From Synaptic Physiology to Synaptic Pathology: The Enigma of α-Synuclein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Aggregation and Toxicity of α-Synuclein
3. Synaptic Location and Function of α-Synuclein
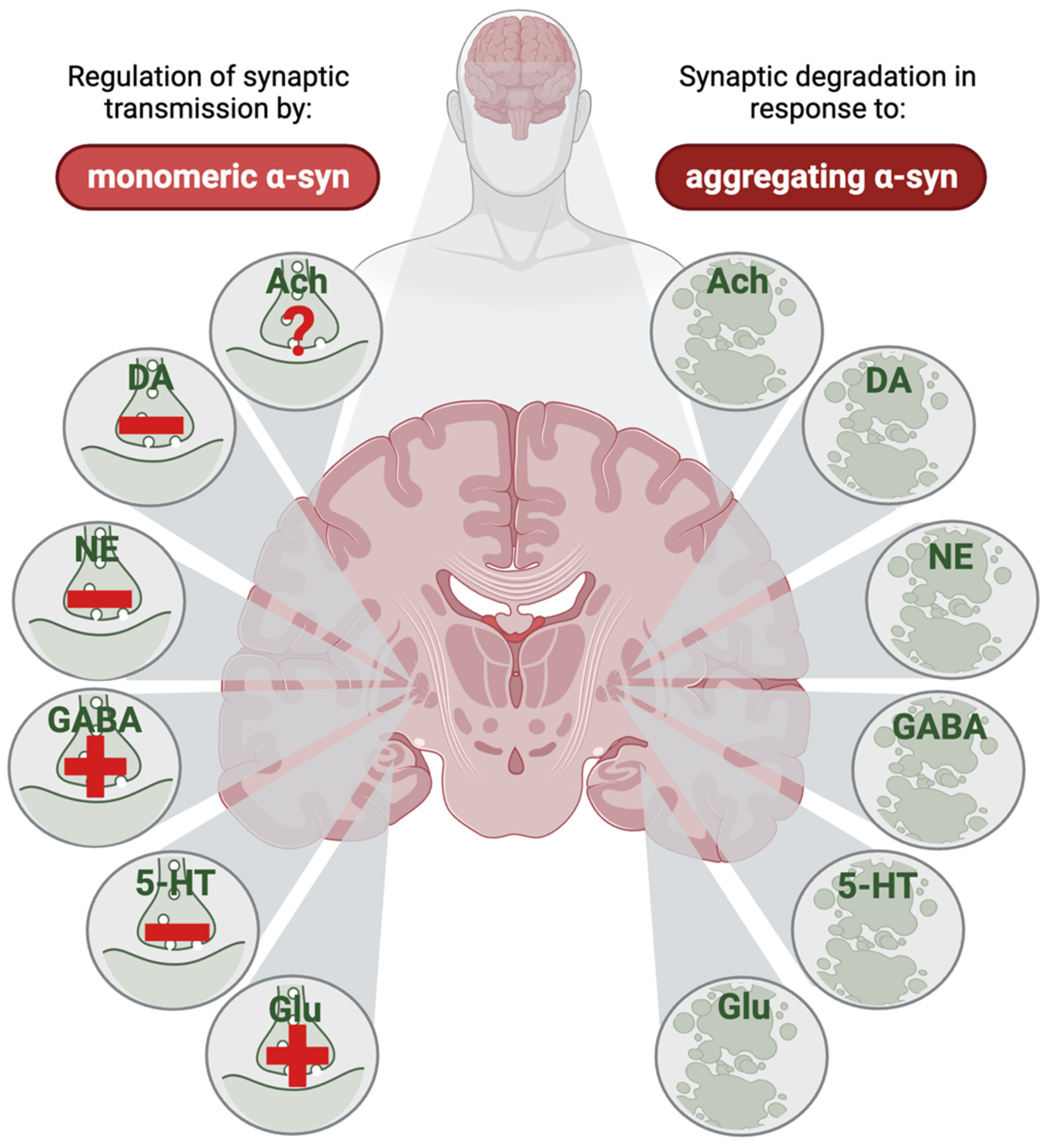
3.1. General Mechanisms of Synaptic α-Synuclein
3.2. The Role of α-Syn in Dopaminergic Synapses
3.3. The Role of α-Syn in Norepinephrine Synapses
3.4. The Role of α-Syn in Serotonergic Synapses
3.5. The Role of α-Syn in Cholinergic Synapses
3.6. The Role of α-Syn in Glutamatergic Synapses
3.7. The Role of α-Syn in GABAergic Synapses
3.8. Converging and Diverging Mechanisms
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spillantini, M.G.; Crowther, R.A.; Jakes, R.; Hasegawa, M.; Goedert, M. α-Synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6469–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Yoshimoto, M.; Tsuji, S.; Takahashi, H. α-Synuclein immunoreactivity in glial cytoplasmic inclusions in multiple system atrophy. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 249, 180–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Rüb, U.; Steur, E.J.; Del Tredici, K.; De Vos, R. Cognitive status correlates with neuropathologic stage in Parkinson disease. Neurology 2005, 64, 1404–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliday, G.M.; Li, Y.W.; Blumbergs, P.C.; Joh, T.H.; Cotton, R.G.; Howe, P.R.; Blessing, W.W.; Geffen, L.B. Neuropathology of immunohistochemically identified brainstem neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 1990, 27, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kish, S.J.; Tong, J.; Hornykiewicz, O.; Rajput, A.; Chang, L.J.; Guttman, M.; Furukawa, Y. Preferential loss of serotonin markers in caudate versus putamen in Parkinson’s disease. Brain J. Neurol. 2008, 131 Pt 1, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillet, A.; Krack, P.; Lhommée, E.; Météreau, E.; Klinger, H.; Favre, E.; Le Bars, D.; Schmitt, E.; Bichon, A.; Pelissier, P.; et al. The prominent role of serotonergic degeneration in apathy, anxiety and depression in de novo Parkinson’s disease. Brain J. Neurol. 2016, 139 Pt 9, 2486–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, N.E.; Lanza, K.; Bishop, C. Pedunculopontine nucleus degeneration contributes to both motor and non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 10, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espay, A.J.; LeWitt, P.A.; Kaufmann, H. Norepinephrine deficiency in Parkinson’s disease: The case for noradrenergic enhancement. Mov. Disord. 2014, 29, 1710–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K.; Rüb, U.; De Vos, R.A.; Steur, E.N.J.; Braak, E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outeiro, T.F.; Koss, D.J.; Erskine, D.; Walker, L.; Kurzawa-Akanbi, M.; Burn, D.; Donaghy, P.; Morris, C.; Taylor, J.-P.; Thomas, A.; et al. Dementia with Lewy bodies: An update and outlook. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jellinger, K.A. More frequent Lewy bodies but less frequent Alzheimer-type lesions in multiple system atrophy as compared to age-matched control brains. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A.; Lantos, P.L. Papp–Lantos inclusions and the pathogenesis of multiple system atrophy: An update. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalls, M.A.; Blauwendraat, C.; Vallerga, C.L.; Heilbron, K.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Chang, D.; Tan, M.; Kia, D.A.; Noyce, A.J.; Xue, A.; et al. Identification of novel risk loci, causal insights, and heritable risk for Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, F.S.; Foo, J.Q.X.; Mai, A.S.; Tan, E.-K. The genetic basis of multiple system atrophy. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orme, T.; Guerreiro, R.; Bras, J. The genetics of dementia with Lewy bodies: Current understanding and future directions. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2018, 18, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, K.; Atarashi, R.; Satoh, K.; Ishibashi, D.; Nakagaki, T.; Iwasaki, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Murayama, S.; Mishima, K.; Nishida, N. Prion-like seeding of misfolded α-synuclein in the brains of dementia with Lewy body patients in RT-QUIC. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 3916–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groveman, B.R.; Orrù, C.D.; Hughson, A.G.; Raymond, L.D.; Zanusso, G.; Ghetti, B.; Campbell, K.J.; Safar, J.; Galasko, D.; Caughey, B. Rapid and ultra-sensitive quantitation of disease-associated α-synuclein seeds in brain and cerebrospinal fluid by αSyn RT-QuIC. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, J.A.; Quansah, E.; Brundin, P. The concept of alpha-synuclein as a prion-like protein: Ten years after. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 373, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdes, H.H.; Bukoreshtliev, N.V.; Barroso, J.F. Tunneling nanotubes: A new route for the exchange of components between animal cells. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 2194–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Kang, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, X. The role of exosomes in the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desplats, P.; Lee, H.-J.; Bae, E.-J.; Patrick, C.; Rockenstein, E.; Crews, L.; Spencer, B.; Masliah, E.; Lee, S.-J. Inclusion formation and neuronal cell death through neuron-to-neuron transmission of α-synuclein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13010–13015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abounit, S.; Bousset, L.; Loria, F.; Zhu, S.; de Chaumont, F.; Pieri, L.; Olivo-Marin, J.; Melki, R.; Zurzolo, C. Tunneling nanotubes spread fibrillar α-synuclein by intercellular trafficking of lysosomes. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 2120–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelova, P.R.; Ludtmann, M.H.R.; Horrocks, M.H.; Negoda, A.; Cremades, N.; Klenerman, D.; Dobson, C.M.; Wood, N.W.; Pavlov, E.V.; Gandhi, S.; et al. Ca2+ is a key factor in α-synuclein-induced neurotoxicity. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 1792–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelova, P.R.; Choi, M.L.; Berezhnov, A.V.; Horrocks, M.H.; Hughes, C.D.; De, S.; Rodrigues, M.; Yapom, R.; Little, D.; Dolt, K.S.; et al. Alpha synuclein aggregation drives ferroptosis: An interplay of iron, calcium and lipid peroxidation. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 2781–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palop, J.J.; Jones, B.; Kekonius, L.; Chin, J.; Yu, G.Q.; Raber, J.; Masliah, E.; Mucke, L. Neuronal depletion of calcium-dependent proteins in the dentate gyrus is tightly linked to Alzheimer’s disease-related cognitive deficits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9572–9577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surguchev, A.A.; Emamzadeh, F.N.; Surguchov, A. Cell responses to extracellular α-synuclein. Molecules 2019, 24, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, D.G.; Temido-Ferreira, M.; Miranda, H.V.; Batalha, V.L.; Coelho, J.E.; Szegö, M.; Marques-Morgado, I.; Vaz, S.H.; Rhee, J.S.; Schmitz, M.; et al. α-synuclein interacts with PrPC to induce cognitive impairment through mGluR5 and NMDAR2B. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 1569–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuele, M.; Esposito, A.; Camerini, S.; Antonucci, F.; Ferrara, S.; Seghezza, S.; Catelani, T.; Crescenzi, M.; Marotta, R.; Canale, C.; et al. Exogenous alpha-synuclein alters pre-and post-synaptic activity by fragmenting lipid rafts. EBioMedicine 2016, 7, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alza, N.P.; Iglesias González, P.A.; Conde, M.A.; Uranga, R.M.; Salvador, G.A. Lipids at the crossroad of α-synuclein function and dysfunction: Biological and pathological implications. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmeier, D.J.; Schumacker, P.T. Calcium, bioenergetics, and neuronal vulnerability in Parkinson’s disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 10736–10741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamzadeh, F.N. Alpha-synuclein structure, functions, and interactions. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2016, 21, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettmer, U.; Ramalingam, N.; von Saucken, V.E.; Kim, T.-E.; Newman, A.J.; Terry-Kantor, E.; Nuber, S.; Ericsson, M.; Fanning, S.; Bartels, T.; et al. Loss of native α-synuclein multimerization by strategically mutating its amphipathic helix causes abnormal vesicle interactions in neuronal cells. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 3466–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Ferreira, R.; Taylor, N.M.; Mona, D.; Ringler, P.; Lauer, M.E.; Riek, R.; Britschgi, M.; Stahlberg, H. Cryo-EM structure of alpha-synuclein fibrils. eLife 2018, 7, e36402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Ferreira, R.; Taylor, N.M.; Arteni, A.A.; Kumari, P.; Mona, D.; Ringler, P.; Britschgi, M.; Lauer, M.E.; Makky, A.; Verasdonck, J.; et al. Two new polymorphic structures of human full-length alpha-synuclein fibrils solved by cryo-electron microscopy. eLife 2019, 8, e48907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winner, B.; Jappelli, R.; Maji, S.K.; Desplats, P.A.; Boyer, L.; Aigner, S.; Hetzer, C.; Loher, T.; Vilar, M.; Campioni, S.; et al. In vivo demonstration that α-synuclein oligomers are toxic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4194–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzen, N.; Nielsen, S.B.; Buell, A.K.; Kaspersen, J.D.; Arosio, P.; Vad, B.S.; Paslawski, W.; Christiansen, G.; Valnickova-Hansen, Z.; Andreasen, M.; et al. The role of stable α-synuclein oligomers in the molecular events underlying amyloid formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3859–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieri, L.; Madiona, K.; Bousset, L.; Melki, R. Fibrillar α-synuclein and huntingtin exon 1 assemblies are toxic to the cells. Biophys. J. 2012, 102, 2894–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danzer, K.M.; Haasen, D.; Karow, A.R.; Moussaud, S.; Habeck, M.; Giese, A.; Kretzschmar, H.; Hengerer, B.; Kostka, M. Different species of α-synuclein oligomers induce calcium influx and seeding. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 9220–9232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parihar, M.S.; Parihar, A.; Fujita, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Ghafourifar, P. Alpha-synuclein overexpression and aggregation exacerbates impairment of mitochondrial functions by augmenting oxidative stress in human neuroblastoma cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 2015–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.L.; Chappard, A.; Singh, B.P.; Maclachlan, C.; Rodrigues, M.; Fedotova, E.I.; Berezhnov, A.V.; De, S.; Peddie, C.J.; Athauda, D.; et al. Pathological structural conversion of α-synuclein at the mitochondria induces neuronal toxicity. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 1134–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremades, N.; Cohen, S.I.; Deas, E.; Abramov, A.Y.; Chen, A.Y.; Orte, A.; Sandal, M.; Clarke, R.W.; Dunne, P.; Aprile, F.A.; et al. Direct observation of the interconversion of normal and toxic forms of α-synuclein. Cell 2012, 149, 1048–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludtmann, M.H.R.; Angelova, P.R.; Horrocks, M.H.; Choi, M.L.; Rodrigues, M.; Baev, A.Y.; Berezhnov, A.V.; Yao, Z.; Little, D.; Banushi, B.; et al. α-synuclein oligomers interact with ATP synthase and open the permeability transition pore in Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vekrellis, K.; Xilouri, M.; Emmanouilidou, E.; Rideout, H.J.; Stefanis, L. Pathological roles of α-synuclein in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, A.; Lee, H.J.; Suk, J.E.; Jung, J.W.; Kim, K.P.; Lee, S.J. Non-classical exocytosis of α-synuclein is sensitive to folding states and promoted under stress conditions. J. Neurochem. 2010, 113, 1263–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, H.Y.; Yuan, B.S.; Hou, X.O.; Zhang, X.J.; Pei, C.S.; Ma, Y.T.; Yang, Y.P.; Fan, Y.; Qin, Z.H.; Liu, C.F.; et al. α-synuclein suppresses microglial autophagy and promotes neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodore, S.; Cao, S.; McLean, P.J.; Standaert, D.G. Targeted overexpression of human alpha-synuclein triggers microglial activation and an adaptive immune response in a mouse model of Parkinson disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 67, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Wolman, L. Ultrastructural observations in Parkinsonism. J. Pathol. 1969, 99, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennyson, V. Phase and electron microscopic observations of Lewy bodies and melanin granules in the substantia nigra and locus coeruleus in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1965, 24, 398–414. [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Tanji, K.; Odagiri, S.; Miki, Y.; Mori, F.; Takahashi, H. The Lewy body in Parkinson’s disease and related neurodegenerative disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 47, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmoradian, S.H.; Lewis, A.J.; Genoud, C.; Hench, J.; Moors, T.E.; Navarro, P.P.; Castaño-Díez, D.; Schweighauser, G.; Graff-Meyer, A.; Goldie, K.N.; et al. Lewy pathology in Parkinson’s disease consists of crowded organelles and lipid membranes. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindström, V.; Fagerqvist, T.; Nordström, E.; Eriksson, F.; Lord, A.; Tucker, S.; Andersson, J.; Johannesson, M.; Schell, H.; Kahle, P.J.; et al. Immunotherapy targeting α-synuclein protofibrils reduced pathology in (Thy-1)-h [A30P] α-synuclein mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 69, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, G.; Taylor, K.I.; Anzures-Cabrera, J.; Marchesi, M.; Simuni, T.; Marek, K.; Postuma, R.B.; Pavese, N.; Stocchi, F.; Azulay, J.-P.; et al. Trial of Prasinezumab in Early-Stage Parkinson’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, A.E.; Siderowf, A.D.; Macklin, E.A.; Poewe, W.; Brooks, D.J.; Fernandez, H.H.; Rascol, O.; Giladi, N.; Stocchi, F.; Tanner, C.M.; et al. Trial of Cinpanemab in Early Parkinson’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevigny, J.; Chiao, P.; Bussière, T.; Weinreb, P.H.; Williams, L.; Maier, M.; Dunstan, R.; Salloway, S.; Chen, T.; Ling, Y.; et al. The antibody aducanumab reduces Aβ plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2016, 537, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dyck, C.H.; Swanson, C.J.; Aisen, P.; Bateman, R.J.; Chen, C.; Gee, M.; Kanekiyo, M.; Li, D.; Reyderman, L.; Cohen, S.; et al. Lecanemab in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totterdell, S.; Hanger, D.; Meredith, G.E. The ultrastructural distribution of alpha-synuclein-like protein in normal mouse brain. Brain Res. 2004, 1004, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totterdell, S.; Meredith, G. Localization of alpha-synuclein to identified fibers and synapses in the normal mouse brain. Neuroscience 2005, 135, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivacqua, G.; Casini, A.; Vaccaro, R.; Fornai, F.; Yu, S.; D’este, L. Different sub-cellular localization of alpha-synuclein in the C57BL\6J mouse’s central nervous system by two novel monoclonal antibodies. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2011, 41, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, G.S.; George, J.M.; Banker, G.A.; Clayton, D.F. Delayed localization of synelfin (synuclein, NACP) to presynaptic terminals in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Dev. Brain Res. 1997, 99, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, D.L.; Troyer, M.D.; Nakamura, K.; Kubo, S.-I.; Anthony, M.D.; Edwards, R.H. Lipid rafts mediate the synaptic localization of α-synuclein. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6715–6723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmozzi, V.; Gentile, G.; Rueda, M.P.C.; Hicks, A.A.; Pramstaller, P.P.; Zanon, A.; Lévesque, M.; Pichler, I. Interaction of alpha-synuclein with lipids: Mitochondrial cardiolipin as a critical player in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 578993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danzer, K.M.; Kranich, L.R.; Ruf, W.P.; Cagsal-Getkin, O.; Winslow, A.R.; Zhu, L.; Vanderburg, C.R.; McLean, P.J. Exosomal cell-to-cell transmission of alpha synuclein oligomers. Mol. Neurodegener. 2012, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-J.; Patel, S.; Lee, S.-J. Intravesicular localization and exocytosis of α-synuclein and its aggregates. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 6016–6024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.; Iwatsubo, T. Extracellular α-synuclein levels are regulated by neuronal activity. Mol. Neurodegener. 2018, 13, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, I.; Zhang, Y.; Seegobin, S.P.; Pruvost, M.; Wang, Q.; Purtell, K.; Zhang, B.; Yue, Z. Microglia clear neuron-released α-synuclein via selective autophagy and prevent neurodegeneration. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.J.; Mallory, M.; Xia, Y.; Veinbergs, I.; Hashimoto, M.; Yoshimoto, M.; Thal, L.J.; Saitoh, T.; Masliah, E. Expression pattern of synucleins (non-Aβ component of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid precursor protein/α-synuclein) during murine brain development. J. Neurochem. 1998, 71, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeliovich, A.; Schmitz, Y.; Fariñas, I.; Choi-Lundberg, D.; Ho, W.-H.; Castillo, P.; Shinsky, N.; García-Verdugo, J.M.; Armanini, M.; Ryan, A.; et al. Mice lacking α-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron 2000, 25, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabin, D.E.; Shimazu, K.; Murphy, D.; Cole, N.B.; Gottschalk, W.; McIlwain, K.L.; Orrison, B.; Chen, A.; Ellis, C.E.; Paylor, R.; et al. Synaptic vesicle depletion correlates with attenuated synaptic responses to prolonged repetitive stimulation in mice lacking α-synuclein. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 8797–8807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, T.; Schoenenberger, P.; Jezek, K.; Oertner, T.G. Developmental refinement of vesicle cycling at Schaffer collateral synapses. Neuron 2013, 77, 1109–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Sheng, J.; Wu, X.-S.; Wu, W.; Luo, F.; Shin, W.; Chiang, H.-C.; Wu, L.-G. Most vesicles in a central nerve terminal participate in recycling. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 8820–8826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Wang, B.; Li, X.; Fu, C.; Wang, C.; Kang, X. α-Synuclein: A multifunctional player in exocytosis, endocytosis, and vesicle recycling. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulzer, D.; Edwards, R.H. The physiological role of α-synuclein and its relationship to Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurochem. 2019, 150, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawk, B.J.; Khounlo, R.; Shin, Y.-K. Alpha-synuclein continues to enhance SNARE-dependent vesicle docking at exorbitant concentrations. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.; Kim, J.; Hawk, B.J.; Shin, Y.-K. α-Synuclein may cross-bridge v-SNARE and acidic phospholipids to facilitate SNARE-dependent vesicle docking. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 2039–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soper, J.H.; Roy, S.; Stieber, A.; Lee, E.; Wilson, R.B.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Burd, C.G.; Lee, V.M. α-Synuclein–induced Aggregation of Cytoplasmic Vesicles in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, J.; Burré, J.; Vivona, S.; Cipriano, D.J.; Sharma, M.; Kyoung, M.; Südhof, T.C.; Brunger, A.T. Native α-synuclein induces clustering of synaptic-vesicle mimics via binding to phospholipids and synaptobrevin-2/VAMP2. eLife 2013, 2, e00592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pifl, C.; Reither, H.; Blesa, J.; Cavada, C.; Obeso, J.A.; Rajput, A.H.; Hornykiewicz, O. Is Parkinson’s disease a vesicular dopamine storage disorder? Evidence from a study in isolated synaptic vesicles of human and nonhuman primate striatum. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 8210–8218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Donakonda, S.; Müller, S.A.; Lichtenthaler, S.F.; Bötzel, K.; Höglinger, G.U.; Koeglsperger, T. Basic fibroblast growth factor 2-induced proteome changes endorse Lewy body pathology in hippocampal neurons. iScience 2020, 23, 101349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, V.; Peng, J.; Chung, C.Y.; Auluck, P.K.; Fanning, S.; Tardiff, D.F.; Bartels, T.; Koeva, M.; Eichhorn, S.W.; Benyamini, H.; et al. Genome-Scale Networks Link Neurodegenerative Disease Genes to α-Synuclein through Specific Molecular Pathways. Cell Syst. 2017, 4, 157–170.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.D.; Rueter, S.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Synucleins are developmentally expressed, and alpha-synuclein regulates the size of the presynaptic vesicular pool in primary hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 3214–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ninan, I.; Antonova, I.; Battaglia, F.; Trinchese, F.; Narasanna, A.; Kolodilov, N.; Dauer, W.; Hawkins, R.D.; Arancio, O. alpha-Synuclein produces a long-lasting increase in neurotransmitter release. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 4506–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, K.E.; Schmitz, Y.; Troyer, M.D.; Mosharov, E.; Dietrich, P.; Quazi, A.Z.; Savalle, M.; Nemani, V.; Chaudhry, F.A.; Edwards, R.H.; et al. Alpha-synuclein overexpression in PC12 and chromaffin cells impairs catecholamine release by interfering with a late step in exocytosis. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 11915–11922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miquel-Rio, L.; Sarriés-Serrano, U.; Pavia-Collado, R.; Meana, J.J.; Bortolozzi, A. The Role of α-Synuclein in the Regulation of Serotonin System: Physiological and Pathological Features. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, G.; Ko, M.S.; Das, T.; Eliezer, D. Molecular and functional interactions of alpha-synuclein with Rab3a. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Yang, D.M.; Lin, C.C.; Kao, L.S. Involvement of Rab3A in vesicle priming during exocytosis: Interaction with Munc13-1 and Munc18-1. Traffic 2011, 12, 1356–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khounlo, R.; Hawk, B.J.D.; Khu, T.-M.; Yoo, G.; Lee, N.K.; Pierson, J.; Shin, Y.-K. Membrane Binding of α-Synuclein Stimulates Expansion of SNARE-Dependent Fusion Pore. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 663431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atias, M.; Tevet, Y.; Sun, J.; Stavsky, A.; Tal, S.; Kahn, J.; Roy, S.; Gitler, D. Synapsins regulate α-synuclein functions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 11116–11118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavsky, A.; Parra-Rivas, L.A.; Tal, S.; Madhivanan, K.; Roy, S.; Gitler, D. Synapsin E-domain is essential for α-synuclein function. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellucci, A.; Longhena, F.; Spillantini, M.G. The role of Rab proteins in Parkinson’s disease synaptopathy. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Donakonda, S.; Müller, S.A.; Bötzel, K.; Höglinger, G.U.; Koeglsperger, T. FGF2 Affects Parkinson’s Disease-Associated Molecular Networks Through Exosomal Rab8b/Rab31. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 572058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabi, A.A.; Tsien, R.W. Perspectives on kiss-and-run: Role in exocytosis, endocytosis, and neurotransmission. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 393–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, W.S.; Jonas, A.; Clayton, D.F.; George, J.M. Stabilization of α-synuclein secondary structure upon binding to synthetic membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 9443–9449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jao, C.C.; Der-Sarkissian, A.; Chen, J.; Langen, R. Structure of membrane-bound α-synuclein studied by site-directed spin labeling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8331–8336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runwal, G.; Edwards, R.H. The membrane interactions of synuclein: Physiology and pathology. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2021, 16, 465–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, T.; Bendor, J.; Toupin, C.; Thorn, K.; Edwards, R.H. α-Synuclein promotes dilation of the exocytotic fusion pore. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bartolo, A.L.; Caparotta, M.; Masone, D. Intrinsic Disorder in α-Synuclein Regulates the Exocytotic Fusion Pore Transition. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 2049–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senior, S.L.; Ninkina, N.; Deacon, R.; Bannerman, D.; Buchman, V.L.; Cragg, S.J.; Wade-Martins, R. Increased striatal dopamine release and hyperdopaminergic-like behaviour in mice lacking both α-synuclein and gamma-synuclein. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 27, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greten-Harrison, B.; Polydoro, M.; Morimoto-Tomita, M.; Diao, L.; Williams, A.M.; Nie, E.H.; Makani, S.; Tian, N.; Castillo, P.E.; Buchman, V.L.; et al. αβγ-Synuclein triple knockout mice reveal age-dependent neuronal dysfunction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19573–19578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pronin, A.N.; Morris, A.J.; Surguchov, A.; Benovic, J.L. Synucleins are a novel class of substrates for G protein-coupled receptor kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 26515–26522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarran, E.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Raju, K.; Dong, A.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Südhof, T.C.; Ding, J.B. Postsynaptic synucleins mediate endocannabinoid signaling. Nat. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, P.E.; Younts, T.J.; Chavez, A.E.; Hashimotodani, Y. Endocannabinoid signaling and synaptic function. Neuron 2012, 76, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno-Shosaku, T.; Kano, M. Endocannabinoid-mediated retrograde modulation of synaptic transmission. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2014, 29, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundt-Revilla, J.; Kegler, K.; Baumgärtner, W.; Tipold, A. Spatial distribution of cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1) in normal canine central and peripheral nervous system. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackie, K. Distribution of cannabinoid receptors in the central and peripheral nervous system. Cannabinoids 2005, 168, 299–325. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, B.; Hillard, C.J.; Liu, Q.-S. Endocannabinoid signaling mediates cocaine-induced inhibitory synaptic plasticity in midbrain dopamine neurons. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, M.; Ohno-Shosaku, T.; Hashimotodani, Y.; Uchigashima, M.; Watanabe, M. Endocannabinoid-mediated control of synaptic transmission. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 309–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heifets, B.D.; Castillo, P.E. Endocannabinoid signaling and long-term synaptic plasticity. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2009, 71, 283–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westphal, C.H.; Chandra, S.S. Monomeric synucleins generate membrane curvature. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 1829–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froula, J.M.; Henderson, B.W.; Gonzalez, J.C.; Vaden, J.H.; Mclean, J.W.; Wu, Y.; Banumurthy, G.; Overstreet-Wadiche, L.; Herskowitz, J.H.; Volpicelli-Daley, L.A. α-Synuclein fibril-induced paradoxical structural and functional defects in hippocampal neurons. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, N.; Xu, Z.Q.; Lindskog, M.; Herrera-Marschitz, M.; Goiny, M.; Haycock, J.; Goldstein, M.; Hökfelt, T.; Fisone, G. Regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase activity and phosphorylation at Ser19 and Ser40 via activation of glutamate NMDA receptors in rat striatum. J. Neurochem. 2000, 74, 2470–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehrer, S.; Rheinstein, P.H. α-synuclein enfolds tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine ß-hydroxylase, potentially reducing dopamine and norepinephrine synthesis. J. Proteins Proteom. 2022, 13, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunkley, P.R.; Bobrovskaya, L.; Graham, M.E.; Von Nagy-Felsobuki, E.I.; Dickson, P.W. Tyrosine hydroxylase phosphorylation: Regulation and consequences. J. Neurochem. 2004, 91, 1025–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Li, Y.-H.; Li, X.; Yu, S.; Fu, G.-L.; Chen, B. Effect of α-synuclein on the promoter activity of tyrosine hydroxylase gene. Neurosci. Bull. 2007, 23, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.S.; Moon, K.R.; Choi, H.J. Interference of alpha-synuclein with cAMP/PKA-dependent CREB signaling for tyrosine hydroxylase gene expression in SK-N-BE(2)C cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, M.J.; O’Farrell, C.; Daya, S.; Ahmad, R.; Miller, D.W.; Hardy, J.; Farrer, M.J.; Cookson, M.R. Co-ordinate transcriptional regulation of dopamine synthesis genes by α-synuclein in human neuroblastoma cell lines. J. Neurochem. 2003, 85, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Jin, L.; Wang, H.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, C.; Duan, C.; Lu, L.; Wu, B.; Yu, S.; Chan, P.; et al. Silencing α-synuclein gene expression enhances tyrosine hydroxylase activity in MN9D cells. Neurochem. Res. 2008, 33, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, K.A.; Rochet, J.-C.; Bieganski, R.M.; Lansbury, P.T., Jr. Kinetic stabilization of the α-synuclein protofibril by a dopamine-α-synuclein adduct. Science 2001, 294, 1346–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, E.H.; Giasson, B.I.; Hodara, R.; Xu, S.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Ischiropoulos, H.; Lee, V.M.-Y. Reversible inhibition of α-synuclein fibrillization by dopaminochrome-mediated conformational alterations. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 21212–21219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, D.E.; Tsika, E.; Mazzulli, J.R.; Gould, N.S.; Kim, H.; Daniels, M.J.; Doshi, S.; Gupta, P.; Grossman, J.L.; Tan, V.X.; et al. Dopamine induces soluble α-synuclein oligomers and nigrostriatal degeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 1560–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.L.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J. Presynaptic α-synuclein aggregates, not Lewy bodies, cause neurodegeneration in dementia with Lewy bodies. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavich, L.; Tanila, H.; Vepsäläinen, S.; Jäkälä, P. Role of alpha-synuclein in presynaptic dopamine recruitment. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 11165–11170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wersinger, C.; Sidhu, A. Disruption of the interaction of α-synuclein with microtubules enhances cell surface recruitment of the dopamine transporter. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 13612–13624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wersinger, C.; Vernier, P.; Sidhu, A. Trypsin disrupts the trafficking of the human dopamine transporter by α-synuclein and its A30P mutant. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 1242–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiguro, H.; Kim, K.; Joh, T.; Kim, K. Neuron-specific expression of the human dopamine beta-hydroxylase gene requires both the cAMP-response element and a silencer region. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 17987–17994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamouroux, A.; Houhou, L.; Biguet, N.F.; Serck-Hanssen, G.; Guibert, B.; Icard-Liepkalns, C.; Mallet, J. Analysis of the human dopamine β-hydroxylase promoter: Transcriptional induction by cyclic AMP. J. Neurochem. 1993, 60, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Park, J.-M.; Moon, J.; Choi, H.J. Alpha-synuclein interferes with cAMP/PKA-dependent upregulation of dopamine β-hydroxylase and is associated with abnormal adaptive responses to immobilization stress. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 252, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wersinger, C.; Jeannotte, A.; Sidhu, A. Attenuation of the norepinephrine transporter activity and trafficking via interactions with α-synuclein. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 3141–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Bjørnevik, K.; Im, D.S.; Flierl, A.; Dong, X.; Locascio, J.J.; Abo, K.M.; Long, E.; Jin, M.; Xu, B.; et al. β2-Adrenoreceptor is a regulator of the α-synuclein gene driving risk of Parkinson’s disease. Science 2017, 357, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, J.H.; LeWitt, P.A.; Burns, R.S.; Foster, N.L.; Lovenberg, W. CSF dopamine-β-hydroxylase activity in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 1985, 35, 565–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, D.S.; Sullivan, P.; Holmes, C.; Lamotte, G.; Lenka, A.; Sharabi, Y. Differential abnormalities of cerebrospinal fluid dopaminergic versus noradrenergic indices in synucleinopathies. J. Neurochem. 2021, 158, 554–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kish, S.J.; Furukawa, Y.; Chang, L.J.; Tong, J.; Ginovart, N.; Wilson, A.; Houle, S.; Meyer, J.H. Regional distribution of serotonin transporter protein in postmortem human brain: Is the cerebellum a SERT-free brain region? Nucl. Med. Biol. 2005, 32, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wersinger, C.; Rusnak, M.; Sidhu, A. Modulation of the trafficking of the human serotonin transporter by human alpha-synuclein. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcón-Arís, D.; Recasens, A.; Galofré, M.; Carballo-Carbajal, I.; Zacchi, N.; Ruiz-Bronchal, E.; Pavia-Collado, R.; Chica, R.; Ferrés-Coy, A.; Santos, M.; et al. Selective α-synuclein knockdown in monoamine neurons by intranasal oligonucleotide delivery: Potential therapy for Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 550–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miquel-Rio, L.; Alarcón-Arís, D.; Torres-López, M.; Cóppola-Segovia, V.; Pavia-Collado, R.; Paz, V.; Ruiz-Bronchal, E.; Campa, L.; Casal, C.; Montefeltro, A.; et al. Human α-synuclein overexpression in mouse serotonin neurons triggers a depressive-like phenotype. Rescue by oligonucleotide therapy. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deusser, J.; Schmidt, S.; Ettle, B.; Plötz, S.; Huber, S.; Müller, C.P.; Masliah, E.; Winkler, J.; Kohl, Z. Serotonergic dysfunction in the A53T alpha-synuclein mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2015, 135, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picciotto, M.R.; Higley, M.J.; Mineur, Y.S. Acetylcholine as a neuromodulator: Cholinergic signaling shapes nervous system function and behavior. Neuron 2012, 76, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descarries, L.; Gisiger, V.; Steriade, M. Diffuse transmission by acetylcholine in the CNS. Prog. Neurobiol. 1997, 53, 603–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaborszky, L. The modular organization of brain systems. Basal Forebrain Last Front. Prog. Brain Res. 2002, 136, 359–372. [Google Scholar]
- Zaborszky, L.; Hoemke, L.; Mohlberg, H.; Schleicher, A.; Amunts, K.; Zilles, K. Stereotaxic probabilistic maps of the magnocellular cell groups in human basal forebrain. Neuroimage 2008, 42, 1127–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Qin, C.; Hu, F.; Tan, J.; Qiu, L.; Zhao, S.; Feng, G.; Luo, M. Habenula “cholinergic” neurons corelease glutamate and acetylcholine and activate postsynaptic neurons via distinct transmission modes. Neuron 2011, 69, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallianatou, T.; Shariatgorji, M.; Nilsson, A.; Fridjonsdottir, E.; Källback, P.; Schintu, N.; Svenningsson, P.; Andrén, P.E. Molecular imaging identifies age-related attenuation of acetylcholine in retrosplenial cortex in response to acetylcholinesterase inhibition. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 44, 2091–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benagiano, V.; Virgintino, D.; Flace, P.; Girolamo, F.; Errede, M.; Roncali, L. Choline acetyltransferase-containing neurons in the human parietal neocortex. Eur. J. Histochem. 2003, 47, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Engelhardt, J.; Eliava, M.; Meyer, A.H.; Rozov, A.; Monyer, H. Functional characterization of intrinsic cholinergic interneurons in the cortex. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 5633–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-Y.; Jensen, P.H.; Dahlström, A. Differential localization of α-, β-and γ-synucleins in the rat CNS. Neuroscience 2002, 113, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahapill, P.A.; Lozano, A.M. The pedunculopontine nucleus and Parkinson’s disease. Brain J. Neurol. 2000, 123, 1767–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrich, M.T.; Geibl, F.F.; Lakshminarasimhan, H.; Stegmann, A.; Giasson, B.I.; Mao, X.; Dawson, V.L.; Dawson, T.M.; Oertel, W.H.; Surmeier, D.J. Determinants of seeding and spreading of α-synuclein pathology in the brain. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarevic, V.; Yang, Y.; Paslawski, W.; Svenningsson, P. α-Synuclein induced cholesterol lowering increases tonic and reduces depolarization-evoked synaptic vesicle recycling and glutamate release. NPJ Park. Dis. 2022, 8, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Nagaraja, C.; Daniels, S.; Fisk, Z.A.; Dvorak, R.; Meyerdirk, L.; Steiner, J.A.; Escobar Galvis, M.L.; Henderson, M.X.; Rousseaux, M.W.C.; et al. Synaptic location is a determinant of the detrimental effects of α-synuclein pathology to glutamatergic transmission in the basolateral amygdala. eLife 2022, 11, e78055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Tsujimura, A.; Tanaka, M. Expression of α-synuclein is regulated in a neuronal cell type-dependent manner. Anat. Sci. Int. 2019, 94, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, K.; Chasapopoulou, Z.; Frahm, S.; Magbagbeolu, M.; Cranston, A.; Harrington, C.R.; Wischik, C.M.; Theuring, F.; Riedel, G. Glutamatergic transmission and receptor expression in the synucleinopathy h-α-synL62 mouse model: Effects of hydromethylthionine. Cell. Signal. 2022, 97, 110386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trudler, D.; Sanz-Blasco, S.; Eisele, Y.S.; Ghatak, S.; Bodhinathan, K.; Akhtar, M.W.; Lynch, W.P.; Piña-Crespo, J.C.; Talantova, M.; Kelly, J.W.; et al. α-Synuclein oligomers induce glutamate release from astrocytes and excessive extrasynaptic NMDAR activity in neurons, thus contributing to synapse loss. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 2264–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diógenes, M.J.; Dias, R.B.; Rombo, D.M.; Miranda, H.V.; Maiolino, F.; Guerreiro, P.; Näsström, T.; Franquelim, H.G.; Oliveira, L.M.; Castanho, M.A.; et al. Extracellular alpha-synuclein oligomers modulate synaptic transmission and impair LTP via NMDA-receptor activation. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 11750–11762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Tsujimura, A.; Tanaka, M. Brain region-dependent differential expression of alpha-synuclein. J. Comp. Neurol. 2016, 524, 1236–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Tsujimura, A.; Tatebe, H.; Miyata, S.; Tokuda, T.; Mizuno, T.; Tanaka, M. Differential expression of alpha-synuclein in hippocampal neurons. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.; Roy, S. α-Synuclein inhibits intersynaptic vesicle mobility and maintains recycling-pool homeostasis. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 10129–10135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, K.L.; Jiang, X.; Taylor, A.A.; Shin, W.; Gillis, K.D.; Mennerick, S. Vesicle pool heterogeneity at hippocampal glutamate and GABA synapses. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 9846–9854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, K.L.; Mennerick, S. Reluctant vesicles contribute to the total readily releasable pool in glutamatergic hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 3842–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burré, J.; Sharma, M.; Tsetsenis, T.; Buchman, V.; Etherton, M.R.; Südhof, T.C. α-Synuclein promotes SNARE-complex assembly in vivo and in vitro. Science 2010, 329, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burré, J. The synaptic function of α-synuclein. J. Park. Dis. 2015, 5, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nordengen, K.; Morland, C. From Synaptic Physiology to Synaptic Pathology: The Enigma of α-Synuclein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25020986
Nordengen K, Morland C. From Synaptic Physiology to Synaptic Pathology: The Enigma of α-Synuclein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(2):986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25020986
Chicago/Turabian StyleNordengen, Kaja, and Cecilie Morland. 2024. "From Synaptic Physiology to Synaptic Pathology: The Enigma of α-Synuclein" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 2: 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25020986
APA StyleNordengen, K., & Morland, C. (2024). From Synaptic Physiology to Synaptic Pathology: The Enigma of α-Synuclein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(2), 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25020986






