, E.E. Classification of Subtype of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Definitions for Use in a Multicenter Clinical Trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 1993, 24, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharia, A.-L.; Tutunaru, D.; Oprea, V.D.; Tănase, C.E.; Croitoru, A.; Stan, B.; Voinescu, D.C.; Ionescu, A.-M.; Coadǎ, C.A.; Lungu, M. Thrombomodulin Serum Levels—A Predictable Biomarker for the Acute Onset of Ischemic Stroke. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
| Variable | Total N = 137 | Control Group N = 68 | AIS Group N = 69 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender N (%) | Female | 56 (40.88) | 30 (44.12) | 26 (37.68) | 0.444 |
| Male | 81 (59.12) | 38 (55.88) | 43 (62.32) | ||
| Age [years] mean ± sd | 69.77 ± 10.69 | 69.28 ± 10.5 | 70.23 ± 11.01 | 0.605 | |
| Residential background N (%) | Urban | 81 (59.12) | 36 (52.94) | 45 (65.22) | 0.144 |
| Rural | 56 (40.88) | 32 (47.06) | 24 (34.78) | ||
| Comorbidities | |||||
| Atrial Fibrillation N (%) | No | 94 (68.61) | 51 (75) | 43 (62.32) | 0.110 |
| Yes | 43 (31.39) | 17 (25) | 26 (37.68) | ||
| Dyslipidemia N (%) | No | 60 (43.8) | 34 (50) | 26 (37.68) | 0.146 |
| Yes | 77 (56.2) | 34 (50) | 43 (62.32) | ||
| Diabetes N (%) | No | 96 (70.07) | 41 (60.29) | 55 (79.71) | 0.013 |
| Yes | 41 (29.93) | 27 (39.71) | 14 (20.29) | ||
| Blood hypertension N (%) | grade 1 | 16 (11.68) | 11 (16.18) | 5 (7.25) | 0.033 |
| grade 2 | 56 (40.88) | 32 (47.06) | 24 (34.78) | ||
| grade 3 | 65 (47.45) | 25 (36.76) | 40 (57.97) |
| Variable | Caspase-3 T1 Median (IQR) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Comorbidities | |||
| Atrial fibrillation N (%) | no | 5.5 (3.25; 7.85) | 0.827 |
| yes | 4.95 (3.58; 7.73) | ||
| Blood hypertension grade N (%) | 1 | 3.3 (1.4; 6) | 0.261 |
| 2 | 5.2 (4.12; 7.18) | ||
| 3 | 5.1 (3.48; 8.53) | ||
| Dyslipidemia N (%) | no | 5.3 (2.72; 9.3) | 0.75 |
| yes | 5.1 (3.7; 6.55) | ||
| Obesity N (%) | no | 5 (3.38; 7.78) | 0.269 |
| yes | 6.2 (5.5; 7.9) | ||
| Diabetes mellitus N (%) | no | 5.1 (3.35; 8.25) | 0.581 |
| yes | 4.7 (4.15; 5.8) | ||
| AIS features | |||
| AIS type N (%) | Cardioembolic | 4.95 (3.58; 7.73) | 0.827 |
| Atherothrombotic | 5.5 (3.25; 7.85) | ||
| Ischemic territory (anatomic segment) N (%) | Left sylvian | 5.5 (3.4; 8.75) | 0.489 |
| Right sylvian | 5.05 (3.45; 7.05) | ||
| Vertebrobasilar | 5.75 (4.3; 8.28) | ||
| NIHSS severity at admission N (%) | 0–4. minor stroke | 5.55 (3.6; 7.45) | 0.543 |
| 5–15. moderate stroke | 5 (3.45; 7.8) | ||
| 16–20. moderate to severe | 4.9 (3.15; 5.5) | ||
| 21–42. severe | 8 (6.2; 9.5) | ||
| NIHSS improvement at 48 h N (%) | no | 5 (3.15; 6.95) | 0.581 |
| yes | 5.55 (3.67; 8.45) | ||
| Early death N (%) | no | 5.1 (3.5; 8) | 0.735 |
| yes | 4.45 (2.65; 5.5) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaharia, A.-L.; Oprea, V.D.; Coadă, C.A.; Tutunaru, D.; Romila, A.; Stan, B.; Croitoru, A.; Ionescu, A.-M.; Lungu, M. Serum Caspase-3 Levels as a Predictive Molecular Biomarker for Acute Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126772
Zaharia A-L, Oprea VD, Coadă CA, Tutunaru D, Romila A, Stan B, Croitoru A, Ionescu A-M, Lungu M. Serum Caspase-3 Levels as a Predictive Molecular Biomarker for Acute Ischemic Stroke. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(12):6772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126772
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaharia, Andrei-Lucian, Violeta Diana Oprea, Camelia Alexandra Coadă, Dana Tutunaru, Aurelia Romila, Bianca Stan, Ana Croitoru, Ana-Maria Ionescu, and Mihaiela Lungu. 2024. "Serum Caspase-3 Levels as a Predictive Molecular Biomarker for Acute Ischemic Stroke" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 12: 6772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126772
APA StyleZaharia, A.-L., Oprea, V. D., Coadă, C. A., Tutunaru, D., Romila, A., Stan, B., Croitoru, A., Ionescu, A.-M., & Lungu, M. (2024). Serum Caspase-3 Levels as a Predictive Molecular Biomarker for Acute Ischemic Stroke. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(12), 6772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25126772






