Pentadecanoic Acid-Releasing PDMS: Towards a New Material to Prevent S. epidermidis Biofilm Formation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
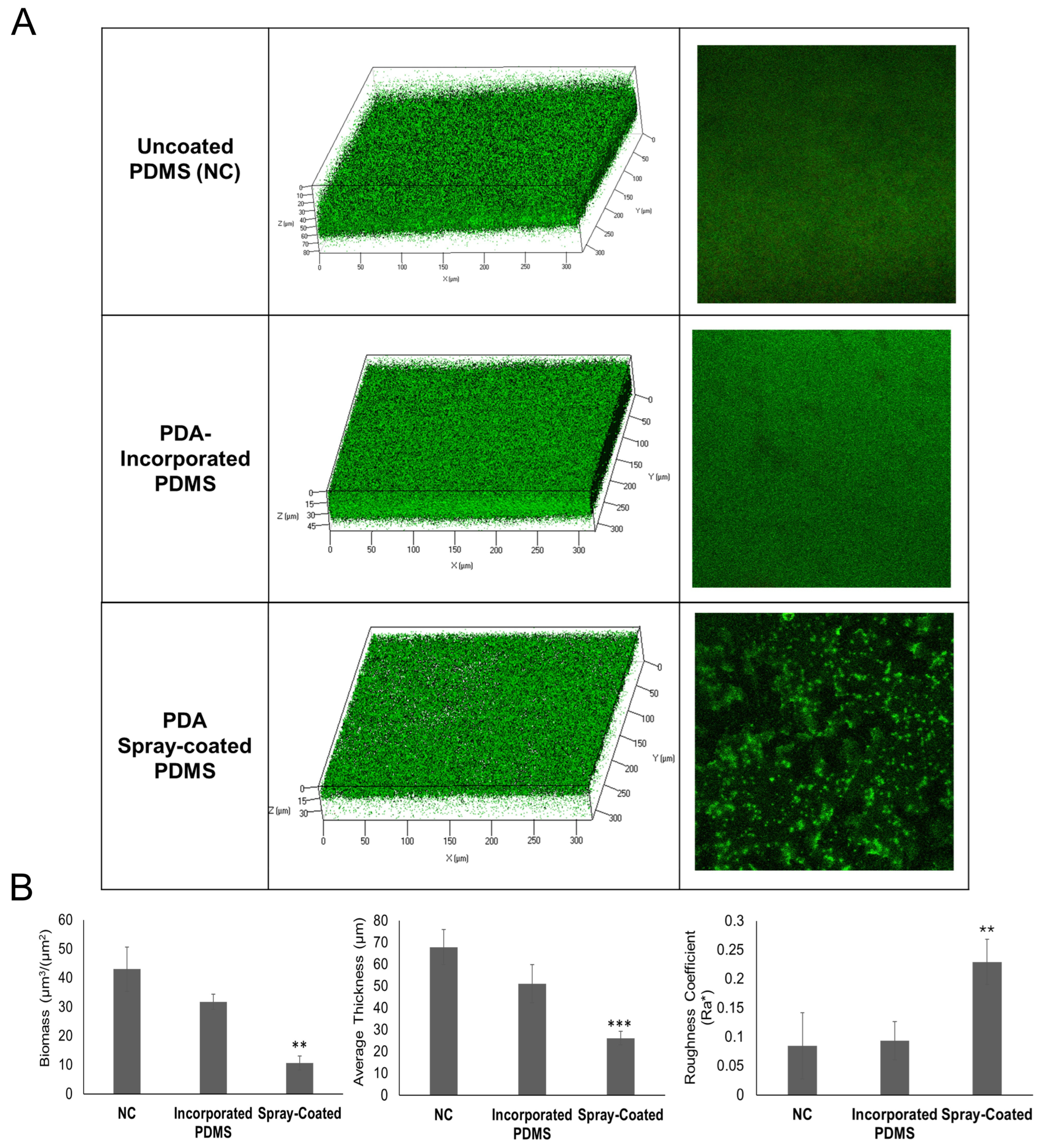
2.1. Optimizing Antibiofilm Coatings of PDMS: Spray-Coating and Incorporation of PDA in PDMS
2.2. Evaluation of Biofilm Formation on Coated PDMS in a Flow Cell System
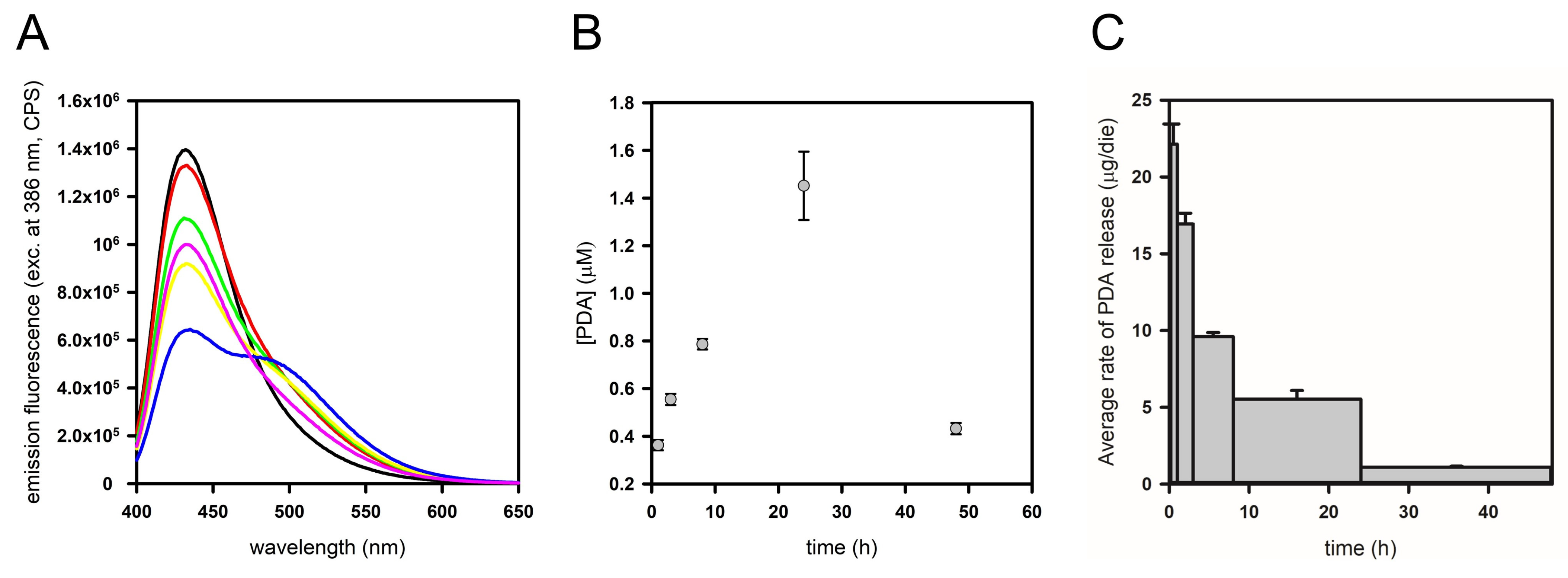
2.3. PDA Release Kinetics from PDMS Functionalized by Spray-Coating in a Fixed-Volume Setup
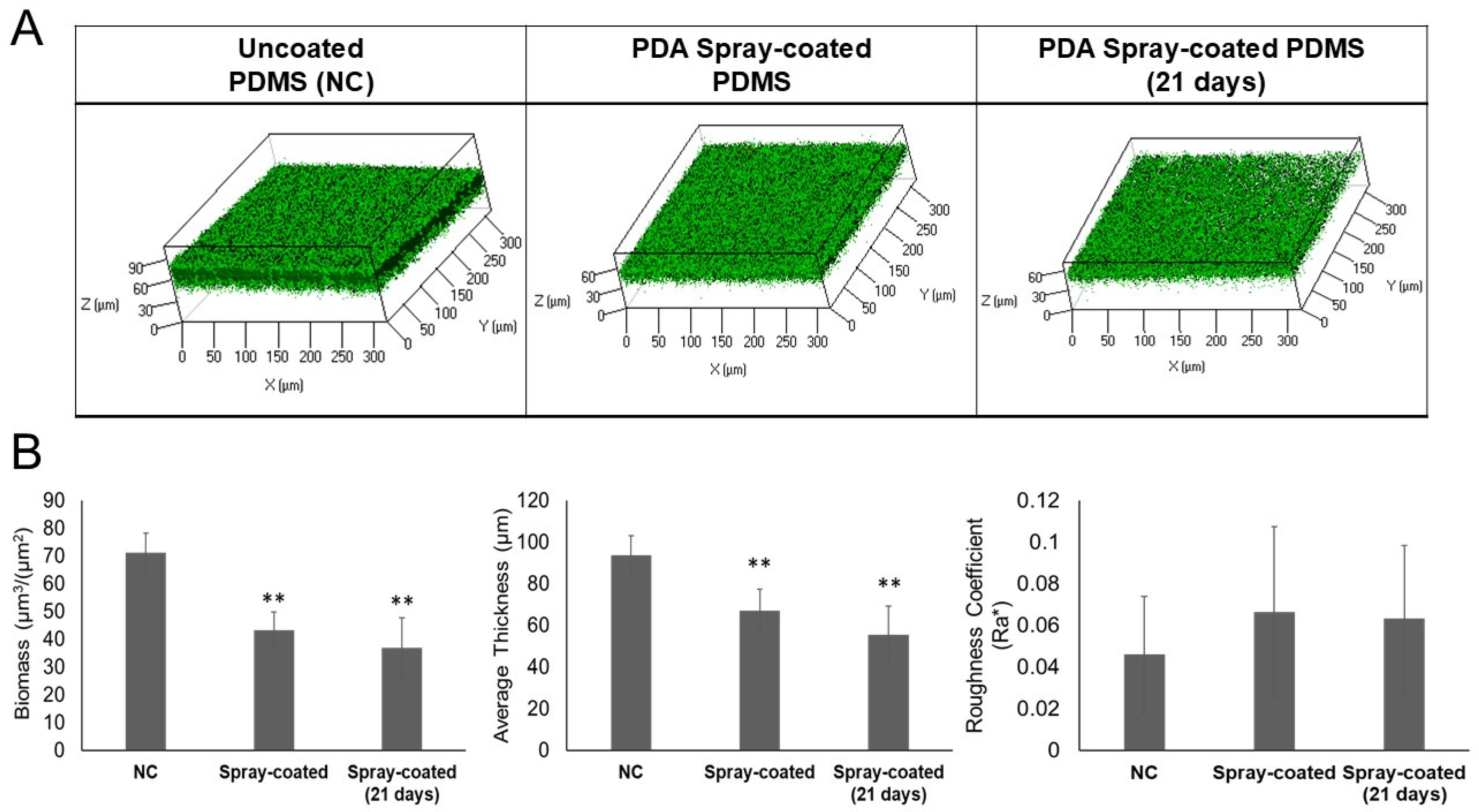
2.4. Long-Term Efficacy of the Antibiofilm Coating on Biofilm Formation in a Flow Cell System
2.5. Evaluation of the Drug-Release Capability of PDA Spray-Coated PDMS in a Cell Flow System and Biocompatibility of Functionalized Material
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
4.2. Preparation of the Antibiofilm PDMS Coatings
4.2.1. Spray-Coating
4.2.2. Incorporation of PDA on/in PDMS
4.3. Contact Angle Measurements
4.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis (FTIR)
4.5. Antibiofilm PDMS Coating Effect on S. epidermidis Biofilm Formation in a Flow Cell System
4.6. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Analysis
4.7. Determination of PDA Release Kinetics from PDMS
4.8. The Antibiofilm PDMS Coating Biocompatibility Assay
4.9. Statistics and Reproducibility of Results
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, Y.; He, L.; Asiamah, T.K.; Otto, M. Colonization of Medical Devices by Staphylococci. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 3141–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatoon, Z.; McTiernan, C.D.; Suuronen, E.J.; Mah, T.F.; Alarcon, E.I. Bacterial Biofilm Formation on Implantable Devices and Approaches to Its Treatment and Prevention. Heliyon 2018, 4, e01067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Aggarwal, A.; Khan, F. Medical Device-Associated Infections Caused by Biofilm-Forming Microbial Pathogens and Controlling Strategies. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhrour, N.; Nibbering, P.H.; Bendali, F. Medical Device-Associated Biofilm Infections and Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens. Pathogens 2024, 13, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigmon, M.M.; Brigmon, R.L. Infectious Diseases Impact on Biomedical Devices and Materials. Biomed. Mater. Devices 2023, 1, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Qiao, S.; Qin, H.; Jandt, K.D. Antibacterial Designs for Implantable Medical Devices: Evolutions and Challenges. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francolini, I.; Donelli, G. Prevention and Control of Biofilm-Based Medical-Device-Related Infections. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Xia, G.; Shi, C.; Wan, J.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, M.; He, H.; et al. Therapeutic Strategies against Bacterial Biofilms. Fundam. Res. 2021, 1, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrocola, G.; Campoccia, D.; Motta, C.; Montanaro, L.; Arciola, C.R.; Speziale, P. Colonization and Infection of Indwelling Medical Devices by Staphylococcus Aureus with an Emphasis on Orthopedic Implants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcus epidermidis—The “accidental” Pathogen. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brescó, M.S.; Harris, L.G.; Thompson, K.; Stanic, B.; Morgenstern, M.; O’Mahony, L.; Richards, R.G.; Moriarty, T.F. Pathogenic Mechanisms and Host Interactions in Staphylococcus epidermidis Device-Related Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, T.D.; Tejera, N.; McNamara, I.; Langridge, G.C.; Wain, J.; Poolman, M.; Singh, D. Genome-Scale Metabolic Modelling Approach to Understand the Metabolism of the Opportunistic Human Pathogen Staphylococcus epidermidis RP62A. Metabolites 2022, 12, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méric, G.; Mageiros, L.; Pensar, J.; Laabei, M.; Yahara, K.; Pascoe, B.; Kittiwan, N.; Tadee, P.; Post, V.; Lamble, S.; et al. Disease-Associated Genotypes of the Commensal Skin Bacterium Staphylococcus Epidermidis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranjec, C.; Angeles, D.M.; Mårli, M.T.; Fernández, L.; García, P.; Kjos, M.; Diep, D.B. Staphylococcal Biofilms: Challenges and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowrishankar, S.; Pandian, S.K. Modulation of Staphylococcus epidermidis (RP62A) Extracellular Polymeric Layer by Marine Cyclic Dipeptide-Cyclo(L-Leucyl-L-Prolyl) Thwarts Biofilm Formation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Choi, Y.; Park, J.; Choi, J. Gelatin-Gallic Acid Microcomplexes Release GO/Cu Nanomaterials to Eradicate Antibiotic-Resistant Microbes and Their Biofilm. ACS Infect. Dis. 2023, 9, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, L.; Abdo, A.I.; Coenye, T.; Swift, S.; Zannettino, A.; Süss, R.; Richter, K. In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation of Diethyldithiocarbamate with Copper Ions and Its Liposomal Formulation for the Treatment of Staphylococcus Aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilms. Biofilm 2023, 5, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamilvanan, S.; Venkateshan, N.; Ludwig, A. The Potential of Lipid- and Polymer-Based Drug Delivery Carriers for Eradicating Biofilm Consortia on Device-Related Nosocomial Infections. J. Control. Release 2008, 128, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siciliano, V.; Passerotto, R.A.; Chiuchiarelli, M.; Leanza, G.M.; Ojetti, V. Difficult-to-Treat Pathogens: A Review on the Management of Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. Life 2023, 13, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, M.; Crulhas, B.P.; Alves, F.C.B.; Pereira, A.F.M.; Andrade, B.F.M.T.; Barbosa, L.N.; Furlanetto, A.; Lyra, L.P.d.S.; Rall, V.L.M.; Júnior, A.F. Antibacterial and Anti-Biofilm Activities of Cinnamaldehyde against S. epidermidis. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 126, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Panda, A.K.; De Mandal, S.; Shakeel, M.; Bisht, S.S.; Khan, J. Natural Anti-Biofilm Agents: Strategies to Control Biofilm-Forming Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 566325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artini, M.; Papa, R.; Vrenna, G.; Trecca, M.; Paris, I.; D’Angelo, C.; Tutino, M.L.; Parrilli, E.; Selan, L. Antarctic Marine Bacteria as a Source of Anti-Biofilm Molecules to Combat ESKAPE Pathogens. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, R.; Parrilli, E.; Sannino, F.; Barbato, G.; Tutino, M.L.; Artini, M.; Selan, L. Anti-Biofilm Activity of the Antarctic Marine Bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125. Res. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, R.; Vrenna, G.; D’angelo, C.; Casillo, A.; Relucenti, M.; Donfrancesco, O.; Corsaro, M.M.; Fiscarelli, E.V.; Assanti, V.T.G.; Tutino, M.L.; et al. Anti-Virulence Activity of the Cell-Free Supernatant of the Antarctic Bacterium Psychrobacter sp. TAE2020 against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates from Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrilli, E.; Papa, R.; Carillo, S.; Tilotta, M.; Casillo, A.; Sannino, F.; Cellini, A.; Artini, M.; Selan, L.; Corsaro, M.M.; et al. Anti-Biofilm Activity of Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis Tac125 against Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilm: Evidence of a Signal Molecule Involvement? Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2015, 28, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, C.; Casillo, A.; Melchiorre, C.; Lauro, C.; Corsaro, M.M.; Carpentieri, A.; Tutino, M.L.; Parrilli, E. CATASAN Is a New Anti-Biofilm Agent Produced by the Marine Antarctic Bacterium Psychrobacter sp. TAE2020. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casillo, A.; Papa, R.; Ricciardelli, A.; Sannino, F.; Ziaco, M.; Tilotta, M.; Selan, L.; Marino, G.; Corsaro, M.M.; Tutino, M.L.; et al. Anti-Biofilm Activity of a Long-Chain Fatty Aldehyde from Antarctic Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125 against Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilm. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardelli, A.; Casillo, A.; Papa, R.; Monti, D.M.; Imbimbo, P.; Vrenna, G.; Artini, M.; Selan, L.; Corsaro, M.M.; Tutino, M.L.; et al. Pentadecanal Inspired Molecules as New Anti-Biofilm Agents against Staphylococcus epidermidis. Biofouling 2018, 34, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardelli, A.; Casillo, A.; Corsaro, M.M.; Tutino, M.L.; Parrilli, E.; Van Der Mei, H.C. Pentadecanal and Pentadecanoic Acid Coatings Reduce Biofilm Formation of Staphylococcus epidermidis on PDMS. Pathog. Dis. 2020, 78, ftaa012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, I.; Souza, A.; Sousa, P.; Ribeiro, J.; Castanheira, E.M.S.; Lima, R.; Minas, G. Properties and Applications of PDMS for Biomedical Engineering: A Review. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariati, R.; Sales, F.; Souza, A.; Lima, R.A.; Ribeiro, J. Polydimethylsiloxane Composites Characterization and Its Applications: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, W.; Hu, X.; He, W.; Zhan, R.; Liu, M.; Zhou, D.; Huang, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, Z.; Fei, G.; et al. Biointerfaces Polydimethylsiloxane Incorporated with Reduced Graphene Oxide (RGO) Sheets for Wound Dressing Application: Preparation and Characterization. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 166, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.P.; Salieb-Beugelaar, G.B.; Hunziker, P. PDMS with Designer Functionalities—Properties, Modifications Strategies, and Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 83, 97–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Cheng, E.; Whitley, J.W.; Horne, R.R.; Leigh, B.; Xu, L.; Jones, B.D.; Guymon, C.A.; Hansen, M.R. Photograftable Zwitterionic Coatings Prevent Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis Adhesion to PDMS Surfaces. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richieri, G.V.; Ogata, R.T.; Kleinfeld, A.M. A Fluorescently Labeled Intestinal Fatty Acid Binding Protein: Interactions with Fatty Acids and Its Use in Monitoring Free Fatty Acids. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 23495–23501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richieri, G.V.; Ogata, R.T.; Kleinfeld, A.M. The Measurement of Free Fatty Acid Concentration with the Fluorescent Probe ADIFAB: A Practical Guide for the Use of the ADIFAB Probe. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1999, 192, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggiano, S.; Ronda, L.; Raboni, S.; Sartor, F.; Cavatorta, V.; Sgarbi, E.; Caivano, G.; Pertile, M.; Mozzarelli, A. Phospholipid Components of the Synthetic Pulmonary Surfactant CHF5633 Probed by Fluorescence Spectroscopy. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 553, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggiano, S.; Ronda, L.; Raboni, S.; Mozzarelli, A. Data in Brief ADIFAB Fluorescence Data Used for the Quantification of Free Fatty Acids in Media at Different pH. Data Br. 2019, 22, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richieri, G.Y.; Ogata, R.T.; Kleinfeld, A.M. Thermodynamic and Kinetic Properties of Fatty Acid Interactions with Rat Liver Fatty Acid-Binding Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 31068–31074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simard, J.R.; Kamp, F.; Hamilton, J.A. Acrylodan-Labeled Intestinal Fatty Acid-Binding Protein to Measure Concentrations of Unbound Fatty Acids. Lipids 2007, 400, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Cheng, L.; Hong, S.; Yang, C.; Lin, Y. Preparation of Anti-Fouling Silicone Elastomers by Covalent Immobilization of Carboxybetaine. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 88456–88463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yin, R.; Cheng, J.; Lin, J. Bacterial Biofilm Formation on Biomaterials and Approaches to Its Treatment and Prevention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Mohler, J.; Mahajan, S.D.; Schwartz, S.A.; Bruggemann, L.; Aalinkeel, R. Microbial Biofilm: A Review on Formation, Infection, Antibiotic Resistance, Control Measures, and Innovative Treatment. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadabadi, H.Y.; Yu, K.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N. Surface Modification Approaches for Prevention of Implant Associated Infections. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 193, 111116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruellhoff, K.; Fiedler, J.; Möller, M.; Groll, J.; Brenner, R.E. Surface Coating Strategies to Prevent Biofilm Formation on Implant Surfaces. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2010, 33, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francolini, I.; Vuotto, C.; Piozzi, A.; Donelli, G. Antifouling and Antimicrobial Biomaterials: An Overview. Apmis 2017, 125, 392–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Kleintschek, T.; Rieder, A.; Cheng, Y.; Baumbach, T.; Obst, U.; Schwartz, T.; Levkin, P.A. Hydrophobic Liquid-Infused Porous Polymer Surfaces for Antibacterial Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 6704–6711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negut, I.; Bita, B.; Groza, A. Polymeric Coatings and Antimicrobial Peptides as Efficient Systems for Treating Implantable Medical Devices Associated-Infections. Polymers 2022, 14, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, J.; Sarkhel, S.; Mukherjee, N.; Jaiswal, A. Nanomaterial-Based Antimicrobial Coating for Biomedical Implants: New Age Solution for Biofilm-Associated Infections. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 45962–45980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, G.; Aveyard, J.; Fothergill, J.L.; McBride, F.; Raval, R.; D’Sa, R.A. Nitric Oxide Releasing Polymeric Coatings for the Prevention of Biofilm Formation. Polymers 2017, 9, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; McHale, G.; Dawson, J.; Armstrong, S.; Wells, G.; Han, R.; Liu, H.; Vollmer, W.; Stoodley, P.; Jakubovics, N.; et al. Slippery Liquid-Like Solid Surfaces with Promising Antibiofilm Performance under Both Static and Flow Conditions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 6307–6319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desrousseaux, C.; Sautou, V.; Descamps, S.; Traoré, O. Modification of the Surfaces of Medical Devices to Prevent Microbial Adhesion and Biofilm Formation. J. Hosp. Infect. 2013, 85, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Song, H.; Loh, J.; She, J.; Deng, L.; Bo, L. Grafting Antibiofilm Polymer Hydrogel Film onto Catheter by SARA SI-ATRP Chao. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2018, 29, 2106–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, J.B. Therapeutic Potential of Biofilm-Dispersing Enzymes. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2009, 32, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chiao, M. Anti-Fouling Coatings of Poly(Dimethylsiloxane) Devices for Biological and Biomedical Applications. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2015, 35, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, F.; Mirzadeh, H.; Katbab, A. Modification of Polysiloxane Polymers for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Polym. Int. 2001, 50, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrea, A.; Molchanova, N.; Jenssen, H. Antibiofilm Peptides and Peptidomimetics with Focus on Surface Immobilization. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, L.; Sorzabal Bellido, I.; Beckett, A.J.; Prior, I.A.; Fothergill, J.; Diaz Fernandez, Y.A.; Raval, R. One-Step Preparation of Antimicrobial Silicone Materials Based on PDMS and Salicylic Acid: Insights from Spatially and Temporally Resolved Techniques. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neut, D.; Van De Belt, H.; Van Horn, J.R.; Van Der Mei, H.C.; Busscher, H.J. Residual Gentamicin-Release from Antibiotic-Loaded Polymethylmethacrylate Beads after 5 Years of Implantation. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 1829–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadunissah, A.; Aazmi, S.; Abd Hamid, U.M.; Abdul-Aziz, A. Multidrug Resistance of Staphylococcus Epidermidis: An Emerging Threat to Global Health. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 12, 001–010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oss, C.J.; Good, R.J.; Chaudhury, M.K. Additive and Nonadditive Surface Tension Components and the Interpretation of Contact Angles. Langmuir 1988, 4, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D'Angelo, C.; Faggiano, S.; Imbimbo, P.; Viale, E.; Casillo, A.; Bettati, S.; Olimpo, D.; Tutino, M.L.; Monti, D.M.; Corsaro, M.M.; et al. Pentadecanoic Acid-Releasing PDMS: Towards a New Material to Prevent S. epidermidis Biofilm Formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910727
D'Angelo C, Faggiano S, Imbimbo P, Viale E, Casillo A, Bettati S, Olimpo D, Tutino ML, Monti DM, Corsaro MM, et al. Pentadecanoic Acid-Releasing PDMS: Towards a New Material to Prevent S. epidermidis Biofilm Formation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(19):10727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910727
Chicago/Turabian StyleD'Angelo, Caterina, Serena Faggiano, Paola Imbimbo, Elisabetta Viale, Angela Casillo, Stefano Bettati, Diana Olimpo, Maria Luisa Tutino, Daria Maria Monti, Maria Michela Corsaro, and et al. 2024. "Pentadecanoic Acid-Releasing PDMS: Towards a New Material to Prevent S. epidermidis Biofilm Formation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 19: 10727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910727
APA StyleD'Angelo, C., Faggiano, S., Imbimbo, P., Viale, E., Casillo, A., Bettati, S., Olimpo, D., Tutino, M. L., Monti, D. M., Corsaro, M. M., Ronda, L., & Parrilli, E. (2024). Pentadecanoic Acid-Releasing PDMS: Towards a New Material to Prevent S. epidermidis Biofilm Formation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(19), 10727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910727












