The Immunosuppressive Receptor CD32b Regulation of Macrophage Polarization and Its Implications in Tumor Progression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. CD32b Expression in Macrophages M1 and M2
2.2. CD32b Expression in Macrophages Transfected with CD32b siRNA
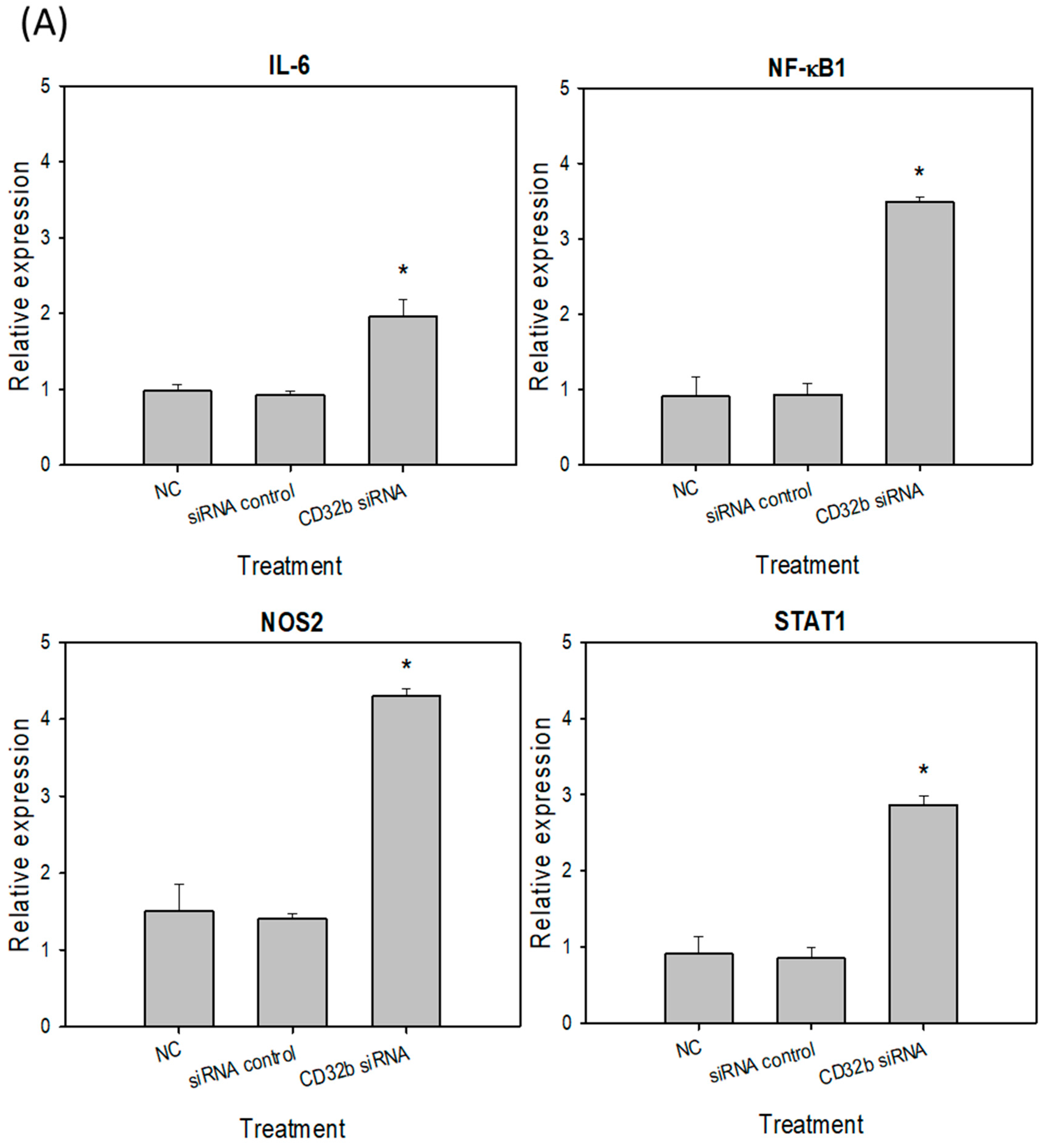
2.3. M1 Marker Expression in Macrophage Raw264.7 Cells and Primary Macrophages from the Mouse Spleens Transfected with CD32b siRNA
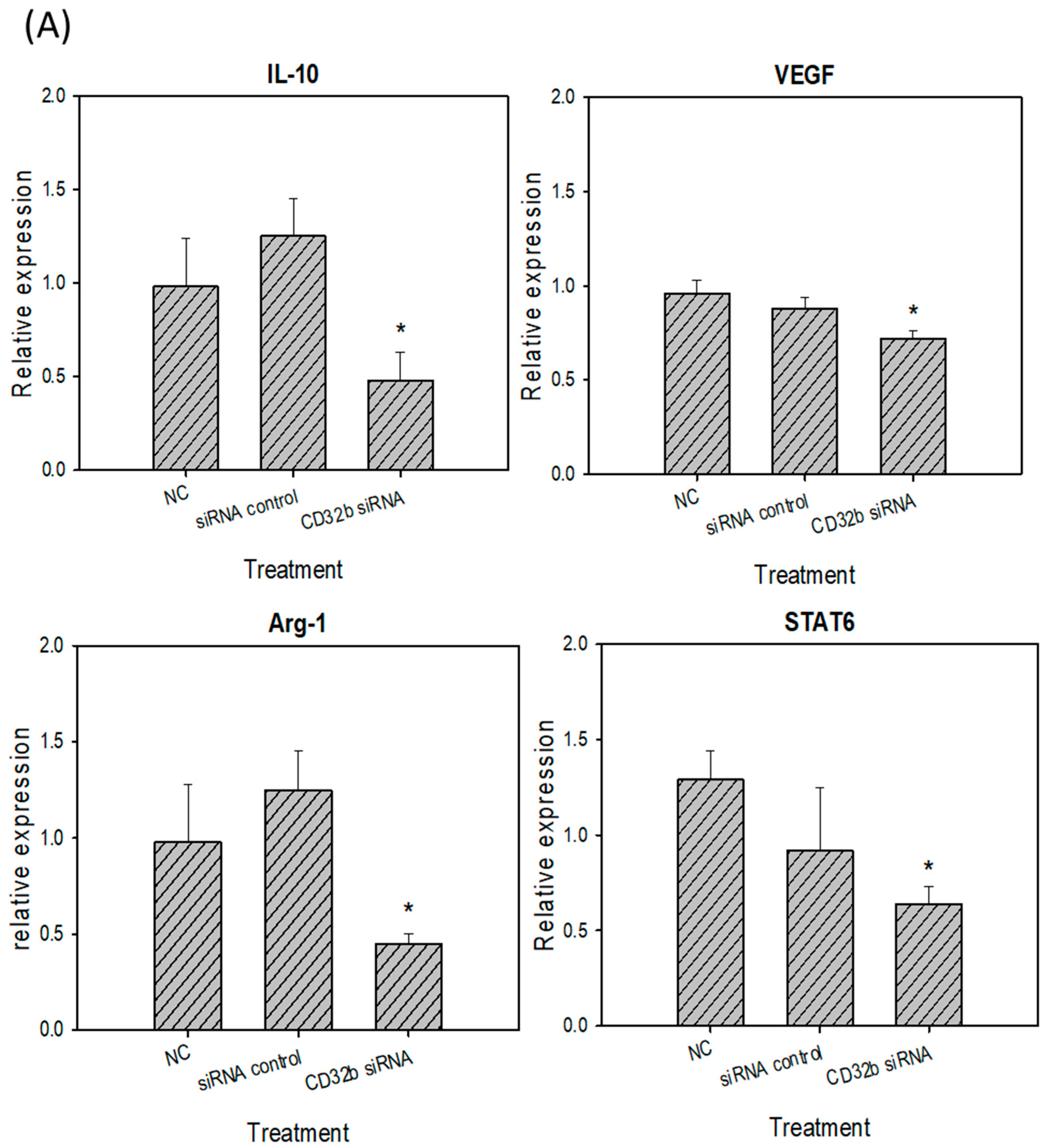
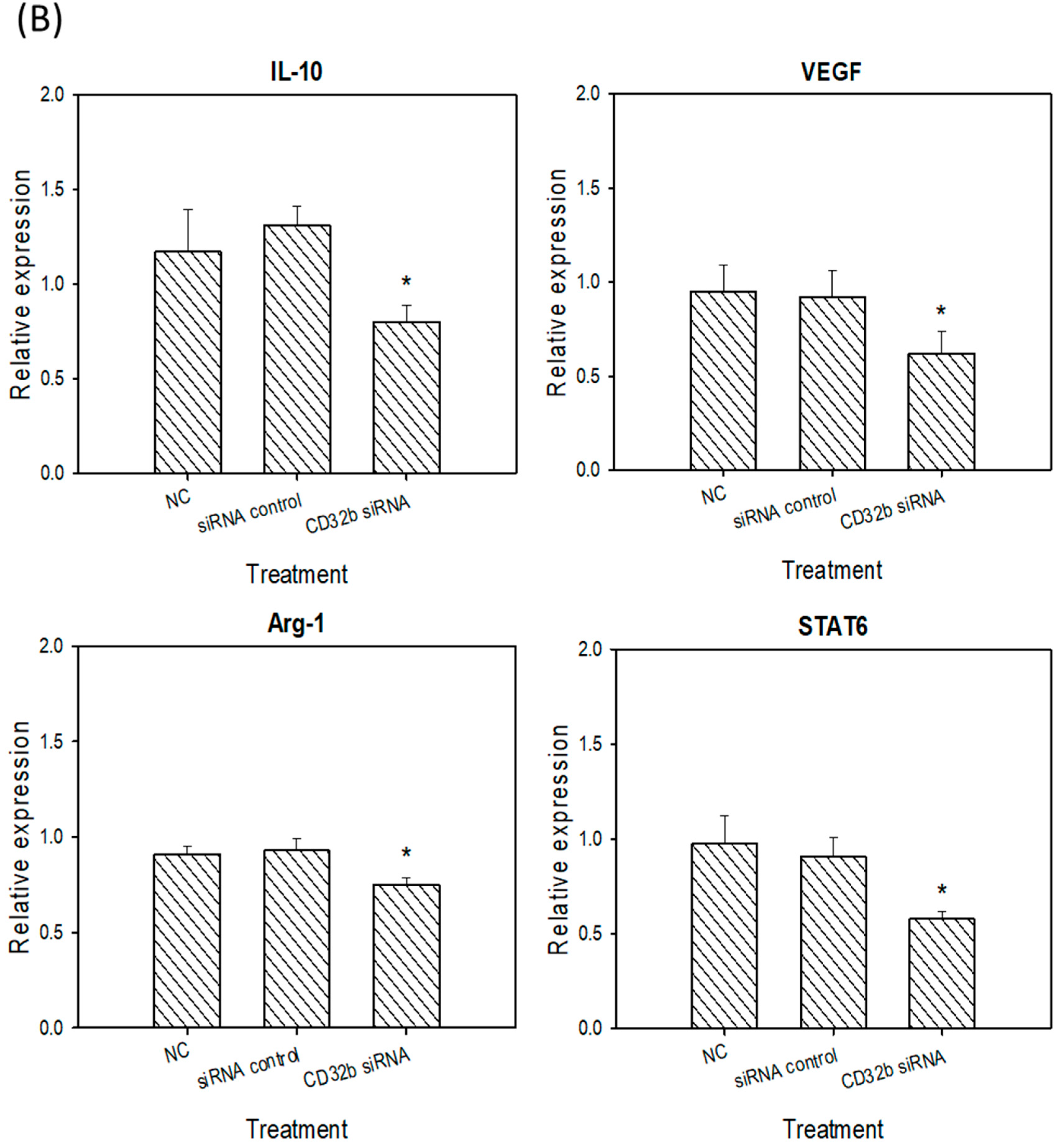
2.4. M2 Marker Expression in Macrophage Raw264.7 Cells and Primary Macrophages from the Mouse Spleens Transfected with CD32b siRNA
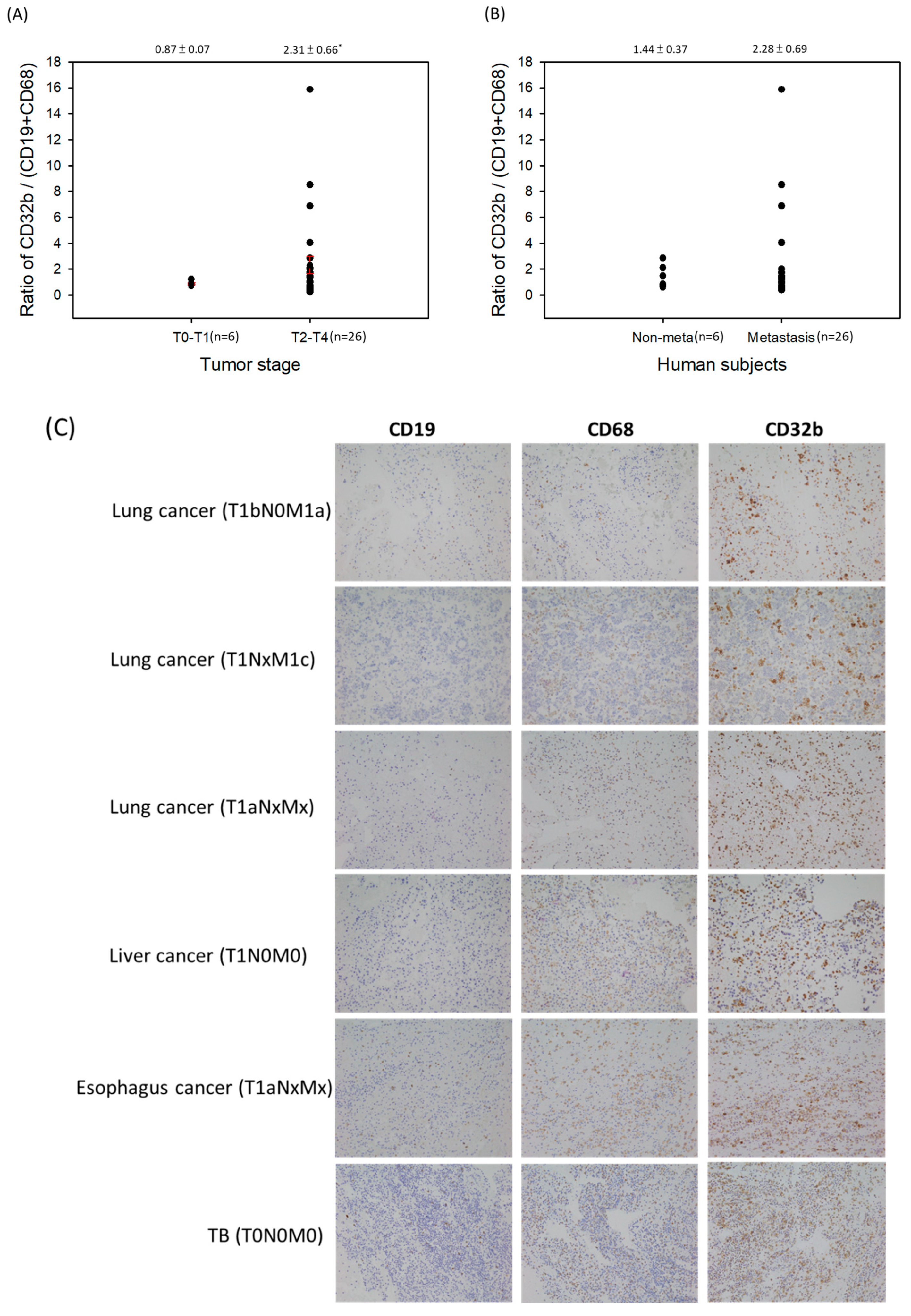
2.5. CD32b Expression in Human Subjects
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells and Animals
4.2. Reverse-Transcription (RT)-qPCR Assay
4.3. Nitric Oxide (NO) Detection
4.4. Surface Marker Assay of CD32b
4.5. CD32b siRNA Transfection and RT-qPCR Assay of M1/M2 Markers
4.6. Human Subjects and Cytopathological Section Assay
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, P.J.; Allen, J.E.; Biswas, S.K.; Fisher, E.A.; Gilroy, D.W.; Goerdt, S.; Gordon, S.; Hamilton, J.A.; Ivashkiv, L.B.; Lawrence, T.; et al. Macrophage activation and polarization: Nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity 2014, 41, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Yuan, H.Q.; Hao, Y.M.; Ren, Z.; Qu, S.L.; Liu, L.S.; Wei, D.H.; Tang, Z.H.; Zhang, J.F.; Jiang, Z.S. Macrophage polarization in atherosclerosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 501, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sioud, M. Tumor-associated macrophage subsets: Shaping polarization and targeting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stöger, J.L.; Gijbels, M.J.; van der Velden, S.; Manca, M.; van der Loos, C.M.; Biessen, E.A.; Daemen, M.J.; Lutgens, E.; de Winther, M.P. Distribution of macrophage polarization markers in human atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2012, 225, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutilier, A.J.; Elsawa, S.F. Macrophage polarization states in the tumor microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolland, S.; Ravetch, J.V. Spontaneous autoimmune disease in Fc(gamma)RIIB- deficient mice results from strain-specific epistasis. Immunity 2000, 13, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svačina, M.K.R.; Meißner, A.; Schweitzer, F.; Ladwig, A.; Pitarokoili, K.; Kofler, D.M.; Sprenger-Svačina, A.; Schneider, C.; Kohle, F.; Klein, I.; et al. Immunomodulatory effects of intravenous and subcutaneous immunoglobulin in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: An observational study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2024, 31, e16079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.T.; Tsuchiya, N.; Kyogoku, C.; Ohashi, J.; Qian, Y.P.; Xu, S.B.; Mao, C.Z.; Chu, J.Y.; Tokunaga, K. Association of Fcgamma receptor IIb polymorphism with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in Chinese: A common susceptibility gene in the Asian populations. Tissue Antigens 2004, 63, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondee, T.; Jaroonwitchawan, T.; Pisitkun, T.; Gillen, J.; Nita-Lazar, A.; Leelahavanichkul, A.; Somparn, P. Decreased protein kinase C-β type II associated with the prominent endotoxin exhaustion in the macrophage of FcGRIIb-/- lupus prone mice is revealed by phosphoproteomic analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silwal, P.; Lee, M.N.; Lee, C.J.; Hong, J.H.; Namgung, U.; Lee, Z.W.; Kim, J.; Lim, K.; Kweon, G.R.; Park, J.I.; et al. Dexamethasone induces FcgRIIb expression in RBL-2H3 cells. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 16, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavenhagen, J.B.; Gorlatov, S.; Tuaillon, N.; Rankin, C.T.; Li, H.; Burke, S.; Huang, L.; Vijh, S.; Johnson, S.; Bonvini, E.; et al. Fc optimization of therapeutic antibodies enhances their ability to kill tumor cells in vitro and controls tumor expansion in vivo via low-affinity activating Fcgamma receptors. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 8882–8890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rankin, C.T.; Veri, M.C.; Gorlatov, S.; Tuaillon, N.; Burke, S.; Huang, L.; Inzunza, H.D.; Li, H.; Thomas, S.; Johnson, S.; et al. CD32B, the human inhibitory Fc- gamma receptor IIB, as a target for monoclonal antibody therapy of B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2006, 108, 2384–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.H.; Vaughan, A.T.; Ashton-Key, M.; Williams, E.L.; Dixon, S.V.; Chan, H.T.; Beers, S.A.; French, R.R.; Cox, K.L.; Davies, A.J.; et al. Fc gamma receptor IIb on target B cells promotes rituximab internalization and reduces clinical efficacy. Blood 2011, 118, 2530–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocaña-Guzman, R.; Vázquez-Bolaños, L.; Sada-Ovalle, I. Receptors that inhibit macrophage activation: Mechanisms and signals of regulation and tolerance. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 8695157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.C.; Hsiao, Y.Y.; Ku, K.L.; Liao, H.F.; Chao, W.C. Mahonia oiwakensis extract and its bioactive compounds exert anti-inflammatory activities and VEGF production through M2-macrophagic polarization and STAT6 activation. J. Med. Food 2018, 21, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bournazos, S.; Gupta, A.; Ravetch, J.V. The role of IgG Fc receptors in antibody-dependent enhancement. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmerjahn, F.; Ravetch, J.V. Fcgamma receptors as regulators of immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmerjahn, F.; Ravetch, J.V. Fcgamma receptors: Old friends and new family members. Immunity 2006, 24, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, O.A.; Gonzalez-Hinojosa, M.D.R.; Arakawa-Hoyt, J.S.; Millan, A.J.; Gotthardt, D.; Nabekura, T.; Lanier, L.L. The CD16 and CD32b Fc-gamma receptors regulate antibody-mediated responses in mouse natural killer cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2023, 113, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musolino, A.; Gradishar, W.J.; Rugo, H.S.; Nordstrom, J.L.; Rock, E.P.; Arnaldez, F.; Pegram, M.D. Role of Fcγ receptors in HER2-targeted breast cancer therapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e003171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.L.; Tutt, A.L.; Beers, S.A.; French, R.R.; Chan, C.H.; Cox, K.L.; Roghanian, A.; Penfold, C.A.; Butts, C.L.; Boross, P.; et al. Immunotherapy targeting inhibitory Fcγ receptor IIB (CD32b) in the mouse is limited by monoclonal antibody consumption and receptor internalization. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4130–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidarsson, G.; Stemerding, A.M.; Stapleton, N.M.; Spliethoff, S.E.; Janssen, H.; Rebers, F.E.; de Haas, M.; van de Winkele, J.G. FcRn: An IgG receptor on phagocytes with a novel role in phagocytosis. Blood 2006, 108, 3573–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spatuzza, C.; Postiglione, L.; Covelli, B.; Ricciardone, M.; Benvenuti, C.; Mondola, P.; Belfiore, A. Effects of berberine and red yeast on proinflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of human subjects. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohmori, Y.; Hamilton, T.A. IL-4-induced STAT6 suppresses IFN-gamma-stimulated STAT1-dependenttranscription in mouse macrophages. J. Immunol. 1997, 159, 5474–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liang, Y.; Wang, L. Shaping polarization of tumor-associated macrophages in cancer immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 888713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.S.; Shiau, A.L.; Su, B.H.; Hsu, T.S.; Wang, C.T.; Su, Y.C.; Tsai, M.S.; Feng, Y.H.; Tseng, Y.L.; Yen, Y.T.; et al. Oct4 promotes M2 macrophage polarization through upregulation of macrophage colony-stimulating factor in lung cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Kang, K.Y.; Kim, Y.; Jung, H.; Rim, Y.A.; Park, N.; Kim, J.; Jung, S.M.; Park, S.H.; Ju, J.H. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate collagen antibody-induced autoimmune arthritis by inducing expression of FCGIIB receptors. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015, 16, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roghanian, A.; Cragg, M.S.; Frendéus, B. Resistance is futile: Targeting the inhibitory FcγRIIB (CD32B) to maximize immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology 2015, 5, e1069939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasahara, Y.; Shirota, H.; Umegaki, S.; Ishioka, C. Contribution of Fcγ receptor IIB to creating a suppressive tumor microenvironment in a mouse model. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 1769–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Mi, Y.; Guan, B.; Zheng, B.; Wei, P.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, S.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomal miR-934 induces macrophage M2 polarization to promote liver metastasis of colorectal cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.X.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhou, W.J.; Li, D.J. Regulatory T cells induce polarization of pro-repair macrophages by secreting sFGL2 into the endometriotic milieu. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modak, M.; Mattes, A.K.; Reiss, D.; Skronska-Wasek, W.; Langlois, R.; Sabarth, N.; Konopitzky, R.; Ramirez, F.; Lehr, K.; Mayr, T.; et al. CD206+ tumor-associated macrophages cross-present tumor antigen and drive antitumor immunity. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e155022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Genes | ID | Primer Sequences |
|---|---|---|
| STAT1 | U06924.1 | 5′-TTCAGCAGCTGGACTCCAAG-3′ 3′-CGAGACATCATAGGCAGCGT-5′ |
| NF-κB1 | NP_032715.2 | 5′-AAGTGATCCAGGCAGCCTTC-3′ 3′-CTGTCACAGACGCTGTCACT-5′ |
| NOS2 | NM_010927.3 | 5′-CTATGGCCGCTTTGATGTGC-3′ 3′-TTGGGATGCTCCATGGTCAC-5′ |
| IL-6 | NM_031168.1 | 5′-GCCTTCTTGGGACTGATGCT-3′ 3′-AGCCTCCGACTTGTGAAGTG-5′ |
| STAT6 | NM_009284.2 | 5′-AGATGGGACCTTCCTCCTCC-3′ 3′-CTGAGCAAGATCCCGGATCC-5′ |
| Arg-1 | NM_007482.3 | 5′-TACATTGGCTTGCGAGACGT-3′ 3′-ATCACCTTGCCAATCCCCAG-5′ |
| IL-10 | NM_010548.2 | 5′-CAGAGAAGCATGGCCCAGAA-3′ 3′-GCTCCACTGCCTTGCTCTTA-5′ |
| VEGFa | AAH61468.1 | 5′-AACGATGAAGCCCTGGAGTG-3′ 3′-CTGCTGTGCTGTAGGAAGCT-5′ |
| Tumor Stage (n) | T0–1 (6) | T2–T4 (26) |
|---|---|---|
| Age range (yr) | 52–89 | 46–92 |
| Pathological site (n) | Lung (3) | Lung (22) |
| Liver (1) | Esophagus (1) | |
| Esophagus (1) | Ovarian (3) | |
| TB (1) | ||
| Gender (F, M) | F (2) | F (13) |
| M (4) | M (13) | |
| Non-Metastasis and metastasis of Tumors (n) | Non-metastasis (6) | Metastasis (26) |
| Age range (yr) | 56–83 | 46–92 |
| Pathological site (n) | Lung (4) | Lung (21) |
| Esophagus (1) | Esophagus (1) | |
| TB (1) | Ovarian (3) | |
| Liver (1) | ||
| Gender (F, M) | F (1) | F (14) |
| M (5) | M (12) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chuang, H.-J.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Chung, Y.-D.; Huang, E.; Huang, C.Y.; Lung, J.; Chen, C.-Y.; Liao, H.-F. The Immunosuppressive Receptor CD32b Regulation of Macrophage Polarization and Its Implications in Tumor Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179737
Chuang H-J, Chen Y-Y, Chung Y-D, Huang E, Huang CY, Lung J, Chen C-Y, Liao H-F. The Immunosuppressive Receptor CD32b Regulation of Macrophage Polarization and Its Implications in Tumor Progression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(17):9737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179737
Chicago/Turabian StyleChuang, Hong-Jing, Ying-Yin Chen, Yi-Da Chung, Evelyn Huang, Cadence Yoshang Huang, Jrhau Lung, Chung-Yu Chen, and Hui-Fen Liao. 2024. "The Immunosuppressive Receptor CD32b Regulation of Macrophage Polarization and Its Implications in Tumor Progression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 17: 9737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179737
APA StyleChuang, H.-J., Chen, Y.-Y., Chung, Y.-D., Huang, E., Huang, C. Y., Lung, J., Chen, C.-Y., & Liao, H.-F. (2024). The Immunosuppressive Receptor CD32b Regulation of Macrophage Polarization and Its Implications in Tumor Progression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(17), 9737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179737







