Peroxymonosulfate Activation by Rice-Husk-Derived Biochar (RBC) for the Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole: The Key Role of Hydroxyl Groups
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
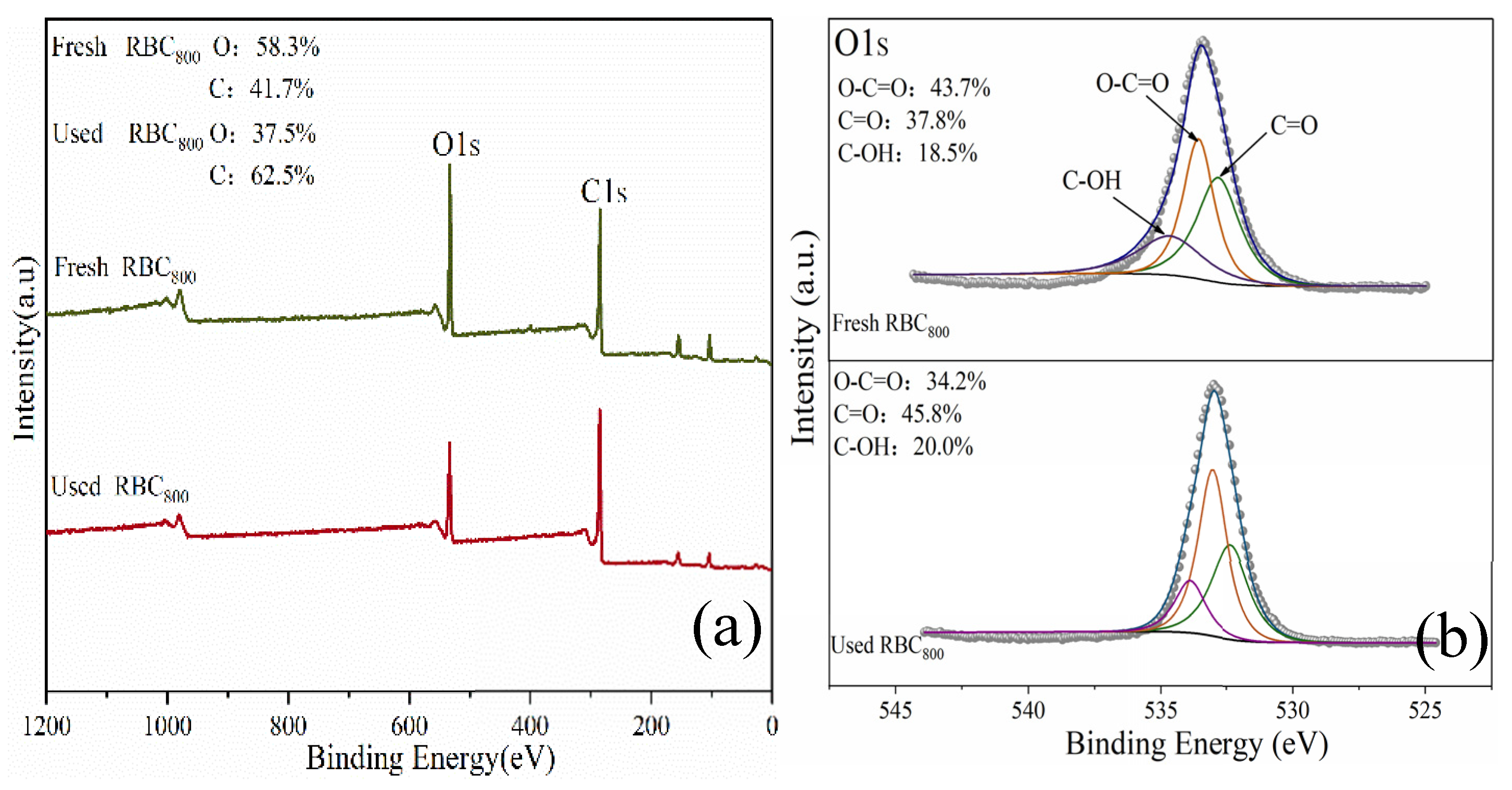
2.1. Characterization of RBC800
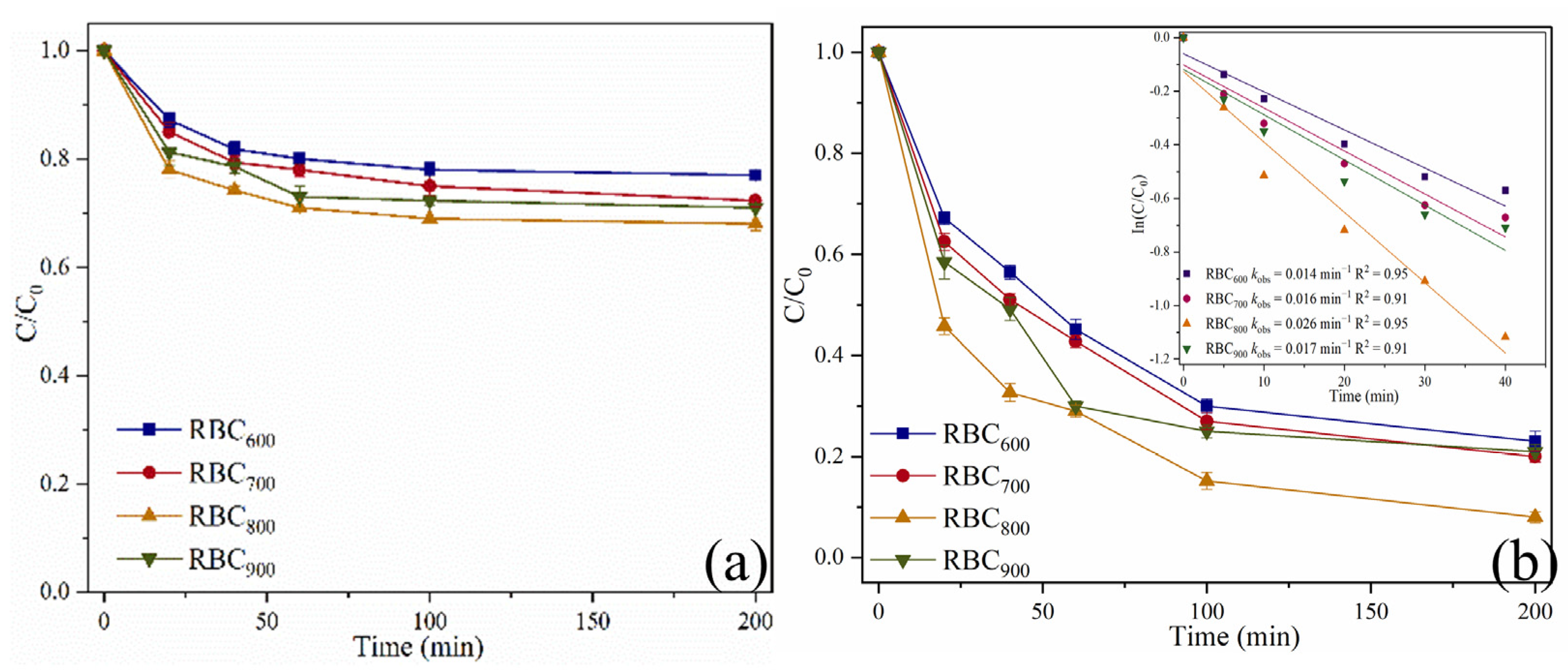
2.2. Catalytic Oxidation of SMX
2.3. Mechanism Discussion
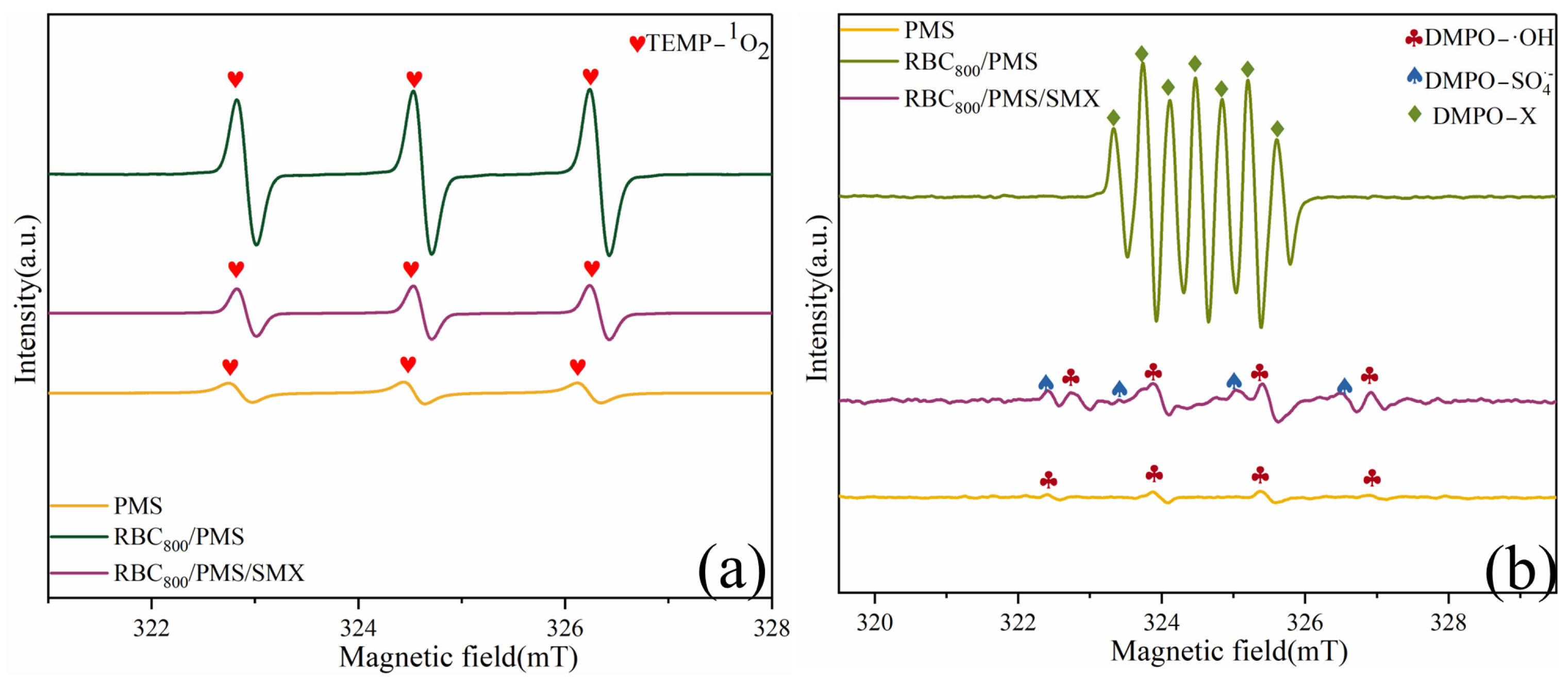
2.3.1. Identification of ROSs
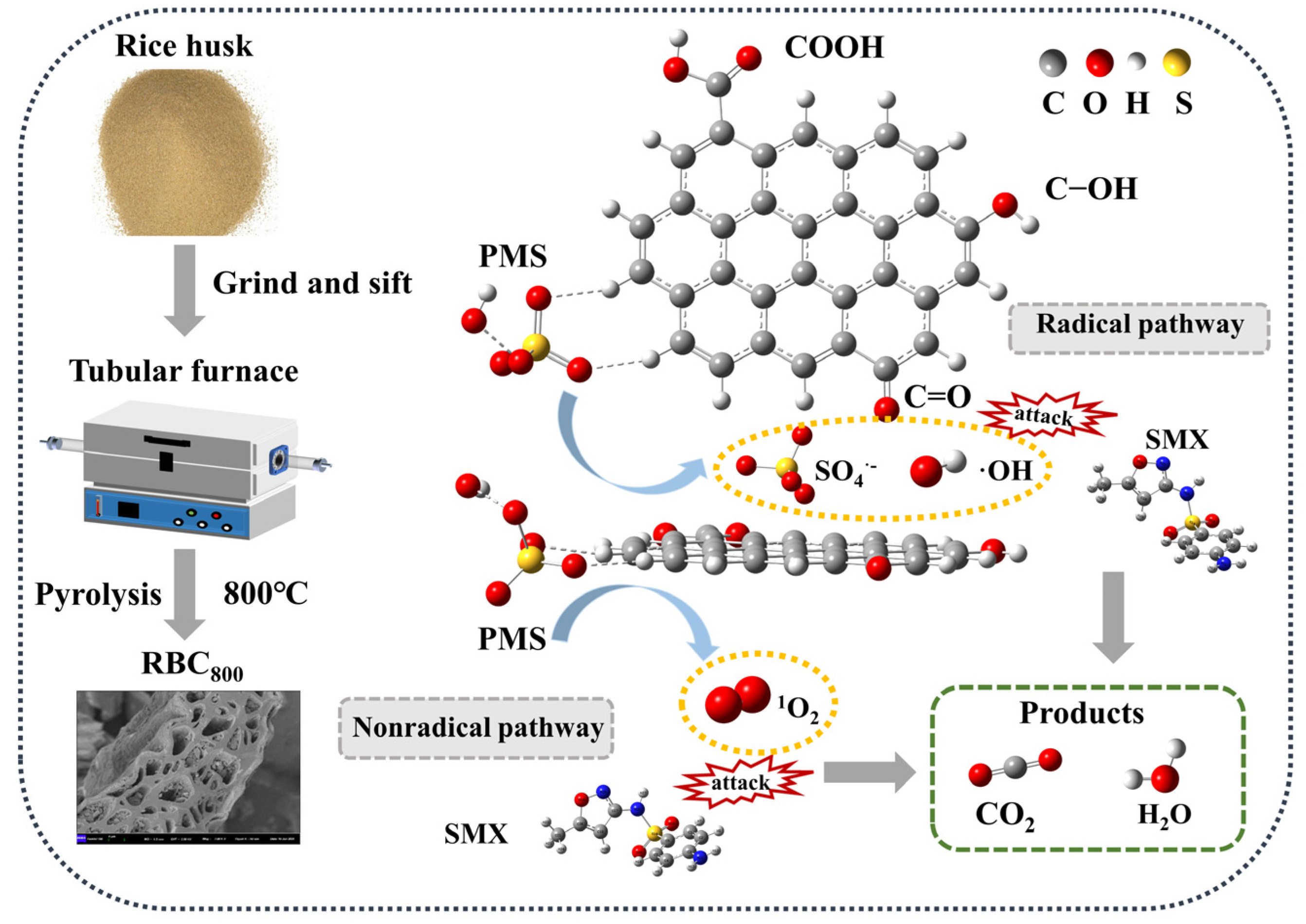
2.3.2. Reaction Mechanism
2.4. Degradation Pathways of SMX
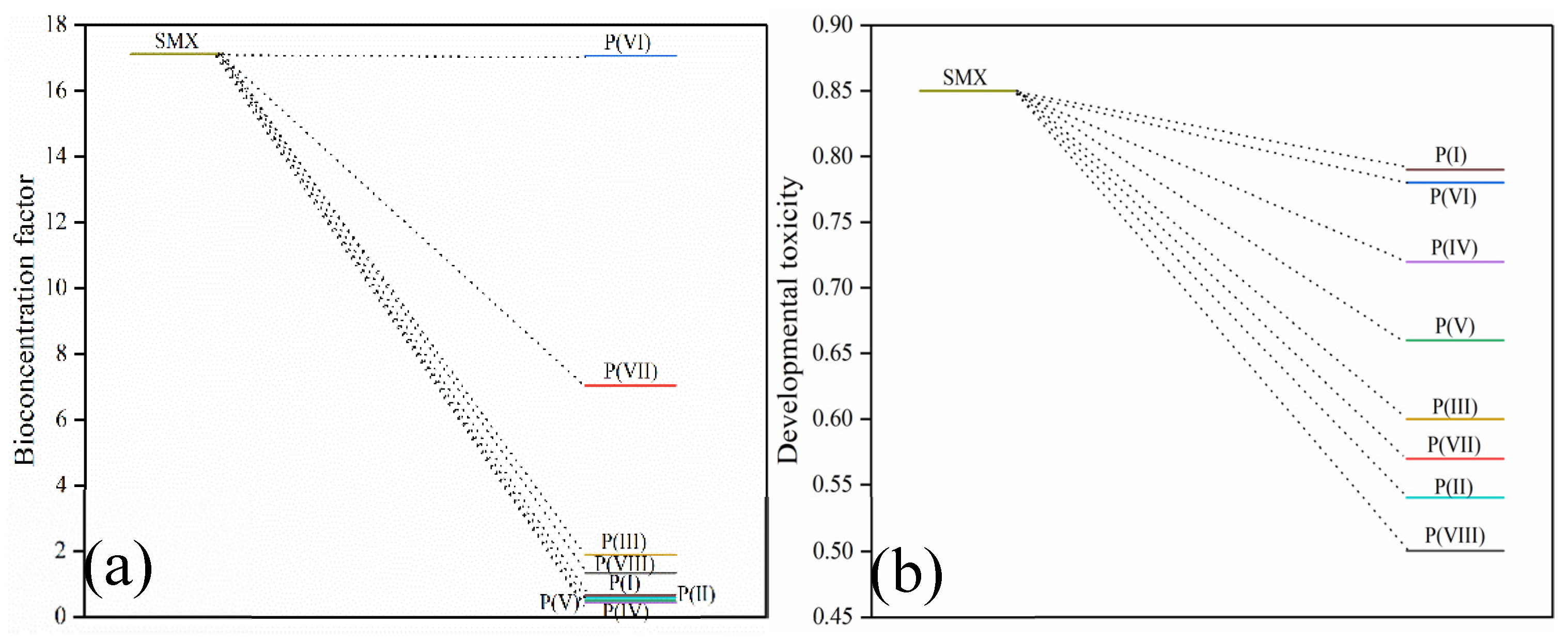
2.5. Toxicity Assessment
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Catalysts
3.2. Reaction Procedures
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adeleye, A.S.; Xue, J.; Zhao, Y.; Taylor, A.A.; Zenobio, J.E.; Sun, Y.; Han, Z.; Salawu, O.A.; Zhu, Y. Abundance, fate, and effects of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in aquatic environments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Yin, R.; Zheng, H.; Feng, X.; Che, D.; Ren, N. Hydroxyl radical dominated degradation of aquatic sulfamethoxazole by Fe(0)/bisulfite/O2: Kinetics, mechanisms, and pathways. Water Res. 2018, 138, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Sui, Q.; Lyu, S.; Zhao, W.; Liu, J.; Cai, Z.; Yu, G.; Barcelo, D. Municipal Solid Waste Landfills: An Underestimated Source of Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products in the Water Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9757–9768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Li, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lai, B.; Chen, X.; Song, L. Catalytic degradation of sulfamethoxazole through peroxymonosulfate activated with expanded graphite loaded CoFe2O4 particles. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Activation of persulfate (PS) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and application for the degradation of emerging contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Ma, B.; Zhang, C.; Ma, X.; Xu, P.; Zhang, G.; Gao, M.; Xin, Y. Catalytic activation of peroxydisulfate by alfalfa-derived nitrogen self-doped porous carbon supported CuFeO2 for nimesulide degradation: Performance, mechanism and DFT calculation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 294, 120247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhuang, X.; Ahmad, S.; Lee, T.; Si, H.; Cao, C.; Ni, S.-Q. Sulfate radicals based heterogeneous peroxymonosulfate system catalyzed by CuO-Fe3O4-Biochar nanocomposite for bisphenol A degradation. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 41, 102078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, W.D.; Zaeni, J.R.J.; Lisak, G.; Lin, K.A.; Leong, K.H.; Choong, Z.Y. Accelerated organics degradation by peroxymonosulfate activated with biochar co-doped with nitrogen and sulfur. Chemosphere 2021, 277, 130313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huang, R.; Sun, R.; Yang, J.; Sillanpää, M. A review on persulfates activation by functional biochar for organic contaminants removal: Synthesis, characterizations, radical determination, and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Cui, K.; Li, C.X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q. Efficient peroxymonosulfate activation by biochar-based nanohybrids for the degradation of pharmaceutical and personal care products in aquatic environments. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 137084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Shao, B.; Yan, M.; Liu, Z.; Liang, Q.; He, Q.; Wu, T.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Huang, J.; et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by biochar-based catalysts and applications in the degradation of organic contaminants: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 416, 128829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Ge, B.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, B.; Wang, C.; Akram, M.; Xu, X. Three-dimensional porous graphene-like biochar derived from Enteromorpha as a persulfate activator for sulfamethoxazole degradation: Role of graphitic N and radicals transformation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 123039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Si, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Luo, H.; Ren, N. B-doped graphitic porous biochar with enhanced surface affinity and electron transfer for efficient peroxydisulfate activation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 396, 125119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lai, C.; Huang, F.; Cheng, M.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Li, B.; Liu, S.; Zhang, M.; Qin, L.; et al. Degradation of naphthalene with magnetic bio-char activate hydrogen peroxide: Synergism of bio-char and Fe-Mn binary oxides. Water Res. 2019, 160, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by sludge-derived biochar for the degradation of triclosan in water and wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Peng, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S.; Xiong, Y.; Tian, S.; Fang, J. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by nitrogen-functionalized sludge carbon for efficient degradation of organic pollutants in water. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-G.; Ko, S.-O. Effects of thermal modification of a biochar on persulfate activation and mechanisms of catalytic degradation of a pharmaceutical. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 399, 125377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Xiao, Y.; Tang, J.; Chen, H.; Sun, H. Persulfate activation with sawdust biochar in aqueous solution by enhanced electron donor-transfer effect. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, P.; Yue, Q.; Li, Y.; Gao, B.; Xu, X. Removal of sulfamethoxazole from water via activation of persulfate by Fe3C@NCNTs including mechanism of radical and nonradical process. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 122004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Feng, H.; Tang, L.; Pang, Y.; Zeng, G.; Lu, Y.; Dong, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, C.; et al. Metal-free carbon materials for persulfate-based advanced oxidation process: Microstructure, property and tailoring. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 111, 100654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Cui, M.; Chen, Y.; Liu, R.; Cui, K.; Wu, K.; Nie, X.; Wang, S. Synthesizing and characterizing Fe3O4 embedded in N-doped carbon nanotubes-bridged biochar as a persulfate activator for sulfamethoxazole degradation. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 353, 131669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Cui, K.; Wang, D.; Wei, Q. Peroxymonosulfate Activation by Fe@N Co-Doped Biochar for the Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole: The Key Role of Pyrrolic N. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10528. [Google Scholar]
- You, S.; Ok, Y.S.; Chen, S.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Kwon, E.E.; Lee, J.; Wang, C.H. A critical review on sustainable biochar system through gasification: Energy and environmental applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 246, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Liang, F.; Liang, J.; Xu, W.; Liu, Z.; Chen, B.; Jiang, X.; Wu, X.; Xu, J.; Beiyuan, J.; et al. Ce-embedded N-enriched porous biochar for peroxymonosulfate activation in metronidazole degradation: Applications, mechanism insight and toxicity evaluation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 134387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhang, R.; Ding, Y.; Ren, Z.; Fu, M.; Cao, X.; Zeng, G. Singlet oxygen-dominated activation of peroxymonosulfate by passion fruit shell derived biochar for catalytic degradation of tetracycline through a non-radical oxidation pathway. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Ao, Z.; Pu, S.; Yao, G.; Lai, B. Core-shell magnetic Fe3O4@Zn/Co-ZIFs to activate peroxymonosulfate for highly efficient degradation of carbamazepine. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 277, 119136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Zhao, P.; Xu, S.; Cheng, G.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, K.; Ma, S. Fabrication of Fe3O4 and graphitized porous biochar composites for activating peroxymonosulfate to degrade p-hydroxybenzoic acid: Insights on the mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 121980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Bai, X.; Ji, Y.; Shen, T. Reduced graphene oxide-supported hollow Co3O4@N-doped porous carbon as peroxymonosulfate activator for sulfamethoxazole degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Duan, X.; Shang, Y.; Gao, B.; Xu, X. Engineered carbon supported single iron atom sites and iron clusters from Fe-rich Enteromorpha for Fenton-like reactions via nonradical pathways. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 287, 119963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Luo, Z.; Du, S.; Yang, J.; Zhi, D.; Zhou, Y. Magnetic MgFe2O4/biochar derived from pomelo peel as a persulfate activator for levofloxacin degradation: Effects and mechanistic consideration. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 346, 126547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Ma, S.; Zhao, P.; Xu, S.; Zhan, S. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by graphitized hierarchical porous biochar and MnFe2O4 magnetic nanoarchitecture for organic pollutants degradation: Structure dependence and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Wu, G.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Garces, H.F.; Yan, K. Fabrication of ultrathin lily-like NiCo2O4 nanosheets via mooring NiCo bimetallic oxide on waste biomass-derived carbon for highly efficient removal of phenolic pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 441, 136066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Cui, K.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Cui, M.; Yao, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S. Removal of chlorophenols in the aquatic environment by activation of peroxymonosulfate with nMnOx@Biochar hybrid composites: Performance and mechanism. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, B.; Chen, L.; Que, C.; Yang, K.; Deng, F.; Deng, X.; Shi, G.; Xu, G.; Wu, M. Adsorption of Antibiotics on Graphene and Biochar in Aqueous Solutions Induced by pi-pi Interactions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31920. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, X.; Jiang, J.; Ma, J.; Liu, G.; Cao, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Pang, S.; Kong, X.; et al. Degradation of sulfamethoxazole by UV, UV/H2O2 and UV/persulfate (PDS): Formation of oxidation products and effect of bicarbonate. Water Res. 2017, 118, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Du, J.; Wu, Q.; Chang, J.-S.; Ren, N. Singlet oxygen-dominated peroxydisulfate activation by sludge-derived biochar for sulfamethoxazole degradation through a nonradical oxidation pathway: Performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 357, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.M.; Chen, C.W.; Huang, C.P.; Shiung Lam, S.; Dong, C.D. Peroxymonosulfate activation by a metal-free biochar for sulfonamide antibiotic removal in water and associated bacterial community composition. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Duan, X.; Xu, X.; Chen, K.; Wu, F.; Qiu, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Cao, X. Biomass-derived pyrolytic carbons accelerated Fe(III)/Fe(II) redox cycle for persulfate activation: Pyrolysis temperature-depended performance and mechanisms. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 297, 120446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, M. Catalytic degradation of sulfamethoxazole by peroxymonosulfate activation system composed of nitrogen-doped biochar from pomelo peel: Important roles of defects and nitrogen, and detoxification of intermediates. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 613, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Tang, L.; Pang, Y.; Zeng, G.; Feng, H.; Zou, J.; Wang, J.; Feng, C.; Zhu, X.; Ouyang, X.; et al. Hierarchical porous biochar from shrimp shell for persulfate activation: A two-electron transfer path and key impact factors. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 260, 118160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Song, Y.; Nengzi, L.-c.; Gou, J.; Li, B.; Cheng, X. Activation of persulfate by a novel magnetic CuFe2O4/Bi2O3 composite for lomefloxacin degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Song, M.; Cao, Q.; Sun, P.; Chen, Y.; Meng, F. The superoxide radicals’ production via persulfate activated with CuFe2O4@Biochar composites to promote the redox pairs cycling for efficient degradation of o-nitrochlorobenzene in soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 122887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, T.; Li, C.-X.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Cui, K.; Wei, Q. Peroxymonosulfate Activation by Rice-Husk-Derived Biochar (RBC) for the Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole: The Key Role of Hydroxyl Groups. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11582. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111582
Liu T, Li C-X, Chen X, Chen Y, Cui K, Wei Q. Peroxymonosulfate Activation by Rice-Husk-Derived Biochar (RBC) for the Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole: The Key Role of Hydroxyl Groups. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(21):11582. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111582
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Tong, Chen-Xuan Li, Xing Chen, Yihan Chen, Kangping Cui, and Qiang Wei. 2024. "Peroxymonosulfate Activation by Rice-Husk-Derived Biochar (RBC) for the Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole: The Key Role of Hydroxyl Groups" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 21: 11582. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111582
APA StyleLiu, T., Li, C.-X., Chen, X., Chen, Y., Cui, K., & Wei, Q. (2024). Peroxymonosulfate Activation by Rice-Husk-Derived Biochar (RBC) for the Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole: The Key Role of Hydroxyl Groups. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(21), 11582. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111582





