Exosomal Preconditioning of Human iPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes Beneficially Alters Cardiac Electrophysiology and Micro RNA Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
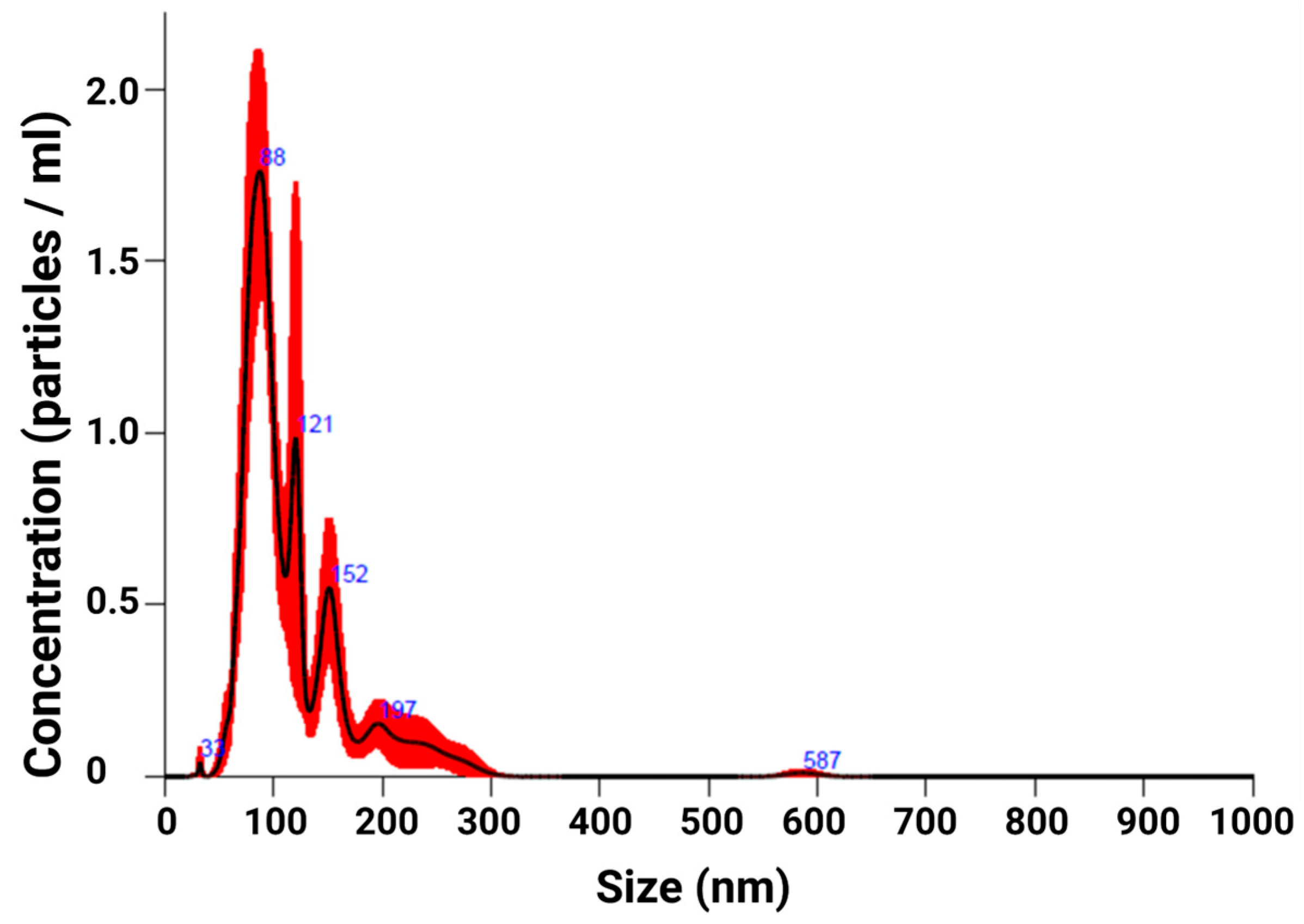
2.1. EXO Isolation
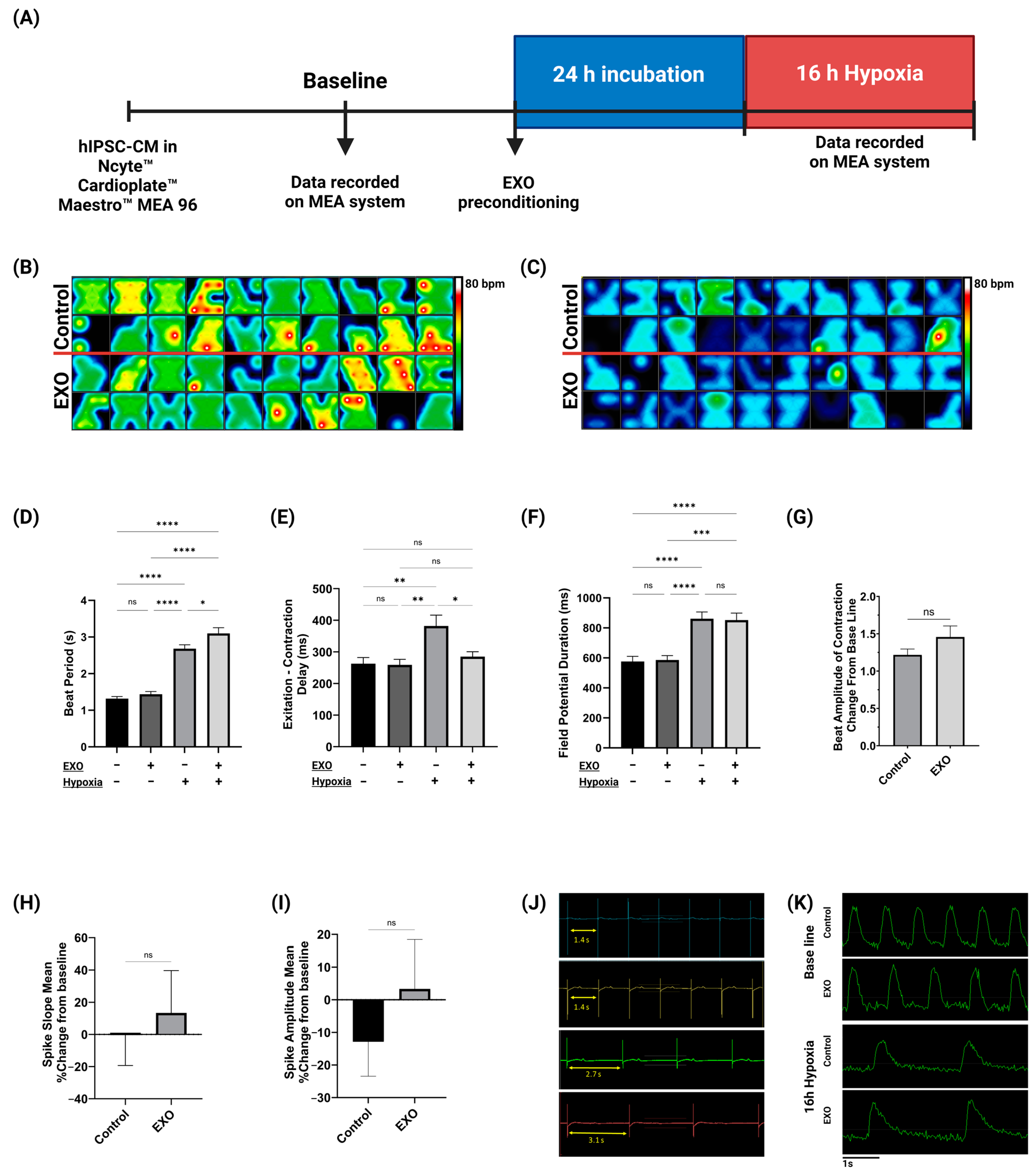
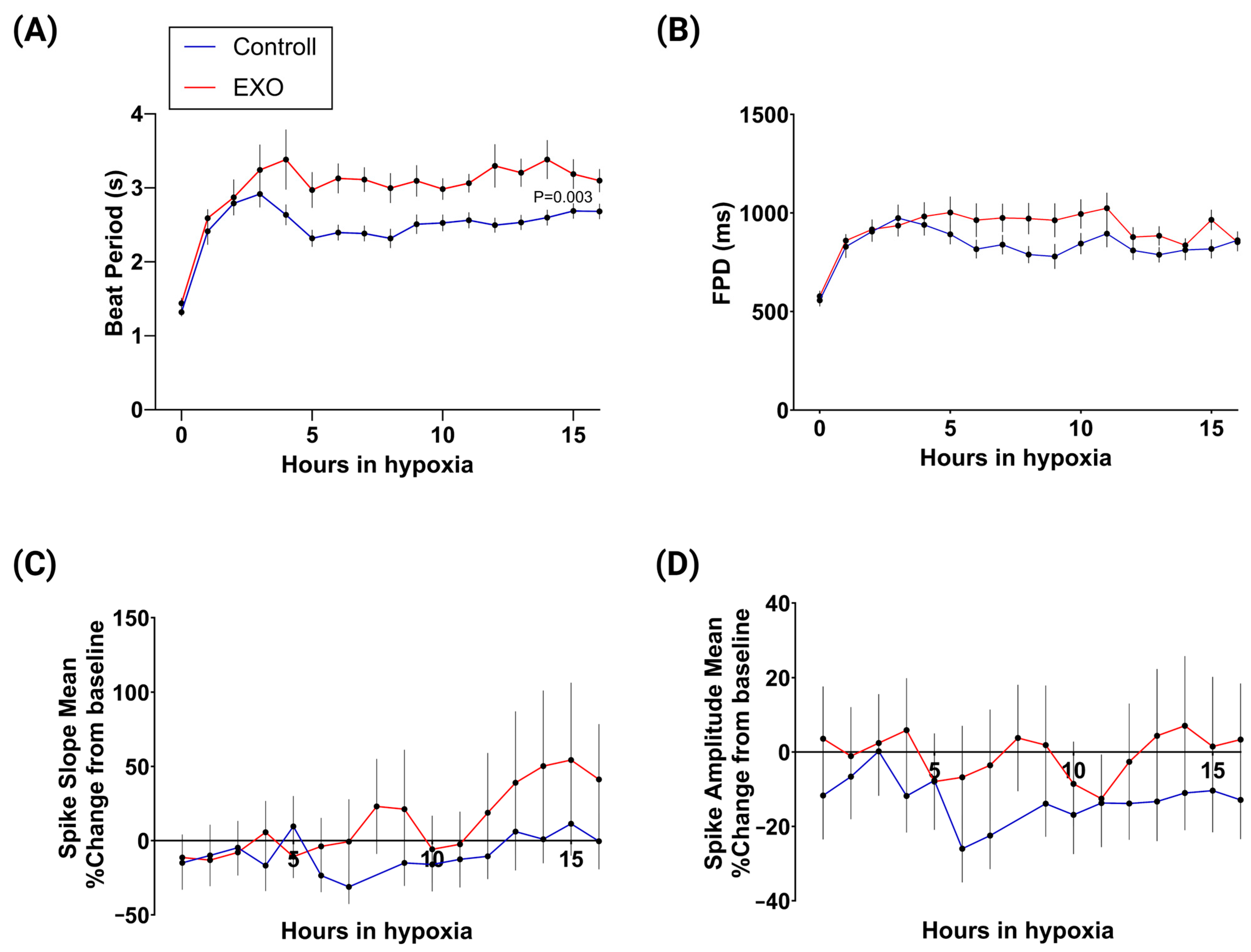
2.2. Electrophysiological Activity of hIPSC-CMs
2.3. miR Sequencing of Non-Treated and Pre-Conditioned hIPSC-CMs
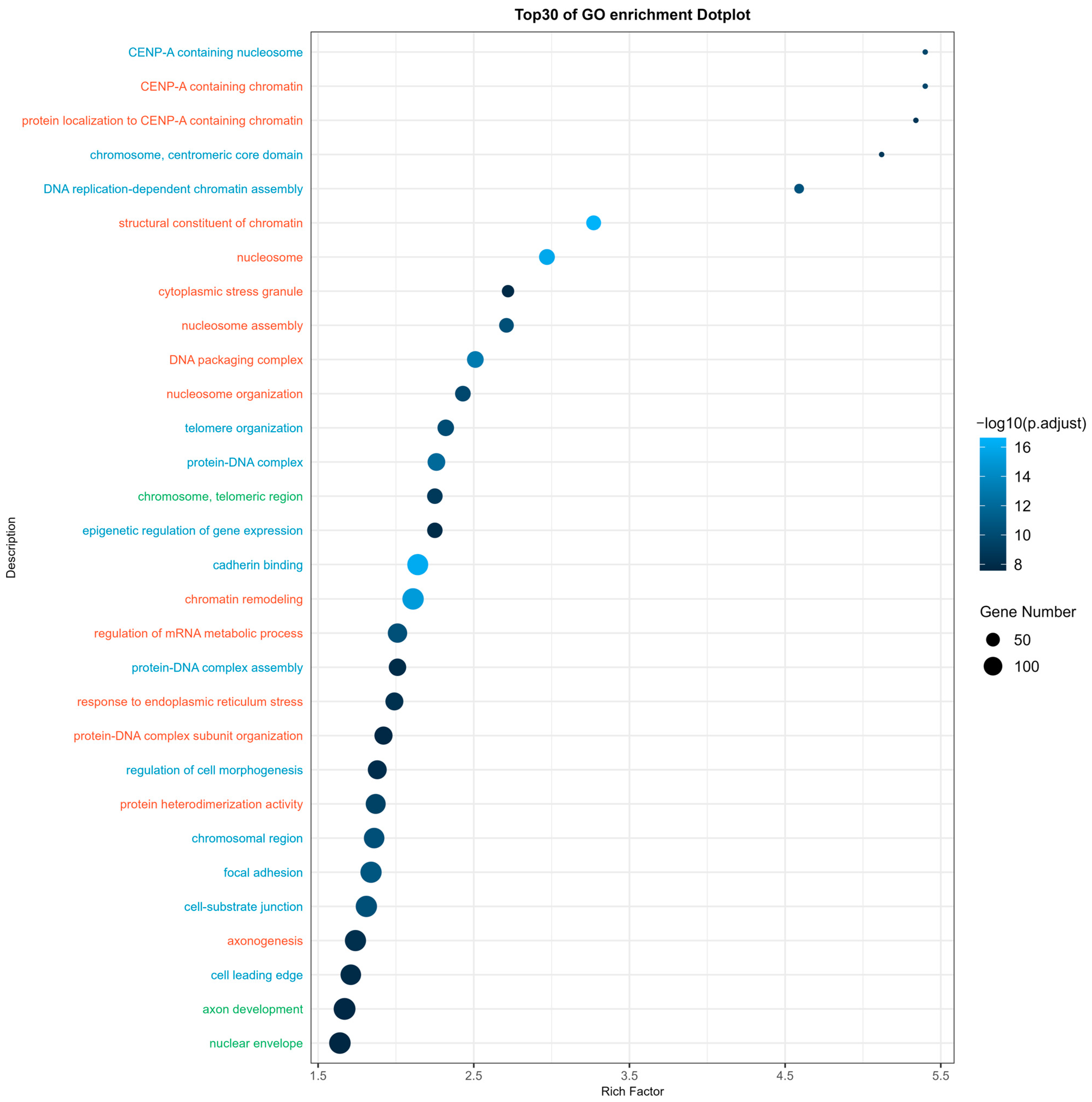
2.4. miR Target Prediction Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. hIPSC-CMs for EXO Production
4.2. EXO Isolation and Resuspension
4.3. EXO Quantification and Characterization
4.4. Culturing and Maintenance of Human IPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes
4.5. EXO Preconditioning
4.6. Hypoxia
4.7. Analysis of Cardiac Electrophysiology on MEA System
4.8. RNA Isolation
4.9. miR Sequencing
4.10. miR Target Prediction Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKT | AKT serine/threonine kinase |
| AMI | acute myocardial infarction |
| ANK2 | ankyrin 2 |
| ANK3 | ankyrin 3 |
| APD | action potential durations |
| APLN | apelin |
| AXIN1 | axin 1 |
| BAK1 | BCL2 antagonist/killer 1 |
| BAX | BCL2-associated X |
| BBC3 | BCL2 binding component 3 |
| BCL2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| BCL2L1 | BCL2-like 1 |
| BCL2L11 | BCL2-like 11 |
| BCL2L2 | BCL2-like 2 |
| BRCA1 | BRCA1 DNA repair associated |
| CACNA1C | calcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha1 C |
| CACNA1D | calcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha1 D |
| CACNA1H | calcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha1 H |
| CACNG8 | calcium voltage-gated channel auxiliary subunit gamma 8 |
| CALM1 | calmodulin 1 |
| CASP3 | caspase 3 |
| CASP9 | caspase 9 |
| DAPK1 | death-associated protein kinase 1 |
| DAPK2 | death-associated protein kinase 2 |
| EC | excitation–contraction |
| EGLN1 | Egl-9 family hypoxia inducible factor 1 |
| EV | extracellular vesicles |
| EXO | exosome |
| FOXO3 | forkhead box O3 |
| FPD | field potential duration |
| GCF | Genomics Core Facility |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| GRK2 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 |
| HCM | hypertrophic cardiomyopathy |
| Hipsc-CM | human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes |
| IHD | ischemic heart disease |
| IPSC | induced pluripotent stem cell |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| LEAP | local extracellular action potential |
| LTCC | L-type Ca2+ channel |
| MCL1 | MCL1 apoptosis regulator |
| MEA | multielectrode array |
| MI | myocardial infarction |
| miR | microRNA |
| MITF | microphthalmia-associated transcription factor |
| NTA | nanoparticle tracing analysis |
| NTNU | Norwegian University of Science and Technology |
| PEDOT | poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophere) |
| PRKCE | protein kinase C epsilon |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SHC1 | SHC adaptor protein 1 |
| SLC25A6 | solute carrier family 25 member 6 |
| SOX4 | SRY-box transcription factor 4 |
| SR | sarcoplasmic reticulum |
| TGF-β1 | transforming growth factor beta |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| XIAP | x-linked inhibitor of apoptosis |
References
- Nowbar, A.N.; Gitto, M.; Howard, J.P.; Francis, D.P.; Al-Lamee, R. Mortality from ischemic heart disease: Analysis of data from the World Health Organization and coronary artery disease risk factors From NCD Risk Factor Collaboration. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2019, 12, e005375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosterd, A.; Hoes, A.W. Clinical epidemiology of heart failure. Heart 2007, 93, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, S.; Gaetano, C.; Martelli, F. HypoxamiR regulation and function in ischemic cardiovascular diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 1202–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertracht, O.; Malka, A.; Atar, S.; Binah, O. The mitochondria as a target for cardioprotection in acute myocardial ischemia. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 142, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogeris, T.; Baines, C.P.; Krenz, M.; Korthuis, R.J. Cell biology of ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 298, 229–317. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.L.; Lei, M. Cardiomyocyte electrophysiology and its modulation: Current views and future prospects. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2023, 378, 20220160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Deschênes, I.; Fu, J.D. Multilayer control of cardiac electrophysiology by microRNAs. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2022, 166, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Muntner, P.; Alonso, A.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Das, S.R. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2019 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, e56–e528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, R.M.; Adam, M.; Hammond, J.; Orr, L.; Turbide, C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 9412–9420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.A.; Ludwig, R.G.; Garcia-Martin, R.; Brandão, B.B.; Kahn, C.R. Extracellular miRNAs: From biomarkers to mediators of physiology and disease. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 656–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, C.; Batkai, S.; Dangwal, S.; Gupta, S.K.; Foinquinos, A.; Holzmann, A.; Just, A.; Remke, J.; Zimmer, K.; Zeug, A.; et al. Cardiac fibroblast-derived microRNA passenger strand-enriched exosomes mediate cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 2136–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegtel, D.M.; Cosmopoulos, K.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A.; van Eijndhoven, M.A.; Hopmans, E.S.; Lindenberg, J.L.; de Gruijl, T.D.; Würdinger, T.; Middeldorp, J.M. Functional delivery of viral miRNAs via exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6328–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, A. Functions of microRNAs in cardiovascular biology and disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 69–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barwari, T.; Joshi, A.; Mayr, M. MicroRNAs in Cardiovascular Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 2577–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Saetrom, P.; Snøve Jr, O.; Rossi, J.J. MicroRNA-directed transcriptional gene silencing in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16230–16235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntzinger, E.; Izaurralde, E. Gene silencing by microRNAs: Contributions of translational repression and mRNA decay. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Li, G. MicroRNA expression and function in cardiac ischemic injury. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2010, 3, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, N.; Pan, Z.; Gao, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, H.; Luo, X.; Bai, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-328 contributes to adverse electrical remodeling in atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2010, 122, 2378–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barana, A.; Matamoros, M.; Dolz-Gaitón, P.; Pérez-Hernández, M.; Amorós, I.; Núñez, M.; Sacristán, S.; Pedraz, Á.; Pinto, Á.; Fernández-Avilés, F.; et al. Chronic atrial fibrillation increases microRNA-21 in human atrial myocytes decreasing L-type calcium current. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2014, 7, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Pan, Z.; Shan, H.; Xiao, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, N.; Lin, H.; Xiao, L.; Maguy, A.; Qi, X.Y.; et al. MicroRNA-26 governs profibrillatory inward-rectifier potassium current changes in atrial fibrillation. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terentyev, D.; Belevych, A.E.; Terentyeva, R.; Martin, M.M.; Malana, G.E.; Kuhn, D.E.; Abdellatif, M.; Feldman, D.S.; Elton, T.S.; Györke, S. miR-1 overexpression enhances Ca(2+) release and promotes cardiac arrhythmogenesis by targeting PP2A regulatory subunit B56alpha and causing CaMKII-dependent hyperphosphorylation of RyR2. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drawnel, F.M.; Wachten, D.; Molkentin, J.D.; Maillet, M.; Aronsen, J.M.; Swift, F.; Sjaastad, I.; Liu, N.; Catalucci, D.; Mikoshiba, K.; et al. Mutual antagonism between IP(3)RII and miRNA-133a regulates calcium signals and cardiac hypertrophy. J. Cell. Biol. 2012, 199, 783–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wan, X.; Dennis, A.T.; Bektik, E.; Wang, Z.; Costa, M.G.S.; Fagnen, C.; Vénien-Bryan, C.; Xu, X.; Gratz, D.H.; et al. MicroRNA Biophysically Modulates Cardiac Action Potential by Direct Binding to Ion Channel. Circulation 2021, 143, 1597–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamiak, M.; Cheng, G.; Bobis-Wozowicz, S.; Zhao, L.; Kedracka-Krok, S.; Samanta, A.; Karnas, E.; Xuan, Y.T.; Skupien-Rabian, B.; Chen, X.; et al. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (iPSC)-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Are Safer and More Effective for Cardiac Repair Than iPSCs. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Harane, N.; Kervadec, A.; Bellamy, V.; Pidial, L.; Neametalla, H.J.; Perier, M.C.; Lima Correa, B.; Thiébault, L.; Cagnard, N.; Duché, A.; et al. Acellular therapeutic approach for heart failure: In Vitro production of extracellular vesicles from human cardiovascular progenitors. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 1835–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barile, L.; Lionetti, V.; Cervio, E.; Matteucci, M.; Gherghiceanu, M.; Popescu, L.M.; Torre, T.; Siclari, F.; Moccetti, T.; Vassalli, G. Extracellular vesicles from human cardiac progenitor cells inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis and improve cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 103, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Huang, W.; Wani, M.; Yu, X.; Ashraf, M. Ischemic preconditioning potentiates the protective effect of stem cells through secretion of exosomes by targeting Mecp2 via miR-22. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahzadi, R.; Fathi, E.; Valipour, B.; Ghaffary, S. Stem cells-derived exosomes as cardiac regenerative agents. IJC Heart Vasc. 2024, 52, 101399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, M.; Raposo, G. Exosomes–vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundararaj, S.; Ravindran, A.; Casarotto, M.G. AHNAK: The quiet giant in calcium homeostasis. Cell Calcium 2021, 96, 102403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yao, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Du, G. PI3K/Akt and HIF-1 signaling pathway in hypoxia-ischemia (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 3547–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBosch, B.; Sambandam, N.; Weinheimer, C.; Courtois, M.; Muslin, A.J. Akt2 regulates cardiac metabolism and cardiomyocyte survival. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 32841–32851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniyama, Y.; Ito, M.; Sato, K.; Kuester, C.; Veit, K.; Tremp, G.; Liao, R.; Colucci, W.S.; Ivashchenko, Y.; Walsh, K.; et al. Akt3 overexpression in the heart results in progression from adaptive to maladaptive hypertrophy. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2005, 38, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sucharski, H.C.; Dudley, E.K.; Keith, C.B.R.; El Refaey, M.; Koenig, S.N.; Mohler, P.J. Mechanisms and Alterations of Cardiac Ion Channels Leading to Disease: Role of Ankyrin-B in Cardiac Function. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makara, M.A.; Curran, J.; Little, S.C.; Musa, H.; Polina, I.; Smith, S.A.; Wright, P.J.; Unudurthi, S.D.; Snyder, J.; Bennett, V.; et al. Ankyrin-G coordinates intercalated disc signaling platform to regulate cardiac excitability in Vivo. Circ. Res. 2014, 115, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, T.; Ramirez-Correa, G.; Gao, W.D. Apelin increases contractility in failing cardiac muscle. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 553, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thrasher, P.; Singh, M.; Singh, K. Ataxia-Telangiectasia Mutated Kinase: Role in Myocardial Remodeling. J. Rare Dis. Res. Treat. 2017, 2, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barwe, S.P.; Jordan, M.C.; Skay, A.; Inge, L.; Rajasekaran, S.A.; Wolle, D.; Johnson, C.L.; Neco, P.; Fang, K.; Rozengurt, N.; et al. Dysfunction of ouabain-induced cardiac contractility in mice with heart-specific ablation of Na,K-ATPase β1-subunit. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2009, 47, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Zhong, J.; Wang, J.; Xiao, J. Ischemia-reperfusion injury in human AC16 cardiomyocytes is modulated by AXIN1 depending on c-Myc regulation. Ann. Med. Surg. 2023, 85, 4844–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Lv, L.; Li, Y.; Fang, R.; Yang, R.; Li, C.; Li, T.; Zhu, D.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; et al. lncRNA MIRF Promotes Cardiac Apoptosis through the miR-26a-Bak1 Axis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic. Acids 2020, 20, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochhauser, E.; Cheporko, Y.; Yasovich, N.; Pinchas, L.; Offen, D.; Barhum, Y.; Pannet, H.; Tobar, A.; Vidne, B.A.; Birk, E. Bax deficiency reduces infarct size and improves long-term function after myocardial infarction. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 47, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandl, A.; Huong Pham, L.; Toth, K.; Zambetti, G.; Erhardt, P. Puma deletion delays cardiac dysfunction in murine heart failure models through attenuation of apoptosis. Circulation 2011, 124, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misao, J.; Hayakawa, Y.; Ohno, M.; Kato, S.; Fujiwara, T.; Fujiwara, H. Expression of bcl-2 protein, an inhibitor of apoptosis, and Bax, an accelerator of apoptosis, in ventricular myocytes of human hearts with myocardial infarction. Circulation 1996, 94, 1506–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korshunova, A.Y.; Blagonravov, M.L.; Neborak, E.V.; Syatkin, S.P.; Sklifasovskaya, A.P.; Semyatov, S.M.; Agostinelli, E. BCL2-regulated apoptotic process in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 47, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Han, Y.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, W.; Su, X.; Yang, K.; Jin, W. MicroRNA-19b-1 reverses ischaemia-induced heart failure by inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis and targeting Bcl2 l11/BIM. Heart Vessel. 2019, 34, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkenazi, A.; Fairbrother, W.J.; Leverson, J.D.; Souers, A.J. From basic apoptosis discoveries to advanced selective BCL-2 family inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, P.C.; Singh, K.K.; Quan, A.; Al-Omran, M.; Teoh, H.; Lovren, F.; Cao, L.; Rovira, I.I.; Pan, Y.; Brezden-Masley, C.; et al. BRCA1 is an essential regulator of heart function and survival following myocardial infarction. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Qin, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, L. Mutations in voltage-gated L-type calcium channel: Implications in cardiac arrhythmia. Channels 2018, 12, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.X.; Liu, X.; Li, J.M.; Liu, L.; Lu, W.; Chen, G.C. Inhibition of CACNA1H can alleviate endoplasmic reticulum stress and reduce myocardial cell apoptosis caused by myocardial infarction. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 12887–12895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, A.; Tarazón, E.; Roselló-Lletí, E.; Gil-Cayuela, C.; Lago, F.; González-Juanatey, J.R.; Cinca, J.; Jorge, E.; Martínez-Dolz, L.; Portolés, M.; et al. Patients with Dilated Cardiomyopathy and Sustained Monomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia Show Up-Regulation of KCNN3 and KCNJ2 Genes and CACNG8-Linked Left Ventricular Dysfunction. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Song, L.S.; Zhu, W.Z.; Chakir, K.; Wang, W.; Wu, C.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, R.P.; Chen, S.R.; Cheng, H. Calmodulin regulation of excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac myocytes. Circ. Res. 2003, 92, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condorelli, G.; Roncarati, R.; Ross Jr, J.; Pisani, A.; Stassi, G.; Todaro, M.; Trocha, S.; Drusco, A.; Gu, Y.; Russo, M.A.; et al. Heart-targeted overexpression of caspase3 in mice increases infarct size and depresses cardiac function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9977–9982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teringova, E.; Tousek, P. Apoptosis in ischemic heart disease. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, X.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Death-Associated Protein Kinase 1 (DAPK1) Protects against Myocardial Injury Induced by Myocardial Infarction in Rats via Inhibition of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 9651092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Nomura, F.; Hoshino, K.; Copeland, N.G.; Gilbert, D.J.; Jenkins, N.A.; Akira, S. Death-associated protein kinase 2 is a new calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase that signals apoptosis through its catalytic activity. Oncogene 1999, 18, 3471–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Pi, X.; Townley-Tilson, W.H.; Li, N.; Wehrens, X.H.; Entman, M.L.; Taffet, G.E.; Mishra, A.; Peng, J.; Schisler, J.C.; et al. PHD2/3-dependent hydroxylation tunes cardiac response to β-adrenergic stress via phospholamban. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 2759–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xin, Z.; Ma, Z.; Jiang, S.; Wang, D.; Fan, C.; Di, S.; Hu, W.; Li, T.; She, J.; Yang, Y. FOXOs in the impaired heart: New therapeutic targets for cardiac diseases. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, P.Y.; Chuprun, J.K.; Ibetti, J.; Cannavo, A.; Drosatos, K.; Elrod, J.W.; Koch, W.J. GRK2 compromises cardiomyocyte mitochondrial function by diminishing fatty acid-mediated oxygen consumption and increasing superoxide levels. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2015, 89, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta Chaudhuri, R.; Banik, A.; Mandal, B.; Sarkar, S. Cardiac-specific overexpression of HIF-1α during acute myocardial infarction ameliorates cardiomyocyte apoptosis via differential regulation of hypoxia-inducible pro-apoptotic and anti-oxidative genes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 537, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeghiazarians, Y.; Honbo, N.; Imhof, I.; Woods, B.; Aguilera, V.; Ye, J.; Boyle, A.J.; Karliner, J.S. IL-15: A novel prosurvival signaling pathway in cardiomyocytes. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2014, 63, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pineda, S.; Nikolova-Krstevski, V.; Leimena, C.; Atkinson, A.J.; Altekoester, A.K.; Cox, C.D.; Jacoby, A.; Huttner, I.G.; Ju, Y.K.; Soka, M.; et al. Conserved Role of the Large Conductance Calcium-Activated Potassium Channel, K(Ca)1.1, in Sinus Node Function and Arrhythmia Risk. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2021, 14, e003144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, M.L.; Taneja, N.; Neininger, A.C.; Wang, L.; Robertson, G.L.; Riffle, S.N.; Shi, L.; Knollmann, B.C.; Burnette, D.T.; Gama, V. MCL-1 Inhibition by Selective BH3 Mimetics Disrupts Mitochondrial Dynamics Causing Loss of Viability and Functionality of Human Cardiomyocytes. iScience 2020, 23, 101015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciarretta, S.; Volpe, M.; Sadoshima, J. Mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in cardiac physiology and disease. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Movsesian, M.; Ahmad, F.; Hirsch, E. Functions of PDE3 Isoforms in Cardiac Muscle. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2018, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, A.; Davies, A.M.; Bertrand, L.; Sharif, I.; Budas, G.R.; Jovanović, S.; Mouton, V.; Kahn, C.R.; Lucocq, J.M.; Gray, G.A.; et al. Deficiency of PDK1 in cardiac muscle results in heart failure and increased sensitivity to hypoxia. Embo J. 2003, 22, 4666–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaou, P.; Kranias, E.G. Role of PP1 in the regulation of Ca cycling in cardiac physiology and pathophysiology. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2009, 14, 3571–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, X.; Macdonnell, S.M.; Kranias, E.G.; Lorenz, J.N.; Leitges, M.; Houser, S.R.; Molkentin, J.D. Protein kinase C[alpha], but not PKC[beta] or PKC[gamma], regulates contractility and heart failure susceptibility: Implications for ruboxistaurin as a novel therapeutic approach. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, J.; Lochner, A.; Opie, L.H.; Sack, M.N.; Essop, M.F. PKCε promotes cardiac mitochondrial and metabolic adaptation to chronic hypobaric hypoxia by GSK3β inhibition. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011, 226, 2457–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, A.; Menabò, R.; Kaludercic, N.; Pelicci, P.; Di Lisa, F.; Giorgio, M. The cardioprotective effects elicited by p66(Shc) ablation demonstrate the crucial role of mitochondrial ROS formation in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Bioenerg. 2009, 1787, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokoszka, J.E.; Waymire, K.G.; Flierl, A.; Sweeney, K.M.; Angelin, A.; MacGregor, G.R.; Wallace, D.C. Deficiency in the mouse mitochondrial adenine nucleotide translocator isoform 2 gene is associated with cardiac noncompaction. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta: Int. J. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 1857, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Lv, L.; Zheng, N.; Li, R.; Yang, R.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, H.; Li, X.; et al. Suppression of Sox4 protects against myocardial ischemic injury by reduction of cardiac apoptosis in mice. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piacentino III, V.; Milano, C.A.; Bolanos, M.; Schroder, J.; Messina, E.; Cockrell, A.S.; Jones, E.; Krol, A.; Bursac, N.; Mao, L.; et al. X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein-mediated attenuation of apoptosis, using a novel cardiac-enhanced adeno-associated viral vector. Hum. Gene. Ther. 2012, 23, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiFrancesco, D. HCN4, Sinus Bradycardia and Atrial Fibrillation. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. Rev. 2015, 4, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, R.; Fox, K. Heart rate reduction in coronary artery disease and heart failure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bers, D. Excitation-Contraction Coupling and Cardiac Contractile Force; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; Volume 237. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.B.; Irving, M. The molecular basis of the steep force-calcium relation in heart muscle. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2010, 48, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, V.; Xie, L.H.; Qu, Z.; Song, Z. Mitochondrial depolarization promotes calcium alternans: Mechanistic insights from a ventricular myocyte model. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1008624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florea, S.M.; Blatter, L.A. The role of mitochondria for the regulation of cardiac alternans. Front. Physiol. 2010, 1, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohlhaas, M.; Nickel, A.G.; Maack, C. Mitochondrial energetics and calcium coupling in the heart. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 3753–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhao, C.; Mao, Y. MiR-218-5p Mediates Myocardial Fibrosis after Myocardial Infarction by Targeting CX43. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 4504–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, X.; Sun, J.; Li, M.; Ma, J.; Ge, L. miR-361-3p mitigates hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte injury via targeting apoptosis initiators caspase-2/-8/-9. Vitr. Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 2022, 58, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, L.; Wei, Z.; Lai, Y.; Ma, X. Differential Expression of microRNAs in Hypertrophied Myocardium and Their Relationship to Late Gadolinium Enhancement, Left Ventricular Hypertrophy and Remodeling in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, K.; An, T.; Zhai, M.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, T.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. Mitochondrial miR-762 regulates apoptosis and myocardial infarction by impairing ND2. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathivanan, S.; Ji, H.; Simpson, R.J. Exosomes: Extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J. Proteom. 2010, 73, 1907–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marwarha, G.; Røsand, Ø.; Scrimgeour, N.; Slagsvold, K.H.; Høydal, M.A. miR-210 regulates apoptotic cell death during cellular hypoxia and reoxygenation in a diametrically opposite manner. Biomedicines 2021, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marwarha, G.; Røsand, Ø.; Slagsvold, K.H.; Høydal, M.A. GSK3β Inhibition Is the Molecular Pivot That Underlies the Mir-210-Induced Attenuation of Intrinsic Apoptosis Cascade during Hypoxia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, H.B.; Nicolini, A.M.; Arrowood, C.A.; Chvatal, S.A.; Wolfson, D.W.; Cho, H.C.; Sullivan, D.D.; Chal, J.; Fermini, B.; Clements, M.; et al. Novel method for action potential measurements from intact cardiac monolayers with multiwell microelectrode array technology. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tastsoglou, S.; Skoufos, G.; Miliotis, M.; Karagkouni, D.; Koutsoukos, I.; Karavangeli, A.; Kardaras, F.S.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-miRPath v4. 0: Expanding target-based miRNA functional analysis in cell-type and tissue contexts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W154–W159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Zuo, Z.; Cai, G.; Kang, S.; Gao, X.; Li, T. miRecords: An integrated resource for microRNA–target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D105–D110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-Y.; Lin, Y.-C.-D.; Cui, S.; Huang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Xu, J.; Bao, J.; Li, Y.; Wen, J.; Zuo, H. miRTarBase update 2022: An informative resource for experimentally validated miRNA–target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D222–D230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagkouni, D.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Chatzopoulos, S.; Vlachos, I.S.; Tastsoglou, S.; Kanellos, I.; Papadimitriou, D.; Kavakiotis, I.; Maniou, S.; Skoufos, G. DIANA-TarBase v8: A decade-long collection of experimentally supported miRNA–gene interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D239–D245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, Y.; Kechris, K.J.; Tabakoff, B.; Hoffman, P.; Radcliffe, R.A.; Bowler, R.; Mahaffey, S.; Rossi, S.; Calin, G.A.; Bemis, L. The multiMiR R package and database: Integration of microRNA–target interactions along with their disease and drug associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, e133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L. Clusterprofiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innov. Camb. 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, P.D.; Ebert, D.; Muruganujan, A.; Mushayahama, T.; Albou, L.P.; Mi, H. PANTHER: Making genome—Scale phylogenetics accessible to all. Protein Sci. 2022, 31, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team, R. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, M.; Pages, H.; Li, N. Carlson M (2019). org.Hs.eg.db: Genome Wide Annotation for Human. R Package, version 3.8.2. 2019.
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.-G.; Yan, G.-R.; He, Q.-Y. DOSE: An R/Bioconductor package for disease ontology semantic and enrichment analysis. Bioinformatics 2014, 31, 608–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosy, A.P.; Fonarow, G.C.; Butler, J.; Chioncel, O.; Greene, S.J.; Vaduganathan, M.; Nodari, S.; Lam, C.S.P.; Sato, N.; Shah, A.N.; et al. The global health and economic burden of hospitalizations for heart failure: Lessons learned from hospitalized heart failure registries. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


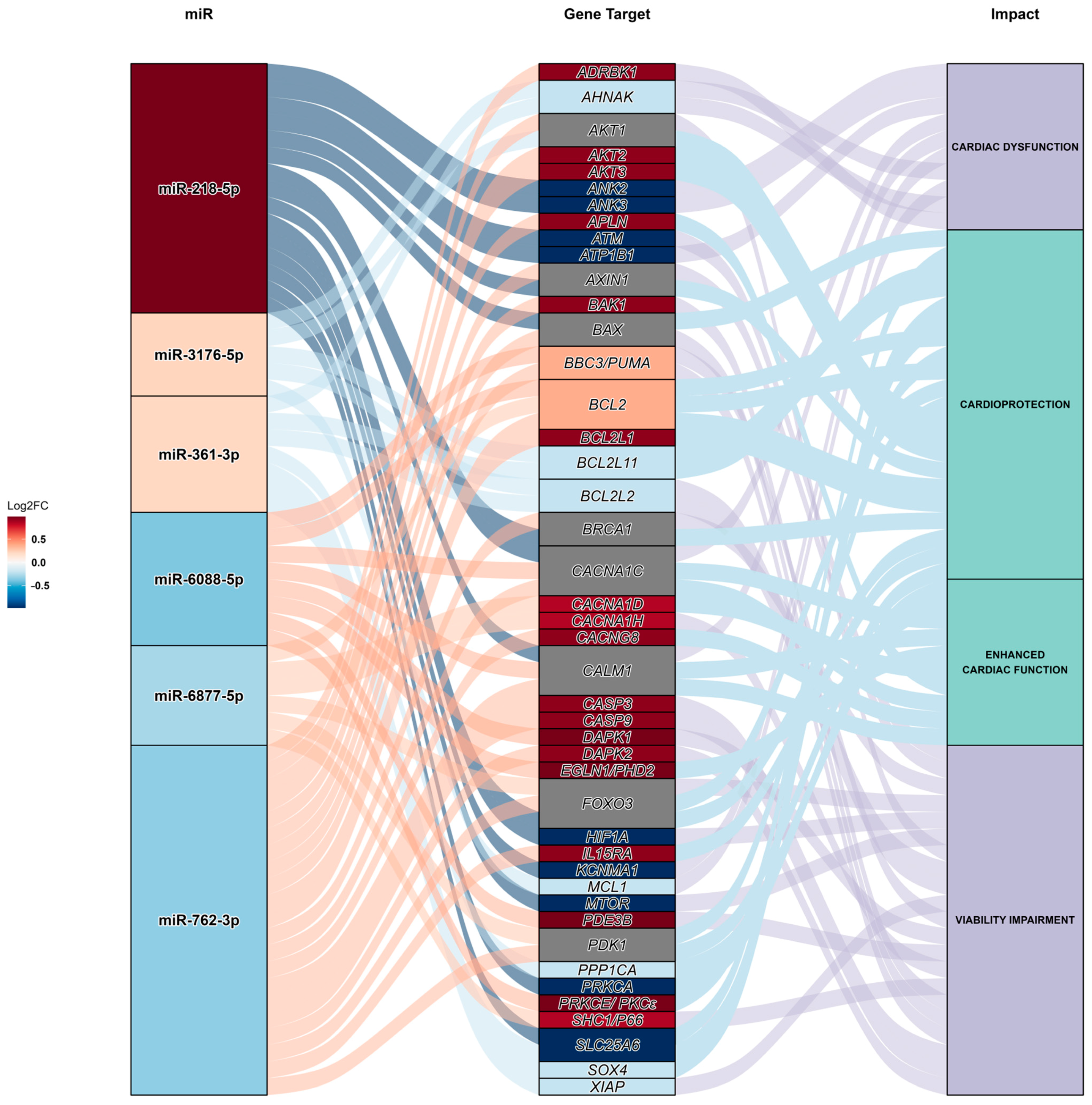
| miR | Adjusted p-Value | Log2FoldChange | Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-1234-3p | 0.0001 | −1.28 | Down |
| miR-6088-5p | 0.0072 | −0.38 | Down |
| miR-9718-3p | 0.0110 | −0.43 | Down |
| miR-762-3p | 0.0110 | −0.34 | Down |
| miR-6877-5p | 0.0373 | −0.29 | Down |
| miR-1293-5p | 0.0668 | −0.26 | Down |
| miR-218-5p | 0.1790 | 0.99 | Up |
| miR-4284-3p | 0.1805 | 0.22 | Up |
| miR-3176-5p | 0.1805 | 0.22 | Up |
| miR-361-3p | 0.1997 | 0.21 | Up |
| Target Genes | Associated Function | Level of Expression in Human Cardiomyocytes | Author |
|---|---|---|---|
| AHNAK nucleoprotein (AHNAK) | Excitation–contraction coupling | Medium | [31] |
| AKT serine/threonine kinase 1 (AKT1) | Cell survival | Medium | [32] |
| AKT serine/threonine kinase 2 (AKT2) | Cell survival | Medium | [33] |
| AKT serine/threonine kinase 3 (AKT3) | Cell survival | Low | [34] |
| Ankyrin 2 (ANK2) | Ca2+ signaling, excitation–contraction coupling | Medium | [35] |
| Ankyrin 3 (ANK3) | Na+ signaling, excitability | Medium | [36] |
| Apelin (APLN) | Ca2+ signaling, contraction | NA | [37] |
| ATM serine/threonine kinase (ATM) | Anti-apoptotic, cardiac survival | Medium | [38] |
| ATPase Na+/K+ transporting subunit beta 1 (ATP1B1) | Contractility | Medium | [39] |
| Axin 1 (AXIN1) | Pro-apoptotic | Medium | [40] |
| BCL2 antagonist/killer 1 (BAK1) | Pro-apoptotic | Low | [41] |
| BCL2-associated X (BAX) | Pro-apoptotic | Medium | [42] |
| BCL2 binding component 3 (BBC3) | Pro-apoptotic | Medium | [43] |
| BCL2 apoptosis regulator (BCL2) | Anti-apoptotic | Medium | [44] |
| BCL2 Like 1 (BCL2L1) | Pro-apoptotic | NA | [45] |
| BCL2 Like 11 (BCL2L11) | Pro-apoptotic | Medium | [46] |
| BCL2-like 2 (BCL2L2) | Anti-apoptotic | Medium | [47] |
| BRCA1 DNA repair-associated (BRCA1) | anti-apoptotic, cell survival | Low | [48] |
| Calcium voltage-gated channel Subunit alpha 1C (CACNA1C) | L-type Ca2+ channel | Medium | [49] |
| Calcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha 1D (CACNA1D) | Ca2+ channel | NA | [49] |
| Calcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha 1H (CACNA1H) | ER stress response | Low | [50] |
| Calcium voltage-gated channel auxiliary subunit gamma 8 (CACNG8) | L-type Ca2+ channel | NA | [51] |
| Calmodulin 1 (CALM1) | Excitation–contraction coupling | Medium | [52] |
| Caspase 3 (CASP3) | Pro-apoptotic | NA | [53] |
| Caspase 9 (CASP9) | Pro-apoptotic | NA | [54] |
| Death-associated protein kinase 1 (DAPK1) | Pro-inflammatory | Medium | [55] |
| Death-associated protein kinase 2 (DAPK2) | Pro-apoptotic | Medium | [56] |
| Egl-9 family hypoxia inducible factor 1 (EGLN1) | Contractility | High | [57] |
| Forkhead box O3 (FOXO3) | Cell survival, mitochondrial function | NA | [58] |
| G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2) | Mitochondrial function | Low | [59] |
| Hypoxia inducible factor 1 subunit alpha (HIF1A) | Cell survival | NA | [60] |
| Interleukin 15 receptor subunit alpha (IL15RA) | Anti-apoptotic | Medium | [61] |
| Potassium calcium-activated channel subfamily M alpha 1 (KCNMA1) | Ca2+ channel, excitation–contraction coupling | NA | [62] |
| MCL1 apoptosis regulator (MCL1) | Anti-apoptotic | Medium | [63] |
| Mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase (MTOR) | Cell survival | High | [64] |
| Phosphodiesterase 3B (PDE3B) | Contractility | NA | [65] |
| Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 (PDK1) | Cardioprotection | Medium | [66] |
| Protein phosphatase 1 catalytic subunit alpha (PPP1CA) | Contractility | Medium | [67] |
| Protein kinase C Alpha (PRKCA) | Contractility | Medium | [68] |
| Protein kinase C Epsilon (PRKCE) | Cardioprotection | NA | [69] |
| SHC adaptor protein 1 (SHC1) | Mitochondrial function | NA | [70] |
| Solute carrier family 25 member 6 (SLC25A6) | ATP synthesis | High | [71] |
| SRY-box transcription factor 4 (SOX4) | Pro-apoptotic | Medium | [72] |
| X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) | Anti-apoptotic | High | [73] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Røsand, Ø.; Wang, J.; Scrimgeour, N.; Marwarha, G.; Høydal, M.A. Exosomal Preconditioning of Human iPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes Beneficially Alters Cardiac Electrophysiology and Micro RNA Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158460
Røsand Ø, Wang J, Scrimgeour N, Marwarha G, Høydal MA. Exosomal Preconditioning of Human iPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes Beneficially Alters Cardiac Electrophysiology and Micro RNA Expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(15):8460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158460
Chicago/Turabian StyleRøsand, Øystein, Jianxiang Wang, Nathan Scrimgeour, Gurdeep Marwarha, and Morten Andre Høydal. 2024. "Exosomal Preconditioning of Human iPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes Beneficially Alters Cardiac Electrophysiology and Micro RNA Expression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 15: 8460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158460
APA StyleRøsand, Ø., Wang, J., Scrimgeour, N., Marwarha, G., & Høydal, M. A. (2024). Exosomal Preconditioning of Human iPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes Beneficially Alters Cardiac Electrophysiology and Micro RNA Expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(15), 8460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25158460







