T-Cell Dynamics Predicts Prognosis of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Receiving Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Baseline Characteristics
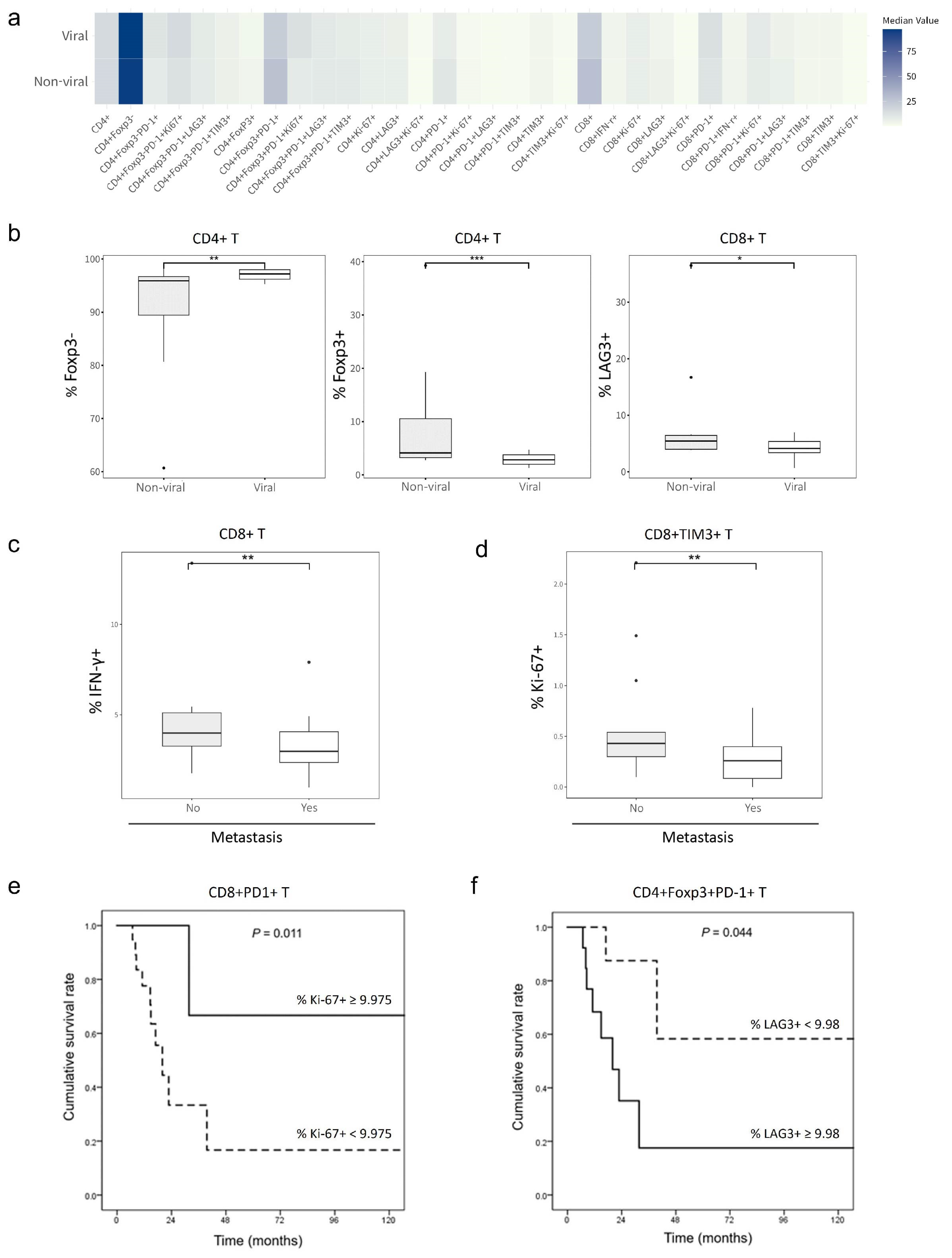
2.2. Effects of T-Cell Phenotypes on HCC Etiology, Extrahepatic Metastasis and Survival Outcomes
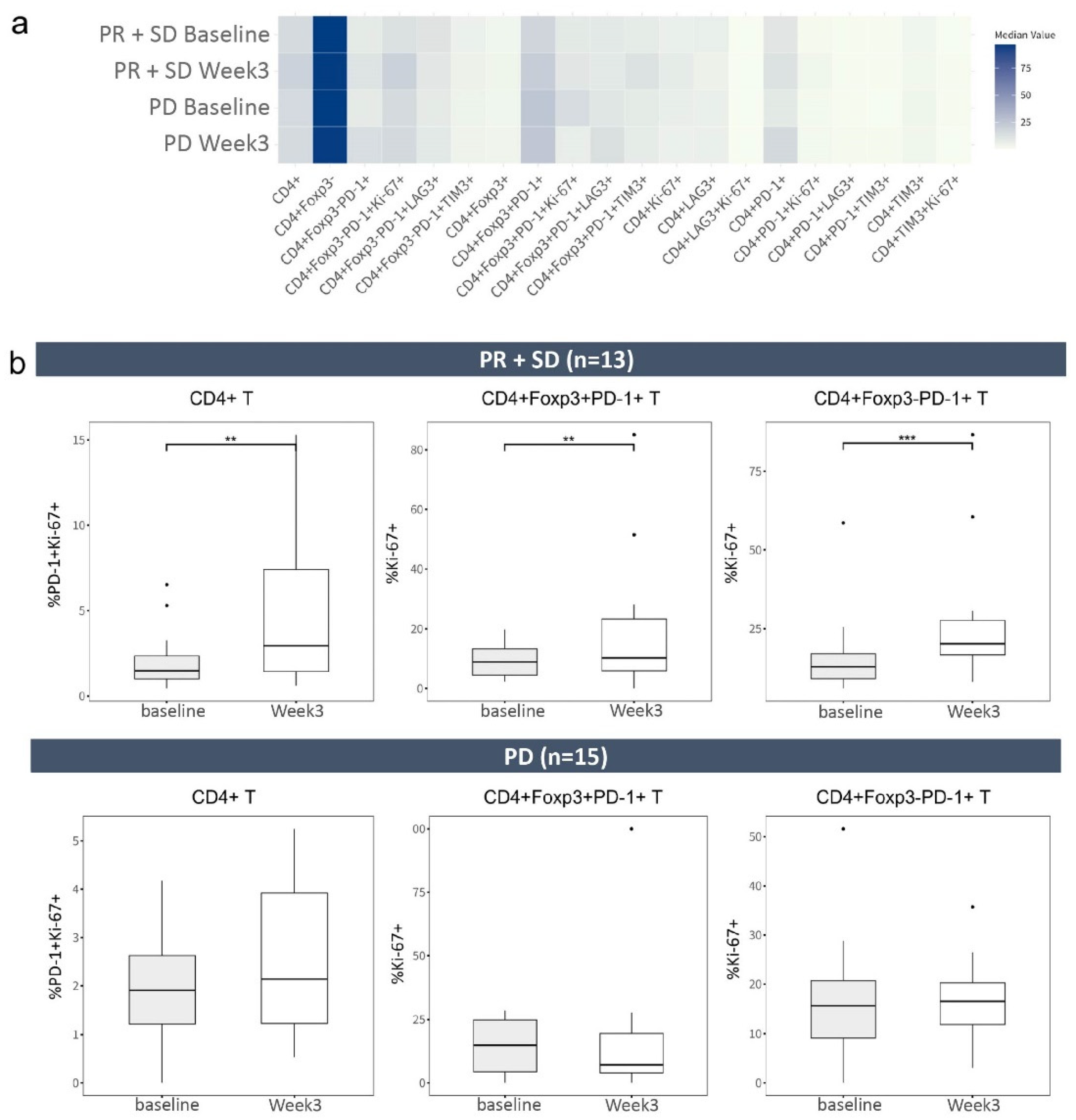
2.3. Frequencies of CD4+ T-Cell Phenotypes before and after Treatment with Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab
2.4. CD8+ T Cells with Inhibitory Receptors Are Reinvigorated by Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Sample Collection and Processing
4.3. Flow Cytometry
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciorusso, A.; Tartaglia, N.; Villani, R.; Serviddio, G.; Ramai, D.; Mohan, B.P.; Chandan, S.; Abd El Aziz, M.A.; Evangelista, J.; Cotsoglou, C.; et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib as first-line therapy of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 2379–2387. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Soria, J.-C.; Kowanetz, M.; Fine, G.D.; Hamid, O.; Gordon, M.S.; Sosman, J.A.; McDermott, D.F.; Powderly, J.D.; Gettinger, S.N. Predictive correlates of response to the anti-pd-l1 antibody mpdl3280a in cancer patients. Nature 2014, 515, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, N.; Hillan, K.J.; Novotny, W. Bevacizumab (avastin), a humanized anti-vegf monoclonal antibody for cancer therapy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 333, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Bentley, G.; Britten, C.D.; Amado, R.; Busuttil, R.W. Targeting vascular endothelial growth factor with the monoclonal antibody bevacizumab inhibits human hepatocellular carcinoma cells growing in an orthotopic mouse model. Liver Int. 2009, 29, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Cho, K.J.; Park, J.Y. Current status and future direction of immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma: What do the data suggest? Immune Netw. 2020, 20, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sia, D.; Jiao, Y.; Martinez-Quetglas, I.; Kuchuk, O.; Villacorta-Martin, C.; de Moura, M.C.; Putra, J.; Camprecios, G.; Bassaganyas, L.; Akers, N. Identification of an immune-specific class of hepatocellular carcinoma, based on molecular features. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 812–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappuyns, S.; Philips, G.; Vandecaveye, V.; Boeckx, B.; Schepers, R.; Van Brussel, T.; Arijs, I.; Mechels, A.; Bassez, A.; Lodi, F. Pd-1-cd45ra+ effector-memory cd8 t cells and cxcl10+ macrophages are associated with response to atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tang, Q.; Huang, J.; Zhan, M.; Zhao, W.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, F.; Lu, L. Prognostic analysis of tumor mutation burden and immune infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma based on tcga data. Aging 2021, 13, 11257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.C.; Postow, M.A.; Orlowski, R.J.; Mick, R.; Bengsch, B.; Manne, S.; Xu, W.; Harmon, S.; Giles, J.R.; Wenz, B. T-cell invigoration to tumour burden ratio associated with anti-pd-1 response. Nature 2017, 545, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalathil, S.; Lugade, A.A.; Miller, A.; Iyer, R.; Thanavala, Y. Higher frequencies of garp+ ctla-4+ foxp3+ t regulatory cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells in hepatocellular carcinoma patients are associated with impaired t-cell functionality. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2435–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugade, A.A.; Kalathil, S.; Miller, A.; Iyer, R.; Thanavala, Y. High immunosuppressive burden in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients: Can effector functions be restored? Oncoimmunology 2013, 2, e24679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Xu, D.; Liu, Z.; Shi, M.; Zhao, P.; Fu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, C. Increased regulatory t cells correlate with cd8 t-cell impairment and poor survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2328–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalathil, S.G.; Lugade, A.A.; Miller, A.; Iyer, R.; Thanavala, Y. Pd-1+ and foxp3+ t cell reduction correlates with survival of hcc patients after sorafenib therapy. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e86182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.; Alrasheed, N.; Richards, H.; Wilson, W.; Henry, J.; Conde, L.; De Massy, M.R.; Herrero, J.; Chain, B.; Quezada, S.A. Increased immune-regulatory receptor expression on effector t cells as early indicators of relapse following autologous stem cell transplantation for multiple myeloma. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 618610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, J.J.; Bendell, J.C.; Funke, R.; Sznol, M.; Korski, K.; Jones, S.; Hernandez, G.; Mier, J.; He, X.; Hodi, F.S. Atezolizumab in combination with bevacizumab enhances antigen-specific t-cell migration in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Cho, J.; Ku, B.M.; Koh, J.; Sun, J.-M.; Lee, S.-H.; Ahn, J.S.; Cheon, J.; Min, Y.J.; Park, S.-H. The first-week proliferative response of peripheral blood pd-1+ cd8+ t cells predicts the response to anti-pd-1 therapy in solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 2144–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, H.; Bai, L.; Tang, H. Identification of cd8+ t-cell exhaustion signatures for prognosis in hbv-related hepatocellular carcinoma patients by integrated analysis of single-cell and bulk rna-sequencing. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, D.; Núñez, N.G.; Pinyol, R.; Govaere, O.; Pinter, M.; Szydlowska, M.; Gupta, R.; Qiu, M.; Deczkowska, A.; Weiner, A. Nash limits anti-tumour surveillance in immunotherapy-treated hcc. Nature 2021, 592, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campani, C.; Imbeaud, S.; Couchy, G.; Ziol, M.; Hirsch, T.Z.; Rebouissou, S.; Noblet, B.; Nahon, P.; Hormigos, K.; Sidali, S.; et al. Circulating tumour DNA in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma across tumour stages and treatments. Gut 2024, 73, 1870–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Y.I.; Lee, S.S.; Demir, T.; Chamseddine, S.; Hu, Z.I.; Xiao, L.; Elsayes, K.; Morris, J.S.; Wolff, R.A.; Hiatia, R.; et al. Circulating tumor DNA (ctdna) as a biomarker of response to therapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with nivolumab. Cancer Biomark. 2024, 41, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumae, T.; Kodama, T.; Myojin, Y.; Maesaka, K.; Sakamori, R.; Takuwa, A.; Oku, K.; Motooka, D.; Sawai, Y.; Oshita, M.; et al. Circulating cell-free DNA profiling predicts the therapeutic outcome in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with combination immunotherapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Association, K.L.C. 2022 klca-ncc korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Liver Cancer 2023, 23, 1126. [Google Scholar]
- Lencioni, R.; Llovet, J.M. Modified recist (mrecist) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin. Liver Dis. 2010, 30, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | Total (n = 29) |
|---|---|
| Age, years | 63.8 ± 11.0 |
| Male sex | 24 (82.8) |
| AST, IU/L | 54.0 (36.0–76.5) |
| ALT, IU/L | 22.0 (16.5–47.0) |
| Total bilirubin, mg/dL | 0.8 (0.7–1.2) |
| Platelet, 103/μL | 156 (100–205) |
| Albumin, g/dL | 4.1 (3.8–4.4) |
| PT INR | 1.03 (0.99–1.10) |
| AFP, ng/mL | 243.8 (13.2–6855.6) |
| PIVKA-II, mAU/mL | 2047 (136–39,774) |
| Causes of HCC | |
| Viral | 17 (58.6) |
| NBNC | 12 (41.4) |
| Portal vein invasion | 12 (41.4) |
| Extrahepatic metastasis | 16 (55.2) |
| Presence of varix | 8 (27.6) |
| Best response | |
| PR | 6 (20.7) |
| SD | 8 (27.6) |
| PD | 15 (51.7) |
| Progression within 6 months | 17 (58.6) |
| PR+SD (n = 14) | PD (n = 15) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 66.4 ± 6.4 | 61.4 ± 13.7 | 0.230 |
| Male sex | 13 (92.9) | 11 (73.3) | 0.164 |
| AST, IU/L | 49.5 (31.5–93.5) | 60.0 (36.0–72.0) | 0.727 |
| ALT, IU/L | 28.5 (10.8–53.5) | 19.0 (17.0–32.0) | 0.631 |
| Total bilirubin, mg/dL | 0.9 (0.6–1.3) | 0.8 (0.7–1.1) | 0.982 |
| Platelet, 103/μL | 159 (113–245) | 134 (90–182) | 0.275 |
| Albumin, g/dL | 4.0 (3.8–4.3) | 4.3 (3.6–4.5) | 0.357 |
| PT INR | 1.02 (0.99–1.08) | 1.07 (0.98–1.12) | 0.358 |
| AFP, ng/mL | 23.9 (6.2–3483.1) | 1162.7 (59.8–34,229.5) | 0.070 |
| AFP ≥ 200 ng/mL | 4 (28.6) | 7 (46.7) | 0.316 |
| PIVKA-II, mAU/mL | 1099 (67–75,000) | 2237 (327–11,661) | 0.827 |
| Causes of HCC | 0.096 | ||
| Viral | 6 (42.9) | 11 (73.3) | |
| NBNC | 8 (57.1) | 4 (26.7) | |
| Portal vein invasion | 6 (42.9) | 6 (40.0) | 0.876 |
| Extrahepatic metastasis | 9 (64.3) | 7 (46.7) | 0.340 |
| Presence of varix | 5 (35.7) | 3 (20.0) | 0.344 |
| Progression within 6 months | 2 (14.3) | 15 (100) | <0.001 |
| Death | 9 (64.3) | 8 (53.3) | 0.550 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.W.; Park, S.; Park, H.J.; Cho, K.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Hwang, B.; Park, J.Y. T-Cell Dynamics Predicts Prognosis of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Receiving Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10958. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252010958
Lee HW, Park S, Park HJ, Cho KJ, Kim DY, Hwang B, Park JY. T-Cell Dynamics Predicts Prognosis of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Receiving Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(20):10958. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252010958
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hye Won, Suebin Park, Hye Jung Park, Kyung Joo Cho, Do Young Kim, Byungjin Hwang, and Jun Yong Park. 2024. "T-Cell Dynamics Predicts Prognosis of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Receiving Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 20: 10958. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252010958
APA StyleLee, H. W., Park, S., Park, H. J., Cho, K. J., Kim, D. Y., Hwang, B., & Park, J. Y. (2024). T-Cell Dynamics Predicts Prognosis of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Receiving Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(20), 10958. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252010958








