Moving Beyond Oxford Nanopore Standard Procedures: New Insights from Water and Multiple Fish Microbiomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Assessment Strategy of ONT Performance and Sequencing Results
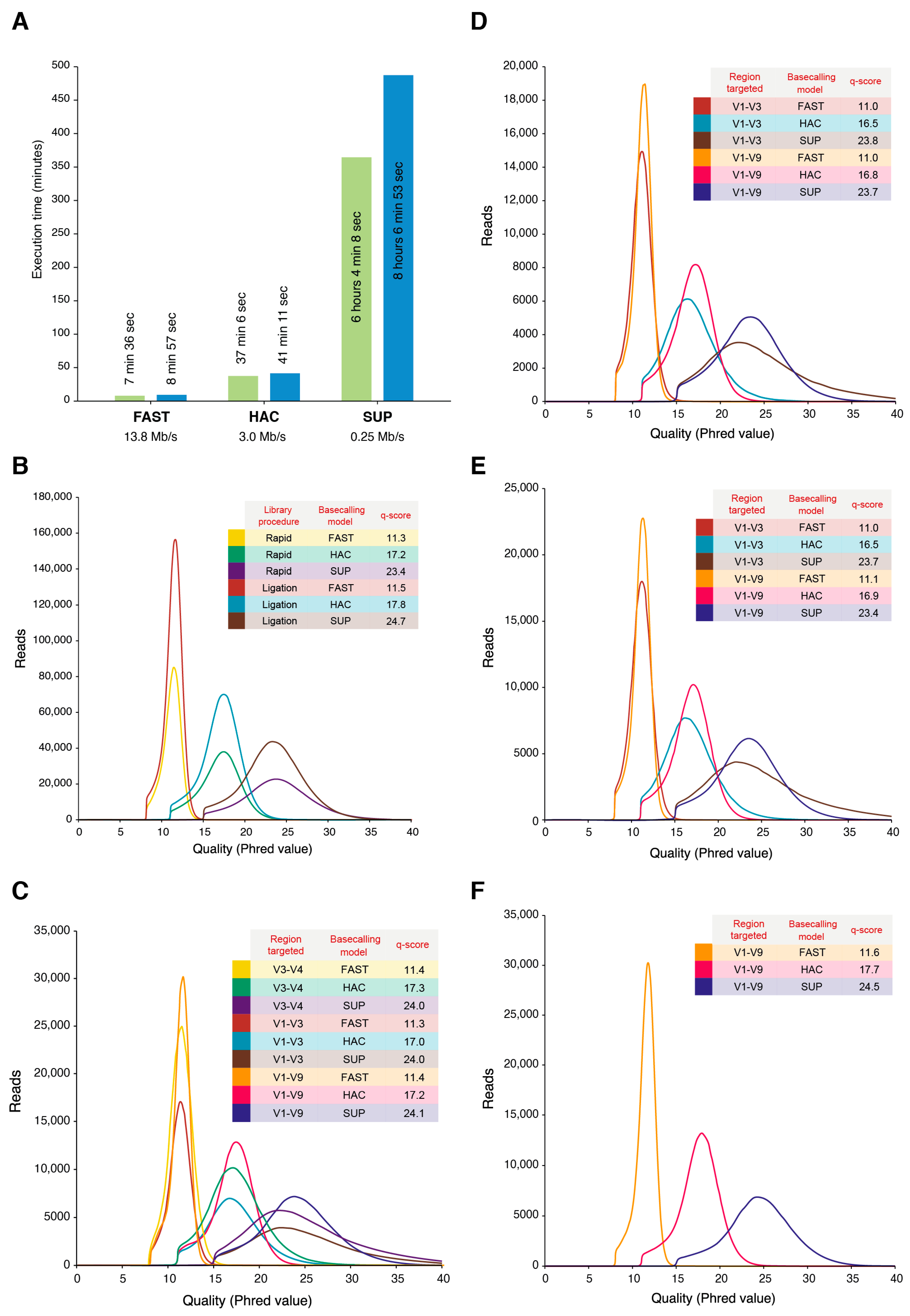
2.2. Amplicon Qualities
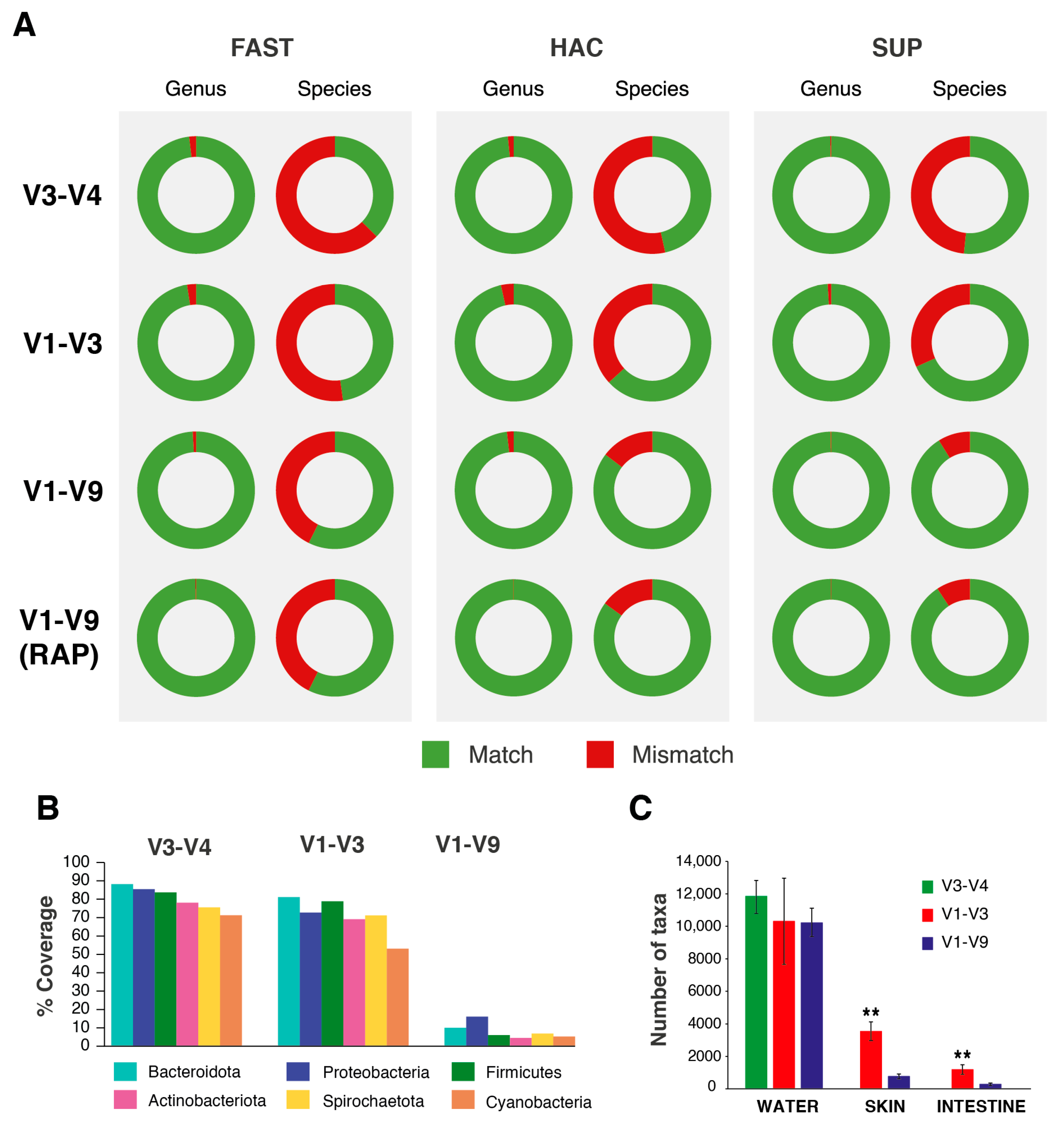
2.3. Effects of Primers on Taxonomy Assignment
2.4. Basecalling Effects on Sequencing Performance
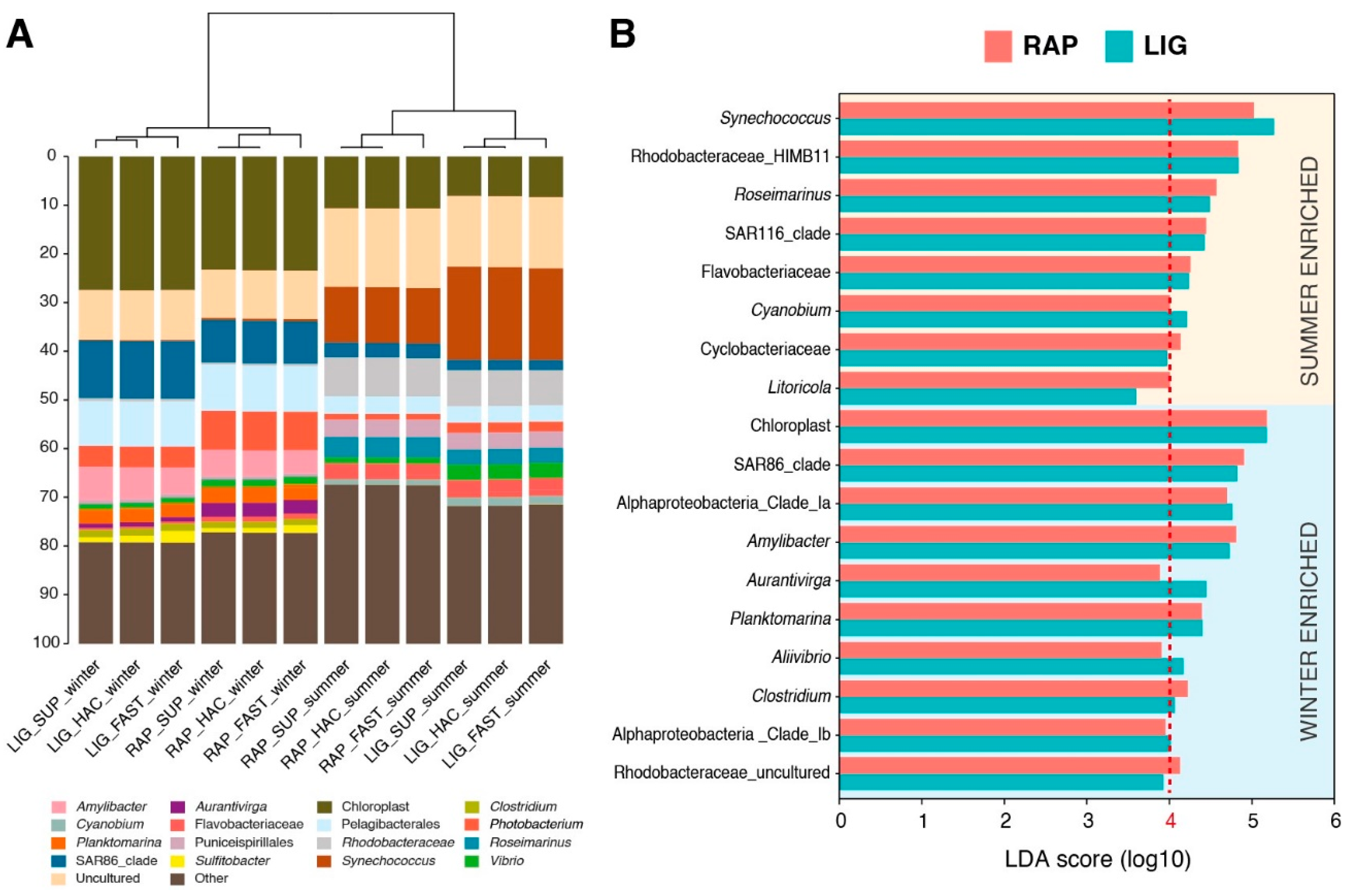
2.5. Effects of Library Preparation Strategy, Primers, and Basecalling Models in Taxonomy Correlations
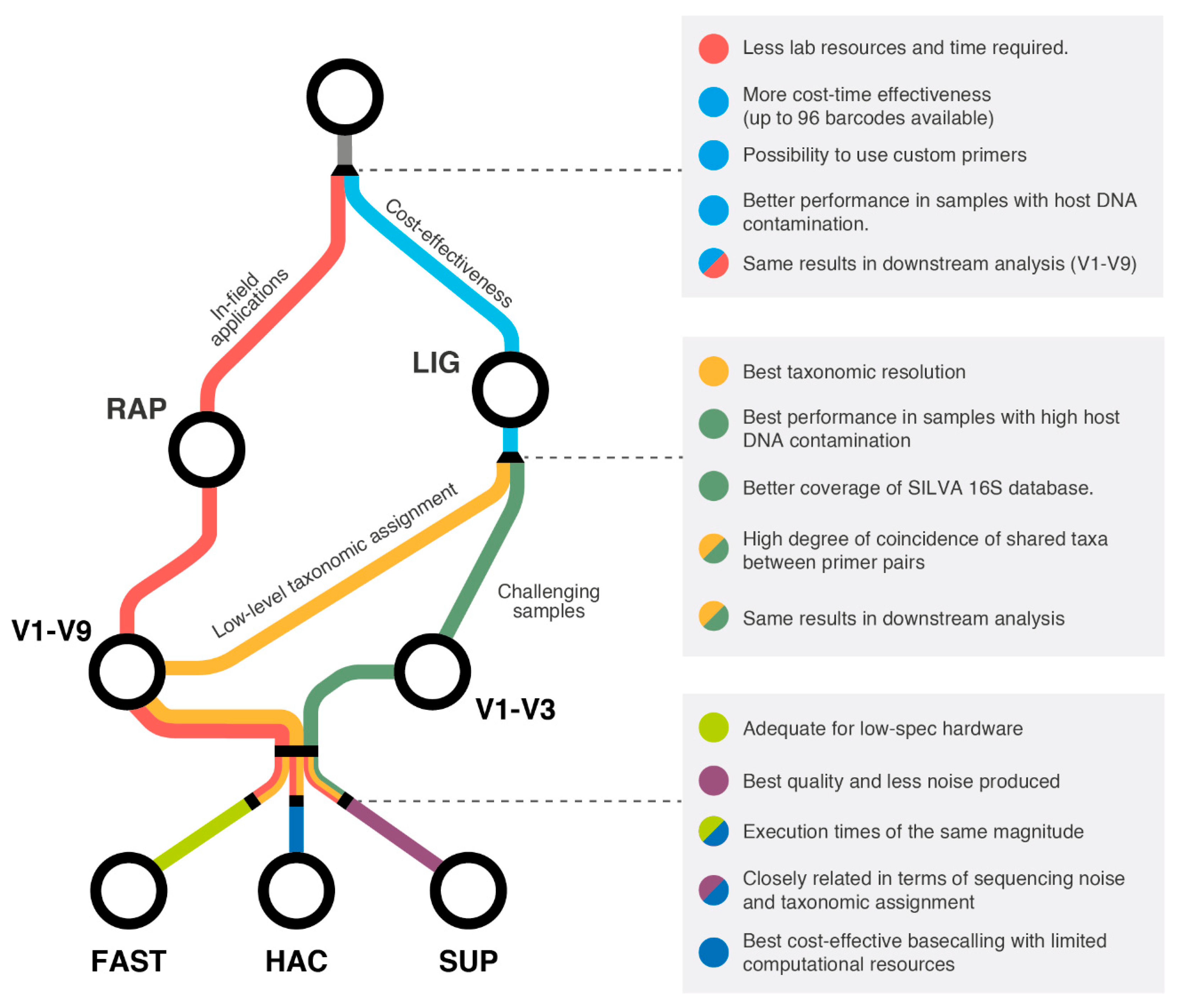
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Mock Community, Water, and Fish Samples
4.3. Rapid 16S Barcoding Kit Sequencing
4.4. Ligation Sequencing of Amplicons
4.5. Basecalling and Bioinformatic Analysis
4.6. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brugman, S.; Ikeda-Ohtsubo, W.; Braber, S.; Folkerts, G.; Pieterse, C.M.J.; Bakker, P.A.H.M. A comparative review on microbiota manipulation: Lessons from fish, plants, livestock, and human research. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorgen-Ritchie, M.; Uren Webster, T.; McMurtrie, J.; Bass, D.; Tyler, C.R.; Rowley, A.; Martin, S.A.M. Microbiomes in the context of developing sustainable intensified aquaculture. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1200997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limborg, M.T.; Alberdi, A.; Kodama, M.; Roggenbuck, M.; Kristiansen, K.; Gilbert, M.T.P. Applied hologenomics: Feasibility and potential in aquaculture. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naya-Català, F.; Piazzon, M.C.; Torrecillas, S.; Toxqui-Rodríguez, S.; Calduch-Giner, J.À.; Fontanillas, R.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Montero, D.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Genetics and nutrition drive the gut microbiota succession and host-transcriptome interactions through the gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) production cycle. Biology 2022, 11, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palladino, G.; Rampelli, S.; Scicchitano, D.; Musella, M.; Quero, G.M.; Prada, F.; Mancuso, A.; Seyfarth, A.M.; Turroni, S.; Candela, M.; et al. Impact of marine aquaculture on the microbiome associated with nearby holobionts: The case of patella caerulea living in proximity of sea bream aquaculture cages. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzon, M.C.; Naya-Català, F.; Perera, E.; Palenzuela, O.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Genetic selection for growth drives differences in intestinal microbiota composition and parasite disease resistance in gilthead sea bream. Microbiome 2020, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, B.; Hafez, A.I.; Naya-Català, F.; Moroni, F.; Moldovan, R.A.; Toxqui-Rodríguez, S.; Piazzon, M.C.; Arnau, V.; Llorens, C.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. SAMBA: Structure-learning of aquaculture microbiomes using a bayesian approach. Genes 2023, 14, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, S.; Matsuo, Y.; Nakagawa, S.; Kryukov, K.; Matsukawa, S.; Tanaka, H.; Iwai, T.; Imanishi, T.; Hirota, K. Rapid bacterial identification by direct pcr amplification of 16s rrna genes using the MinionTM Nanopore sequencer. FEBS Open Bio 2019, 9, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.T.; Collipal-Matamal, R.; Valenzuela-Muñoz, V.; Nuñez-Acuña, G.; Valenzuela-Miranda, D.; Gallardo-Escárate, C. Nanopore sequencing of microbial communities reveals the potential role of sea lice as a reservoir for fish pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Rivera, M.F.; Valenzuela-Miranda, D.; Valenzuela-Muñoz, V.; Nuñez-Acuña, G.; Avendaño-Herrera, R.; Gallardo-Escárate, C. Nanopore sequencing evidenced the presence of fish bacterial pathogens in the sea louse (Caligus rogercresseyi) microbiota collected from distant salmon farms in chile. Aquaculture 2022, 552, 738026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeck, T.; Katzenmeier, S.N.; Breiner, H.W.; Rubel, V. Nanopore duplex sequencing as an alternative to Illumina Miseq sequencing for eDNA-based biomonitoring of coastal aquaculture impacts. Metabarcoding Metagenomics 2024, 8, 45–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarantonello, G.; Cuenca, A. Nanopore-enabled microbiome analysis: Investigating environmental and host-associated samples in rainbow trout aquaculture. Curr. Protoc. 2024, 4, e1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toxqui-Rodríguez, S.; Holhorea, P.G.; Naya-Català, F.; Calduch-Giner, J.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Piazzon, C.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Differential reshaping of skin and intestinal microbiota by stocking density and oxygen availability in farmed gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata): A behavioral and network-based integrative approach. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toxqui-Rodríguez, S.; Naya-Català, F.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Piazzon, M.C.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Fish microbiomics: Strengths and limitations of Minion sequencing of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) intestinal microbiota. Aquaculture 2023, 569, 739388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Sun, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Bai, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, A.; Qiao, F.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, C.; et al. Portable Nanopore-sequencing technology: Trends in development and applications. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1043967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Bollas, A.; Wang, Y.; Au, K.F. Nanopore sequencing technology, bioinformatics and applications. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1348–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Cai, H.; Peng, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Akutsu, T. Causalcall: Nanopore basecalling using a temporal convolutional network. Front. Genet. 2020, 10, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagès-Gallego, M.; de Ridder, J. Comprehensive benchmark and architectural analysis of deep learning models for nanopore sequencing basecalling. Genome Biol. 2023, 24, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.; McLay, T.; Andrew, R.L.; Bruhl, J.J.; Schwessinger, B.; Borevitz, J.; Jones, A. Species-specific basecallers improve actual accuracy of nanopore sequencing in plants. Plant Methods 2022, 18, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrone, J.R.; Rios Glusberger, P.; George, C.D.; Milletich, P.L.; Ahrens, A.P.; Roesch, L.F.W.; Triplett, E.W. RESCUE: A validated nanopore pipeline to classify bacteria through long-read, 16s-its-23s rrna sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1201064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Hao, N.; Zhang, H.H.; Sun, X.; Que, J.; Ding, H. Adapting Nanopore sequencing basecalling models for modification detection via incremental learning and anomaly detection. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalusky, M.P.G.; Gustafson, J.A.; Bohaczuk, S.C.; Mallory, B.; Reed, P.; Wenger, T.; Beckman, E.; Chang, I.J.; Paschal, C.R.; Buchan, J.G.; et al. 3-hour genome sequencing and targeted analysis to rapidly assess genetic risk. Genet. Med. Open 2024, 2, 101833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolmogorov, M.; Billingsley, K.J.; Mastoras, M.; Meredith, M.; Monlong, J.; Lorig-Roach, R.; Asri, M.; Alvarez Jerez, P.; Malik, L.; Dewan, R.; et al. Scalable Nanopore sequencing of human genomes provides a comprehensive view of haplotype-resolved variation and methylation. Nat. Methods 2023, 20, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goenka, S.D.; Gorzynski, J.E.; Shafin, K.; Fisk, D.G.; Pesout, T.; Jensen, T.D.; Monlong, J.; Chang, P.C.; Baid, G.; Bernstein, J.A.; et al. Accelerated identification of disease-causing variants with ultra-rapid nanopore genome sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Liu, X.; Simeneh, Z.M.; Yang, M.; Li, R. Benchmarking of Nanopore R10.4 and R9.4.1 flow cells in single-cell whole-genome amplification and whole-genome shotgun sequencing. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 2352–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, M.; Argyropoulos, C. An introduction to nanopore sequencing: Past, present, and future considerations. Micromachines 2023, 14, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvage, T.; Cormier, A.; Delphine, P. A Comparison of Oxford Nanopore library strategies for bacterial genomics. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Reis, A.L.; Beckley, L.E.; Olivar, M.P.; Jeffs, A.G. Nanopore short-read sequencing: A quick, cost-effective and accurate method for DNA metabarcoding. Environ. DNA 2023, 5, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armougom, F.; Henry, M.; Vialettes, B.; Raccah, D.; Raoult, D. Monitoring bacterial community of human gut microbiota reveals an increase in Lactobacillus in obese patients and methanogens in anorexic patients. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamady, M.; Knight, R. Microbial community profiling for human microbiome projects: Tools, techniques, and challenges. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Gevers, D.; Westcott, S.L. Reducing the effects of pcr amplification and sequencing artifacts on 16S rRNA-based studies. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, Y.; Komiya, S.; Yasumizu, Y.; Yasuoka, Y.; Mizushima, K.; Takagi, T.; Kryukov, K.; Fukuda, A.; Morimoto, Y.; Naito, Y.; et al. Full-Length 16S rRNA gene amplicon analysis of human gut microbiota using MinionTM Nanopore sequencing confers species-level resolution. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feehery, G.R.; Yigit, E.; Oyola, S.O.; Langhorst, B.W.; Schmidt, V.T.; Stewart, F.J.; Dimalanta, E.T.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A.; Davis, T.; Quail, M.A.; et al. A method for selectively enriching microbial DNA from contaminating vertebrate host DNA. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquet, M.; Zöllkau, J.; Pastuschek, J.; Viehweger, A.; Schleußner, E.; Makarewicz, O.; Pletz, M.W.; Ehricht, R.; Brandt, C. Evaluation of microbiome enrichment and host DNA depletion in human vaginal samples using Oxford Nanopore’s adaptive sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naya-Català, F.; Piazzon, M.C.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Diet and host genetics drive the bacterial and fungal intestinal metatranscriptome of gilthead sea bream. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 883738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, T.; Fukuda, S.; Hase, K.; Nishiumi, S.; Izumi, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Hagiwara, T.; Kawashima, R.; Yamazaki, M.; Oshio, T.; et al. Microbiota-derived lactate accelerates colon epithelial cell turnover in starvation-refed mice. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaçin, İ.; Ersoy, Ş.; Doluca, O.; Güngörmüşler, M. Using custom-built primers and Nanopore sequencing to evaluate CO-utilizer bacterial and archaeal populations linked to bio-H2 production. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.J.M.; Ip, Y.C.A.; Bauman, A.G.; Huang, D. MinION-in-ARMS: Nanopore Sequencing to expedite barcoding of specimen-rich macrofaunal samples from autonomous reef monitoring structures. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.J.M.; Ip, Y.C.A.; Ng, C.S.L.; Huang, D. Takeaways from mobile DNA barcoding with Bentolab and Minion. Genes 2020, 11, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carradec, Q.; Poulain, J.; Boissin, E.; Hume, B.C.C.; Voolstra, C.R.; Ziegler, M.; Engelen, S.; Cruaud, C.; Planes, S.; Wincker, P. A framework for in situ molecular characterization of coral holobionts using Nanopore sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munian, K.; Ramli, F.F.; Othman, N.; Mahyudin, N.A.A.; Sariyati, N.H.; Abdullah-Fauzi, N.A.F.; Haris, H.; Ilham-Norhakim, M.L.; Abdul-Latiff, M.A.B. Environmental DNA metabarcoding of freshwater fish in Malaysian tropical rivers using short-read nanopore sequencing as a potential biomonitoring tool. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2024, 24, e13936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dommann, J.; Kerbl-Knapp, J.; Albertos Torres, D.; Egli, A.; Keiser, J.; Schneeberger, P.H.H. A novel barcoded nanopore sequencing workflow of high-quality, full-length bacterial 16S amplicons for taxonomic annotation of bacterial isolates and complex microbial communities. mSystems 2024, 9, e0085924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhee, M.; Floré, K.; Vanthourenhout, S.; Hellemans, J.; Muyldermans, A.; Reynders, M. Implementation of full-length 16S Nanopore sequencing for bacterial identification in a clinical diagnostic setting. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 108, 116156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ONT. Chemistry Technical Document. 2023. Available online: https://nanoporetech.com/document/chemistry-technical-document (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- Drengenes, C.; Eagan, T.M.L.; Haaland, I.; Wiker, H.G.; Nielsen, R. Exploring protocol bias in airway microbiome studies: One versus two PCR steps and 16S rRNA gene region V3 V4 versus V4. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, J.D.; Bloom, R.J.; Jiang, S.; Durand, H.K.; Dallow, E.; Mukherjee, S.; David, L.A. Measuring and mitigating PCR bias in microbiota datasets. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiner, K.; Bik, H.M.; Mächler, E.; Seymour, M.; Lacoursière-Roussel, A.; Altermatt, F.; Creer, S.; Bista, I.; Lodge, D.M.; de Vere, N.; et al. Environmental DNA metabarcoding: Transforming how we survey animal and plant communities. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 5872–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, R.; Vrbanac, A.; Taylor, B.C.; Aksenov, A.; Callewaert, C.; Debelius, J.; Gonzalez, A.; Kosciolek, T.; McCall, L.I.; McDonald, D.; et al. Best practices for analysing microbiomes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Rodriguez, T.M.; Le François, B.; Macklaim, J.M.; Doukhanine, E.; Hollister, E.B. The skin microbiome: Current techniques, challenges, and future directions. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.P.; Barrett, M.; Hogan, G.; Flores Bueso, Y.; Claesson, M.J.; Tangney, M. Non-specific amplification of human dna is a major challenge for 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szoboszlay, M.; Schramm, L.; Pinzauti, D.; Scerri, J.; Sandionigi, A.; Biazzo, M. Nanopore is preferable over Illumina for 16S amplicon sequencing of the gut microbiota when species-level taxonomic classification, accurate estimation of richness, or focus on rare taxa is required. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, A.; Li, S.; Tao, R.; Chen, K.; Huang, P.; Li, L.; Huang, J.; Li, C.; et al. Comparison of the full-length sequence and sub-regions of 16S rRNA gene for skin microbiome profiling. MSystems 2024, 9, e0039924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Tsompana, M.; Ruscitto, A.; Sharma, A.; Genco, R.; Sun, Y.; Buck, M.J. An accurate and efficient experimental approach for characterization of the complex oral microbiota. Microbiome 2015, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robeson, M.S.; O’Rourke, D.R.; Kaehler, B.D.; Ziemski, M.; Dillon, M.R.; Foster, J.T.; Bokulich, N.A. RESCRIPt: Reproducible sequence taxonomy reference database management. PLoS Comp. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Du, X.; Li, Y.; Han, X.; Fang, S.; Geisen, S.; Li, Q. Database and primer selections affect nematode community composition under different vegetations of changbai mountain. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2023, 5, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, G.C.; Smith, J.J.; Cowan, D.A. Review and re-analysis of domain-specific 16S primers. J. Microbiol. Methods 2003, 55, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikema, A.P.; Horst-Kreft, D.; Boers, S.A.; Jansen, R.; Hiltemann, S.D.; de Koning, W.; Kraaij, R.; de Ridder, M.A.J.; van Houten, C.B.; Bont, L.J.; et al. Comparison of Illumina versus Nanopore 16S rRNA gene sequencing of the human nasal microbiota. Genes 2020, 11, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thejaswini, S.; Jojy, S.; Vijayan, A.; Martin Paul, A. Isolation of gut Actinobacteria from fishes. In Methods in Actinobacteriology; Springer Protocols Handbooks; Dharumadurai, D., Ed.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormas, K.A.; Meziti, A.; Mente, E.; Frentzos, A. Dietary Differences Are Reflected on the Gut Prokaryotic Community Structure of Wild and Commercially Reared Sea Bream (Sparus aurata). Microbiologyopen 2014, 3, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meziti, A.; Nikouli, E.; Papaharisis, L.; Kormas, K.A.; Mente, E. The response of gut and fecal bacterial communities of the European sea bass (Dicentrachus labrax) fed a low fish-plant meal and yeast protein supplementation diet. Sustain. Microbiol. 2024, 1, qvae005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molano, L.G.; Vega-abellaneda, S.; Manichanh, C.; Molano, L.G.; Vega-abellaneda, S.; Manichanh, C. Database for 16S rRNA amplicon analysis. MSystems 2024, 9, e0095023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuscó, A.; Catozzi, C.; Viñes, J.; Sanchez, A.; Francino, O. Microbiota profiling with long amplicons using Nanopore sequencing: Full-length 16S rRNA gene and the 16S-ITS-23S of the rrn operon. F1000Research 2019, 7, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buetas, E.; Jordán-López, M.; López-Roldán, A.; D’Auria, G.; Martínez-Priego, L.; De Marco, G.; Carda-Diéguez, M.; Mira, A. Full-Length 16S rRNA gene sequencing by pacbio improves taxonomic resolution in human microbiome samples. BMC Genomics 2024, 25, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pootakham, W.; Mhuantong, W.; Yoocha, T.; Putchim, L.; Sonthirod, C.; Naktang, C.; Thongtham, N.; Tangphatsornruang, S. High resolution profiling of coral-associated bacterial communities using full-length 16S rRNA sequence data from PacBio SMRT sequencing system. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Holt, K.E. Performance of neural network basecalling tools for Oxford Nanopore Sequencing. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazzon, M.C.; Naya-Català, F.; Simó-Mirabet, P.; Picard-Sánchez, A.; Roig, F.J.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Sex, age, and bacteria: How the intestinal microbiota is modulated in a protandrous hermaphrodite fish. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. Gigascience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Coster, W.; Rademakers, R. NanoPack2: Population-scale evaluation of long-read sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. New strategies to improve Minimap2 alignment accuracy. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 4572–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, P.; Parfrey, L.W.; Yarza, P.; Gerken, J.; Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Ludwig, W.; Gloeckner, F.O. The SILVA and “all-species living tree project (LTP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D643–D648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Simko, V. R Package “Corrplot”: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix, version 0.92. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/taiyun/corrplot (accessed on 15 February 2024).
- Cao, Y.; Dong, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Niu, C. MicrobiomeMarker: An R/Bioconductor package for microbiome marker identification and visualization. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 4027–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Tissue/ Standard | Sp. | Samples | Libr. Strategy | Primers | Basecalling |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mock | MOCK | 1 | RAP; LIG | V3–V4; V1–V3; V1–V9 | FAST; HAC; SUP |
| CTRL+ | E. coli DH5α | 1 | |||
| Water | - | 12 | RAP; LIG | V1–V9 | |
| - | 3 | LIG | V3–V4; V1–V3; V1–V9 | ||
| Skin | ESB | 4 | RAP; LIG | V3–V4; V1–V3; V1–V9 | |
| Intestine | ESB | 4 | |||
| Faeces | GSB | 12 | LIG | V1–V9 |
| 16S Gene Region | Primer Pair | PCR Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| V1–V3 (27F-533R) | F: AGA GTT TGA TCM TGG CTC AG R: TTA CCG CGG CKG CTG GCA CG | D: 95 °C 1 min A: 30 × [95 °C 20 s, 56 °C 30 s, 65° 1 min] E: 65 °C 5 min |
| V3–V4 (341F-805R) | F: CCT ACG GGN GGC WGC AG R: GAC TAC HVG GGT ATC TAA TCC | D: 95 °C 1 min A: 30 × [95 °C 20 s, 56 °C 30 s, 65° 1 min] E: 65 °C 5 min |
| V1–V9 (27F-1492R) | F: AGA GTT TGA TCM TGG CTC AG R: CGG TTA CCT TGT TAC GAC TT | D: 95 °C 1 min A: 30 × [95 °C 20 s, 52 °C 30 s, 65° 2 min] E: 65 °C 5 min |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Domingo-Bretón, R.; Moroni, F.; Toxqui-Rodríguez, S.; Belenguer, Á.; Piazzon, M.C.; Pérez-Sánchez, J.; Naya-Català, F. Moving Beyond Oxford Nanopore Standard Procedures: New Insights from Water and Multiple Fish Microbiomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312603
Domingo-Bretón R, Moroni F, Toxqui-Rodríguez S, Belenguer Á, Piazzon MC, Pérez-Sánchez J, Naya-Català F. Moving Beyond Oxford Nanopore Standard Procedures: New Insights from Water and Multiple Fish Microbiomes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(23):12603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312603
Chicago/Turabian StyleDomingo-Bretón, Ricardo, Federico Moroni, Socorro Toxqui-Rodríguez, Álvaro Belenguer, M. Carla Piazzon, Jaume Pérez-Sánchez, and Fernando Naya-Català. 2024. "Moving Beyond Oxford Nanopore Standard Procedures: New Insights from Water and Multiple Fish Microbiomes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 23: 12603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312603
APA StyleDomingo-Bretón, R., Moroni, F., Toxqui-Rodríguez, S., Belenguer, Á., Piazzon, M. C., Pérez-Sánchez, J., & Naya-Català, F. (2024). Moving Beyond Oxford Nanopore Standard Procedures: New Insights from Water and Multiple Fish Microbiomes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(23), 12603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312603





