Nuclear Factor-Kappa-B Mediates the Advanced Glycation End Product-Induced Repression of Slc2a4 Gene Expression in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Advanced Glycated Albumin Modulates Slc2a4 mRNA and GLUT4 Protein Expression in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes in a Time- and Concentration-Dependent Way
2.2. Advanced Glycated Albumin Increases the Expression of Genes of NFKB Subunits p65 and p50
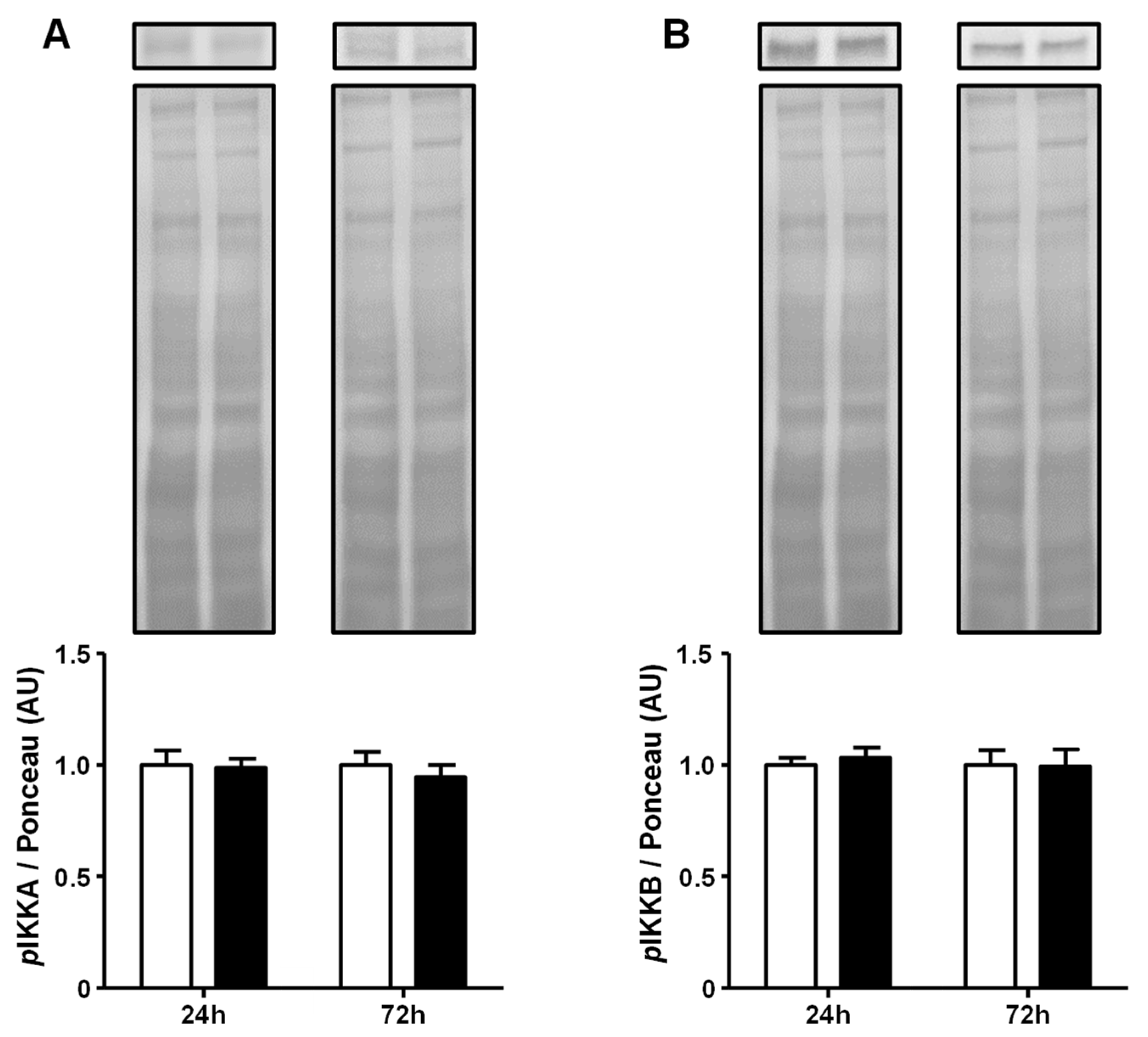
2.3. Advanced Glycated Albumin Does Not Modulate the Activity of the IKKs at 5.4 mg/dL Concentration
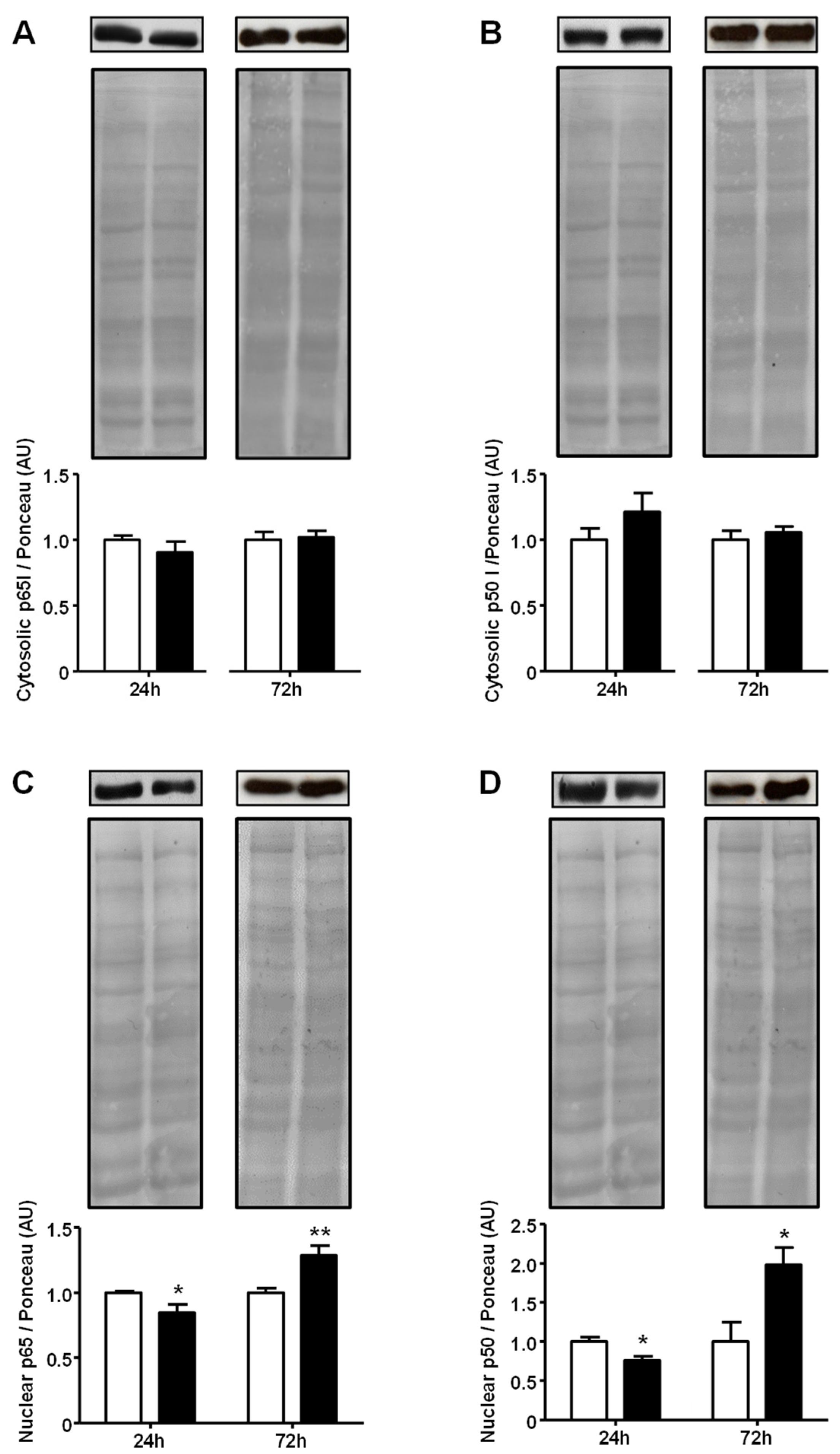
2.4. Advanced Glycated Albumin Increases Nuclear Content of Nuclear Factor NF-kappa-B at 5.4 mg/dL Concentration
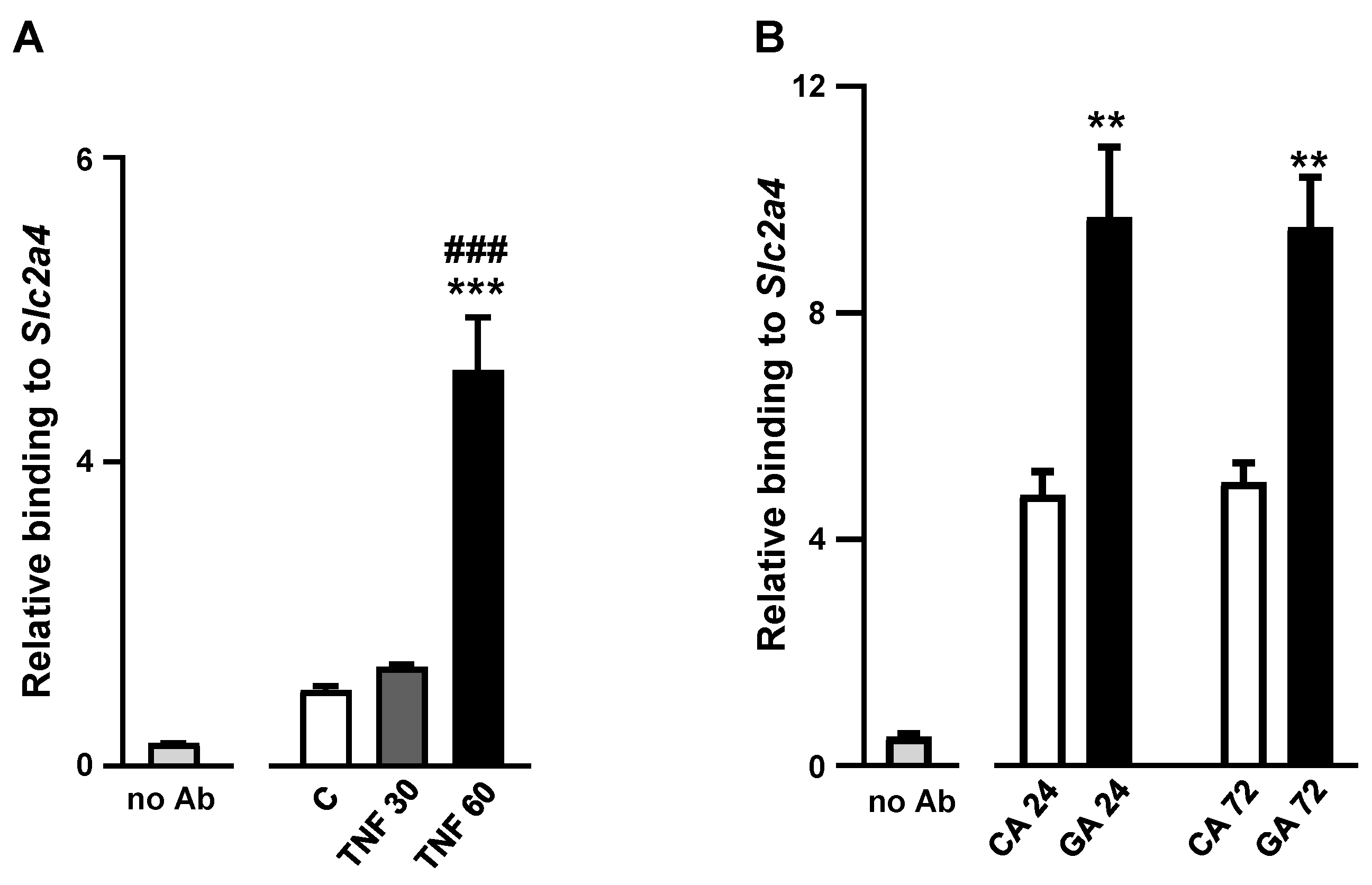
2.5. Advanced Glycated Albumin at 5.4 mg/mL Concentration Increases the Binding Activity of NFKB to the Slc2a4 Gene Promoter
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Modification of Bovine Albumin by Advanced Glycation In Vitro
4.2. Cell Culture and Treatments
4.3. Reverse Transcription and Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
4.4. Western Blotting
4.5. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Assay
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGEs | advanced glycation end products |
| AU | arbitrary units |
| CA | control albumin |
| ChIP | chromatin immunoprecipitation |
| CA | control albumin |
| DM | diabetes mellitus |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| GA | advanced glycated albumin |
| Gapdh | glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (mouse gene) |
| GLUT4 | solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 4 |
| IKBA | NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha |
| IKKA | inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit alpha |
| IKKB | inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit beta |
| MGO | methylglyoxal |
| MTT | tetrazolium salt 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| NFKB | nuclear factor NF-kappa-B |
| NFKB/p50 | nuclear factor NF-kappa-B/subunit 50 |
| NFKB | nuclear factor NF-kappa-B/subunit 65 |
| Nfkb1 | nuclear factor kappa B subunit 1 (mouse gene) codifies the p50 subunit |
| p50/p65 | NFKB/p50 and NFKB/p65 complex |
| Rela | RELA proto-oncogene, NF-kB subunit (mouse gene) codifies the p65 subunit |
| RT-qPCR | reverse transcription and quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| Slc2a4 | solute carrier family 2 member 4 (mouse gene) |
| SLC2A4 | solute carrier family 2 member 4 (human gene) |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
References
- Henning, C.; Glomb, M.A. Pathways of the Maillard reaction under physiological conditions. Glycoconj. J. 2016, 33, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najjar, J.A.; Calvert, J.W. Effects of protein glycation and protective mechanisms against glycative stress. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2024, 76, 102464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passarelli, M.; Machado, U.F. AGEs-Induced and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress/Inflammation-Mediated Regulation of GLUT4 Expression and Atherogenesis in Diabetes Mellitus. Cells 2022, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowotny, K.; Schroter, D.; Schreiner, M.; Grune, T. Dietary advanced glycation end products and their relevance for human health. Ageing Res. Rev. 2018, 47, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Chen, S.; Shi, Y.; Wang, P.; Wu, Y.; Li, G. Dietary advanced glycation end products (dAGEs): An insight between modern diet and health. Food Chem. 2023, 415, 135735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, S.; Burman, A.; Tripathi, A.K. Advanced glycation end products: Key mediator and therapeutic target of cardiovascular complications in diabetes. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 1146–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrean, M.; Stirban, A.; Stratmann, B.; Gawlowski, T.; Horstmann, T.; Götting, C.; Kleesiek, K.; Mueller-Roesel, M.; Koschinsky, T.; Uribarri, J.; et al. Effects of low- and high-advanced glycation endproduct meals on macro- and microvascular endothelial function and oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stirban, A.; Kotsi, P.; Franke, K.; Strijowski, U.; Cai, W.; Götting, C.; Tschoepe, D. Acute macrovascular dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes induced by ingestion of advanced glycated β-lactoglobulins. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1278–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baret, B.; Le Sage, F.; Planesse, C.; Meilhac, O.; Devin, A.; Bourdon, E.; Rondeau, P. Glycated human albumin alters mitochondrial respiration in preadipocyte 3T3-L1 cells. Biofactors 2017, 43, 577–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribarri, J.; Cai, W.; Sandu, O.; Peppa, M.; Goldberg, T.; Vlassara, H. Diet-derived advanced glycation end products are major contributors to the body’s AGE pool and induce inflammation in healthy subjects. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1043, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribarri, J.; Stirban, A.; Sander, D.; Cai, W.; Negrean, M.; Buenting, C.E.; Koschinsky, T.; Vlassara, H. Single oral challenge by advanced glycation end products acutely impairs endothelial function in diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 2579–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portero-Otin, M.; de la Maza, M.P.; Uribarri, J. Dietary Advanced Glycation End Products: Their Role in the Insulin Resistance of Aging. Cells 2023, 12, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Lv, C.; Li, M.; Wang, K.; Chen, Z. Advanced Glycation End Products and Health: A Systematic Review. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klip, A.; Sun, Y.; Chiu, T.T.; Foley, K.P. Signal transduction meets vesicle traffic: The software and hardware of GLUT4 translocation. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2014, 306, C879–C886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klip, A.; McGraw, T.E.; James, D.E. Thirty sweet years of GLUT4. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 11369–11381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.I.; Ashfaq, F.; Alsayegh, A.A.; Hamouda, A.; Khatoon, F.; Altamimi, T.N.; Alhodieb, F.S.; Beg, M.M.A. Advanced glycation end product signaling and metabolic complications: Dietary approach. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 995–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto-Junior, D.C.; Silva, K.S.; Michalani, M.L.; Yonamine, C.Y.; Esteves, J.V.; Fabre, N.T.; Thieme, K.; Catanozi, S.; Okamoto, M.M.; Seraphim, P.M.; et al. Advanced glycation end products-induced insulin resistance involves repression of skeletal muscle GLUT4 expression. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Chang, G.D.; Wen, H.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Chang, S.C.; Liao, J.F.; Chang, C.H. Activation of Akt by advanced glycation end products (AGEs): Involvement of IGF-1 receptor and caveolin-1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Chang, G.D.; Chen, T.H.; Chen, W.L.; Wen, H.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Chang, C.H. Hyperglycemia and advanced glycation end products (AGEs) suppress the differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 55039–55050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilelli, N.C.; Faggian, A.; Favaretto, F.; Milan, G.; Compagnin, C.; Dassie, F.; Bettini, S.; Roverso, M.; Seraglia, R.; Lapolla, A.L.; et al. In vitro chronic glycation induces AGEs accumulation reducing insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and increasing GLP1R in adipocytes. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 320, E976–E988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afridi, S.K.; Aftab, M.F.; Murtaza, M.; Ghaffar, S.; Karim, A.; Mughal, U.R.; Khan, K.M.; Waraich, R.S. A new glycotoxins inhibitor attenuates insulin resistance in liver and fat cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 476, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, S.M.; Dong, H.J.; Li, Z.; Cai, W.; Altomonte, J.; Thung, S.N.; Zeng, F.; Fisher, E.A.; Vlassara, H. Improved insulin sensitivity is associated with restricted intake of dietary glycoxidation products in the db/db mouse. Diabetes 2002, 51, 2082–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.H.; Huang, H.W.; Huang, S.M.; Lin, J.A.; Yeh, C.T.; Yen, G.C. AGE-induced interference of glucose uptake and transport as a possible cause of insulin resistance in adipocytes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 7978–7984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, R.; Paolillo, M.; Papetti, A. A new millifluidic-based gastrointestinal platform to evaluate the effect of simulated dietary methylglyoxal intakes. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 4330–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, N.T.; Thieme, K.; Silva, K.S.; Catanozi, S.; Cavaleiro, A.M.; Pinto, D.A.C., Jr.; Okamoto, M.M.; Morais, M.R.; Falquetto, B.; Zorn, T.M.; et al. Hormetic modulation of hepatic insulin sensitivity by advanced glycation end products. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 447, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, D.T.; Neri, E.A.; Poletto, A.C.; Anhê, G.F.; Freitas, H.S.; Campello, R.S.; Rebouças, N.A.; Machado, U.F. Identification of nuclear factor-κB sites in the Slc2a4 gene promoter. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 370, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winsauer, G.; de Martin, R. Resolution of inflammation: Intracellular feedback loops in the endothelium. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 97, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, N.D.; Gilmore, T.D. Good cop, bad cop: The different faces of NF-kappaB. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tergaonkar, V.; Correa, R.G.; Ikawa, M.; Verma, I.M. Distinct roles of IkappaB proteins in regulating constitutive NF-kappaB activity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 921–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Karin, M. Missing pieces in the NF-kappaB puzzle. Cell 2002, 109, S81–S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assis, S.I.S.; Amendola, L.S.; Okamoto, M.M.; Ferreira, G.D.S.; Iborra, R.T.; Santos, D.R.; Santana, M.F.M.; Santana, K.G.; Correa-Giannella, M.L.; Barbeiro, D.F.; et al. The Prolonged Activation of the p65 Subunit of the NF-Kappa-B Nuclear Factor Sustains the Persistent Effect of Advanced Glycation End Products on Inflammatory Sensitization in Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonamine, C.Y.; Passarelli, M.; Suemoto, C.K.; Pasqualucci, C.A.; Jacob-Filho, W.; Alves, V.A.F.; Marie, S.K.N.; Correa-Giannella, M.L.; Britto, L.R.; Machado, U.F. Postmortem Brains from Subjects with Diabetes Mellitus Display Reduced GLUT4 Expression and Soma Area in Hippocampal Neurons: Potential Involvement of Inflammation. Cells 2023, 12, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Michalani, M.L.E.; Passarelli, M.; Machado, U.F. Nuclear Factor-Kappa-B Mediates the Advanced Glycation End Product-Induced Repression of Slc2a4 Gene Expression in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158242
Michalani MLE, Passarelli M, Machado UF. Nuclear Factor-Kappa-B Mediates the Advanced Glycation End Product-Induced Repression of Slc2a4 Gene Expression in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(15):8242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158242
Chicago/Turabian StyleMichalani, Maria Luiza Estimo, Marisa Passarelli, and Ubiratan Fabres Machado. 2024. "Nuclear Factor-Kappa-B Mediates the Advanced Glycation End Product-Induced Repression of Slc2a4 Gene Expression in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 15: 8242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158242
APA StyleMichalani, M. L. E., Passarelli, M., & Machado, U. F. (2024). Nuclear Factor-Kappa-B Mediates the Advanced Glycation End Product-Induced Repression of Slc2a4 Gene Expression in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(15), 8242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158242





