Mitochondrial Elongation and ROS-Mediated Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer Cells under Therapy with Apalutamide and Complex I Inhibitor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
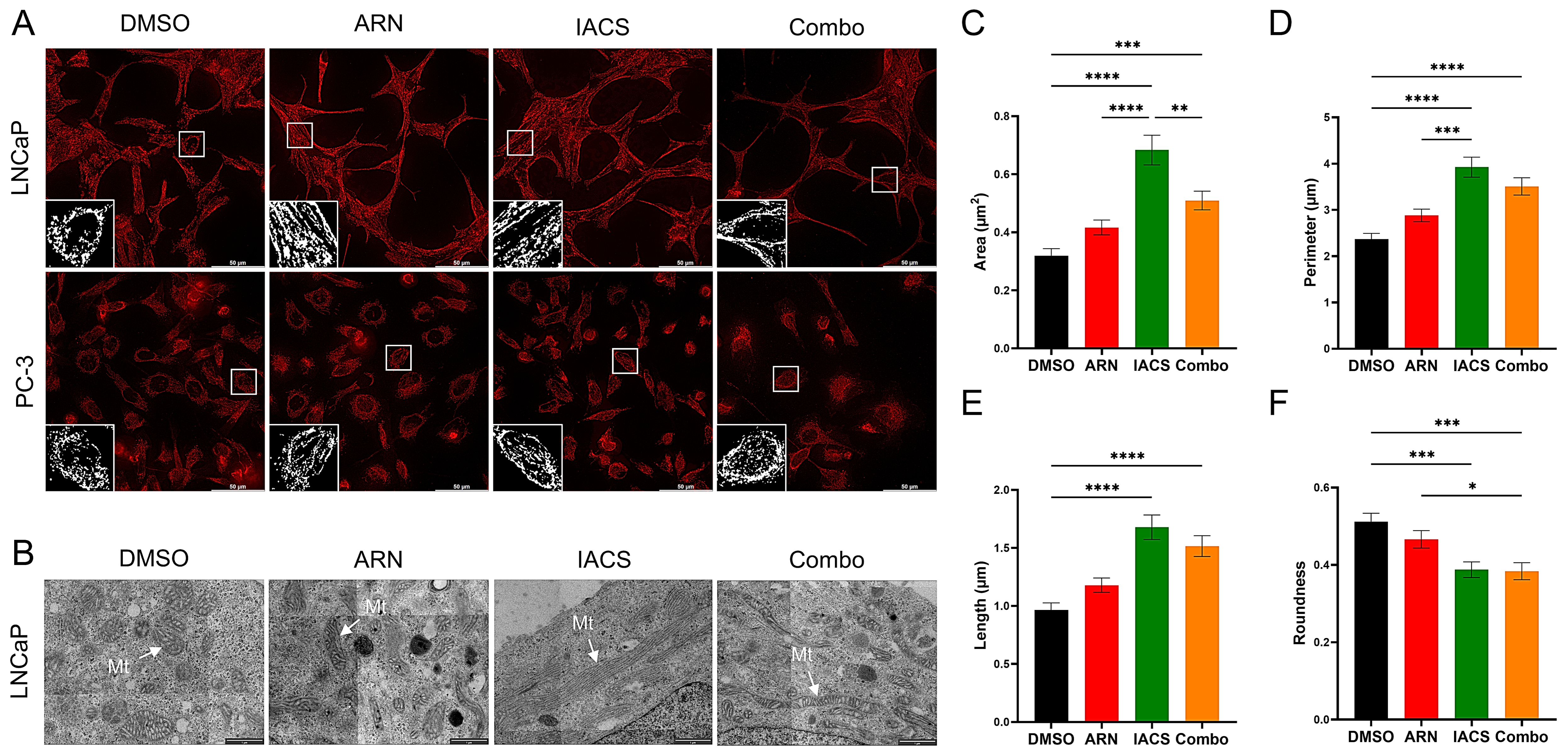
2.1. ARN and IACS Modulate Mitochondrial Network Architecture and Morphology
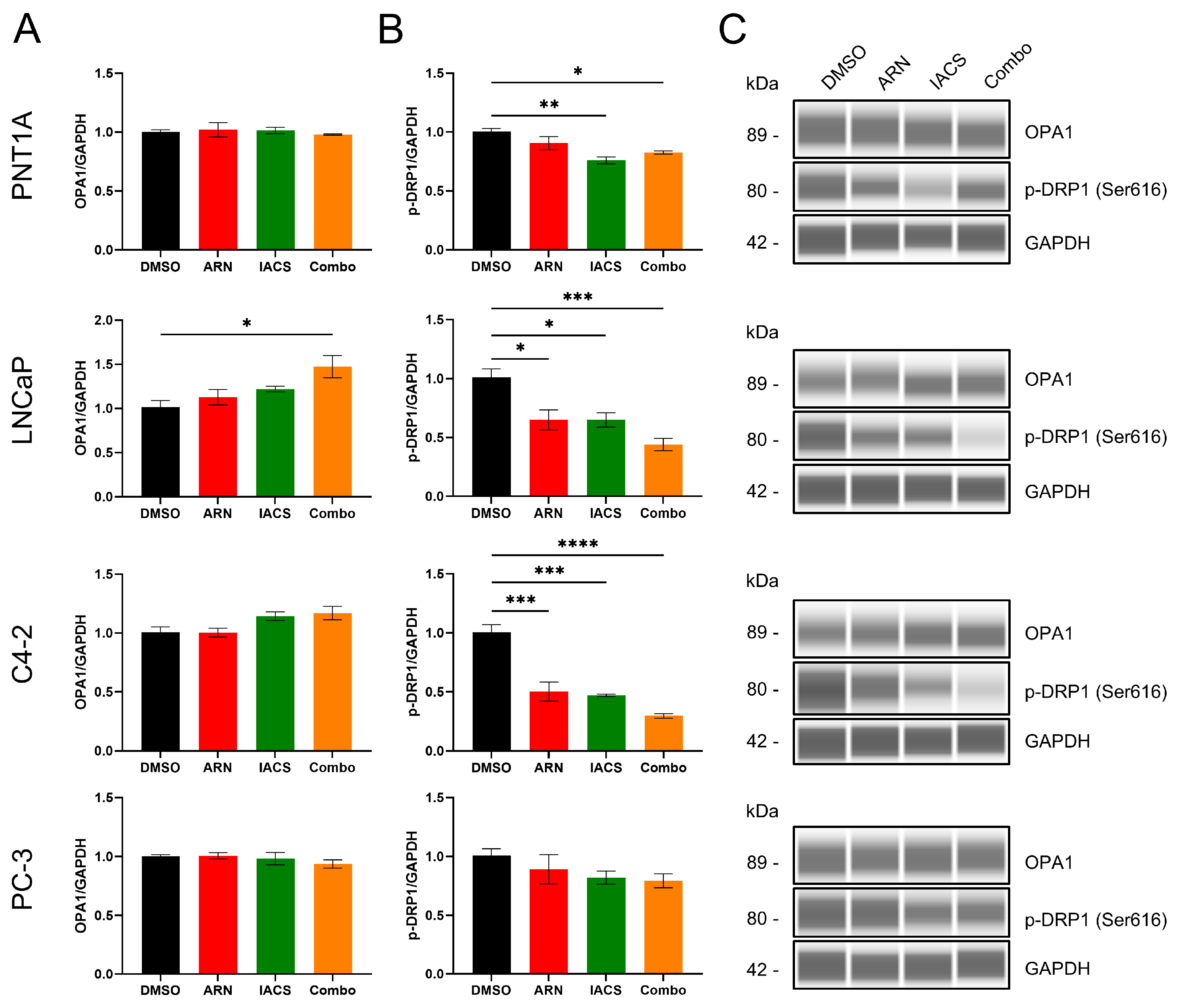
2.2. Impact of Drug-Induced Mitochondrial Network Alterations on Fission and Fusion
2.3. Involvement of Androgen in Mitochondrial Functionality
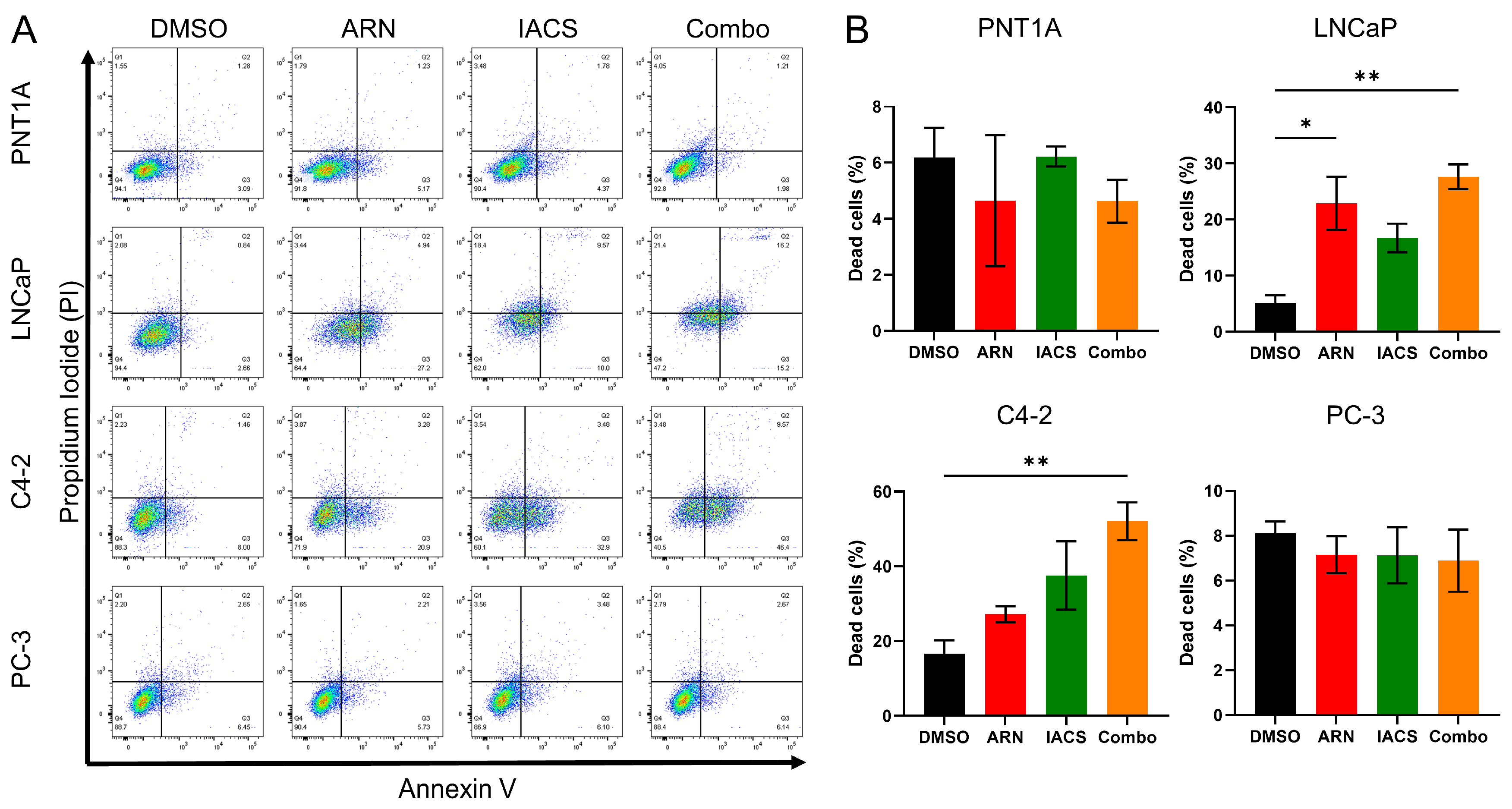
2.4. Cytotoxic Effect of ARN and IACS in PCa Cell Lines
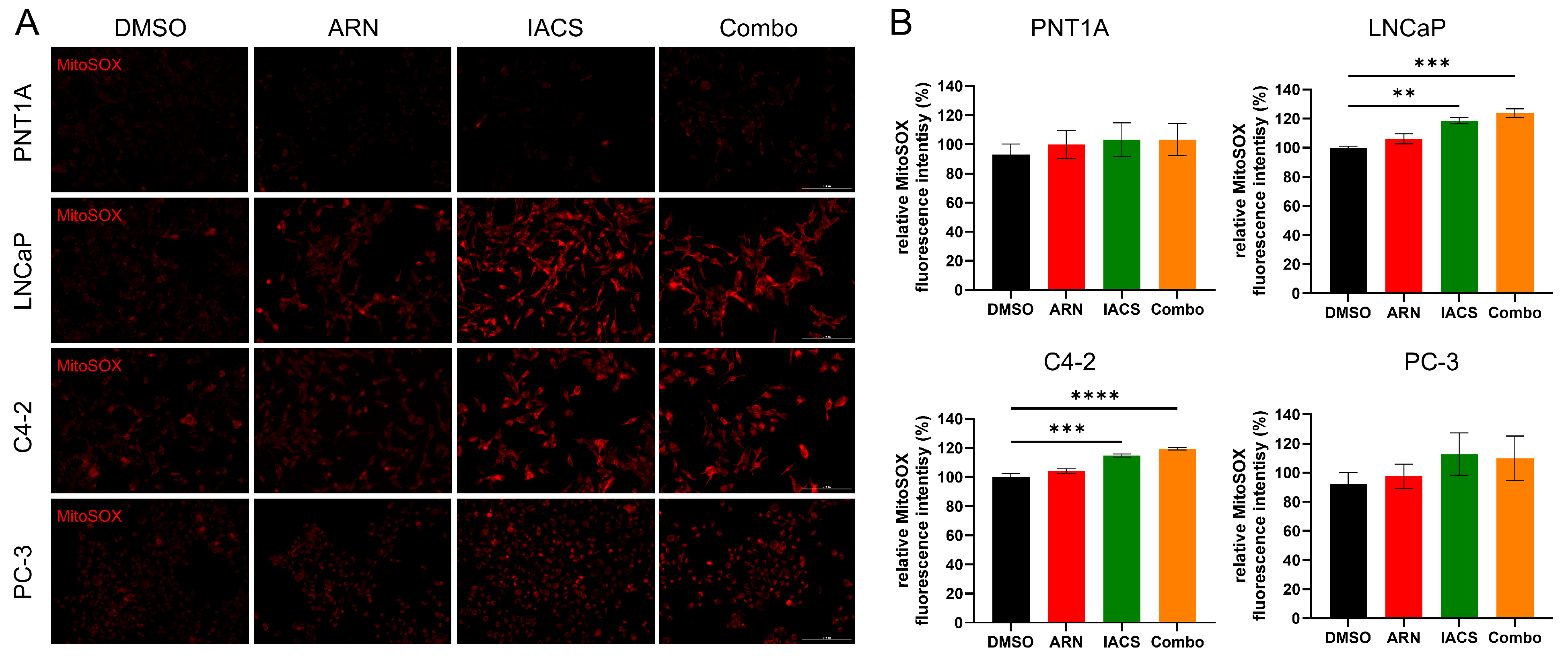
2.5. Treatment-Induced Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress in Androgen-Sensitive PCa Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Pharmacological Compounds
4.2. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
4.3. DHT Treatment
4.4. Automated Western Blotting (WES)
4.5. Seahorse Mito Stress Test
4.6. Immunocytochemistry
4.7. Quantification of Mitochondrial Morphology by TEM
4.8. Measurement of Oxidative Stress
4.9. Apoptosis Assay
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, M.R.; Saad, F.; Chowdhury, S.; Oudard, S.; Hadaschik, B.A.; Graff, J.N.; Olmos, D.; Mainwaring, P.N.; Lee, J.Y.; Uemura, H.; et al. Apalutamide Treatment and Metastasis-free Survival in Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, I.D.; Martin, A.J.; Stockler, M.R.; Begbie, S.; Chi, K.N.; Chowdhury, S.; Coskinas, X.; Frydenberg, M.; Hague, W.E.; Horvath, L.G.; et al. Enzalutamide with Standard First-Line Therapy in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fizazi, K.; Shore, N.; Tammela, T.L.; Ulys, A.; Vjaters, E.; Polyakov, S.; Jievaltas, M.; Luz, M.; Alekseev, B.; Kuss, I.; et al. Darolutamide in Nonmetastatic, Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claessens, F.; Helsen, C.; Prekovic, S.; Van den Broeck, T.; Spans, L.; Van Poppel, H.; Joniau, S. Emerging mechanisms of enzalutamide resistance in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2014, 11, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekar, T.; Yang, J.C.; Gao, A.C.; Evans, C.P. Mechanisms of resistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Transl. Androl. Urol. 2015, 4, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.G.; Ning, S.; Lou, W.; Yang, J.C.; Armstrong, C.M.; Lombard, A.P.; D’Abronzo, L.S.; Evans, C.P.; Gao, A.C.; Liu, C.F. Cross-Resistance Among Next-Generation Antiandrogen Drugs Through the AKR1C3/AR-V7 Axis in Advanced Prostate Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 1708–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faubert, B.; Solmonson, A.; DeBerardinis, R.J. Metabolic reprogramming and cancer progression. Science 2020, 368, aaw5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, X.; Arnoldussen, Y.J.; Storm, M.; Tesikova, M.; Nenseth, H.Z.; Zhao, S.; Fazli, L.; Rennie, P.; Risberg, B.; Waehre, H.; et al. Divergent androgen regulation of unfolded protein response pathways drives prostate cancer. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 788–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catapano, J.; Luty, M.; Wrobel, T.; Pudelek, M.; Piwowarczyk, K.; Kedracka-Krok, S.; Siedlar, M.; Madeja, Z.; Czyz, J. Acquired drug resistance interferes with the susceptibility of prostate cancer cells to metabolic stress. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2022, 27, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, P.; Yarani, R.; Dokaneheifard, S.; Mansouri, K. The emerging role of targeting cancer metabolism for cancer therapy. Tumour Biol. 2020, 42, 1010428320965284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Cherukuri, M.K.; Choyke, P.L. Metabolic reprogramming in prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costello, L.C.; Franklin, R.B. The clinical relevance of the metabolism of prostate cancer; zinc and tumor suppression: Connecting the dots. Mol. Cancer 2006, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bader, D.A.; Hartig, S.M.; Putluri, V.; Foley, C.; Hamilton, M.P.; Smith, E.A.; Saha, P.K.; Panigrahi, A.; Walker, C.; Zong, L.; et al. Mitochondrial pyruvate import is a metabolic vulnerability in androgen receptor-driven prostate cancer. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audet-Walsh, E.; Yee, T.; McGuirk, S.; Vernier, M.; Ouellet, C.; St-Pierre, J.; Giguere, V. Androgen-Dependent Repression of ERRgamma Reprograms Metabolism in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacharias, N.; Lee, J.; Ramachandran, S.; Shanmugavelandy, S.; McHenry, J.; Dutta, P.; Millward, S.; Gammon, S.; Efstathiou, E.; Troncoso, P.; et al. Androgen Receptor Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Alters Hyperpolarized Pyruvate to Lactate Conversion and Lactate Levels In Vivo. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2019, 21, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Huang, Q.; Long, X.; Guo, X.; Sun, X.; Jin, X.; Li, Z.; Ren, T.; Yuan, P.; Huang, X.; et al. Mitochondrial elongation-mediated glucose metabolism reprogramming is essential for tumour cell survival during energy stress. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4901–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, M.; Xie, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wolff, D.W.; Abel, P.W.; Tu, Y. Mitochondrial dynamics regulates migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4814–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.J.; Zhang, S.L.; He, C.Y.; Zhuang, Q.Y.; Han, P.Y.; Jiang, S.W.; Yao, H.; Huang, Y.J.; Ling, W.H.; Lin, Y.C.; et al. Downregulation of mitochondrial cyclooxygenase-2 inhibits the stemness of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by decreasing the activity of dynamin-related protein 1. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1389–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Civenni, G.; Bosotti, R.; Timpanaro, A.; Vazquez, R.; Merulla, J.; Pandit, S.; Rossi, S.; Albino, D.; Allegrini, S.; Mitra, A.; et al. Epigenetic Control of Mitochondrial Fission Enables Self-Renewal of Stem-like Tumor Cells in Human Prostate Cancer. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 303–318.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiratori, R.; Furuichi, K.; Yamaguchi, M.; Miyazaki, N.; Aoki, H.; Chibana, H.; Ito, K.; Aoki, S. Glycolytic suppression dramatically changes the intracellular metabolic profile of multiple cancer cell lines in a mitochondrial metabolism-dependent manner. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, V.; Schaer, D.; Eberli, D.; Salemi, S. Targeting Metabolic Vulnerabilities to Overcome Prostate Cancer Resistance: Dual Therapy with Apalutamide and Complex I Inhibition. Cancers 2023, 15, 5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warburg, O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science 1956, 123, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, P.S.; Thompson, C.B. Metabolic reprogramming: A cancer hallmark even warburg did not anticipate. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porporato, P.E.; Filigheddu, N.; Pedro, J.M.B.; Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L. Mitochondrial metabolism and cancer. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajpai, P.; Koc, E.; Sonpavde, G.; Singh, R.; Singh, K.K. Mitochondrial localization, import, and mitochondrial function of the androgen receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 6621–6634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, Y.; Qi, J.; Liu, L.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, G.; et al. Testosterone Deficiency Caused by Castration Modulates Mitochondrial Biogenesis Through the AR/PGC1alpha/TFAM Pathway. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertega-Gomes, N.; Felisbino, S.; Massie, C.E.; Vizcaino, J.R.; Coelho, R.; Sandi, C.; Simoes-Sousa, S.; Jurmeister, S.; Ramos-Montoya, A.; Asim, M.; et al. A glycolytic phenotype is associated with prostate cancer progression and aggressiveness: A role for monocarboxylate transporters as metabolic targets for therapy. J. Pathol. 2015, 236, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashatus, J.A.; Nascimento, A.; Myers, L.J.; Sher, A.; Byrne, F.L.; Hoehn, K.L.; Counter, C.M.; Kashatus, D.F. Erk2 phosphorylation of Drp1 promotes mitochondrial fission and MAPK-driven tumor growth. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Hu, B. Potential role of mitochondria in gastric cancer detection: Fission and glycolysis. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chan, D.C. Mitochondrial Dynamics in Regulating the Unique Phenotypes of Cancer and Stem Cells. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, B.A.; Zhang, A.; Buschhaus, J.M.; Bevoor, A.; Farfel, A.; Rajendran, S.; Cutter, A.C.; Luker, G.D. Enhanced mitochondrial fission inhibits triple-negative breast cancer cell migration through an ROS-dependent mechanism. iScience 2023, 26, 106788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Rho, J.H.; Jeong, S.Y.; Yun, J.; Yun, I.; Park, H.T.; Yoo, Y.H. Targeted inhibition of mitochondrial Hsp90 induces mitochondrial elongation in Hep3B hepatocellular carcinoma cells undergoing apoptosis by increasing the ROS level. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 1783–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vangapandu, H.V.; Alston, B.; Morse, J.; Ayres, M.L.; Wierda, W.G.; Keating, M.J.; Marszalek, J.R.; Gandhi, V. Biological and metabolic effects of IACS-010759, an OxPhos inhibitor, on chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 24980–24991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donati, G.; Nicoli, P.; Verrecchia, A.; Vallelonga, V.; Croci, O.; Rodighiero, S.; Audano, M.; Cassina, L.; Ghsein, A.; Binelli, G.; et al. Oxidative stress enhances the therapeutic action of a respiratory inhibitor in MYC-driven lymphoma. EMBO Mol. Med. 2023, 15, e16910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.H.; Kim, M.C.; Ji, S.; Yang, Y.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, Y. Glucose starvation induces resistance to metformin through the elevation of mitochondrial multidrug resistance protein 1. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 1256–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, T.A.; Daver, N.; Mahendra, M.; Zhang, J.X.; Kamiya-Matsuoka, C.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Ravandi, F.; Collins, M.E.; Di Francesco, M.E.; et al. Complex I inhibitor of oxidative phosphorylation in advanced solid tumors and acute myeloid leukemia: Phase I trials. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, V.; Kaddour-Djebbar, I.; Lakshmikanthan, V.; Ghazaly, T.; Thangjam, G.S.; Sreekumar, A.; Lewis, R.W.; Mills, I.G.; Bollag, W.B.; Kumar, M.V. Novel role of androgens in mitochondrial fission and apoptosis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.G.; Nam, Y.; Shin, K.J.; Yoon, S.; Park, W.S.; Joung, J.Y.; Seo, J.K.; Jang, J.; Lee, S.; Nam, D.; et al. Androgen-induced expression of DRP1 regulates mitochondrial metabolic reprogramming in prostate cancer. Cancer Lett. 2020, 471, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowell, P.D.; Giafaglione, J.M.; Jones, A.E.; Nunley, N.M.; Hashimoto, T.; Delcourt, A.M.L.; Petcherski, A.; Agrawal, R.; Bernard, M.J.; Diaz, J.A.; et al. MYC is a regulator of androgen receptor inhibition-induced metabolic requirements in prostate cancer. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baumgartner, V.; Schaer, D.; Moch, H.; Salemi, S.; Eberli, D. Mitochondrial Elongation and ROS-Mediated Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer Cells under Therapy with Apalutamide and Complex I Inhibitor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6939. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136939
Baumgartner V, Schaer D, Moch H, Salemi S, Eberli D. Mitochondrial Elongation and ROS-Mediated Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer Cells under Therapy with Apalutamide and Complex I Inhibitor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(13):6939. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136939
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaumgartner, Valentin, Dominik Schaer, Holger Moch, Souzan Salemi, and Daniel Eberli. 2024. "Mitochondrial Elongation and ROS-Mediated Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer Cells under Therapy with Apalutamide and Complex I Inhibitor" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 13: 6939. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136939
APA StyleBaumgartner, V., Schaer, D., Moch, H., Salemi, S., & Eberli, D. (2024). Mitochondrial Elongation and ROS-Mediated Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer Cells under Therapy with Apalutamide and Complex I Inhibitor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(13), 6939. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136939







