Environmental Impact of Xenobiotic Aromatic Compounds and Their Biodegradation Potential in Comamonas testosteroni
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Environmental Impact of Xenobiotic Aromatic Compounds
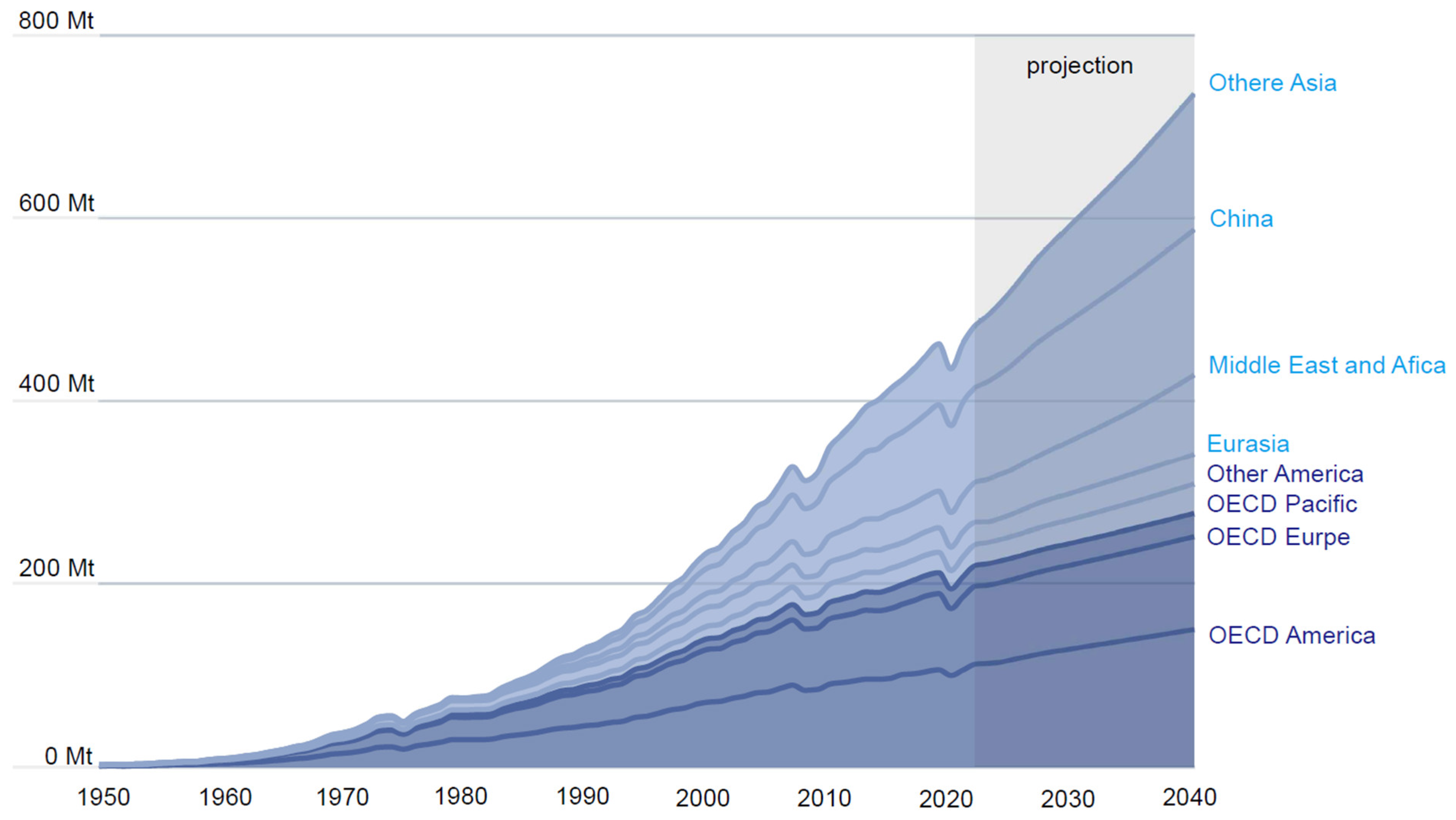
2.1. Plastics-Related Aromatic Compounds
2.2. Pesticides-Related Aromatic Compounds
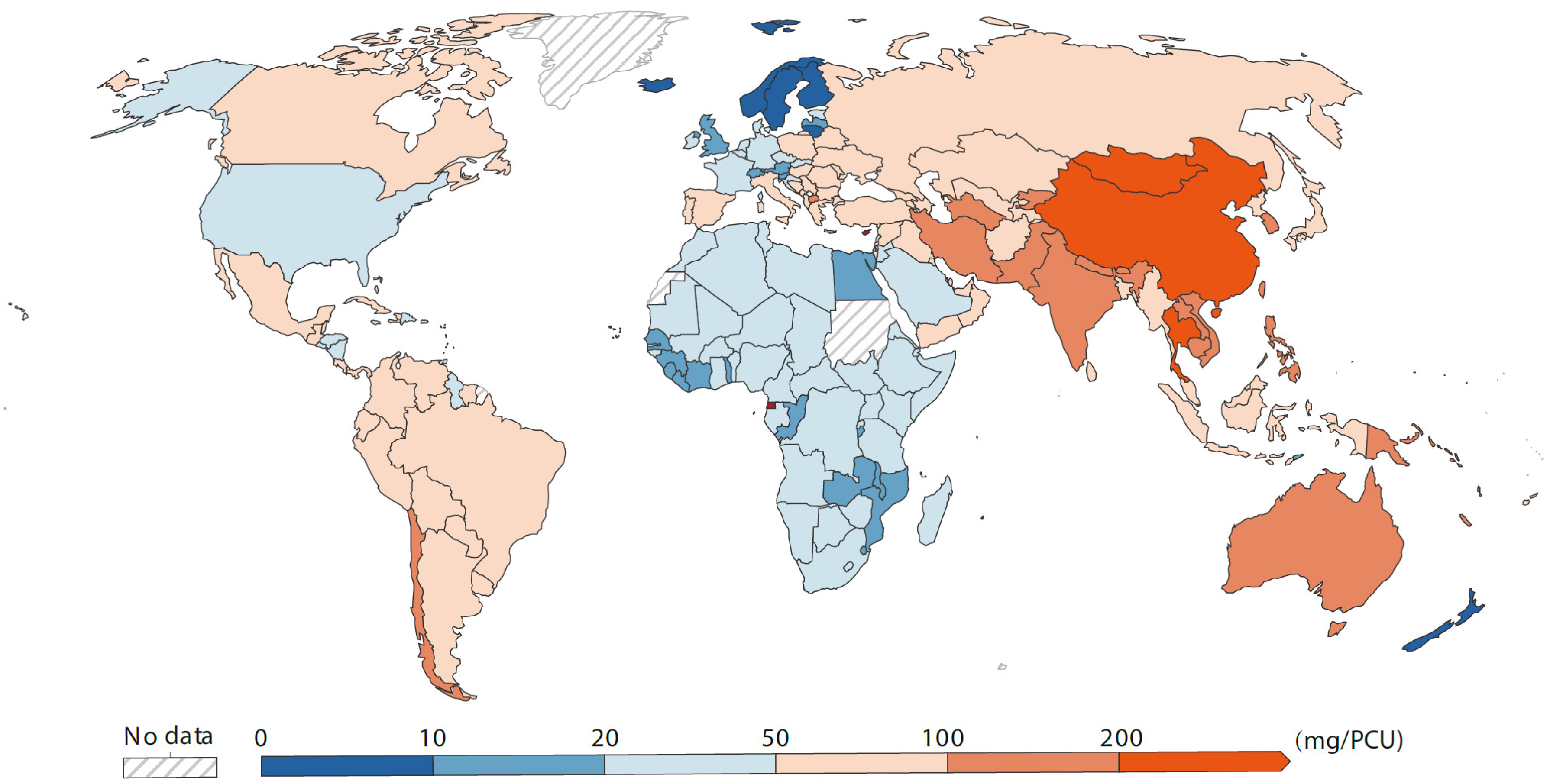
2.3. Antibiotics-Related Aromatic Compounds
3. Biodegradation Strategies for Aromatic Compounds in C. testosteroni
3.1. Biodegradation Pathways in C. testosteroni
3.2. Key Functional Genes and Enzymes
3.3. Regulatory Mechanisms
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Faraday, M. XX. On new compounds of carbon and hydrogen, and on certain other products obtained during the decomposition of oil by heat. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 1825, 115, 440–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sola, M. Aromaticity rules. Nat. Chem. 2022, 14, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capim, S.L.; Santana, S.R.; Oliveira, B.G.d.; Rocha, G.B.; Vasconcellos, M.L.A.A. Revisiting the origin of the preferential π-π stacking conformation of the (+)-8-phenylmenthyl acrylate. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2010, 21, 1718–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.D.; MacCoss, M.; Lawson, A.D. Rings in drugs. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 5845–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikushima, K.; Koyama, H.; Kodama, K.; Dohi, T. Nucleophilic aromatic substitution of polyfluoroarene to access highly functionalized 10-phenylphenothiazine derivatives. Molecules 2021, 26, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.K. Bacilli-Mediated degradation of xenobiotic compounds and heavy Metals. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 570307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilova, A.; Campeau, L.C.; Sherer, E.C.; Stuart, D.R. Analysis of benzenoid substitution patterns in small molecule active pharmaceutical Ingredients. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 13389–13396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Han, W.; He, R. Biodegradation of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol by Rhodococcus sp. isolated from a picric acid-contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, A.R.; Hasan, H.A.; Muhamad, M.H.; Ismail, N.I.; Abdullah, S.R.S. Microbial degradation of microplastics by enzymatic processes: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3057–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jia, Y.; Khanal, S.K.; Lu, H.; Fang, H.; Zhao, Q. Understanding the role of extracellular polymeric substances on ciprofloxacin adsorption in aerobic sludge, anaerobic sludge, and sulfate-reducing bacteria sludge systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 6476–6486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Kumar, P.S.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Rajamohan, N.; Saravanan, R. Microbial degradation of recalcitrant pesticides: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3209–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Policy Scenarios for Eliminating Plastic Pollution by 2040; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.; Yadav, V.; Kumar, Y.; Pramanik, A.; Dubey, K.K. How to deal with xenobiotic compounds through environment friendly approach? Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2024, 44, 1574–1593. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilkes, R.A.; Waldbauer, J.; Carroll, A.; Nieto-Domínguez, M.; Parker, D.J.; Zhang, L.; Guss, A.M.; Aristilde, L. Complex regulation in a Comamonas platform for diverse aromatic carbon metabolism. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2023, 19, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waluda, C.M.; Staniland, I.J. Entanglement of Antarctic fur seals at Bird Island, South Georgia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 74, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fok, L.; Cheung, P.K.; Tang, G.; Li, W.C. Size distribution of stranded small plastic debris on the coast of Guangdong, South China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, A.; Hoellein, T.J.; Mason, S.A.; Schluep, J.; Kelly, J.J. Microplastic is an abundant and distinct microbial habitat in an urban river. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11863–11871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, S.C.; Thompson, R.C. The impact of debris on marine life. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 92, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, K.L.; Thompson, R.C. Microplastics in the seas. Science 2014, 345, 144–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Moos, N.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Köhler, A. Uptake and effects of microplastics on cells and tissue of the blue mussel mytilus edulis L. after an xperimental exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11327–11335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, A.D.; Andrade, A.; Harris, E.P.; Rissman, E.F.; Wolstenholme, J.T. Bisphenol a exposure in utero disrupts hypothalamic gene expression particularly genes suspected in autism spectrum disorders and neuron and hormone signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alengebawy, A.; Abdelkhalek, S.T.; Qureshi, S.R.; Wang, M.Q. Heavy metals and pesticides toxicity in agricultural soil and plants: Ecological risks and human health implications. Toxics 2021, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisayoshi, T.; Kunitoshi, M.; Hiroshi, O.; Masahiro, N.; Toru, T.; Kazuo, Y.; Kiyoshi, T.; Masao, H. Improvement of a two-stage carcinogenesis model to detect modifying effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals on thyroid carcinogenesis in rats. Cancer Lett. 2002, 178, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Roger, J.P.; Amanda, M.G.; Mary, P.S.; David, G.W.; Charles, C.C.; Thomas, G.O.; Brian, G.L. Effect of pyrethrins on cytochrome P450 forms in cultured rat and human hepatocytes. Toxicology 2008, 243, 84–95. [Google Scholar]
- Shuai, X.; Chen, J.; Ray, C. Adsorption, transport and degradation of fipronil termiticide in three Hawaii soils. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herin, F.; Boutet-Robinet, E.; Levant, A.; Dulaurent, S.; Manika, M.; Galatry-Bouju, F.; Caron, P.; Soulat, J.M. Thyroid function tests in persons with occupational exposure to fipronil. Thyroid. 2011, 21, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, D.K.; Alan, M.H. Effects of microsomal enzyme inducers on thyroid follicular cell proliferation and thyroid hormone metabolism. Toxicol. Pathol. 2001, 29, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Liu, J.; Wan, M.; Huang, L.; Yang, D.; Huang, B.; Zhong, Z.; et al. Exposure to pyrazosulfuron-ethyl induces immunotoxicity and behavioral abnormalities in zebrafish embryos. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2022, 131, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.W.; Watkins, K.; Hewlett, A. Infection control through the ages. Am. J. Infect. Control 2012, 40, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.L. Patent review of manufacturing routes to fifth-Generation cephalosporin drugs. Part 1, Ceftolozane. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2017, 21, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brain, R.A.; Johnson, D.J.; Richards, S.M.; Sanderson, H.; Sibley, P.K.; Solomon, K.R. Effects of 25 pharmaceutical compounds to Lemna gibba using a seven-day static-renewal test. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2004, 23, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.L.; Wong, M.H. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs): A review on environmental contamination in China. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Cheng, H. Use of veterinary antimicrobials in China and efforts to improve their rational use. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2015, 3, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Yang, L.; Yang, R. Distribution characteristics of antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes in fresh and composted manures of livestock farms. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Gao, J.; Xie, X.; Zhou, Q. DNA damage and biochemical toxicity of antibiotics in soil on the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulchandani, R.; Wang, Y.; Gilbert, M.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food-producing animals: 2020 to 2030. Glob. Public Health 2023, 3, e0001305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Providenti, M.A.; O’Brien, J.M.; Ruff, J.; Cook, A.M.; Lambert, I.B. Metabolism of isovanillate, vanillate, and veratrate by Comamonas testosteroni strain BR6020. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 3862–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, G.; Boll, M.; Heider, J. Microbial degradation of aromatic compounds—From one strategy to four. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Wang, C.H.; Yang, F.C.; Ismail, W.; Wang, P.H.; Shih, C.J.; Wu, Y.C.; Chiang, Y.R. Identification of Comamonas testosteroni as an androgen degrader in sewage. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Jiang, C.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Wu, J.F.; Han, J.G.; Liu, S.J. Plant-microbe association for rhizoremediation of chloronitroaromatic pollutants with Comamonas sp. strain CNB-1. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamimura, N.; Aoyama, T.; Yoshida, R.; Takahashi, K.; Kasai, D.; Abe, T.; Mase, K.; Katayama, Y.; Fukuda, M.; Masai, E. Characterization of the protocatechuate 4,5-cleavage pathway operon in Comamonas sp. strain E6 and discovery of a novel pathway gene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 8093–8101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasoh, M.; Masai, E.; Ishibashi, S.; Hara, H.; Kamimura, N.; Miyauchi, K.; Fukuda, M. Characterization of the terephthalate degradation genes of Comamonas sp. strain E6. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 1825–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mampel, J.; Providenti, M.A.; Cook, A.M. Protocatechuate 4,5-dioxygenase from Comamonas testosteroni T-2: Biochemical and molecular properties of a new subgroup within class III of extradiol dioxygenases. Arch. Microbiol. 2005, 183, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahto, J.K.; Neetu, N.; Waghmode, B.; Kuatsjah, E.; Sharma, M.; Sircar, D.; Sharma, A.K.; Tomar, S.; Eltis, L.D.; Kumar, P. Molecular insights into substrate recognition and catalysis by phthalate dioxygenase from Comamonas testosteroni. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, B.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.W.; Wang, B.J.; Liu, S.J. Assimilation of aromatic compounds by Comamonas testosteroni: Characterization and spreadability of protocatechuate 4,5-cleavage pathway in bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 6031–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondossi, M.; DBarriault; Sylvestre, M. Metabolism of 2,2’- and 3,3’-dihydroxybiphenyl by the biphenyl catabolic pathway of Comamonas testosteroni B-356. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.F.; Jiang, C.Y.; Wang, B.J.; Ma, Y.F.; Liu, Z.P.; Liu, S.J. Novel partial reductive pathway for 4-chloronitrobenzene and nitrobenzene degradation in Comamonas sp. strain CNB-1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 1759–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimova, M.; Iutynska, G.; Yamborko, N.; Dordevic, D.; Kushkevych, I. Possible processes and mechanisms of hexachlorobenzene decomposition by the selected Comamonas testosteroni bacterial strains. Processes 2022, 10, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.W.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, C.Y.; Liu, S.J. Benzoate metabolism intermediate benzoyl coenzyme A affects gentisate pathway regulation in Comamonas testosteroni. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 4051–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, D.; Iwasaki, T.; Nagai, K.; Araki, N.; Nishi, T.; Fukuda, M. 2,3-Dihydroxybenzoate meta-cleavage pathway is involved in o-phthalate utilization in Pseudomonas sp. strain PTH10. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, H.; Akahira, S.; Ohishi, T.; Maeda, M.; Kudo, T. Adaptation of Cornamonas testosteroni TAM1 to utilize phenol: Organization and regulation of the genes involved in phenol degradation. Microbiology 1998, 144, 2895–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zhu, W.; Cao, Z.; Xu, B.; Wang, G.; Luo, M. High correlation between genotypes and phenotypes of environmental bacteria Comamonas testosteroni strains. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; Chang, Y.; Li, B.; Bian, D.; Yang, W.; Huo, H.; Huo, M.; Zhu, S. Enhancing quinoline and phenol removal by adding Comamonas testosteroni bdq06 in treatment of an accidental dye wastewater. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 115, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, Y.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, M. Application potential of Comamonas testosteroni ZG2 for vegetable cultivation in nickel and cadmium polluted soil. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.J.; Moon, T.S. Mining microbial metabolism. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2023, 19, 544–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Sánchez, F.I.; Vessman, B.; Haym, A.; Alberti, G.; Mitri, S. Artificial selection improves pollutant degradation by bacterial communities. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Name | Structure | Main Function |
|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene terephthalate | 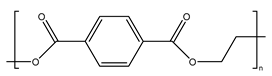 | It is mainly used for electrical components and plastic bottles, most of which are recyclable. |
| Polyphenylene sulfide |  | A high-quality, efficient, and high-temperature-resistant material. |
| Polystyrene |  | It is often used to make foam plastic products. |
| Bisphenol-A-polycarbonate (PC) | 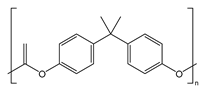 | An engineering plastic used for making transparent components |
| Polyimide |  | Used as a high-temperature insulation material |
| Type | Name | Structure | Main Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insecticide | Carbaryl | 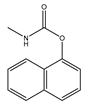 | Prevention and control of cotton bollworms, leaf rollers, etc. |
| Fipronil | 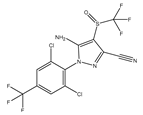 | Used for preventing and killing cockroaches, ants, etc. | |
| Teflubenzuron |  | Inhibition of chitin synthesis | |
| Herbicide | Bipyrazone | 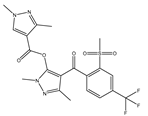 | HPPD inhibitor herbicides for broad-leaved grass in wheat fields |
| Pyrazosulfuron-ethyl |  | Selective systemic conductive herbicide | |
| Cypyrafluone |  | HPPD inhibitor herbicides for wheat field grasses in the Poaceae family | |
| Germicide | Thiophanate-Methyl |  | Broad spectrum systemic low-toxicity fungicide |
| Carbendazim | 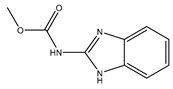 | Effective prevention and control of various crop diseases caused by fungi | |
| Fenaminosulf | 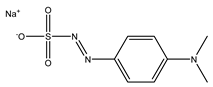 | Protective fungicides used for the prevention and control of vegetable diseases |
| Name | Structure | Main Function |
|---|---|---|
| Amoxicillin | 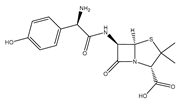 | Used for penicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection |
| Oxacillin sodium salt | 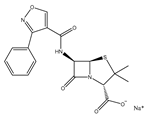 | Broad-spectrum antibiotics suitable for infection caused by sensitive organisms (strains that do not produce β-lactamase) |
| Cephalexin | 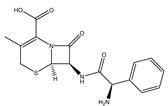 | Broad-spectrum antibiotics suitable for respiratory infections caused by sensitive organisms |
| Tetracycline | 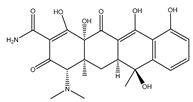 | They are widely used in infections caused by Gram-positive and harmful bacteria, intracellular Mycoplasma, Chlamydia, and Rickettsia. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Fan, H.; Li, B.; Liu, X. Environmental Impact of Xenobiotic Aromatic Compounds and Their Biodegradation Potential in Comamonas testosteroni. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413317
Li Y, Fan H, Li B, Liu X. Environmental Impact of Xenobiotic Aromatic Compounds and Their Biodegradation Potential in Comamonas testosteroni. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(24):13317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413317
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yapeng, Huixin Fan, Boqiao Li, and Xiaobo Liu. 2024. "Environmental Impact of Xenobiotic Aromatic Compounds and Their Biodegradation Potential in Comamonas testosteroni" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 24: 13317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413317
APA StyleLi, Y., Fan, H., Li, B., & Liu, X. (2024). Environmental Impact of Xenobiotic Aromatic Compounds and Their Biodegradation Potential in Comamonas testosteroni. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(24), 13317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413317







