A Novel Trichinella spiralis Galectin Strengthens the Macrophage ADCC Killing of Larvae via Driving M1 Polarization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Bioinformatics Analysis Results of TsGLFP
2.2. Expression, Purification, and Antigenicity Analysis of rTsGLFP
2.3. Transcription and Expression Levels of TsGLFP in Various Stages of Worms
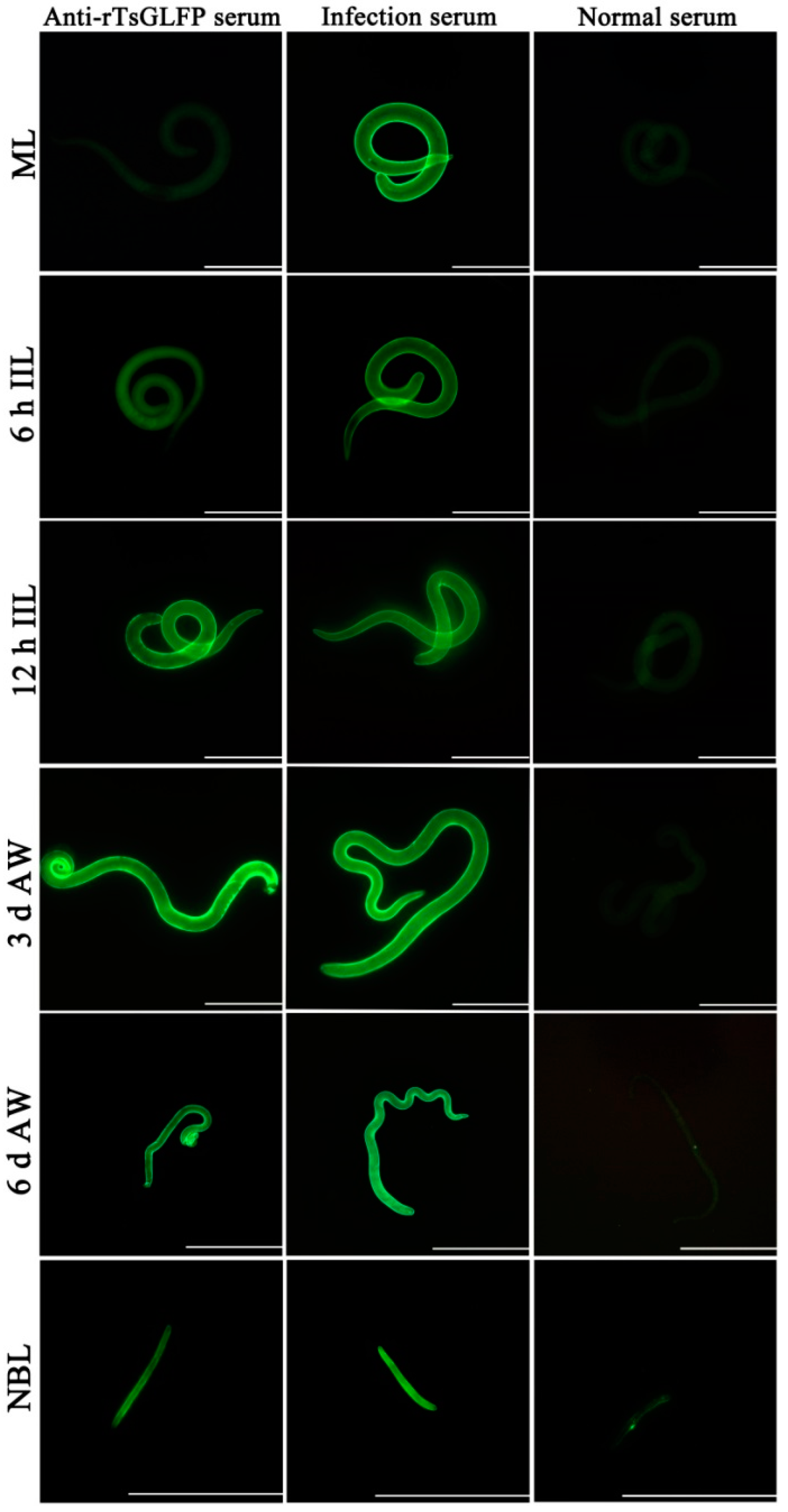
2.4. Expression and Worm Tissue Localization of Natural TsGLFP by IIFT
2.5. rTsGLFP Hemagglutination Activity and Sugar Inhibition
2.6. The Effect of rTsGLFP on the RAW264.7 Cellular Viability
2.7. rTsGLFP Drove the Macrophages’ M1 Polarization
2.8. rTsGLFP Activated the NF-κB Pathway
2.9. Inhibitor Suppressed the rTsGLFP-Driven Macrophages M1 Polarization and NF-κB Pathway Activation
2.10. Inhibitor Suppressed the Transcription Levels of iNOS and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in rTsGLFP-Treated Macrophages
2.11. rTsGLFP Increased the NO Production of Stimulated Macrophages
2.12. rTsGLFP Enhanced the Macrophages’ Cytotoxicity on NBL
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Parasites, Experimental Animals and Cells
4.3. Collection of Various T. spiralis Stages and Preparation of Crude and ES Antigens
4.4. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.5. Cloning, Expression, and Identification of rTsGLFP
4.6. Preparation of Anti-rTsGLFP Serum
4.7. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
4.8. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qPCR) Test
4.9. Indirect Immunofluorescence Test (IIFT)
4.10. Erythrocyte Agglutination Test and Sugar Inhibition Test
4.11. CCK8 Assay of RAW264.7 Cell Viability
4.12. Western Blotting of Expression of M1/M2 Markers, Cytokines, and the NF-κB Pathway in rTsGLFP-Stimulated Macrophages
4.13. Assay of Nitric Oxide (NO)
4.14. Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC) Test
4.15. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pozio, E. The broad spectrum of Trichinella hosts: From cold- to warm-blooded animals. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 132, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostami, A.; Gamble, H.R.; Dupouy-Camet, J.; Khazan, H.; Bruschi, F. Meat sources of infection for outbreaks of human trichinellosis. Food Microbiol. 2017, 64, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malone, C.J.; Oksanen, A.; Mukaratirwa, S.; Sharma, R.; Jenkins, E. From wildlife to humans: The global distribution of Trichinella species and genotypes in wildlife and wildlife-associated human trichinellosis. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2024, 24, 100934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribicich, M.M.; Fariña, F.A.; Aronowicz, T.; Ercole, M.E.; Bessi, C.; Winter, M.; Pasqualetti, M.I. A review on Trichinella infection in South America. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 285, 109234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Wang, Z.Q.; Cui, J. Epidemiology of trichinellosis in the People’s Republic of China during 2009–2020. Acta Trop. 2022, 229, 106388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). The European Union One Health 2022 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e8442. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.Z.; Li, W.H.; Yu, H.J.; Liu, Y.J.; Qin, H.T.; Jia, W.Z.; Fu, B.Q. Novel study on the prevalence of Trichinella spiralis in farmed American minks (Neovison vison) associated with exposure to wild rats (Rattus norvegicus) in China. Zoonoses Public Health 2022, 69, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.J.; Han, L.L.; Liu, R.D.; Long, S.R.; Zhang, X.; Cui, J.; Wang, Z.Q. Oral vaccination of mice with attenuated Salmonella encoding Trichinella spiralis calreticulin and serine protease 1.1 confers protective immunity in BALB/c mice. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Sun, X.; Huang, J.; Zhan, B.; Zhu, X. A Multiple antigen peptide vaccine containing CD4+ T cell epitopes enhances humoral immunity against Trichinella spiralis infection in mice. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 2074803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.W.; Zhang, R.; Guo, X.; Wang, B.N.; Long, S.R.; Liu, R.D.; Wang, Z.Q.; Cui, J. Trichinella spiralis dipeptidyl peptidase 1 suppressed macrophage cytotoxicity by promoting M2 polarization via the STAT6/PPARγ pathway. Vet. Res. 2023, 54, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Li, J.; Li, T.; Xie, Y.; Guan, W.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, M.; Xu, D. Vaccines as a strategy to control Trichinellosis. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 857786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.Y.; Zhang, N.Z.; Li, W.H.; Li, L.; Yan, H.B.; Qu, Z.G.; Li, T.T.; Cui, J.M.; Yang, Y.; Jia, W.Z.; et al. Proteomic analysis of differentially expressed proteins in the three developmental stages of Trichinella spiralis. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 231, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.N.; Liu, R.D.; Song, Y.Y.; Zhuo, T.X.; Guo, K.X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, P.; Wang, Z.Q.; Cui, J. Label-free quantitative proteomic analysis of molting-related proteins of Trichinella spiralis intestinal infective larvae. Vet. Res. 2019, 50, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Despommier, D.D. How does Trichinella spiralis make itself at home? Parasitol. Today 1998, 14, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, M.; Bai, X. Extracellular vesicles from Trichinella spiralis: Proteomic analysis and protective immunity. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilic, N.; Gruden-Movsesijan, A.; Sofronic-Milosavljevic, L. Trichinella spiralis: Shaping the immune response. Immunol. Res. 2012, 52, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilic, N.; Kosanovic, M.; Gruden-Movsesijan, A.; Glamoclija, S.; Sofronic-Milosavljevic, L.; Colic, M.; Tomic, S. Harnessing immunomodulatory mechanisms of Trichinella spiralis to design novel nanomedical approaches for restoring self-tolerance in autoimmunity. Immunol. Lett. 2021, 238, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Bai, X.; Tang, B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, H.; Luo, X.; Yan, H.; Jia, H.; Liu, M.; et al. Primary characterization of the immune response in pigs infected with Trichinella spiralis. Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Li, H.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, L.; He, W.; Xie, H.; Gao, S.; Cheng, R.; Qian, H.; Jiang, H.; et al. Preventive and therapeutic effects of Trichinella spiralis adult extracts on allergic inflammation in an experimental asthma mouse model. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Ge, H.; Huang, G.; Kang, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, Q.; Ren, P.; Kuang, X.; et al. The Trichinella spiralis-derived antigens alleviate HFD-induced obesity and inflammation in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 117, 109924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.R.; Shang, W.X.; Zhang, H.R.; Jiang, M.; Wang, J.J.; Liu, R.D.; Wang, Z.Q.; Cui, J.; Sun, H. Trichinella-derived protein ameliorates colitis by altering the gut microbiome and improving intestinal barrier function. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 127, 111320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.S.; Walia, A.K.; Khattar, J.S.; Singh, D.P.; Kennedy, J.F. Cyanobacterial lectins characteristics and their role as antiviral agents. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 475–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, G.D.; Willment, J.A.; Whitehead, L. C-type lectins in immunity and homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 374–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruden-Movsesijan, A.; Petrovic, M.; Sofronic-Milosavljevic, L. Interaction of mannan-binding lectin with Trichinella spiralis glycoproteins, a possible innate immune mechanism. Parasite Immunol. 2003, 25, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elola, M.T.; Wolfenstein-Todel, C.; Troncoso, M.F.; Vasta, G.R.; Rabinovich, G.A. Galectins: Matricellular glycan-binding proteins linking cell adhesion, migration, and survival. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 1679–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.T.; Stowell, S.R. The role of galectins in immunity and infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Xue, C.; Su, X.Z.; Lu, F. The roles of galectins in parasitic infections. Acta Trop. 2018, 177, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.W.; Yan, X.M.; Qiao, A.J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yang, L.; Huang, H.C.; Shi, H.F.; Yan, B.L. Upregulated galectin-1 in Angiostrongylus cantonensis L5 reduces body fat and increases oxidative stress tolerance. Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loghry, H.J.; Sondjaja, N.A.; Minkler, S.J.; Kimber, M.J. Secreted filarial nematode galectins modulate host immune cells. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 952104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, N.; Laxmanappa, H.S.; Muddapur, U.M.; Cheruvathur, J.; Prakash, S.M.U.; Thulasiram, H.V. Structural, molecular, functional and immunological characterization of Wuchereria bancrofti-galectin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, M.A.; Memon, M.A.; Jamil, T.; Naqvi, S.Z.; Aimulajiang, K.; Gadahi, J.A.; Xu, L.; Song, X.; Li, X.; Yan, R. Galectin domain containing protein from Haemonchus contortus modulates the immune functions of goat PBMCs and regulates CD4+ T-Helper cells in vitro. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Yang, F.; Yang, D.Q.; Jiang, P.; Liu, R.D.; Zhang, X.; Cui, J.; Wang, Z.Q. Molecular characterization of Trichinella spiralis galectin and its participation in larval invasion of host’s intestinal epithelial cells. Vet. Res. 2018, 49, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, B.N.; Song, Y.Y.; Han, L.L.; Zhang, X.Z.; Long, S.R.; Cui, J.; Wang, Z.Q. Trichinella spiralis galectin binding to toll-like receptor 4 induces intestinal inflammation and mediates larval invasion of gut mucosa. Vet. Res. 2023, 54, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, S.W.; Cheng, Y.K.; Zheng, W.W.; Long, S.R.; Wang, Z.Q.; Cui, J. Galactomannan inhibits Trichinella spiralis invasion of intestinal epithelium cells and enhances antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity related killing of larvae by driving macrophage polarization. Parasite 2024, 31, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitreva, M.; Jasmer, D.P.; Zarlenga, D.S.; Wang, Z.; Abubucker, S.; Martin, J.; Taylor, C.M.; Yin, Y.; Fulton, L.; Minx, P.; et al. The draft genome of the parasitic nematode Trichinella spiralis. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bänfer, S.; Jacob, R. Galectins in intra- and extracellular vesicles. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, F.C.; Chen, H.Y.; Kuo, C.C.; Sytwu, H.K. Role of Galectins in tumors and in clinical immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, C.; Oliveira, F.L.; Takiya, C.M.; Palumbo, A.; Hsu, D.K.; Liu, F.T.; Borojevic, R.; Chammas, R.; El-Cheikh, M.C. The involvement of the spleen during chronic phase of Schistosoma mansoni infection in galectin-3-/- mice. Histol. Histopathol. 2012, 27, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, E.Y.; Jeong, M.S.; Park, S.K.; Ha, S.C.; Yu, H.S.; Jang, S.B. Structural basis for carbohydrate recognition and anti-inflammatory modulation by gastrointestinal nematode parasite Toxascaris leonina Galectin. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 25326–25338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.N.; Song, Y.Y.; Ma, K.N.; Wang, B.N.; Long, S.R.; Liu, R.D.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.Q.; Cui, J. A novel C-type lectin from Trichinella spiralis mediates larval invasion of host intestinal epithelial cells. Vet. Res. 2022, 53, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dea-Ayuela, M.A.; Bolas-Fernández, F. Trichinella antigens: A review. Vet. Res. 1999, 30, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bolás-Fernandez, F.; Corral Bezara, L.D. TSL-1 antigens of Trichinella: An overview of their potential role in parasite invasion, survival and serodiagnosis of trichinellosis. Res. Vet. Sci. 2006, 81, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagano, I.; Wu, Z.; Takahashi, Y. Functional genes and proteins of Trichinella spp. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 104, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Liu, X.; Bai, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, X. Trichinella spiralis: Inflammation modulator. J. Helminthol. 2020, 94, e193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawistowska-Deniziak, A.; Bien-Kalinowska, J.; Basalaj, K. Regulation of human THP-1 macrophage polarization by Trichinella spiralis. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.W.; Zhang, N.Z.; Li, W.H.; Qin, H.T.; Liu, Y.J.; Ohiolei, J.A.; Niu, D.Y.; Yan, H.B.; Li, L.; Jia, W.Z.; et al. Trichinella spiralis Thioredoxin Peroxidase 2 regulates protective Th2 immune response in mice by directly inducing alternatively activated macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, P.J.; Allen, J.E.; Biswas, S.K.; Fisher, E.A.; Gilroy, D.W.; Goerdt, S.; Gordon, S.; Hamilton, J.A.; Ivashkiv, L.B.; Lawrence, T.; et al. Macrophage activation and polarization: Nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity 2014, 41, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapouri-Moghaddam, A.; Mohammadian, S.; Vazini, H.; Taghadosi, M.; Esmaeili, S.A.; Mardani, F.; Seifi, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Afshari, J.T.; Sahebkar, A. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6425–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.Q.; Li, A.; Yang, X.; Xiao, X.; Hu, R.; Wang, T.W.; Dou, X.Y.; Yang, D.J.; Dong, Z. Paeoniflorin exerts neuroprotective effects by modulating the M1/M2 subset polarization of microglia/macrophages in the hippocampal CA1 region of vascular dementia rats via cannabinoid receptor 2. Chin. Med. 2018, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegarty, L.M.; Jones, G.R.; Bain, C.C. Macrophages in intestinal homeostasis and inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 538–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolot, M.; Dewals, B.G. Macrophage activation and functions during helminth infection: Recent advances from the laboratory mouse. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 2790627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, M.G.; Herbert, D.R. Immune polarization by hookworms: Taking cues from T helper type 2, type 2 innate lymphoid cells and alternatively activated macrophages. Immunology 2016, 148, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhan, M.K.; Chen, C.L.; Shen, T.J.; Tseng, P.C.; Wang, Y.T.; Satria, R.D.; Yu, C.Y.; Lin, C.F. Polarization of Type 1 Macrophages is associated with the severity of viral encephalitis caused by Japanese encephalitis virus and Dengue virus. Cells 2021, 10, 3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, M.; von der Weid, P.Y. Lipopolysaccharides modulate intestinal epithelial permeability and inflammation in a species-specific manner. Gut Microbes. 2020, 11, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M. NF-κB as a critical link between inflammation and cancer. Csh Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a000141. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Park, M.K.; Yu, H.S. Toll-Like receptor gene expression during Trichinella spiralis infection. Korean J. Parasitol. 2015, 53, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Ye, J. Galectin from Trichinella spiralis alleviates DSS-induced colitis in mice by regulating the intestinal microbiota. Vet. Res. 2024, 55, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashfi, K.; Kannikal, J.; Nath, N. Macrophage reprogramming and cancer therapeutics: Role of iNOS-derived NO. Cells 2021, 10, 3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C.; Xing, N.; Zhou, P.; Jiao, Y. A zinc-modified Anemarrhena asphodeloides polysaccharide complex enhances immune activity via the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 249, 126017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Ayivi-Tosuh, S.M.; Wang, F.; Li, H.; Wang, G. A polysaccharide isolated from the fruits of Physalis alkekengi L. induces RAW264.7 macrophages activation via TLR2 and TLR4-mediated MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saracino, M.P.; Vila, C.C.; Cohen, M.; Gentilini, M.V.; Falduto, G.H.; Calcagno, M.A.; Roux, E.; Venturiello, S.M.; Malchiodi, E.L. Cellular and molecular changes and immune response in the intestinal mucosa during Trichinella spiralis early infection in rats. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebreselassie, N.G.; Moorhead, A.R.; Fabre, V.; Gagliardo, L.F.; Lee, N.A.; Lee, J.J.; Appleton, J.A. Eosinophils preserve parasitic nematode larvae by regulating local Immunity. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gansmuller, A.; Anteunis, A.; Venturiello, S.M.; Bruschi, F.; Binaghi, R.A. Antibody-dependent in-vitro cytotoxicity of newborn Trichinella spiralis larvae: Nature of the cells involved. Parasite Immunol. 1987, 9, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamble, H.R.; Bessonov, A.S.; Cuperlovic, K.; Gajadhar, A.A.; van Knapen, F.; Noeckler, K.; Schenone, H.; Zhu, X. International commission on trichinellosis: Recommendations on methods for the control of in domestic and wild animals intended for human consumption. Vet. Parasitol. 2000, 93, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Nagano, I.; Takahashi, Y.; Maekawa, Y. Practical methods for collecting Trichinella parasites and their excretory-secretory products. Parasitol. Int. 2016, 65, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.G.; Song, Y.Y.; Jiang, P.; Ren, H.N.; Yan, S.W.; Han, Y.; Liu, R.D.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.Q.; Cui, J. Characterization of a Trichinella spiralis putative serine protease. Study of its potential as sero-diagnostic tool. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, T.N.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 4.0: Discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.N.; Bai, S.J.; Wang, Z.; Han, L.L.; Yan, S.W.; Jiang, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.Q.; Cui, J. A metalloproteinase Tsdpy31 from Trichinella spiralis participates in larval molting and development. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 192, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srey, M.T.; Taccogna, A.; Oksov, Y.; Lustigman, S.; Tai, P.Y.; Acord, J.; Selkirk, M.E.; Lamb, T.J.; Guiliano, D.B. Vaccination with novel low-molecular weight proteins secreted from inhibits establishment of infection. PloS Neglect Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, R.D.; Bai, S.J.; Hao, H.N.; Yue, W.W.; Xu, Y.X.Y.; Long, S.R.; Cui, J.; Wang, Z.Q. Molecular characterization of a Trichinella spiralis aspartic protease and its facilitation role in larval invasion of host intestinal epithelial cells. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.X.; Zeng, J.; Hao, H.N.; Xu, Y.X.Y.; Liu, F.; Liu, R.D.; Long, S.R.; Wang, Z.Q.; Cui, J. Biological properties and roles of a Trichinella spiralis inorganic pyrophosphatase in molting and developmental process of intestinal larval stages. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.M.; Meng, S.; Zhang, B.H.; Ruan, R.L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Song, M.X.; Bai, Z.K. Effect of RNA interference with glutamate decarboxylase on acid resistance of Trichinella spiralis. Acta Trop. 2023, 241, 106869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Wang, B.N.; Weng, M.M.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.Q.; Cui, J. Molecular characterization of a novel serine proteinase from Trichinella spiralis and its participation in larval invasion of gut epithelium. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.B.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhen, J.B.; Zhang, J.P.; Pang, Z.X.; Song, X.W.; Lin, L.H.; Sun, F.; Lu, Y.X. Effects of exosomes derived from Trichinella spiralis infective larvae on intestinal epithelial barrier function. Vet. Res. 2022, 53, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lu, Q.Q.; Weng, M.M.; Li, Y.L.; Han, L.L.; Song, Y.Y.; Shi, Y.L.; Liu, R.D.; Cui, J.; Wang, Z.Q. Binding of Trichinella spiralis C-type lectin with syndecan-1 on intestinal epithelial cells mediates larval invasion of intestinal epithelium. Vet. Res. 2023, 54, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Wang, B.N.; Cheng, Y.K.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Long, S.R.; Liu, R.D.; Wang, Z.Q.; Cui, J. A novel Trichinella spiralis serine proteinase disrupted gut epithelial barrier and mediated larval invasion through binding to RACK1 and activating MAPK/ERK1/2 pathway. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0011872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.; Gao, X.; Wang, C.; Huo, X.; Liu, Z.; Sun, H.; Yang, X.; Sun, P.; Ma, X.; Meng, Q.; et al. Protective effects of ginsenoside Rg1 against lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury in mice through inhibiting toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 61, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, M.R.; Parikh, A.A.; Pritts, T.A.; Fischer, J.E.; Cottongim, S.; Szabo, C.; Salzman, A.L.; Hasselgren, P.O. Complement component C3 production in IL-1β-stimulated human intestinal epithelial cells is blocked by NF-κB inhibitors and by transfection with Ser 32/36 mutant IκBα. J. Surg. Res. 1999, 82, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.M.; Kitts, D.D. Evidence for inhibition of nitric oxide and inducible nitric oxide synthase in Caco-2 and RAW 264.7 cells by a Maillard reaction product [5-(5,6-dihydro-4H-pyridin-3-ylidenemethyl)furan-2-yl]-methanol. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 406, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.X.; Xu, Y.X.Y.; Hao, H.N.; Liu, R.D.; Jiang, P.; Long, S.R.; Wang, Z.Q.; Cui, J. Oral vaccination with recombinant Lactobacillus plantarum encoding Trichinella spiralis inorganic pyrophosphatase elicited a protective immunity in BALB/c mice. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovic, I.; Gruden-Movsesijan, A.; Ilic, N.; Mostarica-Stojkovic, M.; Sofronic-Milosavljevic, L. Trichinella spiralis shares epitopes with human autoantigens. Mem. I Oswaldo Cruz. 2012, 107, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, T.P.; Dinguirard, N.; Kunert, J.; Hokke, C.H. Molecular and functional characterization of a tandem-repeat galectin from the freshwater snail, intermediate host of the human blood fluke Schistosoma mansoni. Gene 2008, 411, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francischetti, I.M.B.; Ma, D.Y.; Andersen, J.F.; Ribeiro, J.M.C. Evidence for a lectin specific for sulfated glycans in the salivary gland of the malaria vector, Anopheles gambiae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, C.; Wei, X.; Xu, L.; Li, X. Recombinant galectins of male and female Haemonchus contortus do not hemagglutinate erythrocytes of their natural host. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 144, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Wei, H.; Li, L.; Shan, H.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G. Regulation of recombinant Trichinella spiralis 53-kDa protein (rTsP53) on alternatively activated macrophages via STAT6 but not IL-4Rα in vitro. Cell. Immunol. 2014, 288, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Cheng, P.; Wu, J.Y.; Guo, C.Y. PPARγ/NF-κB and TGF-β1/Smad pathway are involved in the anti-fibrotic effects of levo-tetrahydropalmatine on liver fibrosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 1645–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Bai, X.; Liu, X.L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.X.; Xu, F.Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, M.Y. Disruption of epithelial barrier of Caco-2 cell monolayers by excretory secretory products of Trichinella spiralis might be related to serine protease. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 634185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moczon, T.; Wranicz, M. Trichinella spiralis: Proteinases in the larvae. Parasitol. Res. 1999, 85, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hao, C.; Zhuang, Q.; Zhan, B.; Sun, X.; Huang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhu, X. Excretory/secretory products from Trichinella spiralis adult worms attenuated DSS-induced colitis in mice by driving PD-1-mediated M2 macrophage polarization. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 563784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lv, Z.; Peng, H.; Fung, M.; Yang, L.; Yang, J.; Zheng, H.; Liang, J.; Wu, Z. Effects of a recombinant schistosomal-derived anti-inflammatory molecular (rSj16) on the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced activated RAW264.7. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 110, 2429–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.H.; Wang, T.; Huang, C.X.; Lai, C.H.; Ling, Z.; Yong, Q. Effects of seleno-galactomannan on anti-oxidative and immune function of macrophage. Carbohyd Polym. 2021, 261, 117833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskwa, B. Trichinella spiralis: In vitro cytotoxicity of peritoneal cells against synchronous newborn larvae of different age. Parasitol. Res. 1999, 85, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.C.; Dong, L.W.; Yang, B.; He, Z.T.; Chen, Y.Y.; Deng, T.Z.; Huang, B.L.; Lan, C. Preinduction of heat shock protein 70 protects mice against post-infection irritable bowel syndrome via NF-κB and NOS/NO signaling pathways. Amino Acids. 2015, 47, 2635–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]














| Genes | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| iNOS | GAGACAGGGAAGTCTGAAGCAC | CCAGCAGTAGTTGCTCCTCTTC |
| Arg1 | CATTGGCTTGCGAGACGTAGAC | GCTGAAGGTCTCTTCCATCACC |
| IL-6 | TACCACTTCACAAGTCGGAGGC | CTGCAAGTGCATCATCGTTGTTC |
| TNF-α | TCTTCTCATTCCTGCTTGTGG | CACTTGGTGGTTTGCTACGA |
| IL-10 | CGGGAAGACAATAACTGCACCC | CGGTTAGCAGTATGTTGTCCAGC |
| TGF-β | TGATACGCCTGAGTGGCTGTCT | CACAAGAGCAGTGAGCGCTGAA |
| GAPDH | GGTTGTCTCCTGCGACTTCA | TGGTCCAGGGTTTCTTACTCC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weng, M.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, J.; Zheng, W.; Lu, Q.; Long, S.; Liu, R.; Wang, Z.; Cui, J. A Novel Trichinella spiralis Galectin Strengthens the Macrophage ADCC Killing of Larvae via Driving M1 Polarization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252010920
Weng M, Zhang R, Zhang Z, Wu J, Zheng W, Lu Q, Long S, Liu R, Wang Z, Cui J. A Novel Trichinella spiralis Galectin Strengthens the Macrophage ADCC Killing of Larvae via Driving M1 Polarization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(20):10920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252010920
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeng, Minmin, Ru Zhang, Zhaoyu Zhang, Jinyi Wu, Wenwen Zheng, Qiqi Lu, Shaorong Long, Ruodan Liu, Zhongquan Wang, and Jing Cui. 2024. "A Novel Trichinella spiralis Galectin Strengthens the Macrophage ADCC Killing of Larvae via Driving M1 Polarization" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 20: 10920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252010920
APA StyleWeng, M., Zhang, R., Zhang, Z., Wu, J., Zheng, W., Lu, Q., Long, S., Liu, R., Wang, Z., & Cui, J. (2024). A Novel Trichinella spiralis Galectin Strengthens the Macrophage ADCC Killing of Larvae via Driving M1 Polarization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(20), 10920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252010920






