Effect of Abelmoschus esculentus L. (Okra) on Dyslipidemia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategies
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Risk of Bias (ROB) and Quality Assessment
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selection of Evidence from the Literature
3.2. Risk of Bias (ROB) of the Included Trials
3.3. General Characteristics of Included Evidence
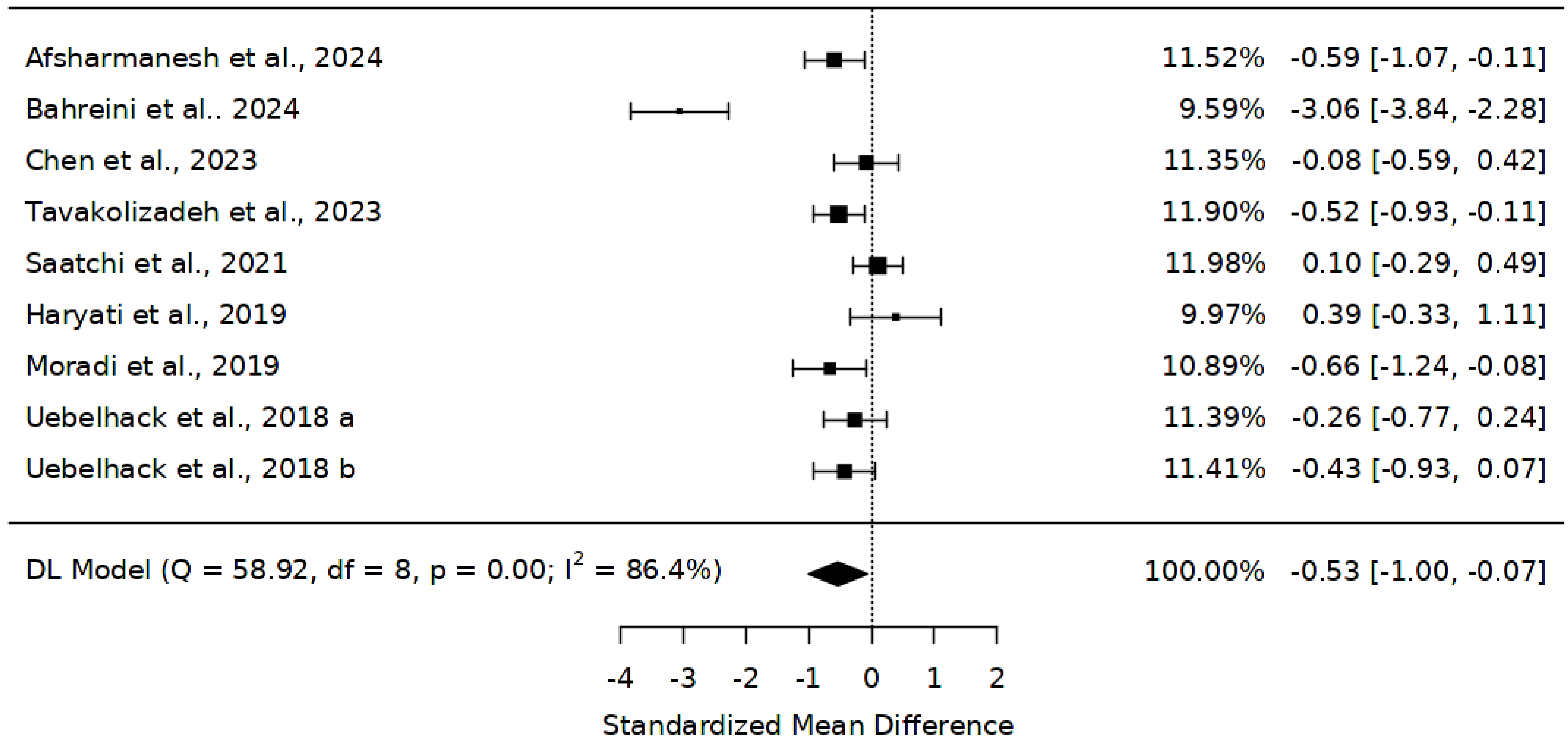
3.4. Effect of Abelmoschus esculentus on Total Cholesterol (TC) Levels
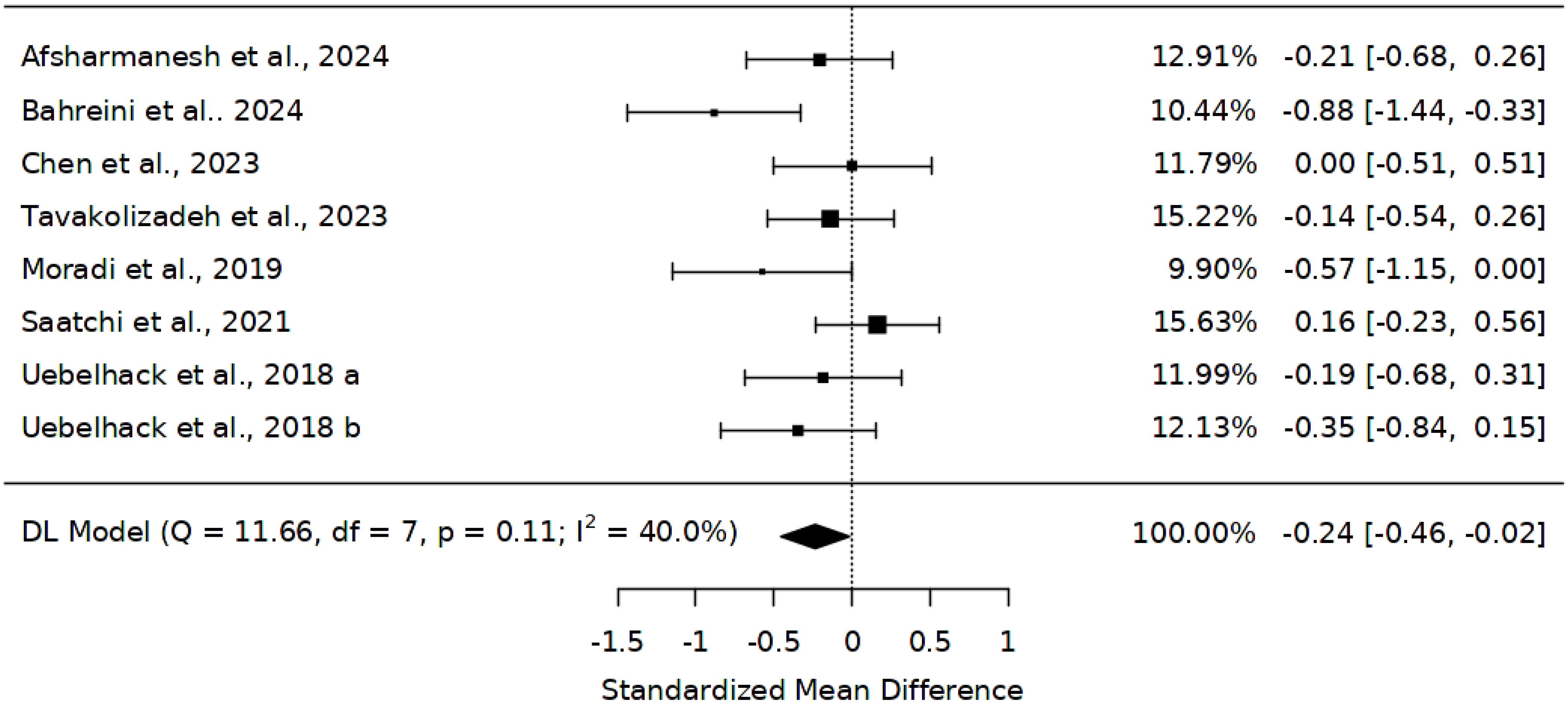
3.5. Effect of Abelmoschus esculentus on Triglyceride (TG) Levels
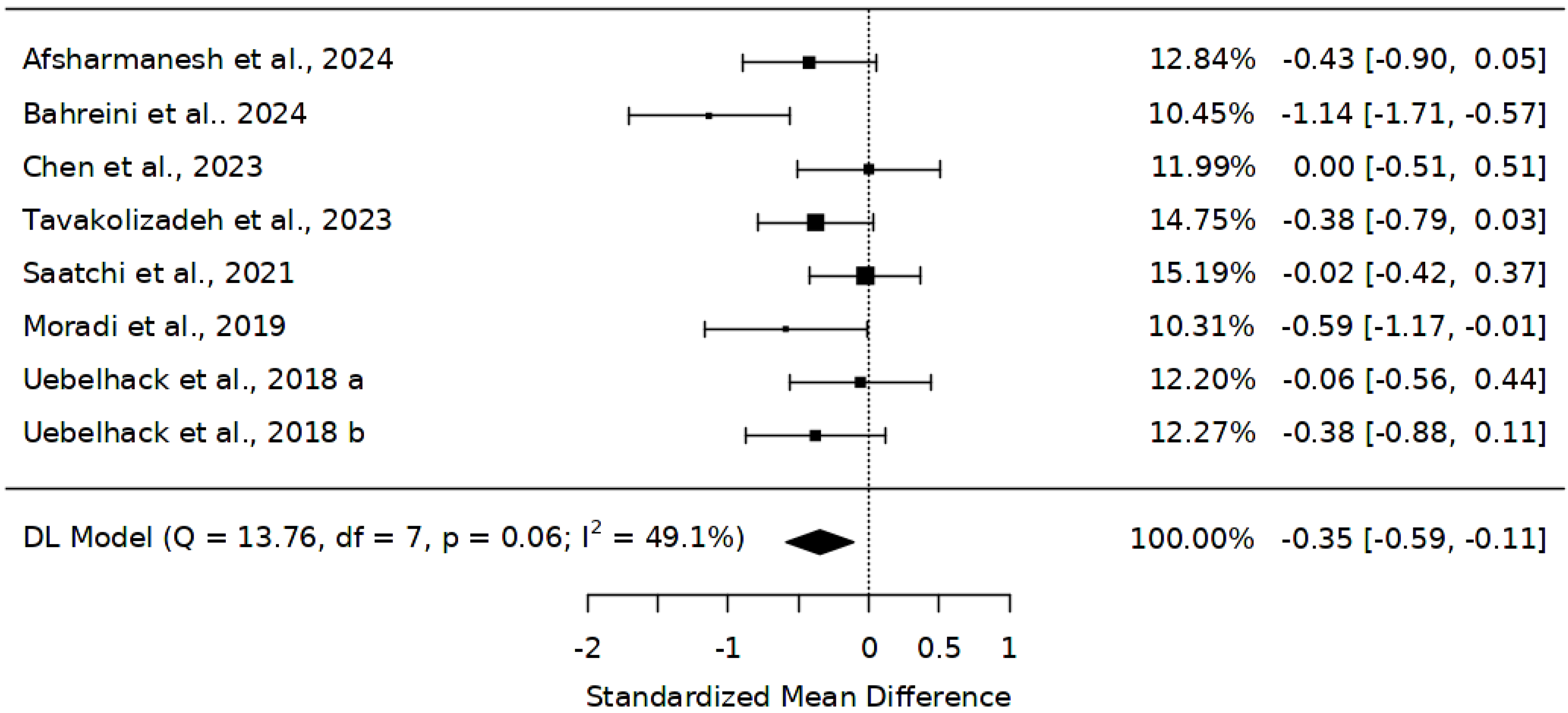
3.6. LDL Levels Following Abelmoschus esculentus Administration
3.7. HDL Following Abelmoschus esculentus Administration
3.8. Publication Bias
3.9. Meta-Regression
3.10. Overall Discussion of the Evidence
Strengths and Limitation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IDF. IDF Diabetes Atlas 10th Edition. Available online: www.diabetesatlas.org (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, Regional and Country-Level Diabetes Prevalence Estimates for 2021 and Projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavan, S.; Vassy, J.L.; Ho, Y.L.; Song, R.J.; Gagnon, D.R.; Cho, K.; Wilson, P.W.F.; Phillips, L.S. Diabetes Mellitus–Related All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in a National Cohort of Adults. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e011295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamrul-Hasan, A.B.M.; Alam, M.S.; Zarin, N.; Kabir, M.A.; Gaffar, A.J.; Hossain, M.F.; Talukder, S.K.; Bin Raunak, A.I.; Nabi, M.M.U.; Asaduzzaman, M.; et al. Prevalence and Patterns of Dyslipidemia among Lipid-Lowering Drug-Naïve Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus—A Countrywide Study in Bangladesh. Endocr. Metab. Sci. 2023, 13, 100152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omodanisi, E.I.; Tomose, Y.; Okeleye, B.I.; Ntwampe, S.K.O.; Aboua, Y.G. Prevalence of Dyslipidaemia among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in the Western Cape, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 8735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.; Tabasum Khan, I.; Junaid Ali, S.; Munir, W.; Khawar, H.; Seemab Amin, Z.; Nida Shehzadi, H.; Author, C. Dyslipidemia In Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. J. Surv. Fish. Sci. 2023, 10, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemework, B.; Woubshet, K.; Tadesse, S.A.; Eshetu, B.; Geleta, D.; Ketema, W. The Burden of Dyslipidemia and Determinant Factors Among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients at Hawassa University Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Hawassa, Ethiopia. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2024, 17, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, E.A.; Myasoedova, V.A.; Melnichenko, A.A.; Grechko, A.V.; Orekhov, A.N. Small Dense Low-Density Lipoprotein as Biomarker for Atherosclerotic Diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 1273042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paublini, H.; López González, A.A.; Busquets-Cortés, C.; Tomas-Gil, P.; Riutord-Sbert, P.; Ramírez-Manent, J.I. Relationship between Atherogenic Dyslipidaemia and Lipid Triad and Scales That Assess Insulin Resistance. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonuga, O.O.; Abbiyesuku, F.M.; Adedapo, K.S.; Sonuga, A.A. Insulin Resistance Index and Proatherogenic Lipid Indices in the Offspring of People with Diabetes. Dubai Diabetes Endocrinol. J. 2019, 25, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borén, J.; John Chapman, M.; Krauss, R.M.; Packard, C.J.; Bentzon, J.F.; Binder, C.J.; Daemen, M.J.; Demer, L.L.; Hegele, R.A.; Nicholls, S.J.; et al. Low-Density Lipoproteins Cause Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: Pathophysiological, Genetic, and Therapeutic Insights: A Consensus Statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2313–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Yang, S.; Lu, J.; Wu, M. Small, Dense Low-Density Lipoprotein-Cholesterol and Atherosclerosis: Relationship and Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 804214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakker, D.; Nair, S.; Pagada, A.; Jamdade, V.; Malik, A. Statin Use and the Risk of Developing Diabetes: A Network Meta-Analysis. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2016, 25, 1131–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daya, R.; Bayat, Z.; Raal, F.J. Prevalence and Pattern of Dyslipidaemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients at a Tertiary Care Hospital. J. Endocrinol. Metab. Diabetes S. Afr. 2017, 22, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Jimenez, L.; Morales-Palomo, F.; Moreno-Cabañas, A.; Ortega, J.F.; Mora-Rodríguez, R. Effects of Statin Therapy on Glycemic Control and Insulin Resistance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 947, 175672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, S.; Rapaka, N.; Prajapati, B.; Mandaliya, D.; Patel, S.; Muggalla, C.S.; Kapadia, B.; Babu, P.P.; Misra, P.; Saxena, U. Statins Exacerbate Glucose Intolerance and Hyperglycemia in a High Sucrose Fed Rodent Model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, F.; Lamendola, C.; Harris, C.S.; Harris, V.; Tsai, M.S.; Tripathi, P.; Abbas, F.; Reaven, G.M.; Reaven, P.D.; Snyder, M.P.; et al. Statins Are Associated with Increased Insulin Resistance and Secretion. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 2786–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besseling, J.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Defesche, J.C.; Hutten, B.A.; Hovingh, G.K. Association between Familial Hypercholesterolemia and Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2015, 313, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroda, V.R.; Ratner, R.E. Metformin and Type 2 Diabetes Prevention. Diabetes Spectr. 2018, 31, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derosa, G.; Maffioli, P. Ertugliflozin: A Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) Inhibitor for Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2018, 14, 1637–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosenzon, O.; Alguwaihes, A.; Leon, J.L.A.; Bayram, F.; Darmon, P.; Davis, T.M.E.; Dieuzeide, G.; Eriksen, K.T.; Hong, T.; Kaltoft, M.S.; et al. CAPTURE: A Multinational, Cross-Sectional Study of Cardiovascular Disease Prevalence in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes across 13 Countries. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Yan, Z.; Li, L.; Tang, W.; Qi, L.; Ye, J.; Ren, J.; Wan, Q.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, D. The Prevalence of Cardiovascular Disease in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes in China: Results from the Cross-Sectional CAPTURE Study. Diabetes Ther. 2022, 13, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Supports Scientifically-Proven Traditional Medicine. Available online: https://www.afro.who.int/news/who-supports-scientifically-proven-traditional-medicine (accessed on 3 August 2024).
- Roglic, G. WHO Global Report on Diabetes: A Summary. Int. J. Non-Commun. Dis. 2016, 1, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabila, M.; Damayanthi, E.; Marliyati, S.A. Extracts of Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.) Improves Dyslipidemia by Ameliorating lipid Profile While Not Affecting hs-CRP Levels in Streptozotocin-Induced Rats. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 196, 012039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokgalaboni, K.; Lebelo, L.S.; Modjadji, P.; Ghaffary, S. Okra Ameliorates Hyperglycaemia in Pre-Diabetic and Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Clinical Evidence. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1132650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoswa, W.N.; Mokgalaboni, K. Comprehensive Overview of the Effects of Amaranthus and Abelmoschus esculentus on Markers of Oxidative Stress in Diabetes Mellitus. Life 2023, 13, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakolizadeh, M.; Peyrovi, S.; Ghasemi-Moghaddam, H.; Bahadori, A.; Mohkami, Z.; Sotoudeh, M.; Ziaee, M. Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench) in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Clinical Trial. Acta Diabetol. 2023, 12, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- List of Plants in the Family Malvaceae. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/topic/list-of-plants-in-the-family-Malvaceae-2040580 (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Singh, P.; Kumar Tiwari, B.; Bilal Ahmad, S. An Overview on Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) and Its Importance as a Nutritive Vegetable in the World. Int. J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2018, 4, 227–233. [Google Scholar]
- Sorapong, B. Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench) as a Valuable Vegetable of the World. Ratar. Povrt. 2012, 49, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Razek, M.A.M.; Abdelwahab, M.F.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Hamed, A.N.E. A Review: Pharmacological Activity and Phytochemical Profile of Abelmoschus esculentus (2010–2022). RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 15280–15294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawuyi, I.F.; Park, J.J.; Lee, W.Y. Effect of Extraction Conditions on Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction of Polyphenolic Compounds from Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.) Leaves. Korean J. Food Preserv. 2020, 27, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, S.; Guo, R.; Xie, C.; Huang, X. Compounds from the Flowers and Fruits of Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench. Asian J. Tradit. Med. 2021, 16, 269–275. [Google Scholar]
- Mokgalabone, T.T.; Mpai, S.; Ndhlala, A.R. Organic Medium Enclosed Trough Growing Technique Improves Abelmoschus esculentus (okra) Growth, Yield and Some Nutritional Components. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, T.L.; Alonso Buriti, F.C.; Florentino, E.R. Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.) as a Potential Functional Food Source of Mucilage and Bioactive Compounds with Technological Applications and Health Benefits. Plants 2021, 10, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhalifa, A.E.O.; Alshammari, E.; Adnan, M.; Alcantara, J.C.; Awadelkareem, A.M.; Eltoum, N.E.; Mehmood, K.; Panda, B.P.; Ashraf, S.A. Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) as a Potential Dietary Medicine with Nutraceutical Importance for Sustainable Health Applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frandsen, T.F.; Bruun Nielsen, M.F.; Lindhardt, C.L.; Eriksen, M.B. Using the Full PICO Model as a Search Tool for Systematic Reviews Resulted in Lower Recall for Some PICO Elements. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2020, 127, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, M.L. Interrater Reliability: The Kappa Statistic. Biochem. Med. 2012, 22, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A Revised Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, T.H.; Habibi, N.; Aromataris, E.; Stone, J.C.; Leonardi-Bee, J.; Sears, K.; Hasanoff, S.; Klugar, M.; Tufanaru, C.; Moola, S.; et al. The Revised JBI Critical Appraisal Tool for the Assessment of Risk of Bias for Quasi-Experimental Studies. JBI Evid. Synth. 2024, 22, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huedo-Medina, T.B.; Sánchez-Meca, J.; Marín-Martínez, F.; Botella, J. Assessing Heterogeneity in Meta-Analysis: Q Statistic or I 2 Index? Psychol. Methods 2006, 11, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, M.B.; VanderWeele, T.J. Sensitivity Analysis for Publication Bias in Meta-Analyses. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C Appl. Stat. 2020, 69, 1091–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reza Afsharmanesh, M.; Reza Mansourian, A.; saghaeian Jazi, M.; Ghaffary, S.; Eshghinia, S.; Behnampour, N.; Mehdi Jafari, S. Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) Intake Improves Lipid Profile and Liver Transaminases in Pre-Diabetic Adults: A Randomized Double-Blinded Trial. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2024, 19, e143074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saatchi, A.; Aghamohammadzadeh, N.; Beheshtirouy, S.; Javadzadeh, Y.; Afshar, F.H.; Ghaffary, S. Anti-Hyperglycemic Effect of Abelmoschus culentesus (okra) on Patients with Diabetes Type 2: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, A.; Tarrahi, M.; Ghasempour, S.; Shafiepour, M.; Clark, C.C.T.; Safavi, S. The Effect of Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) on Lipid Profiles and Glycemic Indices in Type 2 Diabetic Adults: Randomized Double Blinded Trials. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 3325–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uebelhack, R.; Bongartz, U.; Seibt, S.; Bothe, G.; Chong, P.W.; De Costa, P.; Wszelaki, N. Double-Blind, Randomized, Three-Armed, Placebo-Controlled, Clinical Investigation to Evaluate the Benefit and Tolerability of Two Dosages of IQP-AE-103 in Reducing Body Weight in Overweight and Moderately Obese Subjects. J. Obes. 2019, 2019, 3412952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahreini, N.; Saghafi-Asl, M.; Nikpayam, O.; Safaei, E.; Sadra, V.; Fakhr, L.; Beyrampour-Basmenj, H.; Asgharian, P.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M. Effects of Dried Okra Extract on Lipid Profile, Renal Function and Some RAGE-Related Inflammatory Genes Expression in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 2024, 81, 103027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Q.; Sha, W.; Zhang, C.; Shen, T.; Lu, M.; Lei, T. Insulin Resistance and Serum Metabolomics Improvement in Subjects with Impaired Glucose Tolerance Treated with Hibiscus esculentus L. Vojnosanit. Pregl. 2023, 80, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haryati, M.; Rahmawati, S. The Effectiveness of Okra Fruit (Abelmoschus esculentus) on Fasting Blood Sugar and Total Cholesterol Level in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Ann. Trop. Med. Public. Health 2019, 22, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uadia, P.O.; Imagbovomwan, I.O.; Oriakhi, K.; Eze, I.G. Effect of Abelmoschus esculentus (okra)-Based Diet on Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes Mellitus in Adult Wistar Rats. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2020, 19, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Dirin, M.; Dabiri, F.; Sobhanian, S.A.; Ahmadi, A.; Roghani, M. Improvement of Serum Glucose and Lipid Factors by Some Polar and Non-Polar Extracts of Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench and Eryngium Caeruleum M. Bieb. in Streptozotocin-Diabetic Rats. Pharm. Chem. J. 2024, 58, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, B.; Yan, T.; Xu, F.; Xiao, F.; Wu, B.; Bi, K.; Jia, Y. Polysaccharide from Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench) Improves Antioxidant Capacity via PI3K/AKT Pathways and Nrf2 Translocation in a Type 2 Diabetes Model. Molecules 2019, 24, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguekouo, P.T.; Kuate, D.; Kengne, A.P.N.; Woumbo, C.Y.; Tekou, F.A.; Oben, J.E. Effect of Boiling and Roasting on the Antidiabetic Activity of Abelmoschus esculentus (okra) Fruits and Seeds in Type 2 Diabetic Rats. J. Food Biochem. 2018, 42, e12669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majd, N.E.; Tabandeh, M.R.; Shahriari, A.; Soleimani, Z. Okra (Abelmoscus esculentus) Improved Islets Structure, and Down-Regulated PPARs Gene Expression in Pancreas of High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Cell J. 2018, 20, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husen, S.A.; Wahyuningsih, S.P.A.; Ansori, A.N.M.; Hayaza, S.; Susilo, R.J.K.; Winarni, D.; Punnapayak, H.; Darmanto, W. Antioxidant Potency of Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus Moench) Pods Extract on SOD Level and Tissue Glucose Tolerance in Diabetic Mice. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2019, 12, 5683–5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, G.; Ren, D.; Yang, S.T. Hypolipidemic Activity of Okra Is Mediated through Inhibition of Lipogenesis and Upregulation of Cholesterol Degradation. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panighel, G.; Ferrarese, I.; Lupo, M.G.; Sut, S.; Dall’Acqua, S.; Ferri, N. Investigating the in Vitro Mode of Action of Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) as Hypocholesterolemic, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antioxidant Food. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2022, 5, 100126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, E.; Chandra Paul, N.; Kumar Banjerjee, P. Circulating Non-Esterified Free Fatty Acids in Bangladeshi Patients with Type-2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. Int. J. Health Sci. Res. 2024, 14, 364–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Xu, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, J.; Zhang, X.; Pan, B.; Xu, A.; Chen, Y.; et al. Effect of High NEFA Concentration on Lipid Metabolism Disorders in Hepatocytes Based on Lipidomics. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1372296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, F.; Fatema, K.; Rahim, A.T.M.A.; Ali, L. Glucose, Insulin and Non Esterified Fatty Acid Responses to Ladies Finger and Pointed Gourd in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Asian J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 3, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, F.; Zhong, Y.; Su, H.; Lefai, E.; Magaki, S.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Yong, W.H.; Chakravarti, A.; Guo, D. SREBP-1 Upregulates Lipophagy to Maintain Cholesterol Homeostasis in Brain Tumor Cells. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBose-Boyd, R.A.; Ye, J. SREBPs in Lipid Metabolism, Insulin Signaling, and Beyond. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2018, 43, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, J.Y.L.; Ferrell, J.M. Up to Date on Cholesterol 7 Alpha-Hydroxylase (CYP7A1) in Bile Acid Synthesis. Liver Res. 2020, 4, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahlon, T.S.; Chapman, M.H.; Smith, G.E. In Vitro Binding of Bile Acids by Okra, Beets, Asparagus, Eggplant, Turnips, Green Beans, Carrots, and Cauliflower. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warfvinge, C. Exploring the Vital Role of Bile in Digestion and Overall Health. Pancreat. Disord. Ther. 2023, 13, 1000260–1000261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikpayam, O.; Safaei, E.; Bahreini, N.; Saghafi-Asl, M. The Effects of Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.) Products on Glycemic Control and Lipid Profile: A Comprehensive Systematic Review. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.I.; Bayero, A.S.; Shettima, U.I. Levels of Total Phenolic and Flavonoids in Abelmoschus esculentus L. from Some Irrigation Areas of Kano State-Nigeria. Bayero J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2017, 9, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, X.; Rao, S.; Li, Y.; Zang, Y.; Zhu, B. Identification and Quantification of Flavonoids in Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L. Moench) and Antiproliferative Activity In Vitro of Four Main Components Identified. Metabolites 2022, 12, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
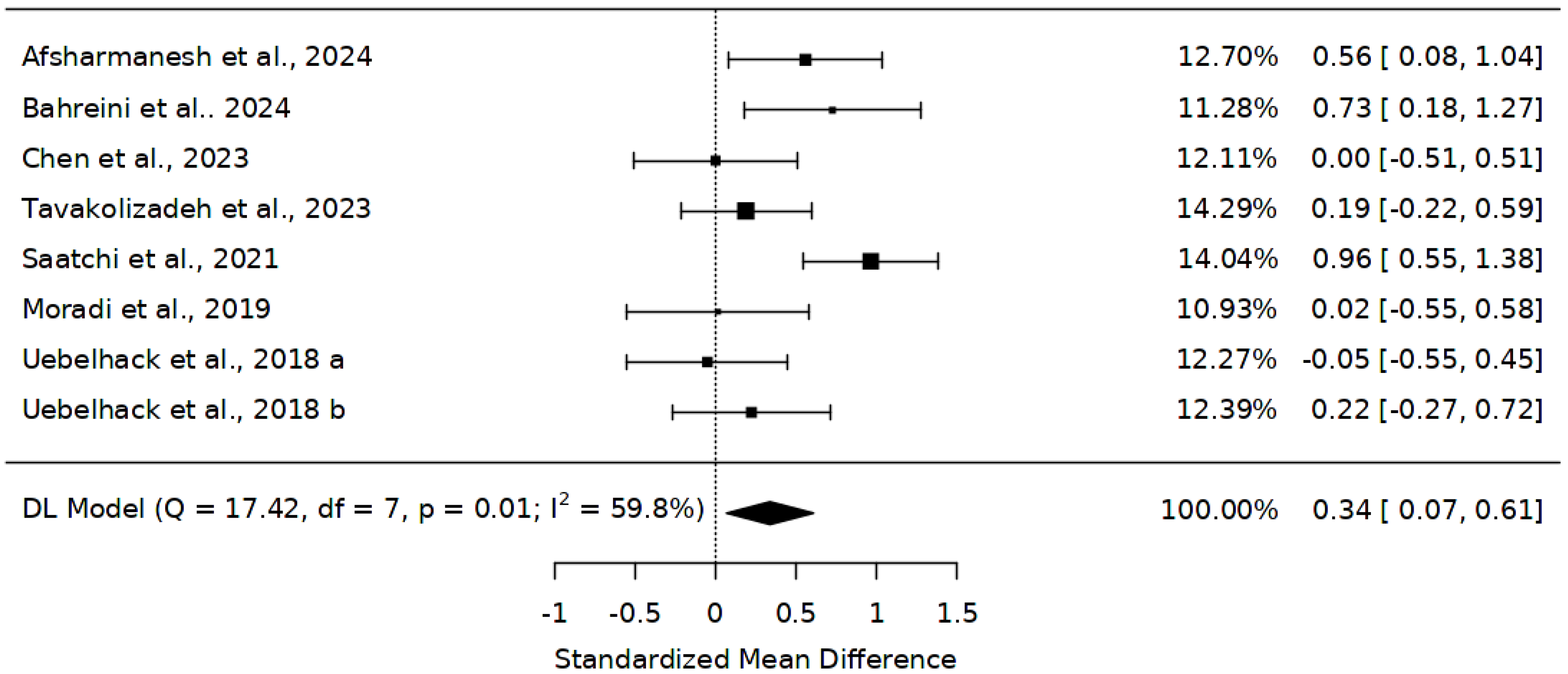
| Leading Author and Year | Study Design | Country | Sample Size and Treatment Groups of Participants | Abelmoschus Esculentus Group BMI (kg/m2) | Age of Participants (years) | Gender (m/f) Treatment/Placebo | Intervention and Period | Summary of Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tavakolizadeh et al. 2023 [28] | Double-blind, randomized, parallel, placebo-controlled trial | Iran | 94 patients with T2D 48 on okra 46 on placebo | 28.6 ± 2.05 | 40–65 | 17/31 13/33 | Six capsules containing 500 mg of powdered okra fruit three times a day for three months | Significant reduction in TC and TG without changes in LDL and HDL. |
| Afsharmanesh et al. 2024 [45] | Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial | Iran | 70 patients with prediabetes 35 on okra 35 on placebo | NR | 30–35 | 15/20 15/20 | Two capsules containing 500 mg of okra three times a day for eight weeks | Significant decrease in TC and LDL and increased HDL without changes in TG. |
| Bahreini et al. 2024 [49] | Triple-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial | Iran | 55 patients with diabetic nephropathy 30 on okra 25 on placebo | NR | 40–70 | 20/10 19/6 | 125 mg of dried okra extract for ten weeks | Significant decrease in TG and increase in HDL post okra treatment. |
| Saatchi et al. 2021 [46] | Double-blind, randomized clinical trial | Iran | 99 patients with T2D 50 on Abelmoschus esculentus 49 on placebo | 30.2 ± 4.3 | 18 and above | 23/26 13/37 | 1000 mg of Abelmoschus esculentus whole-fruit capsules orally every 6 h for eight weeks | No significant changes in TC, TG, LDL, and HDL. |
| Moradi et al. 2019 [47] | Double-blind, single-center, randomized clinical trial | Iran | 48 patients with T2D 25 on okra 23 on placebo | 24.90 ± 3.94 | 30–75 | 9/21 7/23 | 10 g okra powder blended in 150 g conventional yogurt for eight weeks | Significantly decreased TG, TC, and LDL without significant change in HDL. |
| Chen et al. 2023 [50] | RCT | China | 60 patients with IGT 30 on Hibiscus esculentus 30 on placebo | NR | Above 75 | 18/12 14/16 | 20 g of Hibiscus esculentus dried fruit tea daily for 60 days | No significant changes in TC, TG, LDL, and HDL. |
| Uebelhack et al. 2018 a [48] | Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial | Germany | 62 overweight to moderately obese patients 32 okra 30 placebo | 29.15 ± 2.17 | 18–65 | 6/27 9/22 | Two capsules of 165 mg dehydrated okra powder three times a day for 12 weeks | No significant difference in lipid profile after treatment. |
| Uebelhack et al. 2018 b [48] | Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial | Germany | 64 overweight to moderately obese patients 34 on okra 30 on placebo | 29.44 ± 2.31 | 18–65 | 9/26 9/22 | Two capsules of 330 mg dehydrated okra powder three times a day for 12 weeks | No significant difference in lipid profile after treatment. |
| Haryati et al. 2019 [51] | Quasi-experimental | Indonesia | 30 patients with T2D 15 on okra 15 on placebo | NR | 31–60 | 4/11 4/11 | Okra fruit water immersion (250 mL) once a day in the morning for two weeks | Significantly decreased TC. |
| Parameters | Moderators | Effect Size | SE | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total cholesterol [28,45,46,47,48,49,50,51] | Mean age | −0.2107 | 0.3368 | −0.8708 to 0.4493 | 0.5315 |
| Sample size | 0.2297 | 0.4850 | −0.7210 to 1.1803 | 0.6359 | |
| Patient status | −1.0071 | 0.6819 | −2.3436 to 0.3294 | 0.1397 | |
| Country | −1.0038 | 0.4720 | −1.9289 to −0.0786 | 0.0335 * | |
| Design | −0.7448 | 0.4649 | −1.6561 to 0.1664 | 0.1092 | |
| Triglyceride [28,45,46,47,48,49,50] | Mean age | −0.1861 | 0.1726 | −0.5244 to 0.1521 | 0.2808 |
| Sample size | −0.5745 | 0.3535 | −1.2673 to 0.1183 | 0.1041 | |
| Patient status | −0.2332 | 0.3138 | −0.8483 to 0.3819 | 0.4574 | |
| Country | −0.0000 | 0.3678 | −0.7209 to 0.7209 | 1.0000 | |
| Design | −0.1658 | 0.0976 | −0.3571 to 0.0255 | 0.0894 | |
| LDL [28,45,46,47,48,49,50] | Mean age | −0.2202 | 0.1801 | −0.5732 to 0.1327 | 0.2213 |
| Sample size | −0.5916 | 0.3913 | −1.3585 to 0.1753 | 0.1305 | |
| Patient status | −0.4599 | 0.3388 | −1.1239 to 0.2041 | 0.1746 | |
| Country | 0.0000 | 0.3727 | −0.7306 to 0.7306 | 1.0000 | |
| Design | −0.2819 | 0.0964 | −0.4709 to −0.0929 | 0.0035 * | |
| HDL [28,45,46,47,48,49,50] | Mean age | 0.1868 | 0.191 | −0.1890 to 0.5626 | 0.3299 |
| Sample size | 0.0165 | 0.4235 | −0.8135 to 0.8465 | 0.9689 | |
| Patient status | 0.5106 | 0.3775 | −0.2292 to 1.2504 | 0.1762 | |
| Country | 0.0000 | 0.3736 | −0.7322 to 0.7322 | 1.0000 | |
| Design | 0.3335 | 0.1629 | 0.0142 to 0.6527 | 0.0406 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mokgalaboni, K.; Phoswa, W.N.; Mokgalabone, T.T.; Dlamini, S.; Ndhlala, A.R.; Modjadji, P.; Lebelo, S.L. Effect of Abelmoschus esculentus L. (Okra) on Dyslipidemia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252010922
Mokgalaboni K, Phoswa WN, Mokgalabone TT, Dlamini S, Ndhlala AR, Modjadji P, Lebelo SL. Effect of Abelmoschus esculentus L. (Okra) on Dyslipidemia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(20):10922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252010922
Chicago/Turabian StyleMokgalaboni, Kabelo, Wendy N. Phoswa, Tyson T. Mokgalabone, Sanele Dlamini, Ashwell R. Ndhlala, Perpetua Modjadji, and Sogolo L. Lebelo. 2024. "Effect of Abelmoschus esculentus L. (Okra) on Dyslipidemia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Studies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 20: 10922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252010922
APA StyleMokgalaboni, K., Phoswa, W. N., Mokgalabone, T. T., Dlamini, S., Ndhlala, A. R., Modjadji, P., & Lebelo, S. L. (2024). Effect of Abelmoschus esculentus L. (Okra) on Dyslipidemia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(20), 10922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252010922







