Changes in Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Parameters Caused by Addition of Amphotericin B to Cladosporium cladosporioides Melanin and DOPA-Melanin—Free Radical Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. EPR Measurements and Analysis
- -
- δf(x1, x2, …, xn)/δx1, δf(x1, x2, …, xn)/δx2 and δf(x1, x2, …, xn)/δxn are the partial derivatives of functions f(x1, x2, …, xn) over variables x1, x2, and xn;
- -
- |Δx1|, |Δx2| and |Δxn| are the mean maximum errors of the relevant parameters x1, x2, and xn, respectively.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carolus, H.; Pierson, S.; Lagrou, K.; Van Dijck, P. Amphotericin B and Other Polyenes-Discovery, Clinical Use, Mode of Action and Drug Resistance. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, A.; Preuss, C.V. Amphotericin B. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, B.M.; Lancaster, A.K.; Scherz-Shouval, R.; Whitesell, L.; Lindquist, S. Fitness trade-offs restrict the evolution of resistance to amphotericin B. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekar, P. Management of invasive fungal infections: A role for polyenes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, J.M.; Fortwendel, J.R.; Rogers, P.D. Emerging threat of triazole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruthi, H.S. When to Initiate Antifungal Treatment in COVID-19 Patients with Secondary Fungal Co-infection. Curr. Clin. Microbiol. Rep. 2022, 9, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Balushi, A.; Khamis, F.; Klaassen, C.H.W.; Gangneux, J.P.; Van Hellemond, J.J.; Petersen, E. Double Infection With Leishmania tropica and L. major in an HIV Patient Controlled With High Doses of Amphotericin B. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, ofy323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, R.M.; Sarna, T.; Płonka, P.M.; Raman, C.; Brożyna, A.A.; Slominski, A.T. Melanoma, Melanin, and Melanogenesis: The Yin and Yang Relationship. Fron. Oncol. 2022, 12, 842496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, A.T.; Zmijewski, M.A.; Plonka, P.M.; Szaflarski, J.P.; Paus, R. How UV Light Touches the Brain and Endocrine System Through Skin, and Why. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 1992–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, R.M.; Zmijewski, M.A.; Slominski, A.T. The Role of Melanin Pigment in Melanoma. Exp. Deramatol. 2015, 24, 258–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajak, S.; Cieszka, K.; Plonka, P.; Lukiewicz, S.; Mihm, M.; Slominski, A. Transplantable melanomas in gerbils (Meriones unguiculatus). I. Origin, morphology and growth rate. Anticancer Res. 1996, 16, 1203–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Plonka, P.M.; Slominski, A.T.; Pajak, S.; Urbanska, K. Transplantable melanomas in gerbils (Meriones unguiculatus). II: Melanogenesis. Exp. Dermatol. 2003, 12, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Tobin, D.J.; Shibahara, S.; Wortsman, J. Melanin pigmentation in mammalian skin and its hormonal regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 1155–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łopusiewicz, Ł.; Lisiecki, S. Black gold—Melanins in human life. Kosmos 2016, 65, 621–629. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, D.; Paiva, T.G.; Lopes, J.A.; Corvo, M.C.; Sequeira, S.O. Characterization of Fungal Melanins from Black Stains on Paper Artefacts. Heritage 2022, 5, 3049–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witoszyńska, T.; Kulik, M.; Buszman, E.; Trzcionka, J. Amphotericin B binding to pigmented microscopic fungi Cladosporium cladosporioides. Ann. Acad. Med. Siles. 2012, 66, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Felix, C.C.; Hyde, J.S.; Sarna, T.; Sealy, R.C. Interactions of melanin with metal ions. Electron spin resonance evidence for chelate complexes of metal ions with free radicals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1978, 100, 3922–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarna, T.; Swartz, H.M.; Żądło, A. Interaction of Melanin with Metal Ions Modulates Their Cytotoxic Potential. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2022, 53, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żądło, A.C.; Sarna, T. Interaction of iron ions with melanin. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2019, 66, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sealy, R.C.; Hyde, J.S.; Felix, C.C.; Menon, I.A.; Prota, G. Eumelanins and pheomelanins: Characterization by electron spin resonance spectroscopy. Science 1982, 217, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszczyk, M.; Buszman, E.; Pilawa, B.; Witoszyńska, T.; Wilczok, T. Cd2+ effect on free radicals in Cladosporium cladosporioides-melanin tested by EPR spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 394, 366–371. [Google Scholar]
- Al Khatib, M.; Harir, M.; Costa, J.; Baratto, M.C.; Schiavo, I.; Trabalzini, L.; Pollini, S.; Rossolini, G.M.; Basosi, R.; Pogni, R. Spectroscopic Characterization of Natural Melanin from a Streptomyces cyaneofuscatus Strain and Comparison with Melanin Enzymatically Synthesized by Tyrosinase and Laccase. Molecules 2018, 23, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdybel, M.; Pilawa, B.; Buszman, E.; Witoszyńska, T.; Brotoń, B. Paramagnetism of pigmented soil fungi Cladosporium herbarum. Nukleonika 2009, 89–91, 173–175. [Google Scholar]
- Zdybel, M.; Pilawa, B.; Drewnowska, J.M.; Święcicka, I. Comparative EPR studies of free radicals in melanin synthesized by Bacillus weihenstephanensis soil strains. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2017, 679, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pukalski, J.; Marcol, N.; Wolan, N.; Płonka, P.M.; Ryszka, P.; Kowalski, T.; Latowski, D. Detection of a pheomelanin-like pigment by EPR spectroscopy in the mycelium of Plenodomus biglobosus. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2020, 67, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Khatib, M.; Costa, J.; Baratto, M.C.; Basosi, R.; Pogni, R. Paramagnetism and Relaxation Dynamics in Melanin Biomaterials. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 2110–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chodurek, E.; Pilawa, B. Application of EPR spectroscopy in qualitative and quantitative examinations of paramagnetic centers in melanin. Ann. Acad. Med. Siles. 2022, 76, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płonka, P.M.; Grabacka, M. Melanin synthesis in microorganisms—Biotechnological and medical aspects. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2006, 53, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mignon, L.; Desmet, C.M.; Harkemanne, E.; Tromme, I.; Joudio, N.; Wehbi, M.; Baurain, J.F.; Gallex, B. Noninvasive detection of the endogenous free radical melanin in human skin melanomas using electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR). Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 190, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, J.A.; Bolton, J.R. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance: Elementary Theory and Practical Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ushakova, N.; Dontsov, A.; Sakina, N.; Bastrakov, A.; Ostrovsky, M. Antioxidative properties of melanins and ommochromes from black soldier fly Hermetia illucens. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chodurek, E.; Czyżyk, D.; Pilawa, B.; Wilczyński, S. EPR studies of paramagnetic centers in melanin from Sepia officinalis. Eng. Biomater. 2009, 12, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Beberok, A.; Zdybel, M.; Pilawa, B.; Buszman, E.; Wrześniok, D. EPR characteristics of free radicals in DOPA-melanin-moxifloxacin complexes at ambient level of UVA radiation. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2014, 592, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkadi, H. A Review on free radicals and antioxidants. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 20, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pambuk, C.I.A.; Muhammad, F.M. Free radicals: The types generated in biological system. MOJ Cell Sci. Rep. 2018, 5, 72–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.D.; Mazur, M.; Tesler, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dröge, W. Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 47–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martemucci, G.; Costagliola, C.; Mariano, M.; D’Andrea, L.; Napolitano, P.; D’Allesandro, A.G. Free radical properties, source and targets, antioxidant consumption and health. Oxygen 2022, 2, 48–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.; Gribble, L.A.; Hamel, M.C.; Wright, J.B.; Moormann, G.; Bachand, M.; Wright, G.; Bachand, G.D. Evaluating changes in growth and pigmentation of Cladosporium cladosporioides and Paecilomyces variotii in response to gamma and ultraviolet irradiation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel-Fernández, E.; Martínez, M.J.; Galán, T.; Pineda, F. Going over Fungal Allergy: Alternaria alternata and Its Allergens. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval-Denis, M.; Gené, J.; Sutton, D.A.; Wiederhold, N.P.; Cano-Lira, J.F.; Guarro, J. New species of Cladosporium associated with human and animal infections. Persoonia 2016, 36, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.G.; Oh, S.H.; Suh, S.B.; Lee, K.H.; Chung, K.Y. A case of chromoblastomycosis with an unusual clinical manifestation caused by Phialophora verrucosa on an unexposed area: Treatment with a combination of amphotericin B and 5-flucytosine. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 152, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellmann, R.; Smuszkiewicz, P. Pharmacokinetics of antifungal drugs: Practical implications for optimized treatment of patients. Infection 2017, 45, 737–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buszman, E.; Pilawa, B.; Zdybel, M.; Wilczyński, S.; Gondzik, A.; Witoszyńska, T.; Wilczok, T. EPR examination of Zn2+ and Cu2+ binding by pigmented soil fungi Cladosporium cladosporioides. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 363, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binns, F.; Chapman, R.F.; Robson, N.C.; Swan, G.A.; Waggott, A. Studies related to the chemistry of melanins. J. Chem. Soc. 1970, 8, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Tyrawska, D.; Bajan, C.; Makarewskaja, Z.; Popowska-Nowak, E.; Sosak-Swiderska, B.; Grochala, K.; Piechoczek, E. Proceedings of the II Conference: Karkonosze Ecological Studies; Dziekanów Leśny, Poland, 1994; pp. 233–241. [Google Scholar]
- Buszman, E.; Pilawa, B.; Latocha, M.; Wilczok, T.; Tyrawska-Spychałowa, D.; Bajan, C.; Bijak, A.; Bilińska, B. Spectroscopic studies of melanins isolated from pigmented soil fungi of the Karkonosze mountains. Curr. Top. Biophys. 1998, 22, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Buszman, E.; Pilawa, B.; Witoszyńska, T.; Latocha, M.; Wilczok, T. Effect of Zn2+ and Cu2+ on free radical properties of melanin from Cladosporium cladosporioides. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2003, 24, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilawa, B.; Buszman, E.; Gondzik, A.; Wilczyński, S.; Zdybel, M.; Witoszyńska, T.; Wilczok, T. Effect of pH on paramagnetic centers in Cladosporium cladosporioides. Acta Physica Pol. A 2005, 108, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdybel, M.; Pilawa, B.; Buszman, E.; Witoszyńska, T.; Cieśla, H. EPR studies of Cladosporium cladosporioides mycelium with flucytosine. Curr. Top. Biophys. 2010, 33, 271–275. [Google Scholar]
- Najder-Kozdrowska, L.; Pilawa, B.; Buszman, E.; Witoszyńska, T. The application of electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy for study of accumulation of metal ions by Cladosporium cladosporioides. Nat. J. 2011, 44, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Buszman, E.; Wiewióra, A.; Andrzejczyk, J.; Wilczok, T. Physicochemical properties of melanin isolated from Cladosporium cladosporioides. Curr. Top. Biophys. 1992, 16, 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Milanovíc, Ž.; Dimíc, D.; Avdovíc, E.H.; Simijonovíc, D.M.; Nakarada, Ð.; Jakovljevíc, V.; Vojinovíc, R.; Markovic, Z.S. Mechanism of Antiradical Activity of Coumarin-Trihydroxybenzohydrazide Derivatives: A Comprehensive Kinetic DFT Study. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jácimovíc, S.; Kiprovski, B.; Ristivojevíc, P.; Dimíc, D.; Nakarada, Ð.; Dojcinovíc, B.; Sikora, V.; Teslíc, N.; Pantelíc, N.Ð. Chemical Composition, Antioxidant Potential, and Nutritional Evaluation of Cultivated Sorghum Grains: A Combined Experimental, Theoretical, and Multivariate Analysis. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadlo, A.; Mokrzyński, K.; Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K.; Sarna, T. The influence of iron on selected properties of synthetic pheomelanin. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 78, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokrzyński, K.; Sarna, M.; Sarna, T. Photoreactivity and phototoxicity of experimentally photodegraded hair melanosomes from individuals of different skin phototypes. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2023, 243, 112704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehbi, M.; Harkemanne, E.; Mignion, L.; Joudiou, N.; Tromme, I.; Baurain, J.F.; Gallez, B. Towards Characterization of Skin Melanoma in the Clinic by Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) Spectroscopy and Imaging of Melanin. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2024, 26, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meredith, P.; Sarna, T. The physical and chemical properties of eumelanin. Pigment Cell Res. 2006, 19, 572–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godechal, Q.; Gallez, B. The contribution of electron paramagnetic resonance to melanoma research. J. Skin Cancer 2011, 2011, 273280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajanyan, A.E.; Hambardzumyan, A.A.; Hovsepyan, A.S.; Asaturian, R.A.; Vardanyan, A.A.; Saghiyan, A.A. Isolation, purification and physicochemical characterization of water-soluble Bacillus thuringiensis melanin. Pigment Cell Res. 2005, 18, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, G.R.; Eaton, S.S.; Salikhov, K.M. (Eds.) Foundations of Modern EPR; World Scientific: Singapore, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wertz, J.E.; Bolton, J.R. Electron Spin Resonance: Elementary Theory and Practical Applications; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Więckowski, A.B.; Wojtowicz, W.; Śliwa-Nieściór, J. Temperature dependence of the EPR linewidth of ultramarine blue. Magn. Reson. Chem. 1999, 37, S150–S153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalak, S.; Jankowska, A.; Zeidler, S.; Więckowski, A.B. Sulfur radicals embedded in various cages of ultramarine analogs prepared from zeolites. J. Sol. State. Chem. 2007, 180, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najder-Kozdrowska, L.; Więckowski, A.B. Linear anamorphosis of the electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) lineshape of ultramarine blue. In Ethics and Humanism in European Science, Environment and Culture; Jaskuła, M., Buszewski, B., Sękowski, A., Zagórski, Z., Eds.; Societas Humboldtiana Polonorum: Kraków, Poland; Lublin, Poland; Toruń, Poland, 2011; Volume 16, pp. 321–325. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, J.R. An Introduction to Error Analysis: The Study of Uncertainties in Physical Measurements, 3rd ed.; University Science Books: Herndon, VA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
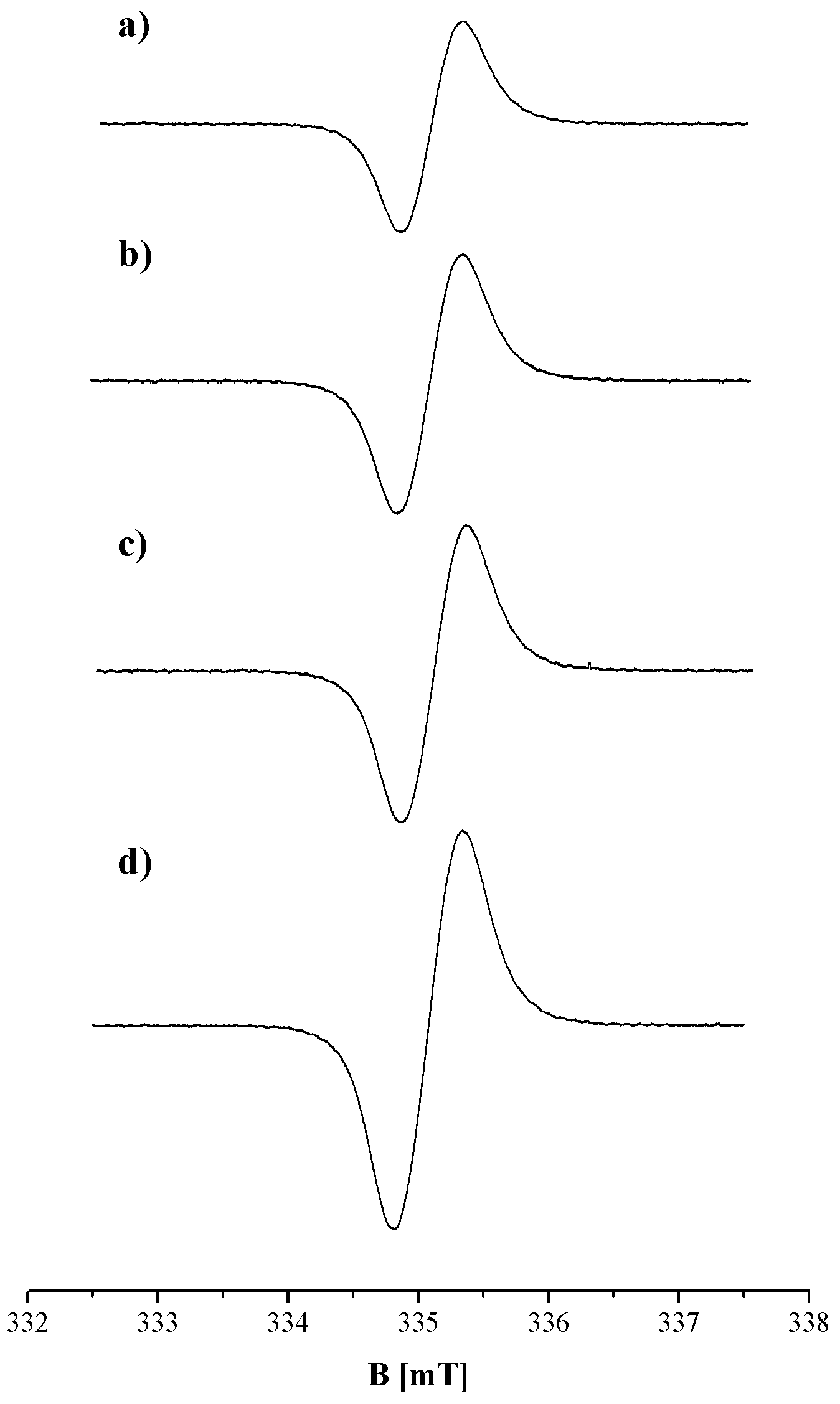
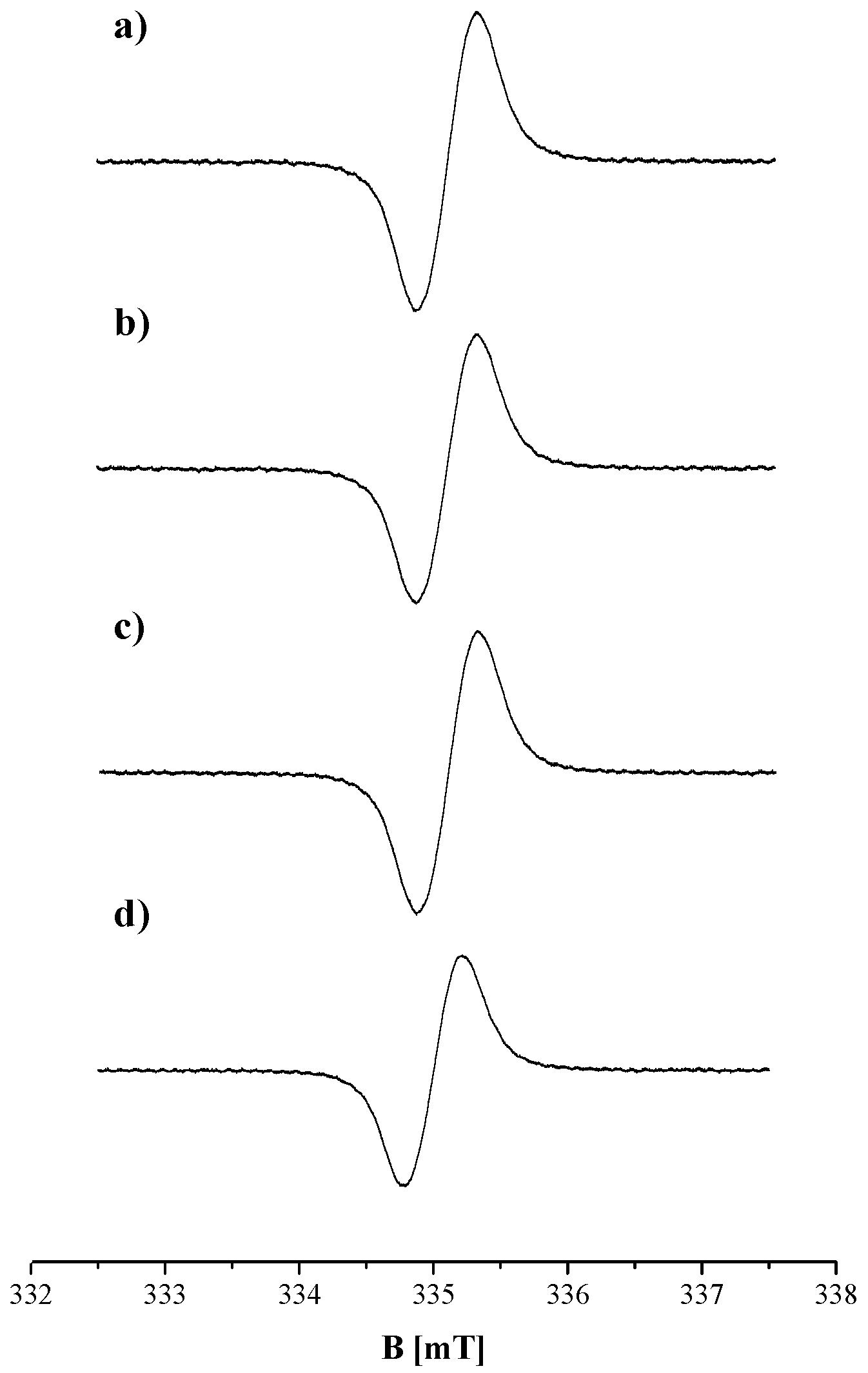

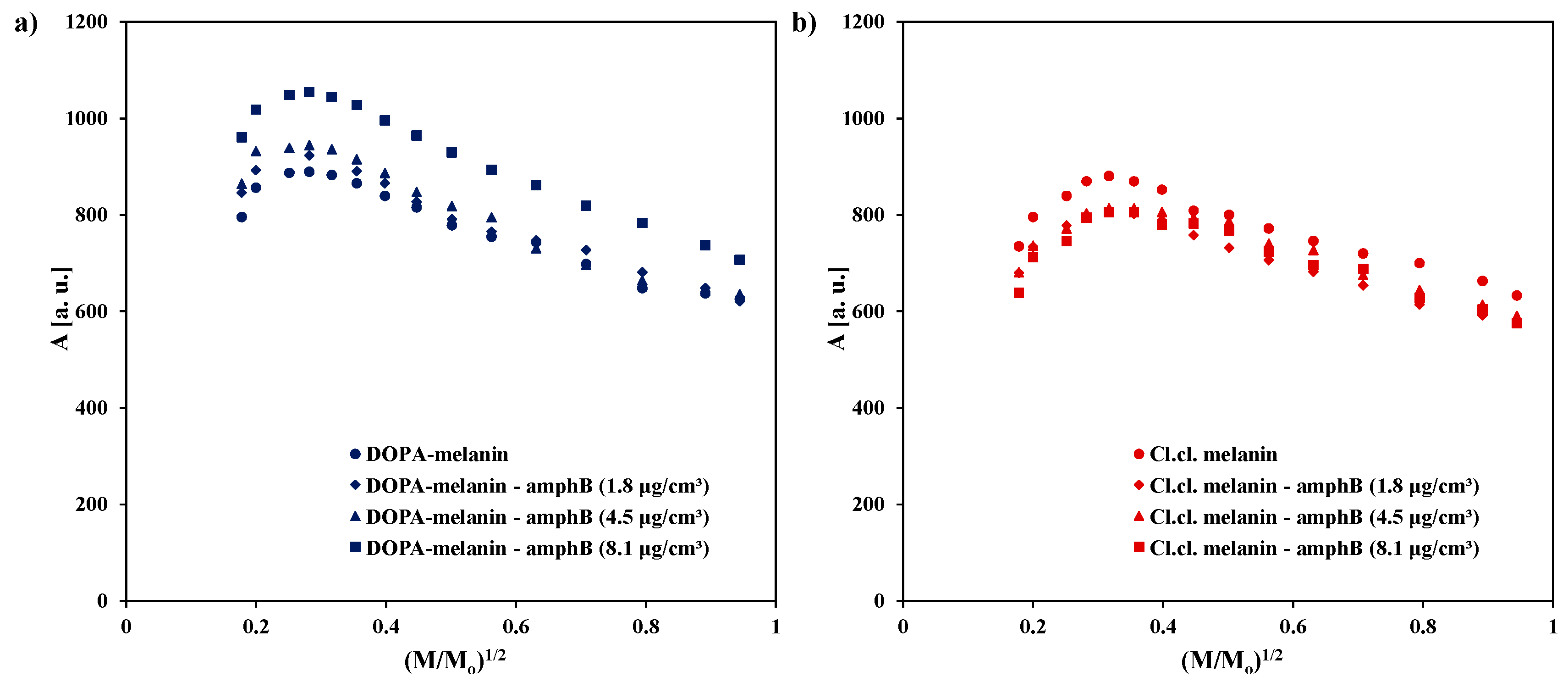
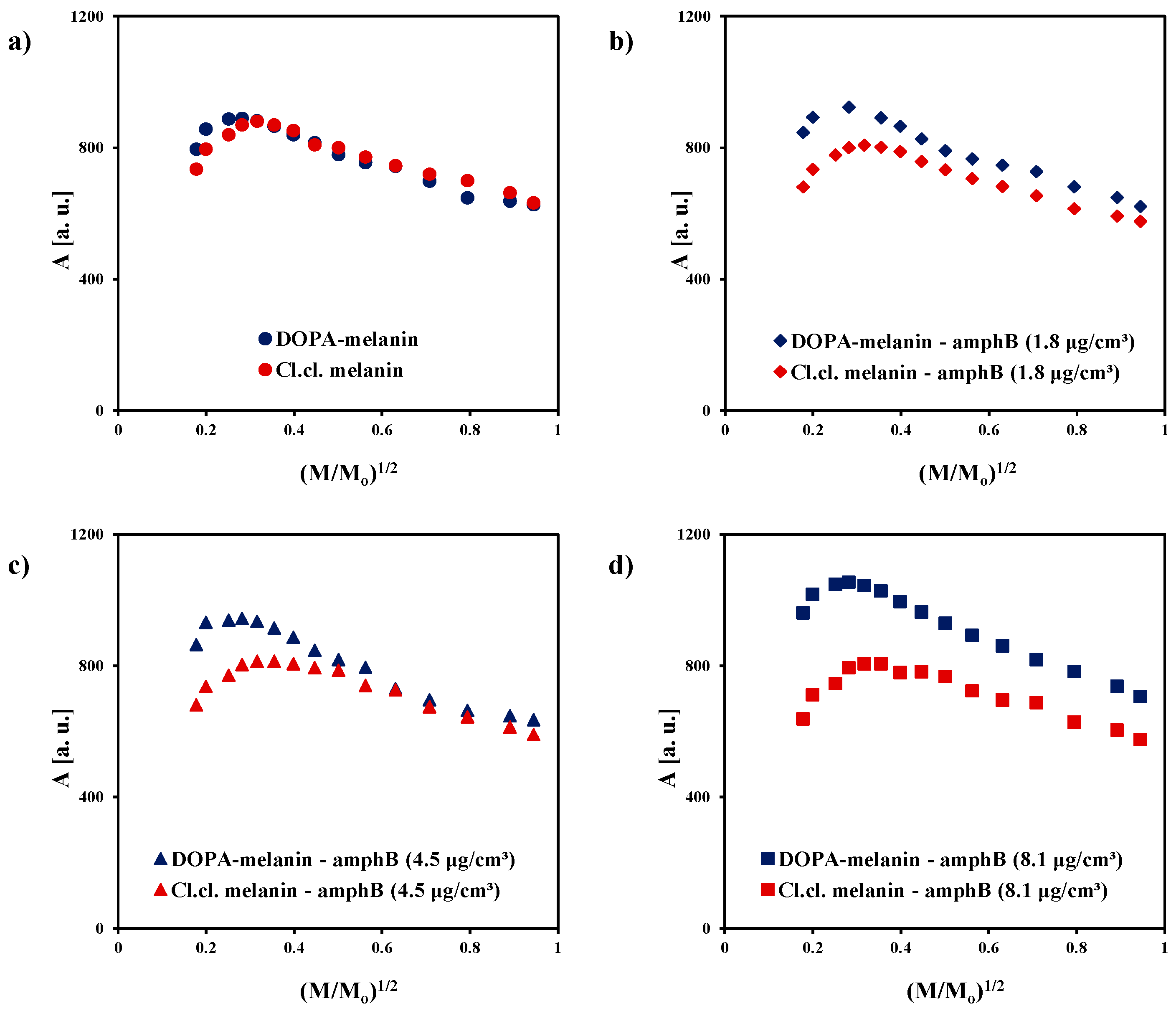
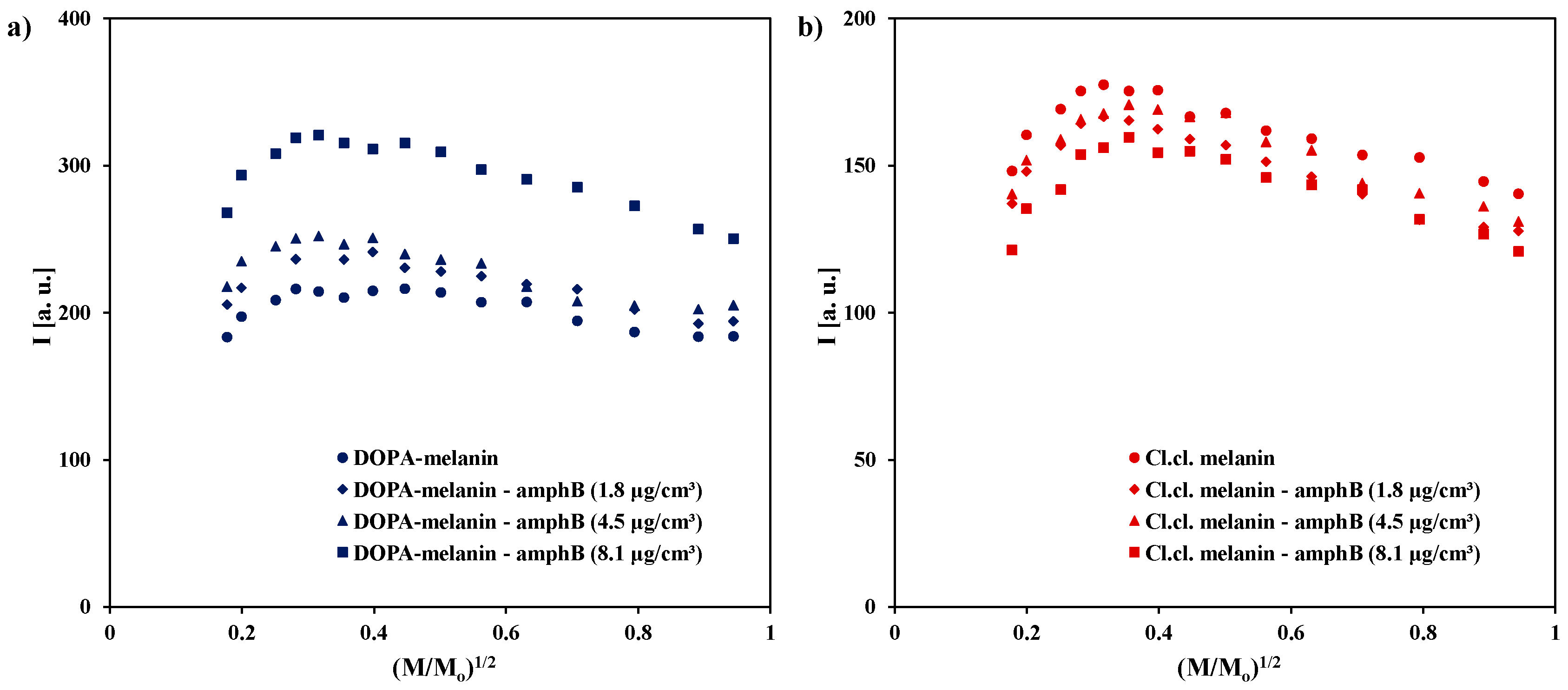
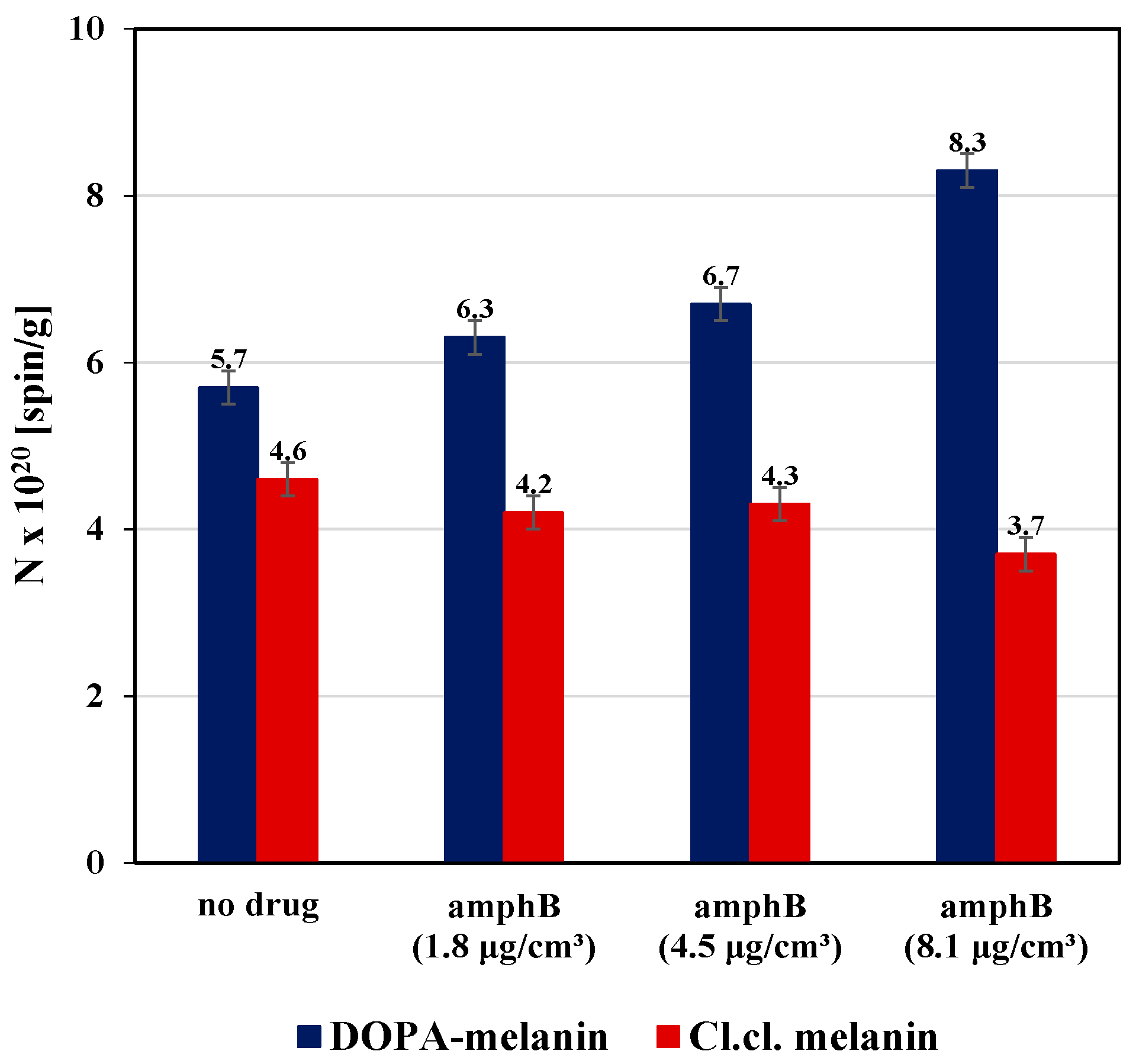
| Sample | g ± 0.0002 | ΔBpp [mT] ± 0.02 | A [a. u.] ± 0.01 | I [a. u.] ± 0.02 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOPA-melanin | 2.0039 | 0.48 | 795.65 | 183.32 |
| DOPA-melanin–amphB (1.8 μg/cm3) | 2.0039 | 0.49 | 846.15 | 205.66 |
| DOPA-melanin–amphB (4.5 μg/cm3) | 2.0039 | 0.50 | 864.41 | 217.83 |
| DOPA-melanin–amphB (8.1 μg/cm3) | 2.0040 | 0.53 | 961.11 | 267.94 |
| Sample | g ± 0.0002 | ΔBpp [mT] ± 0.02 | A [a. u.] ± 0.01 | I [a. u.] ± 0.02 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cl.cl. melanin | 2.0039 | 0.45 | 734.78 | 148.13 |
| Cl.cl. melanin–amphB (1.8 μg/cm3) | 2.0040 | 0.45 | 680.00 | 137.09 |
| Cl.cl. melanin–amphB (4.5 μg/cm3) | 2.0040 | 0.45 | 680.77 | 140.32 |
| Cl.cl. melanin–amphB (8.1 μg/cm3) | 2.0038 | 0.44 | 638.00 | 121.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zdybel, M.; Pilawa, B.; Witoszyńska, T.; Wrześniok, D. Changes in Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Parameters Caused by Addition of Amphotericin B to Cladosporium cladosporioides Melanin and DOPA-Melanin—Free Radical Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9571. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179571
Zdybel M, Pilawa B, Witoszyńska T, Wrześniok D. Changes in Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Parameters Caused by Addition of Amphotericin B to Cladosporium cladosporioides Melanin and DOPA-Melanin—Free Radical Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(17):9571. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179571
Chicago/Turabian StyleZdybel, Magdalena, Barbara Pilawa, Teresa Witoszyńska, and Dorota Wrześniok. 2024. "Changes in Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Parameters Caused by Addition of Amphotericin B to Cladosporium cladosporioides Melanin and DOPA-Melanin—Free Radical Studies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 17: 9571. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179571
APA StyleZdybel, M., Pilawa, B., Witoszyńska, T., & Wrześniok, D. (2024). Changes in Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Parameters Caused by Addition of Amphotericin B to Cladosporium cladosporioides Melanin and DOPA-Melanin—Free Radical Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(17), 9571. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179571






