Suppression of Pathological Allergen-Specific B Cells by Protein-Engineered Molecules in a Mouse Model of Chronic House Dust Mite Allergy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
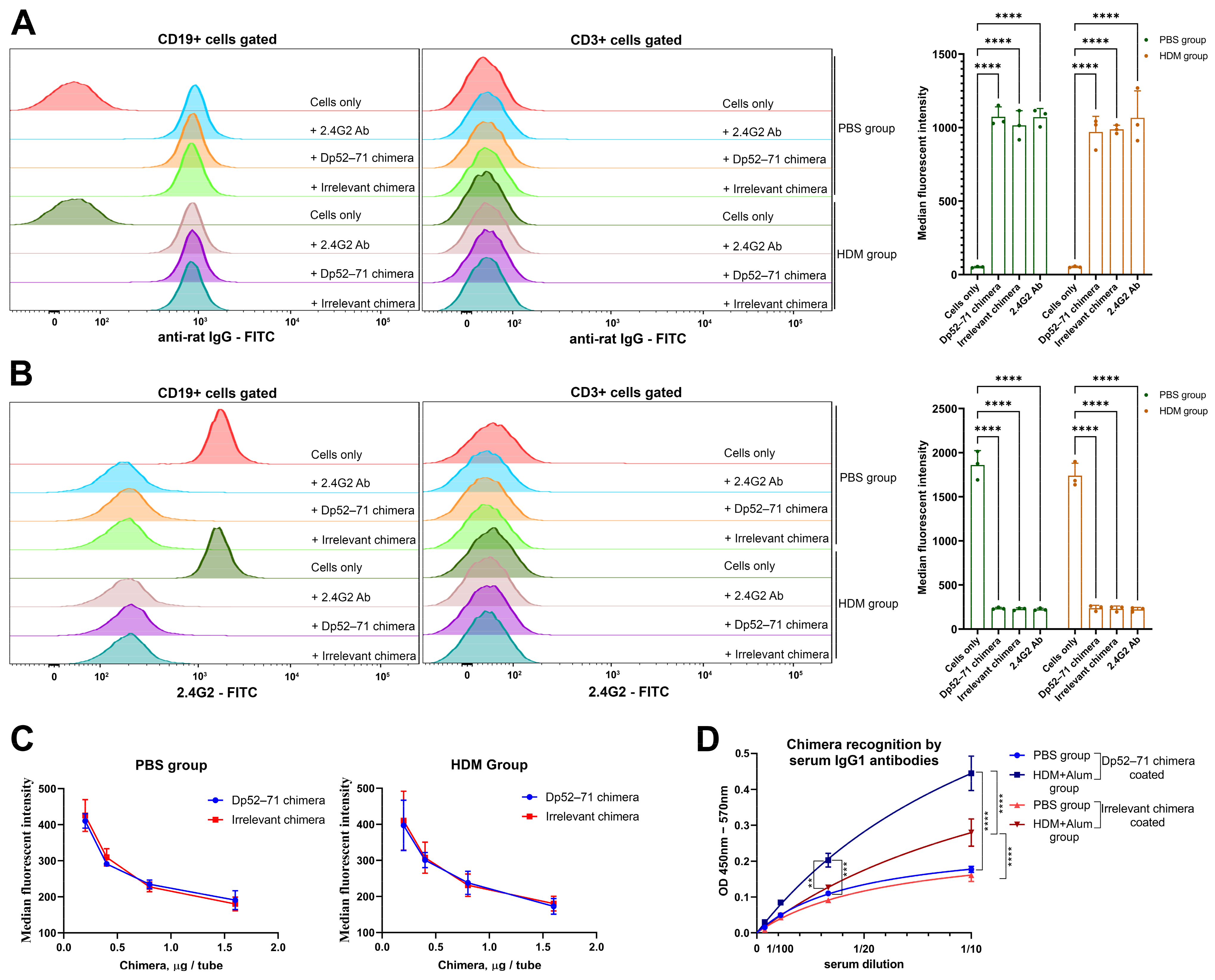
2.1. Characterization of the Chimeric Molecules
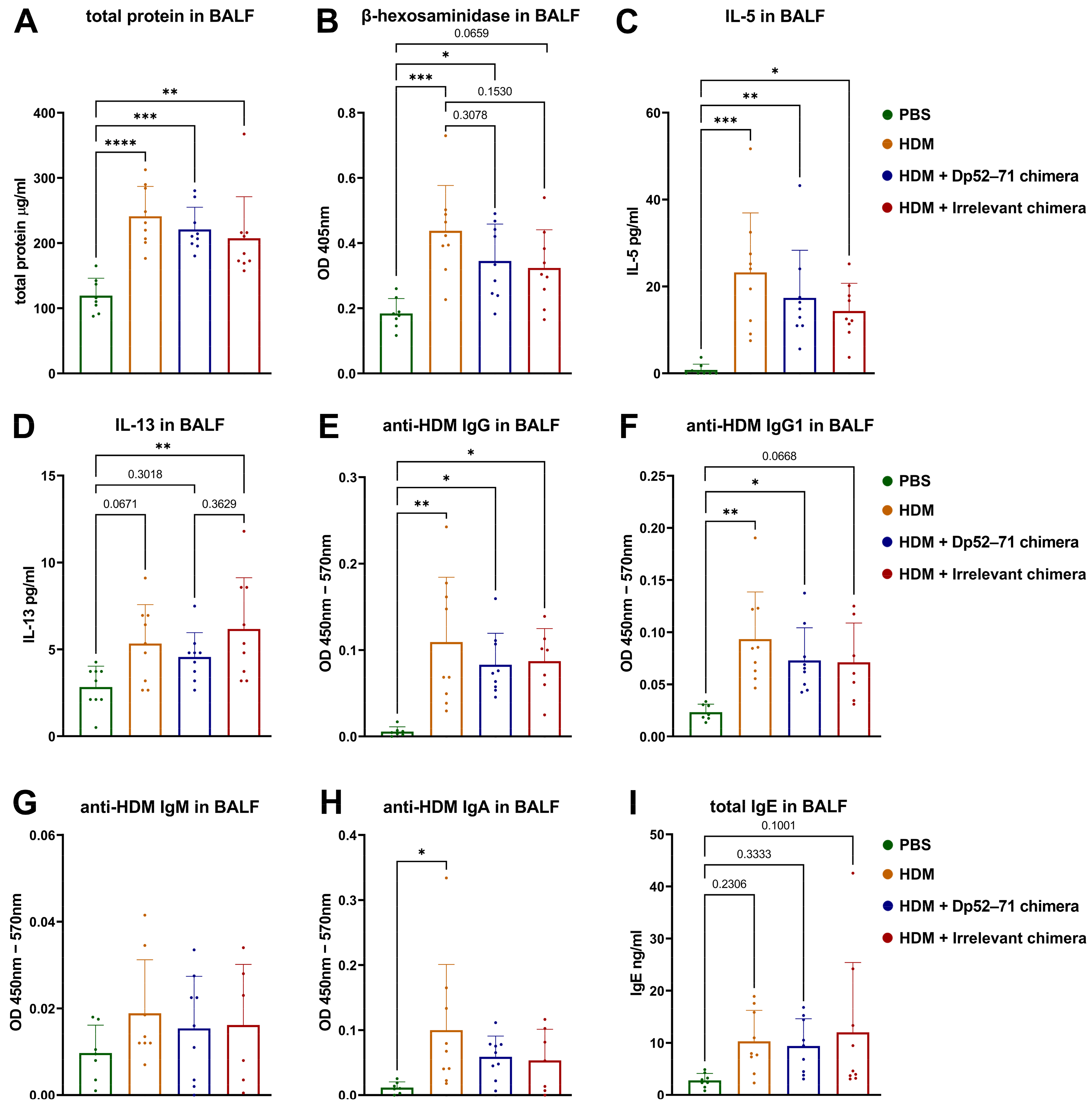
2.2. Serum Levels of HDM-Specific Antibodies and Total IgE
2.3. Protein Analyses of BALF
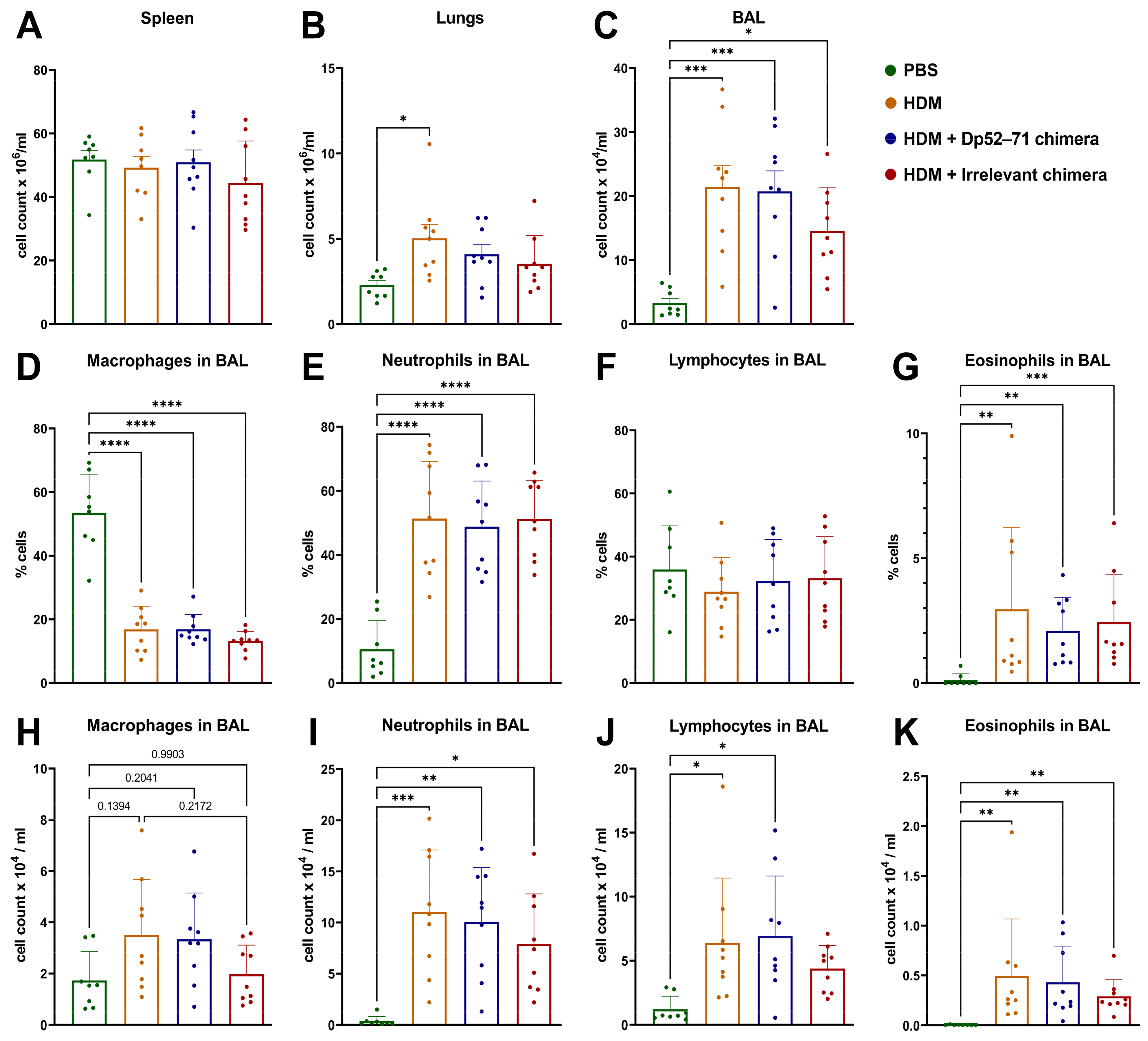
2.4. Total and Differential Cell Count in BAL Fluid
2.5. Phenotyping of Immune Cells in the Lungs
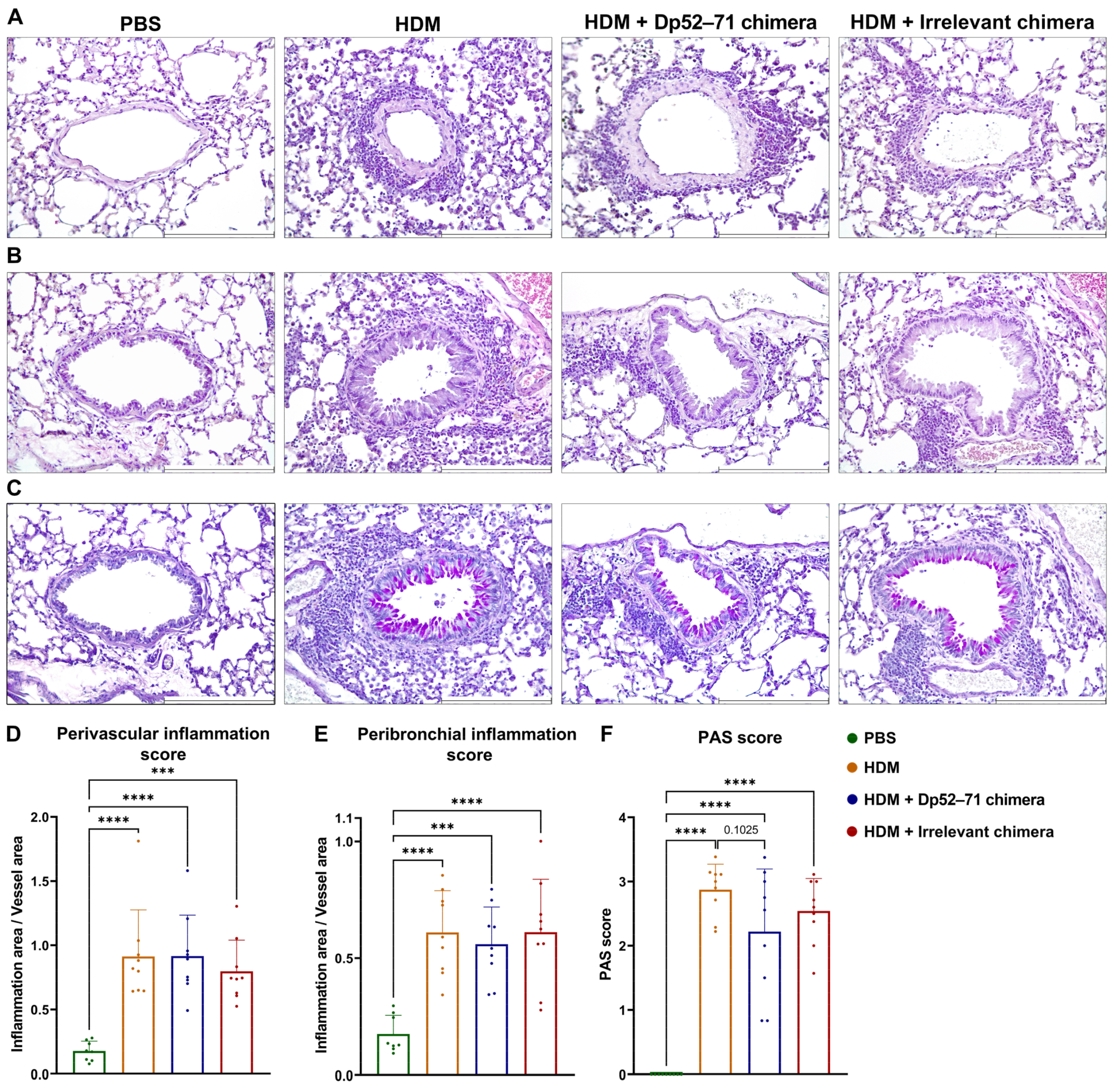
2.6. Histopathological Examination of Mouse Lungs
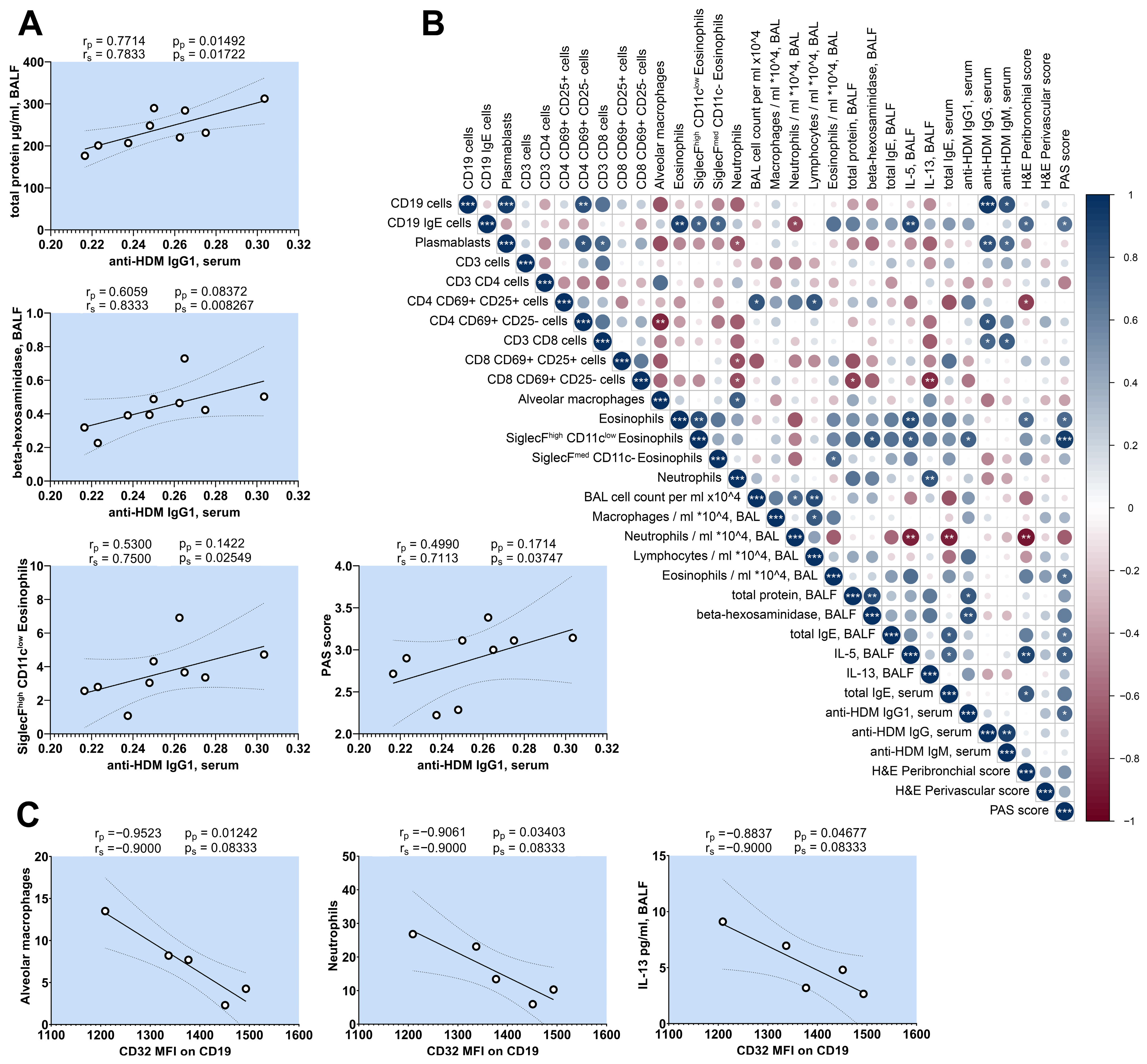
2.7. Correlation Analysis of HDM-Challenged Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Antibodies
4.2. Generation of Protein-Engineered Chimeric Antibody Molecules
4.3. Characterization of the Chimeric Molecules
4.3.1. Recognition of FcγRIIb by Chimeric Molecules
4.3.2. Chimeric Molecule Recognition by Serum IgG1 Antibodies
4.4. Mice
4.5. Generation of Mouse HDM Allergy Model and Treatment Schedule
4.6. BALF Collection and Differential Cell Count
4.7. Detection of Anti-HDM IgG, IgG1, IgM, IgA, and IgE in Sera and BALF
4.8. Assessment of Total IgE Antibodies, IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, and IL-13
4.9. Total Protein and β-Hexosaminidase Activity Measurements in BALF
4.10. Phenotyping of Lung Infiltrates
4.11. Histology
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, H.-J.; Sarzsinszky, E.; Vrtala, S. House dust mite allergy: The importance of house dust mite allergens for diagnosis and immunotherapy. Mol. Immunol. 2023, 158, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderón, M.A.; Linneberg, A.; Kleine-Tebbe, J.; De Blay, F.; de Rojas, D.H.F.; Virchow, J.C.; Demoly, P. Respiratory allergy caused by house dust mites: What do we really know? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 136, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Borges, M.; Fernandez-Caldas, E.; Thomas, W.R.; Chapman, M.D.; Lee, B.W.; Caraballo, L.; Acevedo, N.; Chew, F.T.; Ansotegui, I.J.; Behrooz, L.; et al. International consensus (ICON) on: Clinical consequences of mite hypersensitivity, a global problem. World Allergy Organ. J. 2017, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderón, M.A.; Kleine-Tebbe, J.; Linneberg, A.; De Blay, F.; de Rojas, D.H.F.; Virchow, J.C.; Demoly, P. House Dust Mite Respiratory Allergy: An Overview of Current Therapeutic Strategies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2015, 3, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, M. Review: Side Effects of Some Commonly Used Allergy Medications (Decongestants, Anti-Leukotriene Agents, Antihistamines, Steroids, and Zinc) and Their Safety in Pregnancy. Int. J. Allergy Medicat. 2017, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eifan, A.; A Calderon, M.; Durham, S.R. Allergen immunotherapy for house dust mite: Clinical efficacy and immunological mechanisms in allergic rhinitis and asthma. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2013, 13, 1543–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamant, Z.; van Maaren, M.; Muraro, A.; Jesenak, M.; Striz, I. Allergen immunotherapy for allergic asthma: The future seems bright. Respir. Med. 2023, 210, 107125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virchow, J.C. Allergen immunotherapy (AIT) in asthma. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 46, 101334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, M.F.; Chan, A.; Lim, H.F. House-Dust Mite Immunotherapy in Asthma: Uncertainties and Therapeutic Strategies. Curr. Treat. Options Allergy 2019, 6, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Chen, C.; Yu, D.; Liu, Z. Roles of follicular helper and regulatory T cells in allergic diseases and allergen immunotherapy. Allergy 2020, 76, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomares, O.; Akdis, M.; Martín-Fontecha, M.; Akdis, C.A. Mechanisms of immune regulation in allergic diseases: The role of regulatory T and B cells. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 278, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okayama, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Odajima, H.; Takahagi, S.; Hide, M.; Okubo, K. Roles of omalizumab in various allergic diseases. Allergol. Int. 2020, 69, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’amato, G.; Stanziola, A.; Sanduzzi, A.; Liccardi, G.; Salzillo, A.; Vitale, C.; Molino, A.; Vatrella, A.; D’amato, M. Treating severe allergic asthma with anti-IgE monoclonal antibody (omalizumab): A review. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2014, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, R.; McGowan, J.; Gordon, N.; McCarthy, C.; Mitchell, E.B.; Fitzpatrick, D.A. Proteome and allergenome of the European house dust mite Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reithofer, M.; Jahn-Schmid, B. Allergens with Protease Activity from House Dust Mites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’alessandro, M.; Bergantini, L.; Perrone, A.; Cameli, P.; Beltrami, V.; Alderighi, L.; Pini, L.; Bargagli, E.; Saletti, M. House Dust Mite Allergy and the Der p1 Conundrum: A Literature Review and Case Series. Allergies 2021, 1, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osinski, T.; Pomés, A.; Majorek, K.A.; Glesner, J.; Offermann, L.R.; Vailes, L.D.; Chapman, M.D.; Minor, W.; Chruszcz, M. Structural Analysis of Der p 1–Antibody Complexes and Comparison with Complexes of Proteins or Peptides with Monoclonal Antibodies. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y. Immunoglobulin E-Binding Epitopes of Mite Allergens: From Characterization to Immunotherapy. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 47, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duez, C.; Gras-Masse, H.; Hammad, H.; Akoum, H.; Didierlaurent, A.; André, C.; Tonnel, A.B.; Pestel, J. Modulation of the allergen-induced human ige response in hu-scid mice: Inhibitory effect of human recombinant ifn-γ and allergen-derived lipopeptide. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2001, 12, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jeannin, P.; Pestel, J.; Bossus, M.; Lassalle, P.; Tartar, A.; Tonnel, A. Comparative analysis of biological activities of Der p I-derived peptides on Fc receptor-bearing cells from Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus-sensitive patients. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1993, 92, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerekov, N.; Michova, A.; Muhtarova, M.; Nikolov, G.; Mihaylova, N.; Petrunov, B.; Nikolova, M.; Tchorbanov, A. Suppression of allergen-specific B lymphocytes by chimeric protein-engineered antibodies. Immunobiology 2014, 219, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralchev, N.R.; Kerekov, N.; Mihaylova, N.; Kremlitzka, M.; Hristova, D.; Dzhorev, J.; Erdei, A.; Tchorbanov, A.I. Targeted suppression of Dpt-specific B cells in humanized Rag2- γc- mouse model of HDM allergy. Scand. J. Immunol. 2022, 97, e13241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, H.; Liu, Z.; Yang, F. Benefits and limitations of humanized mouse models for human red blood cell-related disease research. Front. Hematol. 2023, 1, 1062705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, R.; Maruoka, S.; Gon, Y.; Katano, I.; Takahashi, T.; Ito, M.; Izuhara, K.; Nunomura, S. Recent Advances in Allergy Research Using Humanized Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wege, A.K. Humanized Mouse Models for the Preclinical Assessment of Cancer Immunotherapy. BioDrugs 2018, 32, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdei, A.; Kovács, K.G.; Nagy-Baló, Z.; Lukácsi, S.; Mácsik-Valent, B.; Kurucz, I.; Bajtay, Z. New aspects in the regulation of human B cell functions by complement receptors CR1, CR2, CR3 and CR4. Immunol. Lett. 2021, 237, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlev, A.N.; Malkiel, S.; Kurata-Sato, I.; Dorjée, A.L.; Suurmond, J.; Diamond, B. FcγRIIB regulates autoantibody responses by limiting marginal zone B cell activation. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e157250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paunovic, V.; Carter, N.A.; Thalhamer, T.; Blair, D.; Gordon, B.; Lacey, E.; Michie, A.M.; Harnett, M.M. Immune complex-mediated co-ligation of the BCR with FcγRIIB results in homeostatic apoptosis of B cells involving Fas signalling that is defective in the MRL/Lpr model of systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Autoimmun. 2012, 39, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchorbanov, A.I.; Voynova, E.N.; Mihaylova, N.M.; Todorov, T.A.; Nikolova, M.; Yomtova, V.M.; Chiang, B.; Vassilev, T.L. Selective silencing of DNA-specific B lymphocytes delays lupus activity in MRL/lpr mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 3587–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaylova, N.; Voynova, E.; Tchorbanov, A.; Dolashka-Angelova, P.; Bayry, J.; Devreese, B.; Kaveri, S.; Vassilev, T. Simultaneous engagement of FcγIIb and CD22 inhibitory receptors silences targeted B cells and suppresses autoimmune disease activity. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 47, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Moral, I.R.; Veer, C.v.; de Vos, A.F.; de Beer, R.; Roelofs, J.J.T.H.; Morgan, B.P.; van der Poll, T. Complement factor C5 inhibition reduces type 2 responses without affecting group 2 innate lymphoid cells in a house dust mite induced murine asthma model. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, Q.; Lang, J.; Jin, L.; Fang, M.; Cao, B.; Cai, Y.; Ni, Z.; Qiu, F.; Li, C.; Cao, G.; et al. Total glucosides of peony improve ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma by inhibiting mast cell degranulation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 244, 112136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, H.A.; Loffredo, L.F.; Misharin, A.V.; Berdnikovs, S. Phenotypic plasticity and targeting of Siglec-FhighCD11clow eosinophils to the airway in a murine model of asthma. Allergy 2015, 71, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, L.D.; Dockstader, K.; Olbrich, C.L.; Cartwright, I.M.; A Spencer, L. Modulation of surface CD11c expression tracks plasticity in murine intestinal tissue eosinophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2022, 111, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravetch, J.V.; Lanier, L.L. Immune Inhibitory Receptors. Science 2000, 290, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearse, R.N.; Kawabe, T.; Bolland, S.; Guinamard, R.; Kurosaki, T.; Ravetch, J.V. SHIP Recruitment Attenuates FcγRIIB-Induced B Cell Apoptosis. Immunity 1999, 10, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Post, S.; Nawijn, M.C.; Hackett, T.L.; Baranowska, M.; Gras, R.; van Oosterhout, A.J.M.; Heijink, I.H. The composition of house dust mite is critical for mucosal barrier dysfunction and allergic sensitisation. Thorax 2011, 67, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.G.C.; Clatworthy, M.R. FcγRIIB in autoimmunity and infection: Evolutionary and therapeutic implications. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B.; Schwab, I.; Böhm, S.; Lux, A.; Biburger, M.; Nimmerjahn, F. FcγRIIB: A modulator of cell activation and humoral tolerance. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 8, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birrell, M.; Van Oosterhout, A.; Belvisi, M. Do the current house dust mite-driven models really mimic allergic asthma? Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 36, 1220–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conejero, L.; Khouili, S.C.; Martínez-Cano, S.; Izquierdo, H.M.; Brandi, P.; Sancho, D. Lung CD103+ dendritic cells restrain allergic airway inflammation through IL-12 production. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 2, e90420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.R.; Wiley, R.E.; Fattouh, R.; Swirski, F.K.; Gajewska, B.U.; Coyle, A.J.; Gutierrez-Ramos, J.-C.; Ellis, R.; Inman, M.D.; Jordana, M. Continuous Exposure to House Dust Mite Elicits Chronic Airway Inflammation and Structural Remodeling. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 169, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagner, S.; Harb, H.; Zhao, M.; Stein, K.; Holst, O.; Ege, M.J.; Mayer, M.; Matthes, J.; Bauer, J.; von Mutius, E.; et al. Farm-derived Gram-positive bacterium Staphylococcus sciuri W620 prevents asthma phenotype in HDM- and OVA-exposed mice. Allergy 2013, 68, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandenberger, C.; Li, N.; Jackson-Humbles, D.N.; Rockwell, C.E.; Wagner, J.G.; Harkema, J.R. Enhanced allergic airway disease in old mice is associated with a Th17 response. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2014, 44, 1282–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Post, S.; Heijink, I.H.; Petersen, A.H.; de Bruin, H.G.; van Oosterhout, A.J.M.; Nawijn, M.C. Protease-Activated Receptor-2 Activation Contributes to House Dust Mite-Induced IgE Responses in Mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKnight, C.G.; Jude, J.A.; Zhu, Z.; Panettieri, R.A.; Finkelman, F.D. House Dust Mite–Induced Allergic Airway Disease Is Independent of IgE and FcεRIα. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 57, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiba, A.; Hamelmann, E.; Takeda, K.; Bradley, K.L.; E Loader, J.; Larsen, G.L.; Gelfand, E.W. Passive transfer of immediate hypersensitivity and airway hyperresponsiveness by allergen-specific immunoglobulin (Ig) E and IgG1 in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 1398–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyajima, I.; Dombrowicz, D.; Martin, T.R.; Ravetch, J.V.; Kinet, J.P.; Galli, S.J. Systemic anaphylaxis in the mouse can be mediated largely through IgG1 and Fc gammaRIII. Assessment of the cardiopulmonary changes, mast cell degranulation, and death associated with active or IgE- or IgG1-dependent passive anaphylaxis. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 901–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazenbos, W.L.; Gessner, J.; Hofhuis, F.M.; Kuipers, H.; Meyer, D.; Heijnen, I.A.; E Schmidt, R.; Sandor, M.; Capel, P.J.; Daëron, M.; et al. Impaired IgG-Dependent Anaphylaxis and Arthus Reaction in FcγRIII (CD16) Deficient Mice. Immunity 1996, 5, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartwig, C.; Mazzega, M.; Constabel, H.; Krishnaswamy, J.K.; Gessner, J.E.; Braun, A.; Tschernig, T.; Behrens, G.M.N. Fcγ receptor-mediated antigen uptake by lung DC contributes to allergic airway hyper-responsiveness and inflammation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 1284–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.W.; Tjota, M.Y.; Sperling, A.I. The Contribution of Allergen-Specific IgG to the Development of Th2-Mediated Airway Inflammation. J. Allergy 2012, 2012, 236075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, J.R.; Muniz, B.P.; E Fusaro, A.; A de Brito, C.; Taniguchi, E.F.; Duarte, A.J.; Sato, M.N. Maternal immunization with ovalbumin prevents neonatal allergy development and up-regulates inhibitory receptor FcγRIIB expression on B cells. BMC Immunol. 2010, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, M.G.; Oliveira, L.d.M.; Lira, A.A.d.L.; Sgnotto, F.d.R.; Duarte, A.J.d.S.; Sato, M.N.; Victor, J.R. Preconception allergen sensitization can induce B10 cells in offspring: A potential main role for maternal IgG. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2017, 13, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lira, A.A.d.L.; de Oliveira, M.G.; de Oliveira, L.M.; Duarte, A.J.d.S.; Sato, M.N.; Victor, J.R. Maternal immunization with ovalbumin or Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus has opposing effects on FcγRIIb expression on offspring B cells. Allergy, Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2014, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, O.T.; Tamayo, J.M.; Stranks, A.J.; Koleoglou, K.J.; Oettgen, H.C. Allergen-specific IgG antibody signaling through FcγRIIb promotes food tolerance. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 141, 189–201.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, G. Current Strategies to Inhibit High Affinity FcεRI-Mediated Signaling for the Treatment of Allergic Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruhns, P.; Frémont, S.; Daëron, M. Regulation of allergy by Fc receptors. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2005, 17, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.-B.; Xiang, Z.; Smith, K.G.C.; Holmgren, J. Important Role for FcγRIIB on B Lymphocytes for Mucosal Antigen-Induced Tolerance and Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4412–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voynova, E.; Tchorbanov, A.; Prechl, J.; Nikolova, M.; Baleva, M.; Erdei, A.; Vassilev, T. An antibody-based construct carrying DNA-mimotope and targeting CR1(CD35) selectively suppresses human autoreactive B-lymphocytes. Immunol. Lett. 2008, 116, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armbruster, D.A.; Pry, T. Limit of Blank, Limit of Detection and Limit of Quantitation. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2008, 29 (Suppl. S1), S49–S52. [Google Scholar]
- Kujur, W.; Gurram, R.K.; Haleem, N.; Maurya, S.K.; Agrewala, J.N. Caerulomycin A inhibits Th2 cell activity: A possible role in the management of asthma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Chen, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y. SRplot: A free online platform for data visualization and graphing. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ralchev, N.; Bradyanova, S.; Kerekov, N.; Tchorbanov, A.; Mihaylova, N. Suppression of Pathological Allergen-Specific B Cells by Protein-Engineered Molecules in a Mouse Model of Chronic House Dust Mite Allergy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413661
Ralchev N, Bradyanova S, Kerekov N, Tchorbanov A, Mihaylova N. Suppression of Pathological Allergen-Specific B Cells by Protein-Engineered Molecules in a Mouse Model of Chronic House Dust Mite Allergy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(24):13661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413661
Chicago/Turabian StyleRalchev, Nikola, Silviya Bradyanova, Nikola Kerekov, Andrey Tchorbanov, and Nikolina Mihaylova. 2024. "Suppression of Pathological Allergen-Specific B Cells by Protein-Engineered Molecules in a Mouse Model of Chronic House Dust Mite Allergy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 24: 13661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413661
APA StyleRalchev, N., Bradyanova, S., Kerekov, N., Tchorbanov, A., & Mihaylova, N. (2024). Suppression of Pathological Allergen-Specific B Cells by Protein-Engineered Molecules in a Mouse Model of Chronic House Dust Mite Allergy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(24), 13661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413661





