The Secreted Aminopeptidase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PaAP)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. History and Names
3. Activity, Specificity, and Basic Properties
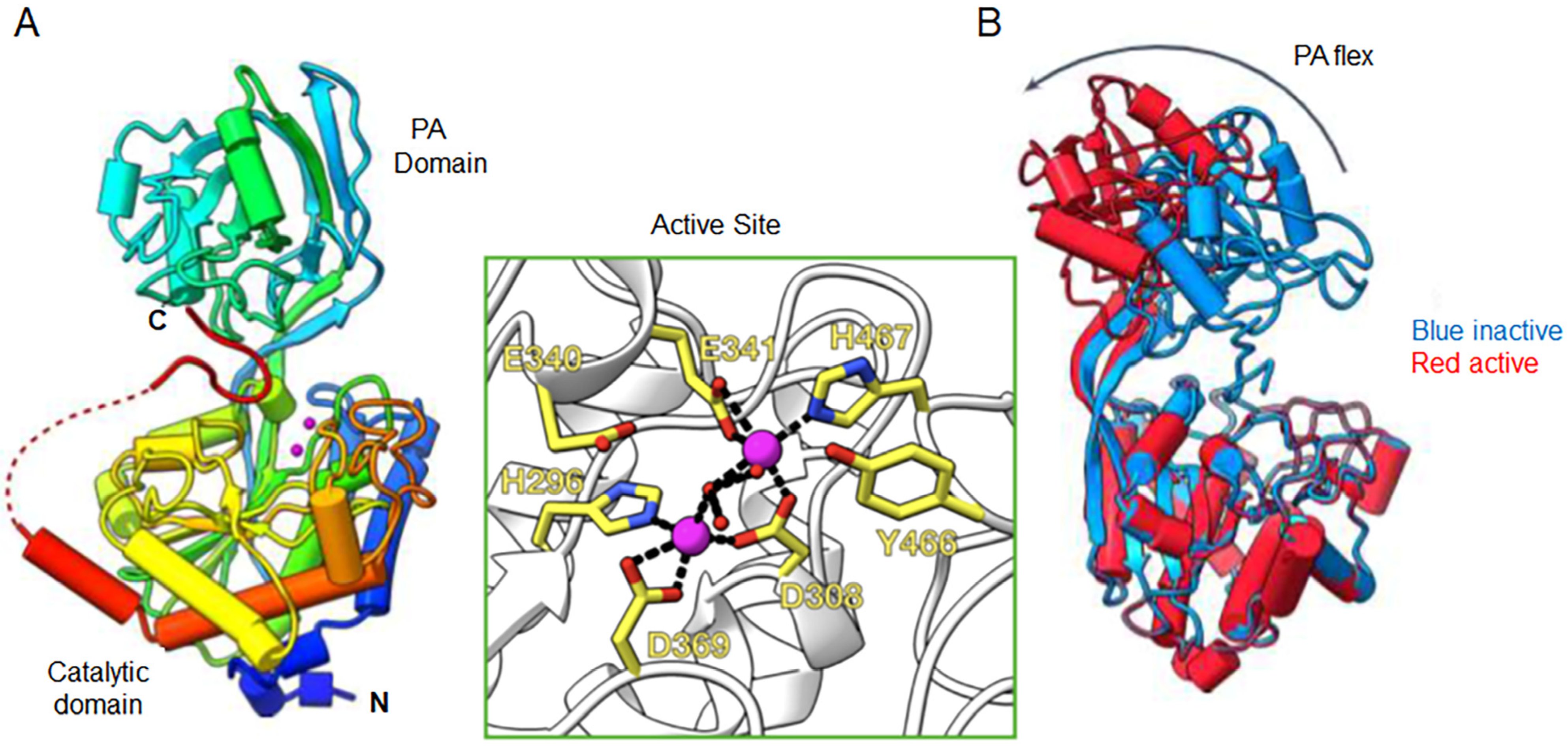
4. Structural Chemistry
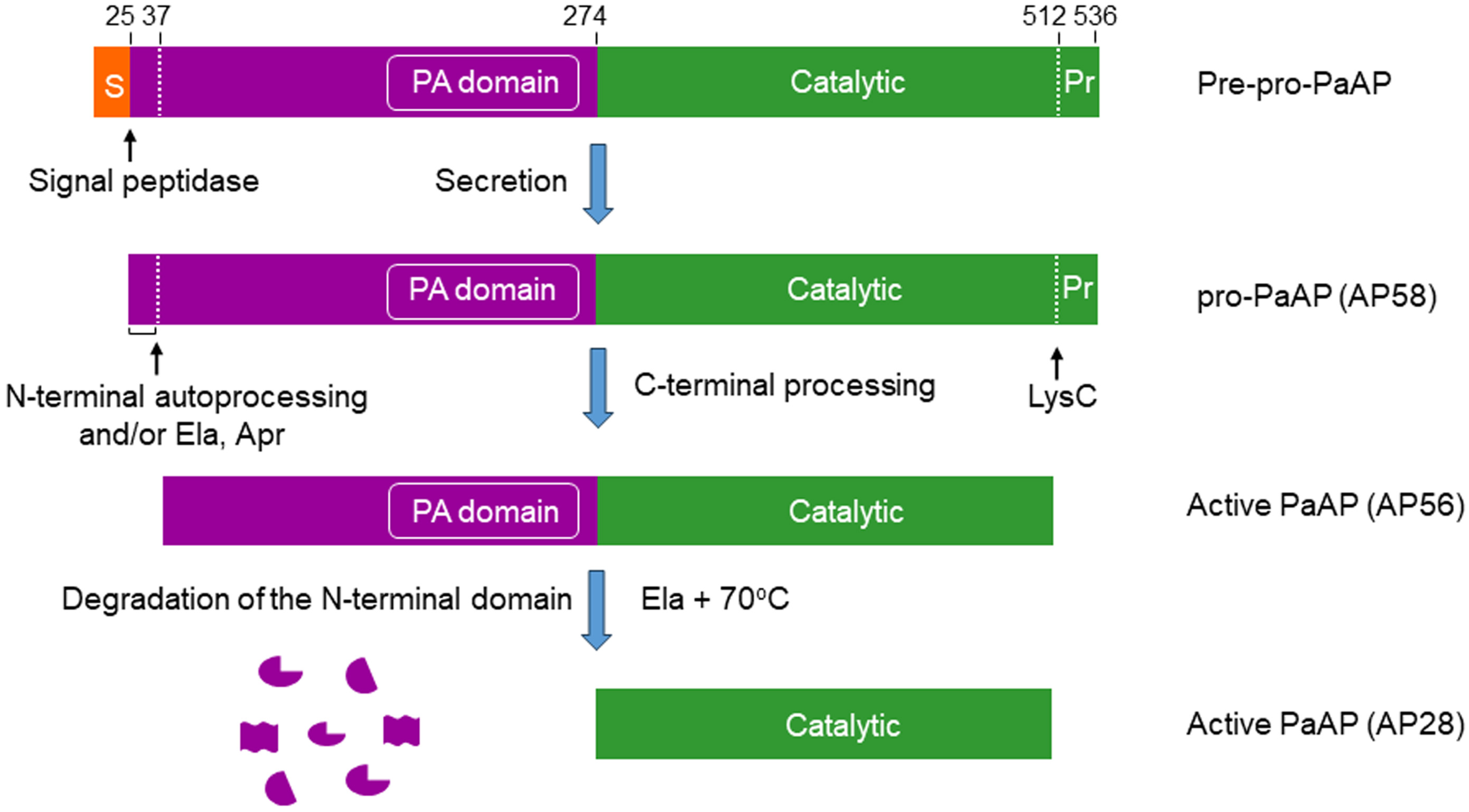
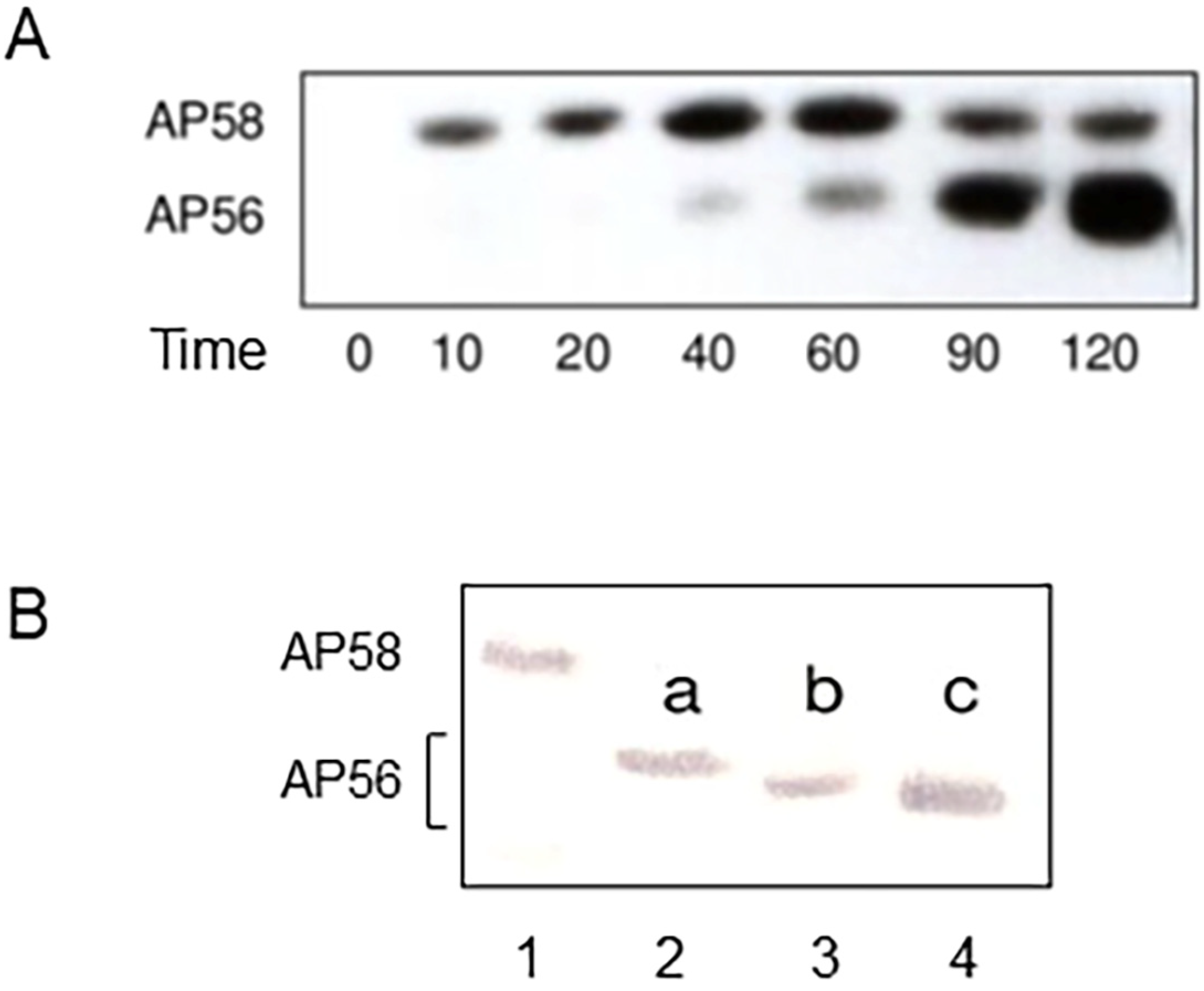
5. Secretion, Maturation, and Regulation
6. Biological and Pathophysiological Aspects
6.1. Role of PaAP in Biofilm Development
6.1.1. Studies with P. aeruginosa Strain PAO1
6.1.2. Studies with Clinical P. aeruginosa Isolates
6.2. Role of PaAP in Nutrition
6.3. PaAP as a Therapeutic Target
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strateva, T.; Mitov, I. Contribution of an arsenal of virulence factors to pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Ann. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diggle, S.P.; Whitely, M. Microbe Profile: Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Opportunistic pathogen and lab rat. Microbiology 2020, 166, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Martin, I.; Sainz-Mejias, M.; McClean, S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: An audacious pathogen with an adaptable arsenal of virulence factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadi, P.; Baráth, Z.; Gajdács, M. It’s not easy being green: A narrative review on the microbiology, virulence and therapeutic prospects of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Huang, X.; Wang, Q.; Yao, D.; Lu, W. Virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and antivirulence strategies to combat its drug resistance. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 926758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, S.; Xiao, X.; Zhou, C.; Deng, X.; Lan, L.; Liang, H.; Song, X.; Wu, M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis, virulence factors, antibiotic resistance, interaction with host, technology advances and emerging therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Targeted Ther. 2022, 7, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, A.J. Proteases. Curr. Protoc. Prot. Sci. 2000, 21.1.1–21.1.12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartley, B.S. Proteolytic enzymes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1960, 29, 45–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, E.; Safrin, M. Elastinolytic and proteolytic enzymes. Pseudomonas Methods Protoc. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1149, 135–169. [Google Scholar]
- Galdino, A.C.M.; Branquinha, M.H.; Santos, A.L.S.; Viganor, L. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its arsenal of proteases: Weapons to battle the host. In Pathophysiological Aspects of Proteases, 1st ed.; Charaborti, S., Dhalla, N.S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 381–397. [Google Scholar]
- Kessler, E.; Ohman, D.E. Pseudolysin. In Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes, 3rd ed.; Rawlings, N.D., Salversen, G.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 582–592. [Google Scholar]
- Everett, M.J.; Davis, D.T. Pseudomonas aeruginsa elastase (LasB) as a therapeutic target. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 2108–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honek, J.F. Aeruginolysin. In Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes, 3rd ed.; Rawlings, N.D., Salversen, G.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 867–872. [Google Scholar]
- Kessler, E.; Ohman, D.E. Staphylolysin. In Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes, 3rd ed.; Rawlings, N.D., Salversen, G.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 1553–1557. [Google Scholar]
- Eliott, B.W.; Cohen, C. Isolation and characterization of a lysine-specific protease from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 261, 11259–11265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malloy, J.L.; Veldhuizen, R.A.W.; Thibodeux, B.A.; O’Callaghan, R.J.; Wright, J.R. Pseudomonas aeruginosa protease IV degrades surfactant proteins and inhibits surfactant host defense and biophysical functions. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2005, 288, L409–L418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahan, R.; Axelrad, I.; Safrin, M.; Ohman, D.E.; Kessler, E. A secreted aminopeptidase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Identification, primary structure, and relationship to other aminopeptidases. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 43645–43652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleve, S.; Viarre, V.; Salacha, R.; Michel, G.P.F.; Filloux, A.; Voulhoux, R. Protein secretion systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A wealth of pathogenic weapons. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 300, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandha, J.; Harjai, K.; Chhibber, S. Revisiting the virulence hallmarks of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A chronicle through the perspective of quorum sensing. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 2630–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyofuku, M.; Roschitzki, B.; Riedel, K.; Eberl, L. Identification of proteins associated with the Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm extracellular matrix. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 4906–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, M.J.; Ma, L.Z. Extracellular aminopeptidase modulates biofilm development of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by affecting matrix exopolysaccharide and bacterial cell death. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2018, 10, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esoda, C.N.; Kuehn, M.J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa leucine aminopeptidase influences early biofilm composition and structure via vesicle-associated antibiofilm activity. mBio 2019, 10, e02548-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, P.; De Groot, A.; Bitter, W.; Tommassen, J. Secretion of elastinolytic enzymes and their propeptides by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 3467–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenblatt, H.M.; Almog, O.; Maras, B.; Spungin-Bialik, A.; Barra, D.; Blumberg, S.; Shoham, G. Streptomyces griseus aminopeptidase: X-ray crystallographic structure at 1.75 Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 265, 620–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Cui, W.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, Z. Over-expression, secretion, biochemical characterisation, and structure analysis of Bacillus subtilis aminopeptidase. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 2810–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevrier, B.; D’Orchymont, H.; Schalk, C.; Tarnus, C.; Moras, D. The structure of the Aeromonas proteolytica aminopeptidase complexed with a hydroxamate inhibitor. Involvement in catalysis of Glu151 and two zinc ions of the co-catalytic unit. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 237, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.; Smith, P.; Alberts, E.R.; Colussi-Pelaez, M.; Schuster, M. Cooperation and cheating through a secreted aminopeptidase in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa RpoS response. mBio 2020, 11, e03090-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauman, S.J.; Kuehn, M.J. Purification of outer membrane vesicles from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and their activation of an IL-8 response. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 2400–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauman, S.J.; Kuehn, M.J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa vesicles associate with and are internalized by human lung epithelial cells. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, C.J.; Bischoff, M.; Bergkessel, M.; Czekster, C.M. An anti-biofilm cyclic peptide targets a secreted aminopeptidase from P. aeruginosa. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2023, 19, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnovsky, R.; Rea, J.; Makowski, M.; Hertle, R.; Kelly, C.; Antignani, A.; Pastrana, D.V.; FitzGerald, D.J. Proteolytic cleavage of a C-terminal prosequence, leading to autoprocessing at the N Terminus, activates leucine aminopeptidase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 10243–10253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.T.; Zhou, N.D.; Zhou, Z.M.; Gao, X.X.; Tian, Y.P. A thermo-stable lysine aminopeptidase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Isolation, purification, characterization, and sequence analysis. J. Basic Microbiol. 2014, 54, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelrad, I.; Safrin, M.; Cahan, R.; Suh, S.-J.; Ohman, D.E.; Kessler, E. Extracellular proteolytic activation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa aminopeptidase (PaAP) and insight into the role of its non-catalytic N-terminal domain. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, R.; Grover, T.; Sharma, R.; Kapoor, S.; Khare, S.K. Purification and characterization of a solvent stable aminopeptidase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Cloning and analysis of aminopeptidase gene conferring solvent stability. Proc. Biochem. 2010, 45, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouwens, A.S.; Beatson, S.A.; Whitchurch, C.B.; Walsh, B.J.; Schweizer, H.P.; Mattick, J.S.; Cordwell, S.J. Proteome analysis of extracellular proteins regulated by the las and rhl quorum sensing systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Microbiology 2003, 149, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales, T.; Robert-Baudouy, J. Bacterial aminopeptidases: Properties and function. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 18, 319–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, J.; Tang, M.; Ma, L.Z.; Lei, X. Development of an effective fluorescence probe for discovery of aminopeptidase inhibitors to suppress biofilm formation. J. Antibiot. 2019, 72, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, A.-X.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Li, Q.-Y.; Qing, Y.-M. Purification and characterization of a novel β-Cypermethrin-degrading aminopeptidase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa GF31. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 9412–9418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, X.-D.; Li, F.; Yue, S.-Y.; Huang, X.-N.; Gao, T.-T.; Jiao, D.-Q.; Wang, C.-H. Production and characterization of novel thermos- and organic solvent-stable keratinase and aminopeptidase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa 4-3 for effective poultry feather degradation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 2480–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahon, P.; Bateman, A. The PA domain: A protease-associated domain. Protein Sci. 2000, 9, 1930–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Hofmann, K. The protease-associated domain: A homology domain associated with multiple classes of proteases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2001, 26, 147–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Li, X.-H.; Kim, S.-K.; Lee, J.-H. Post-secretional activation of protease IV by quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, M.; Lostroh, P.C.; Ogi, T.; Greenberg, E.P. Identification, timing, and signal specificity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-controlled genes: A transcriptome analysis. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 2066–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, M.; Hawkins, A.C.; Harwood, C.S.; Greenberg, E.P. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa RpoS regulon and its relationship to quorum sensing. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 51, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Larrota, J.S.; Eckhard, U. An introduction to bacterial biofilms and their proteases, and their role in host infection and immune evasion. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, M.J.; Nivens, D.E.; Weadge, J.T.; Howell, L.P. Biosynthesis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa extracellular polysaccharides, Alginate, Pel, and Psl. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, S.K. Current knowledge and future directions in developing strategies to combat Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 5509–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Bacerio, J.; Varela, A.C.; Aguado, M.E.; Izquierdo, M.; Méndez, Y.; del Rivero, M.A.; Rivera, D.G. Bacterial metalo-aminopeptidases as targets in human infectious diseases. Curr. Drug Targets 2022, 23, 1155–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Tang, B.L.; Shao, X.; Liu, B.X.; Zheng, X.Y.; Han, X.X.; Li, P.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Song, X.Y.; Chen, X.L. Characterization of a new S8 serine protease from marine sedimentary photobacterium sp. A5-7 and the function of its protease-associated domain. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, S.; Aylward, F.; Miliara, X.; Lau, R.J.; Huemer, C.B.; Giblin, S.P.; Huse, K.K.; Liang, M.; Reeves, L.; Pearson, M.; et al. The protease associated (PA) domain in ScpA from Streptococcus pyogenes plays a role in substrate recruitment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2023, 1871, 140946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| A. Kinetic constants for hydrolysis of several amino acid p-NA derivatives | |||||||||||||
| pNA | Km | Kcat | Kcat/Km | ||||||||||
| Substrate | |||||||||||||
| (mM) | (s−1) | (s−1 mM−1) | |||||||||||
| Leu | 2.3 | 7.5 | 9.41 | 2.7 | 11.5 | 18.7 | 183.3 | 5 | 2.5 | 68.7 | |||
| Ala | 0.9 | ND | ND | 6.5 | 0.53 | ND | 17.4 | 0.59 | ND | 2.7 | |||
| Met | 1.9 | 4.7 | ND | ND | 0.96 | 3.7 | ND | 0.5 | 0.8 | ND | |||
| Arg | 0.9 | 3.9 | ND | 3 | 1.12 | 2.7 | 23.6 | 1.24 | 0.7 | 7.9 | |||
| Lys | 1.5 | 1.2 | 2.32 | ND | 4.1 | 6.9 | ND | 2.73 | 5.8 | ND | |||
| B. Relative hydrolysis rates of the same amino acid p-NA derivatives as in A | |||||||||||||
| pNA | Relative Activity | ||||||||||||
| Substrate | |||||||||||||
| (%) | |||||||||||||
| Leu | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||||||||||
| Ala | 3 | ND | 10 | ||||||||||
| Met | 14 | ND | ND | ||||||||||
| Arg | ND | 45 | 23.3 | ||||||||||
| Lys | ND | 370 | ND | ||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kessler, E. The Secreted Aminopeptidase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PaAP). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158444
Kessler E. The Secreted Aminopeptidase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PaAP). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(15):8444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158444
Chicago/Turabian StyleKessler, Efrat. 2024. "The Secreted Aminopeptidase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PaAP)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 15: 8444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158444
APA StyleKessler, E. (2024). The Secreted Aminopeptidase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PaAP). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(15), 8444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158444





