Prospective Variation of Cytokine Trends during COVID-19: A Progressive Approach from Disease Onset until Outcome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
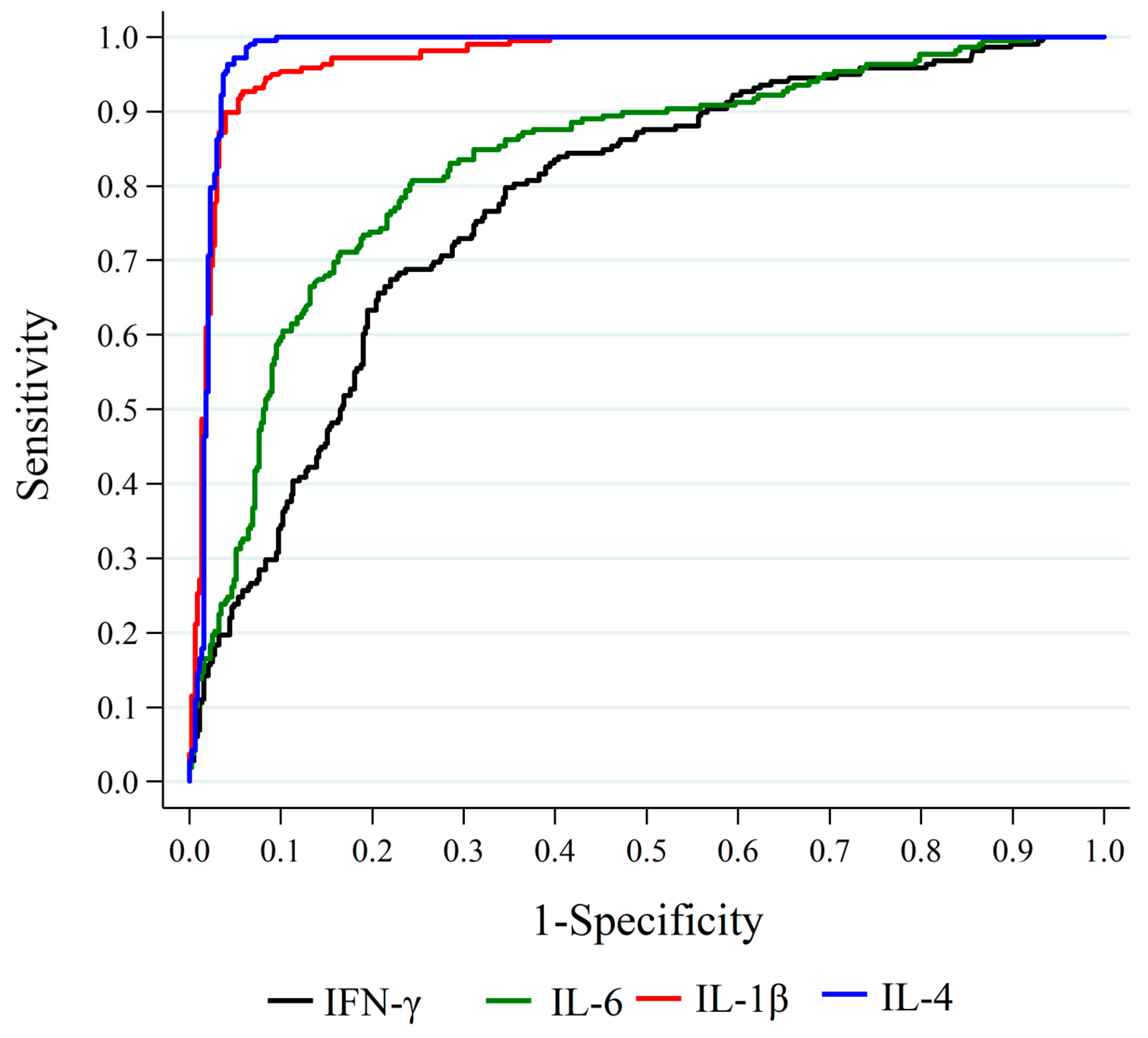
2.1. Association between Cytokine Levels at Hospital Admission and Death
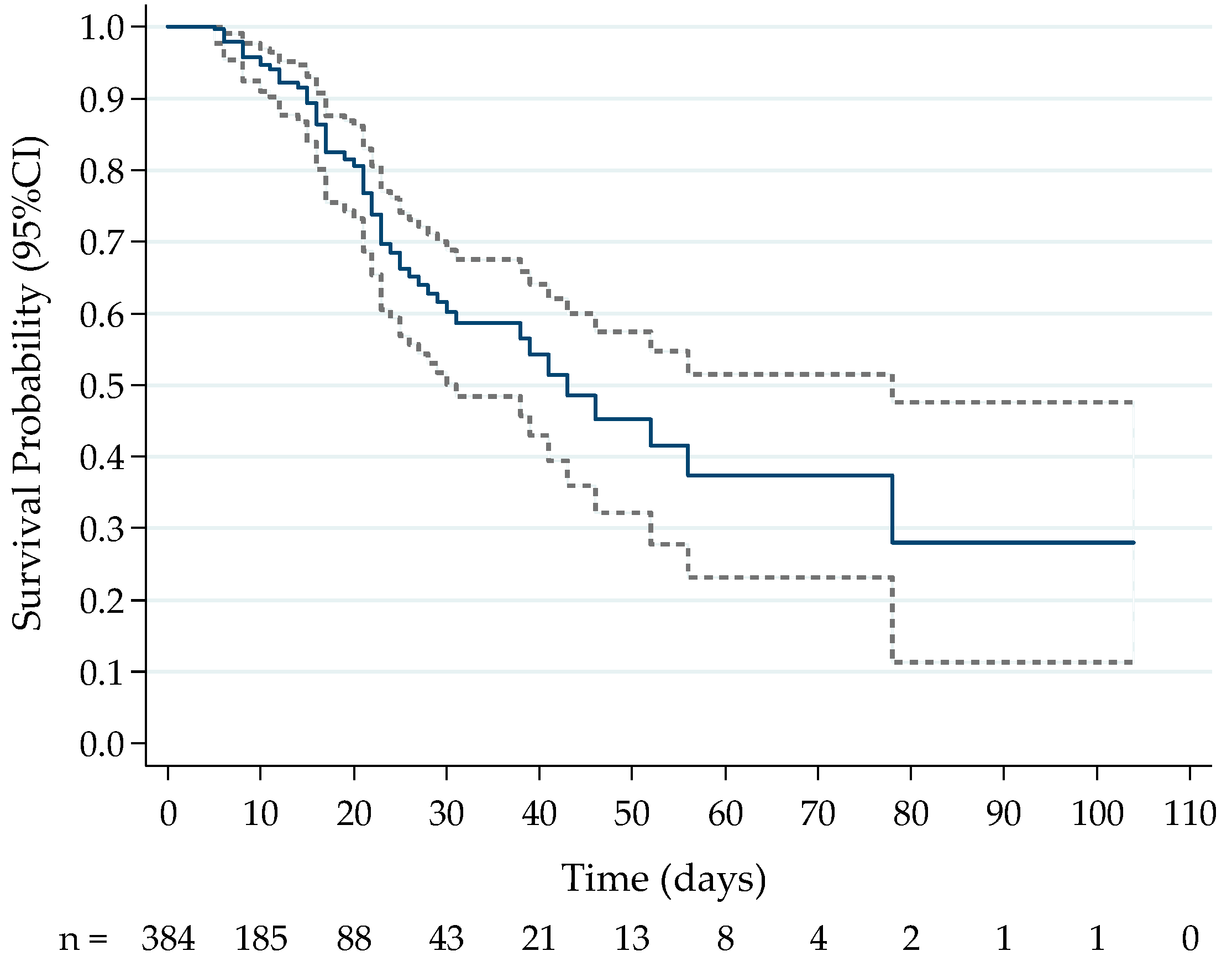
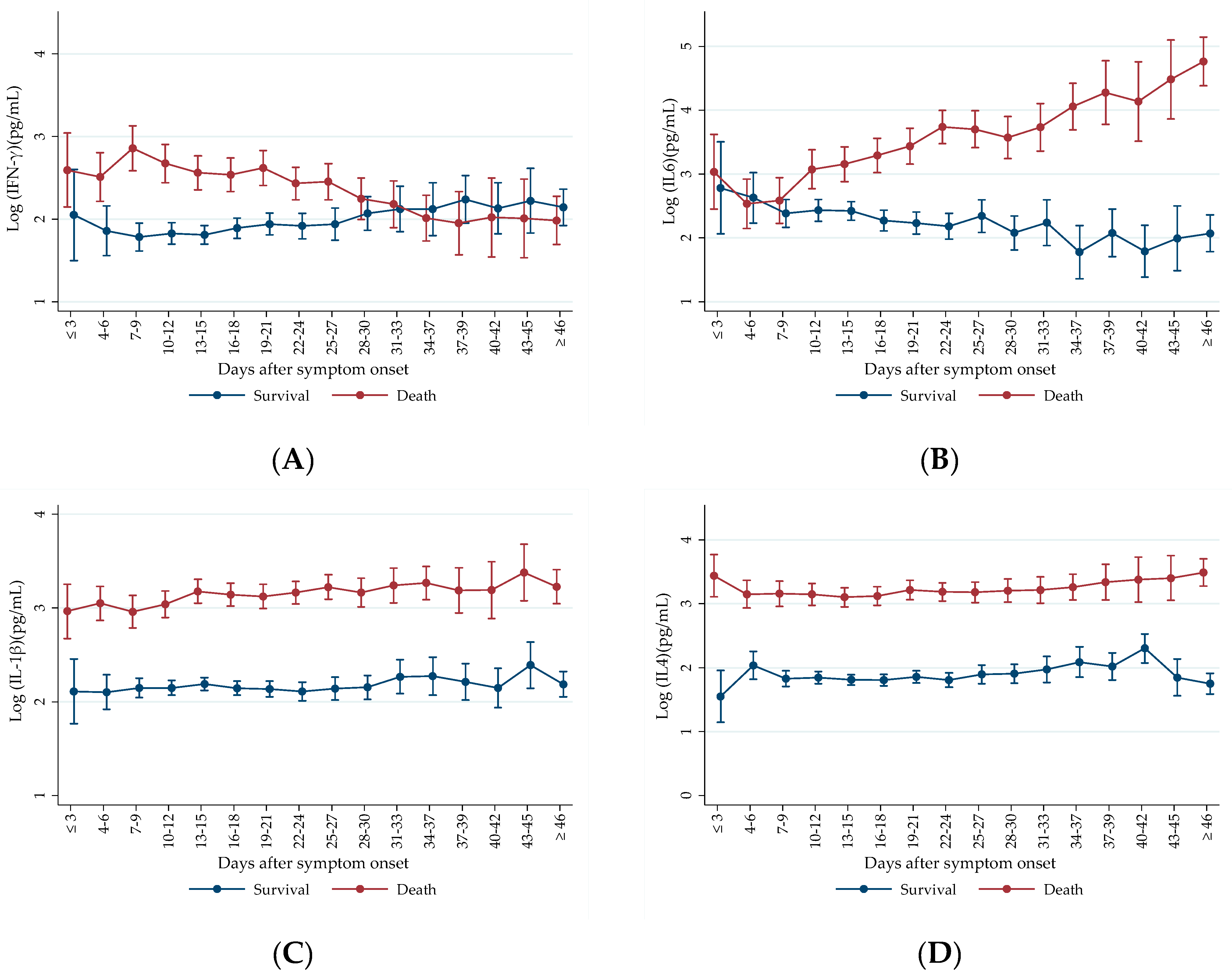
2.2. Prospective Analysis of Cytokine Levels between Outcome Groups
3. Discussion
3.1. First Timepoint Analysis and Mortality
3.2. Prospective Cytokine Patterns
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Patients
4.2. Sample Processing and Cytokine Measurements
4.3. Sample Size Calculation
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Del Valle, D.M.; Kim-Schulze, S.; Huang, H.H.; Beckmann, N.D.; Nirenberg, S.; Wang, B.; Lavin, Y.; Swartz, T.H.; Madduri, D.; Stock, A.; et al. An Inflammatory Cytokine Signature Predicts COVID-19 Severity and Survival. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulchandani, R.; Lyngdoh, T.; Kakkar, A.K. Deciphering the COVID-19 Cytokine Storm: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 51, e13429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merad, M.; Martin, J.C. Pathological Inflammation in Patients with COVID-19: A Key Role for Monocytes and Macrophages. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leisman, D.E.; Ronner, L.; Pinotti, R.; Taylor, M.D.; Sinha, P.; Calfee, C.S.; Hirayama, A.V.; Mastroiani, F.; Turtle, C.J.; Harhay, M.O.; et al. Cytokine Elevation in Severe and Critical COVID-19: A Rapid Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Comparison with Other Inflammatory Syndromes. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fan, Y.; Lai, Y.; Han, T.; Li, Z.; Zhou, P.; Pan, P.; Wang, W.; Hu, D.; Liu, X.; et al. Coronavirus Infections and Immune Responses. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisoncik, J.R.; Korth, M.J.; Simmons, C.P.; Farrar, J.; Martin, T.R.; Katze, M.G. Into the Eye of the Cytokine Storm. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2012, 76, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, B.S.; Laloraya, M. A Cytokine Super Cyclone in COVID-19 Patients with Risk Factors: The Therapeutic Potential of BCG Immunization. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020, 54, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Wang, T.; Cai, D.; Hu, Z.; Chen, J.; Liao, H.; Zhi, L.; Wei, H.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, Y.; et al. Cytokine Storm Intervention in the Early Stages of COVID-19 Pneumonia. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020, 53, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadotti, A.C.; de Castro Deus, M.; Telles, J.P.; Wind, R.; Goes, M.; Garcia Charello Ossoski, R.; de Padua, A.M.; de Noronha, L.; Moreno-Amaral, A.; Baena, C.P.; et al. IFN-γ Is an Independent Risk Factor Associated with Mortality in Patients with Moderate and Severe COVID-19 Infection. Virus Res. 2020, 289, 198171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandikattu, H.K.; Venkateshaiah, S.U.; Kumar, S.; Mishra, A. IL-15 Immunotherapy Is a Viable Strategy for COVID-19. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020, 54, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimabukuro-Vornhagen, A.; Gödel, P.; Subklewe, M.; Stemmler, H.J.; Schlößer, H.A.; Schlaak, M.; Kochanek, M.; Böll, B.; von Bergwelt-Baildon, M.S. Cytokine Release Syndrome. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Louie, M.C.; Vannella, K.M.; Wilke, C.A.; Levine, A.M.; Moore, B.B.; Shanley, T.P. New Concepts of IL-10-Induced Lung Fibrosis: Fibrocyte Recruitment and M2 Activation in a CCL2/CCR2 Axis. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2011, 300, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.Y.; Qiao, K.; Liu, F.; Wu, B.; Xu, X.; Jiao, G.Q.; Lu, R.G.; Li, H.X.; Zhao, J.; Huang, J.; et al. Lung Transplantation as Therapeutic Option in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome for Coronavirus Disease 2019-Related Pulmonary Fibrosis. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 1390–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiau, M.Y.; Chuang, P.H.; Yang, C.P.; Hsiao, C.W.; Chang, S.W.; Chang, K.Y.; Liu, T.M.; Chen, H.W.; Chuang, C.C.; Yuan, S.Y.; et al. Mechanism of Interleukin-4 Reducing Lipid Deposit by Regulating Hormone-Sensitive Lipase. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauridsen, C.; Matte, J.J. Recent Advances in Understanding the Role of Vitamins in Pig Nutrition. In Achieving Sustainable Production of Pig Meat; Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017; pp. 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A.; Hural, J. Functions of IL-4 and Control of Its Expression. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 37, 197–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, C.A.M.; Targ, S.; Allen, C.D.C. IL-21 Is a Broad Negative Regulator of IgE Class Switch Recombination in Mouse and Human B Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20190472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta Junior, J.d.S.; Miggiolaro, A.F.R.d.S.; Nagashima, S.; de Paula, C.B.V.; Baena, C.P.; Scharfstein, J.; de Noronha, L. Mast Cells in Alveolar Septa of COVID-19 Patients: A Pathogenic Pathway That May Link Interstitial Edema to Immunothrombosis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 574862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Escobar, L.G.; Hoffman, K.L.; Choi, J.J.; Borczuk, A.; Salvatore, S.; Alvarez-Mulett, S.L.; Galvan, M.D.; Zhao, Z.; Racine-Brzostek, S.E.; Yang, H.S.; et al. Cytokine Signatures of End Organ Injury in COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirawat, R.; Saifi, M.A.; Godugu, C. Targeting Inflammatory Cytokine Storm to Fight against COVID-19 Associated Severe Complications. Life Sci. 2021, 267, 118923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Kamimura, D.; Hirano, T. Pleiotropy and Specificity: Insights from the Interleukin 6 Family of Cytokines. Immunity 2019, 50, 812–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T.; Murakami, M. COVID-19: A New Virus, but a Familiar Receptor and Cytokine Release Syndrome. Immunity 2020, 52, 731–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanz, T.V.; Ding, Z.; Ho, P.P.; Luo, J.; Agrawal, A.N.; Srinagesh, H.; Axtell, R.; Zhang, H.; Platten, M.; Wyss-Coray, T.; et al. Angiotensin II Sustains Brain Inflammation in Mice via TGF-β. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 2782–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehanire, T.; Ren, L.; Bond, J.; Medina, M.; Li, G.; Bashirov, L.; Chen, L.; Kokosis, G.; Ibrahim, M.; Selim, A.; et al. Angiotensin II Stimulates Canonical TGF-β Signaling Pathway through Angiotensin Type 1 Receptor to Induce Granulation Tissue Contraction. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 93, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmudpour, M.; Roozbeh, J.; Keshavarz, M.; Farrokhi, S. Cytokine COVID-19 Cytokine Storm: The Anger of in Fl Ammation. Cytokine 2020, 133, 155151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martonik, D.; Parfieniuk-Kowerda, A.; Rogalska, M.; Flisiak, R. The Role of Th17 Response in COVID-19. Cells 2021, 10, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yang, X.O. TH17 Responses in Cytokine Storm of COVID-19: An Emerging Target of JAK2 Inhibitor Fedratinib. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 53, 368–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacha, O.; Sallman, M.A.; Evans, S.E. COVID-19: A Case for Inhibiting IL-17? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 345–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Huang, S.; Yin, L. The Cytokine Storm and COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorgham, K.; Quentric, P.; Gökkaya, M.; Marot, S.; Parizot, C.; Sauce, D.; Guihot, A.; Luyt, C.E.; Schmidt, M.; Mayaux, J.; et al. Distinct Cytokine Profiles Associated with COVID-19 Severity and Mortality. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 2098–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinina, O.; Golovkin, A.; Zaikova, E.; Aquino, A.; Bezrukikh, V.; Melnik, O.; Vasilieva, E.; Karonova, T.; Kudryavtsev, I.; Shlyakhto, E. Cytokine Storm Signature in Patients with Moderate and Severe COVID-19. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choreño-Parra, J.A.; Jiménez-Álvarez, L.A.; Cruz-Lagunas, A.; Rodríguez-Reyna, T.S.; Ramírez-Martínez, G.; Sandoval-Vega, M.; Hernández-García, D.L.; Choreño-Parra, E.M.; Balderas-Martínez, Y.I.; Martinez-Sánchez, M.E.; et al. Clinical and Immunological Factors That Distinguish COVID-19 From Pandemic Influenza A(H1N1). Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 593595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical Features of Patients Infected with 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Kilian, C.; Turner, J.E.; Bosurgi, L.; Roedl, K.; Bartsch, P.; Gnirck, A.C.; Cortesi, F.; Schultheiß, C.; Hellmig, M.; et al. Clonal Expansion and Activation of Tissue-Resident Memory-like Th17 Cells Expressing GM-CSF in the Lungs of Severe COVID-19 Patients. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabf6692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenberger, P.; Huang, W.; Ye, P.; Oliver, P.; Manuel, M.; Zhang, Z.; Bagby, G.; Nelson, S.; Kolls, J.K. Requirement of Endogenous Stem Cell Factor and Granulocyte-Colony-Stimulating Factor for IL-17-Mediated Granulopoiesis. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 4783–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Fu, B.; Zheng, X.; Wang, D.; Zhao, C.; Qi, Y.; Sun, R.; Tian, Z.; Xu, X.; Wei, H. Pathogenic T-Cells and Inflammatory Monocytes Incite Inflammatory Storms in Severe COVID-19 Patients. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channappanavar, R.; Perlman, S. Pathogenic Human Coronavirus Infections: Causes and Consequences of Cytokine Storm and Immunopathology. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozger, H.S.; Karakus, R.; Kuscu, E.N.; Bagriacik, U.E.; Oruklu, N.; Yaman, M.; Turkoglu, M.; Erbas, G.; Atak, A.Y.; Senol, E. Serial Measurement of Cytokines Strongly Predict COVID-19 Outcome. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remberto Ramos-González, A.; Eder Cano-Pérez, B.C.; Steev Loyola, B.C.D.; Rita Sierra-Merlano, A.; Doris Gómez-Camargo, B.C. Cytokine Expression and Mortality Risk among COVID-19 Hospitalized Patients over 60 Years of Age in a Referral Hospital in Cartagena, Colombia. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herr, C.; Mang, S.; Mozafari, B.; Guenther, K.; Speer, T.; Seibert, M.; Srikakulam, S.K.; Beisswenger, C.; Ritzmann, F.; Keller, A.; et al. Distinct Patterns of Blood Cytokines beyond a Cytokine Storm Predict Mortality in Covid-19. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 4651–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheer, M.; Saad, E.; Kananeh, M.; Asad, L.; Khayat, O.; Badarne, A.; Abdo, Z.; Arraf, N.; Milhem, F.; Bassal, T.; et al. Cytokine Patterns in COVID-19 Patients: Which Cytokines Predict Mortality and Which Protect Against? Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 4735–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Kaminga, A.C.; Xu, H. Comorbidities’ Potential Impacts on Severe and Non-Severe Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, E24971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa-Parra, G.; Gilbert, E.L.; Valenzuela-Almada, M.O.; Vallejo, S.; Neville, M.R.; Patel, N.J.; Cook, C.; Fu, X.; Hagi, R.; McDermott, G.C.; et al. Risk of Severe COVID-19 Outcomes Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Phenotypic Subgroups: A Retrospective, Comparative, Multicentre Cohort Study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2022, 4, e765–e774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudatsir, M.; Wulandari, L.; Fajar, J.K.; Soegiarto, G.; Ilmawan, M.; Purnamasari, Y.; Mahdi, B.A.; Jayanto, G.D.; Suhendra, S.; Setianingsih, Y.A.; et al. Predictors of COVID-19 Severity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. F1000Research 2020, 9, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasca, D.; Blomberg, B.B.; Paganelli, R. Aging, Obesity, and Inflammatory Age-Related Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinti, M.; Appay, V.; Campisi, J.; Frasca, D.; Fülöp, T.; Sauce, D.; Larbi, A.; Weinberger, B.; Cossarizza, A. Aging of the Immune System: Focus on Inflammation and Vaccination. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 2286–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelman, L.; Pivovarova-Ramich, O.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H.; Grune, T.; Aleksandrova, K. Cytokines for Evaluation of Chronic Inflammatory Status in Ageing Research: Reliability and Phenotypic Characterisation. Immun. Ageing 2019, 16, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.N.; Siddiqui, S.A.; Ibrahim, M.; Hakim, M.L.; Ahammed, M.S.; Kabir, A.; Sultana, F. Inflammatory Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer. SAGE Open Med. 2020, 8, 2050312120965752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Dong, M.; Pan, Q.; Wang, X.; Guo, L. Correlation between Changes in Inflammatory Cytokines and the Combination with Hypertension in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Minerva Endocrinol. 2019, 44, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caiazzo, E.; Sharma, M.; Rezig, A.O.M.; Morsy, M.I.; Czesnikiewicz-Guzik, M.; Ialenti, A.; Sulicka-Grodzicka, J.; Pellicori, P.; Crouch, S.H.; Schutte, A.E.; et al. Circulating Cytokines and Risk of Developing Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 200, 107050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidiropoulos, P.I.; Goulielmos, G.; Voloudakis, G.K.; Petraki, E.; Boumpas, D.T. Inflammasomes and Rheumatic Diseases: Evolving Concepts. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 1382–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Lin, G.J.; Chen, J.W.; Wang, K.C.; Tien, C.H.; Hu, C.F.; Chang, C.N.; Hsu, W.F.; Fan, H.C.; Sytwu, H.K. Immunopathogenic Mechanisms and Novel Immune-Modulated Therapies in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Qi, F.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zou, R.; Yuan, J.; Liao, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; et al. The Transient IFN Response and the Delay of Adaptive Immunity Feature the Severity of COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 816745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Wu, D.; Guo, W.; Cao, Y.; Huang, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Yu, H.; et al. Clinical and Immunological Features of Severe and Moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2620–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Pan, J.; Tao, J.; Guo, D. SARS-CoV Nucleocapsid Protein Antagonizes IFN-β Response by Targeting Initial Step of IFN-β Induction Pathway, and Its C-Terminal Region Is Critical for the Antagonism. Virus Genes 2011, 42, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wathelet, M.G.; Orr, M.; Frieman, M.B.; Baric, R.S. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Evades Antiviral Signaling: Role of Nsp1 and Rational Design of an Attenuated Strain. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 11620–11633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channappanavar, R.; Fehr, A.R.; Vijay, R.; Mack, M.; Zhao, J.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Perlman, S. Dysregulated Type I Interferon and Inflammatory Monocyte-Macrophage Responses Cause Lethal Pneumonia in SARS-CoV-Infected Mice. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetson, D.B.; Mohrs, M.; Reinhardt, R.L.; Baron, J.L.; Wang, Z.E.; Gapin, L.; Kronenberg, M.; Locksley, R.M. Constitutive Cytokine MRNAs Mark Natural Killer (NK) and NK T Cells Poised for Rapid Effector Function. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, C.; Wong, P.; Klein, J.; Castro, T.B.R.; Silva, J.; Sundaram, M.; Ellingson, M.K.; Mao, T.; Oh, J.E.; Israelow, B.; et al. Longitudinal Analyses Reveal Immunological Misfiring in Severe COVID-19. Nature 2020, 584, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagunas-Rangel, F.A.; Chávez-Valencia, V. High IL-6/IFN-γ Ratio Could Be Associated with Severe Disease in COVID-19 Patients. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 1789–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, S.; Butt, A.R.; Bibi, A.; Mushtaq, S.; Ullah, I.; Alshahrani, F.; Khan, A.; Mansoor, A. Expression of IFN-Gamma Is Significantly Reduced during Severity of Covid-19 Infection in Hospitalized Patients. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0291332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjadj, J.; Yatim, N.; Barnabei, L.; Corneau, A.; Boussier, J. Impaired Type I Interferon Activity and Inflammatory Responses in Severe COVID-19 Patients. Science 2020, 724, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.T.; Linster, M.; Tan, C.W.; Le Bert, N.; Chia, W.N.; Kunasegaran, K.; Zhuang, Y.; Tham, C.Y.L.; Chia, A.; Smith, G.J.D.; et al. Early Induction of Functional SARS-CoV-2-Specific T Cells Associates with Rapid Viral Clearance and Mild Disease in COVID-19 Patients. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Chen, Z.; Lui, G.; Wong, C.K.; Wong, W.T.; Ng, R.W.Y.; Tso, E.Y.K.; Fung, K.S.C.; Chan, V.; Yeung, A.C.M.; et al. Longitudinal Cytokine Profile in Patients with Mild to Critical COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 763292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yudhawati, R.; Sakina, S.; Fitriah, M. Interleukin-1β and Interleukin-10 Profiles and Ratio in Serum of COVID-19 Patients and Correlation with COVID-19 Severity: A Time Series Study. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2022, 15, 8043–8054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skurk, T.; Van Harmelen, V.; Hauner, H. Angiotensin II Stimulates the Release of Interleukin-6 and Interleukin-8 from Cultured Human Adipocytes by Activation of NF-ΚB. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical Course and Risk Factors for Mortality of Adult Inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costela-ruiz, V.J.; Illescas-montes, R.; Puerta-puerta, J.M.; Ruiz, C.; Melguizo-rodríguez, L. Cytokine and Growth Factor Reviews SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The Role of Cytokines in COVID-19 Disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020, 54, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeDiego, M.L.; Nieto-Torres, J.L.; Regla-Nava, J.A.; Jimenez-Guardeño, J.M.; Fernandez-Delgado, R.; Fett, C.; Castaño-Rodriguez, C.; Perlman, S.; Enjuanes, L. Inhibition of NF-ΚB-Mediated Inflammation in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-Infected Mice Increases Survival. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Torres, J.L.; DeDiego, M.L.; Verdiá-Báguena, C.; Jimenez-Guardeño, J.M.; Regla-Nava, J.A.; Fernandez-Delgado, R.; Castaño-Rodriguez, C.; Alcaraz, A.; Torres, J.; Aguilella, V.M.; et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Envelope Protein Ion Channel Activity Promotes Virus Fitness and Pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, K.L.; Yuen, K.S.; Castano-Rodriguez, C.; Ye, Z.W.; Yeung, M.L.; Fung, S.Y.; Yuan, S.; Chan, C.P.; Yuen, K.Y.; Enjuanes, L.; et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus ORF3a Protein Activates the NLRP3 Inflammasome by Promoting TRAF3-Dependent Ubiquitination of ASC. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 8865–8877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bülow Anderberg, S.; Luther, T.; Berglund, M.; Larsson, R.; Rubertsson, S.; Lipcsey, M.; Larsson, A.; Frithiof, R.; Hultström, M. Increased Levels of Plasma Cytokines and Correlations to Organ Failure and 30-Day Mortality in Critically Ill Covid-19 Patients. Cytokine 2021, 138, 155389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfadda, A.A.; Siddiqui, K.; Rafiullah, M.; Alkhowaiter, M.; Alotaibi, N.; Alzahrani, M.; Binkhamis, K.; Youssef, A.M.; Altalhi, H.; Almaghlouth, I.; et al. Early Cytokine Signatures of Hospitalized Mild and Severe COVID-19 Patients: A Prospective Observational Study. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 2631–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.J.; Jeon, S.; Unlu, S.; Par-Young, J.; Shin, M.S.; Kuster, J.K.; Afinogenova, Y.; Kang, Y.; Simonov, M.; Buller, G.; et al. A Distinct Association of Inflammatory Molecules with Outcomes of COVID-19 in Younger versus Older Adults. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 232, 108857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Veen, R.C.; Stohlman, S.A. Encephalitogenic Th1 Cells Are Inhibited by Th2 Cells with Related Peptide Specificity: Relative Roles of Interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-10. J. Neuroimmunol. 1993, 48, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muraille, E.; Leo, O. Revisiting the Th1/Th2 Paradigm. Scand. J. Immunol. 1998, 47, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreidler, S.M.; Muller, K.E.; Grunwald, G.K.; Ringham, B.M.; Coker-Dukowitz, Z.T.; Sakhadeo, U.R.; Barón, A.E.; Glueck, D.H. GLIMMPSE: Online Power Computation for Linear Models with and without a Baseline Covariate. J. Stat. Softw. 2013, 54, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Clinical Variables | All Patients n = 384 | Outcome | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Survival n = 324 | Death n = 60 | ||
| Age (years) | 54.6 ± 16.6 | 51.7 ± 15.1 | 70 ± 15.5 ** |
| Age ≥ 65 years | 115 (29.9%) | 71 (21.9%) | 44 (73.3%) ** |
| Males | 240 (62.5%) | 205 (63.3%) | 35 (58.3%) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 30 ± 4.8 | 30.1 ± 4.9 | 29.2 ± 4.8 |
| BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 | 168 (49.7%) | 147 (51.2%) | 21 (41.2%) |
| Temperature at admission (°C) | 36.5 ± 0.6 | 36.5 ± 0.6 | 36.5 ± 0.6 |
| Saturation at admission (%) | 91.6 ± 5.4 | 92.3 ± 4.3 | 87.8 ± 8.2 ** |
| Saturation < 95% | 255 (66.4%) | 207 (63.9%) | 48 (80%) * |
| Systolic blood pressure at admission | 128.7 ± 19.9 | 128.6 ± 18.8 | 128.7 ± 25.2 |
| Diastolic blood pressure at admission | 77.8 ± 15.3 | 78.7 ± 15.4 | 73.2 ± 14.1 * |
| Heart rate at admission | 92.9 ± 18.4 | 93.4 ± 18.6 | 90.4 ± 16.9 |
| Respiratory rate at admission | 22.1 ± 5.3 | 21.5 ± 5.1 | 25.2 ± 5.6 ** |
| Systemic arterial hypertension (SAH) | 152 (39.6%) | 114 (35.2%) | 38 (63.3%) ** |
| Diabetes mellitus | 88 (22.9%) | 68 (21%) | 20 (33.3%) * |
| Dyslipidemia | 81 (21.1%) | 61 (18.8%) | 20 (33.3%) * |
| Cardio-metabolic disease | 51 (13.3%) | 29 (9%) | 22 (36.7%) ** |
| Orotracheal intubation | 115 (29.9%) | 59 (18.2%) | 56 (93.3%) ** |
| Rheumatic disease | 14 (3.6%) | 10 (3.1%) | 4 (6.7%) |
| Respiratory disease | 42 (10.9%) | 29 (9.0%) | 13 (21.7%) ** |
| 2 or more pre-existing comorbidities | 204 (53.1%) | 157 (48.5%) | 47 (78.3%) ** |
| 4 or more pre-existing comorbidities | 69 (18%) | 43 (13.3%) | 26 (43.3%) ** |
| Cytokine | Outcome | n | Median | Minimum | Maximum | IQR | p * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log (IL-6) (pg/mL) | Survival | 323 | 2.29 | 0.69 | 4.60 | 1.05 | |
| Death | 60 | 3.27 | 1.40 | 5.95 | 1.05 | <0.001 | |
| Log (IL-10) (pg/mL) | Survival | 312 | 1.86 | 0.67 | 5.21 | 0.49 | |
| Death | 58 | 2.76 | 0.70 | 5.25 | 1.61 | <0.001 | |
| Log (IFN-γ) (pg/mL) | Survival | 322 | 1.93 | −0.30 | 3.28 | 0.87 | |
| Death | 60 | 2.37 | 1.24 | 4.44 | 0.59 | <0.001 | |
| Log (IL-4) (pg/mL) | Survival | 321 | 1.76 | 0.34 | 3.88 | 0.57 | |
| Death | 60 | 3.21 | 2.50 | 3.54 | 0.40 | <0.001 | |
| Log (TNF-α) (pg/mL) | Survival | 322 | 2.01 | 0.78 | 4.05 | 0.56 | |
| Death | 60 | 3.29 | 0.54 | 4.40 | 0.90 | <0.001 | |
| Log (IL-15) (pg/mL) | Survival | 314 | 1.87 | 0.07 | 3.63 | 0.83 | |
| Death | 55 | 2.40 | 1.87 | 3.54 | 0.35 | <0.001 | |
| Log (IL-1β) (pg/mL) | Survival | 309 | 2.07 | 0.93 | 3.93 | 0.42 | |
| Death | 53 | 3.12 | 2.23 | 4.11 | 0.34 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deus, M.d.C.; Gadotti, A.C.; Dias, E.S.; Monte Alegre, J.B.; Van Spitzenbergen, B.A.K.; Andrade, G.B.; Tozoni, S.S.; Stocco, R.B.; Olandoski, M.; Tuon, F.F.B.; et al. Prospective Variation of Cytokine Trends during COVID-19: A Progressive Approach from Disease Onset until Outcome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910578
Deus MdC, Gadotti AC, Dias ES, Monte Alegre JB, Van Spitzenbergen BAK, Andrade GB, Tozoni SS, Stocco RB, Olandoski M, Tuon FFB, et al. Prospective Variation of Cytokine Trends during COVID-19: A Progressive Approach from Disease Onset until Outcome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(19):10578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910578
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeus, Marina de Castro, Ana Carolina Gadotti, Erika Sousa Dias, Júlia Bacarin Monte Alegre, Beatriz Akemi Kondo Van Spitzenbergen, Gabriela Bohnen Andrade, Sara Soares Tozoni, Rebecca Benicio Stocco, Marcia Olandoski, Felipe Francisco Bondan Tuon, and et al. 2024. "Prospective Variation of Cytokine Trends during COVID-19: A Progressive Approach from Disease Onset until Outcome" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 19: 10578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910578
APA StyleDeus, M. d. C., Gadotti, A. C., Dias, E. S., Monte Alegre, J. B., Van Spitzenbergen, B. A. K., Andrade, G. B., Tozoni, S. S., Stocco, R. B., Olandoski, M., Tuon, F. F. B., Pinho, R. A., de Noronha, L., Baena, C. P., & Moreno-Amaral, A. N. (2024). Prospective Variation of Cytokine Trends during COVID-19: A Progressive Approach from Disease Onset until Outcome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(19), 10578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910578






