Essential Genes Discovery in Microorganisms by Transposon-Directed Sequencing (Tn-Seq): Experimental Approaches, Major Goals, and Future Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Biological and Biotechnological Relevance of Essential Genes
1.2. Detection of Essential Genes in Bacteria Using Transposon-Directed Sequencing (Tn-Seq)
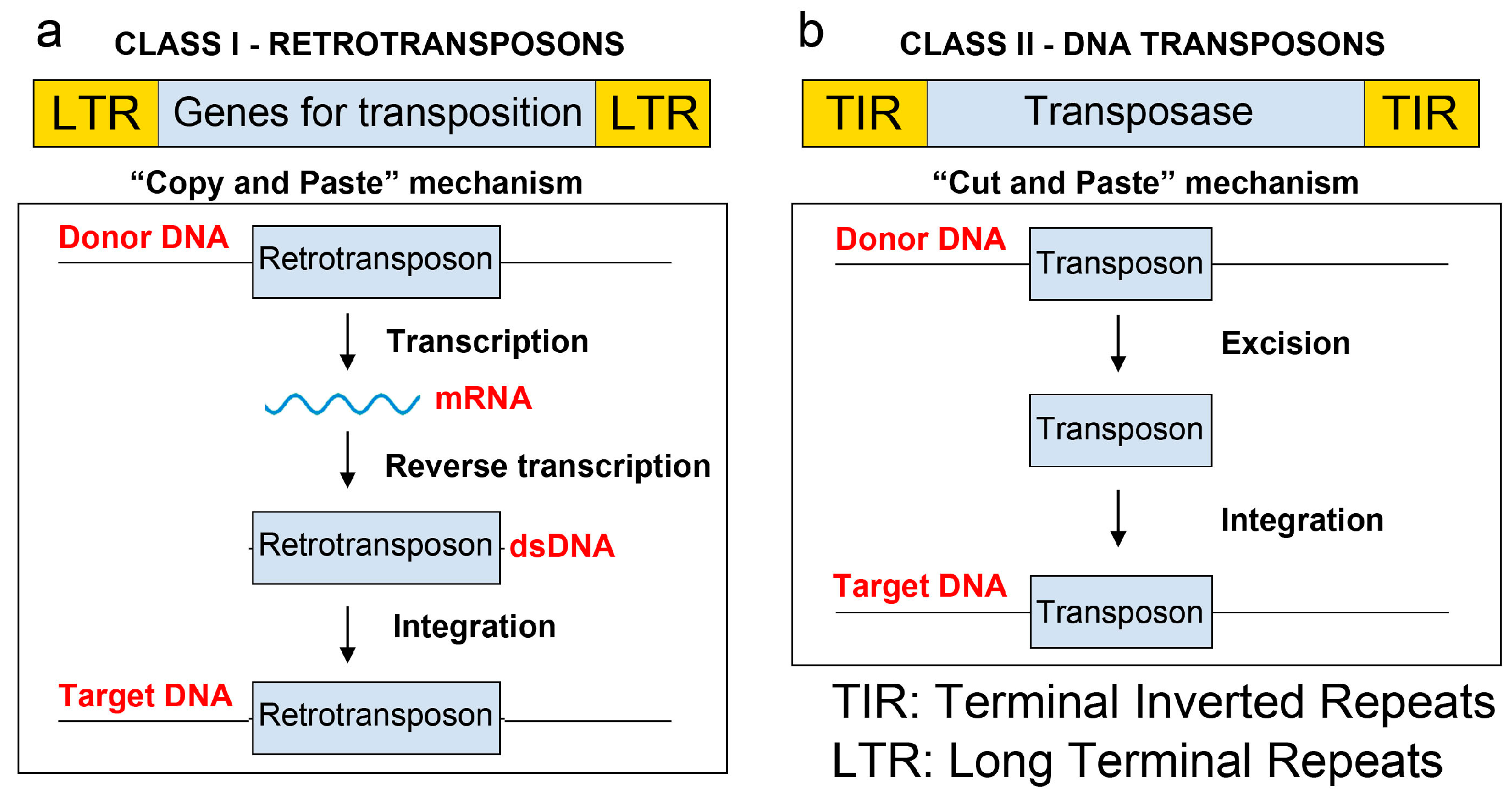
1.3. Main Transposons Used for Random Mutagenesis in Microorganisms
| Methodology | Microorganism | Transposon | Software | Number of Essential Genes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type IIs restriction enzymes | Ralstonia solanacearum | Mariner | TSAS | 465 | [26] |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | Himar1 | Bowtie, CLC, MAQ | 247 | [27] | |
| Streptococcus pyogenes | Krmit | SAMTools, HTseq | 227 and 241 (two strains) | [5] | |
| Streptococcus agalactiae | Himar1 | ESSENTIALS | 317 | [28] | |
| Schizosaccharomyces pombe | Hermes | Perl, Ruby | 1258 | [29] | |
| Herbaspirillum seropedicae | Mariner | ESSENTIALS | 395 | [30] | |
| Circle method | Rhodobacter sphaeroides | Tn5 | TSAS | 493 | [17] |
| Rhodopseudomonas palustris | Tn5 | Perl | 552 | [31] | |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | MiniDs | CLC | 299 | [32] | |
| Random primer method | Azoarcus olearius | Tn5 | Python, Perl, R | 616 | [33] |
| Caulobacter crescentus | Tn5 | MAQ | 480 | [34] | |
| Escherichia coli | Tn5 | CLC | 233 | [35] | |
| Sonication and Illumina adapter ligation | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Tn5371 | TRANSIT | 458 | [36] |
| Salmonella typhimurium | Tn5 | MAQ | 353 | [37] | |
| Porphyromonas gingivalis | Himar1 | Galaxy | 463 | [38] | |
| Burkholderia cenocepacia | Tn5 | Tn-Seq Explorer | 398 | [39] | |
| Pichia pastoris | TcBuster | Bowtie | 1086 | [40] |
| Methodology | Microorganism | Transposon | Software | Developmental Condition | Number of Essential Genes or Conditional Essential Genes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type IIs restriction enzymes | Dickeya dadantii | Himar9 | TRANSIT | Survival in chicory plants | 96 | [44] |
| Salmonella enterica | Tn5 | Python | Diluted LB medium, bile acid, high temperature | 105 | [45] | |
| Vibrio cholerae | Mariner | CLC | Immunity | 8 | [46] | |
| Bacillus subtilis | Mariner | CLC, Bowtie | Swarming motility | 36 | [47] | |
| Listeria monocytogenes | Tn5 | Fastp, Bowtie2 | Low temperature | 140 | [48] | |
| Sonication and Illumina adapter ligation | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Himar1 | TRANSIT | Antibiotic | 50 | [49] |
| Vibrio cholerae | Himar1 | CLC | Intestinal colonisation | 400 | [49] | |
| C-tailing | Escherichia coli | Mini-Tn10 | Galaxy | Antibiotic | 140 | [50] |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Himar1 | Python | Desiccation | 97 | [51] | |
| Salmonella enterica | Tn5 | ARTIST | Desiccation | 61 | [52] | |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | Mariner | Bowtie | Desiccation | 42 | [53] | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | Mariner | Bowtie | Invasive infection | 200 | [54] | |
| Salmonella typhimurium | Tn5 | TRANSIT | Iron-restriction | 336 | [55] | |
| Random barcode (RB-Tn-Seq) | Escherichia coli | Mariner | Perl | Different Bacterium–carbon source combinations | 5196 | [56] |
| Phaeobacter inhibens | ||||||
| Pseudomonas stutzer | ||||||
| Shewanella amazonensis | ||||||
| Shewanella oneidensis |
2. Tn-Seq Approaches in Microorganisms
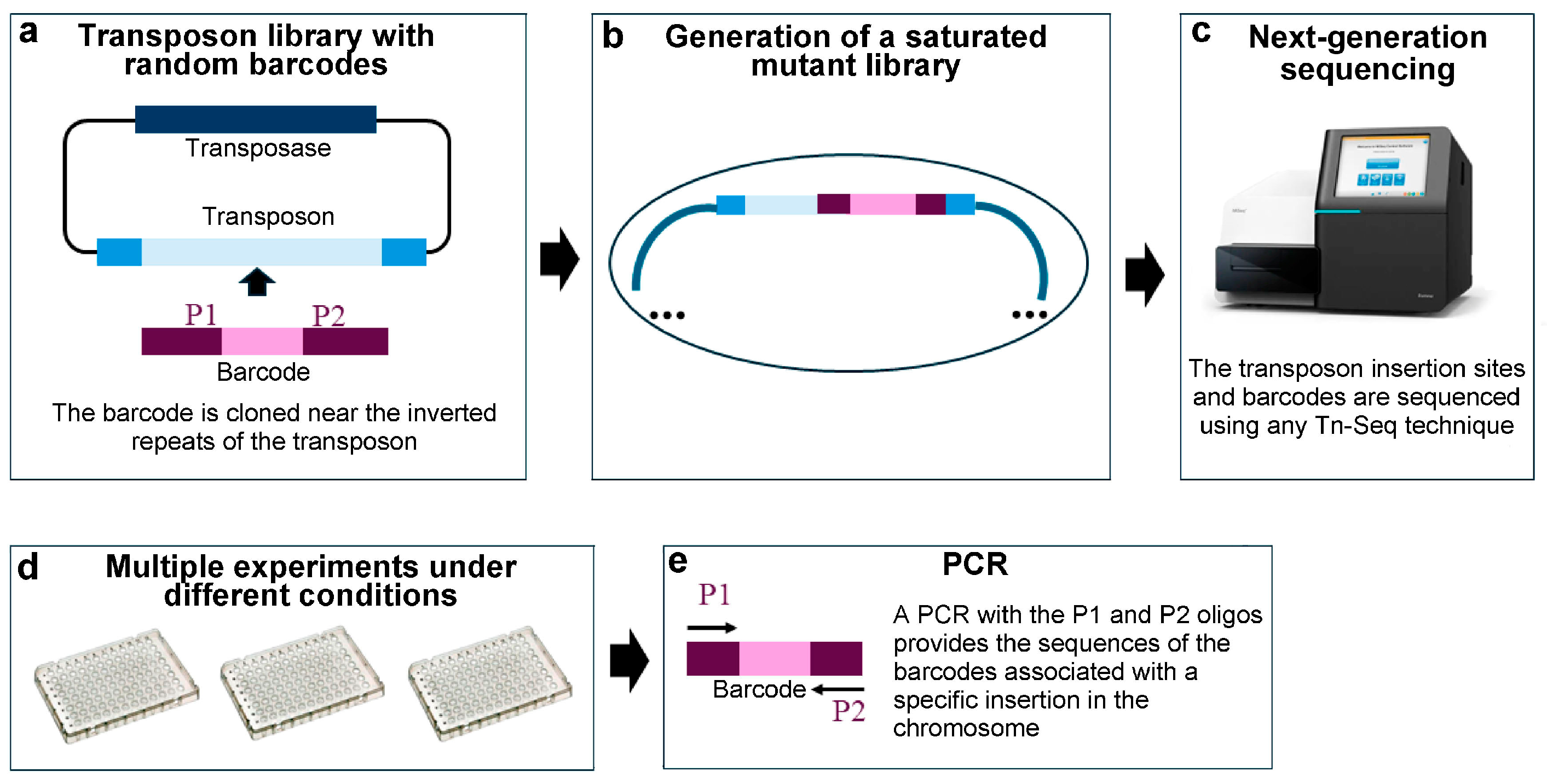
2.1. Number of Transposon Insertional Mutants Required for a Saturated Mutant Library
2.2. Biases in Transposon Mutagenesis
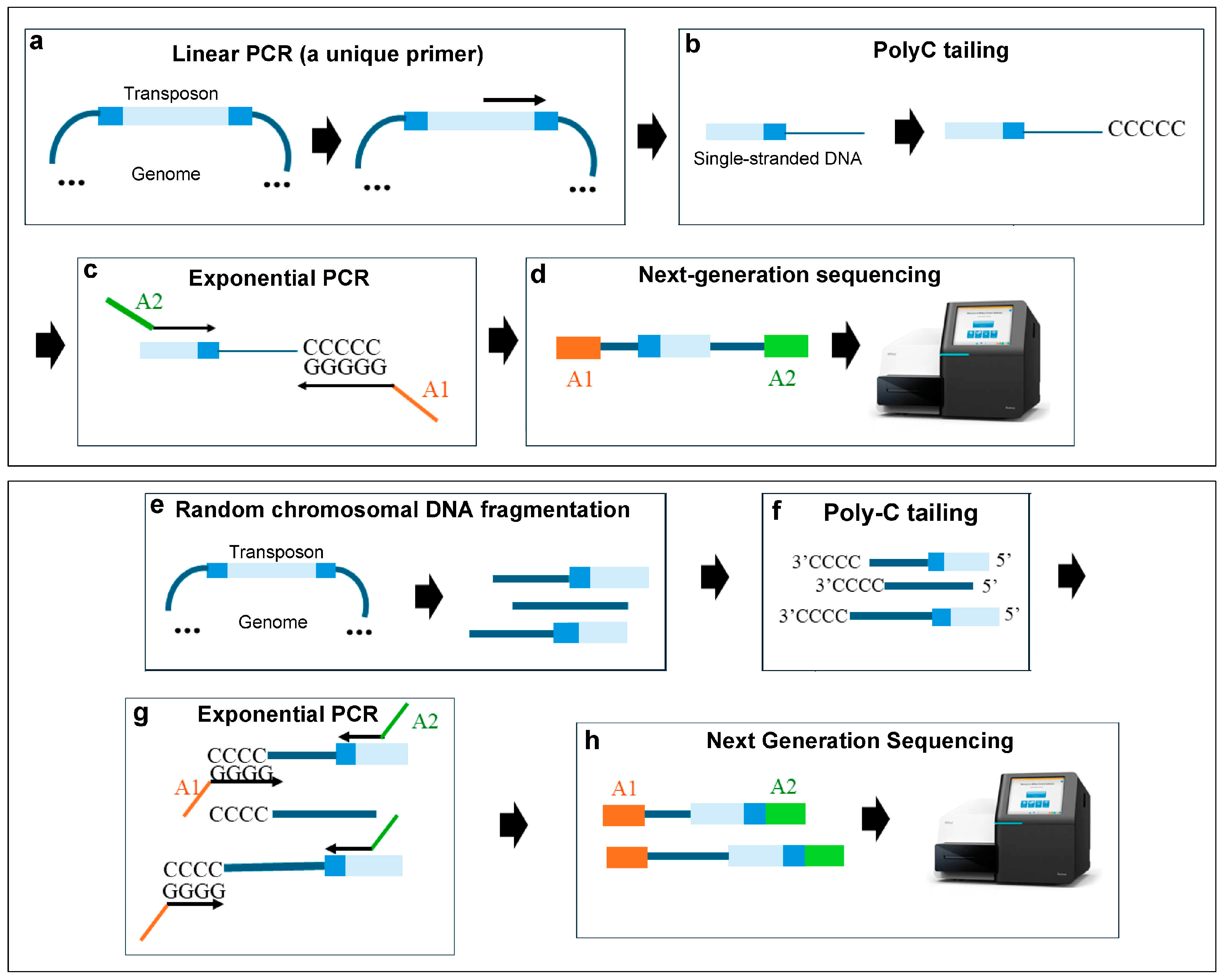
3. Transposon-Directed Sequencing
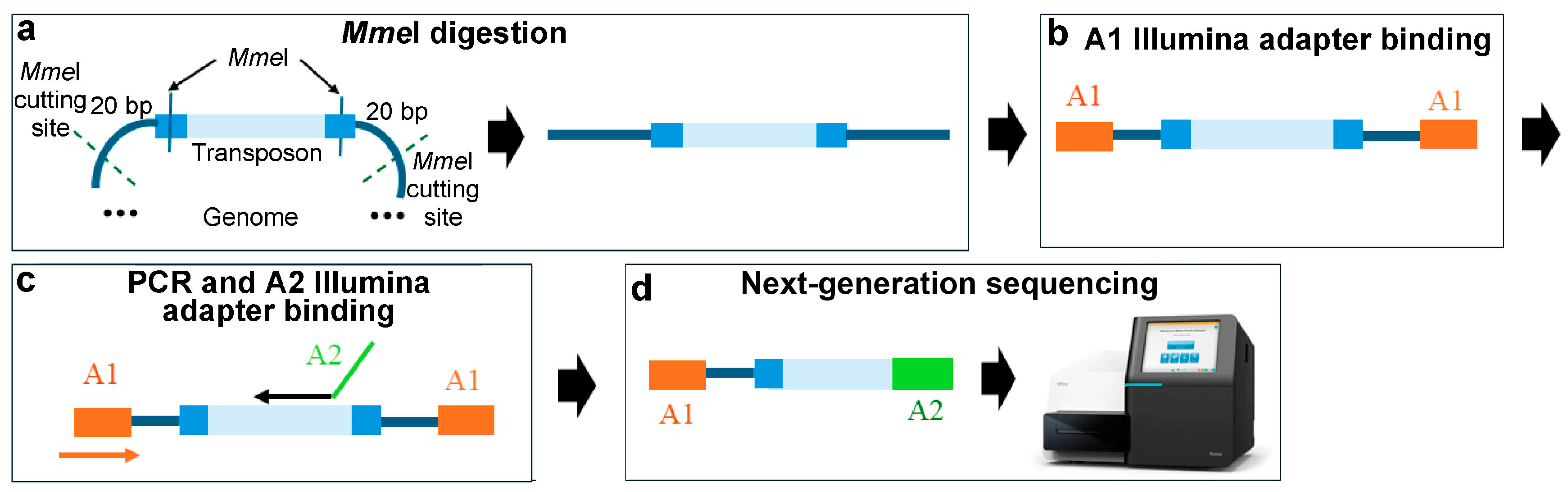
3.1. Methods Based on Type IIs Restriction Enzymes
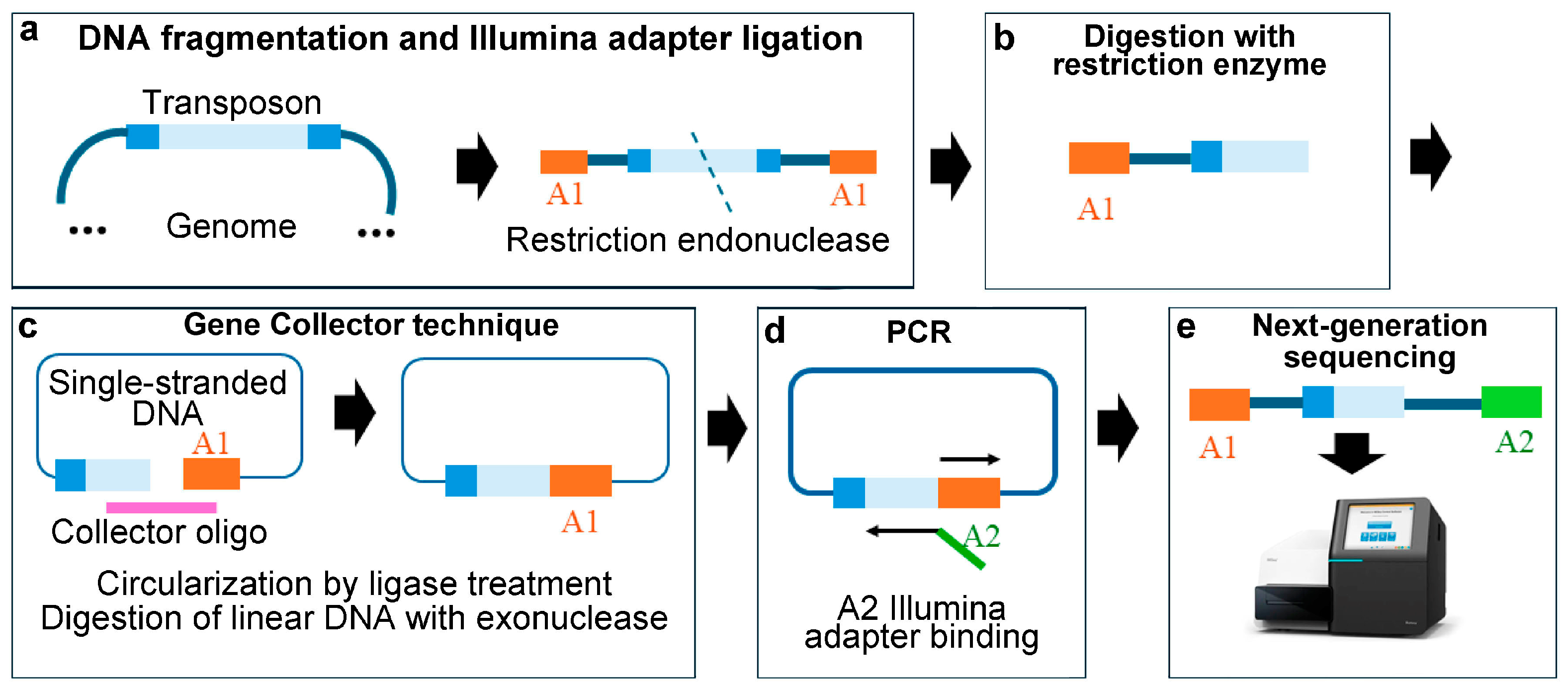
3.2. Circle Method
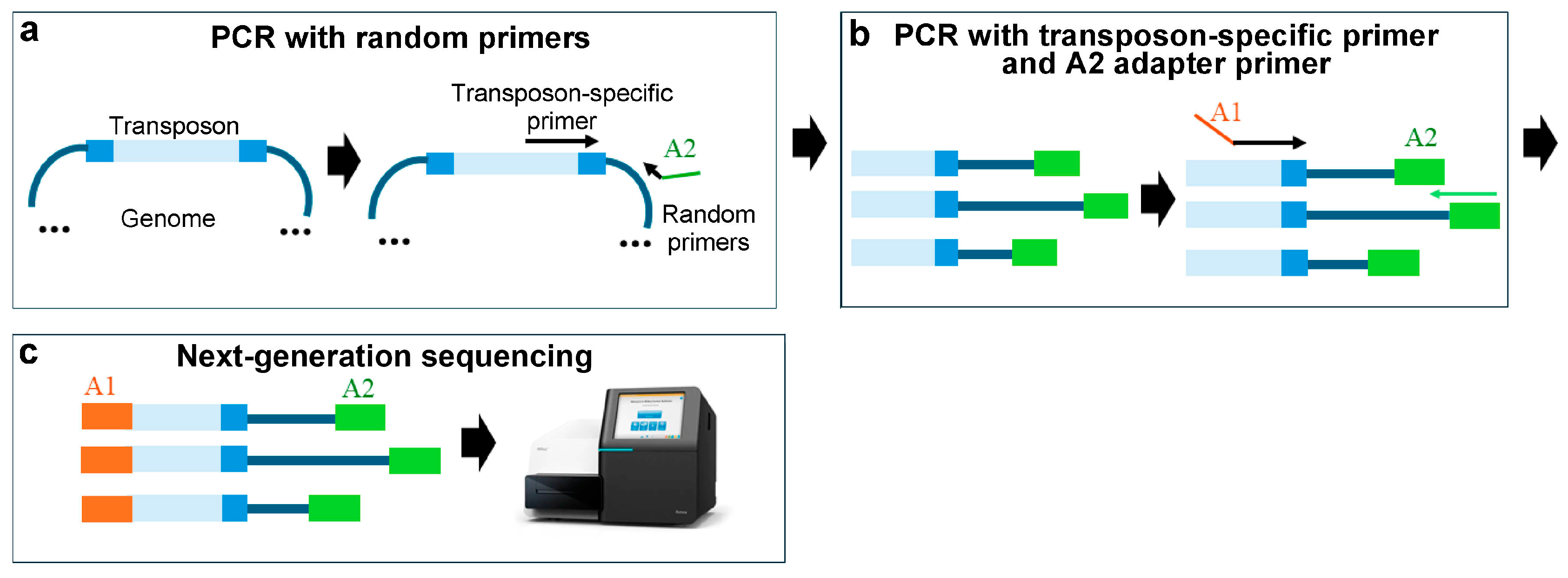
3.3. The Random Primer Method
3.4. Sonication and the Illumina Adapter Ligation Method
3.5. C-Tailing-Based Methods
3.6. Random Barcode Transposon Sequencing (RB-Tn-Seq)
4. Identification of Transposon Insertion Sites Through Bioinformatics Analysis
4.1. Tn-Seq Analysis Software (TSAS)
4.2. TRANSIT Software
4.3. ESSENTIALS Software
4.4. ARTIST Software
4.5. Tn-Seq Analysis Using R, Perl, Ruby, and Python Programming Lenguages
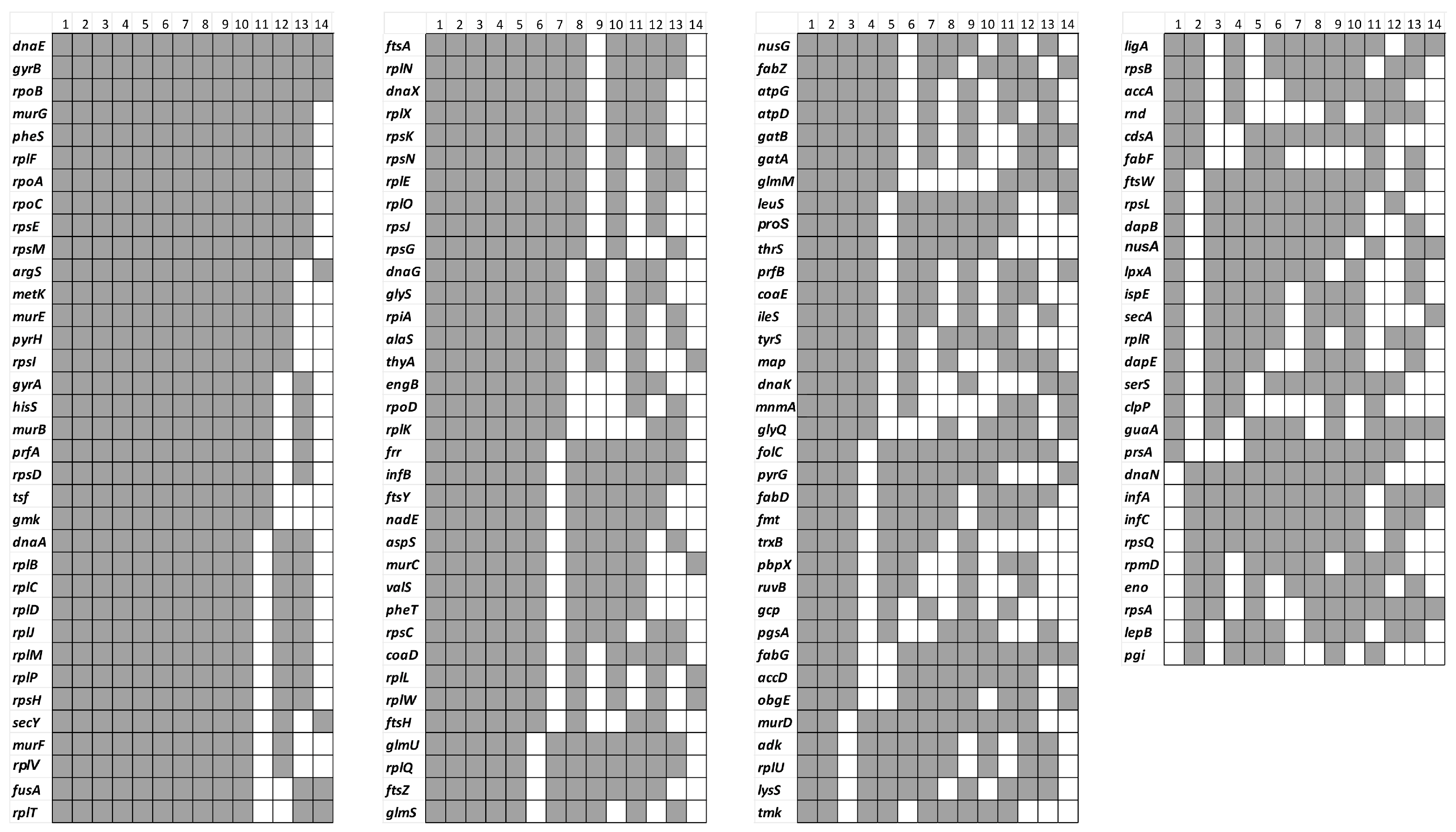
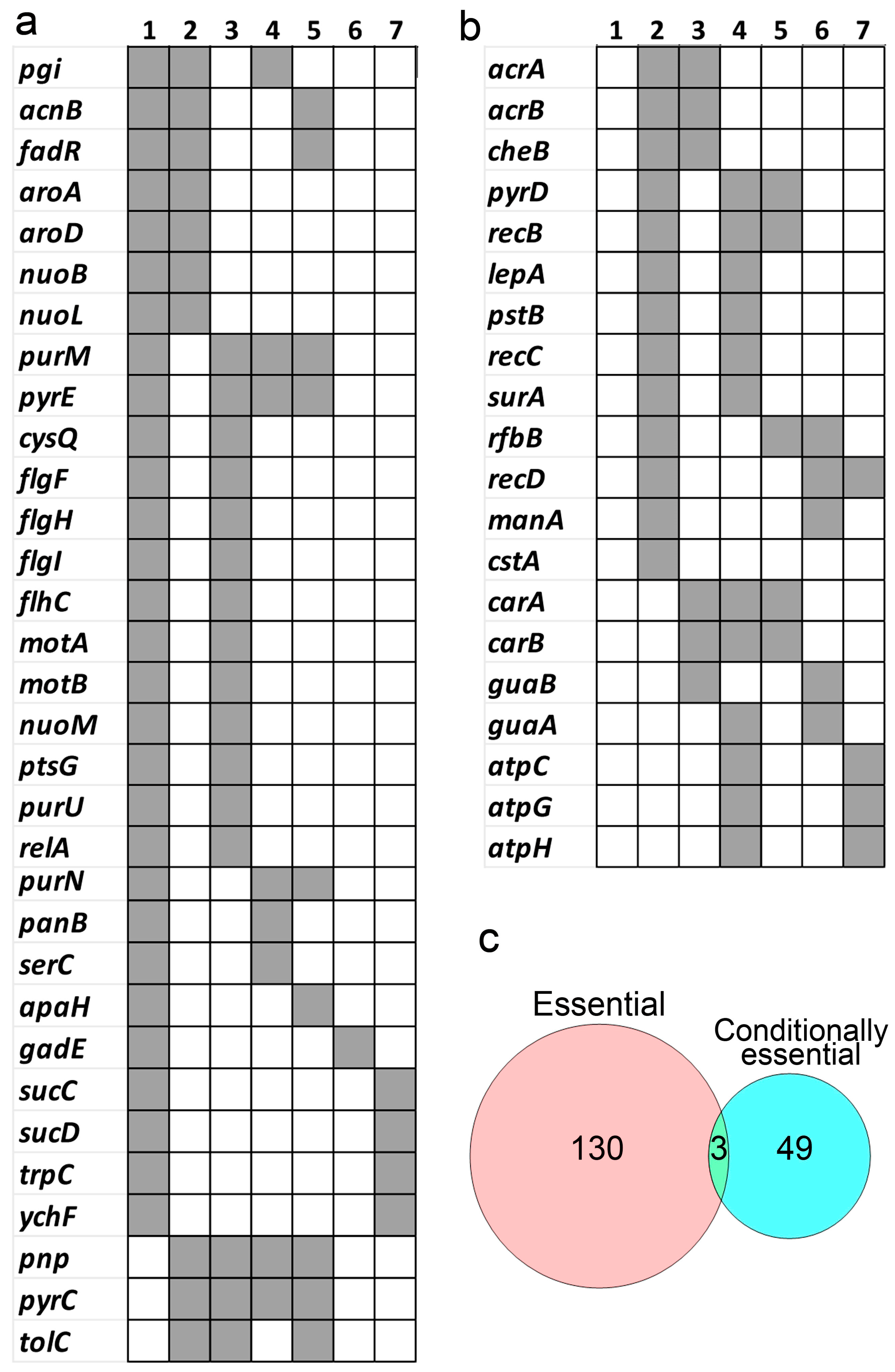
5. Essential and Conditionally Essential Genes in Bacteria Identified by Tn-Seq
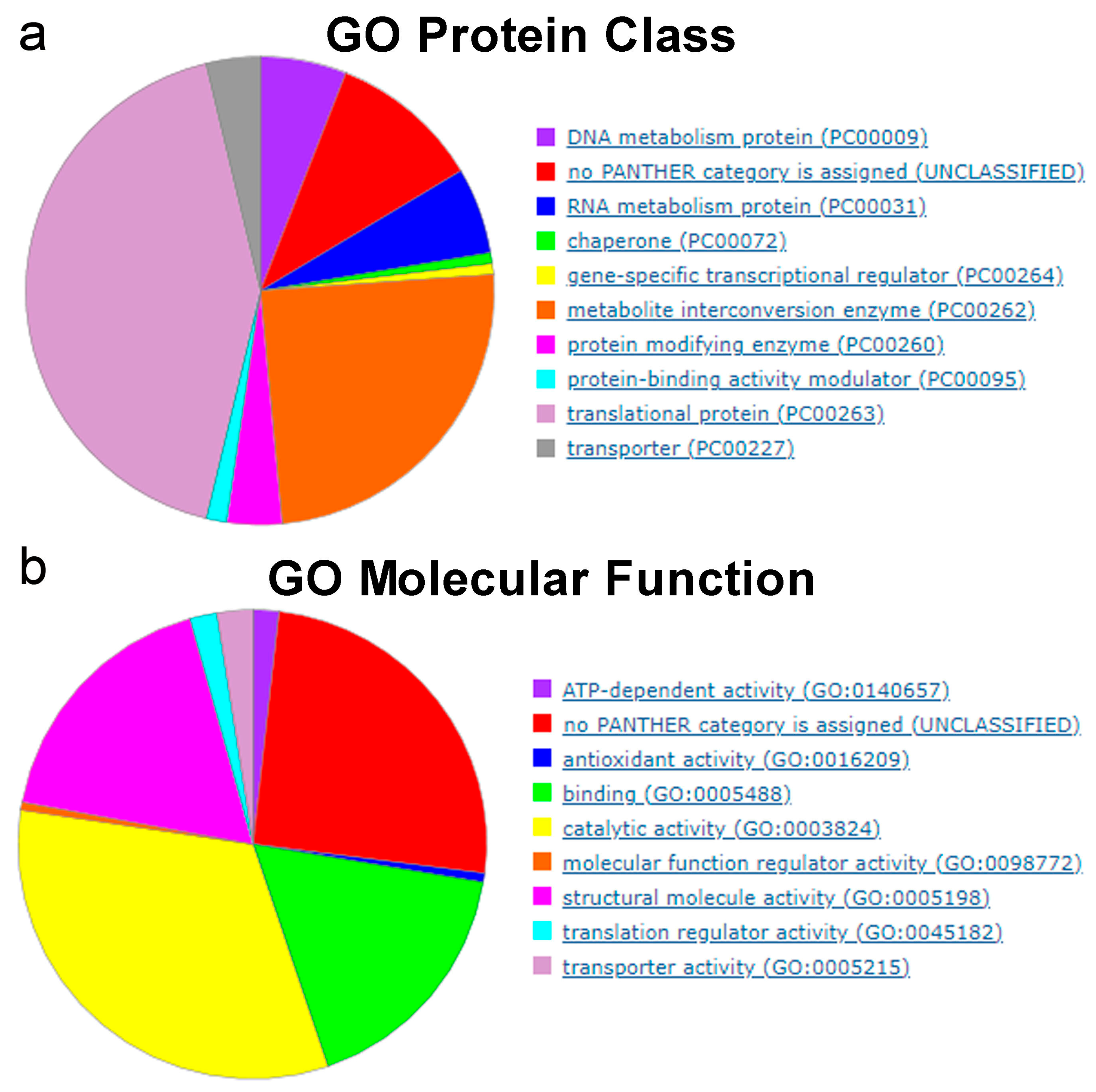
5.1. Essential Genes in Bacteria
5.2. Conditionally Essential Genes in Bacteria
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pugazhendhi, A.S.; Wei, F.; Hughes, M.; Coathup, M. Bacterial adhesion, virulence, and biofilm formation. In Musculoskeletal Infection; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 19–64. [Google Scholar]
- Leseigneur, C.; Le-Bury, P.; Pizarro-Cerda, J.; Dussurget, O. Emerging Evasion Mechanisms of Macrophage Defenses by Pathogenic Bacteria. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 577559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, F.R.; Lee, S.W.; McConnell, M.J. Using bacterial genomes and essential genes for the development of new antibiotics. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 134, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Wang, Z.; Huang, X.; Hu, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X. Developing genome-reduced Pseudomonas chlororaphis strains for the production of secondary metabolites. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Breton, Y.; Belew, A.T.; Valdes, K.M.; Islam, E.; Curry, P.; Tettelin, H.; Shirtliff, M.E.; El-Sayed, N.M.; McIver, K.S. Essential Genes in the Core Genome of the Human Pathogen Streptococcus pyogenes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, R.K.; Jiang, T.; Kwon, Y.M. Essential genome of Campylobacter jejuni. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgens, D.W.; Deans, R.M.; Li, A.; Bassik, M.C. Systematic comparison of CRISPR/Cas9 and RNAi screens for essential genes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 634–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.M.; Marran, K.; Parker, J.S.; Silva, J.; Golding, M.; Schlabach, M.R.; Elledge, S.J.; Hannon, G.J.; Chang, K. Profiling essential genes in human mammary cells by multiplex RNAi screening. Science 2008, 319, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousset, F.; Cui, L.; Siouve, E.; Becavin, C.; Depardieu, F.; Bikard, D. Genome-wide CRISPR-dCas9 screens in E. coli identify essential genes and phage host factors. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.M.; Ricke, S.C.; Mandal, R.K. Transposon sequencing: Methods and expanding applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barquist, L.; Boinett, C.J.; Cain, A.K. Approaches to querying bacterial genomes with transposon-insertion sequencing. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, A.K.; Barquist, L.; Goodman, A.L.; Paulsen, I.T.; Parkhill, J.; van Opijnen, T. A decade of advances in transposon-insertion sequencing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 526–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Opijnen, T.; Levin, H.L. Transposon Insertion Sequencing, a Global Measure of Gene Function. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2020, 54, 337–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrato-Capuchina, A.; Matute, D.R. The Role of Transposable Elements in Speciation. Genes 2018, 9, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Tian, P.; Tan, T. Genomic landscapes of bacterial transposons and their applications in strain improvement. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 6383–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Opijnen, T.; Camilli, A. Transposon insertion sequencing: A new tool for systems-level analysis of microorganisms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, B.T.; Imam, S.; Scarborough, M.J.; Noguera, D.R.; Donohue, T.J. Combining Genome-Scale Experimental and Computational Methods To Identify Essential Genes in Rhodobacter sphaeroides. mSystems 2017, 2, e00015-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zomer, A.; Burghout, P.; Bootsma, H.J.; Hermans, P.W.; van Hijum, S.A. ESSENTIALS: Software for rapid analysis of high throughput transposon insertion sequencing data. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeJesus, M.A.; Ambadipudi, C.; Baker, R.; Sassetti, C.; Ioerger, T.R. TRANSIT—A software tool for Himar1 TnSeq analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaimanpour, S.; Sarmiento, F.; Mrázek, J. Tn-Seq Explorer: A Tool for Analysis of High-Throughput Sequencing Data of Transposon Mutant Libraries. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ruan, J.; Durbin, R. Mapping short DNA sequencing reads and calling variants using mapping quality scores. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 1851–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galaxy, C. The Galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible, and collaborative data analyses: 2024 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W83–W94. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, Q.; Yuan, G.; Zheng, D. The essential genome of Ralstonia solanacearum. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 238, 126500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Opijnen, T.; Bodi, K.L.; Camilli, A. Tn-seq: High-throughput parallel sequencing for fitness and genetic interaction studies in microorganisms. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooven, T.A.; Catomeris, A.J.; Akabas, L.H.; Randis, T.M.; Maskell, D.J.; Peters, S.E.; Ott, S.; Santana-Cruz, I.; Tallon, L.J.; Tettelin, H.; et al. The essential genome of Streptococcus agalactiae. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Park, J.M.; Cui, B.; Humes, E.; Gangadharan, S.; Hung, S.; FitzGerald, P.C.; Hoe, K.-L.; Grewal, S.I.; Craig, N.L. Integration profiling of gene function with dense maps of transposon integration. Genetics 2013, 195, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosconi, F.; de Vries, S.P.; Baig, A.; Fabiano, E.; Grant, A.J. Essential genes for in vitro growth of the endophyte Herbaspirillum seropedicae SmR1 as revealed by transposon insertion site sequencing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 6664–6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechter, K.B.; Gallagher, L.; Pyles, H.; Manoil, C.S.; Harwood, C.S. Essential Genome of the Metabolically Versatile Alphaproteobacterium Rhodopseudomonas palustris. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 198, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, A.H.; Hatakeyama, R.; Kimmig, P.; Arter, M.; Peter, M.; Matos, J.; De Virgilio, C.; Kornmann, B. Functional mapping of yeast genomes by saturated transposition. Elife 2017, 6, e23570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harten, T.; Nimzyk, R.; Gawlick, V.E.A.; Reinhold-Hurek, B. Elucidation of Essential Genes and Mutant Fitness during Adaptation toward Nitrogen Fixation Conditions in the Endophyte Azoarcus olearius BH72 Revealed by Tn-Seq. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0216222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christen, B.; Abeliuk, E.; Collier, J.M.; Kalogeraki, V.S.; Passarelli, B.; Coller, J.A.; Fero, M.J.; McAdams, H.H.; Shapiro, L. The essential genome of a bacterium. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, D.; Kim, U.; Hwang, S.; Seo, S.W.; Kim, D.; Cho, S.; Palsson, B.; Cho, B.K. Revealing Causes for False-Positive and False-Negative Calling of Gene Essentiality in Escherichia coli Using Transposon Insertion Sequencing. mSystems 2023, 8, e0089622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minato, Y.; Gohl, D.M.; Thiede, J.M.; Chacon, J.M.; Harcombe, W.R.; Maruyama, F.; Baughn, A.D. Genomewide Assessment of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Conditionally Essential Metabolic Pathways. mSystems 2019, 4, e00070-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barquist, L.; Langridge, G.C.; Turner, D.J.; Phan, M.-D.; Turner, A.K.; Bateman, A.; Parkhill, J.; Wain, J.; Gardner, P.P. A comparison of dense transposon insertion libraries in the Salmonella serovars Typhi and Typhimurium. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 4549–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, B.A.; Tenorio, E.L.; Lazinski, D.W.; Camilli, A.; Duncan, M.J.; Hu, L.T. Identification of essential genes of the periodontal pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S.; Sanchez-Contreras, M.; Gualdi, S.; Pinto-Carbo, M.; Carlier, A.; Eberl, L. The Essential Genome of Burkholderia cenocepacia H111. J. Bacteriol. 2017, 199, e00260-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Gong, R.; Zhu, Q.; He, Q.; Xu, N.; Xu, Y.; Cai, M.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, M. Genome-Wide Determination of Gene Essentiality by Transposon Insertion Sequencing in Yeast Pichia pastoris. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.R.; Chao, M.C.; Abel, S.; Davis, B.M.; Baranowski, C.; Zhang, Y.J.; Rubin, E.J.; Waldor, M.K. ARTIST: High-resolution genome-wide assessment of fitness using transposon-insertion sequencing. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keel, B.N.; Snelling, W.M. Comparison of burrows-wheeler transform-based mapping algorithms used in high-throughput whole-genome sequencing: Application to illumina data for livestock genomes. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royet, K.; Parisot, N.; Rodrigue, A.; Gueguen, E.; Condemine, G. Identification by Tn-seq of Dickeya dadantii genes required for survival in chicory plants. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 20, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatiwara, A.; Jiang, T.; Sung, S.-S.; Dawoud, T.; Kim, J.N.; Bhattacharya, D.; Kim, H.-B.; Ricke, S.C.; Kwon, Y.M. Genome scanning for conditionally essential genes in Salmonella enterica Serotype Typhimurium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 3098–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, T.G.; Ho, B.T.; Yoder-Himes, D.R.; Mekalanos, J.J. Identification of T6SS-dependent effector and immunity proteins by Tn-seq in Vibrio cholerae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2623–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, S.; Snider, E.V.; Wang, X.; Kearns, D.B. Identification of Genes Required for Swarming Motility in Bacillus subtilis Using Transposon Mutagenesis and High-Throughput Sequencing (TnSeq). J. Bacteriol. 2022, 204, e0008922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Pang, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X. Functional genomics identified novel genes involved in growth at low temperatures in Listeria monocytogenes. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e00710-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, A.F.; Rock, J.M.; Krieger, I.V.; Chase, M.R.; Fernandez-Suarez, M.; Gagneux, S.; Sacchettini, J.C.; Ioerger, T.R.; Fortune, S.M. TnSeq of Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates reveals strain-specific antibiotic liabilities. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Lazinski, D.; Rowe, S.; Camilli, A.; Lewis, K. Genetic basis of persister tolerance to aminoglycosides in Escherichia coli. mBio 2015, 6, e00078-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karash, S.; Yahr, T.L. Genome-Wide Identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Genes Important for Desiccation Tolerance on Inanimate Surfaces. mSystems 2022, 7, e0011422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, R.; Kwon, Y. Global screening of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium genes for desiccation survival. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, A.J.; Rowe, H.M.; Rosch, J.W.; Camilli, A. A Tn-seq screen of Streptococcus pneumoniae uncovers DNA repair as the major pathway for desiccation tolerance and transmission. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e0071320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilde, A.D.; Snyder, D.J.; Putnam, N.E.; Valentino, M.D.; Hammer, N.D.; Lonergan, Z.R.; Hinger, S.A.; Aysanoa, E.E.; Blanchard, C.; Dunman, P.M. Bacterial hypoxic responses revealed as critical determinants of the host-pathogen outcome by TnSeq analysis of Staphylococcus aureus invasive infection. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karash, S.; Kwon, Y.M. Iron-dependent essential genes in Salmonella Typhimurium. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetmore, K.M.; Price, M.N.; Waters, R.J.; Lamson, J.S.; He, J.; Hoover, C.A.; Blow, M.J.; Bristow, J.; Butland, G.; Arkin, A.P.; et al. Rapid quantification of mutant fitness in diverse bacteria by sequencing randomly bar-coded transposons. mBio 2015, 6, e00306-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Phillips, A.P.R.; Wipfler, R.L.; Olsen, G.J.; Whitaker, R.J. The essential genome of the crenarchaeal model Sulfolobus islandicus. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osbourn, A.E.; Field, B. Operons. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 3755–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, C.; Hurst, L.D. Evidence against the selfish operon theory. Trends Genet. 2004, 20, 232–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, S.T.; Mueller, C.L.; Valvano, M.A. Identification of essential operons with a rhamnose-inducible promoter in Burkholderia cenocepacia. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2547–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gallagher, L.A.; Shendure, J.; Manoil, C. Genome-scale identification of resistance functions in Pseudomonas aeruginosa using Tn-seq. mBio 2011, 2, e00315-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson, S.; Baner, J.; Dahl, F.; Chu, A.; Ji, H.; Welch, K.; Davis, R.W. Multiplex amplification of all coding sequences within 10 cancer genes by Gene-Collector. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, T.; Ara, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Takai, Y.; Okumura, Y.; Baba, M.; Datsenko, K.A.; Tomita, M.; Wanner, B.L.; Mori, H. Construction of Escherichia coli K-12 in-frame, single-gene knockout mutants: The Keio collection. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2006, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuth, K.; Niesalla, H.; Hueck, C.J.; Fuchs, T.M. Large-scale identification of essential Salmonella genes by trapping lethal insertions. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 51, 1729–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, J.E.; Gawronski, J.D.; DeJesus, M.A.; Ioerger, T.R.; Akerley, B.J.; Sassetti, C.M. High-resolution phenotypic profiling defines genes essential for mycobacterial growth and cholesterol catabolism. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeJesus, M.A.; Gerrick, E.R.; Xu, W.; Park, S.W.; Long, J.E.; Boutte, C.C.; Rubin, E.J.; Schnappinger, D.; Ehrt, S.; Fortune, S.M. Comprehensive essentiality analysis of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis genome via saturating transposon mutagenesis. MBio 2017, 8, e02133-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Waldor, M.K.; Mekalanos, J.J. Tn-Seq analysis of Vibrio cholerae intestinal colonization reveals a role for T6SS-mediated antibacterial activity in the host. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Lu, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Tao, M.; Pang, X. A novel XRE family regulator that controls antibiotic production and development in Streptomyces coelicolor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 10075–10089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, L.M.; Whitchurch, C.B.; Barquist, L.; Katrib, M.; Boinett, C.J.; Mayho, M.; Goulding, D.; Charles, I.G.; Filloux, A.; Parkhill, J. A global genomic approach uncovers novel components for twitching motility-mediated biofilm expansion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, e000229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorman, M.J.; Feltwell, T.; Goulding, D.A.; Parkhill, J.; Short, F.L. The capsule regulatory network of Klebsiella pneumoniae defined by density-TraDISort. MBio 2018, 9, e01863-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rego, E.H.; Audette, R.E.; Rubin, E.J. Deletion of a mycobacterial divisome factor collapses single-cell phenotypic heterogeneity. Nature 2017, 546, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, D.; Jensen, P.A.; Wood, S.; Qabar, C.; Clark, S.; Shainheit, M.G.; Isberg, R.R.; van Opijnen, T. Droplet Tn-Seq combines microfluidics with Tn-Seq for identifying complex single-cell phenotypes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heumos, L.; Schaar, A.C.; Lance, C.; Litinetskaya, A.; Drost, F.; Zappia, L.; Lücken, M.D.; Strobl, D.C.; Henao, J.; Curion, F. Best practices for single-cell analysis across modalities. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2023, 24, 550–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judson, N.; Mekalanos, J.J. TnAraOut, a transposon-based approach to identify and characterize essential bacterial genes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coe, K.A.; Lee, W.; Stone, M.C.; Komazin-Meredith, G.; Meredith, T.C.; Grad, Y.H.; Walker, S. Multi-strain Tn-Seq reveals common daptomycin resistance determinants in Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, M.; Matano, L.M.; Moussa, S.H.; Gilmore, M.S.; Walker, S.; Meredith, T.C. A new platform for ultra-high density Staphylococcus aureus transposon libraries. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández-García, G.; Valdés-Chiara, P.; Villazán-Gamonal, P.; Alonso-Fernández, S.; Manteca, A. Essential Genes Discovery in Microorganisms by Transposon-Directed Sequencing (Tn-Seq): Experimental Approaches, Major Goals, and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252011298
Fernández-García G, Valdés-Chiara P, Villazán-Gamonal P, Alonso-Fernández S, Manteca A. Essential Genes Discovery in Microorganisms by Transposon-Directed Sequencing (Tn-Seq): Experimental Approaches, Major Goals, and Future Perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(20):11298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252011298
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández-García, Gemma, Paula Valdés-Chiara, Patricia Villazán-Gamonal, Sergio Alonso-Fernández, and Angel Manteca. 2024. "Essential Genes Discovery in Microorganisms by Transposon-Directed Sequencing (Tn-Seq): Experimental Approaches, Major Goals, and Future Perspectives" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 20: 11298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252011298
APA StyleFernández-García, G., Valdés-Chiara, P., Villazán-Gamonal, P., Alonso-Fernández, S., & Manteca, A. (2024). Essential Genes Discovery in Microorganisms by Transposon-Directed Sequencing (Tn-Seq): Experimental Approaches, Major Goals, and Future Perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(20), 11298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252011298






