Involvement of the Na+, K+-ATPase α1 Isoform and Endogenous Cardiac Steroids in Depression- and Manic-like Behaviors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
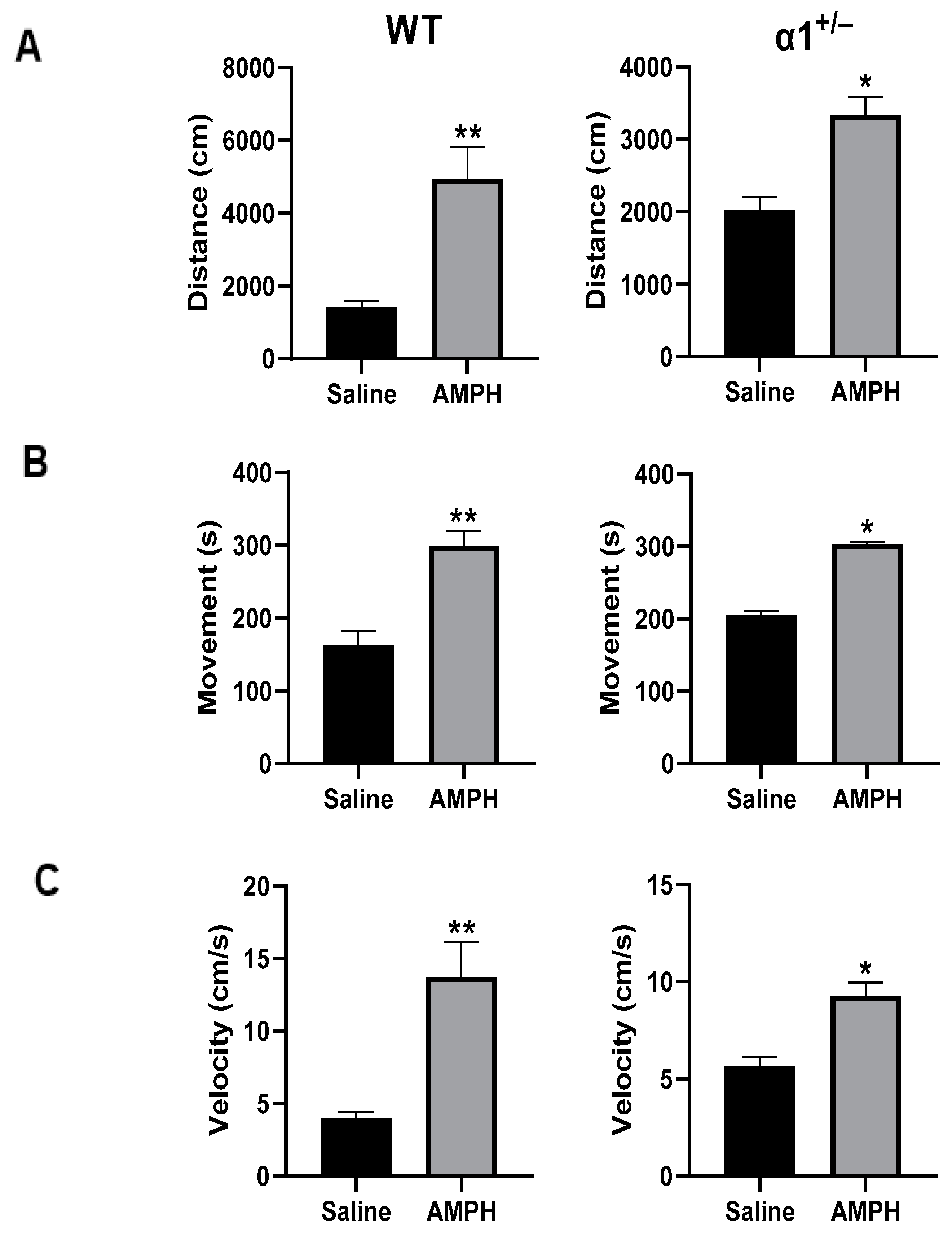
2.1. Decreased Brain ECS Levels Increase Depressive-like Behavior in C57Bl/6 α1+/− Mice
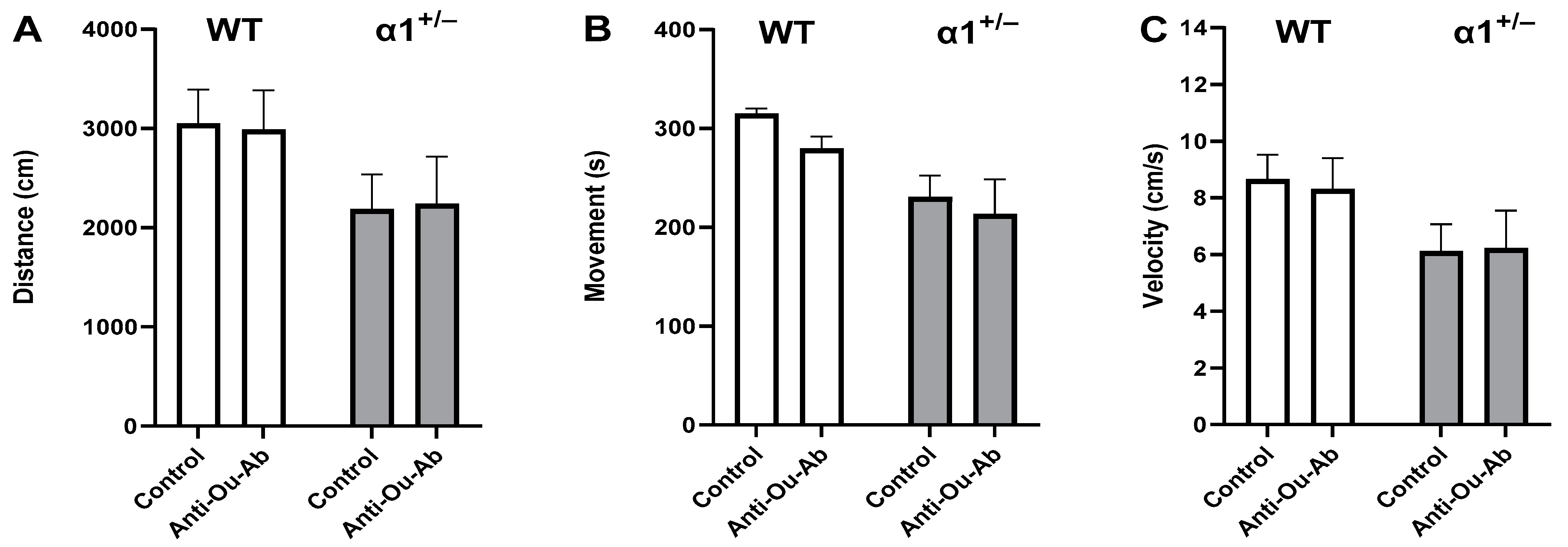
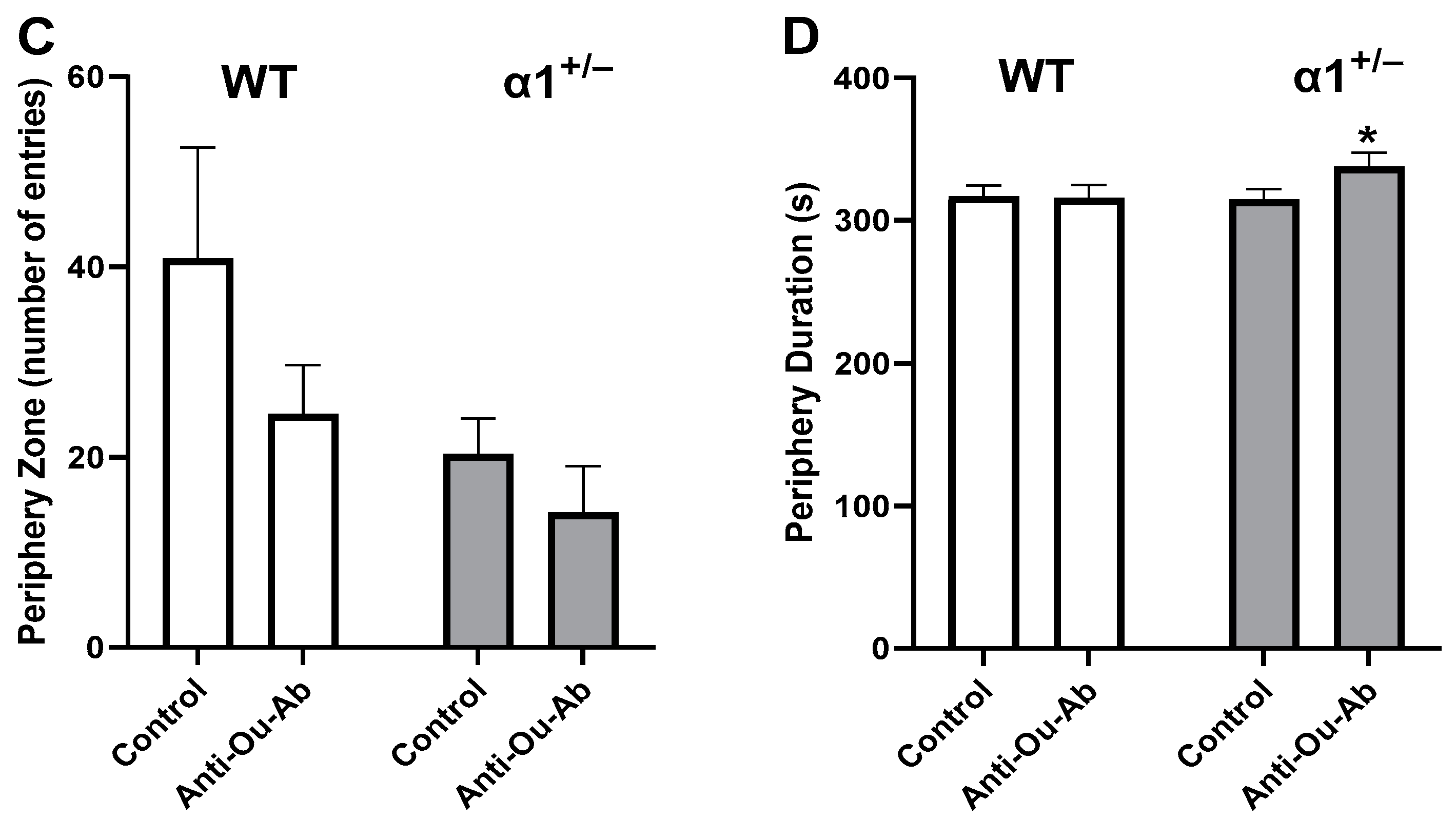
2.2. Decreased Brain ECS Levels Affect Exploratory and Anxiety Behaviors in α1+/− but Not wt C57Bl/6 Mice
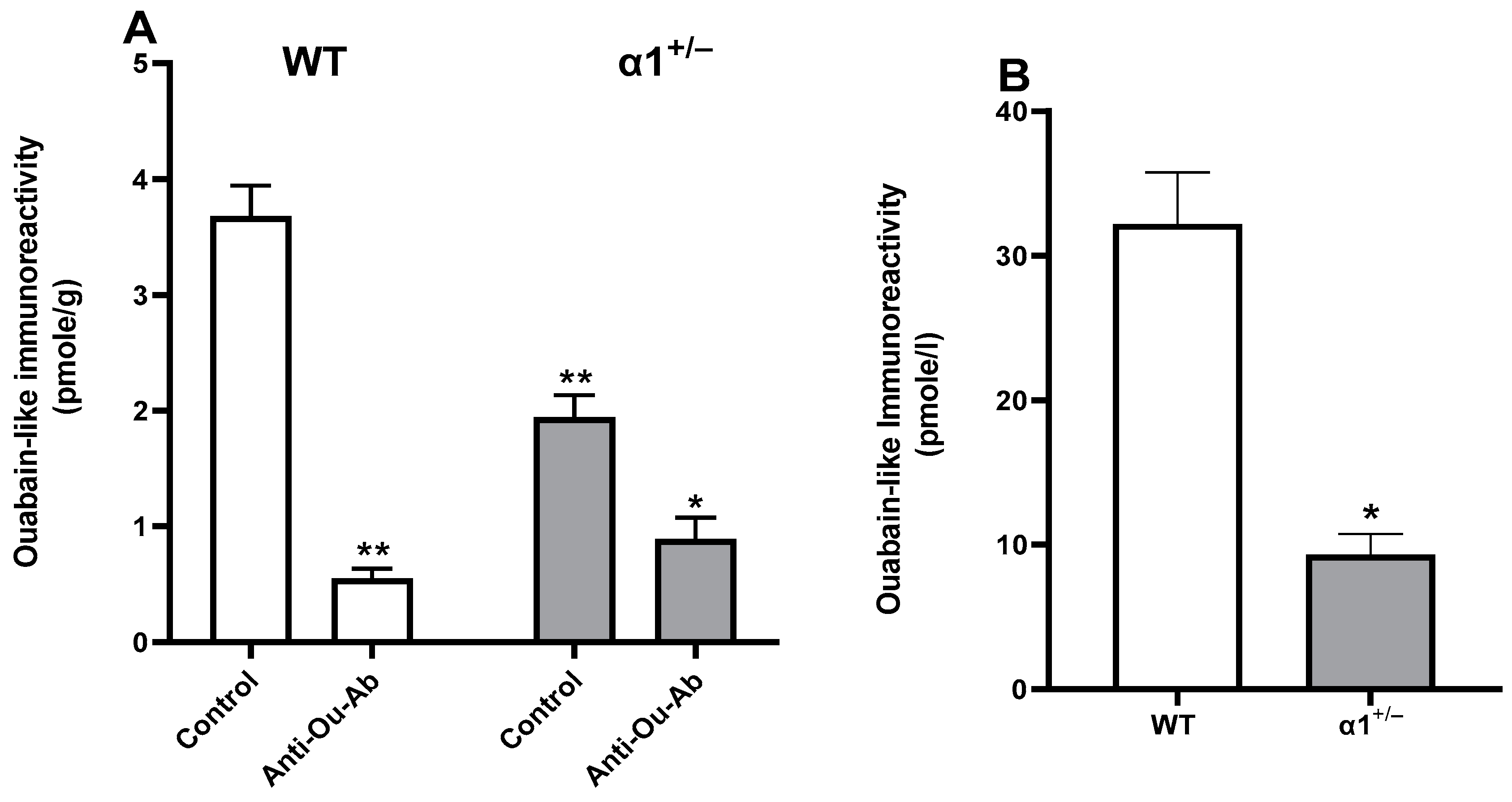
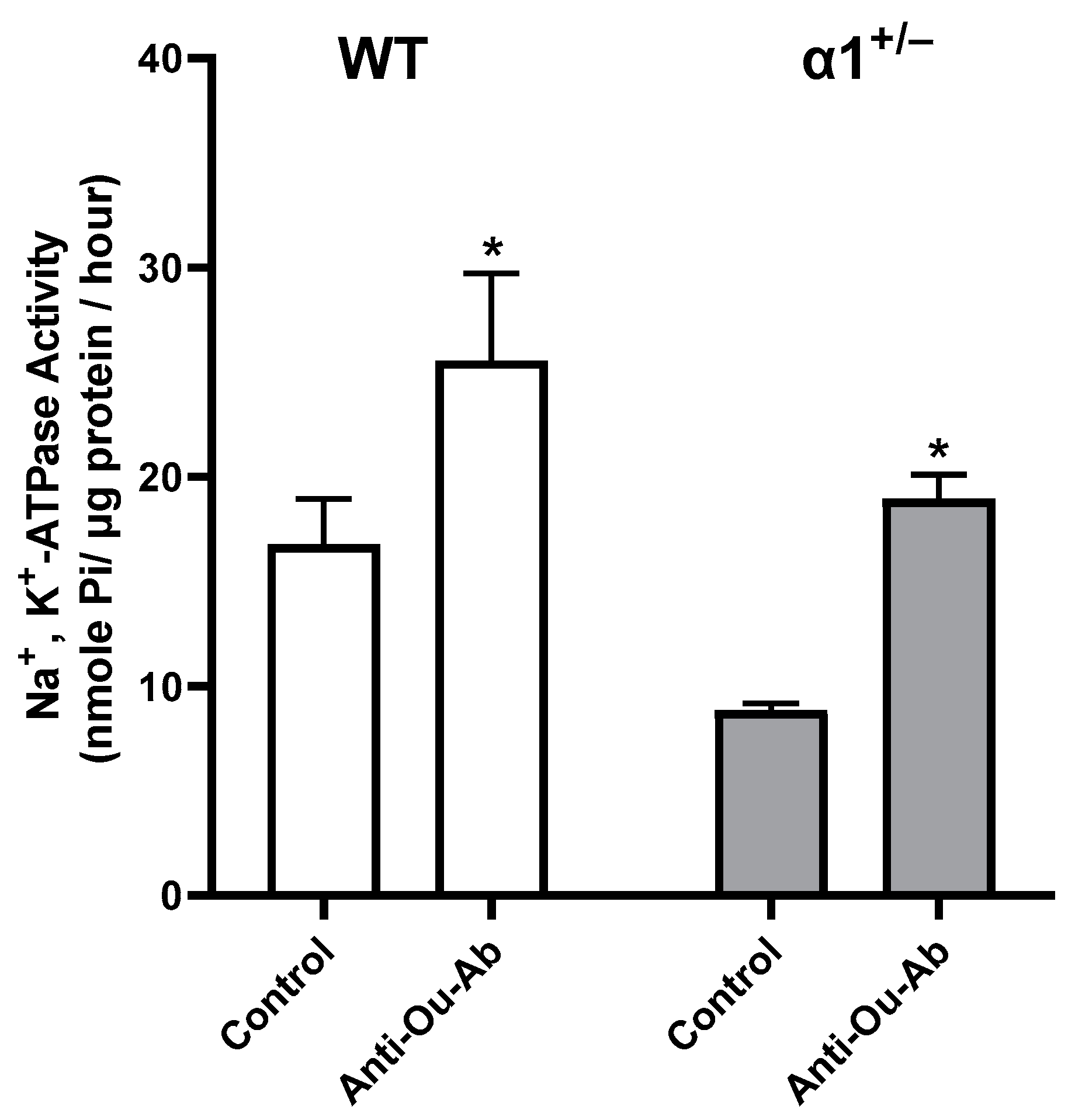
2.3. ECS Levels and Na+, K+-ATPase Activity in the Brain in wt and α1+/− Mice
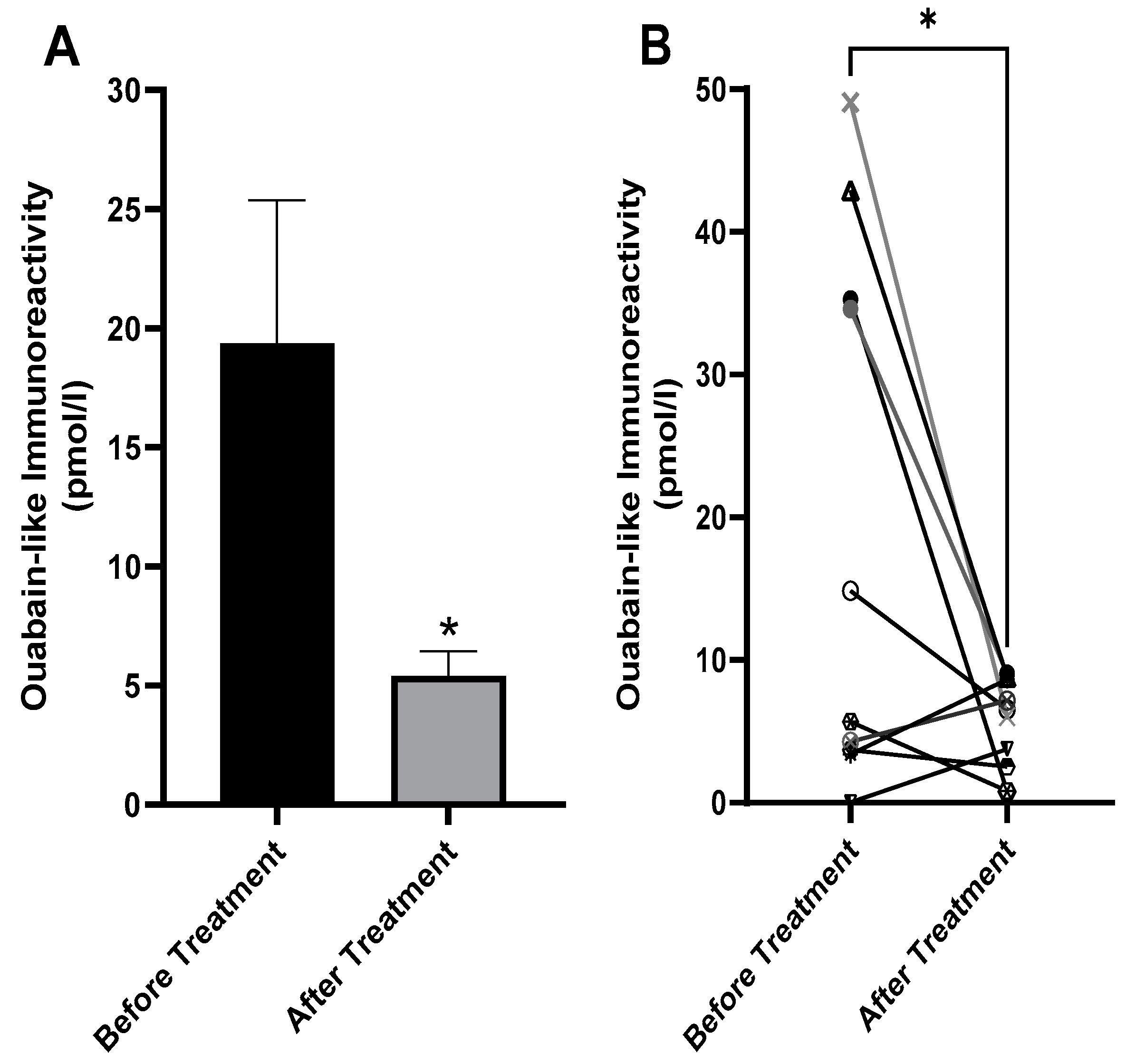
2.4. Decreased Serum ECS in Patients with BD after Treatment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Serum from Patients with BD
4.2. Animals and Behavioral Tests
4.3. Extraction and Determination of Endogenous Cardiac Steroids
4.4. ATPase Activity
4.5. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Sklar, P.; Smoller, J.W.; Fan, J.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Perlis, R.H.; Chambert, K.; Nimgaonkar, V.L.; McQueen, M.B.; Faraone, S.V.; Kirby, A.; et al. Whole-genome association study of bipolar disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2008, 13, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmaker, R.H. Bipolar disorder. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, M.V.; Hilbers, F.; Poulsen, H. The Structure and Function of the Na,K-ATPase Isoforms in Health and Disease. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staehr, C.; Aalkjaer, C.; Matchkov, V.V. The vascular Na,K-ATPase: Clinical implications in stroke, migraine, and hypertension. Clin. Sci. 2023, 137, 1595–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, J.H. Biochemistry of Na,K-ATPase. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 511–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, G.; Mercer, R.W. Isozymes of the Na-K-ATPase: Heterogeneity in structure, diversity in function. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, F633–F650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahler, R.; Gilmore-Hebert, M.; Baldwin, J.C.; Franco, K.; Benz, E.J., Jr. Expression of alpha isoforms of the Na,K-ATPase in human heart. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1993, 1149, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrail, K.M.; Phillips, J.M.; Sweadner, K.J. Immunofluorescent localization of three Na,K-ATPase isozymes in the rat central nervous system: Both neurons and glia can express more than one Na,K-ATPase. J. Neurosci. 1991, 11, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xie, Z.J. The sodium pump and cardiotonic steroids-induced signal transduction protein kinases and calcium-signaling microdomain in regulation of transporter trafficking. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1802, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Cai, T.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Haas, M.; Maksimova, E.; Huang, X.Y.; Xie, Z.J. Binding of Src to Na+/K+-ATPase forms a functional signaling complex. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.A.; Smith, T.W. Pharmacological Treatment of Heart Failure, 9th ed.; McGraw-Hill Comp: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 809–838. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, K.; Linde, H. Collection of Toad Venoms and Chemistry of the Toad Venom Steroids; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971; Volume II. [Google Scholar]
- Hamlyn, J.M.; Blaustein, M.P.; Bova, S.; DuCharme, D.W.; Harris, D.W.; Mandel, F.; Mathews, W.R.; Ludens, J.H. Identification and characterization of a ouabain-like compound from human plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 6259–6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, A.; Ishiguro, T.; Yamada, K.; Ishii, M.; Yoshioka, M.; Eguchi, C.; Shimora, M.; Sugimoto, T. Isolation of a urinary digitalis-like factor indistinguishable from digoxin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1990, 173, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtstein, D.; Gati, I.; Samuelov, S.; Berson, D.; Rozenman, Y.; Landau, L.; Deutsch, J. Identification of digitalis-like compounds in human cataractous lenses. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 216, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorova, O.V.; Shapiro, J.I.; Bagrov, A.Y. Endogenous cardiotonic steroids and salt-sensitive hypertension. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1802, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagrov, A.Y.; Shapiro, J.I.; Fedorova, O.V. Endogenous cardiotonic steroids: Physiology, pharmacology, and novel therapeutic targets. Pharmacol. Rev. 2009, 61, 9–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaustein, M.P.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Song, H.; Raina, H.; Kinsey, S.P.; Izuka, M.; Iwamoto, T.; Kotlikoff, M.I.; Lingrel, J.B.; et al. The pump, the exchanger, and endogenous ouabain: Signaling mechanisms that link salt retention to hypertension. Hypertension 2009, 53, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtstein, D.; Ilani, A.; Rosen, H.; Horesh, N.; Singh, S.V.; Buzaglo, N.; Hodes, A. Na(+), K(+)-ATPase Signaling and Bipolar Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mallakh, R.S.; Gao, Y.; You, P. Role of endogenous ouabain in the etiology of bipolar disorder. Int. J. Bipolar Disord. 2021, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtstein, D.; Rosen, H. Endogenous digitalis-like Na+, K+-ATPase inhibitors, and brain function. Neurochem. Res. 2001, 26, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mallakh, R.S.; Sampath, V.P.; Horesh, N.; Lichtstein, D. Endogenous Cardiac Steroids in Bipolar Disorder: State of the Art. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mynett-Johnson, L.; Murphy, V.; McCormack, J.; Shields, D.C.; Claffey, E.; Manley, P.; McKeon, P. Evidence for an allelic association between bipolar disorder and a Na+, K+ adenosine triphosphatase alpha subunit gene (ATP1A3). Biol. Psychiatry 1998, 44, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, I.; Lerer, E.; Laiba, E.; Mallet, J.; Mujaheed, M.; Laurent, C.; Rosen, H.; Ebstein, R.P.; Lichtstein, D. Association between sodium- and potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase alpha isoforms and bipolar disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, G.J.; McNamee, H.B.; Moody, J.P. Changes in erythrocyte sodium and potassium on recovery from a depressive illness. Br. J. Psychiatry 1971, 118, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, I.; Levy, T.; Galili, D.; Ovadia, H.; Yirmiya, R.; Rosen, H.; Lichtstein, D. Involvement of Na(+), K(+)-ATPase and endogenous digitalis-like compounds in depressive disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 60, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grider, G.; El-Mallakh, R.S.; Huff, M.O.; Buss, T.J.; Miller, J.; Valdes, R., Jr. Endogenous digoxin-like immunoreactive factor (DLIF) serum concentrations are decreased in manic bipolar patients compared to normal controls. J. Affect. Disord. 1999, 54, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mallakh, R.S.; El-Masri, M.A.; Huff, M.O.; Li, X.P.; Decker, S.; Levy, R.S. Intracerebroventricular administration of ouabain as a model of mania in rats. Bipolar Disord. 2003, 5, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.S.; Kim, S.H.; Park, H.G.; Kim, Y.S.; Ahn, Y.M. Intracerebroventricular administration of ouabain, a Na/K-ATPase inhibitor, activates tyrosine hydroxylase through extracellular signal-regulated kinase in rat striatum. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 59, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodes, A.; Rosen, H.; Deutsch, J.; Lifschytz, T.; Einat, H.; Lichtstein, D. Endogenous cardiac steroids in animal models of mania. Bipolar Disord. 2016, 18, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prut, L.; Belzung, C. The open field as a paradigm to measure the effects of drugs on anxiety-like behaviors: A review. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 463, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D. A Review of Behavioral Tests to Evaluate Different Types of Anxiety and Anti-anxiety Effects. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2020, 18, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mallakh, R.S.; Wyatt, R.J. The Na,K-ATPase hypothesis for bipolar illness. Biol. Psychiatry 1995, 37, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Johnson, K.; Moreno, C.; Yano, S.; Holmgren, M. Comparative description of the mRNA expression profile of Na(+) /K(+) -ATPase isoforms in adult mouse nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 2022, 530, 627–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, K.; Kinoshita, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Kuroda, K.; Hoshi, M.; Fukazawa, Y. Region- and neuronal-subtype-specific expression of Na,K-ATPase alpha and beta subunit isoforms in the mouse brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2020, 528, 2654–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingrel, J.B.; Williams, M.T.; Vorhees, C.V.; Moseley, A.E. Na,K-ATPase and the role of alpha isoforms in behavior. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2007, 39, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moseley, A.E.; Williams, M.T.; Schaefer, T.L.; Bohanan, C.S.; Neumann, J.C.; Behbehani, M.M.; Vorhees, C.V.; Lingrel, J.B. Deficiency in Na,K-ATPase alpha isoform genes alters spatial learning, motor activity, and anxiety in mice. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucki, I.; Dalvi, A.; Mayorga, A.J. Sensitivity to the effects of pharmacologically selective antidepressants in different strains of mice. Psychopharmacology 2001, 155, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, S.M.; Safina, D.; Ehrkamp, A.; Faissner, A.; Heumann, R.; Dietzel, I.D. Differential expression patterns of sodium potassium ATPase alpha and beta subunit isoforms in mouse brain during postnatal development. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 128, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaustein, M.P.; Hamlyn, J.M. Ouabain, endogenous ouabain and ouabain-like factors: The Na(+) pump/ouabain receptor, its linkage to NCX, and its myriad functions. Cell Calcium 2020, 86, 102159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, D.; Fedorova, O.V.; Bagrov, A.Y.; Kaphzan, H. Selective ligands for Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase alpha isoforms differentially and cooperatively regulate excitability of pyramidal neurons in distinct brain regions. Neuropharmacology 2017, 117, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostanic-Larson, I.; Lorenz, J.N.; Van Huysse, J.W.; Neumann, J.C.; Moseley, A.E.; Lingrel, J.B. Physiological role of the alpha1- and alpha2-isoforms of the Na+-K+-ATPase and biological significance of their cardiac glycoside binding site. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2006, 290, R524–R528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayi, P.R.; Bagrov, A.Y.; Kaphzan, H. Chronic alpha1-Na/K-ATPase inhibition reverses the elongation of the axon initial segment of the hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons in Angelman syndrome model mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2021, 46, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaphzan, H.; Buffington, S.A.; Ramaraj, A.B.; Lingrel, J.B.; Rasband, M.N.; Santini, E.; Klann, E. Genetic reduction of the alpha1 subunit of Na/K-ATPase corrects multiple hippocampal phenotypes in Angelman syndrome. Cell Rep. 2013, 4, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondo, E.D.; Spontarelli, K.; Ababioh, G.; Mendez, L.; Artigas, P. Diseases caused by mutations in the Na(+)/K(+) pump alpha1 gene ATP1A1. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 321, C394–C408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariel Zilberstein, N.K.; Horesh, N.; Klein, E.; Lichtstein, D. Beneficial effect of digoxin-specific Fab fragments in bipolar disorder- a preliminary study. J. Affect. Disord. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, P.F.; Grupp, I.L.; Grupp, G.; Woo, A.L.; Askew, G.R.; Croyle, M.L.; Walsh, R.A.; Lingrel, J.B. Identification of a specific role for the Na,K-ATPase alpha 2 isoform as a regulator of calcium in the heart. Mol. Cell 1999, 3, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingrel, J.B. The physiological significance of the cardiotonic steroid/ouabain-binding site of the Na,K-ATPase. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvela, M.; Rosen, H.; Ben-Ami, H.C.; Lichtstein, D. Endogenous ouabain regulates cell viability. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2012, 302, C442–C452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baginski, E.; Zak, B. Micro-determination of serum phosphate and phospholipids. Clin. Chim. Acta 1960, 5, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Horesh, N.; Pelov, I.; Pogodin, I.; Zannadeh, H.; Rosen, H.; Mikhrina, A.L.; Dvela-Levitt, M.; Sampath, V.P.; Lichtstein, D. Involvement of the Na+, K+-ATPase α1 Isoform and Endogenous Cardiac Steroids in Depression- and Manic-like Behaviors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031644
Horesh N, Pelov I, Pogodin I, Zannadeh H, Rosen H, Mikhrina AL, Dvela-Levitt M, Sampath VP, Lichtstein D. Involvement of the Na+, K+-ATPase α1 Isoform and Endogenous Cardiac Steroids in Depression- and Manic-like Behaviors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(3):1644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031644
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoresh, Noa, Ilana Pelov, Ilana Pogodin, Hiba Zannadeh, Haim Rosen, Anastasiia Leonidovna Mikhrina, Moran Dvela-Levitt, Vishnu Priya Sampath, and David Lichtstein. 2024. "Involvement of the Na+, K+-ATPase α1 Isoform and Endogenous Cardiac Steroids in Depression- and Manic-like Behaviors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 3: 1644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031644
APA StyleHoresh, N., Pelov, I., Pogodin, I., Zannadeh, H., Rosen, H., Mikhrina, A. L., Dvela-Levitt, M., Sampath, V. P., & Lichtstein, D. (2024). Involvement of the Na+, K+-ATPase α1 Isoform and Endogenous Cardiac Steroids in Depression- and Manic-like Behaviors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(3), 1644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031644





