Alliums as Potential Antioxidants and Anticancer Agents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Origin
3. Methodology
4. IUCN Redlist Allium Species
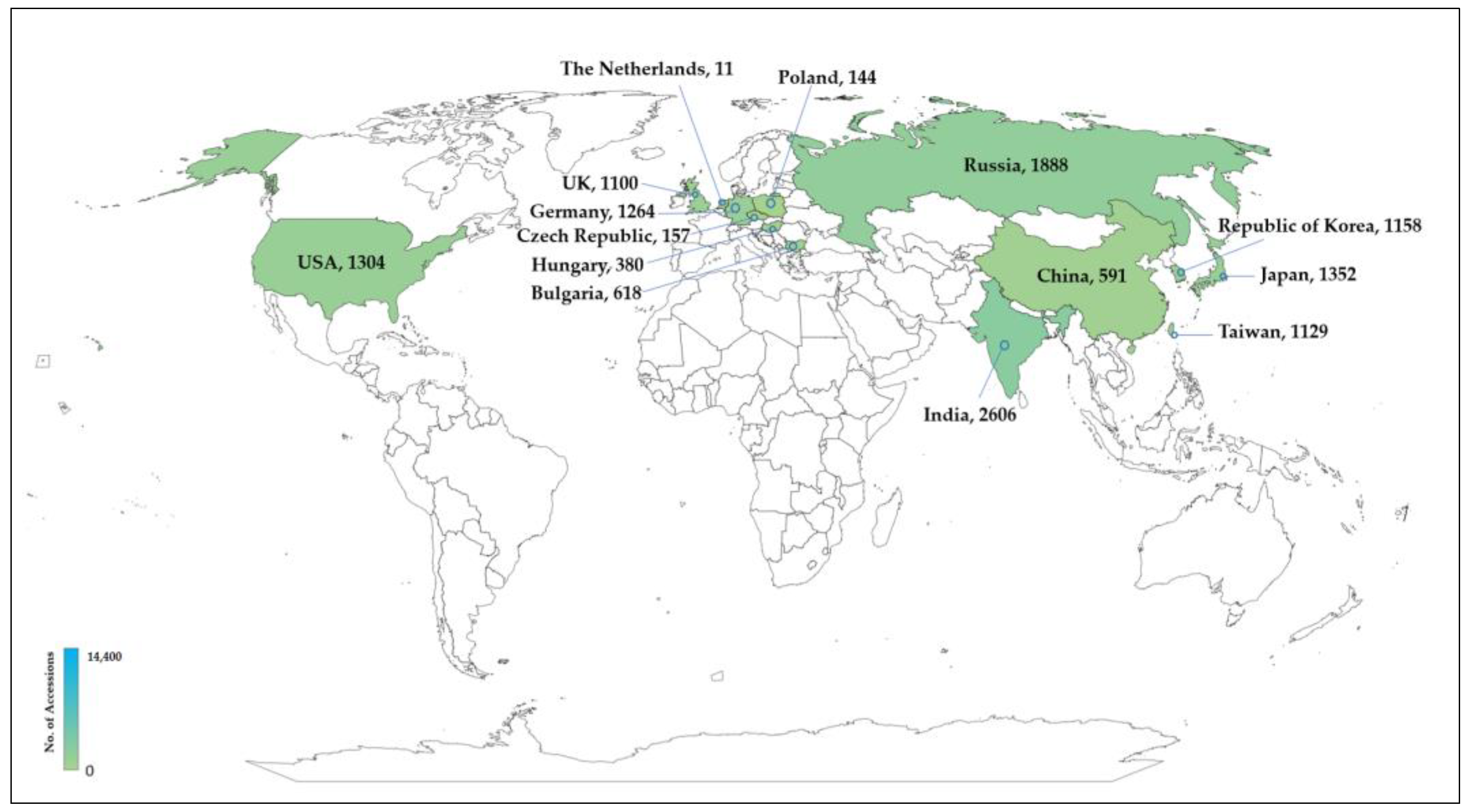
5. Allium in Genebanks
6. Allium as a Potent Resource
7. Phytochemistry of Allium
8. Antioxidant Properties of Various Allium Species
8.1. Allium ampeloprasum L.
8.2. Allium cepa L.
8.3. Allium porrum L. and Allium roseum var. Odoratissimum (Desf.) Coss
8.4. Allium sativum L.
8.5. Allium subhirsutum L. and Allium paradoxum (M.Bieb.) G.Don
8.6. Allium Species
| Allium Species | Plant Parts | Extracts | Constituents | Assay | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. ampeloprasum | Leaves and Seeds | Methanol, ethanol, hexane, petroleum ether, chloroform, and deionized water | Ascorbic acid, dehydroascorbic acid, oxalic acid, glutamic acid, malic acid, citric acid, succinic acid, total α-Tocopherol, β-Tocopherol, γ-Tocopherol, δ-Tocopherol; gallic acid, ellagic acid, caffeic, coumaric, tannic, vanillic, chlorogenic, rutin and quercetin, 3-caffeoylquinic acid | 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical-scavenging activity, reducing power, inhibition of β-carotene bleaching, thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS), ferric-reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assay | [36,37] |
| A. cepa | Bulbs | Aqueous, methanol, ethanol | Chlorogenic acid, gallic acid, ferulic acid, kaempferol, quercetin, Propionaldehyde, 2-Methyl-2-pentenal, Furfuraldehyde, 5-Methyl-2-Furfuraldehyde, 1-Propanethiol, Propylene sulfide, Dimethyl sulfide, Methyl propyl disulfide, cis-Methyl-1-propenyl disulfide, 5-Methyl-1,3-thiazole, trans-Methyl-1-propenyl disulfide, 3,4-Dimethyl thiophene, Methyl-2-propenyl disulfide, Dipropyl disulfide, 1,2,4-Trithiolane, trans-Propenyl propyl disulfide, cis-Propenyl propyl disulfide, Methyl propyl trisulfide, Dipropyl trisulfide, 1,2-Cyclopentanedione, Butyrolactone, Furfuryl alcohol, malic, citric, tartaric, oxalic, ascorbic, succinic, and pyruvic acid; ferulic, gallic and protocatechuic acid, quercetin, kaempferol, Malondialdehyde | DPPH and free radical-scavenging activities (FRSA) CUPRAC, DPPH, FRAP; antioxidant activity (AOA) β-carotene and linoleic acid, antimutagenic activity; Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC), thiobarbituric acid (TBA) assay; ferrous ion-chelating assays; phosphomolybdate and reducing power assays | [38,42,43,45,46,52,55] |
| A. sativum, A. ampeloprasum, and A. cepa | Bulbs | - | Alliin, allicin, cycloalliin, isoalliin, methiin | Oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC) values and 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and 2,2′-azinobis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) (ABTS) radical-scavenging activities | [39] |
| A. cepa and A. fistulosum | Leaves, stalks, and roots | Aqueous | - | Catalase (C-ase), glutathione-peroxidase(GP-ase) peroxidase (P-ase), and superoxide-dismutase (SOD) | [40] |
| A. fistulosum | Bulbs | Aqueous | - | Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC) and ferric-reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assays | [41] |
| A. cepa var. tropicana | Seeds | Heat-treated by boiling water | Alanine, arginine, asparagine, aspartic acid, Gaba, glutamic acid, glutamine, glycine, hystidine, proline, serine, threonine, tyrosine, and valine | Ferric-reducing/antioxidant power, DPPH | [44] |
| A. kurrat | Bulbs | Methanol | Ferulic, gallic, and protocatechuic acid; quercetin, kaempferol; steroids; terpenoids; and saponins | DPPH radical, phosphomolybdate, and reducing power assays | [46] |
| A. porrum | Stem and leaves | Methanol, Ethanol and Aqueous | Apigenin, chlorogenic acid, ferulic acid, gallic acid, dihydroxybenzoic acid, caffeic acid, kaempferol glucoside, myricetin, naringenin, quercetin glucoside, protocatechuic acid, quercetin, rosmarinic acid, rutin, sinapenic acid, syringic acid, and vanillic acid | DPPH radical, phosphomolybdate and reducing power assays, and Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) | [46,71] |
| A. roseum var. odoratissimum | Leaves, flowers, stalks, and bulbs | Methanol | Apigenine, kaempferol-3-O-glucoside, kaempferol-3-O-beta-D-glucoside-7-O-alpha-L-rhamnoside, kaempferol 3,7-di-O-rhamnoside, kaempferol-3-Glucuronide, and luteoline | DPPH, 2-deoxyribose, ferric-reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), reducing power assay | [47] |
| A. sativum, A. bakeri, A. odorum, A. tuberosum, A. fistulosum, A. cepa, and A. ascalonicum | Bulbs | Aqueous | Allicin | Thiobarbituric acid (TBA) | [48] |
| A. sativum | Bulbs | Methanol, aether-petroleum ether and aqueous, aqueous–ethanol | Methanolic extract; crude polysaccharide; ferulic acid, gallic acid, kaempferol, protocatchuic acid, quercetin | DPPH (1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl) assay, β-carotene/linoleic acid assay, and Rancimat method; scavenging activity of superoxide anions, free radical-scavenging capacity (RSC), hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radical-scavenging activity; ferrous ion-chelating assays; phosphomolybdate and reducing power assays | [45,46,49,51,53,54,55] |
| A. neapolitanum, A. subhirsutum, A. roseum | Leaves, flowers bulblets, and flowers, bulbs | Aqueous ethanol | Gallic acid (TPC) | DPPH and FRAP assay | [56] |
| A. cepa, A. sativum, A. schoenoprasum, A. ursinum. | Bulbs | Ethanol | Gallic acid (TPC) | Antioxidant activity (AOA), DPPH assay | [57] |
| A. atroviolaceum, A. dictyoprosum, A. nevsehirense, A. sivasicum, A. scrodoprosum subsp. rotundum | Whole Plant | Methanol | - | DPPH free radical-scavenging and β-carotene/linoleic acid assays | [58] |
| A. subhirsutum | Whole Plant | Ethanol | TPC, TFC, 2-methylene-5-(2,5dioxotetrahydrofuran-3-yl)-6-oxo--10,10-dimethylbicyclo [7:2:0] undecane; (22S)-1α,22,25-trihydroxy-26,27-dimethyl-23,23,24,24-tetradehydro-24ahomovitaminD3/(22S)-1al; L-4-Hydroxy-3-methoxy-amethylphenylalanine; 1-nonadecanoyl-2-(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Zeicosapentaenoyl)-sn-glycerol; TG(16:1(9Z)/17:2(9Z,12Z)/20: 5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z))[iso6]; 11α-acetoxykhivorin; Methyl gamboginate; C16 Sphinganine; 4-Oxomytiloxanthin; Sebacic acid; Linolenoyl lysolecithin; 3β, 7α, 12α-Trihydroxy-5α-cholestan- 26-oic acid; N-(2-hydroxyethyl) stearamide; Cepharanthine; 6α-Hydroxy Castasterone; 6-Deoxocastasterone | DPPH, reducing power, Malignant MatLyLu and Walker 256/B Cell Lines Culture, 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT), Hoechst 33,342 (apoptosis) Assay, AS Extract on breast cancer skeletal metastases | [59] |
| A. paradoxum | Leaves and Bulbs | Aqueous-methanol | Gallic acid (TPC), quercetin (TFC) | DPPH, reducing power, nitric oxide and hydrogen peroxide scavenging, metal-chelating, antihemolytic activities | [60] |
| A. flavum, A. sphaerocephalum, A. atroviolaceum, A. vienale, A. scorodoprasum, A. nutans, A. fistulosum, A. vienale, A. pskemense, A. schenoprasum, A. cepa, A. sativum | Leaves | Crude with 1 mol/L K2HPO4 | Gallic acid (TPC), quercetin (TFC), reduced glutathione, vitamin C, and soluble proteins | Superoxide dismutase, catalase, peroxidase, glutathione peroxidase, quantities of malonyldialdehyde superoxide, and hydroxyl radical-scavenging activities | [61] |
| A. nutans | Leaves, bulb, and root | Crude with 1 mol/L K2HPO4 | Gallic acid (TPC), quercetin (TFC), reduced glutathione, vitamin C, and soluble proteins | Superoxide dismutase, catalase, peroxidase, glutathione peroxidase, quantities of malonyldialdehyde superoxide, and hydroxyl radical-scavenging activities | [62] |
| A. psekemense | Leaves, stalk, and bulb | Crude with 1 mol/L K2HPO4 | Gallic acid (TPC), quercetin (TFC), reduced glutathione, vitamin C, and soluble proteins | Superoxide dismutase, catalase, peroxidase, glutathione peroxidase, quantities of malonyldialdehyde superoxide, and hydroxyl radical-scavenging activities | [63] |
| A. schoenoprasum | Leaves, stalk, and bulb | Crude with 1 mol/L K2HPO4 | Gallic acid (TPC), quercetin (TFC), reduced glutathione, vitamin C, and soluble proteins | Superoxide dismutase, catalase, peroxidase, glutathione peroxidase, quantities of malonyldialdehyde superoxide, and hydroxyl radical-scavenging activities | [64] |
| A. giganteum | Leaves, stalk, and bulb | Crude with 1 mol/L K2HPO4 | Gallic acid (TPC), quercetin (TFC), reduced glutathione, vitamin C, and soluble proteins | Superoxide dismutase, catalase, peroxidase, glutathione peroxidase, quantities of malonyldialdehyde superoxide, and hydroxyl radical-scavenging activities | [65] |
| A. ursinum | Leaves, stalk, and bulb | Crude with 1 mol/L K2HPO4 | Gallic acid (TPC), quercetin (TFC), reduced glutathione, vitamin C, and soluble proteins | Superoxide dismutase, catalase, peroxidase, glutathione peroxidase, quantities of malonyldialdehyde superoxide, and hydroxyl radical-scavenging activities | [66] |
| A. sphaerocephalon | Leaves, stalk, and bulb; flowers | Crude with 1 mol/L K2HPO4, | Gallic acid (TPC), quercetin (TFC), reduced glutathione, vitamin C, and soluble proteins α-cadinol, β-caryophyllene, δ-cadinene, 3,5-diethyl-1,2,4-trithiolane, Shyobunol | Superoxide dismutase, catalase, peroxidase, glutathione peroxidase, quantities of malonyldialdehyde superoxide, and hydroxyl radical-scavenging activities; total antioxidant capacity determined using the Phosphomolybdenum method and antimicrobial activity | [67,72] |
| A. tuberosum, A. senescens, A. thunbergii, and A. sacculiferum | Seedlings | Crude | Caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid, cinnamic acid, coumaric acid, ferulic acid, gentisic acid, hesperiin, homogentisic acid, naringenin, propionic acid, protocatechinic acid, quercetin, and veratric acid | ABTS+ and DPPH-scavenging assays | [68] |
| A. tenuissimum | Flowers | Aqueous, ethanol, ethyl acetate, and petroleum ether | Gallic acid (TPC), quercetin (TFC) | DPPH, ABTS+, and total reducing power | [69,70] |
| A. kurrat | Whole Plant | Methanol | Isorhamntin-O-hexoside-pentoside, Quercetin-tri-O-hexoside, Kaempferol-tri-O-hexoside, Kaempferol-tri-O-hexoside isomer, Kaempferol-di-O-hexoside, Kaempferol-O-trihexoside-hexuronoide, Kaempferol-di-O-hexoside isomer, Quercetin-O-hexoside, Kaempferol-di-O-hexoside isomer, Kaempferol-O-hexoside, Kaempferol-O-hexuronoide, Kaempferol-O-trihexoside-hexuronoide isomer, Kaempferol-O-dihexoside-hexuronoide, Acacetin-7-O-malonoyl hexoside | DPPH, ABTS, and total antioxidant capacity; human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2); and human colon carcinoma (Caco-2) using neutral red assay | [73] |
| A. astrosanguineum | Aerial parts | Crude in methanol | Aqueous and methanolic extracts | DPPH radical-scavenging assay and antimicrobial activity | [74] |
9. Anticancer and Related Activities of Allium Species
9.1. Allium ampeloprasum L. and Allium ascalonicum L.
9.2. Allium affine Ledeb and Allium atropurpureum Waldst. & Kit
9.3. Allium atroviolaceum Boiss and A. austroiranicum R. M. Fritsch
9.4. Allium autumnale P.H. Davis and Allium willeanum Holmboe
9.5. Allium cepa L.
9.6. Allium bakhtiaricum Regel and Allium fistulosum L.
9.7. Allium chinense G. Don
9.8. Allium giganteum Regel and Allium jesdianum Boiss. & Buhse
9.9. Allium kurtzianum Asch. & Sint. ex Kollmann and Allium leucanthum K. Koch
9.10. Allium macrostemon Bunge and Allium ochotense Prokh. (syn.: A. victorialis var. platyphyllum (Hultén) Makino)
9.11. Allium porrum L. and Allium pseudojaponicum Makino
9.12. Allium sativum L.
9.13. Allium saralicum R.M. Fritsch and Allium schoenoprasum L.
9.14. Allium senescens L. and Allium subhirsutum L.
9.15. Allium sivasicum Özhatay & Kollmann and Allium sphaerocephalon L.
9.16. Allium stipitatum Regel (syn.: A. hirtifolium)
9.17. Allium wallichii Kunth and Allium tuberosum Rottler ex Spreng
9.18. Allium ursinum L.
| Allium Species. | Plant Parts | Extracts | Constituents/Extracts | Assay | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. kurrat | Whole Plant | Methanol | Isorhamntin-O-hexoside-pentoside, Quercetin-tri-O-hexoside, Kaempferol-tri-O-hexoside, Kaempferol-tri-O-hexoside isomer, Kaempferol-di-O-hexoside, Kaempferol-O-trihexoside-hexuronoide, Kaempferol-di-O-hexoside isomer, Quercetin-O-hexoside, Kaempferol-di-O-hexoside isomer, Kaempferol-O-hexoside, Kaempferol-O-hexuronoide, Kaempferol-O-trihexoside-hexuronoide isomer, Kaempferol-O-dihexoside-hexuronoide, Acacetin-7-O-malonoyl hexoside. | DPPH, ABTS, and total antioxidant capacity; human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2); and human colon carcinoma (Caco-2) using neutral red assay | [73] |
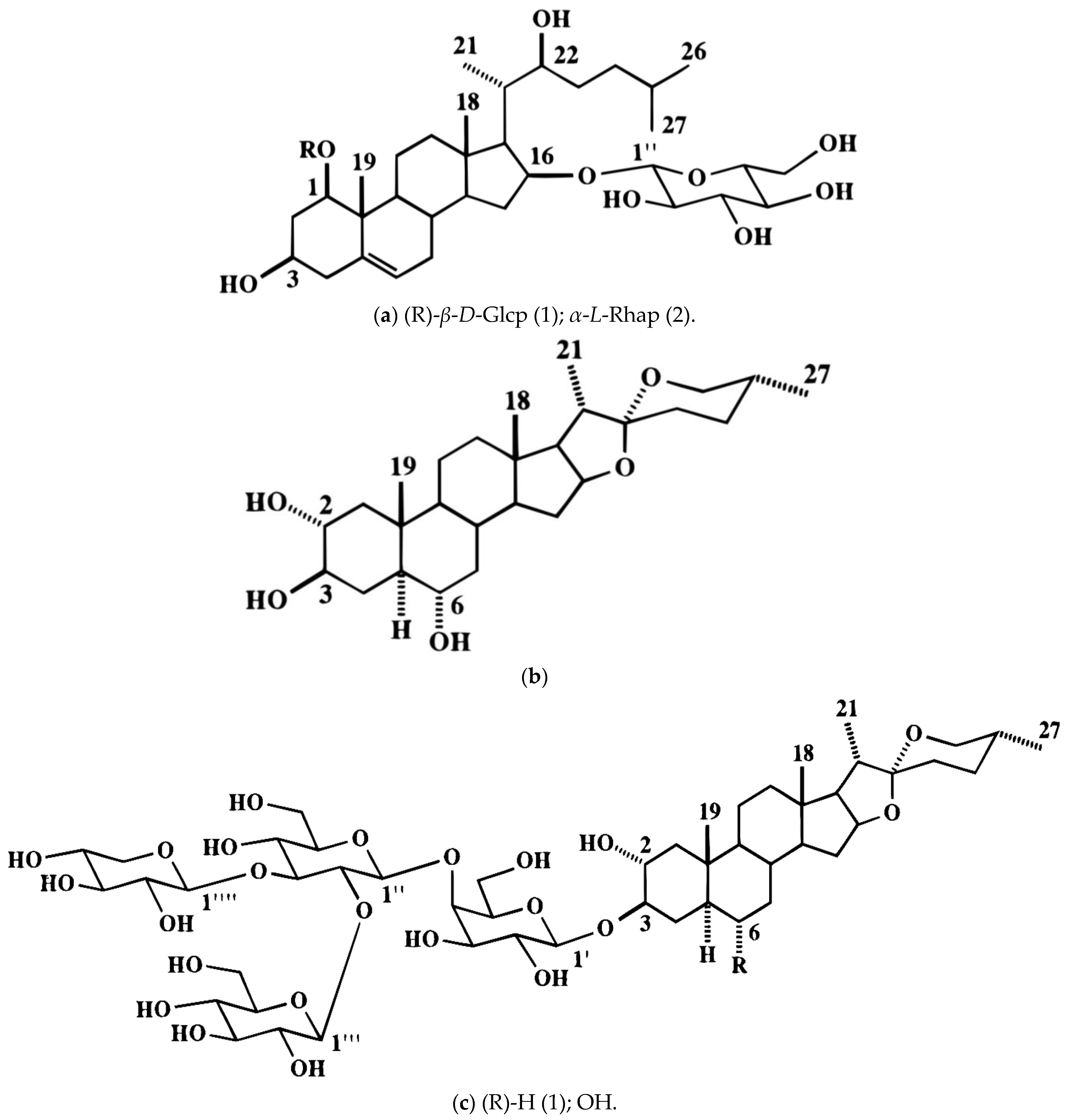
| A. ascalonicum | Bulbs | n-hexane, chloroform, chloroform-methanol (9:1), methanol; aqueous, ethanol, | Ascalonicoside A1, ascalonicoside A2 and ascalonicoside B, furost-5(6)-en-3β,22α-diol 1β-O-β-d-galactopyranosyl 26-O-[α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-β-d-glucopyranoside] (1a), (1b), and furost-5(6),20(22)-dien-3β-ol1β-O-β-d-galactopyranosyl 26-O-[α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-β-d-glucopyranoside; Ethanolic extracts quercetin 3,4′-diglucoside, isorhamnetin 3,4′-diglucoside, quercetin 3-glucoside, quercetin 4′-glucoside, isorhamnetin 4′-glucoside, quercetin aglycone, isrohamnetin | In vitro cytotoxicity, cell line antiproliferative, anti-growth, and anti-inflammatory activity; in vitro anticancer efficacy liver cancer cell line HepG2 using MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) assay; DPPH, anti-inflammatory effect, and human cervical carcinoma (Hela) and human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cell lines—MTT assay | [79,80,81,82] |
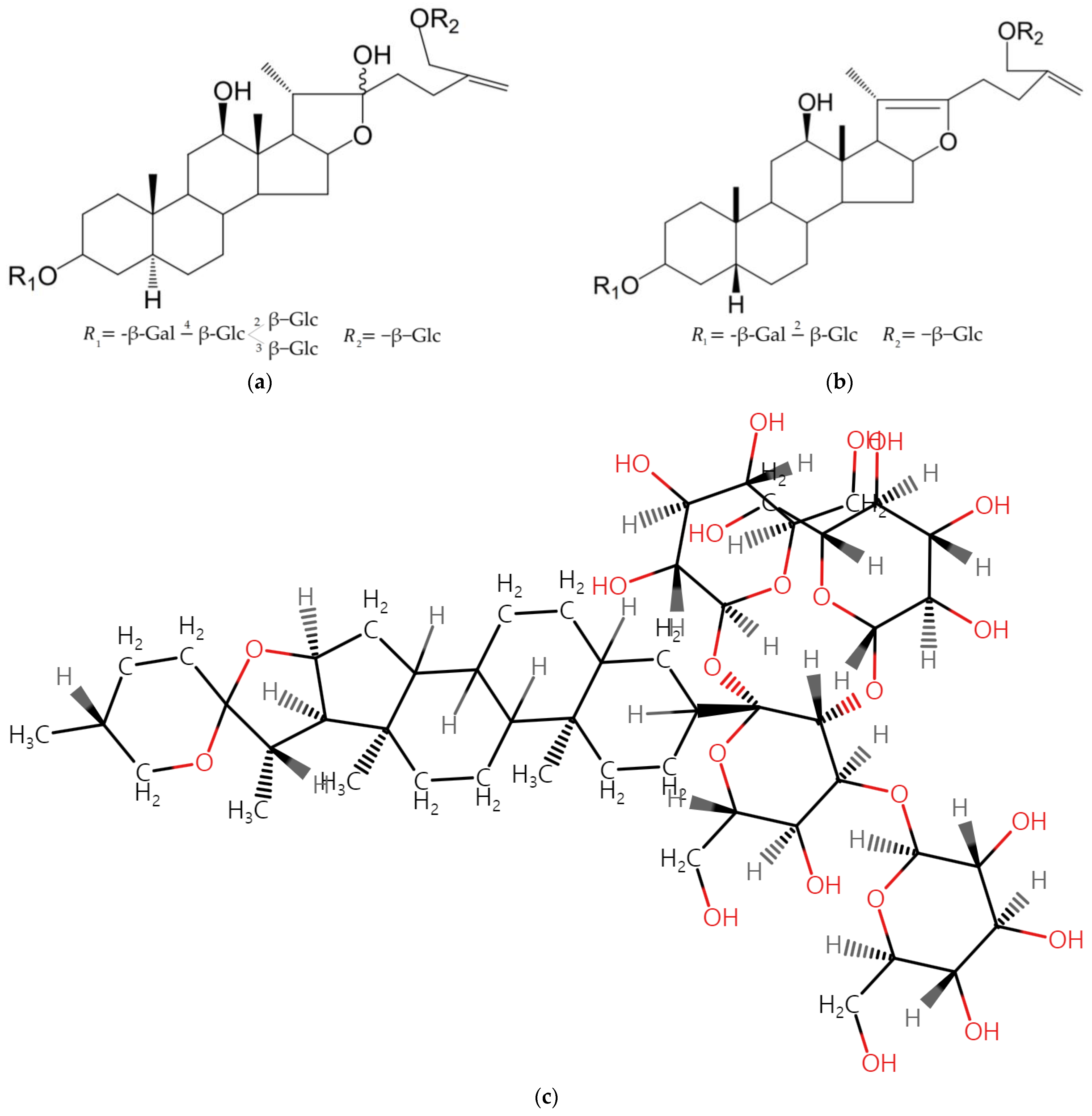
| A. atropurpureum | Bulbs | Methanol | (25S)-26-[(β-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy]-2α,6β,22α-trihydroxy-5α-furostan-3β-yl O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→3)]-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-galactopyranoside; (25S)-2α,6β-dihydroxy-5α-spirostan-3β-yl O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→3)]-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-galactopyranoside; (25S)-2α,6β-dihydroxy-5α-spirostan-3β-yl O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[4-O-(3S)-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→3)]-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-galactopyranoside | Cytotoxicity assay SBC-3 human small-cell lung cancer cells | [83] |
| A. atroviolaceum | Bulb; Flowers | Methanol | - | Cytotoxic activity of MCF7 (human hormone-dependent breast cancer) and MDA-MB-231 (human non-hormone-dependent breast cancer cell line), HeLa (human cervical cancer), HepG2 (human hepatocellular cancer cell line), and 3T3 (mouse embryo fibroblast) cell lines; apoptosis; and normal 3T3 cell lines—MTT assay and apoptosis | [84,85,86] |
| A. austroiranicum | Flower | Hexane, chloroform, chloroform-methanol, and methanol | - | Anti-proliferative effects of OVCAR-3 (ovarian carcinoma), HeLa, and HUVEC (human umbilical vein endothelial) cell lines determined using cytotoxicity assay (MTT) | [87] |
| A. autumnale | Bulb and stem | Ethanol | 9-octadecenoic acid, octadecamethylcyclononasiloxane; tetrapentacosane; l-Isoleucine; heptadecanoic acid; hexadecanoic acid; 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid, diethyl ester; dimethyltrisulfide; (−)-1 L–cyclohex-5-ene-1,3/2,4-tetrol; 14-.β.-h-pregna; pentadecanoic acid; and quinic acid; 9-octadecenoic acid; octadecamethylcyclononasiloxane; tetrapentacosane; heptadecanoic acid; hexadecanoic acid; 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid, diethyl ester; dimethyltrisulfide; (−)-1 L–cyclohex-5-ene-1,3/2,4-tetrol; 14-.β.-h-pregna; pentadecanoic acid | In vitro anti-proliferative, cytotoxic and anti-metastatic effects of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 (breast cancer) cell lines | [88] |
| A. bakhtiaricum | Aerial part | n-hexane, chloroform, ethyl acetate, and methanol | - | In vitro cytotoxicity assay of MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 (human breast adenocarcinoma), HT-29 (human colorectal adenocarcinoma), HepG2 (liver hepatocellular carcinoma), 4 T1 (mouse mammary tumor), and NIH3T3 (mouse embryonic fibroblasts) cell lines and in vivo study using mice | [94] |
| A. cepa | Bulbs | Aqueous, ethyl acetate, ethanol, petroleum ether | Quercetin; silver nano particles using aqueous extracts | Inhibitory effects on Mouse 3T3-L1 preadipocytes (fatty acid synthase) and MDA-MB-231 cell line apoptosis (human breast cancer)—MTT assay; cytotoxicity effects on adrenocortical carcinoma cell line (H295R and SW-13); HeLa (human cervix carcinoma) cell cytotoxicity activity; TROLOX, total antioxidant capacity (TAC) and DPPH-scavenging activity, and apoptosis in colorectal cancer (HT-29 and SW620) cell lines | [90,91,92,93] |
| A. willeanum | Bulbs | Ethanol | Octadecanoic acid 2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl) ethyl ester; hexadecanoic acid; pentadecanoic acid; 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid, diethyl ester | Metastatic effects of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 (breast cancer) cell lines, trypan blue, and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) cytotoxicity assays | [89] |
| A. fistulosum, A. sativum | Bulb | Ethanol | Alliin, Allicin, gentisic acid, chlorogenic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, rutin, Isoquercitrin, p-coumaric, Quercitrin, ferulic acid, quercetin and kaempferol | Normal human fibroblasts (BJ cells) and keratinocytes (HaCaT) cell lines | [97] |
| A. fistulosum | Leaves and bulb | Ethanol and methanol | Quercetin and gallic acid, chlorogenic and p-coumaric acid, | Anti-inflammatory and anticancer activity. | [98] |
| A. chinense | Leaves and bulb | Hexane, ethanol | Phytol, tetratetracontane, perhydrofarnesyl acetone, heptadecane, 2,6-dimethyl, 2-methyloctacosane, tetracontane, eicosane, 10-methyl, heneicosane, octadecyl trifluoroacetate, and 1-heneicosanol, saponins | DPPH antioxidant scavenging, antibacterial and antifungal activity; in vivo anticancer activity of B16 melanoma and 4T1 breast carcinoma cell lines | [99,100] |
| A. giganteum | Flower | Butanol, dichloromethane, chloroform-methanol (9:1). | Steroidal saponin | Cytotoxic and pro-apoptotic effects on MCF-7 and HeLa cell lines using MTT assay | [101] |
| A. hirtifolium | Bulb | - | Allicin | Nerve cell microtubules and cytotoxicity effect on HeLa, MCF-7, and L-929 cell lines | [133] |
| A. jesdianum | Leaves and stems | Ethanol, hydro-alcohol | - | In vitro anti-proliferative and cytotoxic effects, B-CPAP and Thr.C1-PI 33 cancer cell lines using MTT assay; Cytotoxic and migrastatic effect of Glioblastoma multiforme cell line (U87MG) | [102,103,104] |
| A. kurtzianum | Aerial parts and bulb | Methanol | Acacetin, apigenin 7-glucoside, caffeic acid, (+)-Catechin, chrysin, (−)-Epicatechin, (−)-Epigallocatechin, (−)-Epigallocatechin gallate, fumaric acid, herniarin, hispidulin, hyperoside, Luteolin-7-rutinoside, naringenin, nepetin, Nepetin-7-glucoside, Quercetin, quercitrin, rhamnocitrin, rutin | DPPH, FRAP activity (antioxidant), α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibition assays (antidiabetic), DNA-protection activity (DNA nicking assay), cytotoxic activity on human prostate (ATCC CRL-1435, PC-3), human lung (ATCC CCL-185, A549), and human endometrial (ATCC CRL-2923, ECC-1) cancer cell lines using Viability Test using MTS | [105] |
| A. macrostemon | Bulb; whole plant | Ethanol | Steroidal saponins, 26-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-5α-furost-25 (27)-ene-3β, 12β, 22, 26-tetraol-3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl (1→2) [β-D-glucopyranosyl (1→3)]-β-D-glucopyranosyl (1→4)-β-D-galactopyranoside and 26-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-5β-furost-20 (22)-25 (27)-dien-3β, 12β, 26-triol-3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl (1→2)-β-D-galactopyranoside; Macrostemonoside A (steroidal saponin) | In vitro cytotoxic activities on MCF-7, NCI-H460, SF-268, and HepG2 cancer cell lines In vitro anti-proliferative and apoptosis effects on human colorectal cancer cell lines Caco2 and SW480 | [107,108,109] |
| A. ochotense | Bulb | Aqueous and ethanol | - | ABTS, DPPH, FRAP, malondialdehyde (MAD) assays (antioxidant), Alcohol Dehydrogenase (ADH), aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) MTT assays and apoptosis | [110] |
| A. porrum | Whole plant; flower | Chloroform, n-hexane, and methanol, ethyl acetate, butanol, chloroform-methanol–water | Cyclotrisiloxane, 11,13, -Dimethyl-12-tetradecen-1-ol acetate, Hexadecanoic acid, 9, 12, 15-Octadecatrienoic acid, 9, 12-Octadecadienoic acid, Methyl ester Dodecanoic acid and 1,3,5, -Triazine, β-chlorogenin aglycone, spirostanol saponins, 12-ketoporrigenin and 2,12-diketoporrigenin (porrigenin C), cholestane, bidesmosides; Agigenin, Aginoside, 6-deoxyaginoside, Yayoisaponin A and (2α, 3β, 6β, 25R)-2,6-dihydroxyspirostan-3-yl β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)-β-D-glucopranosyl-(1→2)-[β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→3)]-β-D-glucopyranosyl]-(1→4)-β-D-galactopyranoside (Alliporin) | In vitro cytotoxicity using MTT assay on HT-115 (human colon carcinoma) cell line, WEHI 164 (murine fibrosarcoma) J774 (murine monocyte/macrophage) cell lines); in vitro study using mouse and cytotoxicity effect determined using LDH (lactate dehydrogenase) assay | [111,113,114] |
| A. cepa and A. ampeloprasum | Whole plant | Aqueous, ethanol, methanol | Alicin, E-ajoene, S- allylmercapto-cysteine (SAMC), S-allylcysteine (SAC), Dipropyl disulfide, 4′-Desulphate-atractyloside, Entanamide A, Entadamide A-β-D-glucopyranoside, Glucoerucin, 2-Hydroxyxanthiside, Xanthiside, and Xanthiazone | Anticancer effect on MCF-7 cells using cell viability (MTT assay) | [112] |
| A. sativum | Bulbs; leaves | Aqueous | Diallyl sulfide; gallic acid standard (TPC); gold nano particles using aqueous extract | DPPH, superoxide radical, hydrogen peroxide-scavenging activity, and oxidative hepatotoxicity assessed using Rabbit; in vivo analysis of colorectal adeno carcinoma effects in mouse; in vivo analysis of murine transitional cell carcinoma using C3H/HeN female mice; in vitro cell lines study on laryngeal cancer cells (Hep-2) and L929 cells; in vitro cytotoxicity and anticancer assays on HeLa cells by trypan blue exclusion method; cytotoxicity effects on HUVEC (human normal cell line), HT-29, HCT 116 (colorectal carcinoma), HCT-8 [HRT-18] (ileocecal colorectal adenocarcinoma), and Ramos.2G6.4C10: Burkitt’s lymphoma using MTT assay | [90,116,117,118,119,120,121,122] |
| A. saralicum | Plant | Aqueous | Silver nano particles using aqueous extracts | In vitro cytotoxicity effect on breast cancer cell lines (SK-BR-3, MDA-MB-231, AU565 [AU-565], and Hs 281) using MTT Assay | [123] |
| A. schoenoprasum | Flowers; whole plant | Methanol, methanol-aqueous | Caffeic acid, catechin, cinnamic acid, coumaric acid, ferulic acid, gallic acid, resveratrol, rutin, vanillic acid, quercetin and sinapic acid; Spirostane-type glycosides: (20S,25S)-spirost-5-en-3β,12β,21-triol 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside (1), (20S,25S)-spirost-5-en-3β,11α,21-triol 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside (2), laxogenin 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside (3), and (25R)-5α-spirostan-3β,11α-diol 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-galactopyranoside. Prosapogenin A, deltonin and deltoside | Antiproliferative activity on HaCaT cells using the MTT assay; in vitro cytotoxic assay on HCT 116 and HT-29 (human colon cancer) cell lines | [124,125,126,127] |
| A. senescens | Leaves and stems | Methanol | p-coumaric acid | In vitro cytotoxicity effect on Sorafenib-Resistant Human HCC cells (HepG2); proliferative effect on human T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia cells; DPPH radical-scavenging activity, MTT and NBT Assays | [128,129,130] |
| A. sivasicum | Whole plant | Aqueous | - | In vitro cytotoxicity and apoptosis effect on breast cancer (MCF-7, MDA-MB-468) cells using (MTT) proliferation assay and in vivo study in albino Wistar rats | [131] |
| A. stipitatum | Leaves | Aqueous | Silver nano particles using aqueous extracts | Cytotoxicity of cerium oxide nanoparticles on colorectal carcinoma cells (HT-29, HCT116, and CW2) | [133,134,135,136] |
| A. tuberosum | Whole Plant and Leaves | Dichloromethane, methanol, hexane, ethyl-ether, ethyl-acetate, butanol and aqueous, acetone, petrol-eum ether | Crude thiosulfinates, S-methyl methanthiosulfinate and S-methyl 2-propene-1-thiosulfinate; thiosulfinates; methanol, hexane, ethylether, ethylacetate, butanol, and aqueous extract; americine, 9-Hydroxy-9,11,15-octadecatrienoic acid (9-HOTE), Di-n-octyl phthalate, 8-hydroxyoctadeca-9,12-dienoic acid (8S-HODE), 9-hydroperoxy-octadeca-10,12,15-trienoic acid [9(S)-HpOTrE], ɑ-Linolenic Acid, Fumaric acid-di-(2-decyl) ester, 3-ketostearic acid, 1,2-Benzene-di-carboxylic acid butyloctyl ester, N,N′-Pentamethylene-bis-[s-3-aminopropyl thiosulfuric acid, Ethyl 2E,4Z-hexadecadienoate, 9,12-Octadecadien-1-Ol, Eicosanoic acid, methyl ester, petroselinic acid, 10,16-dihydroxy-palmitic acid, Nonadecane,9-methyl, Methaphenilene, 10,11-Epoxy-3,7,11-trimethyl-2E,6E-tridecadienoic acid, Glycerol1,2-diacetate, Leucyl-glutamate | In vitro cytotoxicity on human cancer cells and in vivo apoptosis in MCF-7 cancer cells; in vitro cytotoxicity and apoptosis effect on HT-29 human colon cancer cells; HepG2, HeLa, and SK-N-MC cells using the MTT assay; in vitro effect on malignant melanoma in C57BL/6 mice; inhibitory activity against B-Raf, EGFR, K-Ras, and PI3K of non-small-cell lung cancer targets | [138,139,140,141,142,143] |
| A.tuberosum, A. macrostemon, A. thumbergii | Whole Plant | Aqueous | - | In vitro anti-adipogenic, anti-inflammatory activities, and inhibition effect of MDA-MB-453 cancer cell proliferation | [141] |
| A. ursinum | Whole plant | Aqueous, methanol-acetic acid | - | Proliferation and apoptosis effect of human gastric cancer cells; antioxidant and antiproliferative activity and in vitro gastrointestinal digestion on the cytotoxic activity on human malignant cell lines | [144,145,146,147] |
| A. wallichii | Leaves | Aqueous ethanol | Alkaloids, coumarin, flavonoids, glycosides, quinone, reducing sugars, saponins, steroids, tannins, terpenoids | DPPH free radical-scavenging assay, anti-microbial activity, and MTT/cytotoxicity assay against B-lymphoma cancer cell lines | [137] |
10. Antioxidant and Anticancer Effects of Allium
10.1. Antioxidant Mechanism
10.2. Anticancer Mechanism
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- POWO Plants of the World Online. Available online: http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/ (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Danquah, C.A.; Minkah, P.A.B.; Agana, T.A.; Moyo, P.; Ofori, M.; Doe, P.; Rali, S.; Osei Duah Junior, I.; Amankwah, K.B.; Somuah, S.O. The phytochemistry and pharmacology of Tulbaghia, Allium, Crinum and Cyrtanthus:‘talented’taxa from the Amaryllidaceae. Molecules 2022, 27, 4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takos, A.M.; Rook, F. Towards a molecular understanding of the biosynthesis of Amaryllidaceae alkaloids in support of their expanding medical use. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 11713–11741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, J. The Allium species (onions, garlic, leeks, chives, and shallots). Camb. World Hist. Food 2000, 1, 249–271. [Google Scholar]
- Sood, S.K.; Parmar, S.; Lakhanpal, T. Ethnic Plants of India Used in Cancer Cure—A Compendium; Bishen Singh Mahendra Pal Singh: Dehra Dun, India, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Samiei, L.; Kiani, M.; Zarghami, H.; Memariani, F.; Joharchi, M.R. Genetic diversity and interspecific relationships of some Allium species using inter simple sequence repeat markers. Bangladesh J. Plant Taxon. 2015, 22, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonthananiwatkul, B.; Lim, R.H.; Howard, R.L.; Pibanpaknitee, P.; Williamson, E.M. Traditional medicine use by cancer patients in Thailand. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 168, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritsch, R.M.; Friesen, N. Evolution, domestication and taxonomy. In Allium Crop Science: Recent Advances; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2002; pp. 5–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hanelt, P. Taxonomy, evolution, and history. In Onions and Allied Crops; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Takhtadzhian, A.L. Diversity and Classification of Flowering Plants; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- IUCN the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Ochar, K.; Kim, S.-H. Conservation and Global Distribution of Onion (Allium cepa L.) Germplasm for Agricultural Sustainability. Plants 2023, 12, 3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beretta, H.V.; Bannoud, F.; Insani, M.; Berli, F.; Hirschegger, P.; Galmarini, C.R.; Cavagnaro, P.F. Relationships between bioactive compound content and the antiplatelet and antioxidant activities of six Allium vegetable species. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 55, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suleria, H.A.R.; Butt, M.S.; Anjum, F.M.; Saeed, F.; Khalid, N. Onion: Nature protection against physiological threats. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Mnayer, D.; Tabanelli, G.; Stojanović-Radić, Z.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Yousaf, Z.; Vallone, L.; Setzer, W.; Iriti, M. Plants of the genus Allium as antibacterial agents: From tradition to pharmacy. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2016, 62, 57–68. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelrahman, M.; Mahmoud, H.Y.; El-Sayed, M.; Tanaka, S.; Tran, L. Isolation and characterization of Cepa2, a natural alliospiroside A, from shallot (Allium cepa L. Aggregatum group) with anticancer activity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 116, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.; Zolfaghari, B.; Keyvanlo Shahrestanaki, M.; Sadeghi Dinani, M. Cytotoxic effects of Allium affine Ledeb butanolic fraction on breast and ovary cancer cell lines. J. Med. Plants 2017, 16, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Gao, J.; Liu, G. General Situation of Allium Crops in China. Acta Hortic. 2005, 688, 327–332. [Google Scholar]
- Negi, K.; Pant, K.; Koppar, M.; Thomas, T. Wild relatives of genus Allium L. in himalayas. Indian J. Plant Genet. Resour. 2023, 4, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Mahato, R.; Behera, D.K.; Patra, B.; Das, S.; Lakra, K.; Pradhan, S.N.; Abbas, S.J.; Ali, S.I. Plant-based Natural Products in Cancer Therapeutics. J. Drug Target. 2024, 32, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuete, V.; Seo, E.-J.; Krusche, B.; Oswald, M.; Wiench, B.; Schröder, S.; Greten, H.J.; Lee, I.-S.; Efferth, T. Cytotoxicity and pharmacogenomics of medicinal plants from traditional Korean medicine. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 341724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seca, A.M.; Pinto, D.C. Plant secondary metabolites as anticancer agents: Successes in clinical trials and therapeutic application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Report on Traditional and Complementary Medicine 2019; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yousaf, Z.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Qureshi, R.; Khan, M.; Gilani, S.S. Can complexity of the genus Allium L. be resolved through some numerical techniques? Pak. J. Bot. 2004, 36, 487–502. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donnell, G.; Poeschl, R.; Zimhony, O.; Gunaratnam, M.; Moreira, J.B.; Neidle, S.; Evangelopoulos, D.; Bhakta, S.; Malkinson, J.P.; Boshoff, H.I. Bioactive pyridine-N-oxide disulfides from Allium stipitatum. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najeebullah, S.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Jan, S.A.; Khan, I.; Ali, M. Ethno medicinal and phytochemical properties of genus Allium: A review of recent advances. Pak. J. Bot. 2021, 53, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlinghaus, J.; Albrecht, F.; Gruhlke, M.C.; Nwachukwu, I.D.; Slusarenko, A.J. Allicin: Chemistry and biological properties. Molecules 2014, 19, 12591–12618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratchanova, M.; Nikolova, M.; Pavlova, E.; Yanakieva, I.; Kussovski, V. Composition and properties of biologically active pectic polysaccharides from leek (Allium porrum). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 2046–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krest, I.; Glodek, J.; Keusgen, M. Cysteine sulfoxides and alliinase activity of some Allium species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3753–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adwas, A.A.; Elsayed, A.; Azab, A.E.; Quwaydir, F.A. Oxidative stress and antioxidant mechanisms in human body. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2019, 6, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Engwa, G.A.; Nweke, F.N.; Nkeh-Chungag, B.N. Free radicals, oxidative stress-related diseases and antioxidant supplementation. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2022, 28, 114–128. [Google Scholar]
- Madkour, L.H. Function of reactive oxygen species (ROS) inside the living organisms and sources of oxidants. Pharm. Sci. Anal. Res. J. 2019, 2, 180023. [Google Scholar]
- Nimse, S.B.; Pal, D. Free radicals, natural antioxidants, and their reaction mechanisms. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 27986–28006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Jaén, A.B.; Valls-Bellésa, V.; Codoñer-Franch, P. Antioxidants: A review. J. Pediatr. Biochem. 2013, 3, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Putnik, P.; Gabrić, D.; Roohinejad, S.; Barba, F.J.; Granato, D.; Mallikarjunan, K.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Kovačević, D.B. An overview of organosulfur compounds from Allium spp.: From processing and preservation to evaluation of their bioavailability, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Herrera, P.; Morales, P.; Fernández-Ruiz, V.; Sánchez-Mata, M.C.; Cámara, M.; Carvalho, A.M.; Ferreira, I.C.; Pardo-de-Santayana, M.; Molina, M.; Tardio, J. Nutrients, phytochemicals and antioxidant activity in wild populations of Allium ampeloprasum L. a valuable underutilized vegetable. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd, F.A.E.-R.A.; Ali, R.F.M. Proximate compositions, phytochemical constituents, antioxidant activities and phenolic contents of seed and leaves extracts of Egyptian leek (Allium ampeloprasum var. kurrat). Eur. J. Chem. 2013, 4, 185–190. [Google Scholar]
- Liguori, L.; Califano, R.; Albanese, D.; Raimo, F.; Crescitelli, A.; Di Matteo, M. Chemical composition and antioxidant properties of five white onion (Allium cepa L.) landraces. J. Food Qual. 2017, 2017, 6873651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, D.-B.; Jin, W.; Park, J.; Yoon, W.; Lee, Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, O.-H. Comparative studies of bioactive organosulphur compounds and antioxidant activities in garlic (Allium sativum L.), elephant garlic (Allium ampeloprasum L.) and onion (Allium cepa L.). Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1193–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štajner, D.; Milić, N.; Lazić, B.; Mimica-Dukić, N. Study on antioxidant enzymes in Allium cepa L. and Allium fistulosum L. Phytother. Res. 1998, 12, S15–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, S.; Yamamoto, Y. Antioxidant activity and flavonoid content of Welsh onion (Allium fistulosum) and the effect of thermal treatment. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2007, 13, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, D.; Singh, B.N.; Upadhyay, G. Antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities of phenols from onion (Allium cepa). Food Chem. 2007, 102, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, C.; Joshi, S.; Kapoor, H. Antioxidants in onion (Allium cepa L.) cultivars grown in India. J. Food Biochem. 2009, 33, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini, I.; Tenore, G.C.; Dini, A. Chemical composition, nutritional value and antioxidant properties of Allium caepa L. Var. tropeana (red onion) seeds. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, S.F.C.; Idid, S.Z.; Koya, M.S.; Rehan, A.M.; Kamarudin, K.R. Antioxidant study of garlic and red onion: A comparative study. Pertanika J. Trop. Agric. Sci. 2011, 34, 253–261. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Gawad, M.; Abdel-Aziz, M.; El-Sayed, M.; El-Wakil, E.; Abdel-Lateef, E. In vitro antioxidant, total phenolic and flavonoid contents of six Allium species growing in Egypt. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2014, 3, 343–346. [Google Scholar]
- Dziri, S.; Hassen, I.; Fatnassi, S.; Mrabet, Y.; Casabianca, H.; Hanchi, B.; Hosni, K. Phenolic constituents, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of rosy garlic (Allium roseum var. odoratissimum). J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.-C.; Cheng, W.-S. Antioxidant activity of several Allium members. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 4097–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, Y.S.; Ishimoto, E.Y.; Bastos, D.H.; Sampaio, G.R.; Torres, E.A. Garlic (Allium sativum L.) and ready-to-eat garlic products: In vitro antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.N.; Singh, B.; Singh, R.; Prakash, D.; Singh, D.; Sarma, B.; Upadhyay, G.; Singh, H. Polyphenolics from various extracts/fractions of red onion (Allium cepa) peel with potent antioxidant and antimutagenic activities. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Huang, G. Extraction, characterisation and antioxidant activity of Allium sativum polysaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidhu, J.S.; Ali, M.; Al-Rashdan, A.; Ahmed, N. Onion (Allium cepa L.) is potentially a good source of important antioxidants. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 1811–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozin, B.; Mimica-Dukic, N.; Samojlik, I.; Goran, A.; Igic, R. Phenolics as antioxidants in garlic (Allium sativum L. Alliaceae). Food Chem. 2008, 111, 925–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.-H.; Choi, D.-J.; Lee, S.-J.; Cha, J.-Y.; Sung, N.-J. Antioxidant activity of black garlic (Allium sativum L.). J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 37, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkeblia, N. Free-radical scavenging capacity and antioxidant properties of some selected onions (Allium cepa L.) and garlic (Allium sativum L.) extracts. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2005, 48, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nencini, C.; Menchiari, A.; Franchi, G.G.; Micheli, L. In vitro antioxidant activity of aged extracts of some Italian Allium species. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2011, 66, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenkova, M.; Bystricka, J.; Toth, T.; Hrstkova, M. Vyhodnotenie a porovnanie obsahu celkových polyfenolov a antioxidačnej aktivity vo vybraných druhoch rodu Allium. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2016, 17, 1119–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Tepe, B.; Sokmen, M.; Akpulat, H.A.; Sokmen, A. In vitro antioxidant activities of the methanol extracts of five Allium species from Turkey. Food Chem. 2005, 92, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badraoui, R.; Rebai, T.; Elkahoui, S.; Alreshidi, M.; Veettil, V.N.; Noumi, E.; Al-Motair, K.A.; Aouadi, K.; Kadri, A.; De Feo, V.; et al. Allium subhirsutum L. as a potential source of antioxidant and anticancer bioactive molecules: HR-LCMS phytochemical profiling, in vitro and in vivo pharmacological study. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimzadeh, M.A.; Nabavi, S.F.; Nabavi, S.M.; Eslami, B. Antihemolytic and antioxidant activities of Allium paradoxum. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2010, 5, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stajner, D.; Varga, I.S.I. An evaluation of the antioxidant abilities of Allium species. Acta Biol. Szeged. 2003, 47, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Štajner, D.; Milić, N.; Čanadanović-Brunet, J. An investigation into the antioxidant activity of Allium nutans L. Phytother. Res. 1999, 13, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štajner, D.; Milić-DeMarino, M.; Čanadanović-Bruner, J.; Popović, M. Scavenger activity of Allium psekemense B. Fedtsch. Phytother. Res. 2002, 16, 484–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štajner, D.; Čanadanović-Brunet, J.; Pavlović, A. Allium schoenoprasum L. as a natural antioxidant. Phytother. Res. 2004, 18, 522–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štajner, D.; Milić-Demarino, N.; Čanadanović-Brunet, J.; Štajner, M.; Popović, B. Screening for antioxidant properties of Allium giganteum. Fitoterapia 2006, 77, 268–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štajner, D.; Popović, B.; Čanadanović-Brunet, J.; Štajner, M. Antioxidant and scavenger activities of Allium ursinum. Fitoterapia 2008, 79, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ŝtajner, D.; Milić-DeMarino, M.; Ĉanadanović-Brunet, J. Screening for antioxidant properties of leeks, Allium sphaerocephalon L. J. Herbs Spices Med. Plants 2003, 10, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Seo, K.H.; Lee, E.Y.; Ji, Y.-J.; Lee, Y.J.; Kang, M.H.; Seong, H.-A.; Kim, H.D. Antioxidant and anti-obesity potentials of Korean-native wild vegetables (Allium species). Horticulturae 2021, 7, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ding, P.; Li, R.; Zhang, S.; Guo, C. Antioxidant properties and inhibitory effect on nitrosation of extracts from Allium tenuissimum flowers. Food Res. Dev. 2019, 40, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zhao, X.; Xu, M. Chemical composition, antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of essential oil from Allium tenuissimum L. flowers. Foods 2022, 11, 3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radovanović, B.; Mladenović, J.; Radovanović, A.; Pavlović, R.; Nikolić, V. Phenolic composition, antioxidant, antimicrobial and cytotoxic activites of Allium porrum L.(Serbia) extracts. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2015, 3, 564–569. [Google Scholar]
- Lazarević, J.S.; Ðorđević, A.S.; Zlatković, B.K.; Radulović, N.S.; Palić, R.M. Chemical composition and antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of essential oil of Allium sphaerocephalon L. subsp. sphaerocephalon (Liliaceae) inflorescences. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hady, H.; El-Sayed, M.M.; Abdel-Gawad, M.M.; El-Wakil, E.A.; Abdel-Hameed, E.-S.S.; Abdel-Lateef, E.E.-S. LC-ESI-MS analysis, antitumor and antioxidant activities of methanolic extract of Egyptian Allium kurrat. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 8, 085–092. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, I.; Gul, S.; Khan, R.U.; Khan, M.I.; Rehman, H.U.; Ahmad, N.; Aziz-ud-Din, S.M.; Jawad, Y.I.; Rehman, S.U. Antibacterial and antioxidant activity analysis of some wild medicinal plants. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2017, 5, 1771–1775. [Google Scholar]
- Kamenetsky, R.; Rabinowitch, H.; Baitulin, I.; Agafonova, G.; Ivashenko, A. Expansion and conservation of Allium collection from Kazakhstan and neighboring areas and its evaluation for ornamental, edible and medicinal traits. Yad Hanadiv Grant 1999, 1996–1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kamenetsky, R.; Rabinowitch, H.D. The genus Allium: A developmental and horticultural analysis. Hortic. Rev. 2006, 32, 329–378. [Google Scholar]
- Asemani, Y.; Zamani, N.; Bayat, M.; Amirghofran, Z. Allium vegetables for possible future of cancer treatment. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 3019–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Li, N.; Du, L.; Zhao, R.; Yi, M.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, Y. Allium vegetable consumption and health: An umbrella review of meta-analyses of multiple health outcomes. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2451–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattorusso, E.; Iorizzi, M.; Lanzotti, V.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Chemical composition of shallot (Allium ascalonicum Hort.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 5686–5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi-Motlagh, H.-R.; Mostafaie, A.; Mansouri, K. Anticancer and anti-inflammatory activities of shallot (Allium ascalonicum) extract. Arch. Med. Sci. 2011, 7, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandurangan, V.; Amanulla, S.S.D.; Ramanathan, K. Anticancer efficacy of dry and fresh Allium ascalonicum (shallot) against HepG2 cell line. Natl. J. Physiol. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2016, 6, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, G.-B.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Nguyen, H.-N.; Pham, H.-H.; Ngo, T.M.T. Chemical composition and antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer effects of ethanol extract of black shallot (Allium ascalonicum). Pharmacophore 2020, 11, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Shimazaki, T.; Iguchi, T.; Kanda, A.; Yamamoto, K.; Takahashi, N.; Mimaki, Y. Six unprecedented steroidal glycosides from Allium atropurpureum bulbs and their cytotoxicities against SBC-3 human small-cell lung cancer cells. Phytochem. Lett. 2023, 57, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, S.; Esa, N.M.; Ramachandran, V.; Hamid, R.A.; Pandurangan, A.K.; Etemad, A.; Ismail, P. In vitro antiproliferative and apoptosis inducing effect of Allium atroviolaceum bulb extract on breast, cervical, and liver cancer cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, S.; Ramachandran, V.; Esa, N.M.; Etemad, A.; Moradipoor, S.; Ismail, P. Flower extract of Allium atroviolaceum triggered apoptosis, activated caspase-3 and down-regulated antiapoptotic Bcl-2 gene in HeLa cancer cell line. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 1216–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, S.; Abdul Hamid, R.; Mohd Esa, N.; Ramachandran, V.; Aalam, G.T.F.; Etemad, A.; Ismail, P. Promotion of HepG2 cell apoptosis by flower of Allium atroviolaceum and the mechanism of action. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi Dinani, M.; Zakeri Tehrani, N. Bioassay guided fractionation of Allium austroiranicum by cytotoxic effects against ovary and cervical cancer cell lines. Res. J. Pharmacogn. 2020, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Isbilen, O.; Rizaner, N.; Volkan, E. Anti-proliferative and cytotoxic activities of Allium autumnale PH Davis (Amaryllidaceae) on human breast cancer cell lines MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbilen, O.; Volkan, E. Allium willeanum Holmboe exerts anticancer activities on metastatic breast cancer cells MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurnia, D.; Ajiati, D.; Heliawati, L.; Sumiarsa, D. Antioxidant properties and structure-antioxidant activity relationship of Allium species leaves. Molecules 2021, 26, 7175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, W.-X.; Ma, X.-F. Inhibitory effects of onion (Allium cepa L.) extract on proliferation of cancer cells and adipocytes via inhibiting fatty acid synthase. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 5573–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhuang, W.; Hu, W.; Liu, G.J.; Wu, T.X.; Wu, X.T. Consumption of large amounts of Allium vegetables reduces risk for gastric cancer in a meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiga, A.A.; Irioda, A.C.; Mogharbel, B.F.; Bonatto, S.J.; Souza, L.M. Quercetin-rich extracts from onions (Allium cepa) play potent cytotoxicity on adrenocortical carcinoma cell lines, and quercetin induces important anticancer properties. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vafaee, K.; Dehghani, S.; Tahmasvand, R.; Saeed Abadi, F.; Irian, S.; Salimi, M. Potent antitumor property of Allium bakhtiaricum extracts. BMC Compl. Alter. Med. 2019, 19, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-H.; Yoon, J.B.; Han, J.; Seo, Y.A.; Kang, B.-H.; Lee, J.; Ochar, K. Green Onion (Allium fistulosum): An Aromatic Vegetable Crop Esteemed for Food, Nutritional and Therapeutic Significance. Foods 2023, 12, 4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkrishna, A.; Chaudhary, M.; Sharma, H.; Srivastava, D.; Kukreti, A.; Kumar, A.; Arya, V. Phytochemistry, pharmacology, and medicinal aspects of Allium fistulosum L.: A narrative review. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 13, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Țigu, A.B.; Moldovan, C.S.; Toma, V.-A.; Farcaș, A.D.; Moț, A.C.; Jurj, A.; Fischer-Fodor, E.; Mircea, C.; Pârvu, M. Phytochemical analysis and in vitro effects of Allium fistulosum L. and Allium sativum L. extracts on human normal and tumor cell lines: A comparative study. Molecules 2021, 26, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, Z.; Akhtar, S.; Imran, M.; Nadeem, M.; Gilani, S.; Elnashar, M.; Ahmed, E. Antioxidant activity, anti-inflammatory activities, anti-cancer and chemical composition of spring onion (Allium fistolisum) extracts. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 1880–1890. [Google Scholar]
- Rhetso, T.; Shubharani, R.; Roopa, M.; Sivaram, V. Chemical constituents, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activity of Allium chinense G. Don. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 6, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, F.; Xiao, X.; Ding, X.; He, H.; Rang, J.; Quan, M.; Wang, T.; Zuo, M. Anticancer activity of saponins from Allium chinense against the B16 melanoma and 4T1 breast carcinoma cell. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 725023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, F.; Sadeghi-Dinani, M.; Jahanian-Najafabadi, A. The cytotoxic and pro-apoptotic effects of various extracts of Allium giganteum on MCF-7 and HeLa cell lines. J. Isfahan Med. Sch. 2021, 39, fa578–fa583. [Google Scholar]
- Mimaki, Y.; Kuroda, M.; Fukasawa, T.; Sashida, Y. Steroidal glycosides from the bulbs of Allium jesdianum. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, R.; Shams, N.; Gholami, N.; Rashidi, I.; Jalili, C. Anti-cancer and apoptosis induction effects of allium jesdianum hydroalcoholic extract on thyroid cancer cell lines (b-cpap and THR. C1-PI 33). World Cancer Res. J. 2021, 8, e2104. [Google Scholar]
- Rashidi, I.; Hajalikhani, P.; Jalili, C.; Zhaleh, M. The cytotoxic and migrastatic potentials of Allium Jesdianum hydroalcoholic extract on glioblastoma multiforme cell line model. World Cancer Res. J. 2022, 9, e2151. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz-Ozden, T.; Hasbal-Celikok, G.; Aksoy-Sagirli, P.; Altiparmak-Ulbegi, G.; Kocyigit, M.; Can, A.; Akev, N. Phenolic profile, antioxidant, antidiabetic, DNA protection, and cytotoxic activities of Allium kurtzianum. Int. Food Res. J. 2020, 27, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar]
- Mskhiladze, L.; Legault, J.; Lavoie, S.; Mshvildadze, V.; Kuchukhidze, J.; Elias, R.; Pichette, A. Cytotoxic steroidal saponins from the flowers of Allium leucanthum. Molecules 2008, 13, 2925–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-F.; Wang, G.-H.; Luo, Q.; Wang, N.-L.; Yao, X.-S. Two new steroidal saponins from Allium macrostemon Bunge and their cytotoxity on different cancer cell lines. Molecules 2009, 14, 2246–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Jiang, S.; Li, M.; Wang, X. Anti-colorectal cancer activity of macrostemonoside A mediated by reactive oxygen species. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xu, Q.; Zheng, T.; Huang, F.; Han, L. Metabonomic analysis of Allium macrostemon Bunge as a treatment for acute myocardial ischemia in rats. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 88, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, H.L.; Go, M.J.; Joo, S.G.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Sim, S.J.; Heo, H.J. Protective effect of Allium ochotense Prokh. extract against ethanol-induced cytotoxicity. Food Sci. Preserv. 2023, 30, 526–537. [Google Scholar]
- Alshammari, G.M.; Balakrishnan, A.; Subash-Babu, P.; Al-khalifa, A.; Alshatwi, A.A.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Al-Harbi, L.N.; Alshamlan, G.H.; Albekairi, N.A. Alpha-linolenic acid rich Allium porrum methanolic extract potentially inhibits HT-115 human colon cancer cells proliferation via mitochondria mediated apoptotic mechanism. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2022, 34, 101736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamri, N.; Hamid, H.A. Comparative study of onion (Allium cepa) and leek (Allium ampeloprasum): Identification of organosulphur compounds by UPLC-QTOF/MS and anticancer effect on MCF-7 cells. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2019, 74, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattorusso, E.; Lanzotti, V.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Di Rosa, M.; Ianaro, A. Cytotoxic saponins from bulbs of Allium porrum L. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3455–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmatha, J.; Buděšínský, M.; Zídek, Z.; Kmoníčková, E. Spirostanol saponins from flowers of Allium porrum and related compounds indicating cytotoxic activity and affecting nitric oxide production inhibitory effect in peritoneal macrophages. Molecules 2021, 26, 6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, J.H. Anti-aging effect of Allium pseudojaponicum in UVA–irradiated human epidermal keratinocytes. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2023, 69, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naji, K.M.; Al-Shaibani, E.S.; Alhadi, F.A.; Al-Soudi, S.a.A.; D’souza, M.R. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of single clove garlic against CCl 4-induced hepatic damage in rabbits. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wargovich, M.J. Diallyl sulfide, a flavor component of garlic (Allium sativum), inhibits dimethyihydrazine-induced colon cancer. Carcinogenesis 1987, 8, 487–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, D.R.; DeHaven, J.I.; Lamm, D.L. Allium sativum (garlic) treatment for murine transitional cell carcinoma. Cancer 1997, 79, 1987–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjzadeh, M.; Tavakol Afshari, J.; Ghorbani, A.; Shakeri, M. The effects of aqueous extract of garlic (Allium sativum L.) on laryngeal cancer cells (Hep-2) and L929 cells in vitro. J. Med. Plants 2006, 5, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.; Kusumoto, Y.; Al-Mamun, M.A. Cytotoxicity and cancer (HeLa) cell killing efficacy of aqueous garlic (Allium sativum) extract. J. Sci. Res. 2011, 3, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wu, F.; Chen, Y.; Alrashood, S.T.; Alharbi, S.A. Anti-human colon cancer properties of a novel chemotherapeutic supplement formulated by gold nanoparticles containing Allium sativum L. leaf aqueous extract and investigation of its cytotoxicity and antioxidant activities. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, A.A.; Mahmood, A.; Alsharidah, M.; Mohammed, H.A.; Alenize, S.K.; Bouazzaoui, A.; Al Rugaie, O.; Alnuqaydan, A.M.; Ahmad, R.; Vaali-Mohammad, M.-A.; et al. Bioactivities of the green synthesized silver nanoparticles reduced using Allium cepa L aqueous extracts induced apoptosis in colorectal cancer cell lines. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Amraii, S.A.; Toushmalani, R.; Almasi, M. Formulation of a modern anti-human breast cancer drug from silver nanoparticles green-synthesized using Allium saralicum. J. Eng. Res. 2023, 11, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatlioglu, T. Chive: Allium schoenoprasum L. In Genetic Improvement of Vegetable Crops; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kucekova, Z.; Mlcek, J.; Humpolicek, P.; Rop, O.; Valasek, P.; Saha, P. Phenolic compounds from Allium schoenoprasum, Tragopogon pratensis and Rumex acetosa and their antiproliferative effects. Molecules 2011, 16, 9207–9217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvu, A.; Parvu, M.; Vlase, L.; Miclea, P.; Mot, A.; Silaghi-Dumitrescu, R. Anti-inflammatory effects of Allium schoenoprasum L. leaves. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 65, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Timité, G.; Mitaine-Offer, A.-C.; Miyamoto, T.; Tanaka, C.; Mirjolet, J.-F.; Duchamp, O.; Lacaille-Dubois, M.-A. Structure and cytotoxicity of steroidal glycosides from Allium schoenoprasum. Phytochemistry 2013, 88, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Park, Y.; Shin, H.; Kim, B.; Lee, S. Effect of Allium senescens Extract on Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocarcinoma Cells. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, D.H.; Badamtsetseg, B.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.A. Anti-proliferative effect of Allium senescens L. extract in human T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia cells. Molecules 2020, 26, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-Y.; Kim, G.-H. Inhibitory effects of Allium senescens L. methanol extracts on reactive oxygen species production and lipid accumulation during differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 46, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepe, B.; Tuncer, E.; Saraydın, S.U.; Özer, H.; Şen, M.; Karadayi, K.; Inan, D.S.; Karadayi, S.; Polat, Z.; Akpulat, A.; et al. Antitumoral effects of Allium sivasicum on breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmet, E.; Ceren, E. A comparative study of phenolic profiles and biological activities of Allium sphaerocephalon L. subsp. sphaerocephalon L. and Allium sphaerocephalon L. subsp. trachypus (Boiss. Et Spruner) K. Richter. J. Res. Pharm. 2020, 24, 893–900. [Google Scholar]
- Azadi, H.G.; Riazi, G.H.; Ghaffari, S.M.; Ahmadian, S.; Khalife, T.J. Effects of Allium hirtifolium (Iranian shallot) and its allicin on microtubule and cancer cell lines. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 5030–5037. [Google Scholar]
- Fasihzadeh, S.; Lorigooini, Z.; Jivad, N. Chemical constituents of Allium stipitatum regel (Persian shallot) essential oil. Der Pharm. Lett. 2016, 8, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.-W.; Wang, L.-K.; Fang-Zhou, L.; Yuan, B.-H.; Zou, X.-M.; Wang, R.-T. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles green-formulated by Allium stipitatum and treat the colorectal cancer as a modern chemotherapeutic supplement. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 143, 109781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi-Rika, A.; Beigi-Boroujeni, M.; Rajabzadeh, A.; Zarei, L. Effect of Extract of Allium stipitatum on Excisional Wound Healing in Rats. Iran. J. Vet. Surg. 2021, 16, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bhandari, J.; Muhammad, B.; Thapa, P.; Shrestha, B.G. Study of phytochemical, anti-microbial, anti-oxidant, and anti-cancer properties of Allium wallichii. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-W.; Kim, S.-Y.; Jeong, I.-Y.; Byun, M.-W.; Park, K.-H.; Yamada, K.; Seo, K.-I. Cytotoxic and antitumor activities of thiosulfinates from Allium tuberosum L. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 7957–7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Yang, H.-S.; Park, K.-W.; Kim, J.-Y.; Lee, M.-K.; Jeong, I.-Y.; Shim, K.-H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Yamada, K.; Seo, K.-I. Mechanisms of thiosulfinates from Allium tuberosum L.-induced apoptosis in HT-29 human colon cancer cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 188, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.-J.; Kim, M.-H.; Bae, S.-J. Anticarcinogenic effects of Allium tuberosum on human cancer cells. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 34, 688–693. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.S.; Choi, E.J.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, G.-H. Evaluation of Allium vegetables for anti-Adipogenic, anti-Cancer, and anti-inflammatory activities InVitro. J. Life Sci. 2013, 5, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carolina, C.-B.M.; Carolina, G.-B.A.; Alexandra, C.-R.A.; Paola, P.-B.S.; Andrea, S.-R.M.; Armando, B.-C.R. Allium tuberosum aqueous extract had curative effects on malignant melanoma in C57BL/6 mice. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2020, 7, 007–017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, R.; Singha, S.; Nath, D.; Das, G.; Patra, J.K.; Talukdar, A.D. Phytochemicals from Allium tuberosum Rottler ex Spreng show potent inhibitory activity against B-Raf, EGFR, K-Ras, and PI3K of non-small cell lung cancer targets. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, A.; Mikhova, B.; Najdenski, H.; Tsvetkova, I.; Kostova, I. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of wild garlic Allium ursinum of Bulgarian origin. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 1059–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.-Y.; Song, G.-Q.; Yu, Y.-Q.; Ma, H.-Y.; Ma, L.; Jin, Y.-N. Apoptosis and G2/M arrest induced by Allium ursinum (ramson) watery extract in an AGS gastric cancer cell line. OncoTargets Ther. 2013, 6, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvu, A.E.; Cătoi, F.; Deelawar, S.; Sarup, D.; Parvu, M. Anti-inflammatory effect of Allium ursinum. Not. Sci. Biol. 2014, 6, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanisavljević, N.; Soković Bajić, S.; Jovanović, Ž.; Matić, I.; Tolinački, M.; Popović, D.; Popović, N.; Terzić-Vidojević, A.; Golić, N.; Beškoski, V.; et al. Antioxidant and antiproliferative activity of Allium ursinum and their associated microbiota during simulated in vitro digestion in the presence of food matrix. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 601616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, P.; Dhiman, A.; Kumar, S.; Suhag, R. Garlic (Allium sativum L.): A review on bio-functionality, allicin’s potency and drying methodologies. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 171, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iciek, M.G.; Wlodek, L. Biosynthesis and biological properties of compounds containing highly reactive, reduced sulfane sulfur. Pol. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 53, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Corzo-Martínez, M.; Corzo, N.; Villamiel, M. Biological properties of onions and garlic. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 609–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Ai, C.-X.; Wang, Y.-H.; Zhang, J.-S.; Wu, C.-W. Abrupt salinity stress induces oxidative stress via the Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway in large yellow croaker Pseudosciaena crocea. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, M.F.; Saleem, A.; Rasul, A.; Baig, M.M.F.A.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Daim, M.M.A. Anticancer natural medicines: An overview of cell signaling and other targets of anticancer phytochemicals. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 888, 173488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaram, S.G.; Milner, J.A. Diallyl disulfide induces apoptosis of human colon tumor cells. Carcinogenesis 1996, 17, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, M.A.; Kirby, R. Apoptosis: A review of pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic pathways and dysregulation in disease. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2008, 18, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, M.; Lin, X.; Wang, Y.; He, X. A steroidal saponin isolated from Allium chinense simultaneously induces apoptosis and autophagy by modulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in human gastric adenocarcinoma. Steroids 2020, 161, 108672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, R.K. Garlic induced apoptosis, cell cycle check points and inhibition of cancer cell proliferation. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 5, 35–54. [Google Scholar]
- Amagase, H.; Milner, J.A. Impact of various sources of garlic and their constituents on 7, 12-dimethylbenz [α] anthracene binding to mammary cell DNA. Carcinogenesis 1993, 14, 1627–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Choi, Y.S.; Jeon, Y.E.; Im, K.J.; Choi, Y.M.; Yim, S.Y.; Kim, H.; Seo, S.K.; Lee, B.S. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its soluble receptor-1 in endometriosis. Microvasc. Res. 2012, 83, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Pu, X.; Du, J.; Yang, X.; Yang, T.; Yang, S. Therapeutic role of functional components in alliums for preventive chronic disease in human being. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 9402849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talib, W.H.; Atawneh, S.; Shakhatreh, A.N.; Hamed, R.A.; Al-Yasari, I.H. Anticancer potential of garlic bioactive constituents: Allicin, Z-ajoene, and organosulfur compounds. Pharmacia 2024, 71, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, S.; Mishra, N.; Agarwal, R. Phytochemicals as immunomodulatory molecules in cancer therapeutics. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Allium Species | Status and Year Assessed | Nativity |
|---|---|---|
| A. akirense N.Friesen & Fragman | CR (2015) | Israel |
| A. iatrouanum Trigas (un) | CR (2017) | Greece |
| A. baytopiorum Kollmann & Ozhatay | CR (2007) | E. Türkiye |
| A. czelghauricum Bordz. | CR (2007) | NE Türkiye |
| A. corsicum Jauzein, J.-M.Tison, Deschâtres & H.Couderc | CR (2010) | Corse |
| A. marathasicum Brullo, Pavone & Salmeri | CR (2016) | Cyprus |
| A. pseudocalyptratum Mouterde | EN (2016) | Lebanon, W. Saudi Arabia |
| A. noeanum Reut. ex Regel | EN (2019) | S.E. Türkiye, N. Syria, N. Iraq, N.W. and N. Iran |
| A. sannineum Gomb. | EN (2017) | Lebanon and Israel |
| A. pseudoalbidum N.Friesen & Özhatay | EN (2007) | Türkiye |
| A. struzlianum Ogan. | EN (2007) | S. Transcaucasus |
| A. pervestitum Klokov | EN (2011) | N.E. Black Sea Coast |
| A. diomedeum Brullo, Guglielmo, Pavone & Salmeri | EN (2015) | Italy |
| A. garganicum Brullo, Pavone, Salmeri & Terrasi | EN (2015) | S. Italy |
| A. baeticum Boiss. | EN (2018) | W. Central Portugal, S. Spain, NW. Africa |
| A. agrigentinum Brullo & Pavone | EN (2015) | Sicilia |
| A. peroninianum Azn. | EN (2016) | N. Türkiye |
| A. therinanthum C.Brullo, Brullo, Fragman, Giusso & Salmeri | EN (2015) | E. Mediterranean |
| A. meronense Fragman & R.M.Fritsch | EN (2016) | S. Lebanon to N. Israel |
| A. basalticum Fragman & R.M.Fritsch | EN (2016) | Lebanon to W. Jordan |
| A. pycnotrichum Trigas, Kalpoutz. & Constantin. | EN (2017) | Greece |
| A. makrianum C.Brullo, Brullo, Giusso & Salmeri | EN (2013) | E. Aegean Islands (Chios) |
| A. schmitzii Cout. | VU (2010) | E. Portugal to Central Spain |
| A. pyrenaicum Costa & Vayr. | VU (2010) | Pyrenees |
| A. dumetorum Feinbrun & Szel. | VU (2016) | Lebanon to Israel |
| A. exaltatum (Meikle) Brullo, Pavone, Salmeri & Venora | VU (2010) | Cyprus |
| A. hemisphaericum (Sommier) Brullo | VU (2018) | Sicilia |
| A. castellanense (Garbari, Miceli & Raimondo) Brullo, Guglielmo, Pavone & Salmeri | VU (2018) | Sicilia |
| A. nebrodense Guss. | VU (2015) | Sicilia |
| A. pseudophanerantherum Rech.f. | VU (2016) | Syria |
| A. trichocnemis J.Gay | VU (2018) | Algeria |
| A. pelagicum Brullo, Pavone & Salmeri | VU (2016) | Sicilia |
| A. scaberrimum J.Serres | VU (2018) | N.E. Spain, SE. France (Hautes Alpes) to Italy, N. Algeria to Tunisia |
| A. lojaconoi Brullo, Lanfr. & Pavone | NT (2011) | Malta |
| A. altaicum Pall. | NT (2013) | Siberia to N. China |
| A. carmeli Boiss. | NT (2014) | Syria to Israel |
| A. libani Boiss. | NT (2016) | Lebanon to S.W. Syria |
| A. machmelianum Post | NT (2018) | Syria |
| A. calocephalum Wendelbo | NT (2016) | S.E. Türkiye to N. Iraq |
| A. melananthum Coincy | NT (2010) | SE. Spain |
| A. anzalonei Brullo, Pavone & Salmeri | NT (2015) | Italy |
| A. roylei Stearn | NT (2013) | Afghanistan to W. Himalaya |
| A. telmatum Bogdanovic, Brullo, Giusso & Salmeri | NT (2015) | Croatia |
| A. meikleanum Brullo, Pavone & Salmeri | NT (2016) | Cyprus |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iwar, K.; Ochar, K.; Seo, Y.A.; Ha, B.-K.; Kim, S.-H. Alliums as Potential Antioxidants and Anticancer Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158079
Iwar K, Ochar K, Seo YA, Ha B-K, Kim S-H. Alliums as Potential Antioxidants and Anticancer Agents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(15):8079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158079
Chicago/Turabian StyleIwar, Kanivalan, Kingsley Ochar, Yun Am Seo, Bo-Keun Ha, and Seong-Hoon Kim. 2024. "Alliums as Potential Antioxidants and Anticancer Agents" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 15: 8079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158079
APA StyleIwar, K., Ochar, K., Seo, Y. A., Ha, B.-K., & Kim, S.-H. (2024). Alliums as Potential Antioxidants and Anticancer Agents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(15), 8079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158079









