Abstract
In the eukaryotic cells, the ubiquitin–proteasome system (UPS) plays a crucial role in the intracellular protein turnover. It is involved in several cellular functions such as the control of the regular cell cycle progression, the immune surveillance, and the homeostasis. Within the 20S proteasome barrel-like structure, the catalytic subunits, β1, β2 and β5, are responsible for different proteolytic activities: caspase-like (C-L), trypsin-like (T-L) and chymotrypsin-like (ChT-L), respectively. The β5 subunit is particularly targeted for its role in antitumor activity: the synthesis of β5 subunit inhibitors could be a promising strategy for the treatment of solid and hematologic tumors. In the present work, we performed two combination studies of AM12, a recently developed synthetic proteasome inhibitor, with curcumin and quercetin, two nutraceuticals endowed of many pharmacological properties. We measured the combination index (CI), applying the Chou and Talalay method, comparing the two studies, from 50% to 90% of proteasome inhibition. In the case of the combination AM12 + curcumin, an increasing synergism was observed from 50% to 90% of proteasome inhibition, while in the case of the combination AM12 + quercetin an additive effect was observed only from 50% to 70% of β5 subunit inhibition. These results suggest that combining AM12 with curcumin is a more promising strategy than combining it with quercetin for potential therapeutic applications, especially in treating tumors.
1. Introduction
The ubiquitin–proteasome system (UPS) is indeed a vital component of eukaryotic cells, serving as the primary non-lysosomal proteolytic pathway responsible for degrading unwanted or misfolded proteins [1,2]. It plays key roles in regulating various cellular processes such as cell cycle progression, immune responses, and maintaining cellular homeostasis [3,4]. Structurally, the 26S proteasome is composed of a 20S catalytic core and two 19S regulatory caps [5,6]. The 20S core has a typical barrel-like structure, consisting of four overlapping rings: two outer rings made up of seven α-subunits and two inner rings composed of seven β-subunits [7]. The α-subunits are mainly structural, helping to form the overall barrel shape and control access to the proteolytic chamber. The β-subunits are responsible for the proteolytic functions of the proteasome, with the β1 subunit exhibiting caspase-like (C-L) activity, the β2 subunit showing trypsin-like (T-L) activity, and the β5 subunit displaying chymotrypsin-like (ChT-L) activity [8]. Each of the three proteasome catalytic subunits (β1, β2 and β5) possesses a catalytic site that uses the nucleophilic γ-hydroxyl group of the N-terminal threonine (Thr) to break peptide bonds. This mechanism is a key feature of the proteasome proteolytic activity, enabling the degradation of damaged or misfolded proteins within the cell [3,4].
Dysfunctions in the UPS can indeed contribute to the onset of tumors, particularly in the field of hematological malignancies [6,9,10]. The UPS is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis by regulating protein degradation. When this system is impaired, it can result in the accumulation of damaged or misfolded proteins, leading to cellular stress and potentially contributing to oncogenesis.
Several studies have shown that selective inhibition of the β5 subunit, which is responsible for the ChT-L activity, can induce cytotoxic effects specifically in tumor cells [11]. This selective targeting is beneficial because it can kill cancer cells while sparing healthy cells. In contrast, inhibiting all three catalytic subunits of the proteasome (β1, β2, and β5) can result in a non-selective cytotoxic effect, affecting both cancerous and healthy cells. This is why therapies aimed at selectively inhibiting the β5 subunit are considered promising for cancer treatment, especially in hematologic malignancies [11].
Bortezomib (BZB) became the first proteasome inhibitor approved in 2003 for the treatment of multiple myeloma and mantle cell lymphoma [12]. Several ongoing studies are exploring Bortezomib’s potential for treating solid tumors [13,14]. Recent research has particularly shown its efficacy in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) [15]. In preclinical and early clinical trials, Bortezomib has demonstrated promising antitumor effects both as a standalone treatment and in combination with other therapeutic agents [16,17].
Our research group has been actively working on developing covalent and non-covalent proteasome inhibitors [18,19,20,21,22,23,24], and one of the recent compounds, AM12, was found to be particularly promising (Figure 1) [18]. Indeed, AM12 showed a Ki value of 1.18 µM towards the β5 subunit, along with no inhibition and a lower binding affinity towards β1 and β2 subunits, respectively.
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of AM12, curcumin and quercetin.
In recent years, the combination of synthetic drugs with nutraceuticals has gained significant attention for the treatment of several diseases [25,26,27,28,29,30]. The simultaneous employment of two or more drugs has become a key strategy in several areas, such as cancer, metabolic disorders, and infectious diseases, among others [31]. Relevant advantages, such as the increased efficacy, reduced drug resistance, lower doses of individual drugs, broader spectrum of action, overcoming limitations of monotherapy, reduced metabolic rate, and delayed disease progression, make the use of bioactive molecules in combination a valuable strategy in the management of the whole health system [32].
Given our research group’s expertise in drug combination studies [33,34,35,36], we have conducted two combination studies involving the synthetic proteasome inhibitor AM12 with two well-known nutraceuticals, namely curcumin and quercetin (Figure 1).
In this study, we utilized the Chou–Talalay method, a widely recognized approach for evaluating drug interactions, to examine the effects of combining AM12 with either curcumin or quercetin. This method determines the combination index (CI), which reveals the nature of the interaction between the compounds: a CI value of < 1 indicates synergism, = 1 suggests an additive effect and > 1 signifies antagonism [37,38].
The findings from this analysis enabled a detailed comparison of the two combinations, AM12 + curcumin and AM12 + quercetin, to determine which exhibited a more favorable effect. The results of this investigation are herein reported.
2. Results
AM12 and curcumin were tested on the recombinant human erythrocyte proteasome β5 subunit using Suc-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr-AMC as a fluorogenic substrate. The experiments involved both individual testing and combination studies to evaluate the inhibitory effects and potential synergism of AM12 and curcumin. Initially, a preliminary screening was carried out at concentrations of 100 µM, 1 µM and 0.1 µM, to define the range of activity of the two inhibitors. AM12 and curcumin were then tested separately, in two independent experiments, each of which was performed in duplicate. These experiments were carried out by selecting seven different concentrations, ranging from the minimum dose inhibiting the enzyme up to the maximum dose, which completely inhibits the activity of the proteasome. AM12 was tested in the range 100–1 µM, while curcumin was tested in the range 20–0.0001 µM. The IC50 values were then calculated from the dose–response curves, as reported in Figure 2A,B, obtaining values IC50 of 12.17 ± 1.80 µM for AM12 and 2.46 ± 0.93 µM for curcumin. These findings indicate that curcumin is approximately five-times more potent than AM12 in inhibiting the β5 subunit under the conditions tested. Subsequently, six concentrations were chosen for the compound combinations (1/16 × IC50, 1/4 × IC50, 1/2 × IC50, IC50, 2 × IC50, and 4 × IC50, Table 1), to evaluate whether a synergistic, additive, or antagonistic effect in the combination study of the two inhibitors against the β5 subunit of the human proteasome could occur.
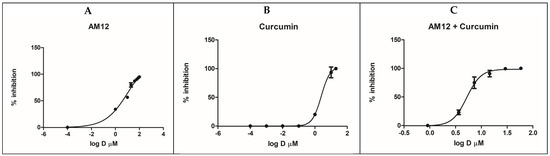
Figure 2.
Dose–response curves for β5 inhibition by AM12 (A), curcumin (B) and AM12 + curcumin in combination (C). Each experiment was performed two times, each in duplicate.

Table 1.
Six selected doses for the combination experiments of AM12 + curcumin.
In this assay, the combination of AM12 + curcumin (molar ratio 4.95:1) provided an IC50 value of 5.21 ± 0.45 µM (Figure 2C). Subsequently, each dose–response curve (Figure 2A–C) was converted into the Median Effect Plot, obtained by plotting the log (fa/fu) on the y-axis versus the log (D) on the x-axis (Figure 3A–C).
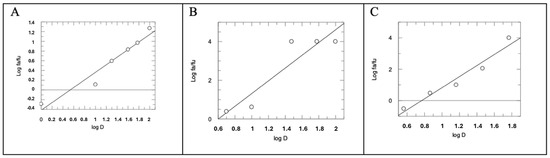
Figure 3.
Median Effect Plot for AM12 (A), curcumin (B) and AM12 + curcumin in combination (molar ratio 4.95:1) (C). D is the dose, and fa and fu the affected and the unaffected fraction of β5 activity, respectively, by the dose D.
In this plot the maximum response corresponds to 1, unlike the dose–response curve where it corresponds to 100. Therefore, fa + fu = 1, where fa corresponds to the “affected fraction” of enzyme, while fu is the “unaffected fraction”, i.e., the residual enzymatic activity. The slope of the straight line of each Median Effect Plot corresponds to the “m” value, when m is the Hill-type coefficient signifying the sigmoidicity of the dose–effect curve. In detail, AM12 showed a value of m1 = 0.7785, curcumin a value of m2 = 3.2946, while the combination assay showed a value of m1,2 = 3.5279, with an AM12/curcumin molar ratio of 4.95:1.
Once the three different m values were calculated by Grafit software, we established the doses capable of inducing each percentage of proteasome inhibition, using the Median Effect Equation: D = IC50 [fa/fu]1/m [37,38].
In the first part of our study, comparing the IC50 of AM12, curcumin, and the combination of AM12 + curcumin (Figure 2) and the related m values to each Median Effect Plot (Figure 3), the following was found: for AM12, an IC50 = 12.17 ± 1.80 µM and m1 = 0.7785, for curcumin, an IC50 = 2.46 ± 0.93 µM and m2 = 3.2946 and for the combination of AM12 + curcumin (molar ratio 4.95:1), an IC50 = 5.215 ± 0.45 µM and m1,2 = 3.5279.
AM12 and quercetin were also tested on the recombinant human erythrocyte proteasome β5 subunit using Suc-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr-AMC as a fluorogenic substrate. Initially, a preliminary screening was carried out at concentrations of 100 µM, 1 µM, and 0.1 µM, to define the range of activity of quercetin.
Quercetin was tested separately in two independent experiments, each of which was performed in duplicate. In the above experiments, seven concentrations were selected for testing quercetin. In particular, quercetin was tested in the range 100–0.001 µM, while experiments with AM12 alone are already described above.
The respective IC50 values were calculated from the dose–response curves (Figure 4A–C). For quercetin, with these new measurements an IC50 value of 2.96 ± 0.77 µM was obtained, while for AM12 the IC50 was equal to 12.17 ± 1.80 µM, as described above. In a subsequent experiment, six concentrations were established for the combination AM12 + quercetin (1/16 × IC50, 1/4 × IC50, 1/2 × IC50, IC50, 2 × IC50, and 4 × IC50, Table 2), with the aim to evaluate whether a synergistic, an additive, or an antagonistic effect occurs in the combination study between the two inhibitors of the β5 subunit of the human erythrocyte proteasome.
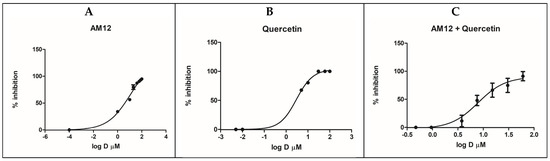
Figure 4.
Dose–response curves for β5 inhibition by AM12 (A), quercetin (B) and AM12 + quercetin in combination (C). Each experiment was performed two times, each in duplicate.

Table 2.
Six selected doses for the combination experiments of AM12 + quercetin.
In this assay, the combined doses of AM12 + quercetin (molar ratio 4.11:1) provided an IC50 value of 7.89 ± 2.52 µM. (Figure 4C).
Subsequently, also in the second study each dose–response curve (Figure 4A–C) was converted into the Median Effect Plot (Figure 5A–C), thus obtaining for AM12 a value of m1 = 0.7785, for quercetin a value of m2 = 2.4004, while for the combination assay it was found that m1,2 =1.2958, with an AM12/quercetin molar ratio of 4.11:1.
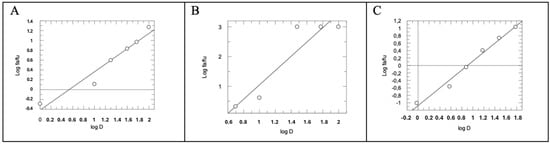
Figure 5.
Median Effect Plot for AM12 (A), quercetin (B) and AM12 + quercetin in combination (molar ratio 4.95:1) (C). D is the dose, and fa and fu the affected and the unaffected fraction of β5 activity, respectively, by the dose D.
By comparing the IC50 (Figure 4A–C) of AM12, quercetin, and the combination of AM12 + quercetin and the relative m values obtained from each Median Effect Plot (Figure 5A–C), an IC50 = 12.17 ± 1.80 µM and m1 = 0.7785 were found for AM12, an IC50 = 2.96 ± 0.77 µM and m2 = 2.4004 for quercetin, and an IC50 = 7.899 ± 1.80 µM and m1,2 = 1.2958 for the combination of AM12 + quercetin (molar ratio 4.11:1).
Then, we calculated the CI, which expresses the nature of the inhibition towards the target enzyme when the two drugs are tested in combination. It is well established that CI > 1 indicates an antagonistic effect, CI = 1 represents an additive effect, whereas CI < 1 suggests a synergistic effect [37,38]. The CI for mutually exclusive drugs, which act independently, was calculated. This method provides a quantitative assessment of how two compounds properly work together. To determine the CI, we used the Grafit software, and the CI was calculated from 50% to 90% of the inhibition of the β5 subunit of the human proteasome for both the combinations AM12 + curcumin and AM12 + quercetin (Table 3 and Figure 6A). In the case of the combination AM12 + curcumin from 50% to 90%, an increasing synergistic action was observed, while in the case of the combination AM12 + quercetin from 50% to 70% only an additive effect was observed (Table 3 and Figure 6B), which then converted into a slight antagonism from 80% to 90% of proteasome inhibition.

Table 3.
Calculated values for the combination index of AM12 + curcumin and AM12 + quercetin for the reduction in the chymotrypsin-like activity of the human erythrocyte 20S proteasome.
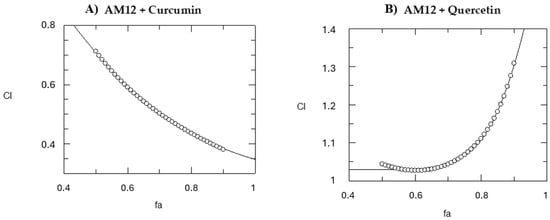
Figure 6.
Computer-generated graphical presentation of the combination index (CI) vs. the fraction affected (fa), i.e., the effect of reduction in proteasome activity exerted by AM12 + curcumin (A) and by AM12 + quercetin (B). The circles indicate the trend of the combination index.
3. Discussion
In this study, we tested the synthetic proteasome inhibitor AM12 in combination with two nutraceuticals: curcumin and quercetin.
Structurally, AM12 is an isoquinolinone derivative with a bicyclic structure featuring two methoxy groups and an allylic spacer, which connects the heterocycle to an amide function with an aliphatic substituent, i.e., the isopentyl, preferred by the β5 catalytic subunit of proteasome. AM12 was obtained using a synthetic pathway of three steps, and only two chromatography purifications were required: the overall yield resulted to be 16.3% (Scheme 1).
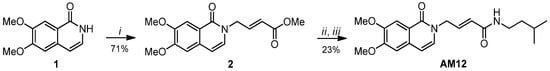
Scheme 1.
Reagents and conditions: (i) NaH, N2, dry DMF, 0 °C, 1, 1 h, and then methyl 4-bromocrotonate, 0 °C to room temperature (rt), 12 h; (ii) MeOH, LiOH, 0° C to rt, TLC monitoring; and (iii) dry DMF, resulting acid from 2, HATU, 0 °C, 10 min and then DIPEA, iso-pentyl amine, 0 °C to rt, 12 h.
Despite the presence of a Michael acceptor moiety, i.e., the α,β-unsaturated amide, the obtained experimental data suggest a non-time dependent, reversible inhibition of the enzymatic activity of proteasome. This reversibility could offer advantages in therapeutics, such as better control of overdosing, reduced risk of off-target effects due to covalent modification of unintended proteins and the potential for fine-tuning inhibitor selectivity by optimizing the reversible interaction. Molecular modeling studies highlighted that AM12 positions its Michael acceptor group far from the catalytic Thr1, ruling out the possibility of this compound to act as a covalent inhibitor. In the β5 subunit, the binding of AM12 is stabilized by interactions of the isopentyl group at the P3 position with residues Ala20, Ala22, Ala27 and Val31. Additionally, two water-mediated hydrogen bonds are established: one between the carbonyl oxygen of the amide bond and the side chain of Lys136, and another between the isoquinolone lactam oxygen and Asp125. The isoquinolone core also engages in hydrophobic contacts with Val127 and Pro126. The presence of the isopentyl group was found to be crucial for the β5 subunit inhibition. Indeed, the incorporation of linear and cyclic aliphatic residues, as well as the introduction of phenyl-containing substituents, led to a significant loss of affinity [18]. Additionally, AM12 showed no biding affinities against the β1 and β2 subunits. In this case, the 6,7-dimethoxy-1-oxoisoquinolinone core seems to be the main responsible for the selectivity towards the β5 subunit, since AM12 analogues, which differ for the N-anchored substituents, exhibited no inhibitory activity or a low percentage of inhibition towards β1 and β2 subunits.
Curcumin, a bioactive compound derived from the spice turmeric (Curcuma longa), is well known for its strong anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antitumor and antimicrobial properties [39,40]. Curcumin has been extensively biologically characterized for its potential therapeutic benefits in a range of conditions, such as cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular disorders, and inflammatory diseases [41,42]. Curcumin exerts its effects through multiple mechanisms, such as inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines, modulating oxidative stress, and interfering with cancer cell proliferation and survival pathways, such as NF-κB and PI3K/Akt [40]. Some studies suggest that curcumin may influence proteasome activity indirectly by affecting proteasome assembly or through interactions with regulatory components rather than by direct inhibition of specific subunits like β5 [43,44,45]. As such, while curcumin’s role in proteasome inhibition might not be extensively characterized in terms of specific subunit inhibition, its overall impact on proteasome function remains a point of interest for its potential therapeutic benefits. Despite its broad pharmacological potential, curcumin’s poor bioavailability is a limitation, leading to efforts to enhance its absorption through formulations or combinations with other agents [46,47]. In combination with other drugs or compounds, such as proteasome inhibitors like AM12, curcumin may enhance therapeutic efficacy or reduce the required dose of the drug, potentially minimizing side effects.
Quercetin is one of the most abundant flavonoids, found in a variety of fruits, vegetables and grains, such as apples, onions, and berries. It is renowned for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties [48]. Quercetin has been studied for its potential benefits in numerous health conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and allergies [49]. Quercetin has demonstrated potential in preclinical studies for its positive effects to promote apoptosis in cancer cells, inhibit tumor growth, and suppress metastasis [50,51]. Several studies have reported that the quercetin effects on apoptosis are mediated by the inhibition of the proteolytic activity of proteasome [52,53]. However, the exact mechanism by which quercetin inhibits proteasomal activity has not been fully elucidated. Quercetin’s proteasome-inhibitory effects can potentially enhance the efficacy of other therapeutic agents, such as proteasome inhibitors like AM12, where it may help enhance therapeutic outcomes and improve cancer treatment efficacy.
The aim of this study was to assess the potential for synergy, additive effects, or antagonism when AM12 was separately combined with curcumin or quercetin.
In the case of the combination of AM12 with curcumin, a progressive enhancement in synergistic activity was observed as the level of proteasome inhibition increased from 50% to 90% (Table 3). Indeed, when the fa was equal to 0.5, the interaction between AM12 and curcumin demonstrated moderate synergy, which progressively intensified as the inhibition level approached higher fa values (0.9). This suggests that the combination of these two agents becomes increasingly effective at higher doses, potentially amplifying their therapeutic impact on proteasome activity. This synergistic interaction may be indicative of complementary mechanisms of action, with curcumin enhancing the efficacy of AM12 in a dose-dependent manner. AM12, when tested individually, exhibited an m1 value equal to 0.7785. This indicates a negative cooperativity in its dose–response curve, meaning that as AM12 binds to the β5 subunit, it may reduce the likelihood of a hypothetical subsequent binding. The dose–response curve for AM12 is not highly sigmoidal (Figure 2A and Figure 4A) but rather shows a more gradual slope, suggesting that the compound’s binding or inhibitory action may not follow a strongly cooperative mechanism. On the other hand, curcumin showed a significantly higher m2 value of 3.2946. These data suggest a strong positive cooperativity, where the binding of one curcumin molecule enhances the likelihood of additional curcumin molecules binding to the β5 subunit. This steep dose–response curve suggests that curcumin’s inhibitory effects become much more pronounced after reaching a certain threshold concentration, likely leading to a sharp increase in proteasome inhibition once multiple binding sites are occupied. For the combination assay of AM12 and curcumin, the m1,2 value was determined to be 3.5279, with a molar ratio of 4.95:1 (AM12:curcumin). This m value, which is even higher than curcumin’s individual m2, suggests that the combination of the two inhibitors induces a more cooperative and steeply sigmoidal dose–response curve than either compound alone. The elevated Hill coefficient indicates a strong synergistic interaction between AM12 and curcumin in combination, where the binding of one compound enhances the inhibitory effect of the other, leading to an amplified response. The molar ratio of 4.95:1 reflects the proportional amounts of AM12 and curcumin used in the combination assay, and it could be optimized based on the observed cooperativity to maximize the synergistic effect. This combination may potentially result in more effective proteasome inhibition at lower concentrations compared to either compound used individually, which is an important factor when considering dose optimization and minimizing toxicity in therapeutic applications.
In contrast, the combination of AM12 with quercetin exhibited a different interaction profile. At proteasome inhibition levels of 50% to 70%, the interaction between AM12 and quercetin was predominantly additive. However, as the inhibition levels reached 80% to 90%, the interaction shifted towards slight antagonism, suggesting that higher concentrations of quercetin may interfere with or diminish the efficacy of AM12 at these concentrations. This shift from an additive to antagonistic effect could be due to complex biological interactions, possibly involving competitive or overlapping pathways between quercetin and AM12 at higher proteasome inhibition thresholds. By analyzing the IC50 values and m values from Figure 4 and Figure 5, respectively, important conclusions about the potency and dose–response characteristics of AM12 and quercetin alone and their combination could be drawn. As above-mentioned, AM12 showed an IC50 value of 12.17 ± 1.80 µM and an m1 equal to 0.7785, which indicates a relatively higher concentration to inhibit 50% of proteasome activity and a negative influence for the likelihood of subsequent binding. Quercetin showed an IC50 of 2.96 ± 0.77 µM and an m2 value of 2.4004. Therefore, quercetin is more potent than AM12 for the inhibition of the β5 subunit of proteasome. The m2 value of 2.4004 is notably higher than 1, suggesting a strong positive cooperativity. These data indicate that quercetin exhibits a steep, sigmoidal dose–response curve, where the binding of one quercetin molecule enhances further binding, resulting in a sharp increase in inhibitory activity once a certain threshold concentration is reached. The combination of AM12 + quercetin yielded an IC50 of 7.9 ± 1.80 µM and an m1,2 value of 1.2958 (molar ratio of 4.11:1). The IC50 of the combination is lower than that of AM12 alone but higher with respect to that of quercetin alone. However, the m1,2 value of 1.2958 indicates a more cooperative, but not extremely sigmoidal, interaction in the combination. Overall, quercetin alone shows a greater potency and stronger positive cooperativity than AM12, while the combination of AM12 and quercetin improves the potency of AM12 but does not fully match the strong positive cooperativity exhibited by quercetin on its own. The combination presents a moderately cooperative dose–response profile, which could offer a balanced approach to achieving effective proteasome inhibition with potentially lower toxicity.
4. Materials and Methods
AM12 was synthesized by our research group, as we already reported [18]. Synthesis was carried out starting from the commercially available starting material (i.e., 6,7-dimethoxyisoquinolin-1(2H)-one, Sigma Aldrich-Merck Life Science, Milan, Italy) in a scale of 5 mmol and 288 mg were obtained. NMR spectra, yields, retention factors, and consistency were comparable with those known in the literature. The overall yield was confirmed (17.1% vs 16.3%). Curcumin and quercetin were purchased from Sigma Aldrich-Merck Life Science (Milan, Italy). The human erythrocyte 20S proteasome was purchased from Enzo Life Science (Farmingdale, NY, USA).
Preliminary screening on the 20S proteasome was performed at a concentration of 100 µM, 1 µM and 0.1 µM to identify the range of activity of AM12, curcumin and quercetin. An equivalent amount of DMSO (Sigma Aldrich-Merck Life Science, Milan, Italy) was used as a negative control; meanwhile, the proteasome inhibitor MG-132 (Cbz-Leu-Leu-Leu-H, Sigma Aldrich-Merck Life Science, Milan, Italy) was used as the positive control. The product release from hydrolysis of the fluorogenic substrate specific for the chymotrypsin-like (ChT-L) activity of the constitutive proteasome (Suc-LLVY-AMC, Bachem, Bubendorf, Switzerland) was determined continuously over a period of 10 min at 30 °C. The assay buffer is composed of 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 0.03% SDS (Sigma Aldrich-Merck Life Science, Milan, Italy). Stock solutions for the three inhibitors were prepared at 20 mM in DMSO. In particular, 2.1 mg of AM12, 1.5 mg of curcumin, and 1.9 mg of quercetin were diluted in 292.94, 203.59, and 314.32 µL of DMSO, respectively. Starting from these, the appropriate dilutions led to the desired concentrations.
In the various assays, AM12, curcumin, and quercetin were tested separately twice in duplicate in 96-well plates (BRAND®, Wertheim, Germany) in a total volume of 200 µL. The following concentrations were used: (i) for AM12, 100 µM, 80 µM, 60 µM, 40 µM, 20 µM, 10 µM, and 1 µM; (ii) for curcumin, 20 µM, 10 µM, 5 µM, 1 µM, 0.1 µM, 0.01 µM, and 0.001 µM; and (iii) for quercetin, 100 µM, 10 µM, 5 µM, 1 µM, 0.1 µM, 0.01 µM, and 0.001 µM.
The fluorescence of the product AMC (7-amino-4-methylcoumarin) released from substrate hydrolysis was measured using an Infinite 200 PRO microplate reader (Tecan, Männedorf, Switzerland). The measurements were taken at room temperature with an excitation filter set to 380 nm and an emission filter set to 460 nm, which are appropriate for detecting AMC’s fluorescent signal. Results are expressed as IC50 values ± SD and have been calculated by fitting the progress curves to the four-parameter IC50 Equation by GraphPad Prism 5.0.3 (GraphPad software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) (1):
with y [∆F/min] as the substrate hydrolysis rate, ymax as the maximum value of the dose−response curve, measured at an inhibitor concentration of [I] = 0 µM, with ymin as the minimum value, obtained at high inhibitor concentrations, and s as the Hill coefficient.
The inhibitory constants (Ki) were calculated according to the Cheng–Prusoff Equation (2):
with [S] as the substrate concentration and Km as the Michaelis–Menten constant.
Ki = IC50/(1 + [S]/Km)
For the calculation of the combination index of the combination AM12 + curcumin or quercetin, six data points were used: 1/32 × IC50F1+F2, 1/4 × IC50F1+F2, 1/2 × IC50F1+F2, IC50F1+F2, 2 × IC50F1+F2, and 4 × IC50F1+F2, where F1 = AM12 while F2 = curcumin or quercetin (See Table 1 and Table 2). Once the IC50 values ± SD for the combination were calculated, each dose–response curve was converted into the corresponding Median Effect Plot, where the maximum response is 1 instead of 100 of the dose–response curve. The fraction of the enzyme that is inhibited is named “affected fraction” (fa), while the fraction of the enzyme that is not inhibited is named “unaffected fraction” (fu), where fa + fu = 1. The Median Effect Plot is obtained by plotting the log (fa/fu) versus the log (D) on the x-axis, in such a way to calculate the “m value”, which represents the Hill-type coefficient, which means the sigmoidal trend (or S-shape) of the dose–response curve.
Once the three different m values were calculated by Grafit software (Version 5.0; Erithacus Software Limited, East Grinstead, West Sussex, UK), we established by means of the Median Effect Equation (3) the single doses that are able to inhibit the enzyme for a specific percentage of inhibition [37,38]:
D = IC50 [fa/fu]1/m
The Chou–Talalay method was then applied to evaluate multiple drug effects [37,38]. The CI for mutually exclusive drugs, which act independently, was calculated on the basis of the following Equation (4):
where the (IC50)1 and (IC50)2 were obtained by dose–response curves, and D1 and D2 are the concentrations able to induce a specific percentage of human erythrocyte proteasome inhibition obtained by the Median Effect Equation (3).
CI = [(D)1/(IC50)1] + [(D)2/(IC50)2]
5. Conclusions
This study investigated the combination of the synthetic proteasome inhibitor AM12 with the nutraceuticals curcumin and quercetin to evaluate their combined effects. The combination of AM12 with curcumin showed a pronounced synergistic interaction that enhances proteasome inhibition, particularly at higher doses, indicating complementary mechanisms of action. In contrast, the combination of AM12 with quercetin exhibited an initially additive effect that shifts to slight antagonism at higher concentrations, underscoring the complex interactions that can arise between these agents. The observed differences in dose–response profiles highlight the necessity of optimizing dosages to maximize the inhibitory properties. Ultimately, these findings suggest that the use of the selective inhibitor of the β5 site of the proteasome alongside the selected nutraceuticals can significantly influence treatment outcomes and warrant further investigation for clinical applications.
Future studies will focus on testing the cytotoxic effects of individual inhibitors and the AM12 + curcumin combination on multiple myeloma and solid tumor cell cultures. A key goal of these studies will be to assess whether combining AM12 with curcumin can reduce toxicity, which is a critical concern in cancer therapy. This approach aligns with the broader therapeutic strategy of using drug combinations to enhance efficacy while minimizing adverse effects, potentially leading to more effective and safer anti-tumor treatments.
Finally, it is important to highlight that, despite the current reference models for evaluating drug synergism having advanced, all of them, including the Chou and Talalay method, still face significant limitations that can impact the interpretation of obtained data about the combination [54]. Indeed, the term synergy is often misused or poorly defined, leading to misconceptions about the true nature of drug interactions. Additionally, a lack of standard reference models and the complexities involved in optimizing dose ratios hinder effective synergy analysis. Another important limitation is the need to optimize the dose ratios in drug combinations, as the interaction of two drugs can create a new dose–effect relationship, necessitating experiments to identify the most effective ratios for achieving synergy before advancing to the in vivo tests and clinical trials. Therefore, despite the progress, existing models for evaluating drug interactions still have limitations, necessitating careful selection based on the study type and future research should integrate various approaches to rigorously assess synergism and elucidate mechanisms of action, potentially utilizing in silico models for further evaluation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.P., J.S., F.D.L., M.L.C., M.Z. and R.E.; Investigation, C.D.C. and R.E; writing—original draft, R.E.; writing—review and editing, S.P., M.Z. and R.E.; supervision, M.Z. and R.E.; funding acquisition, R.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the “Fondo per il finanziamento delle attività base di ricerca” (FFABR 2022), financed by the University of Messina.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Amm, I.; Sommer, T.; Wolf, D.H. Protein quality control and elimination of protein waste: The role of the ubiquitin–proteasome system. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2014, 1843, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.; Wu, H. Ubiquitination-Proteasome System (UPS) and Autophagy Two Main Protein Degradation Machineries in Response to Cell Stress. Cells 2022, 11, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMartino, G.N.; Gillette, T.G. Proteasomes: Machines for All Reasons. Cell 2007, 129, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecker, S.H.; Goldberg, A.L.; Mitch, W.E. Protein Degradation by the Ubiquitin–Proteasome Pathway in Normal and Disease States. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 1807–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bard, J.A.; Goodall, E.A.; Greene, E.R.; Jonsson, E.; Dong, K.C.; Martin, A. Structure and Function of the 26S Proteasome. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2018, 87, 697–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livneh, I.; Cohen-Kaplan, V.; Cohen-Rosenzweig, C.; Avni, N.; Ciechanover, A. The life cycle of the 26S proteasome: From birth, through regulation and function, and onto its death. Cell Res. 2016, 26, 869–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunjappu, M.J.; Hochstrasser, M. Assembly of the 20S proteasome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2014, 1843, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Oanca, G.; Mondal, D.; Warshel, A. Exploring the Proteolysis Mechanism of the Proteasomes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 5626–5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Cho, J.; Song, E.J. Ubiquitin–proteasome system (UPS) as a target for anticancer treatment. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2020, 43, 1144–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Costanzo, A.; Del Gaudio, N.; Conte, L.; Altucci, L. The Ubiquitin Proteasome System in Hematological Malignancies: New Insight into Its Functional Role and Therapeutic Options. Cancers 2020, 12, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlati, F.; Lee, S.J.; Aujay, M.; Suzuki, E.; Levitsky, K.; Lorens, J.B.; Micklem, D.R.; Ruurs, P.; Sylvain, C.; Lu, Y.; et al. Carfilzomib can induce tumor cell death through selective inhibition of the chymotrypsin-like activity of the proteasome. Blood 2009, 114, 3439–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, R.C.; Bross, P.F.; Farrell, A.T.; Pazdur, R. Velcade®: U.S. FDA Approval for the Treatment of Multiple Myeloma Progressing on Prior Therapy. Oncologist 2003, 8, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, G.; Zhang, L.; Wu, M.; Su, R. The Efficacy and Mechanism of Proteasome Inhibitors in Solid Tumor Treatment. Recent Pat. Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 2022, 17, 268–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xu, J.; Zhu, W.; Shu, Y.; Liu, P. Efficacy of Therapy with Bortezomib in Solid Tumors: A Review based on 32 Clinical Trials. Future Oncol. 2014, 10, 1795–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, I.-T.; Dhungel, B.; Shrestha, R.; Bridle, K.R.; Crawford, D.H.G.; Jayachandran, A.; Steel, J.C. Spotlight on Bortezomib: Potential in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2018, 28, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alwahsh, M.; Farhat, J.; Talhouni, S.; Hamadneh, L.; Hergenroeder, R. Bortezomib advanced mechanisms of action in multiple myeloma, solid and liquid tumors along with its novel therapeutic applications. EXCLI J. 2023, 22, 146–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meregalli, C.; Maricich, Y.; Cavaletti, G.; Canta, A.; Carozzi, V.A.; Chiorazzi, A.; Newbold, E.; Marmiroli, P.; Ceresa, C.; Diani, A.; et al. Reversal of Bortezomib-Induced Neurotoxicity by Suvecaltamide, a Selective T-Type Ca-Channel Modulator, in Preclinical Models. Cancers 2021, 13, 5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettari, R.; Iraci, N.; Di Chio, C.; Previti, S.; Danzè, M.; Zappalà, M. Development of isoquinolinone derivatives as immunoproteasome inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 55, 128478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettari, R.; Cerchia, C.; Maiorana, S.; Guccione, M.; Novellino, E.; Bitto, A.; Grasso, S.; Lavecchia, A.; Zappalà, M. Development of Novel Amides as Noncovalent Inhibitors of Immunoproteasomes. ChemMedChem 2019, 14, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccari, R.; Ettari, R.; Adornato, I.; Naß, A.; Wolber, G.; Bitto, A.; Mannino, F.; Aliquò, F.; Bruno, G.; Nicolò, F.; et al. Identification of 2-thioxoimidazolidin-4-one derivatives as novel noncovalent proteasome and immunoproteasome inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giovanni, C.; Ettari, R.; Sarno, S.; Rotondo, A.; Bitto, A.; Squadrito, F.; Altavilla, D.; Schirmeister, T.; Novellino, E.; Grasso, S.; et al. Identification of noncovalent proteasome inhibitors with high selectivity for chymotrypsin-like activity by a multistep structure-based virtual screening. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 121, 578–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troiano, V.; Scarbaci, K.; Ettari, R.; Micale, N.; Cerchia, C.; Pinto, A.; Schirmeister, T.; Novellino, E.; Grasso, S.; Lavecchia, A.; et al. Optimization of peptidomimetic boronates bearing a P3 bicyclic scaffold as proteasome inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 83, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarbaci, K.; Troiano, V.; Ettari, R.; Pinto, A.; Micale, N.; Di Giovanni, C.; Cerchia, C.; Schirmeister, T.; Novellino, E.; Lavecchia, A.; et al. Development of Novel Selective Peptidomimetics Containing a Boronic Acid Moiety, Targeting the 20S Proteasome as Anticancer Agents. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 1801–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarbaci, K.; Troiano, V.; Micale, N.; Ettari, R.; Tamborini, L.; Di Giovanni, C.; Cerchia, C.; Grasso, S.; Novellino, E.; Schirmeister, T.; et al. Identification of a new series of amides as non-covalent proteasome inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 76, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrizzo, A.; Moltedo, O.; Damato, A.; Martinello, K.; Di Pietro, P.; Oliveti, M.; Acernese, F.; Giugliano, G.; Izzo, R.; Sommella, E.; et al. New Nutraceutical Combination Reduces Blood Pressure and Improves Exercise Capacity in Hypertensive Patients Via a Nitric Oxide-Dependent Mechanism. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e014923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimifard, M.; Baeeri, M.; Mousavi, T.; Azarnezhad, A.; Haghi-Aminjan, H.; Abdollahi, M. Combination therapy of cisplatin and resveratrol to induce cellular aging in gastric cancer cells: Focusing on oxidative stress, and cell cycle arrest. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 13, 1068863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Cheng, H.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Z.G.; Zhang, Y.F.; De Luo, B. Synergistic inhibitory effects by the combination of gefitinib and genistein on NSCLC with acquired drug-resistance in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 39, 4971–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, V.; Nagpal, M.; Singh, I.; Singh, M.; Dhingra, G.A.; Huanbutta, K.; Dheer, D.; Sharma, A.; Sangnim, T. A Comprehensive Review on Nutraceuticals: Therapy Support and Formulation Challenges. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.-P.; Chuang, C.-H.; Lee, I.; Yang, N.-C. Lycopene in Combination With Sorafenib Additively Inhibits Tumor Metastasis in Mice Xenografted With Lewis Lung Carcinoma Cells. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 886988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Jiang, W.; Jia, H.; Lei, M. Synergistically Anti-Multiple Myeloma Effects: Flavonoid, Non-Flavonoid Polyphenols, and Bortezomib. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucquier, J.; Guedj, M. Analysis of drug combinations: Current methodological landscape. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3, e00149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourkavoos, N. Unique Risks, Benefits, and Challenges of Developing Drug-Drug Combination Products in a Pharmaceutical Industrial Setting. Comb. Prod. Ther. 2012, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Chio, C.; Previti, S.; Totaro, N.; De Luca, F.; Allegra, A.; Schirmeister, T.; Zappalà, M.; Ettari, R. Dipeptide Nitrile CD34 with Curcumin: A New Improved Combination Strategy to Synergistically Inhibit Rhodesain of Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Chio, C.; Previti, S.; De Luca, F.; Bogacz, M.; Zimmer, C.; Wagner, A.; Schirmeister, T.; Zappalà, M.; Ettari, R. Drug Combination Studies of the Dipeptide Nitrile CD24 with Curcumin: A New Strategy to Synergistically Inhibit Rhodesain of Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettari, R.; Previti, S.; Di Chio, C.; Maiorana, S.; Allegra, A.; Schirmeister, T.; Zappalà, M. Drug Synergism: Studies of Combination of RK-52 and Curcumin against Rhodesain of Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettari, R.; Previti, S.; Maiorana, S.; Allegra, A.; Schirmeister, T.; Grasso, S.; Zappalà, M. Drug combination studies of curcumin and genistein against rhodesain of Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 33, 3577–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.-C. Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C.; Talalay, P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv. Enzym. Regul. 1984, 22, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewlings, S.J.; Kalman, D.S. Curcumin: A Review of Its Effects on Human Health. Foods 2017, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuloria, S.; Mehta, J.; Chandel, A.; Sekar, M.; Rani, N.N.I.M.; Begum, M.Y.; Subramaniyan, V.; Chidambaram, K.; Thangavelu, L.; Nordin, R.; et al. A Comprehensive Review on the Therapeutic Potential of Curcuma longa Linn. in Relation to its Major Active Constituent Curcumin. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 820806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Bordoloi, D.; Padmavathi, G.; Monisha, J.; Roy, N.K.; Prasad, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin, the golden nutraceutical: Multitargeting for multiple chronic diseases. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1325–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordoloi, D.; Roy, N.K.; Monisha, J.; Padmavathi, G.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Multi-Targeted Agents in Cancer Cell Chemosensitization: What We Learnt from Curcumin Thus Far. Recent Pat. Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 2016, 11, 67–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Ji, C.; Mayfield, J.E.; Goel, A.; Xiao, J.; Dixon, J.E.; Guo, X. Ancient drug curcumin impedes 26S proteasome activity by direct inhibition of dual-specificity tyrosine-regulated kinase 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 8155–8160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milacic, V.; Banerjee, S.; Landis-Piwowar, K.R.; Sarkar, F.H.; Majumdar, A.P.N.; Dou, Q.P. Curcumin Inhibits the Proteasome Activity in Human Colon Cancer Cells In vitro and In vivo. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7283–7292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Fu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, M.; Wang, C. Curcumin inhibits proteasome activity in triple-negative breast cancer cells through regulating p300/miR-142-3p/PSMB5 axis. Phytomedicine 2020, 78, 153312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabanelli, R.; Brogi, S.; Calderone, V. Improving Curcumin Bioavailability: Current Strategies and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoncini-Silva, C.; Vlad, A.; Ricciarelli, R.; Fassini, P.G.; Suen, V.M.M.; Zingg, J.-M. Enhancing the Bioavailability and Bioactivity of Curcumin for Disease Prevention and Treatment. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmannová, A.; Bojňanská, T.; Musilová, J.; Lidiková, J.; Cifrová, M. Quercetin as one of the most abundant represented biological valuable plant components with remarkable chemoprotective effects—A review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghababaei, F.; Hadidi, M. Recent Advances in Potential Health Benefits of Quercetin. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, A.; Imran, M.; Khan, I.A.; Ur-Rehman, M.; Gilani, S.A.; Mehmood, Z.; Mubarak, M.S. Anticancer potential of quercetin: A comprehensive review. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 2109–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.A.; Mahmood, S.; Hilles, A.R.; Ali, A.; Khan, M.Z.; Zaidi, S.A.A.; Iqbal, Z.; Ge, Y. Quercetin as a Therapeutic Product: Evaluation of Its Pharmacological Action and Clinical Applications—A Review. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.-L. Inhibitory Effect of Flavonoids on 26S Proteasome Activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9706–9715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.-L.; Wang, C.-H. Combination of quercetin and tannic acid in inhibiting 26S proteasome affects S5a and 20S expression, and accumulation of ubiquitin resulted in apoptosis in cancer chemoprevention. Biol. Chem. 2013, 394, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, D.; Vale, N. Evaluation of synergism in drug combinations and reference models for future orientations in oncology. Curr. Res. Pharmacol. Drug Discov. 2022, 3, 100110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).