Genomic Insights into Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis through Whole-Exome Sequencing: A Case Report of Eight Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Demographics and Clinical Characteristics
2.2. DNA Quality and Sequencing Metrics
2.3. Somatic Variants Identified from WES
- Variants called from blood samples: variants identified in blood samples (Supplementary Table S4);
- Variants called from paired blood/tissue samples: variants identified in the tissue sample that were not present in the corresponding blood sample (Table 2).
| Case | Somatic Variants | SNVs 1 | Indels 2 | PTVs 3 | Pathogenic 4 | Pathogenic/Likely Pathogenic 4 | Likely Pathogenic 4 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strelka2 | Mutect2 | Strelka2 | Mutect2 | Strelka2 | Mutect2 | Strelka2 | Mutect2 | Strelka2 | Mutect2 | Strelka2 | Mutect2 | Strelka2 | Mutect2 | |
| 1 | 57 | 224 | 56 | 219 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 50 | 46 | 48 | 38 | 2 | 7 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 57 | 72 | 56 | 69 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 53 | 52 | 51 | 48 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 56 | 33 | 54 | 28 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 80 | 35 | 79 | 26 | 1 | 8 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | 65 | 39 | 65 | 32 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 8 | 53 | 52 | 52 | 39 | 1 | 11 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Median (range) | 56.5 (50–80) | 49 (23–224) | 55 (48–79) | 38.5 (26–219) | 1 (0–2) | 5.5 (1–11) | 0.5 (0–3) | 5 (4–13) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) |
- CHIT1, altered in Cases 3, 4 and 5, nonsense mutations;
- CEP170, altered in Cases 4 and 5, nonsense mutations;
- CTR9, altered in Cases 7 and 8, nonsense mutation and frameshift deletion, respectively.
2.4. Validation of Somatic Variants with Sanger Sequencing
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
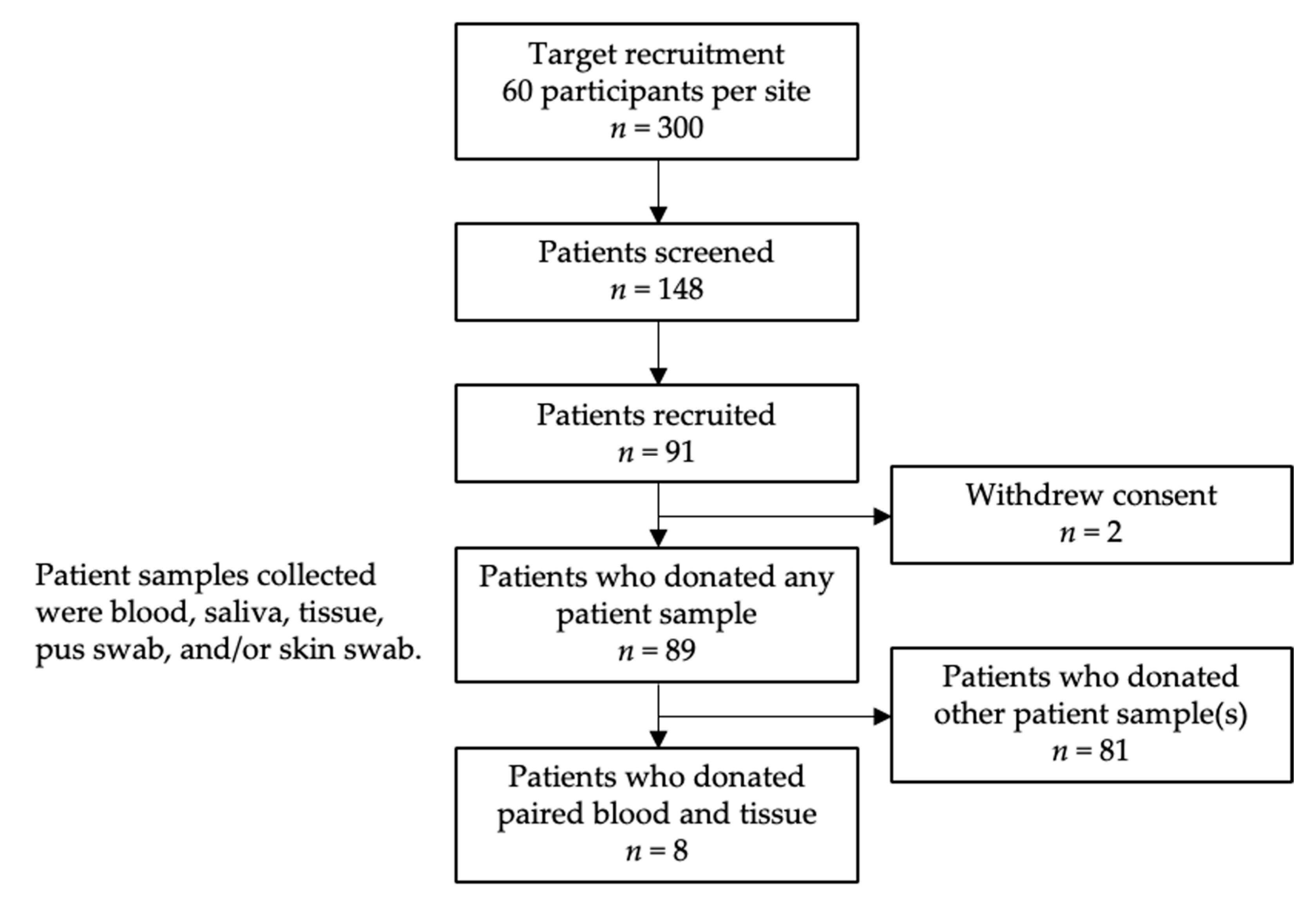
4.1. Patient Recruitment
4.2. Sample Collection
4.3. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
4.4. Quality Control and Somatic Variant Calling
- Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer (COSMIC) Cancer Gene Census (CGC) (data source dated 15 March 2012) [77];
- NCBI dbSNP (data source dated 18 April 2018) [80];
- Human DNA repair genes (data source dated 24 May 2018) [81];
- GENCODE (v34) [84];
- Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD) (v3.1.2) [85];
- Human Genome Organisation (HUGO) Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC) Database (data source dated 30 November 2017) [86].
4.5. Validating Called Variants with Sanger Sequencing
4.6. Gene Set Analysis
4.7. Data and Sample Availability Statement
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Jarrah, A.; Taranikanti, V.; Lakhtakia, R.; Al-Jabri, A.; Sawhney, S. Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis: Diagnostic strategy and therapeutic implications in Omani patients. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2013, 13, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, S.S.; Ho, P.J.; Liow, J.J.K.; Tan, Q.T.; Goh, S.S.N.; Li, J.; Hartman, M. A meta-analysis of idiopathic granulomatous mastitis treatments for remission and recurrence prevention. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1346790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugon-Rodin, J.; Plu-Bureau, G.; Hugol, D.; Gompel, A. Management of granulomatous mastitis: A series of 14 patients. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2012, 28, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baslaim, M.M.; Khayat, H.A.; Al-Amoudi, S.A. Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: A heterogeneous disease with variable clinical presentation. World J. Surg. 2007, 31, 1677–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yukawa, M.; Watatani, M.; Isono, S.; Fujiwara, Y.; Tsujie, M.; Kitani, K.; Hara, J.; Kato, H.; Takeyama, H.; Kanaizumi, H.; et al. Management of granulomatous mastitis: A series of 13 patients who were evaluated for treatment without corticosteroids. Int. Surg. 2015, 100, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, M.I.; Alnaimat, F.; Al-Nazer, M.W.; Awad, H.; Odeh, G.; Al-Najar, M.; Alsayed, S.; El-Asir, L.; Addasi, R.; Melhem, J.M.; et al. Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: Clinical, histopathological, and radiological characteristics and management approaches. Rheumatol. Int. 2023, 43, 1859–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombe, R.F.; Hamed, H. An update on granulomatous mastitis: A rare and complex condition. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2021, 82, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfrum, A.; Kummel, S.; Theuerkauf, I.; Pelz, E.; Reinisch, M. Granulomatous Mastitis: A Therapeutic and Diagnostic Challenge. Breast Care 2018, 13, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulabchand, R.; Hafidi, A.; Van de Perre, P.; Millet, I.; Maria, A.T.J.; Morel, J.; Quellec, A.L.; Perrochia, H.; Guilpain, P. Mastitis in Autoimmune Diseases: Review of the Literature, Diagnostic Pathway, and Pathophysiological Key Players. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pevzner, M.; Dahan, A. Mastitis While Breastfeeding: Prevention, the Importance of Proper Treatment, and Potential Complications. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, S.S.; Xu, J.; Sim, C.K.; Khng, A.J.; Ho, P.J.; Kwan, P.K.W.; Ravikrishnan, A.; Tan, K.B.; Tan, Q.T.; Tan, E.Y.; et al. Profiling Microbial Communities in Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilaveri, C.; Degnim, A.; Lee, C.; DeSimone, D.; Moldoveanu, D.; Ghosh, K. Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis. Breast J. 2024, 2024, 6693720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, S.S.; Sim, J.X.Y.; Chan, C.W.; Ho, P.J.; Lim, Z.L.; Li, J.; Hartman, M. Current Approaches to Diagnosing and Treating Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis in Asia: A Summary from In-Depth Clinician Interviews. SSRN Prepr. Lancet 2024. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Altintoprak, F.; Kivilcim, T.; Ozkan, O.V. Aetiology of idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. World J. Clin. Cases 2014, 2, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, J.R.; Dumitru, D. Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: Presentation, investigation and management. Future Oncol. 2016, 12, 1381–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekin, L.; Dinc Elibol, F. Is There any Relationship Between Granulomatous Mastitis and Seasons? An Analysis of Seasonal Frequency, Clinical, and Radiologic Findings. Eur. J. Breast Health 2020, 16, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basim, P.; Argun, D.; Argun, F. Risk Factors for Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis Recurrence after Patient-Tailored Treatment: Do We Need an Escalating Treatment Algorithm? Breast Care 2022, 17, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velidedeoglu, M.; Umman, V.; Kilic, F.; Celik, V.; Gazioglu, E.; Hatipoglu, E.; Ozturk, T.; Mete, B. Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: Introducing a diagnostic algorithm based on 5 years of follow-up of 152 cases from Turkey and a review of the literature. Surg. Today 2022, 52, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Néel, A.; Hello, M.; Cottereau, A.; Graveleau, J.; De Faucal, P.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Rondeau-Lutz, M.; Lavigne, C.; Chiche, L.; Hachulla, E.; et al. Long-term outcome in idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: A western multicentre study. QJM Int. J. Med. 2013, 106, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyanarayanan, A.; Manda, S.; Poojary, M.; Nagaraj, S.H. Exome Sequencing Data Analysis. In Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology; Ranganathan, S., Gribskov, M., Nakai, K., Schönbach, C., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 164–175. [Google Scholar]
- Sprissler, R.; Perkins, B.; Johnstone, L.; Babiker, H.M.; Chalasani, P.; Lau, B.; Hammer, M.; Mahadevan, D. Rare Tumor-Normal Matched Whole Exome Sequencing Identifies Novel Genomic Pathogenic Germline and Somatic Aberrations. Cancers 2020, 12, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Lin, S.; Li, X.; Du, H. Systematic comparison of somatic variant calling performance among different sequencing depth and mutation frequency. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Du, H.; Zhang, G. Towards an accurate and robust analysis pipeline for somatic mutation calling. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 979928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, Z.; He, L.; Chou, K.C. In-depth comparison of somatic point mutation callers based on different tumor next-generation sequencing depth data. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alioto, T.S.; Buchhalter, I.; Derdak, S.; Hutter, B.; Eldridge, M.D.; Hovig, E.; Heisler, L.E.; Beck, T.A.; Simpson, J.T.; Tonon, L.; et al. A comprehensive assessment of somatic mutation detection in cancer using whole-genome sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroigard, A.B.; Thomassen, M.; Laenkholm, A.V.; Kruse, T.A.; Larsen, M.J. Evaluation of Nine Somatic Variant Callers for Detection of Somatic Mutations in Exome and Targeted Deep Sequencing Data. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Scheffler, K.; Halpern, A.L.; Bekritsky, M.A.; Noh, E.; Kallberg, M.; Chen, X.; Kim, Y.; Beyter, D.; Krusche, P.; et al. Strelka2: Fast and accurate calling of germline and somatic variants. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, A.R.; Smith, E.N.; Matsui, H.; Braekkan, S.K.; Jepsen, K.; Hansen, J.B.; Frazer, K.A. Effective filtering strategies to improve data quality from population-based whole exome sequencing studies. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulygina, E.A.; Borisov, O.V.; Valeeva, E.V.; Semenova, E.A.; Kostryukova, E.S.; Kulemin, N.A.; Larin, A.K.; Nabiullina, R.M.; Mavliev, F.A.; Akhatov, A.M.; et al. Whole genome sequencing of elite athletes. Biol. Sport. 2020, 37, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Ng, C.K.Y.; Lim, R.S.; Jiang, T.; Kumar, S.; Li, X.; Wali, V.B.; Piscuoglio, S.; Gerstein, M.B.; Chagpar, A.B.; et al. Reliability of Whole-Exome Sequencing for Assessing Intratumor Genetic Heterogeneity. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 1446–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, N.; Guan, L.L.; Ma, H.; Wang, X.J.; Wu, B.M.; Shang, F.H.; Wang, D.; Wen, H.; Yu, X. Failure to Identify Somatic Mutations in Monozygotic Twins Discordant for Schizophrenia by Whole Exome Sequencing. Chin. Med. J 2016, 129, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Ren, L.; Chen, Z.; Fang, L.T.; Zhao, Y.; Lack, J.; Guan, M.; Zhu, B.; Jaeger, E.; Kerrigan, L.; et al. Toward best practice in cancer mutation detection with whole-genome and whole-exome sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbitoff, Y.A.; Abasov, R.; Tvorogova, V.E.; Glotov, A.S.; Predeus, A.V. Systematic benchmark of state-of-the-art variant calling pipelines identifies major factors affecting accuracy of coding sequence variant discovery. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belien, J.; Swinnen, S.; D’Hondt, R.; de Juan, L.V.; Dedoncker, N.; Matthys, P.; Bauer, J.; Vens, C.; Moylett, S.; Dubois, B. CHIT1 at diagnosis predicts faster disability progression and reflects early microglial activation in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dymek, B.; Sklepkiewicz, P.; Mlacki, M.; Guner, N.C.; Nejman-Gryz, P.; Drzewicka, K.; Przysucha, N.; Rymaszewska, A.; Paplinska-Goryca, M.; Zagozdzon, A.; et al. Pharmacological Inhibition of Chitotriosidase (CHIT1) as a Novel Therapeutic Approach for Sarcoidosis. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 5621–5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Francesco, A.M.; Verrecchia, E.; Sicignano, L.L.; Massaro, M.G.; Antuzzi, D.; Covino, M.; Pasciuto, G.; Richeldi, L.; Manna, R. The Use of Chitotriosidase as a Marker of Active Sarcoidosis and in the Diagnosis of Fever of Unknown Origin (FUO). J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, M.; Zielinska, A.; Grzybowski, M.M.; Olczak, J.; Fichna, J. Chitinases and Chitinase-Like Proteins as Therapeutic Targets in Inflammatory Diseases, with a Special Focus on Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.J.; Weiden, M.D.; Lee, C.G. Chitotriosidase in the Pathogenesis of Inflammation, Interstitial Lung Diseases and COPD. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2015, 7, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Q.; Shao, Z.M. Identification of immune-related prognostic biomarkers in triple-negative breast cancer. Transl. Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 1707–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiechmann, S.; Ruprecht, B.; Siekmann, T.; Zheng, R.; Frejno, M.; Kunold, E.; Bajaj, T.; Zolg, D.P.; Sieber, S.A.; Gassen, N.C.; et al. Chemical Phosphoproteomics Sheds New Light on the Targets and Modes of Action of AKT Inhibitors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2021, 16, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudero-Hernandez, C.; van Beelen Granlund, A.; Bruland, T.; Sandvik, A.K.; Koch, S.; Ostvik, A.E.; Munch, A. Transcriptomic Profiling of Collagenous Colitis Identifies Hallmarks of Nondestructive Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 12, 665–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, B.; Liu, L.; Sun, S.; Sun, S. Centrosome dysfunction: A link between senescence and tumor immunity. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Lee, J.W.; Yoo, K.D.; Yoo, J.Y.; Lee, J.P.; Kim, D.K.; Chin, H.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Yang, S.H. Cln 3-requiring 9 is a negative regulator of Th17 pathway-driven inflammation in anti-glomerular basement membrane glomerulonephritis. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2016, 311, F505–F519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Bae, E.; Kwon, S.H.; Yu, M.Y.; Cha, R.H.; Lee, H.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, J.P.; Ye, S.K.; Yoo, J.Y.; et al. Transcriptional modulation of the T helper 17/interleukin 17 axis ameliorates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 1481–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinayagam, R.; Cox, J.; Webb, L. Granulomatous Mastitis: A Spectrum of Disease. Breast Care 2009, 4, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, R.; de la Fuente, L.; Del Pozo-Valero, M.; Riveiro-Alvarez, R.; Trujillo-Tiebas, M.J.; Martin-Merida, I.; Avila-Fernandez, A.; Iancu, I.F.; Perea-Romero, I.; Nunez-Moreno, G.; et al. An evaluation of pipelines for DNA variant detection can guide a reanalysis protocol to increase the diagnostic ratio of genetic diseases. NPJ Genom. Med. 2022, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, M.; Pugh, T.J.; Fennell, T.J.; Stewart, C.; Lichtenstein, L.; Meldrim, J.C.; Fostel, J.L.; Friedrich, D.C.; Perrin, D.; Dionne, D.; et al. Discovery and characterization of artifactual mutations in deep coverage targeted capture sequencing data due to oxidative DNA damage during sample preparation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koboldt, D.C. Best practices for variant calling in clinical sequencing. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartz, M.D.; Kim, T.; Niu, J.; Yu, R.K.; Shete, S.; Ionita-Laza, I. Small sample properties of rare variant analysis methods. BMC Proc. 2014, 8, S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Abecasis, G.R.; Boehnke, M.; Lin, X. Rare-variant association analysis: Study designs and statistical tests. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 95, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, C.R.; Chowdhury, S.; Taft, R.J.; Lebo, M.S.; Buchan, J.G.; Harrison, S.M.; Rowsey, R.; Klee, E.W.; Liu, P.; Worthey, E.A.; et al. Best practices for the analytical validation of clinical whole-genome sequencing intended for the diagnosis of germline disease. NPJ Genom. Med. 2020, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corominas, J.; Smeekens, S.P.; Nelen, M.R.; Yntema, H.G.; Kamsteeg, E.J.; Pfundt, R.; Gilissen, C. Clinical exome sequencing-Mistakes and caveats. Hum. Mutat. 2022, 43, 1041–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Liu, H.; Zhao, L.; Yuan, X.; Wang, Y.P.; Wan, M. Detection of False-Positive Deletions from the Database of Genomic Variants. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 8420547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteche-Lopez, A.; Avila-Fernandez, A.; Romero, R.; Riveiro-Alvarez, R.; Lopez-Martinez, M.A.; Gimenez-Pardo, A.; Velez-Monsalve, C.; Gallego-Merlo, J.; Garcia-Vara, I.; Almoguera, B.; et al. Sanger sequencing is no longer always necessary based on a single-center validation of 1109 NGS variants in 825 clinical exomes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.S.; Huang, H.D.; Yeh, K.T.; Chang, J.G. Evaluation of whole exome sequencing by targeted gene sequencing and Sanger sequencing. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 471, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, P.N. Whole-exome sequencing for finding de novo mutations in sporadic mental retardation. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Lian, T.; Lin, J.; Li, S.; Zheng, H.; Cheng, C.; Ye, J.; Jing, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, W. Whole-exome sequencing improves genetic testing accuracy in pulmonary artery hypertension. Pulm. Circ. 2018, 8, 2045894018763682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.H.; Chen, S.X.; Cheng, L.Y.; Rodriguez, A.Y.; Tang, R.; Cabrera, K.; Zhang, D.Y. Confirming putative variants at ≤ 5% allele frequency using allele enrichment and Sanger sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, A.; Tetreault, M.; Dyment, D.A.; Zou, R.; Kernohan, K.; Geraghty, M.T.; Consortium, F.C.; Care4Rare Canada, C.; Hartley, T.; Boycott, K.M. Concordance between whole-exome sequencing and clinical Sanger sequencing: Implications for patient care. Mol. Genet. Genomic Med. 2016, 4, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattini, L.; D’Aurizio, R.; Magi, A. Detection of Genomic Structural Variants from Next-Generation Sequencing Data. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmodlou, R.; Dadkhah, N.; Abbasi, F.; Nasiri, J.; Valizadeh, R. Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: Dilemmas in diagnosis and treatment. Electron. Physician 2017, 9, 5375–5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourhoseingholi, M.A.; Vahedi, M.; Rahimzadeh, M. Sample size calculation in medical studies. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2013, 6, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maione, C.; Palumbo, V.D.; Maffongelli, A.; Damiano, G.; Buscemi, S.; Spinelli, G.; Fazzotta, S.; Gulotta, E.; Buscemi, G.; Lo Monte, A.I. Diagnostic techniques and multidisciplinary approach in idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: A revision of the literature. Acta Biomed. 2019, 90, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, A.S.; Amini, G.; Sajedi, F.; Mehrad-Majd, H. Factors Affecting Recurrence of Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis: A Systematic Review. Breast J. 2023, 2023, 9947797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.Q.; Xiao, S.Y.; Farouk, O.; Du, Y.T.; Sheybani, F.; Tan, Q.T.; Akbulut, S.; Cetin, K.; Alikhassi, A.; Yaghan, R.J.; et al. Management of granulomatous lobular mastitis: An international multidisciplinary consensus (2021 edition). Mil. Med. Res. 2022, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, C.; Kia, D.A.; Vandrovcova, J.; Hardy, J.; Wood, N.W.; Lewis, P.A.; Ferrari, R. Genome, transcriptome and proteome: The rise of omics data and their integration in biomedical sciences. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 19, 286–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanssen, F.; Garcia, M.U.; Folkersen, L.; Pedersen, A.S.; Lescai, F.; Jodoin, S.; Miller, E.; Seybold, M.; Wacker, O.; Smith, N.; et al. Scalable and efficient DNA sequencing analysis on different compute infrastructures aiding variant discovery. NAR Genom. Bioinform. 2024, 6, lqae031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.; Juhos, S.; Larsson, M.; Olason, P.I.; Martin, M.; Eisfeldt, J.; DiLorenzo, S.; Sandgren, J.; Diaz De Stahl, T.; Ewels, P.; et al. Sarek: A portable workflow for whole-genome sequencing analysis of germline and somatic variants. F1000Res 2020, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewels, P.A.; Peltzer, A.; Fillinger, S.; Patel, H.; Alneberg, J.; Wilm, A.; Garcia, M.U.; Di Tommaso, P.; Nahnsen, S. The nf-core framework for community-curated bioinformatics pipelines. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Tommaso, P.; Chatzou, M.; Floden, E.W.; Barja, P.P.; Palumbo, E.; Notredame, C. Nextflow enables reproducible computational workflows. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtzer, G.M.; Sochat, V.; Bauer, M.W. Singularity: Scientific containers for mobility of compute. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxime, U.; Garcia, F.H.; Pedersen, A.S.; Gabernet, G.; WackerO; SusiJo; James, C.; Syme, R.; Åslin, M.; Cantalupo, P.; et al. nf-Core/Sarek: Sarek 3.3.0—Rapaselet. 2023. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/8342469 (accessed on 19 October 2023).
- Li, H. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1303.3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePristo, M.A.; Banks, E.; Poplin, R.; Garimella, K.V.; Maguire, J.R.; Hartl, C.; Philippakis, A.A.; del Angel, G.; Rivas, M.A.; Hanna, M.; et al. A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Auwera, G.A.; Carneiro, M.O.; Hartl, C.; Poplin, R.; Del Angel, G.; Levy-Moonshine, A.; Jordan, T.; Shakir, K.; Roazen, D.; Thibault, J.; et al. From FastQ data to high confidence variant calls: The Genome Analysis Toolkit best practices pipeline. Curr. Protoc. Bioinformatics 2013, 43, 11.10.1–11.10.33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondka, Z.; Bamford, S.; Cole, C.G.; Ward, S.A.; Dunham, I.; Forbes, S.A. The COSMIC Cancer Gene Census: Describing genetic dysfunction across all human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrum, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Riley, G.R.; Jang, W.; Rubinstein, W.S.; Church, D.M.; Maglott, D.R. ClinVar: Public archive of relationships among sequence variation and human phenotype. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D980–D985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.M.; Riggs, E.R.; Maglott, D.R.; Lee, J.M.; Azzariti, D.R.; Niehaus, A.; Ramos, E.M.; Martin, C.L.; Landrum, M.J.; Rehm, H.L. Using ClinVar as a Resource to Support Variant Interpretation. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2016, 89, 8.16.1–8.16.23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherry, S.T.; Ward, M.; Sirotkin, K. dbSNP-database for single nucleotide polymorphisms and other classes of minor genetic variation. Genome Res. 1999, 9, 677–679. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, R.D.; Mitchell, M.; Lindahl, T. Human DNA repair genes, 2005. Mutat Res 2005, 577, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sijmons, R.H.; Burger, G.T. Familial cancer database: A clinical aide-memoire. Fam. Cancer 2001, 1, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sijmons, R.H.; Burger, G.T. The Use of a Diagnostic Database in Clinical Oncogenetics. Hered. Cancer Clin. Pract. 2003, 1, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrow, J.; Frankish, A.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Tapanari, E.; Diekhans, M.; Kokocinski, F.; Aken, B.L.; Barrell, D.; Zadissa, A.; Searle, S.; et al. GENCODE: The reference human genome annotation for The ENCODE Project. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1760–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, S.; Singer-Berk, M.; Watts, N.A.; Phu, W.; Goodrich, J.K.; Solomonson, M.; Genome Aggregation Database, C.; Rehm, H.L.; MacArthur, D.G.; O’Donnell-Luria, A. Variant interpretation using population databases: Lessons from gnomAD. Hum. Mutat. 2022, 43, 1012–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, R.L.; Braschi, B.; Gray, K.; Jones, T.E.M.; Tweedie, S.; Haim-Vilmovsky, L.; Bruford, E.A. Genenames.org: The HGNC resources in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D1003–D1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorvaldsdottir, H.; Robinson, J.T.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): High-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief. Bioinform. 2013, 14, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3--new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koressaar, T.; Remm, M. Enhancements and modifications of primer design program Primer3. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1289–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koressaar, T.; Lepamets, M.; Kaplinski, L.; Raime, K.; Andreson, R.; Remm, M. Primer3_masker: Integrating masking of template sequence with primer design software. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1937–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W90–W97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Bailey, A.; Kuleshov, M.V.; Clarke, D.J.B.; Evangelista, J.E.; Jenkins, S.L.; Lachmann, A.; Wojciechowicz, M.L.; Kropiwnicki, E.; Jagodnik, K.M.; et al. Gene Set Knowledge Discovery with Enrichr. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M. Toward understanding the origin and evolution of cellular organisms. Protein Sci. 2019, 28, 1947–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D587–D592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]



| Demographic and Clinical Parameters | IGM n = 8 |
|---|---|
| Demographics | |
| Median age at diagnosis (years, IQR) | 33.0 (27.3–34.5) |
| Ethnicity (n, %) | |
| Chinese | 4 (50) |
| Malay | 3 (38) |
| Others | 1 (12) |
| Body mass index (kg/m2, IQR) | 27.770 (23.460–33.454) |
| Education level (n, %) | |
| Up to secondary school | 3 (38) |
| Secondary school to pre-university | 3 (38) |
| Tertiary education | 2 (25) |
| Patient characteristics | |
| Parity (n, %) | |
| Yes | 6 (75) |
| No | 2 (25) |
| Number of children (n, %) | |
| No children | 2 (25) |
| 1–2 children | 5 (62) |
| More than 2 children | 1 (12) |
| Smoking (n, %) | |
| Yes | 2 (25) |
| No | 6 (75) |
| Chronic illness 1 diagnosis (n, %) | |
| Yes | 2 (25) |
| No | 6 (75) |
| Family history 2 of breast cancer (n, %) | |
| Yes | 1 (12) |
| No | 7 (88) |
| Case | Somatic Variants | SNVs 1 | Indels 2 | PTVs 3 | Pathogenic 4 | Pathogenic/Likely Pathogenic4 | Likely Pathogenic4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 8 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Median (range) | 2 (1–3) | 2 (1–3) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ong, S.S.; Ho, P.J.; Khng, A.J.; Tan, B.K.T.; Tan, Q.T.; Tan, E.Y.; Tan, S.-M.; Putti, T.C.; Lim, S.H.; Tang, E.L.S.; et al. Genomic Insights into Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis through Whole-Exome Sequencing: A Case Report of Eight Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9058. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25169058
Ong SS, Ho PJ, Khng AJ, Tan BKT, Tan QT, Tan EY, Tan S-M, Putti TC, Lim SH, Tang ELS, et al. Genomic Insights into Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis through Whole-Exome Sequencing: A Case Report of Eight Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(16):9058. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25169058
Chicago/Turabian StyleOng, Seeu Si, Peh Joo Ho, Alexis Jiaying Khng, Benita Kiat Tee Tan, Qing Ting Tan, Ern Yu Tan, Su-Ming Tan, Thomas Choudary Putti, Swee Ho Lim, Ee Ling Serene Tang, and et al. 2024. "Genomic Insights into Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis through Whole-Exome Sequencing: A Case Report of Eight Patients" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 16: 9058. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25169058
APA StyleOng, S. S., Ho, P. J., Khng, A. J., Tan, B. K. T., Tan, Q. T., Tan, E. Y., Tan, S.-M., Putti, T. C., Lim, S. H., Tang, E. L. S., Li, J., & Hartman, M. (2024). Genomic Insights into Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis through Whole-Exome Sequencing: A Case Report of Eight Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(16), 9058. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25169058








