New Insights and Future Perspectives of APRIL in IgA Nephropathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
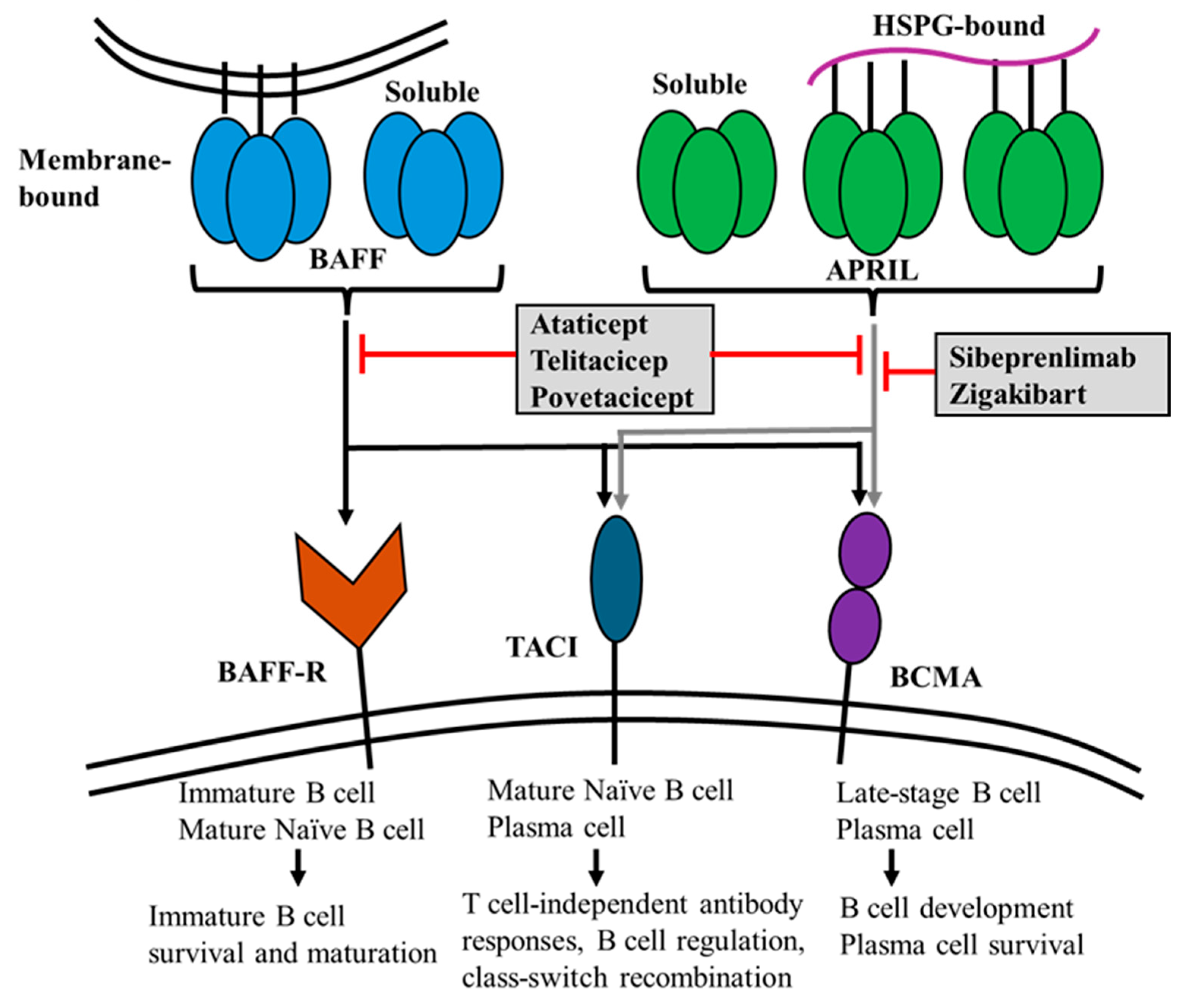
2. Biology and Physiological Functions of APRIL
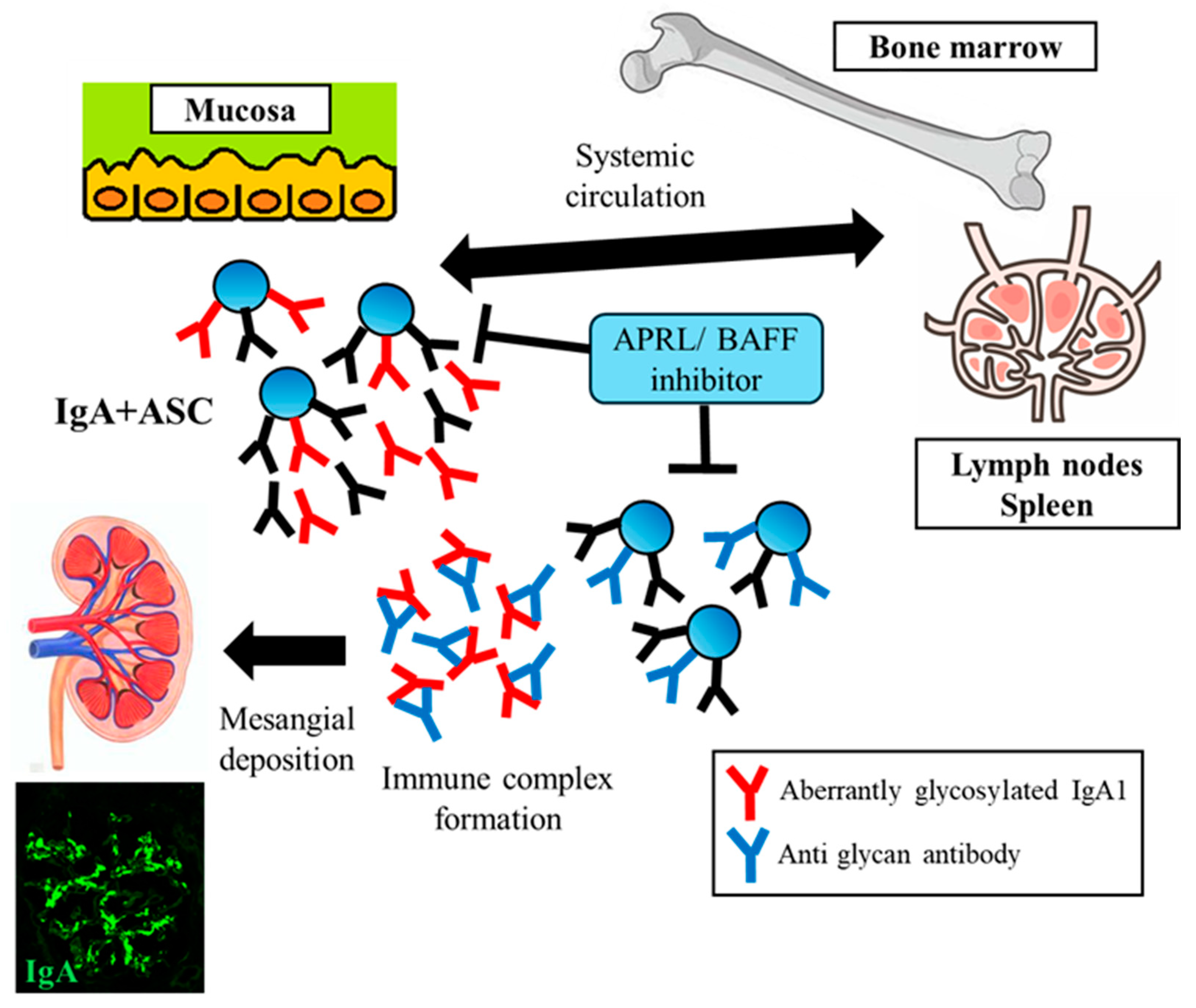
3. The Role of APRIL in IgAN
4. Current and Perspective Therapeutic Strategies Focusing on APRIL-Targeted Therapy
4.1. Systemic Corticosteroid Therapy and Targeting Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissues (GALTs)
4.2. B-Cell and Plasma Cell-Targeted Treatment
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGrogan, A.; Franssen, C.F.M.; de Vries, C.S. The incidence of primary glomerulonephritis worldwide: A systematic review of the literature. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 26, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastings, M.C.; Bursac, Z.; Julian, B.A.; Baca, E.V.; Featherston, J.; Woodford, S.Y.; Bailey, L.; Wyatt, R.J. Life Expectancy for Patients From the Southeastern United States With IgA Nephropathy. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 3, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyama, T.; Tanaka, K.; Iwasaki, C.; Oshima, Y.; Ochi, A.; Kataoka, H.; Itabashi, M.; Takei, T.; Uchida, K.; Nitta, K. Prognosis in IgA Nephropathy: 30-Year Analysis of 1,012 Patients at a Single Center in Japan. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Kiryluk, K.; Novak, J.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Herr, A.B.; Renfrow, M.B.; Wyatt, R.J.; Scolari, F.; Mestecky, J.; Gharavi, A.G.; et al. The Pathophysiology of IgA Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Monteiro, R.C.; Coppo, R.; Suzuki, H. The Phenotypic Difference of IgA Nephropathy and its Race/Gender-dependent Molecular Mechanisms. Kidney360 2021, 2, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, K.; Matsuzaki, K.; Yasuda, T.; Nishikawa, M.; Yasuda, Y.; Koike, K.; Maruyama, S.; Yokoo, T.; Matsuo, S.; Kawamura, T.; et al. Association Between Tonsillectomy and Outcomes in Patients With Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e194772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, K.; Kawamura, T.; Hirano, K.; Nishikawa, M.; Shimizu, A.; Joh, K.; Katafuchi, R.; Hashiguchi, A.; Yano, Y.; Matsuzaki, K.; et al. Clinicopathological prognostic stratification for proteinuria and kidney survival in IgA nephropathy: A Japanese prospective cohort study. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 17, sfad294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovin, B.H.; Adler, S.G.; Barratt, J.; Bridoux, F.; Burdge, K.A.; Chan, T.M.; Cook, H.T.; Fervenza, F.C.; Gibson, K.L.; Glassock, R.J.; et al. KDIGO 2021 Clinical practice guideline for the management of glomerular diseases. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, S1–S276. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, J.; Wong, M.G.; Hladunewich, M.A.; Jha, V.; Hooi, L.S.; Monaghan, H.; Zhao, M.; Barbour, S.; Jardine, M.J.; Reich, H.N.; et al. Effect of oral methylprednisolone on decline in kidney function or kidney failure in patients with IgA nephropathy: The TESTING randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2022, 327, 1888–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-M.; Lv, J.-C.; Wong, M.G.; Zhang, H.; Perkovic, V. Glucocorticoids for IgA nephropathy-pro. Kidney Int. 2023, 103, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.K.; Barratt, J. Further Evidence for the Mucosal Origin of Pathogenic IgA in IgA Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 33, 873–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knoppova, B.; Reily, C.; Maillard, N.; Rizk, D.V.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Mestecky, J.; Raska, M.; Renfrow, M.B.; Julian, B.A.; Novak, J. The Origin and Activities of IgA1-Containing Immune Complexes in IgA Nephropathy. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gesualdo, L.; Di Leo, V.; Coppo, R. The mucosal immune system and IgA nephropathy. Semin. Immunopathol. 2021, 43, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekaran, A.; Julian, B.A.; Rizk, D.V. IgA Nephropathy: An Interesting Autoimmune Kidney Disease. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 361, 176–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, D.; Hase, H.; Kanno, Y.; Kojima, H.; Okumura, K.; Kobata, T. TACI regulates IgA production by APRIL in collaboration with HSPG. Blood 2006, 109, 2961–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Santamaria, R.; Xu, W.; Cols, M.; Chen, K.; Puga, I.; Shan, M.; Xiong, H.; Bussel, J.B.; Chiu, A.; et al. The transmembrane activator TACI triggers immunoglobulin class switching by activating B cells through the adaptor MyD88. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belnoue, E.; Pihlgren, M.; McGaha, T.L.; Tougne, C.; Rochat, A.-F.; Bossen, C.; Schneider, P.; Huard, B.; Lambert, P.-H.; Siegrist, C.-A. APRIL is critical for plasmablast survival in the bone marrow and poorly expressed by early-life bone marrow stromal cells. Blood 2008, 111, 2755–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baert, L.; Manfroi, B.; Casez, O.; Sturm, N.; Huard, B. The role of APRIL-A proliferation inducing ligand-In autoimmune diseases and expectations from its targeting. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 95, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, C.; Cornuel, J.-F.; Billard, C.; Tang, R.; Rouillard, D.; Stenou, V.; Defrance, T.; Ajchenbaum-Cymbalista, F.; Simonin, P.-Y.; Feldblum, S.; et al. Involvement of BAFF and APRIL in the resistance to apoptosis of B-CLL through an autocrine pathway. Blood 2004, 103, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, A.; Xu, W.; He, B.; Dillon, S.R.; Gross, J.A.; Sievers, E.; Qiao, X.; Santini, P.; Hyjek, E.; Lee, J.-W.; et al. Hodgkin lymphoma cells express TACI and BCMA receptors and generate survival and proliferation signals in response to BAFF and APRIL. Blood 2006, 109, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardenberg, G.; Planelles, L.; Schwarte, C.M.; van Bostelen, L.; Le Huong, T.; Hahne, M.; Medema, J.P. Specific TLR ligands regulate APRIL secretion by dendritic cells in a PKR-dependent manner. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 2900–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, V.T.; Fröhlich, A.; Steinhauser, G.; Scheel, T.; Roch, T.; Fillatreau, S.; Lee, J.J.; Löhning, M.; Berek, C. Eosinophils are required for the maintenance of plasma cells in the bone marrow. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthes, T.; Dunand-Sauthier, I.; Santiago-Raber, M.-L.; Krause, K.-H.; Donze, O.; Passweg, J.; McKee, T.; Huard, B. Production of the plasma-cell survival factor a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL) peaks in myeloid precursor cells from human bone marrow. Blood 2011, 118, 1838–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puga, I.; Cols, M.; Barra, C.M.; He, B.; Cassis, L.; Gentile, M.; Comerma, L.; Chorny, A.; Shan, M.; Xu, W.; et al. B cell–helper neutrophils stimulate the diversification and production of immunoglobulin in the marginal zone of the spleen. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 13, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Fraga, M.; Fernández, R.; Albar, J.P.; Hahne, M. Biologically active APRIL is secreted following intracellular processing in the Golgi apparatus by furin convertase. Embo Rep. 2001, 2, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maia, S.; Pelletier, M.; Ding, J.; Hsu, Y.-M.; Sallan, S.E.; Rao, S.P.; Nadler, L.M.; Cardoso, A.A. Aberrant Expression of Functional BAFF-System Receptors by Malignant B-Cell Precursors Impacts Leukemia Cell Survival. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossen, C.; Tardivel, A.; Willen, L.; Fletcher, C.A.; Perroud, M.; Beermann, F.; Rolink, A.G.; Scott, M.L.; Mackay, F.; Schneider, P. Mutation of the BAFF furin cleavage site impairs B-cell homeostasis and antibody responses. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 41, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, E.S.; Cachero, T.G.; Qian, F.; Sun, Y.; Wen, D.; Pelletier, M.; Hsu, Y.-M.; Whitty, A. Selectivity of BAFF/BLyS and APRIL for Binding to the TNF Family Receptors BAFFR/BR3 and BCMA. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 1919–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, F.; Schneider, P.; Rennert, P.; Browning, J. BAFF and APRIL: A Tutorial on B Cell Survival. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 21, 231–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castigli, E.; Wilson, S.A.; Scott, S.; Dedeoglu, F.; Xu, S.; Lam, K.-P.; Bram, R.J.; Jabara, H.; Geha, R.S. TACI and BAFF-R mediate isotype switching in B cells. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castigli, E.; Wilson, S.A.; Elkhal, A.; Ozcan, E.; Garibyan, L.; Geha, R.S. Transmembrane activator and calcium modulator and cyclophilin ligand interactor enhances CD40-driven plasma cell differentiation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossen, C.; Cachero, T.G.; Tardivel, A.; Ingold, K.; Willen, L.; Dobles, M.; Scott, M.L.; Maquelin, A.; Belnoue, E.; Siegrist, C.-A.; et al. TACI, unlike BAFF-R, is solely activated by oligomeric BAFF and APRIL to support survival of activated B cells and plasmablasts. Blood 2008, 111, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihalcik, S.A.; Huddleston, P.M., 3rd; Wu, X.; Jelinek, D.F. The structure of the TNFRSF13C promoter enables differential expression of BAFF-R during B cell ontogeny and terminal differentiation. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, L.G.; Sutherland, A.P.R.; Newton, R.; Qian, F.; Cachero, T.G.; Scott, M.L.; Thompson, J.S.; Wheway, J.; Chtanova, T.; Groom, J.; et al. B Cell-Activating Factor Belonging to the TNF Family (BAFF)-R Is the Principal BAFF Receptor Facilitating BAFF Costimulation of Circulating T and B Cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Lu, G.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Guo, N.; Li, W. BAFF is involved in the pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy by activating the TRAF6/NF-κB signaling pathway in glomerular mesangial cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Wang, D.; Ming, H.; Zhang, H.; Yu, X. BAFF promotes proliferation of human mesangial cells through interaction with BAFF-R. BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarting, A.; Relle, M.; Meineck, M.; Föhr, B.; Triantafyllias, K.; Weinmann, A.; Roth, W.; Weinmann-Menke, J. Renal tubular epithelial cell-derived BAFF expression mediates kidney damage and correlates with activity of proliferative lupus nephritis in mouse and men. Lupus 2017, 27, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreaux, J.; Sprynski, A.; Dillon, S.R.; Mahtouk, K.; Jourdan, M.; Ythier, A.; Moine, P.; Robert, N.; Jourdan, E.; Rossi, J.F.; et al. APRIL and TACI interact with syndecan-1 on the surface of multiple myeloma cells to form an essential survival loop. Eur. J. Haematol. 2009, 83, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadanlick, J.E.; Kaileh, M.; Karnell, F.G.; Scholz, J.L.; Miller, J.P.; Quinn, W.J., 3rd; Brezski, R.J.; Treml, L.S.; Jordan, K.A.; Monroe, J.G.; et al. Tonic B cell antigen receptor signals supply an NF-kappaB substrate for prosurvival BLyS signaling. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.-Q.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Low, H.-Q.; Wei, X.; Wang, J.-Q.; Sun, L.-D.; Sim, K.-S.; Li, Y.; Foo, J.-N.; et al. A genome-wide association study in Han Chinese identifies multiple susceptibility loci for IgA nephropathy. Nat. Genet. 2011, 44, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiryluk, K.; Sanchez-Rodriguez, E.; Zhou, X.-J.; Zanoni, F.; Liu, L.; Mladkova, N.; Khan, A.; Marasa, M.; Zhang, J.Y.; Balderes, O.; et al. Genome-wide association analyses define pathogenic signaling pathways and prioritize drug targets for IgA nephropathy. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 1091–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, D.D.; Kujawa, J.; Wilson, C.; Papandile, A.; Poreci, U.; Porfilio, E.A.; Ward, L.; Lawson, M.A.; Macpherson, A.J.; McCoy, K.D.; et al. Mice overexpressing BAFF develop a commensal flora-dependent, IgA-associated nephropathy. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3991–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallustio, F.; Curci, C.; Chaoul, N.; Fontò, G.; Lauriero, G.; Picerno, A.; Divella, C.; Di Leo, V.; De Angelis, M.; Ben Mkaddem, S.; et al. High levels of gut-homing immunoglobulin A + B lymphocytes support the pathogenic role of intestinal mucosal hyperresponsiveness in immunoglobulin A nephropathy patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muto, M.; Manfroi, B.; Suzuki, H.; Joh, K.; Nagai, M.; Wakai, S.; Righini, C.; Maiguma, M.; Izui, S.; Tomino, Y.; et al. Toll-Like Receptor 9 Stimulation Induces Aberrant Expression of a Proliferation-Inducing Ligand by Tonsillar Germinal Center B Cells in IgA Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 28, 1227–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Chadburn, A.; Jou, E.; Schattner, E.J.; Knowles, D.M.; Cerutti, A. Lymphoma B Cells Evade Apoptosis through the TNF Family Members BAFF/BLyS and APRIL. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 3268–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Dillon, S.R.; Ziesmer, S.C.; Feldman, A.L.; Witzig, T.E.; Ansell, S.M.; Cerhan, J.R.; Novak, A.J. A proliferation-inducing ligand mediates follicular lymphoma B-cell proliferation and cyclin D1 expression through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase–regulated mammalian target of rapamycin activation. Blood 2009, 113, 5206–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, V.T.; Enghard, P.; Schürer, S.; Steinhauser, G.; Rudolph, B.; Riemekasten, G.; Berek, C. Systemic activation of the immune system induces aberrant BAFF and APRIL expression in B cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 2083–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makita, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Kano, T.; Takahata, A.; Julian, B.A.; Novak, J.; Suzuki, Y. TLR9 activation induces aberrant IgA glycosylation via APRIL- and IL-6–mediated pathways in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2019, 97, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myette, J.R.; Kano, T.; Suzuki, H.; Sloan, S.E.; Szretter, K.J.; Ramakrishnan, B.; Adari, H.; Deotale, K.D.; Engler, F.; Shriver, Z.; et al. A Proliferation Inducing Ligand (APRIL) targeted antibody is a safe and effective treatment of murine IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.S.; Yang, S.H.; Choi, M.; Kim, H.-R.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.; Moon, K.C.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.P.; et al. The Role of TNF Superfamily Member 13 in the Progression of IgA Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 3430–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, G.; Shi, W.; Xu, L.-X.; Su, Y.; Yan, L.-J.; Li, K.-S. Serum BAFF is elevated in patients with IgA nephropathy and associated with clinical and histopathological features. J. Nephrol. 2012, 26, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, T.; Bandoh, N.; Yoshizaki, T.; Nozawa, H.; Takahara, M.; Ueda, S.; Hayashi, T.; Harabuchi, Y. Increase in B-cell-activation factor (BAFF) and IFN-gamma productions by tonsillar mononuclear cells stimulated with deoxycytidyl-deoxyguanosine oligodeoxynucleotides (CpG-ODN) in patients with IgA nephropathy. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 126, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, R.J.; Podolsky, D.K. Unravelling the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2007, 448, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Suzuki, H.; Kano, T.; Fukao, Y.; Nakayama, M.; Suzuki, Y. POS-399 Anti-BAFF antibody is effective to inhibit the production of immunoglobulins, but not nephritogenic IgA in murine IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 7, S180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarra, S.V.; Guzmán, R.M.; E Gallacher, A.; Hall, S.; A Levy, R.; E Jimenez, R.; Li, E.K.-M.; Thomas, M.; Kim, H.-Y.; León, M.G.; et al. Efficacy and safety of belimumab in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus: A randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2011, 377, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauen, T.; Eitner, F.; Fitzner, C.; Sommerer, C.; Zeier, M.; Otte, B.; Panzer, U.; Peters, H.; Benck, U.; Mertens, P.R.; et al. Intensive Supportive Care plus Immunosuppression in IgA Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, H.; Wong, M.G.; Jardine, M.J.; Hladunewich, M.; Jha, V.; Monaghan, H.; Zhao, M.; Barbour, S.; Reich, H.; et al. Effect of oral methylprednisolone on clinical outcomes in patients with IgA nephropathy: The TESTING randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, K.; Suzuki, H.; Kikuchi, M.; Koike, K.; Komatsu, H.; Takahashi, K.; Narita, I.; Okada, H. Committee of Clinical Practical Guideline for IgA Nephropathy 2020 Current treatment status of IgA nephropathy in Japan: A questionnaire survey. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2023, 27, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, J.; Rovin, B.H.; Cattran, D.; Floege, J.; Lafayette, R.; Tesar, V.; Trimarchi, H.; Zhang, H. Why target the gut to treat IgA nephropathy? Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 1620–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppo, R. The Gut-Renal Connection in IgA Nephropathy. Semin. Nephrol. 2018, 38, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiryluk, K.; Li, Y.; Scolari, F.; Sanna-Cherchi, S.; Choi, M.; Verbitsky, M.; Fasel, D.; Lata, S.; Prakash, S.; Shapiro, S.; et al. Discovery of new risk loci for IgA nephropathy implicates genes involved in immunity against intestinal pathogens. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, M.; Cai, L.; Fu, D.; Peng, Y.; Guo, L.; Mao, H.; Yu, X.; Li, M. Identification of susceptibility locus shared by IgA nephropathy and inflammatory bowel disease in a Chinese Han population. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 65, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehnberg, J.; Symreng, A.; Ludvigsson, J.F.; Emilsson, L. Inflammatory Bowel Disease Is More Common in Patients with IgA Nephropathy and Predicts Progression of ESKD: A Swedish Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, T.; Kaneko, H.; Okada, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Fujiu, K.; Takeda, N.; Morita, H.; Takeda, N.; Fukui, A.; Yokoo, T.; et al. Association of inflammatory bowel disease with incident immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2024, 19, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brandtzaeg, P.; Carlsen, H.S.; Halstensen, T.S. The B-cell system in inflammatory bowel disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2006, 579, 149–167. [Google Scholar]
- Lafayette, R.; Kristensen, J.; Stone, A.; Floege, J.; Tesař, V.; Trimarchi, H.; Zhang, H.; Eren, N.; Paliege, A.; Reich, H.N.; et al. Efficacy and safety of a targeted-release formulation of budesonide in patients with primary IgA nephropathy (NefIgArd): 2-year results from a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edsbäcker, S.; Andersson, T. Pharmacokinetics of Budesonide (EntocortTM EC) Capsules for Crohn’s Disease. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2004, 43, 803–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimbury, D.; Muto, M.; Bhachu, J.S.; Scionti, K.; Brown, J.; Molyneux, K.; Seikrit, C.; Maixnerová, D.; Pérez-Alós, L.; Garred, P.; et al. Targeted-release budesonide modifies key pathogenic biomarkers in immunoglobulin A nephropathy: Insights from the NEFIGAN trial. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafayette, R.A.; Canetta, P.A.; Rovin, B.H.; Appel, G.B.; Novak, J.; Nath, K.A.; Sethi, S.; Tumlin, J.A.; Mehta, K.; Hogan, M.; et al. A Randomized, Controlled Trial of Rituximab in IgA Nephropathy with Proteinuria and Renal Dysfunction. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 28, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdan, M.; Caraux, A.; Caron, G.; Robert, N.; Fiol, G.; Rème, T.; Bolloré, K.; Vendrell, J.-P.; Le Gallou, S.; Mourcin, F.; et al. Characterization of a Transitional Preplasmablast Population in the Process of Human B Cell to Plasma Cell Differentiation. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 3931–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.E.; Frölich, D.; Giesecke, C.; Loddenkemper, C.; Reiter, K.; Schmidt, S.; Feist, E.; Daridon, C.; Tony, H.P.; Radbruch, A.; et al. Steady-state generation of mucosal IgA+ plasmablasts is not abrogated by B-cell depletion therapy with rituximab. Blood 2010, 116, 5181–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrezenmeier, E.; Jayne, D.; Dörner, T. Targeting B Cells and Plasma Cells in Glomerular Diseases: Translational Perspectives. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 741–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartono, C.; Chung, M.; Perlman, A.S.; Chevalier, J.M.; Serur, D.; Seshan, S.V.; Muthukumar, T. Bortezomib for Reduction of Proteinuria in IgA Nephropathy. Kidney Int. Rep. 2018, 3, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, M.; Barratt, J.; Chacko, B.; Chan, T.M.; Kooienga, L.; Oh, K.-H.; Sahay, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Wong, M.G.; Yarbrough, J.; et al. A Phase 2 Trial of Sibeprenlimab in Patients with IgA Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrill, J.T.; Shanahan, W.R.; Scheinberg, M.; Kalunian, K.C.; Wofsy, D.; Martin, R.S. Phase III trial results with blisibimod, a selective inhibitor of B-cell activating factor, in subjects with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, J.; Hislop, C.; Pennington, J. FR-PO1128 effects of blisibimod, a selective inhibitor of B-cell activating factor, in patients with IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 4B. [Google Scholar]
- Kaegi, C.; Steiner, U.C.; Wuest, B.; Crowley, C.; Boyman, O. Systematic Review of Safety and Efficacy of Atacicept in Treating Immune-Mediated Disorders. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, J.; Tumlin, J.; Suzuki, Y.; Kao, A.; Aydemir, A.; Pudota, K.; Jin, H.; Gühring, H.; Appel, G. Randomized Phase II JANUS Study of Atacicept in Patients With IgA Nephropathy and Persistent Proteinuria. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 7, 1831–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafayette, R.; Barbour, S.; Israni, R.; Wei, X.; Eren, N.; Floege, J.; Jha, V.; Kim, S.G.; Maes, B.; Phoon, R.K.; et al. A phase 2b, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial of atacicept for treatment of IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S. Telitacicept: First Approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 1671–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Ren, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, X.; Jiang, J.; Liu, D.; Hu, P. Pharmacokinetics analysis based on target-mediated drug distribution for RC18, a novel BLyS/APRIL fusion protein to treat systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 159, 105704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Liu, L.; Hao, C.; Li, G.; Fu, P.; Xing, G.; Zheng, H.; Chen, N.; Wang, C.; Luo, P.; et al. Randomized Phase 2 Trial of Telitacicept in Patients With IgA Nephropathy With Persistent Proteinuria. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 8, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zan, J.; Liu, L.; Li, G.; Zheng, H.; Chen, N.; Wang, C.; Xie, D.; Zuo, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, P.; et al. Effect of telitacicept on circulating Gd-IgA1 and IgA-containing immune complexes in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. Rep. 2024, 9, 1067–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madan, A.; Park, I.; Yalavarthy, R.; Mandayam, S.; Kulkarni, H.; Barratt, J.; Davies, R.; Enstrom, A.; Thomas, H.; Li, J.; et al. #1342 Updated results from the RUBY-3 study of povetacicept, an enhanced dual BAFF/APRIL antagonist, in autoantibody-associated glomerulonephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2024, 39, gfae069-0431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, J.; Kooienga, L.; Hour, B.; Agha, I.; Schwartz, B.; Sorensen, B.; Lo, J.; King, A.; Sathaliya, T.; Iyer, S.; et al. MO212: Updated interim results of a phase 1/2 study to investigate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and clinical activity of BION-1301 in patients with IgA nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, 37, i145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, J.; Kim, S.G.; Agha, I.; Kooienga, L.; Madan, A.; Ruiz-Ramon, P.; Thomas, H.; Workeneh, B.; Narayanan, R.; Sorensen, B.; et al. WCN23-1175 updated interim results of a phase 1/2 study of BION-1301 in patients with IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 8, S280–S281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.G.; Lee, E.Y.; Narayanan, R.; Sorensen, B.; Schwartz, B.M.; King, A.J.; Jones-Burton, C.; Barratt, J. WCN23-1107 a phase 1/2 multicenter study to investigate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamis of BION-1301 in healthy volunteers and adults with iga nephropathy. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 8, S280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho-Santos, A.; Kuhnert, L.R.B.; Hahne, M.; Vasconcellos, R.; Carvalho-Pinto, C.E.; Villa-Verde, D.M.S. Anti-inflammatory role of APRIL by modulating regulatory B cells in antigen-induced arthritis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0292028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, N.; Isenberg, D.A.; Jury, E.C.; Ciurtin, C. Exploring BAFF: Its expression, receptors and contribution to the immunopathogenesis of Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cytokine | Mediated by | Function |
|---|---|---|
| APRIL | TACI | B cell isotype switching |
| T-cell-dependent and -independent antibody response | ||
| Differentiation of B cell to plasmablast | ||
| Plasma cell and long-lived plasma cell survival | ||
| Production of antiapoptotic protein | ||
| BCMA | Plasmablast and plasma cell survival | |
| BAFF | BAFF-R | B cell survival and maturation |
| TACI | Regulation of B cell survival and proliferation | |
| T-cell-independent antibody response | ||
| Promotion of long-lived plasma cell survival | ||
| Class switch recombination induction | ||
| BCMA | B cell development |
| Agent | Clinical Trial Name | Phase | Target | Registration No. | Route of Administration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Felzartamab | IGNAZ | II | CD38 | NCT05065970 | IV (depending on the arms) |
| Mezagitamab | I | CD38 | NCT05174221 | Weekly SC | |
| Bortezomib | II | Proteasome | NCT05383547 | IV (monthly cycle) | |
| Sibeprenlimab | ENVISION | II | APRIL | NCT04287985 | 4-weekly IV |
| VISIONARY | III | APRIL | NCT05248646 | 4-weekly SC | |
| II/III | APRIL | NCT05248659 | 4-weekly SC (single-arm, open-label) | ||
| Ataticept | JANUS | II | APRIL + BAFF | NCT02808429 | Weekly SC |
| ORIGIN | IIb | APRIL + BAFF | NCT04716231 | Weekly SC | |
| Telitacicept | II | APRIL + BAFF | NCT04905212 | 4-weekly SC | |
| III | APRIL + BAFF | NCT05799287 | Weekly SC /2-weekly SC | ||
| Zigakibart | ADU-CL-19 | I/II | APRIL | NCT03945318 | 2-weekly IV /2-weekly SC |
| BEYOND | III | APRIL | NCT05852938 | 2-weekly SC | |
| Povetacicept | RUBY-3 | Ib/IIa | APRIL + BAFF | NCT05732402 | 4-weekly SC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muto, M.; Suzuki, H.; Suzuki, Y. New Insights and Future Perspectives of APRIL in IgA Nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910340
Muto M, Suzuki H, Suzuki Y. New Insights and Future Perspectives of APRIL in IgA Nephropathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(19):10340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910340
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuto, Masahiro, Hitoshi Suzuki, and Yusuke Suzuki. 2024. "New Insights and Future Perspectives of APRIL in IgA Nephropathy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 19: 10340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910340
APA StyleMuto, M., Suzuki, H., & Suzuki, Y. (2024). New Insights and Future Perspectives of APRIL in IgA Nephropathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(19), 10340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910340





