Master Regulatory Transcription Factors in β-Aminobutyric Acid-Induced Resistance (BABA-IR): A Perspective on Phytohormone Biosynthesis and Signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana and Hordeum vulgare
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
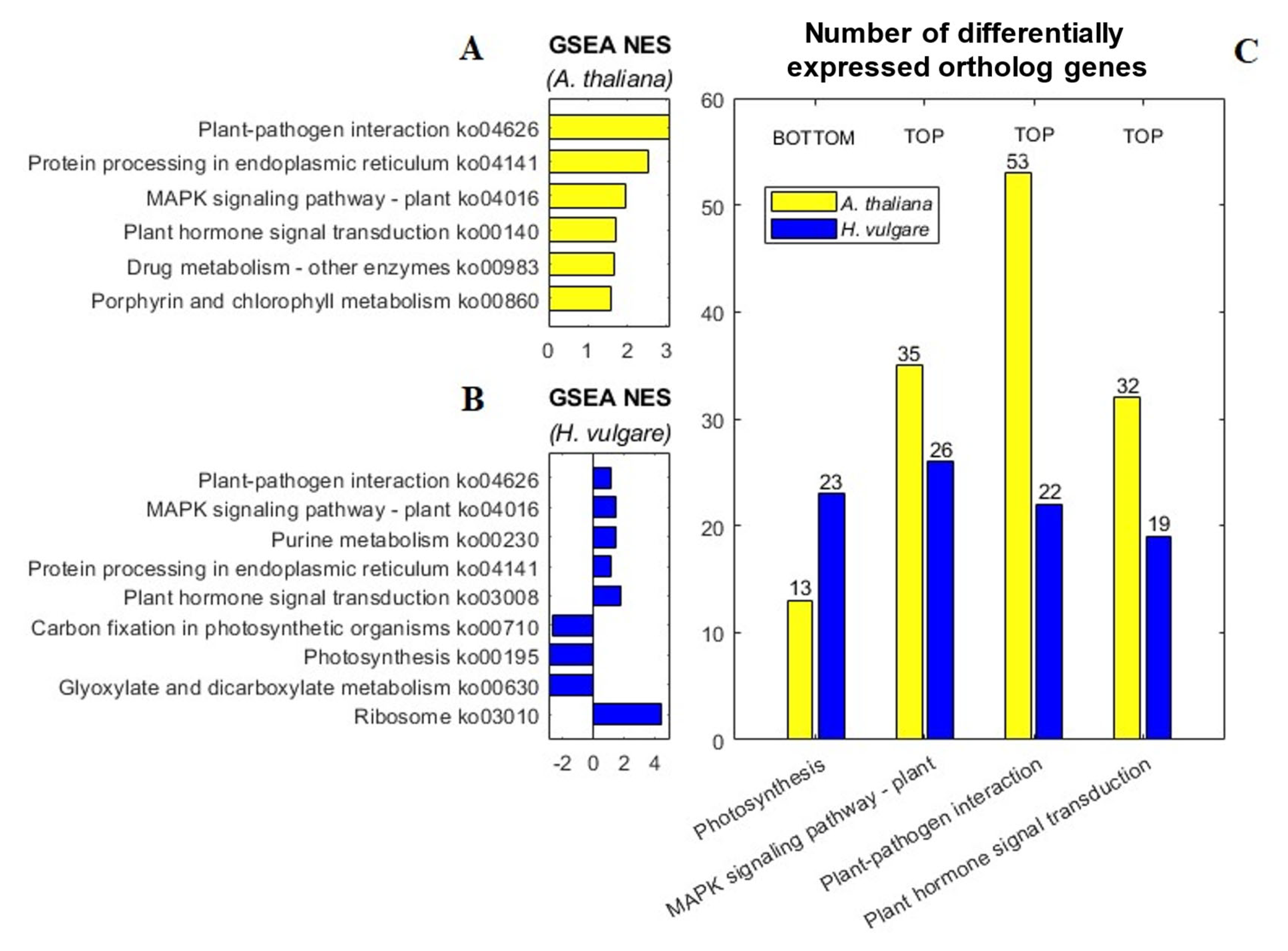
2.1. Pathway Analysis of DEGs Revealed Enhanced MAPK Signaling, Plant–Pathogen Interactions, Plant Hormone Signal Transduction, and Decreased Expression of Photosynthetic Genes in Both Species Following BABA Treatment
2.1.1. BABA Treatment Improved Oxidative Homeostasis in H. vulgare and Enhanced Pathogen Response in A. thaliana through Activation of MAPK Signaling Pathway
2.1.2. After BABA Treatment, the Gene Signaling Cascade Regulated by the WRKY Family Was Upregulated in A. thaliana but Downregulated in H. vulgare as Part of the Plant–Pathogen Interaction Pathway
2.1.3. BABA Treatment Activated Distinct Phytohormone Signal Transduction Cascades in A. thaliana and H. vulgare, Leading to the Induction of Defense-Related Genes
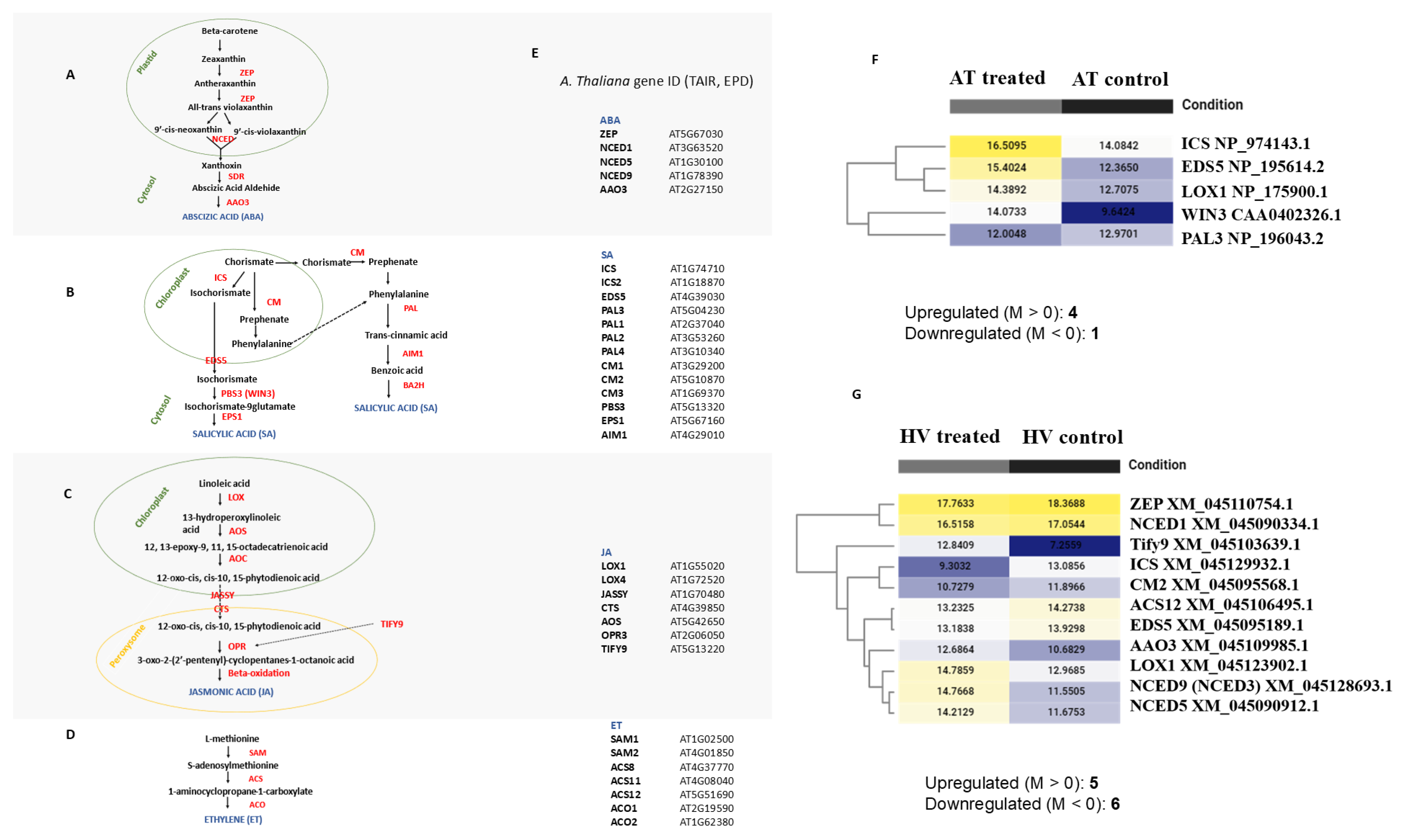
2.2. DEGs Revealed Species-Specificity of ABA, SA, JA, and ET Metabolism Genes, Highlighting Distinct Biosynthetic Pathways Activated Following BABA Treatment
2.3. Identification of Jaspar Core TF Binding Motifs in the Promoters of Genes Involved in Phytohormone Biosynthesis and Signaling, and Their Expression Analysis following BABA Treatment
2.3.1. Screening of Master Regulatory TFs Involved in Phytohormone Signaling Pathways
2.3.2. An Analysis of Promoter Binding Sites Based on the Position Frequency of Master Regulatory TFs
2.3.3. Upregulation of DOF, AHL, and ERF Families as Master Regulatory TFs in A. thaliana and H. vulgare Following BABA Treatment
3. Discussion
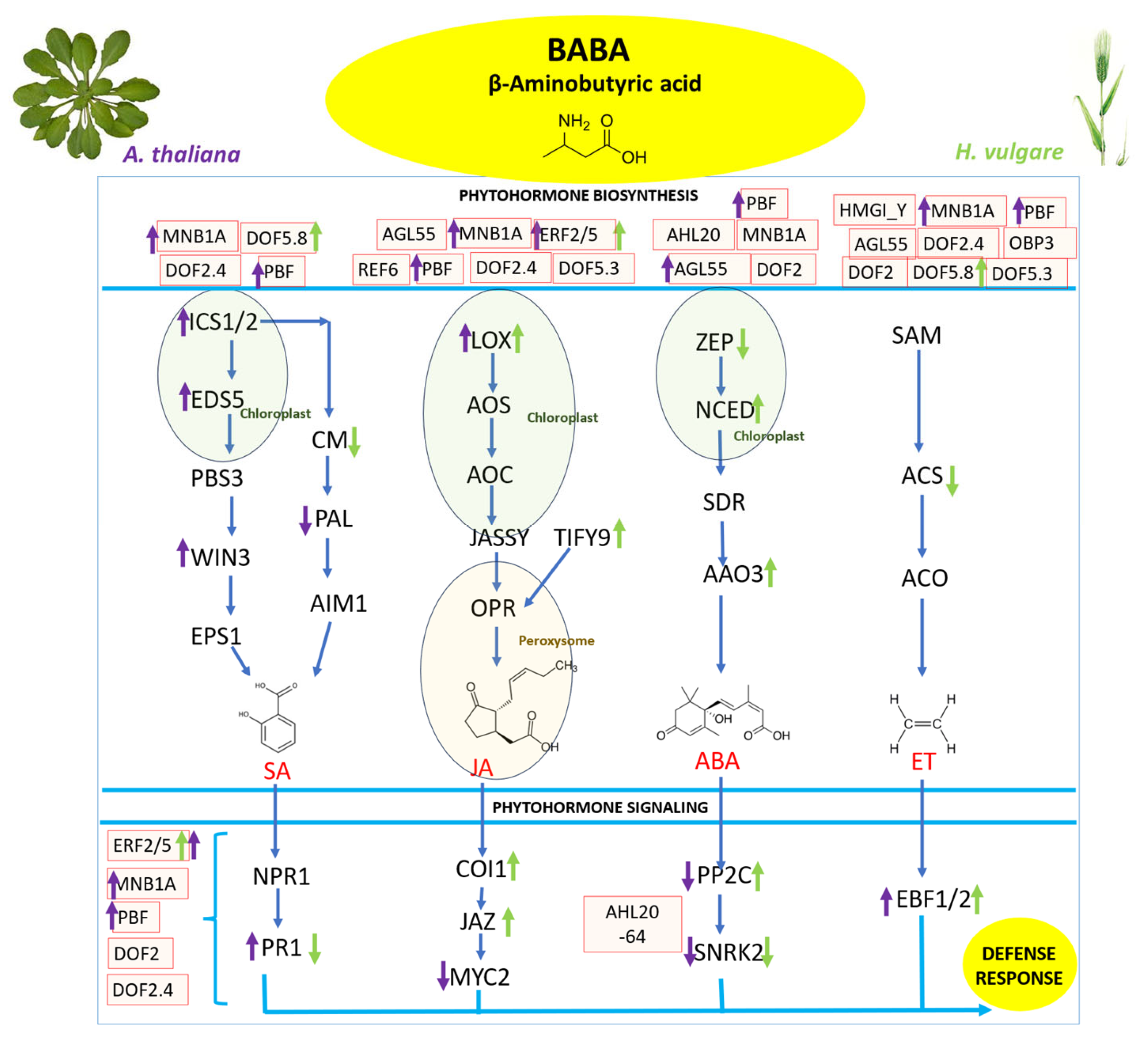
3.1. The BABA Treatment May Stimulate the Negative Regulator EBF1/2 of ET Signal in Both Plants
3.2. BABA Treatment May Negatively Regulate the ABA Signaling Genes PP2C and SNRK2, Potentially through the Action of Master Transcription Factors AHL20, PBF, and MNB1A
3.3. BABA Treatment May Induce Opposing Regulatory Effects of ERFs on SA Biosynthesis in A. thaliana and H. vulgare
3.4. BABA Treatment May Enhance the Expression of the JA Biosynthetic Gene LOX and JA Signaling Genes COI1, JAZ, and MYC2 by Modulating the Activity of the Master Regulatory TFs MNB1A, ERF2/5, and PBF
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Preparation of RNA-Seq Libraries
4.3. Preprocessing and Assembly of RNA-Seq Reads
4.4. The Mapping of RNA-Seq Reads to the Reference
4.5. Gene-Level Quantification and Analysis of Differential Expression of Genes (DEGs)
4.6. KEGG Pathway Analysis
4.7. Expression Analysis of Genes of SA, JA, ABA, and ET Biosynthetic Pathways
4.8. Analysis of Master Regulatory TRFs of Genes of Biosynthesis Having Role in SA, JA, ABA, and ET Pathways
4.9. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression by RT-qPCR
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teshome, D.T.; Zharare, G.E.; Naidoo, S. The threat of the combined effect of biotic and abiotic stress factors in forestry under a changing climate. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 601009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthamilarasan, M.; Prasad, M. Plant innate immunity: An updated insight into defense mechanism. J. Biosci. 2013, 38, 433–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishad, R.; Ahmed, T.; Rahman, V.J.; Kareem, A. Modulation of plant defense system in response to microbial interactions. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachroo, P.; Kachroo, A. The roles of salicylic acid and jasmonic acid in plant immunity. In Molecular Plant Immunity; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 55–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, M.L.; Kang, J.-H.; Howe, G.A. Jasmonate-triggered plant immunity. J. Chem. Ecol. 2014, 40, 657–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidhyasekaran, P. Vidhyasekaran, P. Vidhyasekaran, P. Abscisic acid signaling system in plant innate immunity. In Abscisic Acid Signaling System in Plant Innate Immunity; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 245–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mersmann, S.; Bourdais, G.; Rietz, S.; Robatzek, S. Ethylene signaling regulates accumulation of the FLS2 receptor and is required for the oxidative burst contributing to plant immunity. Plant Physiol. 2010, 154, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevenet, D.; Pastor, V.; Baccelli, I.; Balmer, A.; Vallat, A.; Neier, R.; Glauser, G.; Mauch-Mani, B. The priming molecule β-aminobutyric acid is naturally present in plants and is induced by stress. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccelli, I.; Glauser, G.; Mauch-Mani, B. The accumulation of β-aminobutyric acid is controlled by the plant’s immune system. Planta 2017, 246, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.R. Does GABA act as a signal in plants? Hints from molecular studies: Hints from molecular studies. Plant Signal. Behav. 2007, 2, 408–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papavizas, G.; Davey, C. Effect of amino compounds and related substances lacking sulfur on aphanomyces root rot of peas. Phytopathology 1963, 53, 116–122. [Google Scholar]
- Jakab, G.; Cottier, V.; Toquin, V.; Rigoli, G.; Zimmerli, L.; Métraux, J.-P.; Mauch-Mani, B. β-Aminobutyric acid-induced resistance in plants. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2001, 107, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerli, L.; Jakab, G.; Métraux, J.-P.; Mauch-Mani, B. Potentiation of pathogen-specific defense mechanisms in Arabidopsis by β-aminobutyric acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12920–12925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ton, J.; Jakab, G.; Toquin, V.; Flors, V.; Iavicoli, A.; Maeder, M.N.; Metraux, J.P.; Mauch-Mani, B. Dissecting the β-aminobutyric acid–induced priming phenomenon in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 987–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ton, J.; Mauch-Mani, B. β-amino-butyric acid-induced resistance against necrotrophic pathogens is based on ABA-dependent priming for callose. Plant J. 2004, 38, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conrath, U.; Beckers, G.J.M.; Flors, V.; García-Agustín, P.; Jakab, G.; Mauch, F.; Newman, M.-A.; Pieterse, C.M.J.; Poinssot, B.; Pozo, M.J.; et al. Priming: Getting ready for battle. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2006, 19, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaughter, A.; Daniel, X.; Flors, V.; Luna, E.; Hohn, B.; Mauch-Mani, B. Descendants of primed Arabidopsis plants exhibit resistance to biotic stress. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Y.; Gisi, U. Systemic translocation of 14C-DL-3-aminobutyric acid in tomato plants in relation to induced resistance against Phytophthora infestans. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 1994, 45, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Y.; Reuveni, M.; Baider, A. Local and systemic activity of BABA (DL-3-aminobutyric acid) against Plasmopara viticola in grapevines. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 1999, 105, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Y.R. β-aminobutyric acid-induced resistance against plant pathogens. Plant Dis. 2002, 86, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrath, U.; Pieterse, C.M.; Mauch-Mani, B. Priming in plant–pathogen interactions. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckers, G.J.; Conrath, U. Priming for stress resistance: From the lab to the field. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Ent, S.; Van Hulten, M.; Pozo, M.J.; Czechowski, T.; Udvardi, M.K.; Pieterse, C.M.; Ton, J. Priming of plant innate immunity by rhizobacteria and β-aminobutyric acid: Differences and similarities in regulation. New Phytol. 2009, 183, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liljeroth, E.; Bengtsson, T.; Wiik, L.; Andreasson, E. Induced resistance in potato to Phytphthora infestans—Effects of BABA in greenhouse and field tests with different potato varieties. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2010, 127, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrath, U. Molecular aspects of defence priming. Trends Plant Sci. 2011, 16, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, Y.; Vaknin, M.; Mauch-Mani, B. BABA-induced resistance: Milestones along a 55-year journey. Phytoparasitica 2016, 44, 513–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piękna-Grochala, J.; Kępczyńska, E. Induction of resistance against pathogens by β-aminobutyric acid. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2013, 35, 1735–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hönig, M.; Roeber, V.M.; Schmülling, T.; Cortleven, A. Chemical priming of plant defense responses to pathogen attacks. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1146577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Verk, M.C.; Bol, J.F.; Linthorst, H.J. WRKY transcription factors involved in activation of SA biosynthesis genes. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, I.A.; Verhage, A.; Schuurink, R.C.; Watt, L.G.; Pieterse, C.M.; Van Wees, S.C. Onset of herbivore-induced resistance in systemic tissue primed for jasmonate-dependent defenses is activated by abscisic acid. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruta, V.; Longo, C.; Lepri, A.; De Angelis, V.; Occhigrossi, S.; Costantino, P.; Vittorioso, P. The DOF transcription factors in seed and seedling development. Plants 2020, 9, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-I.; Hong, J.-H.; Ha, J.-O.; Kang, J.-Y.; Kim, S.Y. ABFs, a family of ABA-responsive element binding factors. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rymen, B.; Kawamura, A.; Schäfer, S.; Breuer, C.; Iwase, A.; Shibata, M.; Ikeda, M.; Mitsuda, N.; Koncz, C.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; et al. ABA suppresses root hair growth via the OBP4 transcriptional regulator. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 1750–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyashima, S.; Roszak, P.; Sevilem, I.; Toyokura, K.; Blob, B.; Heo, J.O.; Mellor, N.; Help-Rinta-Rahko, H.; Otero, S.; Smet, W.; et al. Mobile PEAR transcription factors integrate positional cues to prime cambial growth. Nature 2019, 565, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Malviya, N.; Kushwaha, H.; Nasim, J.; Bisht, N.C.; Singh, V.; Yadav, D. Insights into structural and functional diversity of Dof (DNA binding with one finger) transcription factor. Planta 2015, 241, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Zou, Y.; Feng, N. Overexpression of AHL20 negatively regulates defenses in Arabidopsis. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2010, 52, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Folter, S.; Immink, R.G.; Kieffer, M.; Parenicova, L.; Henz, S.R.; Weigel, D.; Busscher, M.; Kooiker, M.; Colombo, L.; Kater, M.M.; et al. Comprehensive interaction map of the Arabidopsis MADS box transcription factors. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 1424–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Li, L.; Li, L.; Guo, M.; Chory, J.; Yin, Y. Modulation of brassinosteroid-regulated gene expression by Jumonji domain-containing proteins ELF6 and REF6 in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7618–7623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husaini, A.M.; Sakina, A.; Cambay, S.R. Host–pathogen interaction in Fusarium oxysporum infections: Where do we stand? Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2018, 31, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, G.H.; Wan, J.; Kim, H.J.; Nguyen, X.C.; Chung, W.S.; Hong, J.C.; Stacey, G. Ethylene-responsive element-binding factor 5, ERF5, is involved in chitin-induced innate immunity response. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2012, 25, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.G.; Singh, K.B. Characterization of salicylic acid-responsive, Arabidopsis Dof domain proteins: Overexpression of OBP3 leads to growth defects. Plant J. 2000, 21, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, M.; Yanagisawa, S. Sequential activation of two Dof transcription factor gene promoters during vascular development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 45, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Su, C.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Z. ATDOF5. 8 protein is the upstream regulator of ANAC069 and is responsive to abiotic stress. Biochimie 2015, 110, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Xi, Y.; Kim, J.; Sung, S. Chromatin architectural proteins regulate flowering time by precluding gene looping. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapletalová, M.; Rancurel, C.; Industri, B.; Bardin, M.; Le Brigand, K.; Nicot, P.; Magnone, V.; Seassau, A.; Barbry, P.; Potěšil, D.; et al. BABA-induced pathogen resistance: A multi-omics analysis of the tomato response reveals a hyper-receptive status involving ethylene. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhad068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baccelli, I.; Mauch-Mani, B. Beta-aminobutyric acid priming of plant defense: The role of ABA and other hormones. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 91, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, F.; Wang, Z.; Mei, J.; Xie, Y.; Liu, T.; Ye, X. β-aminobutyric acid (BABA)-induced resistance to tobacco black shank in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penninckx, I.A.; Thomma, B.P.; Buchala, A.; Métraux, J.-P.; Broekaert, W.F. Concomitant activation of jasmonate and ethylene response pathways is required for induction of a plant defensin gene in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 2103–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, B.M.; Walker, J.M.; Gagne, J.M.; Emborg, T.J.; Hemmann, G.; Bleecker, A.B.; Vierstra, R.D. The Arabidopsis EIN3 binding F-Box proteins EBF1 and EBF2 have distinct but overlapping roles in ethylene signaling. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konishi, M.; Yanagisawa, S. Ethylene signaling in Arabidopsis involves feedback regulation via the elaborate control of EBF2 expression by EIN3. Plant J. 2008, 55, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Guo, H.; Li, W. Endoribonuclease DNE1 Promotes Ethylene Response by Modulating EBF1/2 mRNA Processing in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sós-Hegedűs, A.; Juhász, Z.; Poór, P.; Kondrák, M.; Antal, F.; Tari, I.; Mauch-Mani, B.; Bánfalvi, Z. Soil drench treatment with ß-aminobutyric acid increases drought tolerance of potato. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, C.; Ding, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Dai, J.; Li, J.; Huang, H.; Wang, T.; Zhu, M.; Feng, M.; et al. A plant NLR receptor employs ABA central regulator PP2C-SnRK2 to activate antiviral immunity. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.-N.; Sun, H.-J.; Zuo, Z.-F.; Lee, D.H.; Song, P.-S.; Kang, H.-G.; Lee, H.-Y. Overexpression of ATHG1/AHL23 and ATPG3/AHL20, Arabidopsis AT-hook motif nuclear-localized genes, confers salt tolerance in transgenic Zoysia japonica. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 14, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, M.; Chinnusamy, V. ABA receptors: Prospects for enhancing biotic and abiotic stress tolerance of crops. In Elucidation of Abiotic Stress Signaling in Plants: Functional Genomics Perspectives; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 271–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Kim, H.; Zhong, S.; Chen, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, B. De novo transcriptome assembly for rudimentary leaves in Litchi chinesis Sonn. and identification of differentially expressed genes in response to reactive oxygen species. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagisawa, S. A novel DNA-binding domain that may form a single zinc finger motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23, 3403–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Lin, J.; Li, Z.; Lin, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ming, R. Allele specific expression of Dof genes responding to hormones and abiotic stresses in sugarcane. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerli, L.; Hou, B.H.; Tsai, C.H.; Jakab, G.; Mauch-Mani, B.; Somerville, S. The xenobiotic β-aminobutyric acid enhances Arabidopsis thermotolerance. Plant J. 2008, 53, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janotík, A.; Dadáková, K.; Lochman, J.; Zapletalová, M. L-aspartate and L-glutamine inhibit Beta-aminobutyric acid-induced resistance in tomatoes. Plants 2022, 11, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-H.; Bian, L.; Wan, Y.-T.; Jiao, Z.-L.; Yu, K.-K.; Zhang, G.-H.; Guo, D.-L. Grape (Vitis vinifera) VvDOF3 functions as a transcription activator and enhances powdery mildew resistance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 143, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Memelink, J.; Linthorst, H. AP/ERF and WRKY transcription factors involved in the coordinated regulation of the salicylic acid signaling pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana. In Exploring Novel Regulators and Enzymes in Salicylic Acid-Mediated Plant Defense; Leiden University: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2018; p. 35. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/1887/62028 (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Yang, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, T.; Xu, X.; Jiang, J.; Li, J. Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of the ERF2 gene family in response to disease resistance against Stemphylium lycopersici in tomato. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon-Reyes, A.; Van der Does, D.; De Lange, E.S.; Delker, C.; Wasternack, C.; Van Wees, S.C.M.; Ritsema, T.; Pieterse, C.M.J. Salicylate-mediated suppression of jasmonate-responsive gene expression in Arabidopsis is targeted downstream of the jasmonate biosynthesis pathway. Planta 2010, 232, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Mou, Z. Salicylic acid and its function in plant immunity F. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2011, 53, 412–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, M.; Li, L.; Ma, Y. Functions and application of the AP2/ERF transcription factor family in crop improvement. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2011, 53, 570–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Wenig, M.; Langen, G.; Sharma, S.; Kugler, K.G.; Knappe, C.; Hause, B.; Bichlmeier, M.; Babaeizad, V.; Imani, J.; et al. Bacteria-triggered systemic immunity in barley is associated with WRKY and ETHYLENE RESPONSIVE FACTORs but not with salicylic acid. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 2133–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Vlot, A.C. Ethylene responsive factors in the orchestration of stress responses in monocotyledonous plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walper, E.; Weiste, C.; Mueller, M.J.; Hamberg, M.; Dröge-Laser, W. Screen identifying transcription factors involved in the response to 9-lipoxygenase-derived oxylipins. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wei, Y.; Jiang, S.; Ye, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, F.; Shao, X. Transcriptome analysis reveals that trehalose alleviates chilling injury of peach fruit by regulating ROS signaling pathway and enhancing antioxidant capacity. Food Res. Int. 2024, 186, 114331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, M.; Yan, J.; Khurshid, M.; Weng, W.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, K. Jasmonic acid signaling pathway in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, O.; Piqueras, R.; Sánchez-Serrano, J.J.; Solano, R. ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR1 integrates signals from ethylene and jasmonate pathways in plant defense. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pré, M.; Atallah, M.; Champion, A.; De Vos, M.; Pieterse, C.M.; Memelink, J. The AP2/ERF domain transcription factor ORA59 integrates jasmonic acid and ethylene signals in plant defense. Plant Physiol. 2008, 147, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Hua, X.; Yao, H.; Zhang, Q.; He, J.; Peng, L.; Li, D.; Yang, Y.; Li, X. Abscisic acid receptors are involves in the Jasmonate signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal. Behav. 2021, 16, 1948243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lv, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Network analysis of ABA-dependent and ABA-independent drought responsive genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2018, 41, 624–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virág, E.; Kiniczky, M.; Kutasy, B.; Nagy, Á.; Pallos, J.P.; Laczkó, L.; Freytag, C.; Hegedűs, G. Supplementation of the Plant Conditioner ELICE Vakcina® Product with β-Aminobutyric Acid and Salicylic Acid May Lead to Trans-Priming Signaling in Barley (Hordeum vulgare). Plants 2023, 12, 2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegedűs, G.; Nagy, Á.; Decsi, K.; Kutasy, B.; Virág, E. Transcriptome datasets of β-Aminobutyric acid (BABA)-primed mono-and dicotyledonous plants, Hordeum vulgare and Arabidopsis thaliana. Data Brief 2022, 41, 107983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Retrieved 17 May 2010. 2018. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 6 October 2023).
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mátyás, K.K.; Hegedűs, G.; Taller, J.; Farkas, E.; Decsi, K.; Kutasy, B.; Virág, E. Different expression pattern of flowering pathway genes contribute to male or female organ development during floral transition in the monoecious weed Ambrosia artemisiifolia L. (Asteraceae). PeerJ 2019, 7, e7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazona, S.; García, F.; Ferrer, A.; Dopazo, J.; Conesa, A. NOIseq: A RNA-seq differential expression method robust for sequencing depth biases. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 18–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazona, S.; Furió-Tarí, P.; Turrà, D.; Pietro, A.D.; Nueda, M.J.; Ferrer, A.; Conesa, A. Data quality aware analysis of differential expression in RNA-seq with NOISeq R/Bioc package. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, B.B.; Hegedus, G.; Virag, E.; Pethő, G.T.; Laczko, L.; Fesus, L. Deciphering Species-Specific and Conserved Regulation of Human UCP1 Gene Expression: Insights from Predicted Homeodomain Family Transcription Factor Binding Sites. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virág, E. Phytohormone biosynthesis and signalling in A. thaliana and H. vulgare. Mendeley Data 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



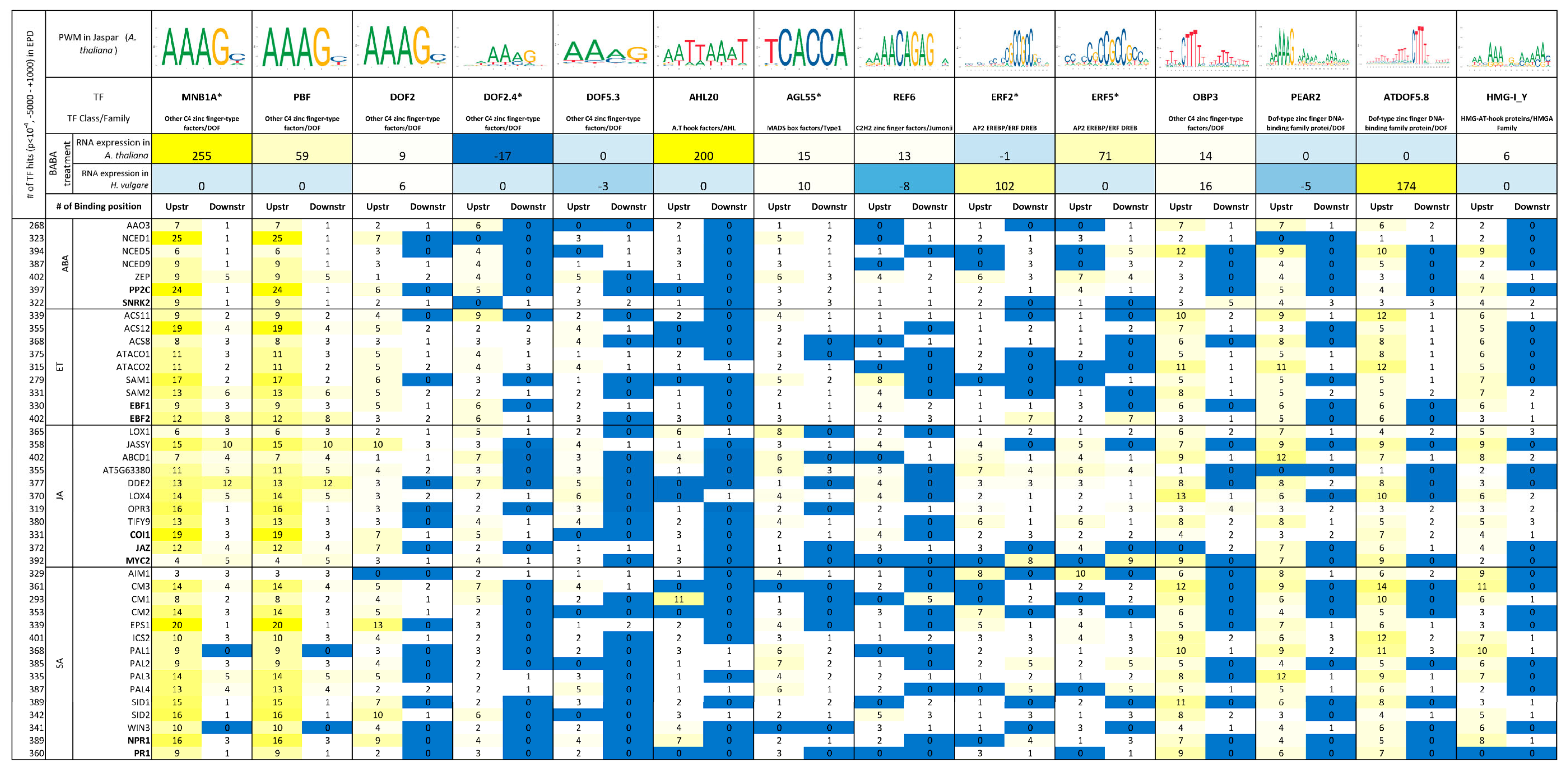

| Master TFs | TAIR ID | Function |
|---|---|---|
| MNB1a | AT1G51700 | It is a DNA-binding protein that interacts with the 35S promoter of cauliflower mosaic virus. MNB1a seems to be a member of a multigene family. It contains the DOF domain. It may form a single zinc finger motif, and may transactivate seed storage protein genes in developing seeds [31]. |
| PBF | AT3G19290 | PBF (ABF) is a bZIP transcription factor. It activates the ABA-inducible expression of LTI65/RD29B. It binds specifically to the ABA-responsive element (ABRE), and acts through SnRK2 pathway [32]. |
| DOF2 | AT3G21270 | DOF2 (ADOF2) encodes a DOF zinc finger protein DOF2. It is preferentially expressed during cell growth. It may have redundant functions with OBP4 regarding cell growth regulation [33]. |
| DOF2.4 | AT2G37590 | DOF2.4 encodes the DOF zinc finger protein PEAR that may concentrate in the peaks of protophloem sieve elements, activating the expression of genes involved in radial growth. DNA binding occurs with one finger [34]. |
| DOF5.3 | AT5G60200 | It encodes a DOF-type transcription factor. The protein PEAR may concentrate in the peaks of protophloem sieve elements, activating the expression of genes involved in radial growth. It has been reported in the preprocambial stage in leaves, suggesting their role in preprocambial development [35]. |
| AHL20 | AT4G14465 | It is an AT-hook protein. Its overexpression results in early flowering in short and long days. It binds AT-rich DNA sequences related to the nuclear matrix attachment regions (MARs) (by similarity), and negatively regulates plant innate immunity (PTI) to pathogens by downregulating PAMP-triggered NHO1 and FRK1 expression [36]. |
| AGL55 | AT1G60920 | It is a MADS-box family protein, a positive regulator of flowering. It may play a role in root development [37]. |
| REF6 | AT3G48430 | It encodes a Jumonji N/C and zinc finger domain-containing protein that acts as a positive regulator of flowering in an FLC-dependent pathway. It may play a role in brassinosteroid signaling by affecting histone methylation in the promoters of BR-responsive genes. It is involved in the transcriptional regulation of hundreds of genes regulating developmental patterning and responses to various stimuli [38]. |
| ERF2 | AT5G47220 | It encodes a member of the ERF (ethylene response factor) subfamily B-3 of the ERF/AP2 transcription factor family (ATERF-2). The protein contains one AP2 domain, and functions as an activator of GCC box-dependent transcription. It is a positive regulator of JA-responsive defense genes and resistance to F. oxysporum, and enhances JA-based inhibition of root elongation [39]. |
| ERF5 | AT5G47230 | It encodes a member of the ERF (ethylene response factor) subfamily B-3 of the ERF/AP2 transcription factor family (ATERF-5). It is involved in regulating gene expression by stress factors and components of stress signal transduction pathways. The mRNA is cell-to-cell mobile. It may play an important role in plant innate immunity, regulating chitin and other plant defense pathways in response to different pathogens [40]. |
| OBP3 | AT3G55370 | It encodes a nuclear-localized DOF domain-containing transcription factor expressed primarily in roots, and is responsive to salicylic acid. Transgenic overexpressors have yellow leaves and short, defective roots [41]. |
| PEAR2 | AT5G02460 | It encodes a PEAR protein involved in the regulation of radial growth. It is probably involved in early processes for vascular development [42]. |
| DOF5.8 | AT5G66940 | The overexpression of DOF5.8 modulates the auxin response, impairing vein formation in A. thaliana. It regulates its direct target gene ANAC069 positively, under abiotic stress conditions such as the presence of salt, drought, and ABA treatment [43]. |
| HMG I_Y | AT1G14900 | It binds A/T-rich DNA with a highly dynamic distribution in the nucleus. It is one of the HMGA proteins affecting the local chromatin structure in several ways, including the bending, straightening, unwinding, and looping of substrate DNA. The biological function of plant HMGA proteins is not known [44]. |
| Gene | Primers | Product Size | Plant Hormone | Melt Peak (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| At_AAO3 | F: TGGGAAGCTCACAGCACTGG | 182 | ABA | 83 |
| R: CGGGAGCTCTCATCGCTGTT | ||||
| At_ZEP | F: CGATGACCGGCTTCGAGAGT | 152 | 81.5 | |
| R: TTCCGACGATGCAAGGTTGA | ||||
| At_OPR1 | F: CTCAGCCTCACGCTGCCATA | 151 | JA | 82.5 |
| R: ATTGGCTTCCATGCCTCCAC | ||||
| At_AOC1 | F: GGCTGGTCTCTGCGTTGTGA | 162 | 83.5 | |
| R: ATTCCAGCGCCACCAGTGAT | ||||
| At_PAL3 | F: CCAAAGCGCAGAGCAGCATA | 195 | SA | 83 |
| R: TTCGCCACCTGACTCACTGC | ||||
| At_ICS1 | F: TGACCAGCAAATCGGAGCAA | 197 | 84 | |
| R: CTGCAGAGCCGATACCAGCA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Virág, E.; Nagy, Á.; Tóth, B.B.; Kutasy, B.; Pallos, J.P.; Szigeti, Z.M.; Máthé, C.; Kardos, G.; Hegedűs, G. Master Regulatory Transcription Factors in β-Aminobutyric Acid-Induced Resistance (BABA-IR): A Perspective on Phytohormone Biosynthesis and Signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana and Hordeum vulgare. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179179
Virág E, Nagy Á, Tóth BB, Kutasy B, Pallos JP, Szigeti ZM, Máthé C, Kardos G, Hegedűs G. Master Regulatory Transcription Factors in β-Aminobutyric Acid-Induced Resistance (BABA-IR): A Perspective on Phytohormone Biosynthesis and Signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana and Hordeum vulgare. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(17):9179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179179
Chicago/Turabian StyleVirág, Eszter, Ágnes Nagy, Beáta B. Tóth, Barbara Kutasy, József Péter Pallos, Zsuzsa Máthéné Szigeti, Csaba Máthé, Gábor Kardos, and Géza Hegedűs. 2024. "Master Regulatory Transcription Factors in β-Aminobutyric Acid-Induced Resistance (BABA-IR): A Perspective on Phytohormone Biosynthesis and Signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana and Hordeum vulgare" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 17: 9179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179179
APA StyleVirág, E., Nagy, Á., Tóth, B. B., Kutasy, B., Pallos, J. P., Szigeti, Z. M., Máthé, C., Kardos, G., & Hegedűs, G. (2024). Master Regulatory Transcription Factors in β-Aminobutyric Acid-Induced Resistance (BABA-IR): A Perspective on Phytohormone Biosynthesis and Signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana and Hordeum vulgare. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(17), 9179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179179







