Mechanisms of Adsorption of Phenoxyalkanoic Herbicides on Fulvic and Humic Acids
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Name | 2,4-DB | DCPP-P | 2,4-D | MCPB | MCPP-P | MCPA | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS name | Structural formula | 4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)butanoic acid | 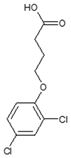 | (2R)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)propanoic acid | 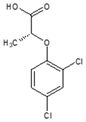 | 2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)acetic acid |  | 4-(4-chloro-2-methylphenoxy)butanoic acid | 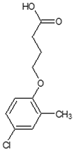 | (2R)-2-(4-chloro-2-methylphenoxy)propanoic acid | 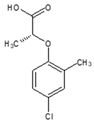 | 2-(4-chloro-2-methylphenoxy)acetic acid |  |
| Mol wt. | 249.1 | 235.1 | 221.0 | 228.7 | 214.6 | 200.6 | |||||||
| pKa (SD) 1 | 4.74 (0.05) | 2.98 (0.02) | 2.93 (0.01) | 5.15 (0.05) | 3.14 (0.01) | 3.06 (0.01) | |||||||
| C log P 2 | 3.42 | 3.04 | 2.73 | 3.39 | 3.01 | 2.70 | |||||||
2. Results
2.1. FTIR Results
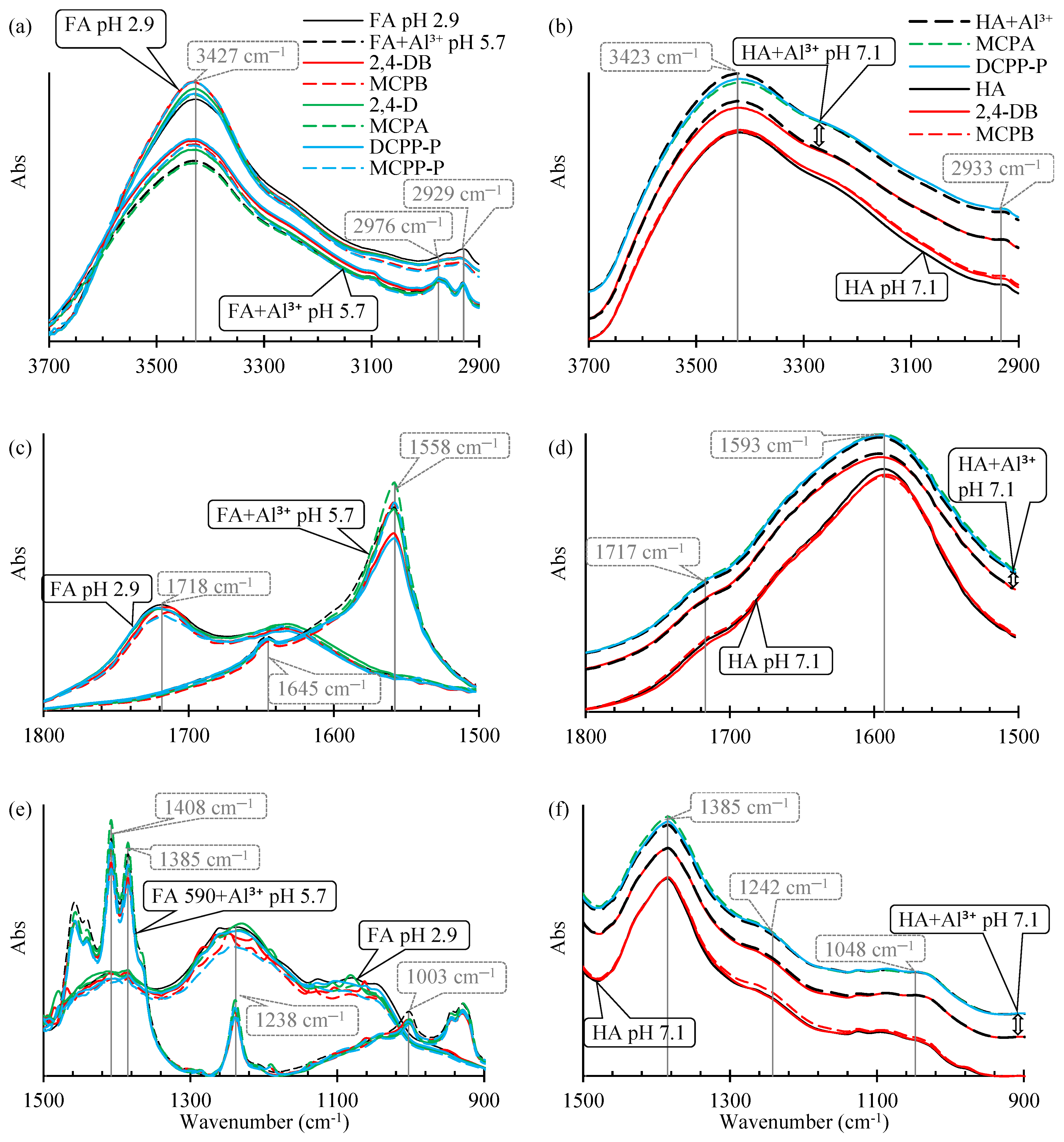
2.1.1. FTIR Spectra of Pure FAs and HAs, and After the Adsorption of Al3+ Species
2.1.2. FTIR Spectra of FAs and FAs+Al3+ After the Adsorption of PAAHs
| Location (cm−1) | Assignment (Comments) | References | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FAs pH 2.9 | FAs pH 5.7 | FAs+Al3+ pH 5.7 | HAs pH 2.9 | HAs pH 7.1 | HAs+Al3+ pH 7.1 | ||
| 3427 | 3425 | 3431 | 3418 | 3420 | 3423 | O–H stretching of hydroxyl groups involved in H-bonds, N–H stretching of amines (weaker) | [38,39] |
| 2958 | 2976 | 2976 | 2959 | Nd 1 | Nd | Asymmetric –CH3 stretching | [38] |
| 2929 | 2932 | 2930 | 2924 | Nd | 2933 | Asymmetric –CH2– stretching | [38] |
| 1718 | Nd | Nd | 1717 | Nd | Nd | C=O stretching in –COOH, ketones and esters | [29,38] |
| 1633 | 1645 | 1645 | 1620 | Nd | Nd | strongly H-bonded C=O, aromatic –C=C– stretching, | [29,31,38] |
| Nd | 1556 | 1558 | Nd | 1593 | 1593 | Asymmetric stretch of –COO−, aromatic –C=C– stretching | [29,31,38] |
| Nd | 1408 | 1408 | 1402 | Nd | Nd | O–H and C–OH stretching of phenols, aromatic –C=C– stretching | [34,35] |
| 1385 | 1385 | 1385 | 1385 | 1385 | 1385 | Symmetric –COO− stretching, | [29,31,38] |
| 1236 | 1240 | 1238 | 1242 | Nd | Nd | C–O stretching and O–H deformation in –COOH, C–O stretching of ethers and alcohols/phenols | [29,31,33,34,38] |
| Nd | 999 | 1003 | 1051 | Nd | 1049 | C–OH stretching in polysaccharides | [35,37,38] |
2.1.3. FTIR Spectra of HAs and HAs+Al3+ After the Adsorption of PAAHs
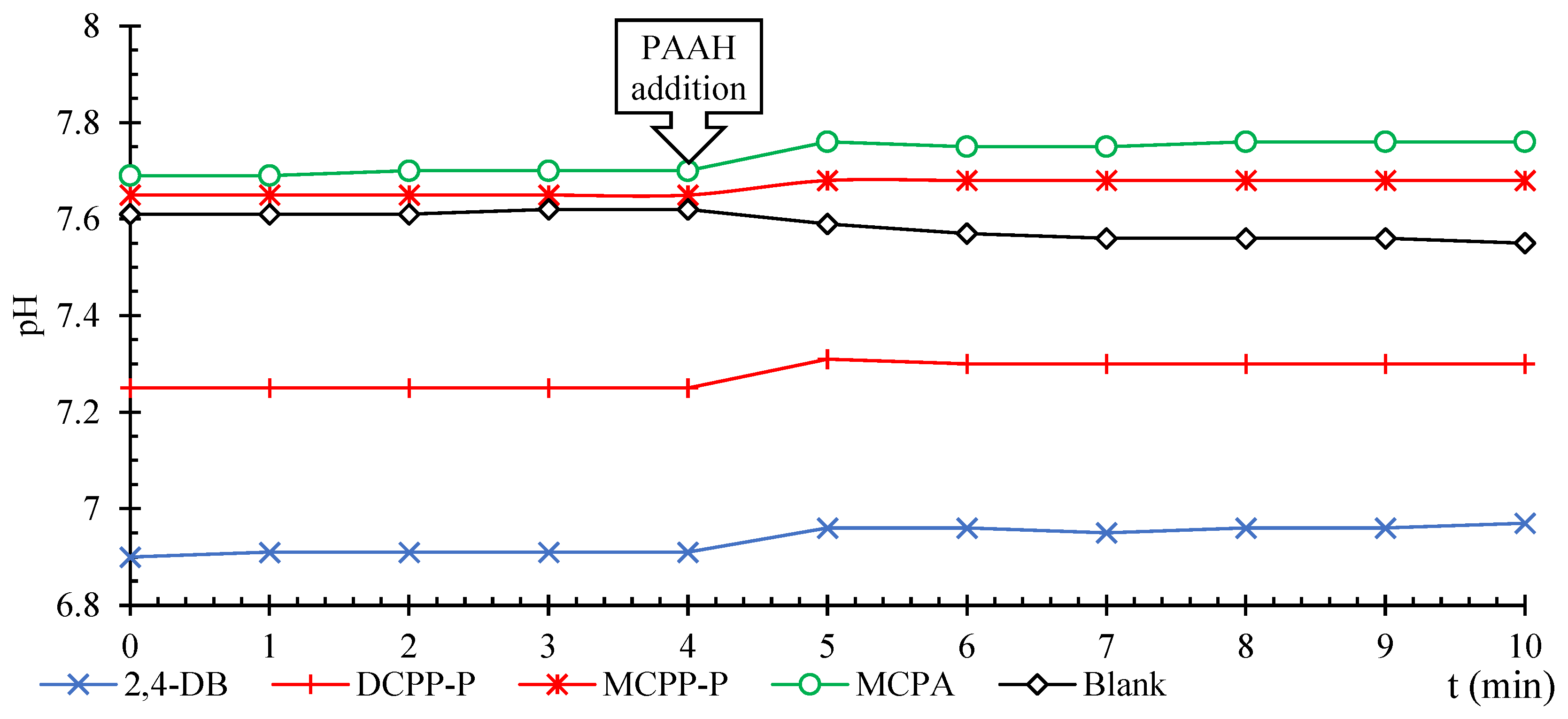
2.2. Thermodynamic Analysis of the Adsorption of PAAH Anions on FAs+Al3+ and HAs+Al3+
2.2.1. Thermodynamic Equilibrium Constant of Adsorption ()
2.2.2. Thermodynamic Parameters of Adsorption
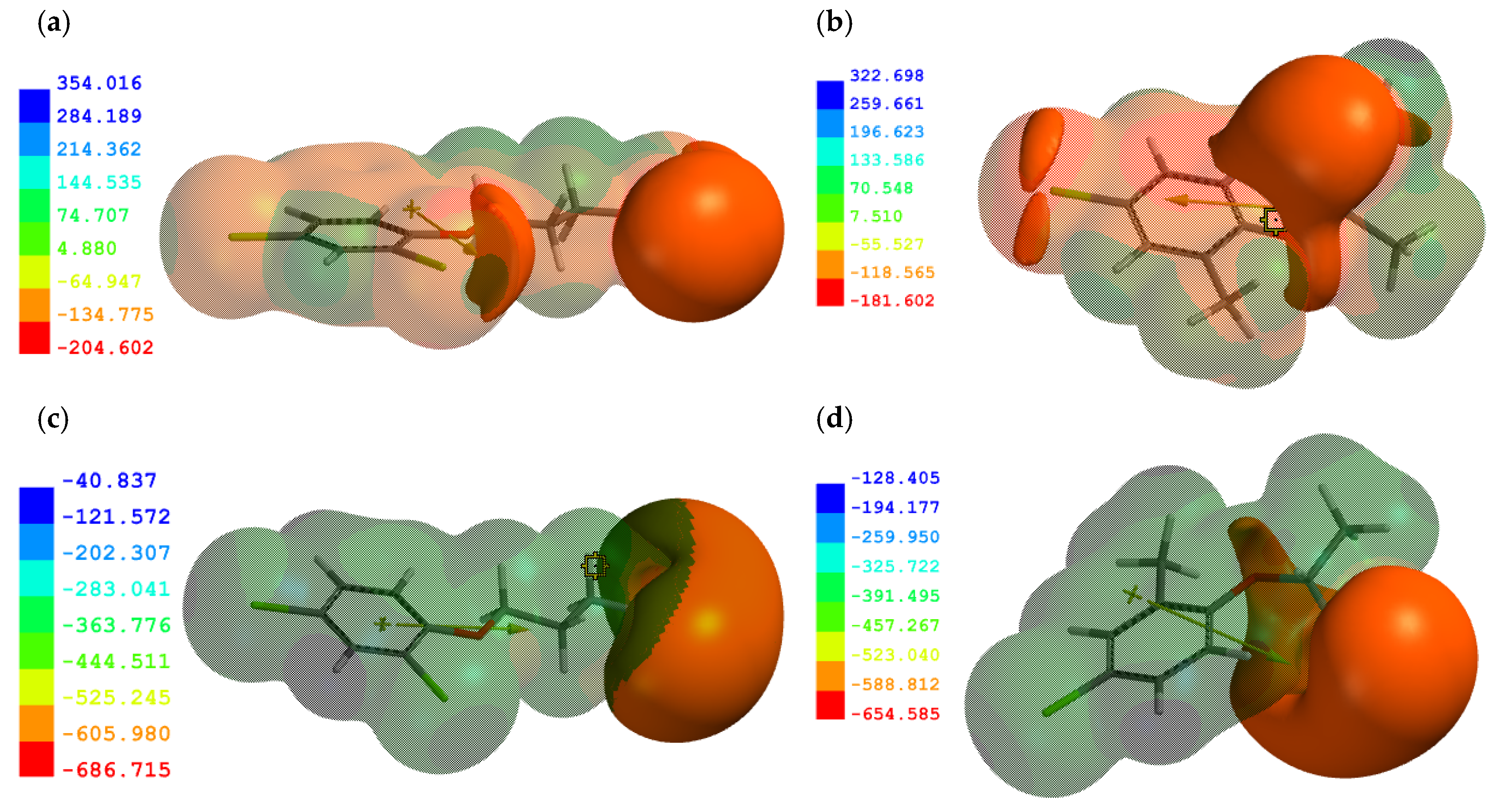
2.3. Molecular Modeling Results
3. Discussion—Adsorption Mechanisms Predicted Based on FTIR Data, Thermodynamic Parameters, and the Results of Molecular Modeling
3.1. Adsorption of the Neutral Forms of PAAHs
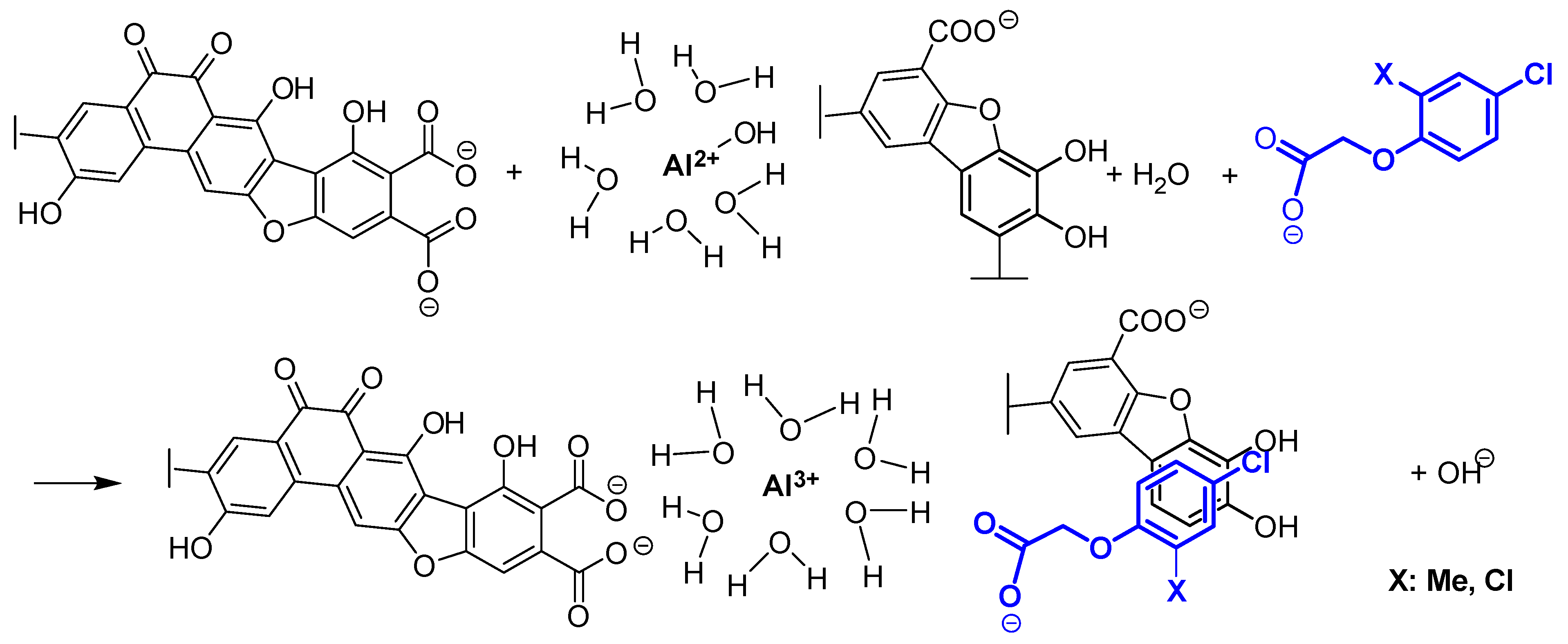
3.2. Adsorption of Al3+ and the Anionic Forms of PAAHs
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Chemicals
4.2. Isolation of FAs and HAs
4.3. Adsorption Experiments
4.3.1. Adsorption of PAAHs on FAs at pH 2.9 and FAs+Al3+ at pH 5.7
4.3.2. Adsorption of PAAHs on HAs, and HAs+Al3+ at pH 7.1
4.4. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
4.5. Molecular Modeling
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zimmermán, P.W.; Hitchcock, A.E. Substituted phenoxy and benzoic acid growth substances and the relation of structure to physiological activity. Contrib. Boyce Thomps. 1942, 12, 321–343. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.M.; Ren, C.Q.; Jiang, L.; Li, Q.F.; Zhang, W.; Wu, C.Y. Characteristic of dissolved organic matter polar fractions with variable sources by spectrum technologies: Chemical properties and interaction with phenoxy herbicide. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos, R.; Locoro, G.; Comero, S.; Contini, S.; Schwesig, D.; Werres, F.; Balsaa, P.; Gans, O.; Weiss, S.; Blaha, L.; et al. Pan-European survey on the occurrence of selected polar organic persistent pollutants in ground water. Water Res. 2010, 44, 4115–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos, R.; Gawlik, B.M.; Locoro, G.; Rimaviciute, E.; Contini, S.; Bidoglio, G. EU-wide survey of polar organic persistent pollutants in European river waters. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paszko, T.; Spadotto, C.A.; Huber, M.; Jerzykiewicz, M.; Matysiak, J.; Skrzypek, A.; Boguta, P. Can the pH-dependent adsorption of phenoxyalkanoic herbicides in soils be described with a single equation? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadotto, C.A.; Hornsby, A.G. Soil sorption of acidic pesticides: Modeling pH effects. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kah, M.; Brown, C.D. Prediction of the adsorption of ionizable pesticides in soils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 2312–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszko, T.; Muszyński, P.; Materska, M.; Bojanowska, M.; Kostecka, M.; Jackowska, I. Adsorption and degradation of phenoxyalkanoic acid herbicides in soils: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.A.; Tzilivakis, J.; Warner, D.J.; Green, A. An international database for pesticide risk assessments and management. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2016, 22, 1050–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariff, R.M. Thermodynamic adsorption-desorption of metolachlor and 2,4-D on agricultural soils. Int. J. Chem. 2011, 3, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.; Xing, S.Y.; Gong, Y.K.; Miyajima, T. Characterization of humic acids by two-dimensional correlation fluorescence spectroscopy. J. Mol. Str. 2008, 883, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, A.; López, R.; Gondar, D.; Antelo, J.; Fiol, S.; Arce, F. Effect of pH and ionic strength on the binding of paraquat and MCPA by soil fulvic and humic acids. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audette, Y.; Longstaffe, J.G.; Gillespie, A.W.; Smith, D.S.; Voroney, R.P. Validation and comparisons of NaOH and Na3PO4 extraction methods for the characterization of organic amendments. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2021, 85, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IHSS. Isolation of IHSS Soil Fulvic and Humic Acids. 2024. Available online: https://humic-substances.org/isolation-of-ihss-soil-fulvic-and-humic-acids/ (accessed on 26 March 2024).
- Khan, S.U. Equilibrium and kinetic studies of adsorption of 2,4-D and picloram on humic acid. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1973, 53, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celis, R.; Hermosin, M.C.; Cox, L.; Cornejo, J. Sorption of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by model particles simulating naturally occurring soil colloids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberhauer, G.; Temmel, B.; Gerzabek, M.H. Influence of dissolved humic substances on the leaching of MCPA in a soil column experiment. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkins, K.M.; Dickerson, M.A.; Traudt, E.M. Fluorescence characterization of the interaction Suwannee river fulvic acid with the herbicide dichlorprop (2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)propionic acid) in the absence and presence of aluminum or erbium. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2011, 105, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćwieląg-Piasecka, I.; Medyńska-Juraszek, A.; Jerzykiewicz, M.; Dębicka, M.; Bekier, J.; Jamroz, E.; Kawałko, D. Humic acid and biochar as specific sorbents of pesticides. J. Soil. Sediments 2018, 18, 2692–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberhauer, G.; Pfeiffer, L.; Gerzabek, M.H. Influence of molecular structure on sorption of phenoxyalkanoic herbicides on soil and its particle size fractions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3722–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kah, M.; Brown, C.D. Adsorption of ionisable pesticides in soils. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2006, 188, 149–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Kim, S.-w.; Rao, R.A.K.; Abou-Shanab, R.A.I.; Bhatnagar, A. Adsorption studies of dichloromethane on some commercially available GACs: Effect of kinetics, thermodynamics and competitive ions. J. Hazards Mater. 2010, 178, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, L.; Guo, L.; Guo, C. Adsorption of Congo red from aqueous solutions onto Ca-bentonite. J. Hazards Mater. 2009, 161, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commision. EU Pesticides Database. 2024. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/plants/pesticides/eu-pesticides-database_en (accessed on 24 April 2024).
- Albert, A.; Serjeant, E.P. The Determination of Ionization Constants. A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed.; Chapman and Hall: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1984; p. 218. [Google Scholar]
- Leo, A.J. Calculating the hydrophobicity of chlorinated hydrocarbon solutes. Sci. Total Environ. 1991, 109, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, A.J. Calculating Log Poct from structures. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 1281–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannino, F.; Violante, A.; Gianfreda, L. Adsorption-desorption of 2,4-D by hydroxy aluminium montmorillonite complexes. Pestic. Sci. 1997, 51, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, A.; Stevenson, F.J. Infrared-spectra of Cu2+, Pb2+, and Ca2+ complexes of soil humic substances. Geoderma 1982, 27, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrivee, E.M.; Elkins, K.M.; Andrews, S.E.; Nelson, D.J. Fluorescence characterization of the interaction of Al and Pd with Suwannee River fulvic acid in the absence and presence of the herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2003, 97, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.K.; Song, J.N.; Wang, X.C.C.; Jin, X. Two-dimensional correlation spectroscopic analysis on the interaction between humic acids and aluminum coagulant. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 64, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.S.; Zhao, B.Z.; Chu, W.Y.; Mao, J.D.; Olk, D.C.; Xin, X.L.; Zhang, J.B. Altered humin compositions under organic and inorganic fertilization on an intensively cultivated sandy loam soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Song, M.; Liu, M.; Jiang, C.; Li, Z. Fungicidal activities of soil humic/fulvic acids related to their chemical structures in greenhouse vegetable fields with cultivation chronosequence. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, C.; Senesi, N.; Polo, A.; Brunetti, G.; García-Gil, J.C.; D’Orazio, V. Soil fulvic acid properties as a means to assess the use of pig slurry amendment. Soil Till. Res. 2003, 74, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavoski, I.; D’Orazio, V.; Miano, T. Interactions between rotenone and humic acids by means of FT-IR and fluorescence spectroscopies. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsson, M. Interactions of aluminium and fulvic acid in moderately acid solutions: Stoichiometry of the H+/Al3+ exchange. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2000, 51, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boguta, P.; D’Orazio, V.; Senesi, N.; Sokolowska, Z.; Szewczuk-Karpisz, K. Insight into the interaction mechanism of iron ions with soil humic acids. The effect of the pH and chemical properties of humic acids. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 245, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, R.M.; Webster, F.X.; Kiemle, D.J. Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds, 7th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; p. 502. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Gao, Q.; Xie, Z.L.; Yang, J.M.; Liu, J.H. Adsorption of nitrification inhibitor nitrapyrin by humic acid and fulvic acid in black soil: Characteristics and mechanism. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sposito, G. The Chemistry of Soils; Oxford Univestity Press: New York, NY, USA; Oxford, UK, 1989; p. 277. [Google Scholar]
- Gensemer, R.W.; Playle, R.C. The bioavailability and toxicity of aluminum in aquatic environments. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 29, 315–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Wu, C.D.; Jia, A.Y.; Hu, B. Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics of the sorption of p-nitrophenol on two variable charge soils of Southern China. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 298, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, A.; Moncada, F.; Charry, J. The any particle molecular orbital approach: A short review of the theory and applications. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2018, 119, e25705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senesi, N. Binding mechanisms of pesticides to soil humic substances. Sci. Total Environ. 1992, 123, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchańska, H.; Czaplicka, M.; Kyzioł-Komosińska, J. Interaction of selected pesticides with mineral and organic soil components. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2020, 46, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffle, J.A.E. Les substances humiques et leurs interactions avec les ions mineraux. In Conference Proceedings de la Commisison d’Hydrologie Appliquee de l’A.G.H.T.M.; l’Universite d’Orsay: Orsay, France, 1977; pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.Q.; Chen, Z.L.; Yang, X.H. Spectroscopic study of aluminium speciation in removing humic substances by Al coagulation. Water Res. 1999, 33, 3271–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissinen, A.; Ilvesniemi, H.; Tanskanen, N. Equilibria of weak acids and organic Al complexes explain activity of H and Al in a salt extract of exchangeable cations. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1999, 50, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, A.J.A.; Tunega, D.; Schaumann, G.E.; Haberhauer, G.; Gerzabek, M.H.; Lischka, H. Proton transfer processes in polar regions of humic substances initiated by aqueous aluminum cation bridges: A computational study. Geoderma 2014, 213, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.Y.; Spinette, R.F.; O’Melia, C.R. Stoichiometry of coagulation revisited. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2582–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, J.; Persson, P.; Laiti, E.; Sjoberg, S. Adsorption of o-phthalate at the water-boehmite (gamma-AlOOH) interface: Evidence for two coordination modes. Langmuir 1997, 13, 4085–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.H.; Shang, C.; Chen, G.H. ATR-FTIR investigation of the role of phenolic groups in the interaction of some NOM model compounds with aluminum hydroxide. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 2074–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, T.; Du, G.; Zheng, M.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; Gao, Z. Effective removal of humic acid from aqueous solution in an Al-based metal-organic framework. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 3624–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, N.D.; Hesketh, N.; Livens, F.R.; Tipping, E.; Jones, M.N. Metal ion-humic interaction. A thermodynamic study. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1998, 94, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, M.B. Environmental Chemistry of Soils; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA; Oxford, UK, 1995; 406p. [Google Scholar]
- González-Gómez, M.A.; Belderbos, S.; Yañez-Vilar, S.; Piñeiro, Y.; Cleeren, F.; Bormans, G.; Deroose, C.M.; Gsell, W.; Himmelreich, U.; Rivas, J. Development of Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles Coated with Polyacrylic Acid and Aluminum Hydroxide as an Efficient Contrast Agent for Multimodal Imaging. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, F.J. Humus Chemistry: Genesis, Comoposition, Reactions; John Willey & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1994; p. 512. [Google Scholar]
- Bieganowski, A.; Witkowska-Walczak, B.; Gliński, J.; Sokołowska, Z.; Sławinski, C.; Brzezinska, M.; Włodarczyk, T. Database of Polish arable mineral soils: A review. Int. Agrophys. 2013, 27, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, Update 2015 International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; World soil Resources Reports No. 106; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Siek, M.; Paszko, T. Factors affecting coupled degradation and time-dependent sorption processes of tebuconazole in mineral soil profiles. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, J.E.; Powell, H.K.J. Acid pyrophosphate extraction of soil fulvic-acids. J. Soil Sci. 1986, 37, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wavefunction. Spartan’10 for Windows, Macintosh and Linux. 2011. Available online: http://downloads.wavefun.com/Spartan10Manual.pdf (accessed on 24 April 2024).
- Santos, C.B.R.; Lobato, C.C.; Braga, F.S.; Morais, S.S.S.; Santos, C.F.; Fernandes, C.P.; Brasil, D.S.B.; Hage-Melim, L.I.S.; Macêdo, W.J.C.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Application of Hartree-Fock method for modeling of bioactive molecules using SAR and QSPR. Comput. Mol. Biosci. 2014, 4, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebpour, Z.; Ghassempour, A.; Shamsipur, M. Study of the pesticide naptalam degradation; theoretical and experimental. J. Mol. Struct. THEOCHEM 2003, 629, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzeski, W.; Matysiak, J.; Kandefer-Szerszeń, M. Anticancer, neuroprotective activities and computational studies of 2-amino-1,3,4-thiadiazole based compound. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 3201–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.C.; Kollman, P.A. An approach to computing electrostatic charges for molecules. J. Comput. Chem. 1984, 5, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Element/Assignment | FAs (%) | HAs (%) |
|---|---|---|
| C | 44.72 | 53.94 |
| H | 4.65 | 3.19 |
| N | 3.25 | 3.15 |
| S | 0.61 | 0.26 |
| Aliphatic (0–110 ppm) | 30.2 | 8.7 |
| Ar (110–157 ppm) | 35.1 | 50.4 |
| CH3 (0–43 ppm) | 7.3 | 4.3 |
| OCH3 (45–60 ppm) | 5.2 | 1.5 |
| Side-chain lignin (43–87 ppm) | 15.7 | 3.0 |
| Ar-OH (145–165 ppm) | Nd 1 | Nd |
| COOH (158–190 ppm) | 41.8 | 18.0 |
| HB 1 | 0.90 | 2.81 |
| Sample | PAAH | pH | T(K) | (kJ/mol) | (kJ/mol) | (J/(mol K)) | R2 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FAs+Al3+ | MCPA | 5.10 | 278.15 | 267.00 | −12.92 | −8.4 | 16.2 | 0.985 |
| 293.15 | 231.49 | −13.27 | ||||||
| 312.15 | 179.74 | −13.47 | ||||||
| FAs+Al3+ | DCPP-P | 5.08 | 278.15 | 450.18 | −14.13 | −2.9 | 40.3 | 0.973 |
| 293.15 | 413.76 | −14.69 | ||||||
| 312.15 | 392.13 | −15.50 | ||||||
| HAs+Al3+ | MCPA | 7.97 | 278.15 | 36.91 | −8.34 | −5.3 | 10.8 | 0.907 |
| 293.15 | 30.59 | −8.34 | ||||||
| 312.15 | 28.68 | −8.71 | ||||||
| HAs+Al3+ | DCPP-P | 7.96 | 278.15 | 58.86 | −9.42 | −2.4 | 25.5 | 0.958 |
| 293.15 | 57.03 | −9.86 | ||||||
| 312.15 | 52.73 | −10.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paszko, T.; Matysiak, J.; Spadotto, C.A.; Boguta, P.; Skic, K. Mechanisms of Adsorption of Phenoxyalkanoic Herbicides on Fulvic and Humic Acids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312699
Paszko T, Matysiak J, Spadotto CA, Boguta P, Skic K. Mechanisms of Adsorption of Phenoxyalkanoic Herbicides on Fulvic and Humic Acids. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(23):12699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312699
Chicago/Turabian StylePaszko, Tadeusz, Joanna Matysiak, Claudio A. Spadotto, Patrycja Boguta, and Kamil Skic. 2024. "Mechanisms of Adsorption of Phenoxyalkanoic Herbicides on Fulvic and Humic Acids" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 23: 12699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312699
APA StylePaszko, T., Matysiak, J., Spadotto, C. A., Boguta, P., & Skic, K. (2024). Mechanisms of Adsorption of Phenoxyalkanoic Herbicides on Fulvic and Humic Acids. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(23), 12699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312699









